NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD
|
|
|
- Rose Bishop
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD for the Occupation of Instrumentation and Control Technician New Blocks 1, 2, 3 and 4 in September 2014 See Page 11 for NS Program Structure Based on the Atlantic Apprenticeship Curriculum Standard Levels 1 & 2 in September 2018 (pg. 12 for Program Structure) 2017 Version #1.0
2 Atlantic Apprenticeship Curriculum Standard Instrumentation and Control Technician
3 Preface This Atlantic Apprenticeship Curriculum Standard is intended to assist instructional staff in the design and delivery of technical, in-class training in support of the Instrumentation and Control Technician program. This document contains all the technical training elements required to complete the Instrumentation and Control Technician apprenticeship program and has been developed based on the 2013 National Occupational Analysis (NOA) and the 2015 Interprovincial Program Guide (IPG). The NOA and IPG can be found on the Red Seal website ( Implementation of this AACS for Apprenticeship training is outlined in the following table. Level Implementation Effective Level Level Level Level ** The above implementation schedule was current at time of printing. Please confirm with Apprenticeship Staff prior to commencing training. Granting of credit or permission to challenge level examinations for pre-employment or pre-apprenticeship training for the Instrumentation and Control Technician trade will be based on the content outlined in this standard. Training providers must contact their provincial apprenticeship authority for more information on the process and requirements for determining eligibility for credit towards an apprenticeship program. Programs which have been deemed acceptable by the jurisdictional apprenticeship authority will be identified in transfer credit matrix developed through the Atlantic Apprenticeship Harmonization Project. 2
4 Acknowledgements The development of the Atlantic Apprenticeship Curriculum Standard (AACS) is an initiative of the Atlantic Apprenticeship Council s Atlantic Apprenticeship Harmonization Project (AAHP) through the Atlantic Workforce Partnership and Employment and Social Development Canada. The Atlantic Apprenticeship Council wishes to acknowledge the contributions of the following industry and instructional representatives on the Atlantic Trade Advisory Committee (ATAC) who participated in the development of this document in May Raymond MacLellan Roger Leblanc Reginald P Hebert William Voisey Cory Kelly Robert Babb Alexander Charles LeBlanc Larry Johnston Paul Mansley New Brunswick New Brunswick New Brunswick Newfoundland and Labrador Newfoundland and Labrador Newfoundland and Labrador Nova Scotia Nova Scotia Nova Scotia Advisory committees, industry representatives, instructors and apprenticeship staff provided valuable input to the development of this document. Without their dedication to quality apprenticeship training, this document could not have been produced. 3
5 Table of Contents Preface...2 Acknowledgements...3 User Guide...5 Glossary of Terms...7 Essential Skills Profiles...9 Profile Chart Nova Scotia Program Structure NOA Sub-Task to AACS Unit Comparison Program Content Level Level Level Level Feedback and Revisions
6 User Guide Atlantic Apprenticeship Curriculum Standards (AACS) are developed based on National Occupational Analyses (NOA), Interprovincial Program Guides (IPG), if available, and extensive industry consultation. This document represents the minimum content to be delivered as part of the harmonized Atlantic program for the Instrumentation and Control Technician trade. The AACS s are deliberately constructed for ease of use and flexibility of structure in order to adapt to all delivery requirements. They detail units of training, unit outcomes and objectives. They do not impose a delivery model or teaching format. Jurisdictions and/or training providers will select and develop delivery materials and techniques that accommodate a variety of learning styles and delivery patterns. The AACS does not dictate study materials, textbooks or learning activities to be used in delivery. The document includes a Level Structure to facilitate mobility for apprentices moving from one jurisdiction to another. Structure The content of the AACS is divided into units. Unit codes are used as a means of identification and are not intended to convey the order of delivery. It is at the discretion of the training provider to deliver the content in the required logical sequence of delivery within the level. Jurisdictions are free to deliver units one at a time or concurrently within a level, provided all outcomes are met. The Learning Outcomes describe what the apprentice should know or be able to do at the end of training. Wording of the Learning Outcomes, Demonstrate knowledge of acknowledges the broad spectrum of ways in which knowledge can be assessed (i.e. practical projects, multiple choice testing, presentations, etc.) by instructional staff within the training. Summative evaluation will be through a multiple-choice Level Examination administered through the jurisdictional Apprenticeship Authority. 5
7 User Guide (continued) The 2015 National Occupational Analysis References (NOA) to AACS Comparison chart outlines the relation between each NOA sub-task and the AACS units. NOA References have also been detailed in each unit to highlight the direct link between the unit and relevant sub-tasks in the NOA. In the Level Structure section, the document identifies suggested hours in order to provide an indication of the time it should take to cover the material in the unit and is provided as a guide only. Adjustments to the suggested hours for each unit may be required to account for rate of apprentice learning, statutory holidays, storm days, registration and examinations. These suggested hours detailed for each unit will represent both theory and practical training (if relevant) and for consistency will be based on a standard of 30 hours per week of training. The true length of time required to deliver an outcome successfully will depend upon the learning activities and teaching methods used. There are two types of objectives found in the AACS document: theoretical and practical. The theoretical objectives represent the material that is to be covered during the technical training in order to convey the required knowledge to the apprentice. The practical objectives represent the tasks or skills that have been deemed by the Atlantic Trade Advisory Committee as critical for the apprentices to receive exposure to while attending technical training. For example, exposure could be done through instructor demonstration or individual or group performance of the skill or task. Training providers are encouraged to use practical demonstration and opportunities for hands-on learning whenever possible. Practical objectives are not intended to replace the on-the-job training component of the apprentice s program or to mirror or replace the logbook skills that are to be taught and evaluated in the workplace. Detailed content for each objective has not been developed. Where detail is required for clarity, content has been provided. 6
8 Glossary of Terms These definitions are intended as a guide to how language is used in the document. ADJUST APPLICATION CHARACTERISTIC COMPONENT DEFINE DESCRIBE EXPLAIN IDENTIFY INTERPRET MAINTAIN METHOD OPERATE PROCEDURE PURPOSE To put in good working order; regulate; bring to a proper state or position. The use to which something is put and/or the circumstance in which an individual would use it. A feature that helps to identify, tell apart or describe recognizably; a distinguishing mark or trait. A part that can be separated from or attached to a system; a segment or unit. To state the meaning of (a word, phrase, etc.). To give a verbal account of; tell about in detail. To make plain or clear; illustrate; rationalize. To point out or name objectives or types. To translate information from observation, charts, tables, graphs and written material. To keep in a condition of good repair or efficiency. A means or manner of doing something that has procedures attached to it. How an object works; to control or direct the functioning of. A prescribed series of steps taken to accomplish an end. The reason for which something exists or is done, made or used. 7
9 Glossary of Terms (continued) SERVICE Routine inspection and replacement of worn or deteriorating parts. An act or business function provided to a customer in the course of an individual s profession (e.g., haircut). TECHNIQUE TEST Within a procedure, the manner in which technical skills are applied. v. To subject to a procedure that ascertains effectiveness, value, proper function or other quality. n. A way of examining something to determine its characteristics or properties, or to determine whether or not it is working correctly. 8
10 Essential Skills Profiles Through extensive research, the Government of Canada and other national and international agencies have identified and validated key essential skills for the workplace. These skills are used in nearly every job and at different levels of complexity. They provide the foundation for learning all other skills and enable people to evolve with their jobs and adapt to workplace change. Essential Skills Profiles describe how workers in various occupations use each of the key essential skills. They include: a brief description of the occupation; examples of tasks that illustrate how each essential skill is applied; and, complexity ratings that indicate the level of difficulty of the example tasks. Essential Skills profiles can be found on the Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) website at The development and improvement of these Essential Skills is inherent throughout the apprenticeship training program as apprentices work towards achieving journeyperson status. 9
11 Profile Chart LEVEL A - COMMON OCCUPATIONAL SKILLS ICT-100 Safety ICT-105 Tools and Equipment ICT-110 Material Handling Equipment ICT-115 Communication and Trade Documentation ICT-120 Introduction to Drawings, Schematics and Specifications ICT-305 Trade Related Computer Use ICT-345 Job Planning LEVEL B - PROCESS MEASURING AND INDICATING DEVICES ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration ICT-255 Process Measurement ICT-325 Process Analyzers I ICT-330 Equipment Monitoring Devices ICT-340 Process Analyzers II ICT-415 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems LEVEL C - SAFETY AND SECURITY SYSTEMS AND DEVICES ICT- 425 Safety Systems and Devices LEVEL D - HYDRAULIC, PNEUMATIC AND ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss ICT-140 Conductors and Cables ICT-145 On-off Control Devices ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-235 Final Control Elements ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory ICT-260 Hydraulic Supply Systems and Control Devices ICT-265 Pneumatic Supply Systems ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) 10
12 Profile Chart (continued) LEVEL E - FINAL CONTROL DEVICES ICT-270 Electronics Components (Circuits and Power Supplies) ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) LEVEL F - COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND DEVICES ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices LEVEL G - CONTROL SYSTEMS AND PROCESS CONTROL ICT-300 Basic Process Control ICT-410 Advanced Process Control ICT-415 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems ICT-420 Human Machine Interface Systems ICT-435 Programmable Logic Controller Systems ICT-440 Distributed Control Systems 11
13 Nova Scotia Program Structure Level 1 7 Weeks Unit Code Unit Title Suggested Hours Page Number ICT-100 Safety ICT-105 Tools and Equipment ICT-110 Material Handling Equipment 6 26 ICT-115 Communication and Trade Documentation 6 27 ICT-120 Introduction to Drawings, Schematics and Specifications ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss ICT-140 Conductors and Cables ICT-145 On-off Control Devices ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems MENT-1801, Level 1, Mentoring I, Integrated Milestone, 6 hrs, Pg Level 2 8 Weeks Unit Code Unit Title Suggested Hours Page Number ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-235 Final Control Elements ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory ICT-255 Process Measurement ICT-260 Hydraulic Supply Systems and Control Devices ICT-265 Pneumatic Supply Systems ICT-270 Electronics Components (Circuits and Power Supplies)
14 Nova Scotia Program Structure (continued) Level 3 7 Weeks Unit Code Unit Title Suggested Hours Page Number ICT-300 Basic Process Control ICT-305 Trade Related Computer Use 6 67 ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) ICT-325 Process Analyzers I ICT-330 Equipment Monitoring Devices ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices ICT-340 Process Analyzers II ICT-345 Job Planning 6 82 Level 4 7 Weeks Unit Code Unit Title Suggested Hours Page Number ICT- 410 Advanced Process Control ICT- 415 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems ICT- 420 Human Machine Interface Systems ICT- 425 Safety Systems and Devices ICT- 435 Programmable Logic Controller Systems ICT- 440 Distributed Control Systems ICT- 600 Program Review MENT-1802, Level 4, Mentoring II, Integrated Milestone, 3 hrs, Pg
15 2013 NOA Sub-task to AAC Unit Comparison NOA Sub-task AACS Unit Task 1 - Performs safety-related functions Maintains safe work environment. ICT-100 Safety 1.02 Uses personal protective ICT-100 Safety equipment (PPE) and safety equipment Performs de-energizing, lock-out and tag-out procedures. ICT-100 Safety Task 2 - Organizes work Uses diagrams, drawings and schematics ICT-120 Introduction to Drawings, Schematics and Specifications 2.02 Plans tasks ICT-345 Job Planning Task 3 - Performs routine trade activities Maintains calibration, ICT-105 Tools and Equipment configuration and test equipment Maintains tools. ICT-105 Tools and Equipment 3.03 Maintains documentation ICT-115 Communication and Trade Documentation ICT-305 Trade Related Computer Use 3.04 Operates material handling equipment. ICT-110 Material Handling Equipment Task 4 Installs and services pressure, temperature, level and flow devices Installs pressure, temperature, level and flow devices. ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration ICT-255 Process Measurement 4.02 Maintains pressure, temperature, level and flow devices. ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration ICT-255 Process Measurement 4.03 Diagnoses pressure, temperature, level and flow devices. ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration ICT-255 Process Measurement 4.04 Repairs pressure, temperature, level and flow devices. ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration ICT-255 Process Measurement Task 5 - Installs and services motion, speed, position and vibration devices Installs motion, speed, position ICT-330 Equipment Monitoring Devices and vibration devices Maintains motion, speed, position and vibration devices. ICT-330 Equipment Monitoring Devices 14
16 NOA Sub-task AACS Unit 5.03 Diagnoses motion, speed, position ICT-330 Equipment Monitoring Devices and vibration devices Repairs motion, speed, position and vibration devices. ICT-330 Equipment Monitoring Devices Task 6 - Installs and services mass, density and consistency devices Installs mass, density and ICT-325 Process Analyzers I consistency devices. ICT-340 Process Analyzers II 6.02 Maintains mass, density, and ICT-325 Process Analyzers I consistency devices. ICT-340 Process Analyzers II 6.03 Diagnoses mass, density, and ICT-325 Process Analyzers I consistency devices. ICT-340 Process Analyzers II 6.04 Repairs mass, density and ICT-325 Process Analyzers I consistency devices. ICT-340 Process Analyzers II Task 7 - Installs and services process analyzers Installs process analyzers. ICT-325 Process Analyzers I ICT-340 Process Analyzers II 7.02 Maintains process analyzers. ICT-325 Process Analyzers I ICT-340 Process Analyzers II 7.03 Diagnoses process analyzers. ICT-325 Process Analyzers I ICT-340 Process Analyzers II 7.04 Repairs process analyzers. ICT-325 Process Analyzers I ICT-340 Process Analyzers II Task 8 - Installs and services multiple variable computing devices Installs multiple variable computing devices. ICT-415 Supervisory and Data Acquisition Systems 8.02 Maintains multiple variable computing devices. ICT-415 Supervisory and Data Acquisition Systems 8.03 Diagnoses multiple variable computing devices. ICT-415 Supervisory and Data Acquisition Systems 8.04 Repairs multiple variable computing devices. ICT-415 Supervisory and Data Acquisition Systems Task 9 - Installs and services safety systems and devices Installs safety systems and devices. ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices 9.02 Maintains safety systems and ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices devices Diagnoses safety systems and ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices devices Repairs safety systems and devices. ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices 15
17 NOA Sub-task AACS Unit Task 10 - Installs and services facility security systems. (NOT COMMON CORE) Installs facility security systems. (NOT COMMON CORE) Maintains facility security systems. (NOT COMMON CORE) Diagnoses facility security systems. (NOT COMMON CORE) Repairs facility security systems. (NOT COMMON CORE) Task 11 - Installs and services safety instrumented systems (SISs) Installs SISs. ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices Configures SISs. ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices Maintains SISs. ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices Diagnoses SISs. ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices Repairs SISs. ICT-425 Safety Systems and Devices Task 12 - Installs and services control devices for hydraulic systems Installs control devices for ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems hydraulic systems. ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-260 Hydraulic Supply Systems and Control Devices Maintains control devices for ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems hydraulic systems. ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-260 Hydraulic Supply Systems and Control Devices Diagnoses control devices and hydraulic systems Repairs control devices for hydraulic systems. ICT-160 ICT-205 ICT-260 ICT-160 ICT-205 ICT-260 Tubing and Piping Systems Introduction to Fluids Hydraulic Supply Systems and Control Devices Tubing and Piping Systems Introduction to Fluids Hydraulic Supply Systems and Control Devices Task 13 - Installs and services pneumatic equipment Installs pneumatic equipment. ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-265 Pneumatic Supply Systems Maintains pneumatic equipment. ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-265 Pneumatic Supply Systems Diagnoses pneumatic equipment. ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems 16
18 NOA Sub-task AACS Unit ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-265 Pneumatic Supply Systems Repairs pneumatic equipment. ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-265 Pneumatic Supply Systems Task 14 - Installs and services electrical and electronic equipment Installs electrical and electronic ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory equipment. ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss ICT-140 Conductors and Cables ICT-145 On-Off Control Devices ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings ICT-270 Electronics Components (Circuits and Power Supplies) ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Maintains electrical and electronic ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory equipment. ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss ICT-140 Conductors and Cables ICT-145 On-Off Control Devices ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings ICT-270 Electronics Components (Circuits and Power Supplies) ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Diagnoses electrical and electronic ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory equipment. ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss ICT-140 Conductors and Cables ICT-145 On-Off Control Devices ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings ICT-270 Electronics Components (Circuits and Power Supplies) ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory 17
19 NOA Sub-task AACS Unit ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Repairs electrical and electronic ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory equipment. ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss ICT-140 Conductors and Cables ICT-145 On-Off Control Devices ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings ICT-270 Electronics Components (Circuits and Power Supplies) ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Task 15 - Installs and services valves Installs valves. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Maintains valves. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Diagnoses valves. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Repairs valves. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Task 16 - Installs and services actuators Installs actuators. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Maintains actuators. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Diagnoses actuators. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Repairs actuators. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Task 17 - Installs and services positioners Installs positioners. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Maintains positioners. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Diagnoses positioners. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Repairs positioners. ICT-235 Final Control Elements Task 18 - Configures and services variable speed drives (VSDs) Configures VSDs. ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Maintains VSDs. ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Diagnoses VSDs. ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Repairs VSDs. ICT-320 Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) Task 19 - Installs and services control network systems Performs installation and configuration on control network systems Diagnoses control network systems Performs maintenance and repairs on control network systems. 18 ICT-335 ICT-335 ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices Communication Systems and Devices Communication Systems and Devices
20 NOA Sub-task AACS Unit Task 20 - Installs and services signal converters Performs installation and configuration of signal converters. ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices Diagnoses signal converters. ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices Performs maintenance and repairs on signal converters. ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices Task 21 - Installs and services gateways, bridges and media converters Performs installation and configuration of gateways, bridges ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices and media converters Diagnoses gateways, bridges and media converters. ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices Performs maintenance and repairs on gateways, bridges and media converters. ICT-335 Communication Systems and Devices Task 22 - Establishes and optimizes process control strategies Determines process control ICT-300 Basic Process Control strategy. ICT-410 Advanced Process Control Optimizes process control. ICT-300 Basic Process Control ICT-410 Advanced Process Control Task 23 - Installs and services stand-alone controllers (SACs) Installs SACs. ICT-300 Basic Process Control ICT-410 Advanced Process Control Configures SACs. ICT-300 Basic Process Control ICT-410 Advanced Process Control Performs maintenance, diagnostics ICT-300 Basic Process Control and repairs on SACs. ICT-410 Advanced Process Control Task 24 - Installs and services programmable logic controllers (PLCs) Installs PLCs. ICT-435 Programmable Logic Controller Systems Configures PLCs. ICT-435 Programmable Logic Controller Systems Performs maintenance, diagnosis and repairs on PLCs. ICT-435 Programmable Logic Controller Systems Task 25 - Installs and services distributed control systems (DCSs) Installs DCSs. ICT-440 Distributed Control Systems Configures DCSs. ICT-440 Distributed Control Systems Performs maintenance, diagnosis and repairs on DCSs. ICT-440 Distributed Control Systems Task 26 - Installs and services human machine interface (HMI). 19
21 NOA Sub-task AACS Unit Installs HMIs. ICT-420 Human Machine Interface Systems Configures HMIs. ICT-420 Human Machine Interface Systems Performs maintenance, diagnosis and repairs on HMIs. ICT-420 Human Machine Interface Systems Task 27 - Installs and services Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems Installs SCADA systems. ICT-415 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems Configures SCADA systems. ICT-415 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems Performs maintenance, diagnosis and repairs on SCADA systems. ICT-415 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems 20
22 Level 1 Unit Code Title Hours Page ICT-100 Safety ICT-105 Tools and Equipment ICT-110 Material Handling Equipment 6 26 ICT-115 Communication and Trade Documentation 6 27 ICT-120 Introduction to Drawings, Schematics and Specifications ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss ICT-140 Conductors and Cables ICT-145 On-off Control Devices ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems
23 ICT-100 Safety Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of safety equipment, their applications, maintenance and procedures for use. - Demonstrate knowledge of safe work practices. - Demonstrate knowledge of regulatory requirements pertaining to safety National Occupational Analysis Reference: 1.01 Maintains safe work environment Uses personal protective equipment (PPE) and safety equipment Performs de-energizing, lock-out and tag-out procedures. Suggested Hours: 12 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Identify types of personal protective equipment (PPE) and clothing and describe their applications and limitations. 2. Describe the procedures used to care for and maintain PPE. 3. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices. i) personal ii) workplace - energy state awareness - isolation and de-energizing procedures - tag out/lockout - confined space - fire - heights - nuclear - chemical/gas - arc flash - temperature extremes 22
24 iii) environmental - discharge/spills 4. Identify and describe workplace safety and health regulations. i) federal - Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) - Workplace Hazardous Material Information System (WHMIS) - Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) - Atomic Energy Control Act and Regulations ii) provincial/territorial iii) municipal Practical Objectives N/A 23
25 ICT-105 Tools and Equipment Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of tools and equipment, their applications, maintenance and procedures for use. - Demonstrate knowledge of installation and mounting hardware and their applications National Occupational Analysis Reference: 3.01 Maintains calibration, configuration and test equipment Maintains tools. Suggested Hours: 12 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Identify types of hand tools and describe their applications and procedures for use. 2. Describe the procedures used to inspect and maintain hand tools. 3. Identify types of portable power tools and describe their applications and procedures for use. i) electric ii) hydraulic iii) pneumatic iv) powder actuated tools 4. Describe the procedures used to inspect and maintain portable power tools. 5. Identify types of stationary power tools and describe their applications and procedures for use. i) electric ii) hydraulic iii) pneumatic 24
26 6. Describe the procedures used to inspect and maintain stationary power tools. 7. Identify types of calibration, configuration and test equipment and describe their applications and their care. 8. Identify types of installation and mounting hardware and describe their applications. Practical Objectives N/A 25
27 ICT-110 Material Handling Equipment Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of material handling equipment and accessories, their applications and limitations National Occupational Analysis Reference: 3.04 Operates material handling equipment. Suggested Hours: 6 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with material handling equipment and accessories. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to material handling. i) load considerations ii) supervision of material handling iii) securing work area iv) communication 3. Identify codes and regulations pertaining to material handling. 4. Identify types of material handling equipment and accessories and describe their applications and limitations. i) rigging equipment ii) pallet jacks iii) forklifts iv) stationary cranes 5. Describe the procedures used to inspect and store material handling equipment. Practical Objectives N/A 26
28 ICT-115 Communication and Trade Documentation Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of effective communication practices. - Demonstrate knowledge of trade related documentation and its use National Occupational Analysis Reference: 3.03 Maintains documentation. Suggested Hours: 6 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Describe the importance of effective verbal and non-verbal communication. i) other tradespersons ii) colleagues iii) supervisors iv) suppliers/manufacturers 2. Identify types of trade related documentation and describe their purpose, applications and procedures for use. i) manufacturers specifications/manuals ii) codes and standards iii) work orders iv) maintenance schedules v) commissioning/calibration/maintenance records Practical Objectives N/A 27
29 ICT-120 Introduction to Drawings, Schematics and Specifications Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of drawings, schematics and specifications and their applications. - Demonstrate knowledge of interpreting and extracting information from drawings, schematics and specifications. - Demonstrate knowledge of maintaining drawings, schematics and specifications National Occupational Analysis Reference: 2.01 Uses diagrams, drawings and schematics. Suggested Hours: 12 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with drawings, schematics and specifications. 2. Identify types of drawings and describe their applications. i) mechanical - plant layout - process equipment details ii) process - piping and instrument drawings (P&ID) - Scientific Apparatus Manufacturers Association (SAMA) - loop drawings - International Society of Automation (ISA) iii) electrical - schematics - wiring diagrams 3. Interpret and extract information from drawings. i) lines ii) legends 28
30 iii) iv) symbols and abbreviations notes and specifications 4. Interpret and extract information from schematics and specifications. 5. Describe the procedures used to revise drawings, schematics and specifications. i) as-builts ii) document control Practical Objectives N/A 29
31 ICT-125 Direct Current (DC) Theory Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of direct current (DC) electricity, its characteristics and associated principles. - Demonstrate knowledge of Ohm s law. - Demonstrate knowledge of units of measure and symbols relating to DC electricity. - Demonstrate knowledge of the instruments and procedures used to measure electricity National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs electrical and electronic equipment Maintains electrical and electronic equipment Diagnoses electrical and electronic equipment Repairs electrical and electronic equipment. Suggested Hours: 30 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with DC electricity. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to DC electricity. 3. Explain the atomic structure of matter. 4. Identify the forms of energy that produce electricity and describe their associated principles. i) chemical action ii) piezoelectric effect iii) magnetism iv) heat v) light and solar vi) friction 30
32 5. Identify the components of an electric circuit and describe the procedures used to analyze them. i) electron path (conductors) - closed circuit - open circuit - short circuit ii) load iii) source iv) control 6. Identify units of measure and symbols pertaining to DC electricity. 7. Explain Ohm s Law. 8. Identify the basic electrical properties and describe their relationship. i) voltage ii) current iii) resistance iv) power 9. Explain the effects of resistance/capacitance (RC) on DC circuits. 10. Identify instruments used for measuring electricity and describe their applications and procedures for use. 11. Perform calculations to determine electricity related values. Practical Objectives 1. Use multi-meters to measure DC components and circuits. 31
33 ICT-130 Series and Parallel Circuits Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of series, parallel and complex circuits, their characteristics and operation National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs electrical and electronic equipment Maintains electrical and electronic equipment Diagnoses electrical and electronic equipment Repairs electrical and electronic equipment. Suggested Hours: 30 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with series and parallel circuits. 2. Explain the characteristics and operation of series circuits. 3. Explain the characteristics and operation of parallel circuits. 4. Identify complex series-parallel circuits and describe their characteristics and operation. 5. Explain Kirchhoff s Laws. i) current ii) voltage 6. Perform calculations to determine series, parallel and complex circuit related values. 7. Describe the procedures used to troubleshoot series, parallel and complex circuits. Practical Objectives 1. Use multi-meters to measure series, parallel and complex circuits. 32
34 ICT-135 Voltage Drop and Power Loss Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of voltage drop and power loss and its impact on a circuit National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs electrical and electronic equipment Maintains electrical and electronic equipment Diagnoses electrical and electronic equipment Repairs electrical and electronic equipment. Suggested Hours: 12 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with voltage drop and power loss. 2. Interpret codes and regulations pertaining to voltage drop and power loss. i) Canadian Electrical Code 3. Identify types of conductors and describe their characteristics and applications. 4. Identify the units of measure used to describe conductor size. 5. Identify types of insulators and describe their characteristics and applications. 6. Explain conductor resistance and its effect on a circuit. 7. Describe the procedures used to determine conductor resistance. 8. Explain line voltage drop and its effect on a circuit. 9. Perform calculations to determine line voltage drop. 33
35 10. Explain power loss and its effect on a circuit. 11. Perform calculations to determine power loss. Practical Objectives N/A 34
36 ICT-140 Conductors and Cables Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of conductor and cable components. - Demonstrate knowledge of conductor and cable accessories. - Demonstrate knowledge of the procedures used to install conductors and cables. - Demonstrate knowledge of the procedures used to terminate conductors National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs electrical and electronic equipment Maintains electrical and electronic equipment Diagnoses electrical and electronic equipment Repairs electrical and electronic equipment. Suggested Hours: 18 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with conductors and cables. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to conductors and cables. 3. Identify tools and equipment relating to conductors and cables and describe their applications and procedures for use. 4. Interpret codes and regulations pertaining to conductors and cables. i) Canadian Electrical Code 5. Interpret information pertaining to conductors and cables found on drawings and specifications. 6. Identify types of conductors and cables and describe their characteristics and applications. i) power/distribution 35
37 ii) iii) signal/control communication/data 7. Identify cable components and describe their characteristics and applications. i) mechanical ii) electrical 8. Identify conductor and cable accessories and describe their characteristics and applications. i) connectors ii) supports 9. Identify methods of circuit protection and describe their characteristics and applications. i) fuses ii) circuit breakers 10. Identify the considerations used when selecting conductors and cables and their associated components and accessories. 11. Describe the procedures used to install conductors and cables and their associated components and accessories. 12. Describe the procedures used to ground, bond and shield conductors and cables. i) power/distribution ii) signal/control iii) communication/data 13. Describe the methods used to terminate conductors. i) terminal blocks ii) conical springs (twist-on wire connectors, wire nuts) iii) crimp lugs iv) solder joints Practical Objectives N/A 36
38 ICT-145 On-off Control Devices Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of on-off control devices, their components, operation and applications. - Demonstrate knowledge of the procedures used to install, maintain, troubleshoot and replace on-off control devices National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs electrical and electronic equipment Maintains electrical and electronic equipment Diagnoses electrical and electronic equipment Repairs electrical and electronic equipment. Suggested Hours: 30 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with on-off control devices. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to on-off control devices. i) energy state awareness 3. Interpret codes and regulations pertaining to on-off control devices. 4. Interpret information pertaining to on-off control devices found on drawings, specifications and nameplates. 5. Identify types of on-off control devices and describe their characteristics. i) pushbuttons ii) switches - limit - proximity - centrifugal 37
39 iii) iv) - thermal photo sensors relays 6. Identify the applications for on-off control devices. i) hazardous locations ii) non-hazardous locations iii) environment conditions iv) process conditions 7. Describe the procedures used to install on-off control devices. 8. Describe the procedures used to maintain, troubleshoot and replace on-off control devices. Practical Objectives 1. Troubleshoot on/off control devices. 38
40 ICT-150 Wireways, Raceways and Fittings Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of wireways, raceways and fittings, their characteristics and applications. - Demonstrate knowledge of the procedures used to install wireways, raceways and fittings National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs electrical and electronic equipment Maintains electrical and electronic equipment Diagnoses electrical and electronic equipment Repairs electrical and electronic equipment. Suggested Hours: 12 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with wireways, raceways and fittings. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to wireways, raceways and fittings. 3. Identify tools and equipment relating to wireways, raceways and fittings and describe their applications and procedures for use. 4. Interpret codes and regulations pertaining to wireways, raceways and fittings. 5. Interpret information pertaining to wireways, raceways and fittings found on drawings and specifications. 6. Identify types of wireways and raceways and describe their characteristics and applications. i) cable tray - power 39
41 ii) iii) - instrument conduit - rigid - PVC - flexible electrical metallic tubing (EMT) 7. Identify wireway and raceway accessories and describe their characteristics and applications. 8. Describe the procedures used to bend conduit and EMT. 9. Describe the procedures used to install wireways and raceways and their fittings and accessories. Practical Objectives N/A 40
42 ICT-155 Introduction to Pressure Measurement and Calibration Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of pressure measurement and calibration. - Demonstrate knowledge of the procedures used to install, calibrate, maintain and troubleshoot basic pressure measurement devices National Occupational Analysis Reference: 4.01 Installs pressure, temperature, level and flow devices Maintains pressure, temperature, level and flow devices Diagnoses pressure, temperature, level and flow devices Repairs pressure, temperature, level and flow devices. Suggested Hours: 18 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with pressure measurement and calibration. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to pressure measurement and calibration. i) physical locations ii) process conditions iii) electrical 3. Identify tools and equipment relating to pressure measurement and calibration and describe their applications and procedures for use. 4. Interpret information pertaining to pressure measuring devices found on drawings, specifications and nameplates. 5. Interpret and maintain calibration records. 6. Identify units of measure used to express pressure measurement values. 41
43 7. Perform conversions and calculations relating to pressure measurement. 8. Explain the principles of pressure measurement and its relationship to temperature, level and flow. 9. Identify types of basic pressure measurement fluid mediums and describe their applications. i) pneumatic ii) hydraulic 10. Identify pressure related calibration standards and describe their applications. i) primary ii) secondary 11. Identify pressure related calibration test equipment and describe their applications. i) dead weight tester ii) manometer iii) test gauges and calibrators 12. Describe the procedures used to install basic pressure measurement devices. i) gauges ii) recorders iii) switches iv) transmitters 13. Describe the procedures used to maintain and troubleshoot basic pressure measurement devices. Practical Objectives 1. Calibrate basic pressure measurement devices. 42
44 ICT-160 Tubing and Piping Systems Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of tubing and piping systems, their components and operation. - Demonstrate knowledge of the procedures used to install, maintain and troubleshoot tubing and piping systems and their components National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs control devices for hydraulic systems Maintains control devices for hydraulic systems Diagnoses control devices for hydraulic systems Repairs control devices for hydraulic systems Installs pneumatic equipment Maintains pneumatic equipment Diagnoses pneumatic equipment Repairs pneumatic equipment. Suggested Hours: 12 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with tubing and piping systems. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to tubing and piping systems. 3. Identify tools and equipment relating to tubing and piping systems and describe their applications and procedures for use. 4. Interpret codes and regulations pertaining to tubing and piping systems. 5. Interpret information pertaining to tubing and piping systems found on drawings and specifications. 43
45 6. Identify types of tubing and piping systems and describe their applications. i) rigid ii) flexible - tubing - hoses iii) ferrous iv) non-ferrous 7. Identify types of tubing and piping and describe their compatibility, characteristics and applications. i) hydraulic ii) pneumatic 8. Identify types of tube and pipe fittings and accessories and describe their characteristics and applications. 9. Identify types of valves used in tubing and piping systems and describe their applications and operation. i) isolation ii) throttling iii) regulating 10. Describe the procedures used to select and install tubing and piping system components and accessories. 11. Describe the procedures used to maintain and troubleshoot tubing and piping systems and components. Practical Objectives 1. Perform tube bending, installation and pressure test. 2. Cut, thread and ream rigid pipe. 44
46 Level 2 Unit Code Title Hours Page ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids ICT-235 Final Control Elements ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory ICT-255 Process Measurement ICT-260 Hydraulic Supply Systems and Control Devices ICT-265 Pneumatic Supply Systems ICT-270 Electronics Components (Circuits and Power Supplies)
47 ICT-205 Introduction to Fluids Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of the principles and applications of fluids National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs control devices for hydraulic systems Maintains control devices for hydraulic systems Diagnoses control devices for hydraulic systems Repairs control devices for hydraulic systems Installs pneumatic equipment Maintains pneumatic equipment Diagnoses pneumatic equipment Repairs pneumatic equipment. Suggested Hours: 12 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with fluids. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to fluids. i) pressure ii) temperature iii) chemical 3. Explain the principles and theories of fluids. i) Pascal s law ii) Boyle s law iii) Charles law iv) Combined Gas law v) Bernoulli s principle 4. Describe units of measure as they relate to fluids. 46
48 5. Identify fluid related formulas and describe their applications. 6. Identify fluid related symbols and abbreviations found on drawings and schematics. Practical Objectives N/A 47
49 ICT-235 Final Control Elements Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of final control elements, their accessories, components and operation. - Demonstrate knowledge of the procedures used to install, maintain, troubleshoot and replace final control elements, their accessories and components National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs valves Maintains valves Diagnoses valves Repairs valves Installs actuators Maintains actuators Diagnoses actuators Repairs actuators Installs positioners Maintains positioners Diagnoses positioners Repairs positioners. Suggested Hours: 42 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with final control elements. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to final control elements. i) energy state awareness - pressure - voltage - mechanical - temperature 48
50 ii) iii) chemical isolation/lock-out/tag-out 3. Identify tools and equipment relating to final control elements and describe their applications and procedures for use. 4. Interpret codes and regulations pertaining to final control elements. 5. Interpret information pertaining to final control elements found on drawings, specifications and nameplates. 6. Identify types of final control elements and describe their components, applications and operation. i) valves ii) dampers/louvres iii) positive displacement metering pumps iv) motors v) process regulators 7. Identify types of energy systems used to operate final control elements and describe their characteristics and applications. i) hydraulic ii) pneumatic iii) electric iv) manual operation 8. Identify final control element accessories and describe their components, purpose and operation. i) actuators - hydraulic - pneumatic - electric ii) boosters - volume - pressure iii) positioners - electric - pneumatic - smart iv) regulators v) switches 49
51 vi) vii) hand wheels variable speed drives (VSDs) 9. Describe the procedures used to select, size and install final control elements, their accessories and components. 10. Describe the procedures used to maintain, troubleshoot and replace final control elements, their accessories and components. Practical Objectives 1. Disassemble and assemble a control valve. 2. Install a positioner. 50
52 ICT-245 Alternating Current (AC) Theory Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate knowledge of single-phase electricity, its characteristics and associated principles. - Demonstrate basic knowledge of AC electrical generation, its characteristics and associated principles. - Demonstrate knowledge of alternating current (AC) devices and their characteristics National Occupational Analysis Reference: Installs electrical and electronic equipment Maintains electrical and electronic equipment Diagnoses electrical and electronic equipment Repairs electrical and electronic equipment. Suggested Hours: 30 Hours Objectives and Content: Theoretical Objectives 1. Define terminology associated with single-phase electricity. 2. Identify hazards and describe safe work practices pertaining to single-phase electricity. 3. Identify units of measure and symbols pertaining to single-phase electricity. 4. Explain the principles of magnetism. 5. Explain the principles of electromagnetism. 6. Explain the principles of electromagnetic induction. 7. Identify the types of electromagnetic induction and describe their characteristics and applications. 51
NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD
 NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD for the Red Seal Occupation of Based on the Interprovincial Program Guide Levels 3 & 4 in September 2018 (pg. 12 for Program Structure) Construction Electrician
NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD for the Red Seal Occupation of Based on the Interprovincial Program Guide Levels 3 & 4 in September 2018 (pg. 12 for Program Structure) Construction Electrician
Wisconsin Technical College System Curriculum Standards Model & Program Design Summary ELECTRICAL & INSTRUMENTATION APPRENTICE
 Curriculum Standards Model & Program Design Summary 50-414-2 ELECTRICAL & INSTRUMENTATION APPRENTICE Program Information Program Electrical & Instrumentation Technicians install, service, troubleshoot;
Curriculum Standards Model & Program Design Summary 50-414-2 ELECTRICAL & INSTRUMENTATION APPRENTICE Program Information Program Electrical & Instrumentation Technicians install, service, troubleshoot;
Electromechanical Technology /Electromechanical Engineering Technology CIP Task Grid
 1 Secondary Task List 100 DEMONSTRATE KNOWLEDGE OF TECHNICAL REPORTS 101 Identify components of technical reports. 102 Demonstrate knowledge of the common components of technical documents. 103 Maintain
1 Secondary Task List 100 DEMONSTRATE KNOWLEDGE OF TECHNICAL REPORTS 101 Identify components of technical reports. 102 Demonstrate knowledge of the common components of technical documents. 103 Maintain
Instrumentation and Control Technician A Guide to Course Content Implementation Beginning with Level 1 April 2013
 Instrumentation and Control Technician A Guide to Course Content Implementation Beginning with Level 1 April 2013 Instrumentation and Control Technicians maintain, diagnose, calibrate and repair measurement
Instrumentation and Control Technician A Guide to Course Content Implementation Beginning with Level 1 April 2013 Instrumentation and Control Technicians maintain, diagnose, calibrate and repair measurement
Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement. Documentation item: Secondary Competency Task List Coversheet
 Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement Documentation item: Secondary Task List Coversheet The Secondary School agrees to: A. Implement the approved PDE Program(s) of Study. B. Provide assessment of student
Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement Documentation item: Secondary Task List Coversheet The Secondary School agrees to: A. Implement the approved PDE Program(s) of Study. B. Provide assessment of student
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) ELECTROMECHANICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNICIAN Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC)
 Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) ELECTROMECHANICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNICIAN Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) ELECTROMECHANICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNICIAN Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles
apprenticeship curriculum standard NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD SHEET METAL WORKER
 apprenticeship curriculum standard NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD SHEET METAL WORKER 2018 2015 Based on the CCDA for the Harmonization Occupation of Recommendations and the Interprovincial
apprenticeship curriculum standard NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD SHEET METAL WORKER 2018 2015 Based on the CCDA for the Harmonization Occupation of Recommendations and the Interprovincial
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNOLOGIST Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC)
 Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNOLOGIST Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNOLOGIST Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles
Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) Level 4
 Level 4 Rev. September 2005 Unit: A3 Pre-Interprovincial Review 50 hours Theory: Practical: 50 hours 0 hours This unit offers apprentices a systematic review of skills and knowledge required to pass the
Level 4 Rev. September 2005 Unit: A3 Pre-Interprovincial Review 50 hours Theory: Practical: 50 hours 0 hours This unit offers apprentices a systematic review of skills and knowledge required to pass the
NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD
 NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD for the Occupation of Based on the Interprovincial Program Guide (pg. 12 for Program Structure) Machinist New Levels 1, 2, 3 & 4 in September 2014 See Page
NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD for the Occupation of Based on the Interprovincial Program Guide (pg. 12 for Program Structure) Machinist New Levels 1, 2, 3 & 4 in September 2014 See Page
SHEET METAL WORKER 2015
 apprenticeship curriculum standard NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD SHEET METAL WORKER 2015 2014 for the Occupation of Based on the Interprovincial Program Guide Based on the Interprovincial
apprenticeship curriculum standard NOVA SCOTIA APPRENTICESHIP CURRICULUM STANDARD SHEET METAL WORKER 2015 2014 for the Occupation of Based on the Interprovincial Program Guide Based on the Interprovincial
Interprovincial Program Guide. Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) 2015
 Interprovincial Program Guide Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) 2015 Interprovincial Program Guide Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) 2015 Trades and Apprenticeship Division Labour Market Integration Directorate
Interprovincial Program Guide Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) 2015 Interprovincial Program Guide Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) 2015 Trades and Apprenticeship Division Labour Market Integration Directorate
Thank you for your interest in the Electrical Technician program. Following is the application process:
 Thank you for your interest in the Electrical Technician program. Following is the application process: Information Session: Attendance at an Information Session is a prerequisite to acceptance into EHOVE
Thank you for your interest in the Electrical Technician program. Following is the application process: Information Session: Attendance at an Information Session is a prerequisite to acceptance into EHOVE
Mechatronics-Level 1
 Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Mechatronics-Level 1 Test Code: 2040 / Version: 01 Copyright 2012 General Assessment Information General Assessment Information Written Assessment
Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Mechatronics-Level 1 Test Code: 2040 / Version: 01 Copyright 2012 General Assessment Information General Assessment Information Written Assessment
Industrial Maintenance Mechanics
 Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Industrial Maintenance Mechanics Test Code: 2074 / Version: 01 Copyright 2007 General Assessment Information Industrial Maintenance Mechanics Blueprint
Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Industrial Maintenance Mechanics Test Code: 2074 / Version: 01 Copyright 2007 General Assessment Information Industrial Maintenance Mechanics Blueprint
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNOLOGIST Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC)
 Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNOLOGIST Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles involving
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNOLOGIST Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles involving
CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS MECHATRONICS MÉCATRONIQUE POST- SECONDARY / NIVEAUX POSTSECONDAIRE
 CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS MECHATRONICS MÉCATRONIQUE POST- SECONDARY / NIVEAUX POSTSECONDAIRE Table of Contents 1 THE ESSENTIAL SKILLS FOR CAREERS IN THE SKILLED TRADES AND TECHNOLOGY...
CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS MECHATRONICS MÉCATRONIQUE POST- SECONDARY / NIVEAUX POSTSECONDAIRE Table of Contents 1 THE ESSENTIAL SKILLS FOR CAREERS IN THE SKILLED TRADES AND TECHNOLOGY...
TEACHER ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ELECTRICAL CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY. Test Code: 5171 Version: 01
 TEACHER ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ELECTRICAL CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY Test Code: 5171 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: OSHA Regulations and Electrical Safety Practices
TEACHER ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ELECTRICAL CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY Test Code: 5171 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: OSHA Regulations and Electrical Safety Practices
Principles of Engineering
 Principles of Engineering 2004 (Fifth Edition) Clifton Park, New York All rights reserved 1 The National Academy of Sciences Standards: 1.0 Science Inquiry 1.1 Ability necessary to do scientific inquiry
Principles of Engineering 2004 (Fifth Edition) Clifton Park, New York All rights reserved 1 The National Academy of Sciences Standards: 1.0 Science Inquiry 1.1 Ability necessary to do scientific inquiry
TROUBLESHOOTING A TECHNICIAN S GUIDE 2ND EDITION. William L. Mostia, Jr., P. E. ISA TECHNICIAN SERIES
 TROUBLESHOOTING A TECHNICIAN S GUIDE 2ND EDITION William L. Mostia, Jr., P. E. ISA TECHNICIAN SERIES TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 1 Learning to Troubleshoot........................ 1 1.1 Experience..............................
TROUBLESHOOTING A TECHNICIAN S GUIDE 2ND EDITION William L. Mostia, Jr., P. E. ISA TECHNICIAN SERIES TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 1 Learning to Troubleshoot........................ 1 1.1 Experience..............................
INSTRUMENTATION DESIGN ENGINEERING: Oil & Gas
 SmartBrains Engineers & Technologist Pvt. Ltd. DESIGN ENGINEERING: Oil & Gas Building Nation Through SmartBrains Skill Development & Enterpreneurship Website : www.samrtbrains.in To Apply Please contact
SmartBrains Engineers & Technologist Pvt. Ltd. DESIGN ENGINEERING: Oil & Gas Building Nation Through SmartBrains Skill Development & Enterpreneurship Website : www.samrtbrains.in To Apply Please contact
AMTEC Modules. AMT 102: General PM and Predictive Maintenance AMT 1021: Basic PM AMT 1022: Advanced Technologies
 AMT 100: Computer Literacy AMT 1001: Orientation to Computer Systems AMT 1002: Operating Systems AMT 1003: Computer Applications AMT 1004: Internet/Intranet AMT 101: Fluid Power and Electrohydraulics/Pneumatics
AMT 100: Computer Literacy AMT 1001: Orientation to Computer Systems AMT 1002: Operating Systems AMT 1003: Computer Applications AMT 1004: Internet/Intranet AMT 101: Fluid Power and Electrohydraulics/Pneumatics
M i c r o p r o c e s s o r s ( 1 2 C )
 9 0 5 2 M i c r o p r o c e s s o r s ( 1 2 C ) 40S/40E/40M An Electronics Technology Course 9 0 5 2 : M i c r o p r o e s s o r s ( 1 2 C ) 4 0 S / 4 0 E / 4 0 M Course Description This course focuses
9 0 5 2 M i c r o p r o c e s s o r s ( 1 2 C ) 40S/40E/40M An Electronics Technology Course 9 0 5 2 : M i c r o p r o e s s o r s ( 1 2 C ) 4 0 S / 4 0 E / 4 0 M Course Description This course focuses
Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) On-the-Job Training Guide
 Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) On-the-Job Training Guide Industrial Mechanics (Millwright) install, maintain and repair machinery in factories, mines and production facilities. Training Requirements:
Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) On-the-Job Training Guide Industrial Mechanics (Millwright) install, maintain and repair machinery in factories, mines and production facilities. Training Requirements:
Engineering and Electronics Technology
 Engineering and Electronics Technology Degrees: AAS Engineering and Electronics Technology 60-68 Tracks: Electronics 62-64 Computer Maintenance 63-66 Apprenticeship 66-68 Mechanical 64-67 Industrial 66-68
Engineering and Electronics Technology Degrees: AAS Engineering and Electronics Technology 60-68 Tracks: Electronics 62-64 Computer Maintenance 63-66 Apprenticeship 66-68 Mechanical 64-67 Industrial 66-68
INDUSTRIAL MECHANIC (MILLWRIGHT)
 Interim Logbook Department of Advanced Education and Skills Apprenticeship and Trades Certification Division INDUSTRIAL MECHANIC (MILLWRIGHT) Note to Apprenticeship Applicants This form can only be used
Interim Logbook Department of Advanced Education and Skills Apprenticeship and Trades Certification Division INDUSTRIAL MECHANIC (MILLWRIGHT) Note to Apprenticeship Applicants This form can only be used
ENTRY-LEVEL INDUSTRIAL MECHANIC
 ENTRY-LEVEL INDUSTRIAL MECHANIC Definition: An entry-level industrial mechanics technician fabricates/repairs machinery, troubleshoots, installs, inspects, and maintains industrial equipment using mechanical,
ENTRY-LEVEL INDUSTRIAL MECHANIC Definition: An entry-level industrial mechanics technician fabricates/repairs machinery, troubleshoots, installs, inspects, and maintains industrial equipment using mechanical,
Duration : 1 Year Timing: Morning Batch : 9.30 AM to 1.00 PM or Afternoon Batch : 1.30 PM to 5.00 PM. 5 Months Timing: Full Time : 9.30 AM to 5.
 1 Head Office: Main Road, Thalayolaparambu, Kottayam Dist., Kerala, India, PIN: 686 605 : 0489 236669, : 99617336611 / 12 / 13, e-mail : siit@siitonline.com, www.siitonline.com Eligibility : 10 th and
1 Head Office: Main Road, Thalayolaparambu, Kottayam Dist., Kerala, India, PIN: 686 605 : 0489 236669, : 99617336611 / 12 / 13, e-mail : siit@siitonline.com, www.siitonline.com Eligibility : 10 th and
WESTERN IOWA TECH COMMUNITY COLLEGE. Course Syllabus. Electrical Technician Level 2
 Course Title: Electrical Technician Level Total Hours:56 Meeting time/ location :TBA Instructor: Chris Sewalson Phone:712-274-8733 ext1407 E-mail Chris.sewalson@witcc.edu Office Location: Lemars Center
Course Title: Electrical Technician Level Total Hours:56 Meeting time/ location :TBA Instructor: Chris Sewalson Phone:712-274-8733 ext1407 E-mail Chris.sewalson@witcc.edu Office Location: Lemars Center
NZQA unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 5. Demonstrate and apply intermediate knowledge of instrumentation and control system engineering
 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate and apply intermediate knowledge of instrumentation and control system engineering Level 5 Credits 15 Purpose This unit standard covers intermediate knowledge of the concepts
Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate and apply intermediate knowledge of instrumentation and control system engineering Level 5 Credits 15 Purpose This unit standard covers intermediate knowledge of the concepts
INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION AND MODERN CONTROL SYSTEMS Selection, Applications, Operation and Diagnostics TOPICS COVERED. Expert Course Faculty Leader
 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION AND MODERN CONTROL SYSTEMS Selection, Applications, Operation and Diagnostics 3 for 2 Bundle Offer. SGD 2040 each for Team of 3! TOPICS COVERED Equipment Operation Equipment
INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION AND MODERN CONTROL SYSTEMS Selection, Applications, Operation and Diagnostics 3 for 2 Bundle Offer. SGD 2040 each for Team of 3! TOPICS COVERED Equipment Operation Equipment
Industrial Electrician Level 3
 Industrial Electrician Level 3 Industrial Electrician Unit: C1 Industrial Electrical Code I Level: Three Duration: 77 hours Theory: Practical: 77 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide
Industrial Electrician Level 3 Industrial Electrician Unit: C1 Industrial Electrical Code I Level: Three Duration: 77 hours Theory: Practical: 77 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide
ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE SKILLS
 ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE SKILLS FOR INSTRUMENTATION PERSONNEL COURSE 120: 7 DAYS: Max 8 Candidates The end objectives are identical to those of the Electrical maintenance skills (Course 110) but this starts
ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE SKILLS FOR INSTRUMENTATION PERSONNEL COURSE 120: 7 DAYS: Max 8 Candidates The end objectives are identical to those of the Electrical maintenance skills (Course 110) but this starts
Manufacturing Operations
 End of Course (EOC) Bank Blueprints Manufacturing Operations Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 About Test Blueprints... 2 Gas Metal Arc Welding... 3 Shielded Metal Arc Welding... 4 Flux Cored Arc
End of Course (EOC) Bank Blueprints Manufacturing Operations Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 About Test Blueprints... 2 Gas Metal Arc Welding... 3 Shielded Metal Arc Welding... 4 Flux Cored Arc
ENGINEERING. Unit 4 Electrical, electronic engineering operations and application Suite. Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 2
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 2 ENGINEERING Unit 4 Electrical, electronic engineering operations and L/615/2134 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 1 September 2016 ocr.org.uk/engineering LEVEL 2
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 2 ENGINEERING Unit 4 Electrical, electronic engineering operations and L/615/2134 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 1 September 2016 ocr.org.uk/engineering LEVEL 2
SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARD ELECTRICAL GROUNDING Effective Date: 07/17/10 Standard: Document Number: KUCSH0039 Rev: 4
 SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARD ELECTRICAL GROUNDING Effective Date: 07/17/10 Standard: 16.10 Document Number: KUCSH0039 Rev: 4 16.10.1 INTRODUCTION 16.10.1.1 The intent of this standard is to ensure that continuity
SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARD ELECTRICAL GROUNDING Effective Date: 07/17/10 Standard: 16.10 Document Number: KUCSH0039 Rev: 4 16.10.1 INTRODUCTION 16.10.1.1 The intent of this standard is to ensure that continuity
Qualification Specification. Level 1 Diploma in Providing a Gateway to Smart Engineering
 Qualification Specification Level 1 Diploma in Providing a Gateway to Smart Engineering ProQual 2017 Contents Page Introduction 3 Qualification profile 3 Centre requirements 5 Support for candidates 5
Qualification Specification Level 1 Diploma in Providing a Gateway to Smart Engineering ProQual 2017 Contents Page Introduction 3 Qualification profile 3 Centre requirements 5 Support for candidates 5
Electronics Technology
 Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Electronics Technology Test Code: 4035 / Version: 01 Copyright 2010. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Electronics Technology Test Code: 4035 / Version: 01 Copyright 2010. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information
Engineering and Design
 End of Course (EOC) Bank Blueprints Engineering and Design Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 About Test Blueprints... 2 Engineering Design... 3 Engineering Principles... 4 Manufacturing Operations...
End of Course (EOC) Bank Blueprints Engineering and Design Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 About Test Blueprints... 2 Engineering Design... 3 Engineering Principles... 4 Manufacturing Operations...
Insteel Industries, Inc. Job Description
 Job Description Insteel Industries, Inc. Job Description Job Title: Department: Location: Reports To: FLSA Status: Maintenance - Electrical (027) Maintenance (075) Insteel Wire Products, St. Joseph, MO
Job Description Insteel Industries, Inc. Job Description Job Title: Department: Location: Reports To: FLSA Status: Maintenance - Electrical (027) Maintenance (075) Insteel Wire Products, St. Joseph, MO
JOB DESCRIPTION. Coachella Valley Water District October 12, DEPARTMENT: Facilities and Maintenance REPORTING RELATIONSHIP:
 Coachella Valley Water District October 12, 2017 TITLE: Electronic Technician II SECTION: Electronics Shop DEPARTMENT: Facilities and Maintenance REPORTING RELATIONSHIP: Reports to: Electronics Supervisor,
Coachella Valley Water District October 12, 2017 TITLE: Electronic Technician II SECTION: Electronics Shop DEPARTMENT: Facilities and Maintenance REPORTING RELATIONSHIP: Reports to: Electronics Supervisor,
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS Automotive Scanner Certification: Mechanical & Electronic Torque Instruments Certification:
 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS All classes include teaching strategies for effective delivery and integration ideas on how to seamlessly weave these certifications into your program s already existing curriculum.
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS All classes include teaching strategies for effective delivery and integration ideas on how to seamlessly weave these certifications into your program s already existing curriculum.
KeyTrain Applied Technology Course Objectives, Outlines and Estimated Times of Completion
 KeyTrain Applied Technology Course Objectives, Outlines and Estimated Times of Completion Applied Technology Course Description: KeyTrain's Applied Technology course teaches the ability to solve work-place
KeyTrain Applied Technology Course Objectives, Outlines and Estimated Times of Completion Applied Technology Course Description: KeyTrain's Applied Technology course teaches the ability to solve work-place
Pressure Transducer Handbook
 123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
Machinist Level 4 Rev. December 12, 2012
 Machinist Level 4 Machinist Unit: A14 Reconditioning Level: Four Duration: 12 hours Theory: Practical: 12 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is designed to introduce knowledge of the procedures
Machinist Level 4 Machinist Unit: A14 Reconditioning Level: Four Duration: 12 hours Theory: Practical: 12 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is designed to introduce knowledge of the procedures
Estimated Program Length & Cost * Award Length Credit Hours Tuition Fees Books Tools Supplies
 - 170 The College for Real Careers Program Information The Program at Trenholm State Community College is a multi-craft curriculum. Many crafts are a part of the training process. Craft related instructors
- 170 The College for Real Careers Program Information The Program at Trenholm State Community College is a multi-craft curriculum. Many crafts are a part of the training process. Craft related instructors
Construction Electrician/Industrial Electrician/Power Electrician Common Core Level 2
 Common Core Level 2 Unit: B1 Commercial Electrical Code Level: Two Duration: 60 hours Theory: Practical: 60 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge about
Common Core Level 2 Unit: B1 Commercial Electrical Code Level: Two Duration: 60 hours Theory: Practical: 60 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge about
National Craft Assessment and Certification Program S P E C I F I C A T I O N S
 National Craft Assessment and Certification Program S P E C I F I C A T I O N S INDUSTRIAL MAINTENANCE MECHANIC V4 MEMT32_04 Released June 2013 Focus Statement A journey-level Industrial Maintenance Mechanic
National Craft Assessment and Certification Program S P E C I F I C A T I O N S INDUSTRIAL MAINTENANCE MECHANIC V4 MEMT32_04 Released June 2013 Focus Statement A journey-level Industrial Maintenance Mechanic
AUTOMOTIVE TECHNICIAN Technical Diploma
 AUTOMOTIVE TECHNICIAN Technical Diploma Program Code: 32-404-2 our graduates INDEMAND 2017/2018 mstc.edu automotive technician career pathway AUTOMOTIVE TECHNICIAN Mid-State s Automotive Technician program
AUTOMOTIVE TECHNICIAN Technical Diploma Program Code: 32-404-2 our graduates INDEMAND 2017/2018 mstc.edu automotive technician career pathway AUTOMOTIVE TECHNICIAN Mid-State s Automotive Technician program
Modulating control valve
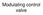 Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
Select, wear adjust, use and maintain personal protective equipment
 ANALYSIS PROFILE PROTECT SELF AND OTHERS Identify, interpret and apply applicable Acts, Codes and regulations Select, wear adjust, use and maintain personal protective Recognize and assess hazards and
ANALYSIS PROFILE PROTECT SELF AND OTHERS Identify, interpret and apply applicable Acts, Codes and regulations Select, wear adjust, use and maintain personal protective Recognize and assess hazards and
CONTEST DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRONICS ÉLECTRONIQUE POST-SECONDARY NIVEAU POSTSECONDAIRE
 CONTEST DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRONICS ÉLECTRONIQUE POST-SECONDARY NIVEAU POSTSECONDAIRE 1. The Importance of Essential Skills for Careers in the Skilled Trades and Technology SCC is currently
CONTEST DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRONICS ÉLECTRONIQUE POST-SECONDARY NIVEAU POSTSECONDAIRE 1. The Importance of Essential Skills for Careers in the Skilled Trades and Technology SCC is currently
Utility and Energy Systems Program
 Utility and Energy Systems Program Electrical Technology Associate in Applied Science Degree Electrical Technology, Construction Electrical Utility/Lineworker Electrical Tech. Control/Maintenance Electrical
Utility and Energy Systems Program Electrical Technology Associate in Applied Science Degree Electrical Technology, Construction Electrical Utility/Lineworker Electrical Tech. Control/Maintenance Electrical
CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ÉLECTRIQUES SECONDARY / NIVEAUX SECONDAIRE
 CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ÉLECTRIQUES SECONDARY / NIVEAUX SECONDAIRE Table of Contents 1 THE ESSENTIAL SKILLS FOR CAREERS IN THE SKILLED TRADES
CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ÉLECTRIQUES SECONDARY / NIVEAUX SECONDAIRE Table of Contents 1 THE ESSENTIAL SKILLS FOR CAREERS IN THE SKILLED TRADES
CHAPTER 29 ELECTRICIAN S MATE (EM) NAVPERS G CH-70
 CHAPTER 29 ELECTRICIAN S MATE (EM) NAVPERS 18068-29G CH-70 Updated: April 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS ELECTRICIAN S MATE, NUCLEAR POWER (EMN) SCOPE OF RATING GENERAL INFORMATION SUBMARINE PROPULSION PLANT ELECTRICAL
CHAPTER 29 ELECTRICIAN S MATE (EM) NAVPERS 18068-29G CH-70 Updated: April 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS ELECTRICIAN S MATE, NUCLEAR POWER (EMN) SCOPE OF RATING GENERAL INFORMATION SUBMARINE PROPULSION PLANT ELECTRICAL
A i r c r a f t C o m p o n e n t s a n d F u n c t i o n s ( 1 1 A )
 8 5 4 5 A i r c r a f t C o m p o n e n t s a n d F u n c t i o n s ( 1 1 A ) 30S/30E/30M An Aviation and Aerospace Technologies Course 8 5 4 5 : A i r c r a f t C o m p o n e n t s a n d F u n c t i
8 5 4 5 A i r c r a f t C o m p o n e n t s a n d F u n c t i o n s ( 1 1 A ) 30S/30E/30M An Aviation and Aerospace Technologies Course 8 5 4 5 : A i r c r a f t C o m p o n e n t s a n d F u n c t i
1.0 INTRODUCTION DEFINITIONS DRAWING CONTROL PREPARATION OF SPECIFICATIONS AND DATASHEETS... 5
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 2.0 DEFINITIONS... 4 3.0 DRAWING CONTROL... 4 4.0 PREPARATION OF SPECIFICATIONS AND DATASHEETS... 5 5.0 GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION OF DRAWINGS... 5 6.0 CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 2.0 DEFINITIONS... 4 3.0 DRAWING CONTROL... 4 4.0 PREPARATION OF SPECIFICATIONS AND DATASHEETS... 5 5.0 GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION OF DRAWINGS... 5 6.0 CONTENTS
TRAFFIC SIGNAL ELECTRICIAN, 3819
 01-31-92 TRAFFIC SIGNAL ELECTRICIAN, 3819 Summary of Duties: A Traffic Signal Electrician performs skilled technical work and acts as a lead for and works with a signal construction crew constructing,
01-31-92 TRAFFIC SIGNAL ELECTRICIAN, 3819 Summary of Duties: A Traffic Signal Electrician performs skilled technical work and acts as a lead for and works with a signal construction crew constructing,
NZQA registered unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 8. Demonstrate knowledge of theory for registration of electrical installers
 Page 1 of 8 Title Demonstrate knowledge of theory for registration of electrical installers Level 3 Credits 3 Purpose This unit standard covers the theory assessment required for registration as an electrical
Page 1 of 8 Title Demonstrate knowledge of theory for registration of electrical installers Level 3 Credits 3 Purpose This unit standard covers the theory assessment required for registration as an electrical
Industrial Maintenance Technology (INT)
 Technology 199 The College for Real Careers Technology (INT) Program Information The Technology Program at H. Councill Trenholm State Community College is a multi-craft curriculum. Many crafts are a part
Technology 199 The College for Real Careers Technology (INT) Program Information The Technology Program at H. Councill Trenholm State Community College is a multi-craft curriculum. Many crafts are a part
JIET - TRAINING SCHEDULE PAGE 1 TRADE: ELECTRICIAN. ID3 Recall applicable grievance procedures. Pass a questionnaire with at least 80%.
 JIET - TRAINING SCHEDULE PAGE 1 TRADE: ELECTRICIAN INDUCTION ID1 Recall applicable sections of the Manpower Training Act (No 56, 1981), with special reference to discipline and legal responsibilities.
JIET - TRAINING SCHEDULE PAGE 1 TRADE: ELECTRICIAN INDUCTION ID1 Recall applicable sections of the Manpower Training Act (No 56, 1981), with special reference to discipline and legal responsibilities.
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF ACADEMIC AFFAIRS AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY PROGRAM ASSESSMENT PLANNING TEMPLATE May 15, 2009 Department/Program Physics and Technology Automotive Technology Program Department
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF ACADEMIC AFFAIRS AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY PROGRAM ASSESSMENT PLANNING TEMPLATE May 15, 2009 Department/Program Physics and Technology Automotive Technology Program Department
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) POWER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNICIAN Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC)
 Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) POWER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNICIAN Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles involving
Canadian Technology Accreditation Criteria (CTAC) POWER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY - TECHNICIAN Technology Accreditation Canada (TAC) Preamble These CTAC are applicable to programs having titles involving
INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS ENGINEERING
 Training Title INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS ENGINEERING Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Introduction to Process Engineering 5 12 16 May $3,750 Abu Dhabi, UAE In any of the 5 star hotel. The
Training Title INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS ENGINEERING Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Introduction to Process Engineering 5 12 16 May $3,750 Abu Dhabi, UAE In any of the 5 star hotel. The
FOUNDATION Fieldbus: the Diagnostics Difference Fieldbus Foundation
 FOUNDATION Fieldbus: the Diagnostics Difference There s Diagnostics and There s Diagnostics. The Value of Fieldbus Diagnostics Physical Layer Diagnostics Managing the Diagnostics Storm PAM and IDM Software,
FOUNDATION Fieldbus: the Diagnostics Difference There s Diagnostics and There s Diagnostics. The Value of Fieldbus Diagnostics Physical Layer Diagnostics Managing the Diagnostics Storm PAM and IDM Software,
NCCER Progress Blvd, Alachua, Florida Phone: (888)
 NCCER 13614 Progress Blvd, Alachua, Florida 32615 Phone: (888) 622-3720 E-mail: info@nccer.org PIPEFITTING Competencies / Objectives Level One MODULE 08101-06 - ORIENTATION TO THE TRADE 1. Describe the
NCCER 13614 Progress Blvd, Alachua, Florida 32615 Phone: (888) 622-3720 E-mail: info@nccer.org PIPEFITTING Competencies / Objectives Level One MODULE 08101-06 - ORIENTATION TO THE TRADE 1. Describe the
Curriculum. Technology Education ELECTRONICS
 Curriculum Technology Education ELECTRONICS Supports Academic Learning Expectation # 3 Students and graduates of Ledyard High School will employ problem-solving skills effectively Approved by Instructional
Curriculum Technology Education ELECTRONICS Supports Academic Learning Expectation # 3 Students and graduates of Ledyard High School will employ problem-solving skills effectively Approved by Instructional
REVISIONS. App Thom. App Sud. App PC IG 2014/09/19
 /0 REVISIONS Rev Description Rev n by Sud PC Thom VB LH Clyd Act Issue Date YYYY/MM/DD Gen. updates to content, format and spec number. Previously 560-0.0.0 FF 204/09/9 IG 204/09/9 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
/0 REVISIONS Rev Description Rev n by Sud PC Thom VB LH Clyd Act Issue Date YYYY/MM/DD Gen. updates to content, format and spec number. Previously 560-0.0.0 FF 204/09/9 IG 204/09/9 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Basic Electrical Training
 Basic Electrical Training Electricians Tools Explain how various hand tools are used by an electrician Discuss the safe use of hand tools and power tools Perform basic calculations and measurement conversions
Basic Electrical Training Electricians Tools Explain how various hand tools are used by an electrician Discuss the safe use of hand tools and power tools Perform basic calculations and measurement conversions
Interprovincial Program Guide. Machinist. Human Resources and Skills Development Canada. Ressources humaines et Développement des compétences Canada
 Interprovincial Program Guide 2012 Machinist Human Resources and Skills Development Canada Ressources humaines et Développement des compétences Canada Interprovincial Program Guide Machinist 2012 Trades
Interprovincial Program Guide 2012 Machinist Human Resources and Skills Development Canada Ressources humaines et Développement des compétences Canada Interprovincial Program Guide Machinist 2012 Trades
Producing platework components and assemblies
 Unit 823 Producing platework components and assemblies UAN: R/600/5880 Level: Level 2 Credit value: 14 GLH: 64 Relationship to NOS: Endorsement by a sector or regulatory body: Aim: This unit has been derived
Unit 823 Producing platework components and assemblies UAN: R/600/5880 Level: Level 2 Credit value: 14 GLH: 64 Relationship to NOS: Endorsement by a sector or regulatory body: Aim: This unit has been derived
ENGINEERING SHORT COURSES
 www.forthvalley.ac.uk ENGINEERING SHORT COURSES 02 FORTH VALLEY COLLEGE Our mission is to Make Learning Work and our vision, shaping the future, developing a world class service! The College is based in
www.forthvalley.ac.uk ENGINEERING SHORT COURSES 02 FORTH VALLEY COLLEGE Our mission is to Make Learning Work and our vision, shaping the future, developing a world class service! The College is based in
Industrial Maintenance: Mechanic
 Industrial Maintenance: Mechanic 00101-09 Basic Safety Explains the safety obligations of workers, supervisors, and managers to ensure a safe workplace. Discusses the causes and results of accidents and
Industrial Maintenance: Mechanic 00101-09 Basic Safety Explains the safety obligations of workers, supervisors, and managers to ensure a safe workplace. Discusses the causes and results of accidents and
PROGRAM OUTLINE. Instrumentation and Control Technician (Industrial Instrument Mechanic)
 PROGRAM OUTLINE Instrumentation and Control Technician (Industrial Instrument Mechanic) The latest version of this document is available in PDF format on the ITA website www.itabc.ca To order printed copies
PROGRAM OUTLINE Instrumentation and Control Technician (Industrial Instrument Mechanic) The latest version of this document is available in PDF format on the ITA website www.itabc.ca To order printed copies
GTU- Centre of Excellence in Automation
 Gujarat Technological University Centre of Excellence in Automation LABS UNDER CENTER OF EXCELLENCE Hydraulic Lab. Pneumatic Lab. Sensor Lab. Programmable logic controller(plc) Robotics & Mechatronics
Gujarat Technological University Centre of Excellence in Automation LABS UNDER CENTER OF EXCELLENCE Hydraulic Lab. Pneumatic Lab. Sensor Lab. Programmable logic controller(plc) Robotics & Mechatronics
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA 101 BASIC ELECTRICITY. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Roy H. Stueve March 28, 2010
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA 101 BASIC ELECTRICITY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Roy H. Stueve March 28, 2010 Mary Beth Ottinger, Division Chair Elizabeth Check, Dean 2 HRA 101 BASIC ELECTRICITY
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA 101 BASIC ELECTRICITY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Roy H. Stueve March 28, 2010 Mary Beth Ottinger, Division Chair Elizabeth Check, Dean 2 HRA 101 BASIC ELECTRICITY
Multiple Category Scope and Sequence: Scope and Sequence Report For Course Standards and Objectives, Content, Skills, Vocabulary
 Multiple Category Scope and Sequence: Scope and Sequence Report For Course Standards and Objectives, Content, Skills, Vocabulary Wednesday, August 20, 2014, 1:16PM Unit Course Standards and Objectives
Multiple Category Scope and Sequence: Scope and Sequence Report For Course Standards and Objectives, Content, Skills, Vocabulary Wednesday, August 20, 2014, 1:16PM Unit Course Standards and Objectives
Education & Training
 Distribution System Operator Certificate This program provides you with a proficient working knowledge in modern electric power distribution systems. These four classes are designed to walk students through
Distribution System Operator Certificate This program provides you with a proficient working knowledge in modern electric power distribution systems. These four classes are designed to walk students through
OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES
 Training Title OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Operation Skills Enhancement - Measurement & Instrument For
Training Title OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Operation Skills Enhancement - Measurement & Instrument For
QPEO2/003N Credit Value: 4 QCF Level: 2 GLH: 29 Using and communicating technical information
 Performing Engineering Operations QPEO2/003N Credit Value: 4 QCF Level: 2 GLH: 29 Using and communicating technical information Learner Name: EAL Assessment Route Summary This EAL assessment route covers
Performing Engineering Operations QPEO2/003N Credit Value: 4 QCF Level: 2 GLH: 29 Using and communicating technical information Learner Name: EAL Assessment Route Summary This EAL assessment route covers
Heating Ventilating Air Conditioning - Refrigeration COURSE SYLLABUS
 Heating Ventilating Air Conditioning - Refrigeration COURSE SYLLABUS 2017-2018 Course Description The Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration (HVACR) Technology program provides a balance
Heating Ventilating Air Conditioning - Refrigeration COURSE SYLLABUS 2017-2018 Course Description The Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration (HVACR) Technology program provides a balance
Electrical Construction Technology
 Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Electrical Construction Technology Test Code: 4130 / Version: 01 Copyright 2011 General Assessment Information Electrical Construction Technology
Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Electrical Construction Technology Test Code: 4130 / Version: 01 Copyright 2011 General Assessment Information Electrical Construction Technology
Fundamentals of Industrial Control
 Fundamentals of Industrial Control 2nd Edition D. A. Coggan, Editor Practical Guides for Measurement and Control Preface ix Contributors xi Chapter 1 Sensors 1 Applications of Instrumentation 1 Introduction
Fundamentals of Industrial Control 2nd Edition D. A. Coggan, Editor Practical Guides for Measurement and Control Preface ix Contributors xi Chapter 1 Sensors 1 Applications of Instrumentation 1 Introduction
CAREER PATHWAY ELECTRICAL OCCUPATIONS CIP Code Pennsylvania's Targeted Industry Cluster: Architecture & Construction
 CAREER PATHWAY ELECTRICAL OCCUPATIONS CIP Code 46.0399 Pennsylvania's Targeted Industry Cluster: Architecture & Construction Potential Careers 47-1011 Supervisors-Construction Trades & Extraction Workers
CAREER PATHWAY ELECTRICAL OCCUPATIONS CIP Code 46.0399 Pennsylvania's Targeted Industry Cluster: Architecture & Construction Potential Careers 47-1011 Supervisors-Construction Trades & Extraction Workers
One line and Three line diagrams Schematics Wiring Diagrams Logic ladders Ancillary prints Pictorial instructions
 One line and Three line diagrams Schematics Wiring Diagrams Logic ladders Ancillary prints Pictorial instructions One line diagram (1) One line diagrams will typically show in a simple fashion an over
One line and Three line diagrams Schematics Wiring Diagrams Logic ladders Ancillary prints Pictorial instructions One line diagram (1) One line diagrams will typically show in a simple fashion an over
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Program Outline Major: EETY Length: 3 Years Delivery: 6 Semesters, plus 3 work terms Credential: Ontario College Advanced Diploma, Co-op Effective: 2013-2014 Location:
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Program Outline Major: EETY Length: 3 Years Delivery: 6 Semesters, plus 3 work terms Credential: Ontario College Advanced Diploma, Co-op Effective: 2013-2014 Location:
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT. Inspection. H.H. Sheik Sultan Tower (0) Floor Corniche Street Abu Dhabi U.A.E
 ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT Inspection H.H. Sheik Sultan Tower (0) Floor Corniche Street Abu Dhabi U.A.E www.ictd.ae ictd@ictd.ae Course Introduction: The course begins with the fundamental principles that always
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT Inspection H.H. Sheik Sultan Tower (0) Floor Corniche Street Abu Dhabi U.A.E www.ictd.ae ictd@ictd.ae Course Introduction: The course begins with the fundamental principles that always
Construction Electrician Level 2
 Level 2 Rev. September 2008 Unit: B1 Electrical Code II Level: Two Duration: 120 hours Theory: Practical: 99 hours 21 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is designed to provide the Electrician apprentice
Level 2 Rev. September 2008 Unit: B1 Electrical Code II Level: Two Duration: 120 hours Theory: Practical: 99 hours 21 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is designed to provide the Electrician apprentice
Plumber Level 1 Rev. May 2011
 Plumber Level 1 Plumber Unit: A1 Introduction To Your Apprenticeship Level: One Duration: 7 hours Theory: Practical: 7 hours 0 hours Overview: Jobsite learning and teaching have long been fundamental to
Plumber Level 1 Plumber Unit: A1 Introduction To Your Apprenticeship Level: One Duration: 7 hours Theory: Practical: 7 hours 0 hours Overview: Jobsite learning and teaching have long been fundamental to
Owner Operator Guide to Emerging Smart Technology
 Owner Operator Guide to Emerging Smart Technology Fluor s SmartPlant Implementation Initiative 2013 Fluor. All Rights Reserved. By: John Dressel Instrument Technological Revolution Process Measurement
Owner Operator Guide to Emerging Smart Technology Fluor s SmartPlant Implementation Initiative 2013 Fluor. All Rights Reserved. By: John Dressel Instrument Technological Revolution Process Measurement
ICE065 Practical Process Control & Instrumentation:
 ICE065 Practical Process Control & Instrumentation: Measurement & Sensors H.H. Sheikh Sultan Tower (0) Floor Corniche Street Abu Dhabi U.A.E www.ictd.ae ictd@ictd.ae Course Introduction: Globalization
ICE065 Practical Process Control & Instrumentation: Measurement & Sensors H.H. Sheikh Sultan Tower (0) Floor Corniche Street Abu Dhabi U.A.E www.ictd.ae ictd@ictd.ae Course Introduction: Globalization
Sheet Metal Worker A Guide to Course Content
 Sheet Metal Worker A Guide to Course Content Sheet Metal Workers use metal of 10 gauge or lighter to make and repair products and buildings. Training Requirements: To graduate from each level of the apprenticeship
Sheet Metal Worker A Guide to Course Content Sheet Metal Workers use metal of 10 gauge or lighter to make and repair products and buildings. Training Requirements: To graduate from each level of the apprenticeship
SCNC OCMT ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ÉLECTRIQUES SKILLS CANADA NATIONAL COMPETITION OLYMPIADES CANADIENNES DES MÉTIERS ET DES TECHNOLOGIES
 SCNC SKILLS CANADA NATIONAL COMPETITION OCMT OLYMPIADES CANADIENNES DES MÉTIERS ET DES TECHNOLOGIES CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ÉLECTRIQUES SECONDARY
SCNC SKILLS CANADA NATIONAL COMPETITION OCMT OLYMPIADES CANADIENNES DES MÉTIERS ET DES TECHNOLOGIES CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ÉLECTRIQUES SECONDARY
Educ8 Engineering. Apprenticeship (NVQ/QCF) Levels 2, 3 and 4
 Educ8 Engineering Apprenticeship (NVQ/QCF) Levels 2, 3 and 4 Are you thinking of growing your business? Do you need to consider succession planning? Does your current workforce need upskilling? If the
Educ8 Engineering Apprenticeship (NVQ/QCF) Levels 2, 3 and 4 Are you thinking of growing your business? Do you need to consider succession planning? Does your current workforce need upskilling? If the
SCNC OCMT ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ELECTRIQUES SKILLS CANADA NATIONAL COMPETITION OLYMPIADES CANADIENNES DES MÉTIERS ET DES TECHNOLOGIES
 SCNC SKILLS CANADA NATIONAL COMPETITION OCMT OLYMPIADES CANADIENNES DES MÉTIERS ET DES TECHNOLOGIES CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ELECTRIQUES POST-
SCNC SKILLS CANADA NATIONAL COMPETITION OCMT OLYMPIADES CANADIENNES DES MÉTIERS ET DES TECHNOLOGIES CONTEST DESCRIPTION / DESCRIPTION DE CONCOURS ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS INSTALLATIONS ELECTRIQUES POST-
VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVE SPECIFICATION
 VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVE SPECIFICATION 1.0. SUMMARY The use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) in conjunction with wastewater lift stations has been identified as a means improve efficiency and to moderate
VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVE SPECIFICATION 1.0. SUMMARY The use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) in conjunction with wastewater lift stations has been identified as a means improve efficiency and to moderate
IE045: Practical Process Control & Instrumentation: Measurement and Sensors
 IE045: Practical Process Control & Instrumentation: Measurement and Sensors IE045 Rev.001 CMCT COURSE OUTLINE Page 1 of 5 Training Description: Globalization has placed increasing demands on modern process
IE045: Practical Process Control & Instrumentation: Measurement and Sensors IE045 Rev.001 CMCT COURSE OUTLINE Page 1 of 5 Training Description: Globalization has placed increasing demands on modern process
Skills Canada National Competition. Contest Description. 16 Electronics / Secondary May 27-30, Saskatoon
 Skills Canada National Competition Contest Description 16 Electronics / Secondary May 27-30, 2015 - Saskatoon 1. The Importance of Essential Skills for Careers in the Skilled Trades and Technology SCC
Skills Canada National Competition Contest Description 16 Electronics / Secondary May 27-30, 2015 - Saskatoon 1. The Importance of Essential Skills for Careers in the Skilled Trades and Technology SCC
PARKER HANNIFIN TEST STAND
 PARKER HANNIFIN TEST STAND Dan Laird Abstract This paper will review a partnership between Parker-Hannifin Mobile Cylinders and Youngstown State University (YSU). The Mobile Cylinders Group makes hydraulic
PARKER HANNIFIN TEST STAND Dan Laird Abstract This paper will review a partnership between Parker-Hannifin Mobile Cylinders and Youngstown State University (YSU). The Mobile Cylinders Group makes hydraulic
SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 12
 SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained
SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained
