are equally illuminated, the lamp I 1
|
|
|
- Sheryl Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Student ID: Exam: RR - PRACTICAL EXERCISE ADVANCED ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam. If you need to exit before completing the exam, click Cancel Exam. Questions 1 to 20: Select the best answer to each question. Note that a question and its answers may be split across a page break, so be sure that you have seen the entire question and all the answers before choosing an answer. 1. Look at the amplifier circuit shown above. Which of the following statements about this circuit is correct? A. This is a common-collector circuit that's characterized by a low input impedance and a high output impedance. B. This is a common-emitter circuit that's characterized by a high input impedance and a low output impedance. C. This is a common-collector circuit that's characterized by a high input impedance and a low output impedance. D. This is a common-emitter circuit that's characterized by a low input impedance and a high output impedance. 2. Look at the circuit diagram shown in the figure above. When R 1 and R 2 are equally illuminated, the lamp I 1 glows dimly. Which of the following will happen if R 2 is covered so that no light can reach it? A. Lamp I 1 glows brighter, because the forward bias on Q 1 is decreased. B. Lamp I 1 goes out, because the forward bias on Q 1 is decreased.
2 C. Lamp I 1 goes out, because the forward bias on Q 1 increases. D. Lamp I 1 glows brighter, because the voltage on the base of Q 1 goes positive. 3. Look at the circuit diagram that's shown in the figure above. What is the voltage between point A and ground? A. +25 V B. +6 V C. 6 V D. 25 V 4. The output voltage of a power supply is measured at 12 V with no load connected. The manufacturer's specifications say the power supply has a regulation of 10 percent. What is the full-load output voltage of the power supply? A V B. 1.2 V C V D V
3 9. Two electronics technicians are discussing LC and RC oscillators. Technician A says that an RC oscillator doesn't require a resonant circuit. Technician B says that an LC oscillator can be tuned only by varying the inductance, and that an RC oscillator can't produce a sine wave. Which of the following statements is correct? 5. Look at the circuit diagram and the four waveforms that are shown in the figure above. Assume that diode D 1 in the circuit is opened. Which of the four waveforms shown in the figure would appear across R L? A. Waveform 3 B. Waveform 4 C. Waveform 1 D. Waveform 2 6. Which of the following is essential for the operation of an oscillator? A. An LC circuit B. A unity gain amplifier C. Degenerative feedback D. Positive feedback 7. A 100 khz oscillator that's followed by a doubler and two triplers will produce an output frequency of A. 500 khz. B. 180 khz. C. 1.8 MHz. D. 800 khz. 8. Negative clipping of an output signal occurs when the A. output impedance is too high. B. power supply voltage is too high. C. input impedance is too high. D. input amplitude is too high.
4 A. Both of the technicians are correct. B. Only Technician B is correct. C. Only Technician A is correct. D. Neither of the two technicians is correct. 10. In the circuit shown in the figure above, what is the current through R 2? A. 2.5 ma B. 25 ma C. 60 ma D. 6.0 ma
5 11. Look at the figure above. Which of the following circuits is a properly biased common-emitter circuit? A. Circuit B B. Circuit A C. Circuit D D. Circuit C 12. Two electronics technicians are comparing a full-wave bridge rectifier to a full-wave rectifier that uses two diodes and a center-tapped secondary. Technician A says that the two-diode rectifier has a lower ripple frequency and can supply greater current than the full-wave bridge rectifier. Technician B says that the fullwave bridge rectifier results in full secondary voltage at the output. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Both of the technicians are correct. B. Only Technician A is correct. C. Only Technician B is correct. D. Neither of the two technicians is correct. 13. A full-wave power supply with a capacitor-input filter is connected to a 400 Hz AC source. The frequency of the ripple waveform at the input to the filter is A. 100 Hz. B. 400 Hz. C. 800 Hz.
6 D. 0 Hz (DC). 14. Look at the circuit diagram shown in the figure above. What is the power level at point B in the circuit? A. 62 mw B. 620 mw C. 3.1 mw D mw 15. Look at the circuit diagram and the four waveforms that are shown in the figure above. Assume that the circuit's switch is closed momentarily, then opened. Which of the four waveforms shown will appear between terminals A and B after the switch is opened? A. Waveform 4 B. Waveform 1 C. Waveform 3 D. Waveform 2
7 16. Look at the four circuit diagrams that are shown above. Which of these four diagrams represents a correctly configured full-wave bridge rectifier circuit? A. Circuit 3 B. Circuit 1 C. Circuit 4 D. Circuit A modulation technique that's used in fiber-optic transmission in which the width of pulses is varied in accordance with the modulation signal is called A. PWM. B. PAM. C. PRM. D. PPM. 18. One advantage of using photon coupling for signal transmission is the A. lower cost of signal-handling components. B. lower power required for transmission. C. greater immunity to noise pickup. D. greater adaptability to digital transmission. 19. What would happen at the output of a full-wave bridge rectifier circuit if one of the diodes in the bridge opened? A. The ripple frequency would remain the same, and the voltage would decrease. B. The ripple frequency would increase, and the voltage would decrease. C. The ripple frequency would decrease, and the voltage would decrease. D. The ripple frequency would remain the same, and the voltage would increase.
8 20. In the circuit shown in the figure above, what is the power level at point A? A mw B. 31 mw C. 3.1 mw D. 310 mw End of exam
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
CHAPTER 4 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER. AC DC Conversion
 CHAPTER 4 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER AC DC Conversion SINGLE PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER The objective of a full wave rectifier is to produce a voltage or current which is purely dc or has some specified dc component.
CHAPTER 4 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER AC DC Conversion SINGLE PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER The objective of a full wave rectifier is to produce a voltage or current which is purely dc or has some specified dc component.
Power Amplifiers. Class A Amplifier
 Power Amplifiers The Power amplifiers amplify the power level of the signal. This amplification is done in the last stage in audio applications. The applications related to radio frequencies employ radio
Power Amplifiers The Power amplifiers amplify the power level of the signal. This amplification is done in the last stage in audio applications. The applications related to radio frequencies employ radio
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
In-Class Exercises for Lab 2: Input and Output Impedance
 In-Class Exercises for Lab 2: Input and Output Impedance. What is the output resistance of the output device below? Suppose that you want to select an input device with which to measure the voltage produced
In-Class Exercises for Lab 2: Input and Output Impedance. What is the output resistance of the output device below? Suppose that you want to select an input device with which to measure the voltage produced
4. Forward bias of a silicon P-N junction will produce a barrier voltage of approximately how many volts? A. 0.2 B. 0.3 C. 0.7 D. 0.
 1. The dc current through each diode in a bridge rectifier equals A. the load current B. half the dc load current C. twice the dc load current D. one-fourth the dc load current 2. When matching polarity
1. The dc current through each diode in a bridge rectifier equals A. the load current B. half the dc load current C. twice the dc load current D. one-fourth the dc load current 2. When matching polarity
The Hartley Oscillator
 The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10
 DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10 In this experiment we will measure the I vs V characteristics of Si, Ge, and Zener p-n junction diodes, and
DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10 In this experiment we will measure the I vs V characteristics of Si, Ge, and Zener p-n junction diodes, and
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS. Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi
 EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
(A) im (B) im (C)0.5 im (D) im.
 Dr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, Pollachi. (An Autonomous Institution affiliated to Anna University) Regulation 2014 Fourth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering 141EE0404
Dr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, Pollachi. (An Autonomous Institution affiliated to Anna University) Regulation 2014 Fourth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering 141EE0404
Electronics I Circuit Drawings. Robert R. Krchnavek Rowan University Spring, 2018
 Electronics I Circuit Drawings Robert R. Krchnavek Rowan University Spring, 2018 Ideal Diode Piecewise Linear Models of a Diode Piecewise Linear Models of a Diode 1 r d Piecewise Linear Models of a Diode
Electronics I Circuit Drawings Robert R. Krchnavek Rowan University Spring, 2018 Ideal Diode Piecewise Linear Models of a Diode Piecewise Linear Models of a Diode 1 r d Piecewise Linear Models of a Diode
Feedback and Oscillator Circuits
 Chapter 14 Chapter 14 Feedback and Oscillator Circuits Feedback Concepts The effects of negative feedback on an amplifier: Disadvantage Lower gain Advantages Higher input impedance More stable gain Improved
Chapter 14 Chapter 14 Feedback and Oscillator Circuits Feedback Concepts The effects of negative feedback on an amplifier: Disadvantage Lower gain Advantages Higher input impedance More stable gain Improved
Questions from the same exercise can be combined together to increase difficulty. Which one of the following properties of the diode is NOT true:
 Questions from the same exercise can be combined together to increase difficulty. 21 1 Which one of the following properties of the diode is NOT true: a) When no voltage is applied across the diode, it
Questions from the same exercise can be combined together to increase difficulty. 21 1 Which one of the following properties of the diode is NOT true: a) When no voltage is applied across the diode, it
Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators
 Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
(b) 25% (b) increases
 Homework Assignment 07 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) 1. In the circuit 10 V, 10, and 5K. What current flows through? Answer: By op-amp action the voltage across is and the current through
Homework Assignment 07 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) 1. In the circuit 10 V, 10, and 5K. What current flows through? Answer: By op-amp action the voltage across is and the current through
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers
 Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Figure 1: Closed Loop System
 SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit
 Contents p. v Preface p. ix Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit Analysis p. 16 MultiSIM Lab
Contents p. v Preface p. ix Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit Analysis p. 16 MultiSIM Lab
Sheet 2 Diodes. ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering. Problem (1) Draw the
 Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall 2014 Sheet 2 Diodes Problem (1) Draw the i) Charge density distribution, ii) Electric field distribution iii) Potential distribution,
Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall 2014 Sheet 2 Diodes Problem (1) Draw the i) Charge density distribution, ii) Electric field distribution iii) Potential distribution,
1. In the circuit shown in the figure above, what will happen when switches S 1
 Student ID: 22133336 Exam: 002001RR - Introduction to Electronics When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam.
Student ID: 22133336 Exam: 002001RR - Introduction to Electronics When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam.
GATE SOLVED PAPER - IN
 YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
Precision Rectifier Circuits
 Precision Rectifier Circuits Rectifier circuits are used in the design of power supply circuits. In such applications, the voltage being rectified are usually much greater than the diode voltage drop,
Precision Rectifier Circuits Rectifier circuits are used in the design of power supply circuits. In such applications, the voltage being rectified are usually much greater than the diode voltage drop,
DEFINITION: Classification of oscillators Based on the frequency generated Oscillator type Frequency range
 DEFINITION: An oscillator is just an electronic circuit which converts dc energy into AC energy of required frequency. (Or) An oscillator is an electronic circuit which produces an ac output without any
DEFINITION: An oscillator is just an electronic circuit which converts dc energy into AC energy of required frequency. (Or) An oscillator is an electronic circuit which produces an ac output without any
II/IV B. TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOVEMBER Second Semester EC/EE ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. Time : Three Hours Max.
 Total No. of Questions : 9] [Total No. of Pages : 02 B.Tech. II/ IV YEAR DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY - 2014 (Second Semester) EC/EE/EI Electronic Circuit Analysis Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Q1)
Total No. of Questions : 9] [Total No. of Pages : 02 B.Tech. II/ IV YEAR DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY - 2014 (Second Semester) EC/EE/EI Electronic Circuit Analysis Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Q1)
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT. Infrared Transmitter/Receiver
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
Exercise 2: AC Voltage and Power Gains
 Exercise 2: AC Voltage and Power Gains an oscilloscope. Signals of equal magnitude but opposite polarity are needed for each transistor (Q1 and Q2). Center-tapped input transformer T1 is used as a phase
Exercise 2: AC Voltage and Power Gains an oscilloscope. Signals of equal magnitude but opposite polarity are needed for each transistor (Q1 and Q2). Center-tapped input transformer T1 is used as a phase
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:041 Electronic Circuits Oscillators Sections of Chapter 15 + Additional Material A. Kruger Oscillators 1 Stability Recall definition of loop gain: T(jω) = βa A f ( j) A( j) 1 T( j) If T(jω) = -1, then
55:041 Electronic Circuits Oscillators Sections of Chapter 15 + Additional Material A. Kruger Oscillators 1 Stability Recall definition of loop gain: T(jω) = βa A f ( j) A( j) 1 T( j) If T(jω) = -1, then
Chapter 6. FM Circuits
 Chapter 6 FM Circuits Topics Covered 6-1: Frequency Modulators 6-2: Frequency Demodulators Objectives You should be able to: Explain the operation of an FM modulators and demodulators. Compare and contrast;
Chapter 6 FM Circuits Topics Covered 6-1: Frequency Modulators 6-2: Frequency Demodulators Objectives You should be able to: Explain the operation of an FM modulators and demodulators. Compare and contrast;
Project 6: Oscillator Circuits
 : Oscillator Circuits Ariel Moss The purpose of this experiment was to design two oscillator circuits: a Wien-Bridge oscillator at 3 khz oscillation and a Hartley Oscillator using a BJT at 5 khz oscillation.
: Oscillator Circuits Ariel Moss The purpose of this experiment was to design two oscillator circuits: a Wien-Bridge oscillator at 3 khz oscillation and a Hartley Oscillator using a BJT at 5 khz oscillation.
Operation and Maintenance Manual
 WeiKedz 0-30V 2mA-3A Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply DIY Kit Operation and Maintenance Manual The WeiKedz Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply provides continuously variable output voltage between
WeiKedz 0-30V 2mA-3A Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply DIY Kit Operation and Maintenance Manual The WeiKedz Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply provides continuously variable output voltage between
EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
 EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER 1. What is feedback? What are the types of feedback? 2. Define positive feedback. What are its merits and demerits? 3. Define negative feedback.
EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER 1. What is feedback? What are the types of feedback? 2. Define positive feedback. What are its merits and demerits? 3. Define negative feedback.
SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter
 EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
Amplitude Modulation Methods and Circuits
 Amplitude Modulation Methods and Circuits By: Mark Porubsky Milwaukee Area Technical College Electronic Technology Electronic Communications Milwaukee, WI Purpose: The various parts of this lab unit will
Amplitude Modulation Methods and Circuits By: Mark Porubsky Milwaukee Area Technical College Electronic Technology Electronic Communications Milwaukee, WI Purpose: The various parts of this lab unit will
Low frequency tuned amplifier. and oscillator using simulated. inductor*
 CHAPTER 5 Low frequency tuned amplifier and oscillator using simulated inductor* * Partial contents of this Chapter has been published in. D.Susan, S.Jayalalitha, Low frequency amplifier and oscillator
CHAPTER 5 Low frequency tuned amplifier and oscillator using simulated inductor* * Partial contents of this Chapter has been published in. D.Susan, S.Jayalalitha, Low frequency amplifier and oscillator
Expect to be successful, expect to be liked,
 Thought of the Day Expect to be successful, expect to be liked, expect to be popular everywhere you go. Oscillators 1 Oscillators D.C. Kulshreshtha Oscillators 2 Need of an Oscillator An oscillator circuit
Thought of the Day Expect to be successful, expect to be liked, expect to be popular everywhere you go. Oscillators 1 Oscillators D.C. Kulshreshtha Oscillators 2 Need of an Oscillator An oscillator circuit
Diodes (non-linear devices)
 C H A P T E R 4 Diodes (non-linear devices) Ideal Diode Figure 4.2 The two modes of operation of ideal diodes and the use of an external circuit to limit (a) the forward current and (b) the reverse voltage.
C H A P T E R 4 Diodes (non-linear devices) Ideal Diode Figure 4.2 The two modes of operation of ideal diodes and the use of an external circuit to limit (a) the forward current and (b) the reverse voltage.
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II
 NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II Prepared by, C.P.SREE BALA LEKSHMI (Lect/ECE) ELECTRONICS
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II Prepared by, C.P.SREE BALA LEKSHMI (Lect/ECE) ELECTRONICS
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lesson Five PREVIEW COPY
 Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
A Simple Notch Type Harmonic Distortion Analyzer
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Nov. 28, 2009, rev. Nov. 29, 2009 Introduction This note describes a simple notch type harmonic distortion analyzer that can be constructed with basic parts. It is intended for use in
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Nov. 28, 2009, rev. Nov. 29, 2009 Introduction This note describes a simple notch type harmonic distortion analyzer that can be constructed with basic parts. It is intended for use in
2) The larger the ripple voltage, the better the filter. 2) 3) Clamping circuits use capacitors and diodes to add a dc level to a waveform.
 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A diode conducts current when forward-biased and blocks current when reverse-biased. 1) 2) The larger the ripple voltage,
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A diode conducts current when forward-biased and blocks current when reverse-biased. 1) 2) The larger the ripple voltage,
EXPERIMENT #2 CARRIER OSCILLATOR
 EXPERIMENT #2 CARRIER OSCILLATOR INTRODUCTION: The oscillator is usually the first stage of any transmitter. Its job is to create a radio-frequency carrier that can be amplified and modulated before being
EXPERIMENT #2 CARRIER OSCILLATOR INTRODUCTION: The oscillator is usually the first stage of any transmitter. Its job is to create a radio-frequency carrier that can be amplified and modulated before being
Lecture (04) Diode applications, cont.
 Lecture (04) Diode applications, cont. By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Agenda Full wave rectifier, cont.,.. Filters Voltage Regulators Diode limiters Diode Clampers ١ ٢ Bridge Full Wave Rectifier Operation uses
Lecture (04) Diode applications, cont. By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Agenda Full wave rectifier, cont.,.. Filters Voltage Regulators Diode limiters Diode Clampers ١ ٢ Bridge Full Wave Rectifier Operation uses
Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Chapter.8: Oscillators
 Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Examples to Power Supply
 Examples to Power Supply Example-1: A center-tapped full-wave rectifier connected to a transformer whose each secondary coil has a r.m.s. voltage of 1 V. Assume the internal resistances of the diode and
Examples to Power Supply Example-1: A center-tapped full-wave rectifier connected to a transformer whose each secondary coil has a r.m.s. voltage of 1 V. Assume the internal resistances of the diode and
PartIIILectures. Multistage Amplifiers
 University of missan Electronic II, Second year 2015-2016 PartIIILectures Assistant Lecture: 1 Multistage and Compound Amplifiers Basic Definitions: 1- Gain of Multistage Amplifier: Fig.(1-1) A general
University of missan Electronic II, Second year 2015-2016 PartIIILectures Assistant Lecture: 1 Multistage and Compound Amplifiers Basic Definitions: 1- Gain of Multistage Amplifier: Fig.(1-1) A general
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
Electronics & Comm. Lab
 Course name Electronics & Comm. Lab Lecture 1 Dr. Bedir B. Yousif E-mail: bedir.yousif@gmail.com Third Year-Comm Eng. Lecture: 1 hr. /week Section : 3 hrs. /week Subject Marks: 100 (50 works term + 50
Course name Electronics & Comm. Lab Lecture 1 Dr. Bedir B. Yousif E-mail: bedir.yousif@gmail.com Third Year-Comm Eng. Lecture: 1 hr. /week Section : 3 hrs. /week Subject Marks: 100 (50 works term + 50
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab. Facebook: Twitter:
 Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
Administrative-Master Syllabus form approved June/2006 revised Page 1 of 1
 revised 11-02-06 Page 1 of 1 Administrative - Master Syllabus I. Topical Outline Each offering of this course must include the following topics (be sure to include information regarding lab, practicum,
revised 11-02-06 Page 1 of 1 Administrative - Master Syllabus I. Topical Outline Each offering of this course must include the following topics (be sure to include information regarding lab, practicum,
Ham Radio 101 SOARA Workshop 3 Stage General Purpose Amplifier By Hal Silverman WB6WXO SOARA Education Director
 Ham Radio 101 SOARA Workshop 3 Stage General Purpose Amplifier By Hal Silverman WB6WXO SOARA Education Director Several months ago I started to put together a workshop where students could breadboard and
Ham Radio 101 SOARA Workshop 3 Stage General Purpose Amplifier By Hal Silverman WB6WXO SOARA Education Director Several months ago I started to put together a workshop where students could breadboard and
CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO).
 1. 1 To study CRO. CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO). Apparatus: - C.R.O, Connecting probe (BNC cable). Theory:An CRO is easily the most useful instrument available for testing
1. 1 To study CRO. CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO). Apparatus: - C.R.O, Connecting probe (BNC cable). Theory:An CRO is easily the most useful instrument available for testing
LINEAR MODELING OF A SELF-OSCILLATING PWM CONTROL LOOP
 Carl Sawtell June 2012 LINEAR MODELING OF A SELF-OSCILLATING PWM CONTROL LOOP There are well established methods of creating linearized versions of PWM control loops to analyze stability and to create
Carl Sawtell June 2012 LINEAR MODELING OF A SELF-OSCILLATING PWM CONTROL LOOP There are well established methods of creating linearized versions of PWM control loops to analyze stability and to create
Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter
 SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LAB
 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LAB 1 2 STATE INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Rough record and Fair record are needed to record the experiments conducted in the laboratory.
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LAB 1 2 STATE INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Rough record and Fair record are needed to record the experiments conducted in the laboratory.
CHAPTER 3 MODIFIED FULL BRIDGE ZERO VOLTAGE SWITCHING DC-DC CONVERTER
 53 CHAPTER 3 MODIFIED FULL BRIDGE ZERO VOLTAGE SWITCHING DC-DC CONVERTER 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter introduces the Full Bridge Zero Voltage Switching (FBZVSC) converter. Operation of the circuit is
53 CHAPTER 3 MODIFIED FULL BRIDGE ZERO VOLTAGE SWITCHING DC-DC CONVERTER 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter introduces the Full Bridge Zero Voltage Switching (FBZVSC) converter. Operation of the circuit is
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
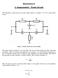 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Class XII Chapter 7 Alternating Current Physics
 Question 7.1: A 100 Ω resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply. (a) What is the rms value of current in the circuit? (b) What is the net power consumed over a full cycle? Resistance of the resistor,
Question 7.1: A 100 Ω resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply. (a) What is the rms value of current in the circuit? (b) What is the net power consumed over a full cycle? Resistance of the resistor,
Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB Amplifiers
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
Applications of Diode
 Applications of Diode Diode Approximation: (Large signal operations): 1. Ideal Diode: When diode is forward biased, resistance offered is zero, When it is reverse biased resistance offered is infinity.
Applications of Diode Diode Approximation: (Large signal operations): 1. Ideal Diode: When diode is forward biased, resistance offered is zero, When it is reverse biased resistance offered is infinity.
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 2 Tuned Amplifier Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 2 Tuned Amplifier Eng. Anas Alashqar
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
B.Tech II SEM Question Bank. Electronics & Electrical Engg UNIT-1
 UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
Assume availability of the following components to DESIGN and DRAW the circuits of the op. amp. applications listed below:
 ========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
Homework Assignment 06
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 06 1. True or false: when transforming a circuit s diagram to a diagram of its small-signal model, we replace dc constant current sources
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 06 1. True or false: when transforming a circuit s diagram to a diagram of its small-signal model, we replace dc constant current sources
Electronics EECE2412 Spring 2016 Exam #1
 Electronics EECE2412 Spring 2016 Exam #1 Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University 18 February 2016 File:12140/exams/exam1 Name: : Row # : Seat
Electronics EECE2412 Spring 2016 Exam #1 Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University 18 February 2016 File:12140/exams/exam1 Name: : Row # : Seat
PRACTICE. Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination. Advanced Qualification
 Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique Canada Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2018-06-30 To pass this
Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique Canada Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2018-06-30 To pass this
BENE 2163 ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
 UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENE 263 ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS LAB SESSION 3 WEIN BRIDGE OSCILLATOR Revised: February 20 Lab 3 Wien Bridge Oscillator
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENE 263 ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS LAB SESSION 3 WEIN BRIDGE OSCILLATOR Revised: February 20 Lab 3 Wien Bridge Oscillator
3 Circuit Theory. 3.2 Balanced Gain Stage (BGS) Input to the amplifier is balanced. The shield is isolated
 Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: Coil Losses:
 TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
An Oscillator is a circuit which produces a periodic waveform at its output with only the dc supply voltage at the input. The output voltage can be
 An Oscillator is a circuit which produces a periodic waveform at its output with only the dc supply voltage at the input. The output voltage can be either sinusoidal or non sinusoidal depending upon the
An Oscillator is a circuit which produces a periodic waveform at its output with only the dc supply voltage at the input. The output voltage can be either sinusoidal or non sinusoidal depending upon the
EE351 Laboratory Exercise 1 Diode Circuits
 revised July 19, 2009 The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to gain experience and understanding working with diodes. Focus on taking good data so that the plots and calculations you will do later
revised July 19, 2009 The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to gain experience and understanding working with diodes. Focus on taking good data so that the plots and calculations you will do later
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
 Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual EDC-I For Second Year Students Manual made by A.A.Sayar Author JNEC, Aurangabad 1 MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College N-6, CIDCO, Aurangabad
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual EDC-I For Second Year Students Manual made by A.A.Sayar Author JNEC, Aurangabad 1 MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College N-6, CIDCO, Aurangabad
Emitter base bias. Collector base bias Active Forward Reverse Saturation forward Forward Cut off Reverse Reverse Inverse Reverse Forward
 SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS-2 [Transistor, constructional characteristics, biasing of transistors, transistor configuration, transistor as an amplifier, transistor as a switch, transistor as an oscillator] Transistor
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS-2 [Transistor, constructional characteristics, biasing of transistors, transistor configuration, transistor as an amplifier, transistor as a switch, transistor as an oscillator] Transistor
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology INDEX
 Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology Diploma EE Semester III 3330905: ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS AND CIRCUITS INDEX Sr. No. Title Page Date Sign Grade 1 Obtain I-V characteristic of Diode. 2 To
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology Diploma EE Semester III 3330905: ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS AND CIRCUITS INDEX Sr. No. Title Page Date Sign Grade 1 Obtain I-V characteristic of Diode. 2 To
Differential-Mode Emissions
 Differential-Mode Emissions In Fig. 13-5, the primary purpose of the capacitor C F, however, is to filter the full-wave rectified ac line voltage. The filter capacitor is therefore a large-value, high-voltage
Differential-Mode Emissions In Fig. 13-5, the primary purpose of the capacitor C F, however, is to filter the full-wave rectified ac line voltage. The filter capacitor is therefore a large-value, high-voltage
LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers
 LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers General Description The LM2900 series consists of four independent dual input internally compensated amplifiers which were designed specifically to operate off of a
LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers General Description The LM2900 series consists of four independent dual input internally compensated amplifiers which were designed specifically to operate off of a
Electronic Devices. Floyd. Chapter 2. Ninth Edition. Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd
 Electronic Devices Ninth Edition Floyd Chapter 2 Agenda Diode Circuits and Applications Half-wave Rectifier Full-wave Rectifier Power Supply Filter Power Supply Regulator Diode Limiting Circuits Diode
Electronic Devices Ninth Edition Floyd Chapter 2 Agenda Diode Circuits and Applications Half-wave Rectifier Full-wave Rectifier Power Supply Filter Power Supply Regulator Diode Limiting Circuits Diode
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK Subject with Code : Electronic Circuit Analysis (16EC407) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK Subject with Code : Electronic Circuit Analysis (16EC407) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem
Lecture (04) PN Diode applications II
 Lecture (04) PN Diode applications II By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda Full wave rectifier, cont.,.. Filters Voltage Regulators ٢ RMS The RMS value of a set of values (or a continuous time waveform) is
Lecture (04) PN Diode applications II By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda Full wave rectifier, cont.,.. Filters Voltage Regulators ٢ RMS The RMS value of a set of values (or a continuous time waveform) is
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name:
 ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad Pakistan SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I
 SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Yousaf Hameed Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Yousaf Hameed Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
DESIGN OF AN ANALOG FIBER OPTIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
 DESIGN OF AN ANALOG FIBER OPTIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM OBJECTIVE To design and build a complete analog fiber optic transmission system, using light emitting diodes and photodiodes. INTRODUCTION A fiber optic
DESIGN OF AN ANALOG FIBER OPTIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM OBJECTIVE To design and build a complete analog fiber optic transmission system, using light emitting diodes and photodiodes. INTRODUCTION A fiber optic
BE Assignment. (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source.
 BE Assignment chapter-1 (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source. (2) Explain practical current source and ideal current
BE Assignment chapter-1 (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source. (2) Explain practical current source and ideal current
Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits EE 111 Electrical Engineering Majmaah University 2 nd Semester 1432/1433 H. Chapter 2. Diodes and Applications
 Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits EE 111 Electrical Engineering Majmaah University 2 nd Semester 1432/1433 H Chapter 2 Diodes and Applications 1 Diodes A diode is a semiconductor device with a single
Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits EE 111 Electrical Engineering Majmaah University 2 nd Semester 1432/1433 H Chapter 2 Diodes and Applications 1 Diodes A diode is a semiconductor device with a single
ITT Technical Institute. ET215 Devices I Chapter 2 Sections
 ITT Technical Institute ET215 Devices I Chapter 2 Sections 2.8-2.10 Chapter 2 Section 2.8 Special-Purpose Diodes The preceding discussions of diodes has focused on applications that exploit the fact that
ITT Technical Institute ET215 Devices I Chapter 2 Sections 2.8-2.10 Chapter 2 Section 2.8 Special-Purpose Diodes The preceding discussions of diodes has focused on applications that exploit the fact that
UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES
 UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES 1. a) Derive the equation for the overall voltage gain of a multistage amplifier in terms of the individual voltage gains. b) what are the multi-stage amplifiers? 2. Describe
UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES 1. a) Derive the equation for the overall voltage gain of a multistage amplifier in terms of the individual voltage gains. b) what are the multi-stage amplifiers? 2. Describe
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Reading Horowitz & Hill handout Notes, Chapter 9 Introduction and Objective In this lab we will examine op-amps. We will look at a few of their vast number of uses and also investigate
Operational Amplifiers Reading Horowitz & Hill handout Notes, Chapter 9 Introduction and Objective In this lab we will examine op-amps. We will look at a few of their vast number of uses and also investigate
The Tuned Circuit. Aim of the experiment. Circuit. Equipment and components. Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R.
 The Tuned Circuit Aim of the experiment Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R. Circuit Equipment and components 1 Rastered socket panel 1 Resistor R 1 = 10 Ω, 1 Resistor R 2 = 1 kω
The Tuned Circuit Aim of the experiment Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R. Circuit Equipment and components 1 Rastered socket panel 1 Resistor R 1 = 10 Ω, 1 Resistor R 2 = 1 kω
