X-RAY IMAGING EE 472 F2017. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
|
|
|
- Richard Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 X-RAY IMAGING EE 472 F2017 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
2 Recommended Textbook Stewart C. Bushong, Radiologic Science for Technologists: Physics, Biology, and Protection, 10 th ed., Mosby, (ISBN )
3 X-Ray Production
4 X-Ray Production Bremsstrahlung x-rays are produced when a projectile electron is slowed by the nuclear field of a target atom nucleus In the diagnostic range, most x-rays are bremsstrahlung x-rays Characteristic x-rays are emitted when an outer-shell electron fills an inner-shell void This type of x-radiation is called characteristic because it is characteristic of the target element Only the K-characteristic x-rays of tungsten are useful for imaging Approximately 99% of the kinetic energy of projectile electrons is converted to heat (Anode heat)
5 Quantity and Quality of X-ray Beam General shape of an emission spectrum is always the same, but its relative position along the energy axis can change The farther to the right a spectrum is, the higher the effective energy or quality of the x-ray beam The larger the area under the curve, the higher is the x-ray intensity or quantity
6 Effect of ma and mas A change in ma or mas results in a proportional change in the amplitude of the x-ray emission spectrum at all energies.
7 Effect of kvp As kvp is raised, area under curve increases by approximating the square of the factor by which kvp was increased Accordingly, x-ray quantity increases with the square of this factor Change in kvp affects both amplitude and position of x-ray emission spectrum In diagnostic range, 15% increase in kvp is equivalent to doubling mas
8 Effect of Added Filtration Adding filtration to the useful x-ray beam reduces x-ray beam intensity while increasing the average energy The result of added filtration is an increase in the average energy of the x-ray beam with an accompanying reduction in x-ray quantity
9 Effect of Target Material The atomic number of the target affects both the number (quantity) and the effective energy (quality) of x-rays As the atomic number of the target material increases, the efficiency of the production of bremsstrahlung radiation increases, and high-energy x-rays increase in number to a greater extent than low-energy x-rays.
10 Effect of Voltage Waveform There are five voltage waveforms: half-wave rectified, fullwave rectified, three-phase/six-pulse, three-phase/12-pulse, and high-frequency waveforms Both quantity and quality decrease by ripple Because of reduced ripple, operation with three-phase power or high frequency is equivalent to an approximate 12% Increase in kvp, or almost a doubling of mas over single phase power.
11 Factors Affecting X-Ray Quantity
12 Factors Affecting X-Ray Quality
13 Half-Value Layer (HVL) In radiography, quality of x-rays is measured by the HVL Diagnostic x-ray usually has HVL 3 to 5 mm Al or 3 to 6 cm of soft tissue Although x-rays are attenuated exponentially, high-energy x- rays are more penetrating than low-energy x-rays 100-keV x-rays are attenuated at rate of 3%/cm of soft tissue 10-keV x-rays are attenuated at 15%/cm of soft tissue
14 X-Ray Interaction with Matter Coherent scattering (energy < 10 kev) Compton scattering Photoelectric effect Pair production (energy > 1.02 MeV) Important in making an x-ray image
15 Compton (Incoherent) Scattering
16 Photoelectric Effect
17 Photoelectric Effect
18 Differential Absorption
19 X-Ray Exponential Attenuation The total reduction in the number of x- rays remaining in an x-ray beam after penetration through a given thickness of tissue is called attenuation When broad beam of x-rays is incident on any tissue, some x-rays are absorbed, and some are scattered The result is a reduced number of x-rays, a condition referred to as x-ray attenuation
20 Radiologic Units Air Kerma (Kinetic Energy Released in Matter) (Gy a ) Kinetic energy transferred from photons to electrons during ionization and excitation measured in J/kg where 1 J/kg = 1 gray (Gy a ) Absorbed Dose (Gy t ) Radiation energy absorbed in tissue per unit mass with units of J/kg or Gy t (gray) which depends on tissue type Sievert (Sv): quantity of radiation received by radiation workers and populations Becquerel (Bq): quantity of radioactive material, not the radiation emitted by that material Radioactivity and the becquerel have nothing to do with x-rays
21 Radiologic Units
22 X-Ray Tube External structures Support structure Protective housing Glass or metal enclosure. The internal Internal structures Anode and cathode
23 X-Ray Tube Support Structure X-ray tube and housing assembly are quite heavy Require support mechanism so radiologic technologist can position them Mainly ceiling, floor or C-arm support systems
24 Protective Housing When x-rays are produced, they are emitted isotropically That is, with equal intensity in all directions Only x-rays emitted through window are called useful beam X-rays that escape through protective housing: leakage radiation Leakage radiation contributes nothing to diagnostic information and result in unnecessary exposure of patient and radiologic technologist Protective housing guards against excessive radiation exposure and electric shock Also mechanically protects x-ray tube
25 Metal or Glass Enclosure X-ray tube is an electronic vacuum tube with components contained within a glass or metal enclosure vacuum allows for more efficient x-ray production and longer tube life As glass enclosure tube ages, some tungsten vaporizes and coats the inside of glass enclosure Alter electrical properties of the tube, allowing tube current to stray and interact with the glass enclosure resulting in arcing and tube failure Most common cause of tube failure Metal enclosures maintain constant electric potential between electrons of tube current and enclosure Longer life and less likely to fail Virtually all high-capacity x-ray tubes now use metal enclosures
26 Cathode Cathode is the negative side of the x-ray tube It has two primary parts, a filament and a focusing cup Dual-filament cathode allows two focal spots (e.g., 0.5 and 1.5 mm) Focusing cup is a metal shroud that surrounds filament Tube current is adjusted by controlling filament current
27 Anode Anode is the positive side of the x-ray tube Two types: stationary (dental) and rotating (general purpose) Higher tube currents and shorter exposure times are possible with rotating anode because of their better heat dissipation Three functions in an x-ray tube: Electrical conductor that receives electrons emitted by cathode and conducts them through the tube to the connecting cables and back to the high-voltage generator Mechanical support for the target Thermal dissipation
28 Target The target is area of anode struck by electrons from cathode
29 Focal Spot Focal spot is the area of target from which x-rays are emitted The smaller the focal spot, the better the spatial resolution of the image Unfortunately, as the size of focal spot decreases, heating of target is concentrated onto a smaller area (limiting factor to focal spot size Line-focus principle: angling target makes effective area of the target much smaller than actual area of electron interaction
30 Radiographic Image Quality Definition: fidelity with which anatomical structure being examined is rendered on radiograph Spatial resolution: ability to image small objects Contrast resolution: ability to distinguish anatomical structures Radiographic noise: random fluctuation in intensity of image Film graininess, structure mottle, quantum mottle, and scatter radiation
31 Geometric Factors: Magnification
32 Geometric Factors: Distortion Unequal magnification of different portions of the same object is called shape distortion Distortion depends on object thickness, position, and shape Thick objects are more distorted than thin objects If object plane and image plane are not parallel, distortion occurs
33 Geometric Factors: Focal-Spot Blur Focal-spot blur is caused by effective size of focal spot The most important factor for determining spatial resolution Smaller on anode side than cathode side of the image (Heel effect)
34 Subject Factors kvp is the most important influence on subject contrast
35 Control of Scatter Radiation Reduced image contrast results from scattered x-rays Restricting x-ray beam (collimation) reduces scattering
36 Beam Restricting Devices Collimation reduces patient radiation dose and improves contrast resolution
37 Radiographic Grids Effective device for reducing level of scatter radiation that reaches image receptor The principal function of a grid is to improve image contrast
38 Radiographic Grids High-ratio and high-frequency grids increase patient radiation dose When grid is used, radiographic technique must be increased to produce same image receptor signal by a factor called Bucky (Grid) factor (B) As Bucky factor increases, radiographic technique and patient dose increases The higher the grid ratio, the higher is the Bucky factor The Bucky factor increases with increasing kvp
39 Radiographic Grids Grid Cutoff: undesirable absorption of primary x-rays by grid Greater Attenuation of primary x-rays near edges of image receptor
40 Radiographic Grids Types Parallel, Crossed and Focused Moving Grid (Bucky): reciprocating and oscillating (-) Require a bulky mechanism that is subject to failure (-) Distance between patient and the image receptor is increased (-) Moving grids can introduce motion into cassette-holding device Advantages of moving grids far outweigh disadvantages
41 Computed Radiography (CR) Filmless radiology using special imaging plates Photostimulable luminescence (PSL)
42 Computed Radiography (CR) Screen-Film Radiography Proper radiographic technique and exposure are essential Computed Radiography Radiographic technique is not so critical
43 Digital Fluoroscopy (DF) Fluoroscopy: real-time dynamic viewing of anatomic structures Advantages of DF include the speed of image acquisition and postprocessing to enhance image contrast
44 Interventional Radiology Performing surgical procedures under guidance from radiographic equipment
45 Digital Mammography Radiographic examination of the breast Digital Mammography spatial resolution limited by pixel size Superior contrast resolution principally because of postprocessing
46 Operating Console Allows radiologist to control x-ray tube current and voltage so that useful x-ray beam is of proper quantity and quality Radiation quantity refers to number of x-rays or intensity of x-ray beam Radiation quality refers to penetrability of x-ray beam and is expressed in kilovolt peak (kvp) or, more precisely, half-value layer (HVL)
47 Autotransformer Power supplied to x-ray imaging system is delivered first to autotransformer where it provides controlled but variable voltage to high-voltage transformer It is much safer and easier to control a low voltage and then increase it than to increase a low voltage to the kilovolt level and then control its magnitude
48 Adjustment of Kilovolt Peak (kvp) kvp determines the quality of the x-ray beam Appropriate autotransformer connections can be selected with an adjustment knob, a push button, or a touch screen This low voltage from autotransformer becomes the input to high-voltage step-up transformer that increases voltage to chosen kilovolt peak Note: kvp meter placed across output terminals of autotransformer actually reads voltage, not kvp. It registers kilovolts because of the known multiplication factor of high voltage transformer
49 Control of Milliamperage (ma) The x-ray tube current, crossing from cathode to anode, is measured in milliamperes (ma) Number of electrons emitted by filament is determined by filament temperature (controlled in turn by filament current) Thermionic emission is the release of electrons from a heated filament Space Charge Effect: As the kvp is raised, anode becomes more attractive to electrons that would not have enough energy to leave the filament. Hence, this effectively increases ma with kvp and hence should be corrected for by special circuit
50 Exposure Timer Most exposure timers are electronic, controlled by microprocessor Allow wide range of time intervals to be selected and are accurate to intervals as small as 1 ms Special kind of electronic timer, called an mas timer, monitors product of ma and exposure time and terminates exposure when desired mas value is reached Because the mas timer must monitor actual tube current, it is located on the secondary side of the high-voltage transformer
51 Automatic Exposure Control (AEC) AEC is a device that measures quantity of radiation that reaches image receptor and automatically terminates exposure when image receptor has received required radiation intensity
52 High-Voltage Generator Function: increases output voltage from autotransformer to the kvp necessary for x-ray production High-voltage generator contains three primary parts: highvoltage transformer, filament transformer, and rectifiers Note: Although some heat is generated in the high-voltage section and is conducted to oil, the oil is used primarily for electrical insulation
53 High-Voltage Transformer High voltage transformer is a step-up transformer Turns ratio of is usually between 500:1 and 1000:1
54 High-Voltage Rectification Rectification is the process of converting AC to DC Rectification is accomplished with diodes Transformers operate AC while x-ray tubes need DC X-rays are produced by acceleration of electrons from cathode to anode and cannot be produced by electrons flowing in reverse
55 Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Three-phase power is a more efficient way to produce x-rays than is single-phase power With three-phase power, voltage applied across the x-ray tube is nearly constant, never dropping to zero during exposure.
56 High-Frequency Generator High-frequency generators produce nearly constant potential voltage waveform, improving image quality Rectified power at 60 Hz is inverted to a higher frequency, from 500 to 25,000 Hz, then transformed to high voltage Advantage: much smaller size than 60-Hz high-voltage generators
57 Voltage Ripple Comparison Less voltage ripple results in greater radiation quantity and quality
58 Power Rating Transformers and high-voltage generators usually are identified by their power rating in kilowatts (kw) Power (W) = Current (A) Potential (V) For specifying high-voltage generators, the industry standard is to use the maximum tube current (ma) possible at 100 kvp for an exposure of 100 ms This generally results in the maximum available power Use RMS voltage factor to account for voltage ripples 0.7 of peak in single phase generators Close enough to 1 in three-phase and high-frequency generators
59 X-Ray Circuit
60 Cardinal Principles for Radiation Protection Simplified rules designed to ensure safety in radiation areas for occupational workers
61 Cardinal Principles for Radiation Protection Minimize Time Dose is directly related to duration of radiation exposure Exposure = Exposure rate Exposure time Maximize Distance As distance between source of radiation and person increases, radiation exposure decreases rapidly by inverse square law If distance from source exceeds 5 times source diameter, it can be treated as point source (assume true and apply inverse square law) Use Shielding Positioning shielding between radiation source and exposed persons greatly reduces level of radiation exposure Shielding used in diagnostic radiology usually consists of lead, although conventional building materials also are used
62 Shielding Estimate dose reduction using half-value layer (HVL) or tenthvalue layer (TVL) of barrier material (1 TVL = 3.3 HVL) Protective apparel Protective aprons usually contain 0.5 mm Pb (2 HVL reduction to 25%). Actual measurements show reduction to approximately 10%
63 Effective Dose Effective dose is the equivalent whole-body dose When only part of body is exposed, as in medical x-ray imaging, risk is proportional to effective dose (E) Equivalent whole-body dose is the weighted average of the radiation dose to various organs and tissues
64 Patient and Occupational Effective Dose
65 Covered Material and Suggest Problems Chapters 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 35 of textbook Attempt questions at the end of each chapter
X-rays. X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated and collide with a target. X-rays are sometimes characterized by the generating voltage
 X-rays Ouch! 1 X-rays X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated and collide with a target Bremsstrahlung x-rays Characteristic x-rays X-rays are sometimes characterized by the generating voltage
X-rays Ouch! 1 X-rays X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated and collide with a target Bremsstrahlung x-rays Characteristic x-rays X-rays are sometimes characterized by the generating voltage
Mammography is a radiographic procedure specially designed for detecting breast pathology Approximately 1 woman in 8 will develop breast cancer over
 Mammography is a radiographic procedure specially designed for detecting breast pathology Approximately 1 woman in 8 will develop breast cancer over a lifetime Breast cancer screening programs rely on
Mammography is a radiographic procedure specially designed for detecting breast pathology Approximately 1 woman in 8 will develop breast cancer over a lifetime Breast cancer screening programs rely on
X-ray Tube and Generator Basic principles and construction
 X-ray Tube and Generator Basic principles and construction Dr Slavik Tabakov - Production of X-rays OBJECTIVES - X-ray tube construction - Anode - types, efficiency - X-ray tube working characteristics
X-ray Tube and Generator Basic principles and construction Dr Slavik Tabakov - Production of X-rays OBJECTIVES - X-ray tube construction - Anode - types, efficiency - X-ray tube working characteristics
Beam-Restricting Devices
 Beam-Restricting Devices Three factors contribute to an increase in scatter radiation: Increased kvp Increased Field Size Increased Patient or Body Part Size. X-ray Interactions a some interact with the
Beam-Restricting Devices Three factors contribute to an increase in scatter radiation: Increased kvp Increased Field Size Increased Patient or Body Part Size. X-ray Interactions a some interact with the
- KiloVoltage. Technique 101: Getting Back to Basics
 Why do I need to know technique? Technique 101: Getting Back to Basics Presented by: Thomas G. Sandridge, M.S., M.Ed., R.T.(R) Program Director Northwestern Memorial Hospital School of Radiography Chicago,
Why do I need to know technique? Technique 101: Getting Back to Basics Presented by: Thomas G. Sandridge, M.S., M.Ed., R.T.(R) Program Director Northwestern Memorial Hospital School of Radiography Chicago,
1. Carlton, Richard R., and Arlene M. Adler. Principles of Radiographic Imaging: An Art and a Science, 5th edition (2013).
 CODE: RADT 151 INSTITUTE: Health Science TITLE: Radiographic Exposure DEPARTMENT: Radiologic Technology COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course covers the principles of radiographic exposure selection and manipulation
CODE: RADT 151 INSTITUTE: Health Science TITLE: Radiographic Exposure DEPARTMENT: Radiologic Technology COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course covers the principles of radiographic exposure selection and manipulation
RADIOGRAPHIC EXPOSURE
 RADIOGRAPHIC EXPOSURE Receptor Exposure Receptor Exposure the that interacts with the receptor. Computed Radiography ( ) requires a. Direct Digital Radiography (DR) requires a. Exposure Indicators Exposure
RADIOGRAPHIC EXPOSURE Receptor Exposure Receptor Exposure the that interacts with the receptor. Computed Radiography ( ) requires a. Direct Digital Radiography (DR) requires a. Exposure Indicators Exposure
X-ray Tube and Generator Basic principles and construction
 X-ray Tube and Generator Basic principles and construction Dr Slavik Tabakov - Production of X-rays and Patient Dose OBJECTIVES - X-ray tube construction - Anode - types, efficiency - Classical X-ray generator
X-ray Tube and Generator Basic principles and construction Dr Slavik Tabakov - Production of X-rays and Patient Dose OBJECTIVES - X-ray tube construction - Anode - types, efficiency - Classical X-ray generator
Overview. Professor Roentgen was a Physicist!!! The Physics of Radiation Oncology X-ray Imaging
 The Physics of Radiation Oncology X-ray Imaging Charles E. Willis, Ph.D. DABR Associate Professor Department of Imaging Physics The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas Overview
The Physics of Radiation Oncology X-ray Imaging Charles E. Willis, Ph.D. DABR Associate Professor Department of Imaging Physics The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas Overview
P R E S E N T E D B Y. K A M A R U L A M I N A B D U L L A H Dip. MED. IMG., BSc. MED. IMG. (UiTM)
 + - P R E S E N T E D B Y K A M A R U L A M I N A B D U L L A H Dip. MED. IMG., BSc. MED. IMG. (UiTM) 1 I N T R O D U C T I O N : An x-ray generator is a device that Supplies electrical power to x-ray
+ - P R E S E N T E D B Y K A M A R U L A M I N A B D U L L A H Dip. MED. IMG., BSc. MED. IMG. (UiTM) 1 I N T R O D U C T I O N : An x-ray generator is a device that Supplies electrical power to x-ray
LECTURE 1 The Radiographic Image
 LECTURE 1 The Radiographic Image Prepared by:- KAMARUL AMIN ABDULLAH @ ABU BAKAR UiTM Faculty of Health Sciences Medical Imaging Department 11/23/2011 KAMARUL AMIN (C) 1 Lesson Objectives At the end of
LECTURE 1 The Radiographic Image Prepared by:- KAMARUL AMIN ABDULLAH @ ABU BAKAR UiTM Faculty of Health Sciences Medical Imaging Department 11/23/2011 KAMARUL AMIN (C) 1 Lesson Objectives At the end of
1-1. GENERAL 1-2. DISCOVERY OF X-RAYS
 1-1. GENERAL Radiography is a highly technical field, indispensable to the modern dental practice, but presenting many potential hazards. The dental radiographic specialist must be thoroughly familiar
1-1. GENERAL Radiography is a highly technical field, indispensable to the modern dental practice, but presenting many potential hazards. The dental radiographic specialist must be thoroughly familiar
X-RAYS - NO UNAUTHORISED ENTRY
 Licencing of premises Premises Refer Guidelines A radiation warning sign and warning notice, X-RAYS - NO UNAUTHORISED ENTRY must be displayed at all entrances leading to the rooms where x-ray units are
Licencing of premises Premises Refer Guidelines A radiation warning sign and warning notice, X-RAYS - NO UNAUTHORISED ENTRY must be displayed at all entrances leading to the rooms where x-ray units are
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: RADG 212 Department: Radiography Course Title: Equip. Operation & Maint. Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ Unit One: The X-ray
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: RADG 212 Department: Radiography Course Title: Equip. Operation & Maint. Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ Unit One: The X-ray
Course Outline: At the completion of each chapter the student should be able to
 Radiographic Imaging Equipment (RADR 2309) Credit: 3 semester credit hours (3 hours lecture) Prerequisite: RADR 1313 Principles of Radiographic Imaging I Course Description: Equipment and physics of x-ray
Radiographic Imaging Equipment (RADR 2309) Credit: 3 semester credit hours (3 hours lecture) Prerequisite: RADR 1313 Principles of Radiographic Imaging I Course Description: Equipment and physics of x-ray
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 RA110 test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An object 35 cm in width is radiographed at 100 cm SID and at a 50 cm SOD. What
RA110 test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An object 35 cm in width is radiographed at 100 cm SID and at a 50 cm SOD. What
X-ray Imaging. PHYS Lecture. Carlos Vinhais. Departamento de Física Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto
 X-ray Imaging PHYS Lecture Carlos Vinhais Departamento de Física Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto cav@isep.ipp.pt Overview Projection Radiography Anode Angle Focal Spot Magnification Blurring
X-ray Imaging PHYS Lecture Carlos Vinhais Departamento de Física Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto cav@isep.ipp.pt Overview Projection Radiography Anode Angle Focal Spot Magnification Blurring
Veterinary Science Preparatory Training for the Veterinary Assistant. Floron C. Faries, Jr., DVM, MS
 Veterinary Science Preparatory Training for the Veterinary Assistant Floron C. Faries, Jr., DVM, MS Radiology Floron C. Faries, Jr., DVM, MS Objectives Determine the appropriate machine settings for making
Veterinary Science Preparatory Training for the Veterinary Assistant Floron C. Faries, Jr., DVM, MS Radiology Floron C. Faries, Jr., DVM, MS Objectives Determine the appropriate machine settings for making
CR Basics and FAQ. Overview. Historical Perspective
 Page: 1 of 6 CR Basics and FAQ Overview Computed Radiography is a term used to describe a system that electronically records a radiographic image. Computed Radiographic systems use unique image receptors
Page: 1 of 6 CR Basics and FAQ Overview Computed Radiography is a term used to describe a system that electronically records a radiographic image. Computed Radiographic systems use unique image receptors
I. PERFORMANCE OF X-RAY PRODUCTION COMPONENTS FLUOROSCOPIC ACCEPTANCE TESTING: TEST PROCEDURES & PERFORMANCE CRITERIA
 FLUOROSCOPIC ACCEPTANCE TESTING: TEST PROCEDURES & PERFORMANCE CRITERIA EDWARD L. NICKOLOFF DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY NEW YORK, NY ACCEPTANCE TESTING GOALS PRIOR TO 1st CLINICAL USAGE
FLUOROSCOPIC ACCEPTANCE TESTING: TEST PROCEDURES & PERFORMANCE CRITERIA EDWARD L. NICKOLOFF DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY NEW YORK, NY ACCEPTANCE TESTING GOALS PRIOR TO 1st CLINICAL USAGE
Introduction. Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology. Primary radiological image. Primary radiological image
 Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
Mammography: Physics of Imaging
 Mammography: Physics of Imaging Robert G. Gould, Sc.D. Professor and Vice Chair Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California San Francisco, California Mammographic Imaging: Uniqueness
Mammography: Physics of Imaging Robert G. Gould, Sc.D. Professor and Vice Chair Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California San Francisco, California Mammographic Imaging: Uniqueness
MaxRay Handheld X-ray Systems Operator Training Exam
 MaxRay Handheld X-ray Systems Operator Training Exam Employee: Instructor: ate: Score: Instructions Read each question carefully and choose the best answer. 1) LR is 2) 3) 4) a. a safety principle meant
MaxRay Handheld X-ray Systems Operator Training Exam Employee: Instructor: ate: Score: Instructions Read each question carefully and choose the best answer. 1) LR is 2) 3) 4) a. a safety principle meant
Visibility of Detail
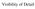 Visibility of Detail Radiographic Quality Quality radiographic images represents the, and information is for diagnosis. The of the anatomic structures and the accuracy of their ( ) determine the overall
Visibility of Detail Radiographic Quality Quality radiographic images represents the, and information is for diagnosis. The of the anatomic structures and the accuracy of their ( ) determine the overall
RAD 150 RADIOLOGIC EXPOSURE TECHNIQUE II
 RAD 150 RADIOLOGIC EXPOSURE TECHNIQUE II APPROVED 12/O2/2011 EFFECTIVE SPRING 2013-14 Prefix & Number RAD 150 Course Title: Radiologic Exposure Technique II & Lab Purpose of this submission: New Change/Updated
RAD 150 RADIOLOGIC EXPOSURE TECHNIQUE II APPROVED 12/O2/2011 EFFECTIVE SPRING 2013-14 Prefix & Number RAD 150 Course Title: Radiologic Exposure Technique II & Lab Purpose of this submission: New Change/Updated
DENTAL RADIOGRAPHY KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABU BAKAR
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPHY KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH @ ABU BAKAR Components of the Dental X-Ray Machine Dental x-ray machines may vary somewhat in size and appearance, but all machines will have three primary
DENTAL RADIOGRAPHY KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH @ ABU BAKAR Components of the Dental X-Ray Machine Dental x-ray machines may vary somewhat in size and appearance, but all machines will have three primary
PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems
 PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems (Lecture-8 Medical Imaging Systems) (Imaging Systems Basics, X-ray and CT) Dr. Manish Arora CPDM, IISc Course Website: http://cpdm.iisc.ac.in/utsaah/courses/
PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems (Lecture-8 Medical Imaging Systems) (Imaging Systems Basics, X-ray and CT) Dr. Manish Arora CPDM, IISc Course Website: http://cpdm.iisc.ac.in/utsaah/courses/
Joint ICTP/IAEA Advanced School on Dosimetry in Diagnostic Radiology and its Clinical Implementation May 2009
 2033-6 Joint ICTP/IAEA Advanced School on Dosimetry in Diagnostic Radiology and its Clinical Implementation 11-15 May 2009 Dosimetry for Fluoroscopy Basics Renato Padovani EFOMP Joint ICTP-IAEA Advanced
2033-6 Joint ICTP/IAEA Advanced School on Dosimetry in Diagnostic Radiology and its Clinical Implementation 11-15 May 2009 Dosimetry for Fluoroscopy Basics Renato Padovani EFOMP Joint ICTP-IAEA Advanced
RULES OF TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION DIVISION OF RADIOLOGICAL HEALTH CHAPTER USE OF X-RAY APPARATUS
 RULES OF TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION DIVISION OF RADIOLOGICAL HEALTH CHAPTER 0400-20-06 USE OF X-RAY APPARATUS TABLE OF CONTENTS 0400-20-06-.01 Purpose 0400-20-06-.06 Veterinary
RULES OF TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION DIVISION OF RADIOLOGICAL HEALTH CHAPTER 0400-20-06 USE OF X-RAY APPARATUS TABLE OF CONTENTS 0400-20-06-.01 Purpose 0400-20-06-.06 Veterinary
COMPUTED RADIOGRAPHY CHAPTER 4 EFFECTIVE USE OF CR
 This presentation is a professional collaboration of development time prepared by: Rex Christensen Terri Jurkiewicz and Diane Kawamura New Technology https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ptkzznazb 7U COMPUTED
This presentation is a professional collaboration of development time prepared by: Rex Christensen Terri Jurkiewicz and Diane Kawamura New Technology https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ptkzznazb 7U COMPUTED
Digital Imaging Considerations Computed Radiography
 Digital Imaging Considerations Digital Radiography Computed Radiography o Cassette based Direct or Indirect Digital Radiography o Cassetteless Computed Radiography 1 CR Image Acquisition Most like conventional
Digital Imaging Considerations Digital Radiography Computed Radiography o Cassette based Direct or Indirect Digital Radiography o Cassetteless Computed Radiography 1 CR Image Acquisition Most like conventional
COURSE SYLLABUS. Instructor Information. Course Description. Prerequisites/Corequisites SCANS. End-of-Course Outcomes/Objectives
 COURSE SYLLABUS Department: Course Title: Radiologic Technology Principles of Radiographic Imaging I Section Name: RADR 1313 Start Date: 01/17/2012 End Date: 05/14/2012 Modality: FACE-TO-FACE Credits:
COURSE SYLLABUS Department: Course Title: Radiologic Technology Principles of Radiographic Imaging I Section Name: RADR 1313 Start Date: 01/17/2012 End Date: 05/14/2012 Modality: FACE-TO-FACE Credits:
Acquisition, Processing and Display
 Acquisition, Processing and Display Terri L. Fauber, R.T. (R)(M) Department of Radiation Sciences School of Allied Health Professions Virginia Commonwealth University Topics Image Characteristics Image
Acquisition, Processing and Display Terri L. Fauber, R.T. (R)(M) Department of Radiation Sciences School of Allied Health Professions Virginia Commonwealth University Topics Image Characteristics Image
X-rays in medical diagnostics
 X-rays in medical diagnostics S.Dolanski Babić 2017/18. History W.C.Röntgen (1845-1923) discovered a new type of radiation Nature, Jan. 23. 1896.; Science, Feb.14. 1896. X- rays: Induced the ionization
X-rays in medical diagnostics S.Dolanski Babić 2017/18. History W.C.Röntgen (1845-1923) discovered a new type of radiation Nature, Jan. 23. 1896.; Science, Feb.14. 1896. X- rays: Induced the ionization
China Resources Wandong Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. High Frequency 50kW, 150kV Radiography System - HF50-R
 China Resources Wandong Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. High Frequency 50kW, 150kV Radiography System - HF50-R Building 3, No.9, Jiuxianqiaodong Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100015, P.R. China E-mail:
China Resources Wandong Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. High Frequency 50kW, 150kV Radiography System - HF50-R Building 3, No.9, Jiuxianqiaodong Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100015, P.R. China E-mail:
STUDENT REVIEW QUESTION SET K CR/DR CONTENT AREA
 STUDENT REVIEW QUESTION SET K CR/DR CONTENT AREA RADT 2913 COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW 1 The CR cassette is backed by aluminum that: A. reflects x-rays B. absorbs x-rays C. captures the image D. transmits x-rays
STUDENT REVIEW QUESTION SET K CR/DR CONTENT AREA RADT 2913 COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW 1 The CR cassette is backed by aluminum that: A. reflects x-rays B. absorbs x-rays C. captures the image D. transmits x-rays
Ludlum Medical Physics
 Ludlum Medical Physics Medical Imaging Radiology QA Test Tools NEW LUDLUM PRODUCT LINE Medical Physics Products Medical Physics Products What are they? Products used to measure radiation output and to
Ludlum Medical Physics Medical Imaging Radiology QA Test Tools NEW LUDLUM PRODUCT LINE Medical Physics Products Medical Physics Products What are they? Products used to measure radiation output and to
SPECIFICATION. Kilovoltage X-ray calibration system for protection and diagnostic level dosimetry. Prepared by
 SPECIFICATION Kilovoltage X-ray Prepared by Igor Gomola, Technical Officer, Project ECU6023, Date 2015-Oct-06 Revision Date Status Comments 0.1 2015-Oct-06 Draft Igor Gomola Page 1 of 12 1. Scope This
SPECIFICATION Kilovoltage X-ray Prepared by Igor Gomola, Technical Officer, Project ECU6023, Date 2015-Oct-06 Revision Date Status Comments 0.1 2015-Oct-06 Draft Igor Gomola Page 1 of 12 1. Scope This
Photons interaction with matter
 ب س م هللا الر ح من الر حیم Photons interaction with matter Ionization Ionization is the process of removing an electron from an electrically neutral atom to produce an ion pair. An ion is an atom or subatomic
ب س م هللا الر ح من الر حیم Photons interaction with matter Ionization Ionization is the process of removing an electron from an electrically neutral atom to produce an ion pair. An ion is an atom or subatomic
Essentials of Digital Imaging
 Essentials of Digital Imaging Module 6 Transcript 2016 ASRT. All rights reserved. Essentials of Digital Imaging Module 6 Dose Reduction and Patient Safety 1. ASRT Animation 2. Welcome Welcome to Essentials
Essentials of Digital Imaging Module 6 Transcript 2016 ASRT. All rights reserved. Essentials of Digital Imaging Module 6 Dose Reduction and Patient Safety 1. ASRT Animation 2. Welcome Welcome to Essentials
Digital Imaging started in the 1972 with Digital subtraction angiography Clinical digital imaging was employed from the 1980 ~ 37 years ago Amount of
 Digital Imaging started in the 1972 with Digital subtraction angiography Clinical digital imaging was employed from the 1980 ~ 37 years ago Amount of radiation to the population due to Medical Imaging
Digital Imaging started in the 1972 with Digital subtraction angiography Clinical digital imaging was employed from the 1980 ~ 37 years ago Amount of radiation to the population due to Medical Imaging
Exposure System Selection
 Principles of Imaging Science II (RAD120) Exposure Systems Exposure System Selection Radiographic exposure is a very complex process Best technique systems manipulate one variable while holding others
Principles of Imaging Science II (RAD120) Exposure Systems Exposure System Selection Radiographic exposure is a very complex process Best technique systems manipulate one variable while holding others
Seminar 8. Radiology S8 1
 Seminar 8 Radiology Medical imaging. X-ray image formation. Energizing and controlling the X-ray tube. Image detectors. The acquisition of analog and digital images. Digital image processing. Selected
Seminar 8 Radiology Medical imaging. X-ray image formation. Energizing and controlling the X-ray tube. Image detectors. The acquisition of analog and digital images. Digital image processing. Selected
X-RAY. Lecture No.4. Image Characteristics:
 Lecture No.4 X-RAY أ.م.د. اسامة مراد ابراهيم Image Characteristics: *Radiographic density: It s the degree of blackness of the film. when a film is exposed by an x-ray beam (or by light in case of screenfilm
Lecture No.4 X-RAY أ.م.د. اسامة مراد ابراهيم Image Characteristics: *Radiographic density: It s the degree of blackness of the film. when a film is exposed by an x-ray beam (or by light in case of screenfilm
Exposure Indices and Target Values in Radiography: What Are They and How Can You Use Them?
 Exposure Indices and Target Values in Radiography: What Are They and How Can You Use Them? Definition and Validation of Exposure Indices Ingrid Reiser, PhD DABR Department of Radiology University of Chicago
Exposure Indices and Target Values in Radiography: What Are They and How Can You Use Them? Definition and Validation of Exposure Indices Ingrid Reiser, PhD DABR Department of Radiology University of Chicago
Medical Imaging. X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Medical Imaging X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging From: Physics for the IB Diploma Coursebook 6th Edition by Tsokos, Hoeben and Headlee And Higher Level Physics 2 nd Edition
Medical Imaging X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging From: Physics for the IB Diploma Coursebook 6th Edition by Tsokos, Hoeben and Headlee And Higher Level Physics 2 nd Edition
SYLLABUS. TITLE: Equipment Operation I. DEPARTMENT: Radiologic Technology
 CODE: RADT 156 INSTITUTE: Health Science TITLE: Equipment Operation I DEPARTMENT: Radiologic Technology COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course covers the principles of equipment operation and maintenance of radiographic
CODE: RADT 156 INSTITUTE: Health Science TITLE: Equipment Operation I DEPARTMENT: Radiologic Technology COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course covers the principles of equipment operation and maintenance of radiographic
The X-ray circuit: part II
 The X-ray circuit: part II By Dr. Mohsen Dashti 357 Radiologic Processing & Procedure Lecture notes #2 Key issues Types of x-ray equipment. Power for x-ray generator. A basic x-ray circuit. Generators.
The X-ray circuit: part II By Dr. Mohsen Dashti 357 Radiologic Processing & Procedure Lecture notes #2 Key issues Types of x-ray equipment. Power for x-ray generator. A basic x-ray circuit. Generators.
10/26/2015. Study Harder
 This presentation is a professional collaboration of development time prepared by: Rex Christensen Terri Jurkiewicz and Diane Kawamura Study Harder CR detection is inefficient, inferior to film screen
This presentation is a professional collaboration of development time prepared by: Rex Christensen Terri Jurkiewicz and Diane Kawamura Study Harder CR detection is inefficient, inferior to film screen
INTRODUCTION TO FLEXIBLE BRONCHOSCOPY. Fluoroscopy Synopsis HENRI G COLT MD SECOND EDITION THE BRONCHOSCOPY EDUCATION PROJECT SERIES
 SECOND EDITION INTRODUCTION TO FLEXIBLE BRONCHOSCOPY Fluoroscopy Synopsis HENRI G COLT MD With contributions from Dr. S. Murgu THE BRONCHOSCOPY EDUCATION PROJECT SERIES FLUOROSCOPY SYNOPSIS The purpose
SECOND EDITION INTRODUCTION TO FLEXIBLE BRONCHOSCOPY Fluoroscopy Synopsis HENRI G COLT MD With contributions from Dr. S. Murgu THE BRONCHOSCOPY EDUCATION PROJECT SERIES FLUOROSCOPY SYNOPSIS The purpose
10/15/2012 SECTION III - CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL FLUOROSCOPY RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING
 RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section III: Chapter 6 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION III - CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL FLUOROSCOPY RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section III: Chapter 6 RADT 3463 Computerized
RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section III: Chapter 6 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION III - CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL FLUOROSCOPY RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section III: Chapter 6 RADT 3463 Computerized
RaySafe X2. Effortless measurements of X-ray
 RaySafe X2 Effortless measurements of X-ray At your fingertips We ve grown accustomed to intuitive interactions with our devices. After all, it s not the device that s most important, but what you can
RaySafe X2 Effortless measurements of X-ray At your fingertips We ve grown accustomed to intuitive interactions with our devices. After all, it s not the device that s most important, but what you can
Test Equipment for Radiology and CT Quality Control Contents
 Test Equipment for Radiology and CT Quality Control Contents Quality Control Testing...2 Photometers for Digital Clinical Display QC...3 Primary Workstations...3 Secondary Workstations...3 Testing of workstations...3
Test Equipment for Radiology and CT Quality Control Contents Quality Control Testing...2 Photometers for Digital Clinical Display QC...3 Primary Workstations...3 Secondary Workstations...3 Testing of workstations...3
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF. W. Scott Helms for the degree of Master of Science in Radiation Health Physics
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF W. Scott Helms for the degree of Master of Science in Radiation Health Physics presented on November 24, 2014 Title: A Quantitative Comparison of Cardiovascular Imaging Systems
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF W. Scott Helms for the degree of Master of Science in Radiation Health Physics presented on November 24, 2014 Title: A Quantitative Comparison of Cardiovascular Imaging Systems
Unit thickness. Unit area. σ = NΔX = ΔI / I 0
 Unit thickness I 0 ΔI I σ = ΔI I 0 NΔX = ΔI / I 0 NΔX Unit area Δx Average probability of reaction with atom for the incident photons at unit area with the thickness of Delta-X Atom number at unit area
Unit thickness I 0 ΔI I σ = ΔI I 0 NΔX = ΔI / I 0 NΔX Unit area Δx Average probability of reaction with atom for the incident photons at unit area with the thickness of Delta-X Atom number at unit area
ProX Intraoral X-ray. PLANMECA is proud to introduce a new intraoral X-ray unit to its comprehensive collection of imaging products- the ProX.
 The premium intraoral X-ray unit... ProX Intraoral X-ray PLANMECA is proud to introduce a new intraoral X-ray unit to its comprehensive collection of imaging products- the ProX. This advanced unit provides
The premium intraoral X-ray unit... ProX Intraoral X-ray PLANMECA is proud to introduce a new intraoral X-ray unit to its comprehensive collection of imaging products- the ProX. This advanced unit provides
Do you have any other questions? Please call us at (Toll Free) or , or
 INSTRUCTIONS Read the appropriate course/ textbook. This is an open book test. A score of 75% or higher is needed to receive CE credit. You will have a maximum of three attempts to pass this course. Please
INSTRUCTIONS Read the appropriate course/ textbook. This is an open book test. A score of 75% or higher is needed to receive CE credit. You will have a maximum of three attempts to pass this course. Please
Maltase cross tube. D. Senthilkumar P a g e 1
 Thermionic Emission Maltase cross tube Definition: The emission of electrons when a metal is heated to a high temperature Explanation: In metals, there exist free electrons which are able to move around
Thermionic Emission Maltase cross tube Definition: The emission of electrons when a metal is heated to a high temperature Explanation: In metals, there exist free electrons which are able to move around
Investigation of the line-pair pattern method for evaluating mammographic focal spot performance
 Investigation of the line-pair pattern method for evaluating mammographic focal spot performance Mitchell M. Goodsitt, a) Heang-Ping Chan, and Bob Liu Department of Radiology, University of Michigan, Ann
Investigation of the line-pair pattern method for evaluating mammographic focal spot performance Mitchell M. Goodsitt, a) Heang-Ping Chan, and Bob Liu Department of Radiology, University of Michigan, Ann
Enhanced Functionality of High-Speed Image Processing Engine SUREengine PRO. Sharpness (spatial resolution) Graininess (noise intensity)
 Vascular Enhanced Functionality of High-Speed Image Processing Engine SUREengine PRO Medical Systems Division, Shimadzu Corporation Yoshiaki Miura 1. Introduction In recent years, digital cardiovascular
Vascular Enhanced Functionality of High-Speed Image Processing Engine SUREengine PRO Medical Systems Division, Shimadzu Corporation Yoshiaki Miura 1. Introduction In recent years, digital cardiovascular
CIRCLEX 0.3/0.8P324&0.6/1.2P324DK-85
 PD53-012 p Rotating Anode X-ray tube Assembly 0.3/0.8P32&0.6/1.2P32DK-85 GENERAL The Shimadzu 0.3/0.8P32DK-85 & 0.6/1.2P32DK-85, Rotating Anode X-ray tube assemblies are rated to 150kV and feature a 100mm
PD53-012 p Rotating Anode X-ray tube Assembly 0.3/0.8P32&0.6/1.2P32DK-85 GENERAL The Shimadzu 0.3/0.8P32DK-85 & 0.6/1.2P32DK-85, Rotating Anode X-ray tube assemblies are rated to 150kV and feature a 100mm
10/3/2012. Study Harder
 This presentation is a professional collaboration of development time prepared by: Rex Christensen Terri Jurkiewicz and Diane Kawamura Study Harder CR detection is inefficient, inferior to film screen
This presentation is a professional collaboration of development time prepared by: Rex Christensen Terri Jurkiewicz and Diane Kawamura Study Harder CR detection is inefficient, inferior to film screen
Precision Performance Power
 ODYSSEY HF SERIES ULTRA High Frequency X-Ray Technology Precision Performance Power Innovations in Digital Imaging. TM STEP 1 Select anatomical region STEP 2 Select anatomical view STEP 3 Ready for exposure
ODYSSEY HF SERIES ULTRA High Frequency X-Ray Technology Precision Performance Power Innovations in Digital Imaging. TM STEP 1 Select anatomical region STEP 2 Select anatomical view STEP 3 Ready for exposure
Technical data CAMARGUE CS-VH50/300. VARIABLE Height Bucky Table With Ceiling Suspension
 Technical data VARIABLE Height Bucky Table With Ceiling Suspension Model Variations CAMARGUE FH (Fixed Height) CAMARGUE FH Tomo CAMARGUE FH Ceiling suspension CAMARGUE VH (Variable Height) CAMARGUE VH
Technical data VARIABLE Height Bucky Table With Ceiling Suspension Model Variations CAMARGUE FH (Fixed Height) CAMARGUE FH Tomo CAMARGUE FH Ceiling suspension CAMARGUE VH (Variable Height) CAMARGUE VH
ODYSSEY HF SERIES. ULTRA High Frequency X-Ray Technology. Precision... Performance... Power. Innovations in Digital Imaging.
 ODYSSEY HF SERIES ULTRA High Frequency X-Ray Technology Precision... Performance... Power Innovations in Digital Imaging. TM STEP 1 Select anatomical region STEP 2 Select anatomical view STEP 3 Ready for
ODYSSEY HF SERIES ULTRA High Frequency X-Ray Technology Precision... Performance... Power Innovations in Digital Imaging. TM STEP 1 Select anatomical region STEP 2 Select anatomical view STEP 3 Ready for
Radiology. Radiograph: Is the image of an object made with use of X- ray instead of light.
 Radiology د. اريج Lec. 3 X Ray Films Radiograph: Is the image of an object made with use of X- ray instead of light. Dental x- ray film: Is a recording media on which image of the object was made by exposing
Radiology د. اريج Lec. 3 X Ray Films Radiograph: Is the image of an object made with use of X- ray instead of light. Dental x- ray film: Is a recording media on which image of the object was made by exposing
Radiographic Techniques, Contrast, and Noise in X-Ray Imaging
 Residents Section Physics Minimodule Huda and Abrahams Techniques, Contrast, and Noise in Radiography Residents Section Physics Minimodule Residents inradiology Walter Huda 1 R. Brad Abrahams 2 Huda W,
Residents Section Physics Minimodule Huda and Abrahams Techniques, Contrast, and Noise in Radiography Residents Section Physics Minimodule Residents inradiology Walter Huda 1 R. Brad Abrahams 2 Huda W,
MXHF-1500RF is controlled by Digital key panel console that displays KV, ma and mas with APR menu programmed.
 R/F TV X-RAY SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC RADIOGRAPHIC FLUOROSCOPIC TV SYSTEM MXHF-1500RF SYSTEM OUTLINE Product Data No. 041021-01 MXHF-1500RF is controlled by Digital key panel console that displays KV, ma and
R/F TV X-RAY SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC RADIOGRAPHIC FLUOROSCOPIC TV SYSTEM MXHF-1500RF SYSTEM OUTLINE Product Data No. 041021-01 MXHF-1500RF is controlled by Digital key panel console that displays KV, ma and
Version 1.0. TechnicVR. Student Guide
 Version 1.0 TechnicVR s h a d e r w a r e. c o m Student Guide TechnicVR s h a d e r w a r e. c o m Student Guide shaderware 2008 PO Box 103 Saltburn Cleveland TS12 1WP w w w. s h a d e r w a r e. c o
Version 1.0 TechnicVR s h a d e r w a r e. c o m Student Guide TechnicVR s h a d e r w a r e. c o m Student Guide shaderware 2008 PO Box 103 Saltburn Cleveland TS12 1WP w w w. s h a d e r w a r e. c o
HISTORY. CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging SUNDAY. Shawn D. Teague, MD
 CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging Shawn D. Teague, MD DISCLOSURES 3DR- advisory committee CT PHYSICS WITH AN EMPHASIS ON APPLICATION IN THORACIC AND CARDIAC IMAGING
CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging Shawn D. Teague, MD DISCLOSURES 3DR- advisory committee CT PHYSICS WITH AN EMPHASIS ON APPLICATION IN THORACIC AND CARDIAC IMAGING
Maximizing clinical outcomes
 Maximizing clinical outcomes Digital Tomosynthesis Dual Energy Subtraction Automated Long Length Imaging Improved image quality at a low dose Xray Xray Patented ISS capture technology promotes high sensitivity
Maximizing clinical outcomes Digital Tomosynthesis Dual Energy Subtraction Automated Long Length Imaging Improved image quality at a low dose Xray Xray Patented ISS capture technology promotes high sensitivity
4. Contrast is the. There must The function of contrast is to:. The types of contrast are.
 RADIOGRAPHIC VISIBILITY OF DETAIL STUDY QUESTIONS 1. What is visibility of detail? It is controlled by properties. What are the two factors that affect it? 2. What is sharpness of detail? It is controlled
RADIOGRAPHIC VISIBILITY OF DETAIL STUDY QUESTIONS 1. What is visibility of detail? It is controlled by properties. What are the two factors that affect it? 2. What is sharpness of detail? It is controlled
Image Quality. HTC Grid High Transmission Cellular Grid provides higher contrast images
 B R E A S T I M A G I N G S O L U T I O N S Setting the benchmark for mammography M-IV Series Innovations in breast imaging The Lorad M-IV Series exemplifies Hologic's commitment to developing advanced
B R E A S T I M A G I N G S O L U T I O N S Setting the benchmark for mammography M-IV Series Innovations in breast imaging The Lorad M-IV Series exemplifies Hologic's commitment to developing advanced
Ch. 223 VETERINARY MEDICINE CHAPTER 223. VETERINARY MEDICINE GENERAL PROVISIONS X-RAYS RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL. Authority
 Ch. 223 VETERINARY MEDICINE 25 223.1 CHAPTER 223. VETERINARY MEDICINE Sec. 223.1. Purpose and scope. 223.2. [Reserved]. 223.2a. Definitions. 223.3 223.6. [Reserved]. 223.7. Structural shielding. 223.8.
Ch. 223 VETERINARY MEDICINE 25 223.1 CHAPTER 223. VETERINARY MEDICINE Sec. 223.1. Purpose and scope. 223.2. [Reserved]. 223.2a. Definitions. 223.3 223.6. [Reserved]. 223.7. Structural shielding. 223.8.
V SALAI SELVAM, AP & HOD, ECE, Sriram Engg. College, Perumalpattu 1 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS UNIT IV
 V SALAI SELVAM, AP & HOD, ECE, Sriram Engg. College, Perumalpattu 1 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS UNIT IV Ionizing and non-ionizing radiations: The radiation that ionizes the gases through which it travels is known
V SALAI SELVAM, AP & HOD, ECE, Sriram Engg. College, Perumalpattu 1 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS UNIT IV Ionizing and non-ionizing radiations: The radiation that ionizes the gases through which it travels is known
Image Quality. HTC Grid High Transmission Cellular Grid provides higher contrast images
 B R E A S T I M A G I N G S O L U T I O N S Setting the benchmark for mammography M-IV Series Innovations in breast imaging The Lorad M-IV Series exemplifies Hologic s commitment to developing advanced
B R E A S T I M A G I N G S O L U T I O N S Setting the benchmark for mammography M-IV Series Innovations in breast imaging The Lorad M-IV Series exemplifies Hologic s commitment to developing advanced
BASICS OF FLUOROSCOPY
 Medical Physics Residents Training Program BASICS OF FLUOROSCOPY Dr. Khalid Alyousef, PhD Department of Medical Imaging King Abdulaziz Medical City- Riyadh Edison examining the hand of Clarence Dally with
Medical Physics Residents Training Program BASICS OF FLUOROSCOPY Dr. Khalid Alyousef, PhD Department of Medical Imaging King Abdulaziz Medical City- Riyadh Edison examining the hand of Clarence Dally with
Y11-DR Digital Radiography (DR) Image Quality
 Y11-DR Digital Radiography (DR) Image Quality Image quality is stressed for all systems in Safety Code 35. In the relevant sections Health Canada s advice is the manufacturer s recommended test procedures
Y11-DR Digital Radiography (DR) Image Quality Image quality is stressed for all systems in Safety Code 35. In the relevant sections Health Canada s advice is the manufacturer s recommended test procedures
Nuclear medicine imaging has been an integral component
 CONTINUING EDUCATION X-Ray Imaging Physics for Nuclear Medicine Technologists. Part 1: Basic Principles of X-Ray Production* J. Anthony Seibert, PhD Department of Radiology, Imaging Research Center, University
CONTINUING EDUCATION X-Ray Imaging Physics for Nuclear Medicine Technologists. Part 1: Basic Principles of X-Ray Production* J. Anthony Seibert, PhD Department of Radiology, Imaging Research Center, University
JEFFERSON COLLEGE. Radiographic Exposures
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS RAD140 Radiographic Exposures 3 Credit Hours Revised by: Janet E. Akers BS RT (R)(M) Date: September 30, 2013 Kenny Wilson, Director, Health Occupation Programs Dena McCaffrey,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS RAD140 Radiographic Exposures 3 Credit Hours Revised by: Janet E. Akers BS RT (R)(M) Date: September 30, 2013 Kenny Wilson, Director, Health Occupation Programs Dena McCaffrey,
Using Carbon Nano-Tube Field Emitters to Miniaturize X-Ray Tubes
 Using Carbon Nano-Tube Field Emitters to Miniaturize X-Ray Tubes Authors: Martin Pesce, RT(R), Xiaohui Wang, PhD, Peter Rowland X-rays are produced by the impact of an accelerated electron beam on a tungsten
Using Carbon Nano-Tube Field Emitters to Miniaturize X-Ray Tubes Authors: Martin Pesce, RT(R), Xiaohui Wang, PhD, Peter Rowland X-rays are produced by the impact of an accelerated electron beam on a tungsten
Nuclear Associates
 Nuclear Associates 07-649 CDRH Fluoroscopic Phantom Users Manual March 2005 Manual No. 07-649-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks
Nuclear Associates 07-649 CDRH Fluoroscopic Phantom Users Manual March 2005 Manual No. 07-649-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks
LECTURE 10. Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry
 LECTURE 10 Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry Components for the source include: -Line voltage supply -high-voltage generator -x-ray tube X-ray source requires -high
LECTURE 10 Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry Components for the source include: -Line voltage supply -high-voltage generator -x-ray tube X-ray source requires -high
Nuclear Associates
 Nuclear Associates 07-591 Focal Spot Test Tool Users Manual February 2005 Manual No. 07-591-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks
Nuclear Associates 07-591 Focal Spot Test Tool Users Manual February 2005 Manual No. 07-591-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks
The Evaluation of Collimator Alignment of Diagnostic X-ray Tube Using Computed Radiography System
 The Evaluation of Collimator Alignment of Diagnostic X-ray Tube Using Computed Radiography System The Evaluation of Collimator Alignment of Diagnostic X-ray Tube Using Computed Radiography System Manus
The Evaluation of Collimator Alignment of Diagnostic X-ray Tube Using Computed Radiography System The Evaluation of Collimator Alignment of Diagnostic X-ray Tube Using Computed Radiography System Manus
80 Physics Essentials Workbook Stage 2 Physics
 80 Physics Essentials Workbook Stage 2 Physics the thickness of the tissue: Obviously, the thicker the tissue through which the X-rays have to pass the more they will be absorbed from the beam passing
80 Physics Essentials Workbook Stage 2 Physics the thickness of the tissue: Obviously, the thicker the tissue through which the X-rays have to pass the more they will be absorbed from the beam passing
Minnesota Rules, Chapter 4732 X-ray Revision
 Minnesota Rules, Chapter 4732 X-ray Revision DRAFT FLUOROSCOPIC X-RAY SYSTEMS, 1.0 Subpart 1. Applicability. Subpart 2. Limitation of the useful beam. Subpart 3. Measuring compliance; primary protective
Minnesota Rules, Chapter 4732 X-ray Revision DRAFT FLUOROSCOPIC X-RAY SYSTEMS, 1.0 Subpart 1. Applicability. Subpart 2. Limitation of the useful beam. Subpart 3. Measuring compliance; primary protective
MILADY. Product Data. Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 The MILADY Mammographic Unit offers the best quality-to-price ratio to our customers worldwide. The unit advanced technology together with the application of industrial production standards,
Page 1 of 8 The MILADY Mammographic Unit offers the best quality-to-price ratio to our customers worldwide. The unit advanced technology together with the application of industrial production standards,
The importance of radiation quality for optimisation in radiology
 Available online at http://www.biij.org/2007/2/e38 doi: 10.2349/biij.3.2.e38 biij Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal COMMENTARY The importance of radiation quality for optimisation in radiology
Available online at http://www.biij.org/2007/2/e38 doi: 10.2349/biij.3.2.e38 biij Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal COMMENTARY The importance of radiation quality for optimisation in radiology
Distributed by. Ecotron Anyview Series. The Intelligent C-Arm System
 Distributed by Ecotron Anyview Series The Intelligent C-Arm System The Ecotron Anyview Series is a new standard for C-arm imaging Excellent radiographic imaging at an economical price Advanced X-ray Generator
Distributed by Ecotron Anyview Series The Intelligent C-Arm System The Ecotron Anyview Series is a new standard for C-arm imaging Excellent radiographic imaging at an economical price Advanced X-ray Generator
Principle of X-Ray Systems
 Principle of X-Ray Systems Hossein Ebrahimi Nasab PHYSICS OF X-RAYS Nature of X-rays Energy unit Interaction with matter INTERACTION WITH THE MATTER In vacuum: photon move along a straight line In materials,
Principle of X-Ray Systems Hossein Ebrahimi Nasab PHYSICS OF X-RAYS Nature of X-rays Energy unit Interaction with matter INTERACTION WITH THE MATTER In vacuum: photon move along a straight line In materials,
PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND EFFECTS OF METALLIC SCREEN FLUORESCENCE AND BACKSCATTER CONTROL IN GAMMA COMPUTED RADIOGRAPHY
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND EFFECTS OF METALLIC SCREEN FLUORESCENCE AND BACKSCATTER CONTROL IN GAMMA COMPUTED RADIOGRAPHY Steven MANGO 1 1 Carestream
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND EFFECTS OF METALLIC SCREEN FLUORESCENCE AND BACKSCATTER CONTROL IN GAMMA COMPUTED RADIOGRAPHY Steven MANGO 1 1 Carestream
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING IN X-RAY IMAGING
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING IN X-RAY IMAGING Shalini Kumari 1, Bachan Prasad 2,Aliya Nasim 3 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering R.V.S College of Engineering & Technology, Jamshedpur,
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING IN X-RAY IMAGING Shalini Kumari 1, Bachan Prasad 2,Aliya Nasim 3 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering R.V.S College of Engineering & Technology, Jamshedpur,
Features and Weaknesses of Phantoms for CR/DR System Testing
 Physics testing of image detectors Parameters to test Features and Weaknesses of Phantoms for CR/DR System Testing Spatial resolution Contrast resolution Uniformity/geometric distortion Dose response/signal
Physics testing of image detectors Parameters to test Features and Weaknesses of Phantoms for CR/DR System Testing Spatial resolution Contrast resolution Uniformity/geometric distortion Dose response/signal
Radiographic Testing (RT) [10]
![Radiographic Testing (RT) [10] Radiographic Testing (RT) [10]](/thumbs/74/70215439.jpg) Radiographic Testing (RT) [10] Definition: An NDT method that utilizes x-rays or gamma radiation to detect discontinuities in materials, and to present their images on recording medium. 1> Electromagnetic
Radiographic Testing (RT) [10] Definition: An NDT method that utilizes x-rays or gamma radiation to detect discontinuities in materials, and to present their images on recording medium. 1> Electromagnetic
Radiology Physics Lectures: Digital Radiography. Digital Radiography. D. J. Hall, Ph.D. x20893
 Digital Radiography D. J. Hall, Ph.D. x20893 djhall@ucsd.edu Background Common Digital Modalities Digital Chest Radiograph - 4096 x 4096 x 12 bit CT - 512 x 512 x 12 bit SPECT - 128 x 128 x 8 bit MRI -
Digital Radiography D. J. Hall, Ph.D. x20893 djhall@ucsd.edu Background Common Digital Modalities Digital Chest Radiograph - 4096 x 4096 x 12 bit CT - 512 x 512 x 12 bit SPECT - 128 x 128 x 8 bit MRI -
3/31/2011. Objectives. Emory University. Historical Development. Historical Development. Historical Development
 Teaching Radiographic Technique in a Digital Imaging Paradigm Objectives 1. Discuss the historical development of digital imaging. Dawn Couch Moore, M.M.Sc., RT(R) Assistant Professor and Director Emory
Teaching Radiographic Technique in a Digital Imaging Paradigm Objectives 1. Discuss the historical development of digital imaging. Dawn Couch Moore, M.M.Sc., RT(R) Assistant Professor and Director Emory
Nuclear Associates
 Nuclear Associates 07-647 R/F QC Phantom Operators Manual March 2005 Manual No. 07-647-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. All product names are trademarks of their respective companies
Nuclear Associates 07-647 R/F QC Phantom Operators Manual March 2005 Manual No. 07-647-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. All product names are trademarks of their respective companies
Calibration of KAP meters
 Calibration of KAP meters Alexandr Malusek! Division of Radiological Sciences Department of Medical and Health Sciences Linköping University! 2014-04-15 1 Outline 1. KAP meter construction 2. Air kerma-area
Calibration of KAP meters Alexandr Malusek! Division of Radiological Sciences Department of Medical and Health Sciences Linköping University! 2014-04-15 1 Outline 1. KAP meter construction 2. Air kerma-area
DISC QC/QA Program for Digital Imaging Systems using the DR Radchex Plus Meter
 DISC QC/QA Program for Digital Imaging Systems using the DR Radchex Plus Meter Revision Date: January 5th, 2017 www.disc-imaging.com Table of Contents Section A: Preliminary Setup Requirements... 4 Tools
DISC QC/QA Program for Digital Imaging Systems using the DR Radchex Plus Meter Revision Date: January 5th, 2017 www.disc-imaging.com Table of Contents Section A: Preliminary Setup Requirements... 4 Tools
