RF circuits design Grzegorz Beziuk. RF characteristics of lumped passive and active elements. References
|
|
|
- Marcia Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RF circuits design Grzegorz Beziuk RF characteristics of lumped passive and active elements References [1] Tietze U., Schenk C., Electronic circuits : handbook for design and application, Springer 2008 [2] Golio M., RF and microwave passive and active technologies in: RF and Microwave handbook, 2008, CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group [3] Vishay, 50 GHz Thin Film Microwave Resistors, Products Data Sheet, Vishay 2009, ( [4] AVX RF, AVX RF/Microwave products version 8.1, Products Data Sheet, ( [5] Panasonic, Chip inductors, Products Data Sheet, ( [6] Vishay semicondutors, BFR 93 - Silicon NPN Planar RF Transistor, Product Data Sheet, 2000, Vishay. [7] NXP Semiconductors, BFU725F/N1 NPN wideband silicon germanium RF transistor, Product Data Sheet, 2009, NXP Semiconductors (
2 References [8] Infineon Technologies, BFP 620 NPN Silicon Germanium RF Transistor, Product Data Sheet, 2004, Infineon Technologies (http// [9] ON Semiconductors, MMBFU310LT1G JFET Transistor N Channel, Product Data Sheet, 2009, ON Semiconductors ( [10] EPCOS, SAW Components, Data Sheet R 850, 2002, EPCOS, ( [11] Fabian Wai Lee Kung, RF/Microwave Circuit Design, 2008, Multimedia University, (open source lectures: [12] Microsemi, KV1911A KV1991A VARACTOR DIODES UHF Microwave Super-Hyperabrupt Junction, 2007, Products Data Sheet, Microsemi [13] Hawlett Packard, Surface mount microwave Schottky detector diodes HSMS 2850, HSMS 2860 series, Technical data, Hawlett Packard [14] Maccom Technology Solutions, MA4AGBLP912 AlGaAs Beamlead PIN Diode, Products Data Sheet, Maccom Technology Solutions [15] Vishay Telefunken, BF966S N Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode, Depletion Mode, Product Data Sheet, 1999, Vishay Telefunken [16] Murata Manufacturing, SAW resonators, Products Data Sheet, 2001, Murata Manufacturing Resistors Equivalent circuits SMD resistor: a) for low frequencies range, b) for high frequencies
3 Z R Resistors R + j ( ) [ ω( LR CRR ) ω LRCR ] jω ( 1 ω LC ) + ω C R R R R Inductive properties: Capacitive properties: R < L R / C R R > L R / C R Reflection factor: Γ ( jω) R Z Z R R ( jω) Z0 ( jω) + Z0 Impedance of SMD resistors od the size 1206 with L R 3nH, C R 0.2pF Resistors * Taken from Electronic circuits : handbook for design and application Tietze U., Schenk C. [1]
4 Resistors Typical very high frequency performance electrical model The external reactance (Lc and CG) depends on the PCB material, the layout and assembly technology. Resistors Impedance as a function of frequency for a chip resistor N termination (wraparound) * Taken from 50 GHz Thin Film Microwave Resistors, Products Data Sheet, Vishay [3]
5 Resistors Impedance as a function of frequency for a chip resistor (F and P terminations) * Taken from 50 GHz Thin Film Microwave Resistors, Products Data Sheet, Vishay [3] Capacitors Equivalent circuits SMD capacitor: a) for low frequencies range, b) for high frequencies
6 Capacitors Impedance of capacitor: Resonant frequency: Quality factor (QF): Q C 2 1+ scrc + s LCC ZC ( s) sc f Q res res ( f ) 1 2 π L 1 R Im Re C C C LC C f < fres / 4 { ZC ( j2πf )} 1 { ZC ( j2πf )} 2πfCRC Magnitude of impedance for SMD capacitors of size 1206 with R C 0.2Ω, L C 3nH Capacitors * Taken from Electronic circuits : handbook for design and application Tietze U., Schenk C. [1]
7 Capacitors Example of parameters of the high frequency capacitors * Taken from AVX RF/Microwave products version 8.1, Products Data Sheet, AVX RF [4] Chip Inductors Equivalent circuits SMD inductors: a) for low frequencies range, b) for high frequencies
8 Chip Inductors Parasitic resistance R ( f ) k f L RL (skin effect!!!) Resistive losses coefficient For 1206 size inductor: k L k RL 600Ω / k L L ( Hz H ) For 1812 size inductor: k L 1200Ω / ( Hz H ) For inductors larger than 1812 size, and L>10µH : ( ) 0. 7 k RL 20Ω / Hz L Resonant frequency: Phase resonant frequency Magnitude resonant frequency Chip Inductors f f f Q res res resph resmax Quality factor (QF): Q ( f ) L 1 2π LC f Im Re 2π k res f RL res 4 L L C 3 L 1 1 Q 2 res 1 1 2Q 4 res f < fres / 4 { ZL ( j2 f )} 2πfL { Z ( j2πf )} R ( f ) L (an impedance of inductor has a real value) π 2πL k L RL f
9 Chip Inductors Magnitudes of impedance and inductor quality for SMD inductors of size 1206 with k L 1200Ω /( Hz H ) and C L 0.2pF * Taken from Electronic circuits : handbook for design and application Tietze U., Schenk C. [1] Chip Inductors * Taken from Chip inductors, Panasonic Products Data Sheet, [5]
10 Chip Inductors * Taken from Chip inductors, Panasonic Products Data Sheet, [5] Chokes Choke is a kind of inductor. Chokes are used below 2 GHz, but there are some chokes applications extends to tens of GHz. Chokes: - for high frequency are high impedance elements - for low frequency and direct current have very little loss Chockes are use in the bias circuits of active elements. Because the choke is an inductors with ferrite core, for high frequency (f>2ghz) its resonances are absorbed by losses in a ferrite.
11 Ferrite Baluns Ferrite balluns are cross between transmission lines and chokes. Ferrrite baluns are most useful between 10 khz and 2 GHz. Manufacturers desigh baluns for specific impedance levels and bandwitdths. Basic structure of Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) resonator SAW filters 1-port SAW RESONATOR has one IDT (Inter Digital Transducer), which generates and receives SAW, and two grating reflectors, which reflect SAW and generate a standing wave between the two reflectors. IDT and reflectors are fabricated on quartz crystal substrate by photolithographic process. Frequency range: from 50kHz 1GHz. * Taken from SAW resonators, Murata Manufacturing Products Data Sheet, [16]
12 Features of the SAW: SAW filters - high Oscillation Frequency Stability - adjustment free - SAW resonator is stable against peripheral circuit or supply voltage fluctuation - simple/low cost circuit by fundamental oscillation - oscillates with its fundamental mode - small size package - they can be applied Colpitts Oscillator circuit SAW filters SAW equivalent circuit * Taken from SAW resonators, Murata Manufacturing Products Data Sheet, [16]
13 SAW filters * Taken from SAW resonators, Murata Manufacturing Products Data Sheet, [16] Z ε d D For R0, G0: 0 L C 1 2π µ ln ε ' Caoxial Cables RLCG parameters: Z o 50, 75, 93 Ω. 60 D d ( D / d ) ln ε reff ε ε ' jε '' R + πσδ D d µ L ln( D / d ) 2π 2πε ' C ln ( D / d ) 2πωε '' G ln ( D / d )
14 Caoxial Cables Cut-off frequency: f cut off 7.51 ε reff 1 D + d Velocity of propagation: v p c ε reff Maximum peak power: 2 E max P max D ( D / d ) ( D / d ) 2 ln Caoxial Cables * Taken from Introduction to high-speed PCB design, Kung [11]
15 Caoxial Cables Why 50Ω? * Taken from Introduction to high-speed PCB design, Kung [11] Caoxial Cables * Taken from Introduction to high-speed PCB design, Kung [11]
16 Connectors and Adapters * Taken from Introduction to high-speed PCB design, Kung [11] Connectors and Adapters * Taken from Introduction to high-speed PCB design, Kung [11]
17 Connectors and Adapters Connector type BNC SMB SMC TNC Type-N 7 mm SMA 3.5 mm 2.9 mm 2.4 mm Cut-off frequency [GHz] (0.3) Varactors Varactors applications: - harmonic generation - parametric amplification - mixing - detection - voltage variable tuning Advantages of varactors: - low loss - low noise Non-symetric Symetric
18 Varactors Example of varactors characteristics * Taken from KV1911A KV1991A VARACTOR DIODES, Microsemi [12] Schottky diode Schottky diode (metal-semiconductor juntion) applications: - harmonic generators (mutipliers) GHz and THz - mixers - detectors In frequency mutliplication is used a nonlinear capacitans versus voltage.
19 Schottky diode * Taken from Surface mount microwave Schottky detector diodes HSMS 2850, HSMS 2860 series, Hawlet Packard [13] PIN diodes PIN diodes applications: - RF and microwave attenuators - RF and microwave tunable matching circuits - RF and microwave switches
20 PIN diodes * Taken from MA4AGBLP912 AlGaAs Beamlead PIN Diode, Maccom Technology Solutions [14] Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) Base Emmiter N P N Colector I E IB I C U BE - + U CB - +
21 Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) - HF bipolar transistors are NPN type because electron mobility is much higher than hole mobility - the BASE thickness is very thin to improve current gain β (h fe ) - Inter-digital BASE and EMITTER contacts are employed to reduce base spreading resistance r bb and to reduce the noise generated by the transistor - Commercial RF transistors in discrete form can have f T up to 10GHz. Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) Bias circuits of BJT read the textbooks about basics of an electronic circuits
22 Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) * Taken from Electronic circuits : handbook for design and application Tietze U., Schenk C. [1] Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) B r bb' B' c B'C C c B'E r B'E g m U B'E r CE E Hybrid π (Giacoletto) model of the BJT.
23 Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) r B' E βi ϕ CQ T c B' E ICQ 2 πf ϕ T T gm ω T g m ICQ ϕ T U r CE I EY CQ c BC ' U cbc ' 0 1 U Hybrid π model elements. CB DC m For frequencies above 300 MHz transistor should be modelled by S parameters. Bipolar junction transistors(bjts)
24 Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) Example of HF package equivalent circuit of BJT BFP 620 * Taken from BFP 620 NPN Silicon Germanium RF Transistor, Product Data Sheet, 2004, Infineon Technologies [8] Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) * Taken from BFR 93 - Silicon NPN Planar RF Transistor, Product Data Sheet, 2000, Vishay [6]
25 Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) * Taken from BFR 93 - Silicon NPN Planar RF Transistor, Product Data Sheet, 2000, Vishay [6] Bipolar junction transistors(bjts) * Taken from BFR 93 - Silicon NPN Planar RF Transistor, Product Data Sheet, 2000, Vishay [6]
26 FET Drain D Gate p+ n p+ Gate G Source N-channel FET S FET ID U GS1 < U GS2 I D U DS 0.1V + n U DS 0.1V + p+ n p+ - p+ p+ - - U GS1 - U GS2 + barrier layer + barrier layer
27 FET ID U GS1 < U GS2 I D U DS 10V + n U DS 10V + p+ n p+ - p+ p+ - - U GS1 - U GS2 + barrier layer + barrier layer FET Bias circuits of FET and FET with P chanel read the textbooks about basics of an electronic circuits
28 MOSFET Source Gate Drain Source Gate Drain Source Gate Drain Source Gate Drain SiO 2 SiO 2 SiO 2 SiO 2 p+ p p+ n+ p n+ p+ p+ n+ n+ n p n p Base Base Base Base There are the MOSFET with two gates, too. MOSFET U DS 0.1V U DS 10V - + I D D n+ - + I D D n+ G SiO 2 p G SiO 2 p + U GS S n+ + U GS S n+ - - N-channel MOSFET
29 MOSFET Bias circuits of MOSFET and more information about other types of MOSFETs read the textbooks about basics of an electronic circuits FET and MOSFET FET and MOSFET hybrid π model
30 FET and MOSFET FET and MOSFET * Taken from BF966S N Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode, Depletion Mode, Product Data Sheet, 1999, Vishay Telefunken [15]
31 FET and MOSFET * Taken from BF966S N Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode, Depletion Mode, Product Data Sheet, 1999, Vishay Telefunken [15] FET and MOSFET * Taken from BF966S N Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode, Depletion Mode, Product Data Sheet, 1999, Vishay Telefunken [15]
32 FET and MOSFET * Taken from BF966S N Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode, Depletion Mode, Product Data Sheet, 1999, Vishay Telefunken [15] FET and MOSFET * Taken from BF966S N Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode, Depletion Mode, Product Data Sheet, 1999, Vishay Telefunken [15]
33 Other types of RF and microwave transistors There are other types of the microwaves transistors: - Heterostructure Bipolar Transistor (HBTs) - High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) They are commercialy avaible such as the discrete elements. They are integrated in microwave IC such as i. e. LNA, power amplifiers.
Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde
 Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde Noise in Oscillators with Active Inductors Presented to the Faculty 3 : Mechanical engineering, Electrical engineering and industrial engineering, Brandenburg University of Technology
Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde Noise in Oscillators with Active Inductors Presented to the Faculty 3 : Mechanical engineering, Electrical engineering and industrial engineering, Brandenburg University of Technology
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Homework Assignment 05
 Homework Assignment 05 Question (2 points each unless otherwise indicated)(20 points). Estimate the parallel parasitic capacitance of a mh inductor with an SRF of 220 khz. Answer: (2π)(220 0 3 ) = ( 0
Homework Assignment 05 Question (2 points each unless otherwise indicated)(20 points). Estimate the parallel parasitic capacitance of a mh inductor with an SRF of 220 khz. Answer: (2π)(220 0 3 ) = ( 0
BJT Amplifier. Superposition principle (linear amplifier)
 BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
ECEN 5014, Spring 2009 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits Zoya Popovic, University of Colorado, Boulder
 ECEN 5014, Spring 2009 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits Zoya opovic, University of Colorado, Boulder LECTURE 3 MICROWAVE AMLIFIERS: INTRODUCTION L3.1. TRANSISTORS AS BILATERAL MULTIORTS Transistor
ECEN 5014, Spring 2009 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits Zoya opovic, University of Colorado, Boulder LECTURE 3 MICROWAVE AMLIFIERS: INTRODUCTION L3.1. TRANSISTORS AS BILATERAL MULTIORTS Transistor
Understanding VCO Concepts
 Understanding VCO Concepts OSCILLATOR FUNDAMENTALS An oscillator circuit can be modeled as shown in Figure 1 as the combination of an amplifier with gain A (jω) and a feedback network β (jω), having frequency-dependent
Understanding VCO Concepts OSCILLATOR FUNDAMENTALS An oscillator circuit can be modeled as shown in Figure 1 as the combination of an amplifier with gain A (jω) and a feedback network β (jω), having frequency-dependent
Lecture 3: Transistors
 Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
Case Study: Osc2 Design of a C-Band VCO
 MICROWAVE AND RF DESIGN Case Study: Osc2 Design of a C-Band VCO Presented by Michael Steer Reading: Chapter 20, 20.5,6 Index: CS_Osc2 Based on material in Microwave and RF Design: A Systems Approach, 2
MICROWAVE AND RF DESIGN Case Study: Osc2 Design of a C-Band VCO Presented by Michael Steer Reading: Chapter 20, 20.5,6 Index: CS_Osc2 Based on material in Microwave and RF Design: A Systems Approach, 2
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY)
 SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
TRANSISTOR TRANSISTOR
 It is made up of semiconductor material such as Si and Ge. Usually, it comprises of three terminals namely, base, emitter and collector for providing connection to the external circuit. Today, some transistors
It is made up of semiconductor material such as Si and Ge. Usually, it comprises of three terminals namely, base, emitter and collector for providing connection to the external circuit. Today, some transistors
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I
 Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Chapter.8: Oscillators
 Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
 Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics
 High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : EC6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES SEM / YEAR: II / I year B.E.ECE
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : EC6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES SEM / YEAR: II / I year B.E.ECE
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK Subject with Code : Electronic Circuit Analysis (16EC407) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK Subject with Code : Electronic Circuit Analysis (16EC407) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity)
 BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
Application Note 5057
 A 1 MHz to MHz Low Noise Feedback Amplifier using ATF-4143 Application Note 7 Introduction In the last few years the leading technology in the area of low noise amplifier design has been gallium arsenide
A 1 MHz to MHz Low Noise Feedback Amplifier using ATF-4143 Application Note 7 Introduction In the last few years the leading technology in the area of low noise amplifier design has been gallium arsenide
Page 1. Telecommunication Electronics ETLCE - A2 06/09/ DDC 1. Politecnico di Torino ICT School. Amplifiers
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Amplifiers Telecommunication Electronics A2 Transistor amplifiers» Bias point and circuits,» Small signal models» Gain and bandwidth» Limits of linear analysis Op Amp amplifiers
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Amplifiers Telecommunication Electronics A2 Transistor amplifiers» Bias point and circuits,» Small signal models» Gain and bandwidth» Limits of linear analysis Op Amp amplifiers
Application Note A008
 Microwave Oscillator Design Application Note A008 Introduction This application note describes a method of designing oscillators using small signal S-parameters. The background theory is first developed
Microwave Oscillator Design Application Note A008 Introduction This application note describes a method of designing oscillators using small signal S-parameters. The background theory is first developed
Streamlined Design of SiGe Based Power Amplifiers
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 13, Number 1, 2010, 22 32 Streamlined Design of SiGe Based Power Amplifiers Mladen BOŽANIĆ1, Saurabh SINHA 1, Alexandru MÜLLER2 1 Department
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 13, Number 1, 2010, 22 32 Streamlined Design of SiGe Based Power Amplifiers Mladen BOŽANIĆ1, Saurabh SINHA 1, Alexandru MÜLLER2 1 Department
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
Microwave Oscillator Design. Application Note A008
 Microwave Oscillator Design Application Note A008 NOTE: This publication is a reprint of a previously published Application Note and is for technical reference only. For more current information, see the
Microwave Oscillator Design Application Note A008 NOTE: This publication is a reprint of a previously published Application Note and is for technical reference only. For more current information, see the
4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
 4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) The Metal Oxide Semitonductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) has two modes of operation, the depletion mode, and the enhancement mode.
4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) The Metal Oxide Semitonductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) has two modes of operation, the depletion mode, and the enhancement mode.
COLLECTOR DRAIN BASE GATE EMITTER. Applying a voltage to the Gate connection allows current to flow between the Drain and Source connections.
 MOSFETS Although the base current in a transistor is usually small (< 0.1 ma), some input devices (e.g. a crystal microphone) may be limited in their output. In order to overcome this, a Field Effect Transistor
MOSFETS Although the base current in a transistor is usually small (< 0.1 ma), some input devices (e.g. a crystal microphone) may be limited in their output. In order to overcome this, a Field Effect Transistor
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS. Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi
 EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
Application Note 1360
 ADA-4743 +17 dbm P1dB Avago Darlington Amplifier Application Note 1360 Description Avago Technologies Darlington Amplifier, ADA-4743 is a low current silicon gain block RFIC amplifier housed in a 4-lead
ADA-4743 +17 dbm P1dB Avago Darlington Amplifier Application Note 1360 Description Avago Technologies Darlington Amplifier, ADA-4743 is a low current silicon gain block RFIC amplifier housed in a 4-lead
Application Note 1299
 A Low Noise High Intercept Point Amplifier for 9 MHz Applications using ATF-54143 PHEMT Application Note 1299 1. Introduction The Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode PHEMT designed
A Low Noise High Intercept Point Amplifier for 9 MHz Applications using ATF-54143 PHEMT Application Note 1299 1. Introduction The Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode PHEMT designed
VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011
 VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011 Report due 2/18/2011 VCO DESIGN GOALS. Design, build, and test a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). 1. Design VCO for highest center frequency (< 400 MHz). 2. At
VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011 Report due 2/18/2011 VCO DESIGN GOALS. Design, build, and test a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). 1. Design VCO for highest center frequency (< 400 MHz). 2. At
Radio Frequency Electronics
 Radio Frequency Electronics Active Components IV Samuel Morse Born in 79 in Massachusetts Fairly accomplished painter After witnessing various electrical experiments, got intrigued by electricity Designed
Radio Frequency Electronics Active Components IV Samuel Morse Born in 79 in Massachusetts Fairly accomplished painter After witnessing various electrical experiments, got intrigued by electricity Designed
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET. BLT70 UHF power transistor. Product specification 1996 Feb 06
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET 1996 Feb 6 FEATURES Very high efficiency Low supply voltage. APPLICATIONS 4 Hand-held radio equipment in common emitter class-ab operation in the 9 MHz communication
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET 1996 Feb 6 FEATURES Very high efficiency Low supply voltage. APPLICATIONS 4 Hand-held radio equipment in common emitter class-ab operation in the 9 MHz communication
ABA GHz Broadband Silicon RFIC Amplifier. Application Note 1349
 ABA-52563 3.5 GHz Broadband Silicon RFIC Amplifier Application Note 1349 Introduction Avago Technologies ABA-52563 is a low current silicon gain block RFIC amplifier housed in a 6-lead SC 70 (SOT- 363)
ABA-52563 3.5 GHz Broadband Silicon RFIC Amplifier Application Note 1349 Introduction Avago Technologies ABA-52563 is a low current silicon gain block RFIC amplifier housed in a 6-lead SC 70 (SOT- 363)
i. At the start-up of oscillation there is an excess negative resistance (-R)
 OSCILLATORS Andrew Dearn * Introduction The designers of monolithic or integrated oscillators usually have the available process dictated to them by overall system requirements such as frequency of operation
OSCILLATORS Andrew Dearn * Introduction The designers of monolithic or integrated oscillators usually have the available process dictated to them by overall system requirements such as frequency of operation
ECE 255, MOSFET Amplifiers
 ECE 255, MOSFET Amplifiers 26 October 2017 In this lecture, the basic configurations of MOSFET amplifiers will be studied similar to that of BJT. Previously, it has been shown that with the transistor
ECE 255, MOSFET Amplifiers 26 October 2017 In this lecture, the basic configurations of MOSFET amplifiers will be studied similar to that of BJT. Previously, it has been shown that with the transistor
Scheme Q.1 Attempt any SIX of following: 12-Total Marks a) Draw symbol NPN and PNP transistor. 2 M Ans: Symbol Of NPN and PNP BJT (1M each)
 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
Application Note 5379
 VMMK-1225 Applications Information Application Note 5379 Introduction The Avago Technologies VMMK-1225 is a low noise enhancement mode PHEMT designed for use in low cost commercial applications in the
VMMK-1225 Applications Information Application Note 5379 Introduction The Avago Technologies VMMK-1225 is a low noise enhancement mode PHEMT designed for use in low cost commercial applications in the
EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS. 1. Define diffusion current.
 EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS 1. Define diffusion current. A movement of charge carriers due to the concentration gradient in a semiconductor is called process
EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS 1. Define diffusion current. A movement of charge carriers due to the concentration gradient in a semiconductor is called process
ATLCE - A3 01/03/2016. Analog and Telecommunication Electronics 2016 DDC 1. Politecnico di Torino - ICT School. Lesson A3: BJT Amplifiers
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» ltage gain» Frequency response AY 2015-16 Biasing Output
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» ltage gain» Frequency response AY 2015-16 Biasing Output
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated RF Oscillator with Buffered Outputs. Typical Operating Circuit. 10nH 1000pF MAX2620 BIAS SUPPLY
 19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02
 EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
1. What is the unit of electromotive force? (a) volt (b) ampere (c) watt (d) ohm. 2. The resonant frequency of a tuned (LRC) circuit is given by
 Department of Examinations, Sri Lanka EXAMINATION FOR THE AMATEUR RADIO OPERATORS CERTIFICATE OF PROFICIENCY ISSUED BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS, SRI LANKA 2004 (NOVICE CLASS) Basic Electricity,
Department of Examinations, Sri Lanka EXAMINATION FOR THE AMATEUR RADIO OPERATORS CERTIFICATE OF PROFICIENCY ISSUED BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS, SRI LANKA 2004 (NOVICE CLASS) Basic Electricity,
4 Transistors. 4.1 IV Relations
 4 Transistors Due date: Sunday, September 19 (midnight) Reading (Bipolar transistors): HH sections 2.01-2.07, (pgs. 62 77) Reading (Field effect transistors) : HH sections 3.01-3.03, 3.11-3.12 (pgs. 113
4 Transistors Due date: Sunday, September 19 (midnight) Reading (Bipolar transistors): HH sections 2.01-2.07, (pgs. 62 77) Reading (Field effect transistors) : HH sections 3.01-3.03, 3.11-3.12 (pgs. 113
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1
 Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
RF circuits design Grzegorz Beziuk. RF Amplifier design. References
 RF circuits design Grzegorz Beziuk RF Amplifier design References [1] Tietze U., Schenk C., Electronic circuits : handbook for design and applications, Springer 008 [] Pozar D. M., Microwave engineering
RF circuits design Grzegorz Beziuk RF Amplifier design References [1] Tietze U., Schenk C., Electronic circuits : handbook for design and applications, Springer 008 [] Pozar D. M., Microwave engineering
TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS. B.Sc. Part - I
 TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS THEORY B.Sc. Part - I Elec. 101 Paper I Circuit Elements and Networks Pd/W Exam. Max. (45mts.) Hours Marks 150 2 3 50 Elec. 102 Paper
TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS THEORY B.Sc. Part - I Elec. 101 Paper I Circuit Elements and Networks Pd/W Exam. Max. (45mts.) Hours Marks 150 2 3 50 Elec. 102 Paper
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1
 Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 51 Hours
 Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 5s Unit I: Electrical Engineering materials:(10) Crystal structure & defects; Ceramic materials-structures, composites, processing and uses; Insulating laminates for electronics,
Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 5s Unit I: Electrical Engineering materials:(10) Crystal structure & defects; Ceramic materials-structures, composites, processing and uses; Insulating laminates for electronics,
EE70 - Intro. Electronics
 EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent
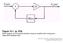 Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Code: 9A Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
 II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics
 Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» Voltage gain» Frequency response 12/03/2012-1 ATLCE -
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» Voltage gain» Frequency response 12/03/2012-1 ATLCE -
SAW Resonators SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVE RESONATORS. Cat.No.P36E. P36E.pdf Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
 !Note Please read rating and!caution (for storage and operating, rating, soldering and mounting, handling) in this PDF catalog to prevent smoking and/or burning, etc. P36E.pdf 02.8.5 This catalog has only
!Note Please read rating and!caution (for storage and operating, rating, soldering and mounting, handling) in this PDF catalog to prevent smoking and/or burning, etc. P36E.pdf 02.8.5 This catalog has only
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/CD/CM/CW/IF] Basic Electronics
![F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/CD/CM/CW/IF] Basic Electronics F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/CD/CM/CW/IF] Basic Electronics](/thumbs/78/77332946.jpg) F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/CD/CM/CW/IF] Basic Electronics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solutions [Marks : 100 Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following : [20] Q.1(a) Give the classification of capacitor.
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/CD/CM/CW/IF] Basic Electronics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solutions [Marks : 100 Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following : [20] Q.1(a) Give the classification of capacitor.
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Second Semester
 WK 5 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 27184 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Time : Three hours Second Semester Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES
WK 5 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 27184 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Time : Three hours Second Semester Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES
ATF High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT
 ATF-54143 High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the 185 191 MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1222 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode
ATF-54143 High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the 185 191 MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1222 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
AN Demonstration of a 1GHz discrete VCO based on the BFR92A. Document information. Keywords Abstract
 Rev. 1.0 26 June 2012 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content Discrete, VCO, BFR92A, EVB, Design, Evaluation, Measurements This document provides an example of a discrete Voltage
Rev. 1.0 26 June 2012 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content Discrete, VCO, BFR92A, EVB, Design, Evaluation, Measurements This document provides an example of a discrete Voltage
Analog Circuits and Systems
 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 10: Electronic Devices for Analog Circuits 1 Multipliers Multipliers provide multiplication of two input voltages or currents Multipliers can
Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 10: Electronic Devices for Analog Circuits 1 Multipliers Multipliers provide multiplication of two input voltages or currents Multipliers can
Field Effect Transistors
 Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
This article describes the design of a multiband,
 A Low-Noise Amplifier for 2 GHz Applications Using the NE334S01 Transistor By Ulrich Delpy NEC Electronics (Europe) This article describes the design of a multiband, low-noise amplifier (LNA) using the
A Low-Noise Amplifier for 2 GHz Applications Using the NE334S01 Transistor By Ulrich Delpy NEC Electronics (Europe) This article describes the design of a multiband, low-noise amplifier (LNA) using the
ECE 255, Discrete-Circuit Amplifiers
 ECE 255, Discrete-Circuit Amplifiers 20 March 2018 In this lecture, we will continue with the study of transistor amplifiers with the presence of biasing circuits and coupling capacitors in place. We will
ECE 255, Discrete-Circuit Amplifiers 20 March 2018 In this lecture, we will continue with the study of transistor amplifiers with the presence of biasing circuits and coupling capacitors in place. We will
Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
1 of 7 12/20/ :04 PM
 1 of 7 12/20/2007 11:04 PM Trusted Resource for the Working RF Engineer [ C o m p o n e n t s ] Build An E-pHEMT Low-Noise Amplifier Although often associated with power amplifiers, E-pHEMT devices are
1 of 7 12/20/2007 11:04 PM Trusted Resource for the Working RF Engineer [ C o m p o n e n t s ] Build An E-pHEMT Low-Noise Amplifier Although often associated with power amplifiers, E-pHEMT devices are
CHAPTER 3: OSCILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 3: OSCILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING CIRCUITS In the design of electronic systems, the need frequently arises for signals having prescribed standard waveforms (e.g., sinusoidal, square, triangle,
CHAPTER 3: OSCILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING CIRCUITS In the design of electronic systems, the need frequently arises for signals having prescribed standard waveforms (e.g., sinusoidal, square, triangle,
Fully Integrated Low Phase Noise LC VCO. Desired Characteristics of VCOs
 Fully Integrated ow Phase Noise C VCO AGENDA Comparison with other types of VCOs. Analysis of two common C VCO topologies. Design procedure for the cross-coupled C VCO. Phase noise reduction techniques.
Fully Integrated ow Phase Noise C VCO AGENDA Comparison with other types of VCOs. Analysis of two common C VCO topologies. Design procedure for the cross-coupled C VCO. Phase noise reduction techniques.
UNIT-VI FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR. 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s.
 UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: 1/
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 12025 Model Answer Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 12025 Model Answer Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
INTRODUCTION: Basic operating principle of a MOSFET:
 INTRODUCTION: Along with the Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), there is another type of Field Effect Transistor available whose Gate input is electrically insulated from the main current carrying
INTRODUCTION: Along with the Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), there is another type of Field Effect Transistor available whose Gate input is electrically insulated from the main current carrying
The Miller Approximation. CE Frequency Response. The exact analysis is worked out on pp of H&S.
 CE Frequency Response The exact analysis is worked out on pp. 639-64 of H&S. The Miller Approximation Therefore, we consider the effect of C µ on the input node only V ---------- out V s = r g π m ------------------
CE Frequency Response The exact analysis is worked out on pp. 639-64 of H&S. The Miller Approximation Therefore, we consider the effect of C µ on the input node only V ---------- out V s = r g π m ------------------
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05010204 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering,
Code No: R05010204 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering,
AE103 ELECTRONIC DEVICES & CIRCUITS DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
Lecture 16 Microwave Detector and Switching Diodes
 Basic Building Blocks of Microwave Engineering Prof. Amitabha Bhattacharya Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 16 Microwave Detector
Basic Building Blocks of Microwave Engineering Prof. Amitabha Bhattacharya Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 16 Microwave Detector
ECE 255, MOSFET Basic Configurations
 ECE 255, MOSFET Basic Configurations 8 March 2018 In this lecture, we will go back to Section 7.3, and the basic configurations of MOSFET amplifiers will be studied similar to that of BJT. Previously,
ECE 255, MOSFET Basic Configurations 8 March 2018 In this lecture, we will go back to Section 7.3, and the basic configurations of MOSFET amplifiers will be studied similar to that of BJT. Previously,
6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 14 Voltage Controlled Oscillators
 6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 14 Voltage Controlled Oscillators Massachusetts Institute of Technology March 29, 2005 Copyright 2005 by Michael H. Perrott VCO Design for Narrowband
6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 14 Voltage Controlled Oscillators Massachusetts Institute of Technology March 29, 2005 Copyright 2005 by Michael H. Perrott VCO Design for Narrowband
R a) Draw and explain VI characteristics of Si & Ge diode. (8M) b) Explain the operation of SCR & its characteristics (8M)
 SET - 1 1. a) Define i) transient capacitance ii) Diffusion capacitance (4M) b) Explain Fermi level in intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor (4M) c) Derive the expression for ripple factor of Half wave
SET - 1 1. a) Define i) transient capacitance ii) Diffusion capacitance (4M) b) Explain Fermi level in intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor (4M) c) Derive the expression for ripple factor of Half wave
CHAPTER 3 CMOS LOW NOISE AMPLIFIERS
 46 CHAPTER 3 CMOS LOW NOISE AMPLIFIERS 3.1 INTRODUCTION The Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) plays an important role in the receiver design. LNA serves as the first block in the RF receiver. It is a critical
46 CHAPTER 3 CMOS LOW NOISE AMPLIFIERS 3.1 INTRODUCTION The Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) plays an important role in the receiver design. LNA serves as the first block in the RF receiver. It is a critical
Chapter 6. FM Circuits
 Chapter 6 FM Circuits Topics Covered 6-1: Frequency Modulators 6-2: Frequency Demodulators Objectives You should be able to: Explain the operation of an FM modulators and demodulators. Compare and contrast;
Chapter 6 FM Circuits Topics Covered 6-1: Frequency Modulators 6-2: Frequency Demodulators Objectives You should be able to: Explain the operation of an FM modulators and demodulators. Compare and contrast;
The Design of 2.4GHz Bipolar Oscillator by Using the Method of Negative Resistance Cheng Sin Hang Tony Sept. 14, 2001
 The Design of 2.4GHz Bipolar Oscillator by Using the Method of Negative Resistance Cheng Sin Hang Tony Sept. 14, 2001 Introduction In this application note, the design on a 2.4GHz bipolar oscillator by
The Design of 2.4GHz Bipolar Oscillator by Using the Method of Negative Resistance Cheng Sin Hang Tony Sept. 14, 2001 Introduction In this application note, the design on a 2.4GHz bipolar oscillator by
Homework Assignment 12
 Homework Assignment 12 Question 1 Shown the is Bode plot of the magnitude of the gain transfer function of a constant GBP amplifier. By how much will the amplifier delay a sine wave with the following
Homework Assignment 12 Question 1 Shown the is Bode plot of the magnitude of the gain transfer function of a constant GBP amplifier. By how much will the amplifier delay a sine wave with the following
6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors, Passive Components, Gain- Bandwidth Issue for Broadband Amplifiers
 6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors, Passive Components, Gain- Bandwidth Issue for Broadband Amplifiers Massachusetts Institute of Technology February 17, 2005 Copyright 2005
6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors, Passive Components, Gain- Bandwidth Issue for Broadband Amplifiers Massachusetts Institute of Technology February 17, 2005 Copyright 2005
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME & CODE: EC2403 & RF AND MICROWAVE ENGINEERING UNIT I
 FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai -625 020 An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai -625 020 An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
ETI , Good luck! Written Exam Integrated Radio Electronics. Lund University Dept. of Electroscience
 und University Dept. of Electroscience EI170 Written Exam Integrated adio Electronics 2010-03-10, 08.00-13.00 he exam consists of 5 problems which can give a maximum of 6 points each. he total maximum
und University Dept. of Electroscience EI170 Written Exam Integrated adio Electronics 2010-03-10, 08.00-13.00 he exam consists of 5 problems which can give a maximum of 6 points each. he total maximum
Electronics 1. Lecture 4
 Electronics 1 Lecture 4 Bipolar Junction Transistors. Structure, Characteristics, Basic Circuit Configurations, Biasing Literature 1. Tony R. Kuphaldt: Lessons In Electric Circuits, Volume II AC, 2007
Electronics 1 Lecture 4 Bipolar Junction Transistors. Structure, Characteristics, Basic Circuit Configurations, Biasing Literature 1. Tony R. Kuphaldt: Lessons In Electric Circuits, Volume II AC, 2007
Radio Frequency Electronics
 Radio Frequency Electronics Preliminaries IV Born 22 February 1857, died 1 January 1894 Physicist Proved conclusively EM waves (theorized by Maxwell ), exist. Hz names in his honor. Created the field of
Radio Frequency Electronics Preliminaries IV Born 22 February 1857, died 1 January 1894 Physicist Proved conclusively EM waves (theorized by Maxwell ), exist. Hz names in his honor. Created the field of
Chapter 2. The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review
 Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
II/IV B. TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOVEMBER Second Semester EC/EE ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. Time : Three Hours Max.
 Total No. of Questions : 9] [Total No. of Pages : 02 B.Tech. II/ IV YEAR DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY - 2014 (Second Semester) EC/EE/EI Electronic Circuit Analysis Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Q1)
Total No. of Questions : 9] [Total No. of Pages : 02 B.Tech. II/ IV YEAR DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY - 2014 (Second Semester) EC/EE/EI Electronic Circuit Analysis Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Q1)
SYLLABUS OSMANIA UNIVERSITY (HYDERABAD)
 UNIT - 1 i SYLLABUS OSMANIA UNIVERSITY (HYDERABAD) JUNCTION DIODE Different Types of PN Junction Formation Techniques, PN Junction Characteristics, Biasing, Band Diagrams and Current Flow, Diode Current
UNIT - 1 i SYLLABUS OSMANIA UNIVERSITY (HYDERABAD) JUNCTION DIODE Different Types of PN Junction Formation Techniques, PN Junction Characteristics, Biasing, Band Diagrams and Current Flow, Diode Current
RF/Microwave Circuits I. Introduction Fall 2003
 Introduction Fall 03 Outline Trends for Microwave Designers The Role of Passive Circuits in RF/Microwave Design Examples of Some Passive Circuits Software Laboratory Assignments Grading Trends for Microwave
Introduction Fall 03 Outline Trends for Microwave Designers The Role of Passive Circuits in RF/Microwave Design Examples of Some Passive Circuits Software Laboratory Assignments Grading Trends for Microwave
Up to 6 GHz Low Noise Silicon Bipolar Transistor Chip. Technical Data AT-41400
 Up to 6 GHz Low Noise Silicon Bipolar Transistor Chip Technical Data AT-1 Features Low Noise Figure: 1.6 db Typical at 3. db Typical at. GHz High Associated Gain: 1.5 db Typical at 1.5 db Typical at. GHz
Up to 6 GHz Low Noise Silicon Bipolar Transistor Chip Technical Data AT-1 Features Low Noise Figure: 1.6 db Typical at 3. db Typical at. GHz High Associated Gain: 1.5 db Typical at 1.5 db Typical at. GHz
UNIT I BIASING OF DISCRETE BJT AND MOSFET PART A
 UNIT I BIASING OF DISCRETE BJT AND MOSFET PART A 1. Why do we choose Q point at the center of the load line? 2. Name the two techniques used in the stability of the q point.explain. 3. Give the expression
UNIT I BIASING OF DISCRETE BJT AND MOSFET PART A 1. Why do we choose Q point at the center of the load line? 2. Name the two techniques used in the stability of the q point.explain. 3. Give the expression
Simulation Study of Broadband LNA for Software Radio Application.
 Simulation Study of Broadband LNA for Software Radio Application. Yazid Mohamed, Norsheila Fisal and Mazlina Esa June 000 Telemetics and Optic Panel Faculty of Electrical Engineering University Technology
Simulation Study of Broadband LNA for Software Radio Application. Yazid Mohamed, Norsheila Fisal and Mazlina Esa June 000 Telemetics and Optic Panel Faculty of Electrical Engineering University Technology
S.No. Name of the Subject/Lab Semester Page No. 1 Electronic devices II 2 2 Circuit theory II 6
 V.S.B. ENGINEERING COLLEGE, KARUR Academic Year: 2016-2017 (EVEN Semester) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Course Materials (2013 Regulations) Question Bank S.No. Name of the Subject/Lab
V.S.B. ENGINEERING COLLEGE, KARUR Academic Year: 2016-2017 (EVEN Semester) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Course Materials (2013 Regulations) Question Bank S.No. Name of the Subject/Lab
UNIT-4. Microwave Engineering
 UNIT-4 Microwave Engineering Microwave Solid State Devices Two problems with conventional transistors at higher frequencies are: 1. Stray capacitance and inductance. - remedy is interdigital design. 2.Transit
UNIT-4 Microwave Engineering Microwave Solid State Devices Two problems with conventional transistors at higher frequencies are: 1. Stray capacitance and inductance. - remedy is interdigital design. 2.Transit
K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Three Terminal Devices
 Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II. Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS
 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS 1. Explain microwave power measurement. 2. Why we can not use ordinary diode and transistor in microwave detection and microwave amplification? 3.
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS 1. Explain microwave power measurement. 2. Why we can not use ordinary diode and transistor in microwave detection and microwave amplification? 3.
