Electronic materials and components-semiconductor packages
|
|
|
- Eric Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electronic materials and components-semiconductor packages Semiconductor back-end processes We will learn much more about semiconductor back end processes in subsequent modules, but you need to understand at least something of the terminology and what is involved in turning a chip into a finished package1. 1 It is always very dangerous to point people at sources of information on packaging, especially now that the wonderful Fullman site has disappeared. However, you might like to take a look at what a doctoral student can achieve at The starting point for semiconductors is the wafer, which contains a (very large) number of devices, separated by small gaps, and electrically isolated from each other as part of the processing. Starting with a blank wafer of extremely pure silicon, building up layers by deposition techniques, etching patterns, and implanting dopants into the silicon structure using high energy particles, the semiconductor fab ships a wafer which is partially probe-tested, but needs terminations in order to communicate with the outside world. These front end processes attract the headlines, but the back end of the pantomime horse is just as important! The back end process consists of sawing the wafer into individual dice (the terms chip and die are equivalent), mounting the die on a lead-frame or other mount using conductive adhesive, and finally making fine wire connections to the top surface this wire bonding process uses gold and aluminium wires typically µm in diameter. Because wires and semiconductor are relatively fragile and easy to contaminate, the die will then be protected in some way. A silicon wafer
2 Lead-frame for a 128-pin QFP Silicon die wire-bonded onto a ceramic substrate The first solid state devices were incorporated into high reliability military and telecommunications applications, and needed a hermetic package to prevent junction leakage and degradation of transistor gain caused by moisture and contamination. Packages were made either of metal, with glass-to-metal seals isolating the leads, or of ceramic: both technologies were expensive, and often relatively large and mechanically fragile. However development of silicon planar technology, improvements in methods of passivation for the die surface, and advances in polymer formulation and purity, combined to make it possible to mount a silicon die on a free-standing lead-frame, encapsulate the assembly in resin (usually by transfer-moulding), and create a protected device reliable enough for most applications. Discrete semiconductors Transistors and diodes
3 Discrete transistors and diodes are generally available in standard Small Outline Transistor (SOT) packages originally designed for use in hybrid microelectronics assembly. Although there are moves to introduce smaller variants, the most common of these is the SOT-23 (now renamed in the American JEDEC standard as TO-236). The construction of a typical SOT-23 package is shown in Figure 1. The SOT-23 can accommodate almost any semiconductor with a die size up to about 0.75 mm square, and its power handling capabilities make it suitable for smallsignal transistors. Figure 1: Construction of the SOT-23 package [ [SOT-23 (Small Outline Transistor or Diode) package] There have been many criticisms of the design, which was an early-1970s compromise, and comparatively large. Improved internal constructions have made
4 it possible to develop a range of more compact devices, which are more compatible with the smaller multi-layer ceramic capacitors now in common use. The smallest of these currently has a moulding size of mm, with a seated height of 0.7 mm, and lead centres on 1.0 mm pitch, occupying only 30% of the mounting area of a standard SOT-23. There are a number of similar packages, differing in their size, power handling capacity and number of leads, but using the same basic concept. In all cases the trend is towards smaller packages, and finer lead pitches. Dissipating more heat generally demands a heavier metal leadframe. As an example, semiconductors on chips up to about 1.5 mm square can be packaged in the SOT-89 format, shown schematically in Figure 2. Its three leads are all along the same edge of the package but the centre one extends across the bottom to improve the thermal conductivity. Whilst the SOT-23 can dissipate typically 200 mw in free air at 25 C, the SOT-89 can handle up to 500 mw under the same conditions. Figure 2: Design of the SOT-89 package
5 [SOT-89 package (for increased dissipation)] SOT-223 package (updated SOT-89) Diode formats Discrete diodes are frequently packaged in SOT-23 format: one of the three contacts may be redundant, although diode pairs with either anodes or cathodes connected together are common. However, several two-terminal hermetically sealed glass-to-metal packages have been developed especially for diodes, the two most popular both being cylindrical. The MELF is so-called because its appearance and dimensions (Figure 3) are similar to those of the earlier MELF (metal electrode face bonded) resistors. With adequate cooling, power dissipation can be as high as 2 W.
6 Figure 3: MELF diode MELF (Metal Electrode Face Bonded) diode The SOD-80 ( Small Outline Diode ) encapsulation (or MiniMELF ) is 3.6 mm long and 1.6 mm in diameter. It is cheaper, lighter, and requires less board space than the SOT-23, but has no flat top surface and can be more difficult to handle. Its construction is specifically designed for small diode chips and the package dissipation is limited to 250 mw. Cylindrical packages have no flat top surface and are sometimes difficult to handle. The manufacturing costs of glass parts may also be higher than for plastic encapsulations. For these reasons, moulded plastic packages such as the DO-214 (Figure 4) are becoming increasingly common. Different sizes of package, with
7 more or less heat sinking, are selected according to the die size and current/power rating of the application. Figure 4: Typical dimensions of DO-214 package Moulded plastic diode package Although originally applied to resistors, and to diodes in glass encapsulation, the end cap concept is also seen applied to square bodies for other types of component. Power devices As you will have deduced from the different Small Outline packages for transistors, higher power means that more heat energy has to be removed from the package, and this usually means the incorporation of a larger metal structure in order to conduct heat from the die where it is dissipated.
8 Full consideration of this topic is beyond the scope of this module, but you should be aware that, in power devices, adaptations have to be made to the ways in which bonds are made to the die reverse and to the top surface. Typically requirements for external heat sinking must be observed in order to prevent the component burning out. Power devices are also generally associated with higher-than-average currents, and this aspect is one more factor to be considered during board design. Integrated circuits Dual-in-line packages The dual-in-line package (DIL or DIP) has a number of disadvantages which began to become apparent as the pressure increased for higher lead-count devices: A DIP with large numbers of pins in a double row at a (0.1 inch) pitch becomes relatively expensive because of excessive size and material use The DIP format results in long internal lead lengths for the pins towards the ends of the package, with consequent higher inductance and inter-lead capacitance, limiting device performance The package occupies more board area than is necessary, since board manufacturing technology has advanced to accommodate much smaller lead pitches. Figure 5 shows a typical design plan of a 64-pin DIP and demonstrates how inefficient is its use of board area Larger sizes of DIP become progressively difficult to handle robotically and to insert automatically into plated through-holes. In short, it is the mechanical properties of the package that have physically limited the size to which the DIP can grow.
9 Figure 5: Schematic of a typical 64-pin DIP lead-out pattern As the technology of surface mounting has developed, a range of packaging types has therefore emerged, some by transposition from the hybrid microelectronics industry and some by development in their own right. Leaded IC packages The small outline transistor (SOT) and the small outline integrated circuit (SOIC, or simply SO) packages have a longer history of use than other surface mounting devices. The SO package was developed in Europe in the mid-1970s particularly for the emerging electronic watch market. The SOIC is a plastic package, available in 6, 8, 10, 14, and 16 pin versions with a body width of 4 mm, and in 16, 20, 24 and 28 pin versions with a wider body of 7.6 mm. The flattened leads are on standard 1.27 mm (0.05 inch) centres and are formed outwards in a gull wing fashion, so that the tips of the leads lie in contact with the PCB. The package outline and typical dimensions of the SOIC range are given in Figure 6 and Table 7. They may vary very slightly from one manufacturer to another except for the lead pitch which must be 1.27 mm.
10 QFP gull wing terminations The low lead-count SOICs require less than half the area of their DIP equivalents and weigh only one-tenth as much. Figure 6: Design of the SOIC range of packages
11 SOIC-14 (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) Table 7: Dimensions of SOIC packages SOIC-20 The SOP concept has more recently been extended to include a wide range of thinner, smaller packages, many with smaller pitch centres. Quad flatpacks The basic construction of the SO package is also seen in the Quad Flat-Pack (QFP), which has leads on all four sides (Figure 7). The leads are also formed to a gullwing profile to bring their ends level with the bottom of the package, but in this case there are many variants: some devices have very flat profiles, whilst other styles are much deeper. As with the SOP, the QFP trend has been towards thinner packages, with more and finer leads: computers typically use components with leads on 0.4 mm or 0.5 mm pitch.
12 Figure 7: Views of a gull wing Quad Flat Pack [Quad flat package (1.27mm pitch leads)] Pitch spacings down to 0.4 mm (0.016 in) allow pin counts of over 200. Typical examples have 44 to 150 leads with body sizes up to 25.4 mm square and lead pitches of 0.5 to 0.8 mm.
13 Trend towards QFPs with finer pitch leads At high lead counts, the gull-wing leads are very thin and narrow, and therefore in danger of being deformed during handling. This puts a constraint on both placement machines and operators to avoid such damage. The chip carrier concept The term chip carrier refers to a range of IC packages that are square or rectangular, with terminations brought out on all four sides. The first of these to be developed was the leadless ceramic chip carrier (LCCC). This can be envisaged as the useful active centre of a hermetic DIP, with all the leads and excess packaging material discarded. Since it is constructed of the same materials and in the same manner as hermetic DIPs, it is at least as reliable. Leadless ceramic chip carriers were commonly available in sizes from 5 mm square to 25 mm square and above, with 1.27 mm (0.050 in) lead pitch, and from 20 leads to upwards of 100. Leadless ceramic chip carriers are constructed in a variety of ways that are dictated by the end product use and the cost of manufacture. The principle of the construction is that the IC chip is bonded to a ceramic base and connections are made with fine wires to metallisation patterns that are brought out to external solderable contact pads (castellations) as shown in Figure 8.
14 Leadless chip carrier castellations For the most demanding applications, where cost is not a major constraint, a threelayer construction is used with a flat gold plated lid sealed using a gold-tin solder preform. This style of package is still used for many RF devices, although cheaper alternatives have been devised, as indicated in Figure 8. Glass sealing, using a preglassed ceramic lid with a three layer chip carrier, results in some cost saving. The use of a single layer chip carrier having a pre-glassed cavity and a ceramic cupshaped lid gives a device of about half the price. Even further economies are obtained, if there is no need for hermeticity, by encapsulating the device on its ceramic base, in epoxy resin.
15 Figure 8: LCCC construction, showing three types of enclosure Leadless chip carrier mounted on a ceramic substrate LCCCs were originally designed to be soldered to the ceramic substrate of hybrid circuits. In this application the thermal expansion coefficients of substrate and component are matched, but this is not the case with assemblies on FR-4 laminate. Consequently, for PCB applications, the LCCC has been superseded by devices with compliant leads, to compensate for CTE mismatch between the component and the board. The Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier Plastic leaded chip carriers (PLCCs) are manufactured by fully automated high volume processes. The methods of die bond, wire bond and transfer moulding are conceptually exactly the same as for the SOT-23, although the number of bonds and mould complexity are both much greater, with standard packages ranging from 20 to 84 leads with dimensions up to 30 mm square. As shown in Figure 9, leads have a J shape, folded underneath the package to save board space.
16 Figure 9: Lead form of a J-leaded PLCC J-leaded PLCC Any gain in component density may, however, be paid for by problems in wave soldering (skipped joints), in reflow soldering (wicking), and in increased difficulties at inspection (which requires oblique viewing optics) and electrical test (difficult probe access to leads). There are also mechanical limitations in forming leads on smaller pitch centres, although fine-pitch SOP equivalents with J-leads (SOJ packages) have been produced for memory devices.
17 The leads of most PLCCs are on a standard 1.27 mm pitch, with package sizes and formats similar to the LCCC. The leads are intended to be sufficiently compliant to accommodate any thermal expansion mismatch between the component and the PCB, and are commonly made of a copper alloy with a plated tin-lead coating to ensure good solderability. Ball grid arrays The increase in die complexity which has driven the electronics revolution in recent years has been mirrored by an increase in the number of lead-outs per device. For surface mount devices, this was first accommodated both by using all four sides of the packages, and by reducing the lead pitch progressively from 0.1 inch to 0.05 inch to inch centres. This trend was fuelled by improvements in solder paste, printing and component placement, and fine pitch devices were introduced, first at 0.5 mm and then at 0.4 mm pitch, with some parts even produced with leads at 0.3 mm centres. Unfortunately, with practical circuits, there are problems in meeting the fine-pitch requirement and at the same time depositing enough solder paste for larger parts. More seriously, defect rates (typically open circuits and bridges) increase markedly at the finest pitches, and few companies routinely handle parts with pitches less than 0.4 mm. The concept of an area array, where connections are not confined to the periphery of the package had already been proven with the through-hole Pin Grid Array. The rationale for the area array is that, compared to edge leads, this design allows many more connections to be made at the same pitch in the same area or, conversely, the same number of connections to be made in the same area with a greater spacing between connections. Having a coarser pitch improves yield and widens the process window. The Ball Grid Array (BGA) adapts the earlier through-hole package by having solder balls or columns instead of pins, and reflowing them onto the board, rather than inserting and wave-soldering. BGA is, however, a generic concept, not a specific product the only common features are that all BGAs have: some means of chip attach and interconnect to a mini-substrate chip carrier, sometimes referred to as an interposer, with balls or columns of solder or polymer underneath, and some means of chip protection or encapsulation
18 The most common construction is the type of Polymer Ball Grid Array (PBGA) represented by the Motorola OMPAC (Figure 10). This uses epoxy die attach and gold wire bonding, with an interposer of BT resin laminate for higher Tg, transfer moulded single-sided encapsulation, and eutectic solder balls on 1.27 mm pitch. Figure 10: Example of a Polymer Ball Grid Array A BGA built on a thin PCB
19 Ball terminations on a PBGA device The term PBGA encompasses a variety of techniques, for example with TAB or flipchip replacing wire bonding, and a glob-top polymer encapsulation instead of transfer moulding, but there are many other package formats. One which is significantly different in terms of cost and reliability is the IBM standard column BGA. This is designed to minimise internal TCE differences, and also reduce the stresses both by under-filling with adhesive and by increasing the stand-off between interposer and board. The CBGA uses flip-chip die attach onto an alumina or low-temperature co-fired ceramic interposer, and columns of 90:10 Pb:Sn highmelting solder on the package which are not completely dissolved in the eutectic solder on the substrate. Ceramic Ball Grid Array termination Thinner, smaller packages The rapid growth in surface mount has spawned a number of packages which are relatively thinner and smaller than their standard counterparts. These packages have been developed to meet two types of requirement: For applications such as memory products, where the die is large but the number of leads needed is comparatively small. Examples are the TSSOP (thin, shrink SO package) and the SOJ (J-leaded SO package) For high pin count circuits, where area arrays of lead-outs are more effective than peripheral arrangements. The Ball Grid Array (BGA) is a common example of such a package. Many modern package variants are substantially thinner than the OMPAC.
20 The Tape BGA a thinner form of the BGA package This topic is one of the subjects of the Technology Awareness module. At this stage, the key point to make about such packages is that they are usually more fragile than their conventional package equivalents, and need more attention to handling and process control. Chip-Scale Packages Over the past 10 years a number of different packaging approaches have been used to create smaller building blocks for surface mount assembly. The aim is to have a package which does not add significantly to the area occupied by die: IPC define a Chip Scale Package (CSP) as one where the area is less than 1.5 times that of the die (linear dimensions less than 1.2 times). Some CSPs are based on direct chip mounting, some on flip chip, and others on TAB: overall, the package may take a wide variety of different forms, but the improvement in size which can be achieved is shown dramatically in Figure 11.
21 Figure 11: The advantage of Chip Scale Author: Martin Tarr Source:
Chapter 11 Testing, Assembly, and Packaging
 Chapter 11 Testing, Assembly, and Packaging Professor Paul K. Chu Testing The finished wafer is put on a holder and aligned for testing under a microscope Each chip on the wafer is inspected by a multiple-point
Chapter 11 Testing, Assembly, and Packaging Professor Paul K. Chu Testing The finished wafer is put on a holder and aligned for testing under a microscope Each chip on the wafer is inspected by a multiple-point
B. Flip-Chip Technology
 B. Flip-Chip Technology B1. Level 1. Introduction to Flip-Chip techniques B1.1 Why flip-chip? In the development of packaging of electronics the aim is to lower cost, increase the packaging density, improve
B. Flip-Chip Technology B1. Level 1. Introduction to Flip-Chip techniques B1.1 Why flip-chip? In the development of packaging of electronics the aim is to lower cost, increase the packaging density, improve
Sherlock Solder Models
 Introduction: Sherlock Solder Models Solder fatigue calculations in Sherlock are accomplished using one of the many solder models available. The different solder models address the type of package that
Introduction: Sherlock Solder Models Solder fatigue calculations in Sherlock are accomplished using one of the many solder models available. The different solder models address the type of package that
Electronics Materials-Stress caused by thermal mismatch
 Electronics Materials-Stress caused by thermal mismatch The point was well made in the early 1970s by David Boswell that surface mount assemblies have many issues in common with civil engineering. For
Electronics Materials-Stress caused by thermal mismatch The point was well made in the early 1970s by David Boswell that surface mount assemblies have many issues in common with civil engineering. For
CHAPTER 11: Testing, Assembly, and Packaging
 Chapter 11 1 CHAPTER 11: Testing, Assembly, and Packaging The previous chapters focus on the fabrication of devices in silicon or the frontend technology. Hundreds of chips can be built on a single wafer,
Chapter 11 1 CHAPTER 11: Testing, Assembly, and Packaging The previous chapters focus on the fabrication of devices in silicon or the frontend technology. Hundreds of chips can be built on a single wafer,
Benzocyclobutene Polymer dielectric from Dow Chemical used for wafer-level redistribution.
 Glossary of Advanced Packaging: ACA Bare Die BCB BGA BLT BT C4 CBGA CCC CCGA CDIP or CerDIP CLCC COB COF CPGA Anisotropic Conductive Adhesive Adhesive with conducting filler particles where the electrical
Glossary of Advanced Packaging: ACA Bare Die BCB BGA BLT BT C4 CBGA CCC CCGA CDIP or CerDIP CLCC COB COF CPGA Anisotropic Conductive Adhesive Adhesive with conducting filler particles where the electrical
BGA/CSP Re-balling Bob Doetzer Circuit Technology Inc.
 BGA/CSP Re-balling Bob Doetzer Circuit Technology Inc. www.circuittechnology.com The trend in the electronics interconnect industry towards Area Array Packages type packages (BGA s, CSP s, CGA s etc.)
BGA/CSP Re-balling Bob Doetzer Circuit Technology Inc. www.circuittechnology.com The trend in the electronics interconnect industry towards Area Array Packages type packages (BGA s, CSP s, CGA s etc.)
Chapter 2. Literature Review
 Chapter 2 Literature Review 2.1 Development of Electronic Packaging Electronic Packaging is to assemble an integrated circuit device with specific function and to connect with other electronic devices.
Chapter 2 Literature Review 2.1 Development of Electronic Packaging Electronic Packaging is to assemble an integrated circuit device with specific function and to connect with other electronic devices.
An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging. Prof. G. V. Mahesh. Department of Electronic Systems Engineering
 An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering India Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 02 Lecture No. # 08 Wafer Packaging Packaging
An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering India Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 02 Lecture No. # 08 Wafer Packaging Packaging
Tape Automated Bonding
 Tape Automated Bonding Introduction TAB evolved from the minimod project begun at General Electric in 1965, and the term Tape Automated Bonding was coined by Gerard Dehaine of Honeywell Bull in 1971. The
Tape Automated Bonding Introduction TAB evolved from the minimod project begun at General Electric in 1965, and the term Tape Automated Bonding was coined by Gerard Dehaine of Honeywell Bull in 1971. The
Application Bulletin 240
 Application Bulletin 240 Design Consideration CUSTOM CAPABILITIES Standard PC board fabrication flexibility allows for various component orientations, mounting features, and interconnect schemes. The starting
Application Bulletin 240 Design Consideration CUSTOM CAPABILITIES Standard PC board fabrication flexibility allows for various component orientations, mounting features, and interconnect schemes. The starting
23. Packaging of Electronic Equipments (2)
 23. Packaging of Electronic Equipments (2) 23.1 Packaging and Interconnection Techniques Introduction Electronic packaging, which for many years was only an afterthought in the design and manufacture of
23. Packaging of Electronic Equipments (2) 23.1 Packaging and Interconnection Techniques Introduction Electronic packaging, which for many years was only an afterthought in the design and manufacture of
Application Note AN-1011
 AN-1011 Board Mounting Application Note for 0.800mm Pitch Devices For part numbers IRF6100, IRF6100PBF, IR130CSP, IR130CSPPBF, IR140CSP, IR140CSPPBF, IR1H40CSP, IR1H40CSPPBF By Hazel Schofield and Philip
AN-1011 Board Mounting Application Note for 0.800mm Pitch Devices For part numbers IRF6100, IRF6100PBF, IR130CSP, IR130CSPPBF, IR140CSP, IR140CSPPBF, IR1H40CSP, IR1H40CSPPBF By Hazel Schofield and Philip
MA4P7470F-1072T. Non Magnetic MELF PIN Diode. Features. Description and Applications. Designed for Automated Assembly
 Features Non-Magnetic Package Suitable for MRI Applications Rectangular MELF SMQ Ceramic Package Hermetically Sealed Low Rs for Low Insertion Loss Long τ L for Low Intermodulation Distortion Low Cj for
Features Non-Magnetic Package Suitable for MRI Applications Rectangular MELF SMQ Ceramic Package Hermetically Sealed Low Rs for Low Insertion Loss Long τ L for Low Intermodulation Distortion Low Cj for
Two major features of this text
 Two major features of this text Since explanatory materials are systematically made based on subject examination questions, preparation
Two major features of this text Since explanatory materials are systematically made based on subject examination questions, preparation
MASW P. SURMOUNT PIN Diode Switch Element with Thermal Terminal. Features. Description. Ordering Information 2.
 Features Specified Bandwidth: 45MHz 2.5GHz Useable 30MHz to 3.0GHz Low Loss 40dB High C.W. Incident Power, 50W at 500MHz High Input IP3, +66dBm @ 500MHz Unique Thermal Terminal for
Features Specified Bandwidth: 45MHz 2.5GHz Useable 30MHz to 3.0GHz Low Loss 40dB High C.W. Incident Power, 50W at 500MHz High Input IP3, +66dBm @ 500MHz Unique Thermal Terminal for
Endoscopic Inspection of Area Array Packages
 Endoscopic Inspection of Area Array Packages Meeting Miniaturization Requirements For Defect Detection BY MARCO KAEMPFERT Area array packages such as the family of ball grid array (BGA) components plastic
Endoscopic Inspection of Area Array Packages Meeting Miniaturization Requirements For Defect Detection BY MARCO KAEMPFERT Area array packages such as the family of ball grid array (BGA) components plastic
What the Designer needs to know
 White Paper on soldering QFN packages to electronic assemblies. Brian J. Leach VP of Sales and Marketing AccuSpec Electronics, LLC Defect free QFN Assembly What the Designer needs to know QFN Description:
White Paper on soldering QFN packages to electronic assemblies. Brian J. Leach VP of Sales and Marketing AccuSpec Electronics, LLC Defect free QFN Assembly What the Designer needs to know QFN Description:
1. Exceeding these limits may cause permanent damage.
 Silicon PIN Diode s Features Switch & Attenuator Die Extensive Selection of I-Region Lengths Hermetic Glass Passivated CERMACHIP Oxide Passivated Planar s Voltage Ratings to 3000V Faster Switching Speed
Silicon PIN Diode s Features Switch & Attenuator Die Extensive Selection of I-Region Lengths Hermetic Glass Passivated CERMACHIP Oxide Passivated Planar s Voltage Ratings to 3000V Faster Switching Speed
QUALITY SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
 Q QUALITY SEMICONDUCTOR, INC. AN-20 Board Assembly Techniques for 0.4mm Pin Pitch Surface Mount Packages Application Note AN-20 The need for higher performance systems continues to push both silicon and
Q QUALITY SEMICONDUCTOR, INC. AN-20 Board Assembly Techniques for 0.4mm Pin Pitch Surface Mount Packages Application Note AN-20 The need for higher performance systems continues to push both silicon and
!"#$"%&' ()#*+,-+.&/0(
 !"#$"%&' ()#*+,-+.&/0( Multi Chip Modules (MCM) or Multi chip packaging Industry s first MCM from IBM. Generally MCMs are horizontal or two-dimensional modules. Defined as a single unit containing two
!"#$"%&' ()#*+,-+.&/0( Multi Chip Modules (MCM) or Multi chip packaging Industry s first MCM from IBM. Generally MCMs are horizontal or two-dimensional modules. Defined as a single unit containing two
POSSUM TM Die Design as a Low Cost 3D Packaging Alternative
 POSSUM TM Die Design as a Low Cost 3D Packaging Alternative The trend toward 3D system integration in a small form factor has accelerated even more with the introduction of smartphones and tablets. Integration
POSSUM TM Die Design as a Low Cost 3D Packaging Alternative The trend toward 3D system integration in a small form factor has accelerated even more with the introduction of smartphones and tablets. Integration
Specifications subject to change Packaging
 VCSEL Standard Product Packaging Options All standard products are represented in the table below. The Part Number for a standard product is determined by replacing the x in the column Generic Part Number
VCSEL Standard Product Packaging Options All standard products are represented in the table below. The Part Number for a standard product is determined by replacing the x in the column Generic Part Number
Workshop Part Identification Lecture N I A G A R A C O L L E G E T E C H N O L O G Y D E P T.
 Workshop Part Identification Lecture N I A G A R A C O L L E G E T E C H N O L O G Y D E P T. Identifying Resistors Resistors can be either fixed or variable. The variable kind are called potentiometers
Workshop Part Identification Lecture N I A G A R A C O L L E G E T E C H N O L O G Y D E P T. Identifying Resistors Resistors can be either fixed or variable. The variable kind are called potentiometers
An introduction to surface mounting
 Data Pack H Issued March 1997 232-5569 An introduction to surface mounting What is surface mounting? In conventional board assembly technology the component leads are inserted into holes through the and
Data Pack H Issued March 1997 232-5569 An introduction to surface mounting What is surface mounting? In conventional board assembly technology the component leads are inserted into holes through the and
CHAPTER I. Introduction. 1.1 Overview of Power Electronics Packaging
 CHAPTER I Introduction 1.1 Overview of Power Electronics Packaging Basically, power electronics packages provide mechanical support, device protection, cooling and electrical connection and isolation for
CHAPTER I Introduction 1.1 Overview of Power Electronics Packaging Basically, power electronics packages provide mechanical support, device protection, cooling and electrical connection and isolation for
Application Note 5026
 Surface Laminar Circuit (SLC) Ball Grid Array (BGA) Eutectic Surface Mount Assembly Application Note 5026 Introduction This document outlines the design and assembly guidelines for surface laminar circuitry
Surface Laminar Circuit (SLC) Ball Grid Array (BGA) Eutectic Surface Mount Assembly Application Note 5026 Introduction This document outlines the design and assembly guidelines for surface laminar circuitry
Innovations Push Package-on-Package Into New Markets. Flynn Carson. STATS ChipPAC Inc Kato Rd Fremont, CA 94538
 Innovations Push Package-on-Package Into New Markets by Flynn Carson STATS ChipPAC Inc. 47400 Kato Rd Fremont, CA 94538 Copyright 2010. Reprinted from Semiconductor International, April 2010. By choosing
Innovations Push Package-on-Package Into New Markets by Flynn Carson STATS ChipPAC Inc. 47400 Kato Rd Fremont, CA 94538 Copyright 2010. Reprinted from Semiconductor International, April 2010. By choosing
Brief Introduction of Sigurd IC package Assembly
 Brief Introduction of Sigurd IC package Assembly Content Package Development Trend Product Brief Sawing type QFN Representative MEMS Product LGA Light Sensor Proximity Sensor High Yield Capability Low
Brief Introduction of Sigurd IC package Assembly Content Package Development Trend Product Brief Sawing type QFN Representative MEMS Product LGA Light Sensor Proximity Sensor High Yield Capability Low
Bob Willis Process Guides
 What is a Printed Circuit Board Pad? What is a printed circuit board pad, it may sound like a dumb question but do you stop to think what it really does and how its size is defined and why? A printed circuit
What is a Printed Circuit Board Pad? What is a printed circuit board pad, it may sound like a dumb question but do you stop to think what it really does and how its size is defined and why? A printed circuit
Hermetic Packaging Solutions using Borosilicate Glass Thin Films. Lithoglas Hermetic Packaging Solutions using Borosilicate Glass Thin Films
 Hermetic Packaging Solutions using Borosilicate Glass Thin Films 1 Company Profile Company founded in 2006 ISO 9001:2008 qualified since 2011 Headquarters and Production in Dresden, Germany Production
Hermetic Packaging Solutions using Borosilicate Glass Thin Films 1 Company Profile Company founded in 2006 ISO 9001:2008 qualified since 2011 Headquarters and Production in Dresden, Germany Production
Handling and Processing Details for Ceramic LEDs Application Note
 Handling and Processing Details for Ceramic LEDs Application Note Abstract This application note provides information about the recommended handling and processing of ceramic LEDs from OSRAM Opto Semiconductors.
Handling and Processing Details for Ceramic LEDs Application Note Abstract This application note provides information about the recommended handling and processing of ceramic LEDs from OSRAM Opto Semiconductors.
USING SIGNATURE IDENTIFICATION FOR RAPID AND EFFECTIVE X-RAY INSPECTION OF BALL GRID ARRAYS
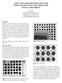 USING SIGNATURE IDENTIFICATION FOR RAPID AND EFFECTIVE X-RAY INSPECTION OF BALL GRID ARRAYS Gil Zweig Glenbrook Technologies, Inc. Randolph, New Jersey USA gzweig@glenbrooktech.com ABSTRACT Although X-ray
USING SIGNATURE IDENTIFICATION FOR RAPID AND EFFECTIVE X-RAY INSPECTION OF BALL GRID ARRAYS Gil Zweig Glenbrook Technologies, Inc. Randolph, New Jersey USA gzweig@glenbrooktech.com ABSTRACT Although X-ray
FLIP CHIP LED SOLDER ASSEMBLY
 As originally published in the SMTA Proceedings FLIP CHIP LED SOLDER ASSEMBLY Gyan Dutt, Srinath Himanshu, Nicholas Herrick, Amit Patel and Ranjit Pandher, Ph.D. Alpha Assembly Solutions South Plainfield,
As originally published in the SMTA Proceedings FLIP CHIP LED SOLDER ASSEMBLY Gyan Dutt, Srinath Himanshu, Nicholas Herrick, Amit Patel and Ranjit Pandher, Ph.D. Alpha Assembly Solutions South Plainfield,
INDEX BY DEVICE TYPE OF REGISTERED MICROELECTRONIC OUTLINES (MO) REGISTRATION NO.
 AXIAL QUAD 1.56 mm (.065") Pitch MO-010 Pins: 12 2.54 mm (.100") Pitch MO-017 Pins: 52, 64 BALL GRID ARRAY (BGA) Tape BGA 1, 1.27. 1.5 mm Pitch Pins: 100 thru 2401 Plastic BGA 1, 1.27, 1.5mm Pitch Pins:
AXIAL QUAD 1.56 mm (.065") Pitch MO-010 Pins: 12 2.54 mm (.100") Pitch MO-017 Pins: 52, 64 BALL GRID ARRAY (BGA) Tape BGA 1, 1.27. 1.5 mm Pitch Pins: 100 thru 2401 Plastic BGA 1, 1.27, 1.5mm Pitch Pins:
Throughout the course best practice will be observed as described in International Standard IPC 610.
 SOLDERING COURSE 560: 3 DAYS: Max 8 Candidates This provides all the skills necessary to work on modern electronic printed circuit boards. It is intended for candidates who have an understanding of electronics
SOLDERING COURSE 560: 3 DAYS: Max 8 Candidates This provides all the skills necessary to work on modern electronic printed circuit boards. It is intended for candidates who have an understanding of electronics
Assembly Instructions for SCC1XX0 series
 Technical Note 82 Assembly Instructions for SCC1XX0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI's 32-lead Dual In-line Package (DIL-32)...2 3 DIL-32 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
Technical Note 82 Assembly Instructions for SCC1XX0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI's 32-lead Dual In-line Package (DIL-32)...2 3 DIL-32 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
MA4L Series. Silicon PIN Limiters RoHS Compliant. M/A-COM Products Rev. V12. Features. Chip Outline. Description. Applications
 Features Low Insertion Loss and Noise Figure High Peak and Average Operating Power Various P1dB Compression Powers Low Flat Leakage Power Proven Reliable, Silicon Nitride Passivation Chip Outline A Square
Features Low Insertion Loss and Noise Figure High Peak and Average Operating Power Various P1dB Compression Powers Low Flat Leakage Power Proven Reliable, Silicon Nitride Passivation Chip Outline A Square
MICROELECTRONICS ASSSEMBLY TECHNOLOGIES. The QFN Platform as a Chip Packaging Foundation
 West Coast Luncheon January 15, 2014. PROMEX PROMEX INDUSTRIES INC. MICROELECTRONICS ASSSEMBLY TECHNOLOGIES The QFN Platform as a Chip Packaging Foundation 3075 Oakmead Village Drive Santa Clara CA Ɩ 95051
West Coast Luncheon January 15, 2014. PROMEX PROMEX INDUSTRIES INC. MICROELECTRONICS ASSSEMBLY TECHNOLOGIES The QFN Platform as a Chip Packaging Foundation 3075 Oakmead Village Drive Santa Clara CA Ɩ 95051
Semiconductor Back-Grinding
 Semiconductor Back-Grinding The silicon wafer on which the active elements are created is a thin circular disc, typically 150mm or 200mm in diameter. During diffusion and similar processes, the wafer may
Semiconductor Back-Grinding The silicon wafer on which the active elements are created is a thin circular disc, typically 150mm or 200mm in diameter. During diffusion and similar processes, the wafer may
Technology Trends and Future History of Semiconductor Packaging Substrate Material
 Review 6 Technology Trends and Future History of Semiconductor Packaging Substrate Material Yoshihiro Nakamura Advanced Performance Materials Operational Headquarters Advanced Core Materials Business Sector
Review 6 Technology Trends and Future History of Semiconductor Packaging Substrate Material Yoshihiro Nakamura Advanced Performance Materials Operational Headquarters Advanced Core Materials Business Sector
Thermal Cycling and Fatigue
 Thermal Cycling and Fatigue Gil Sharon Introduction The majority of electronic failures are thermo-mechanically related by thermally induced stresses and strains. The excessive difference in coefficients
Thermal Cycling and Fatigue Gil Sharon Introduction The majority of electronic failures are thermo-mechanically related by thermally induced stresses and strains. The excessive difference in coefficients
HMPP-386x Series MiniPak Surface Mount RF PIN Diodes
 HMPP-86x Series MiniPak Surface Mount RF PIN Diodes Data Sheet Description/Applications These ultra-miniature products represent the blending of Avago Technologies proven semiconductor and the latest in
HMPP-86x Series MiniPak Surface Mount RF PIN Diodes Data Sheet Description/Applications These ultra-miniature products represent the blending of Avago Technologies proven semiconductor and the latest in
High Efficient Heat Dissipation on Printed Circuit Boards. Markus Wille, R&D Manager, Schoeller Electronics Systems GmbH
 High Efficient Heat Dissipation on Printed Circuit Boards Markus Wille, R&D Manager, Schoeller Electronics Systems GmbH m.wille@se-pcb.de Introduction 2 Heat Flux: Q x y Q z The substrate (insulation)
High Efficient Heat Dissipation on Printed Circuit Boards Markus Wille, R&D Manager, Schoeller Electronics Systems GmbH m.wille@se-pcb.de Introduction 2 Heat Flux: Q x y Q z The substrate (insulation)
Enabling concepts: Packaging Technologies
 Enabling concepts: Packaging Technologies Ana Collado / Liam Murphy ESA / TEC-EDC 01/10/2018 ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Enabling concepts: Packaging Technologies Drivers for the future: Higher
Enabling concepts: Packaging Technologies Ana Collado / Liam Murphy ESA / TEC-EDC 01/10/2018 ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Enabling concepts: Packaging Technologies Drivers for the future: Higher
SNT Package User's Guide
 (Small outline Non-leaded Thin package) [Target Packages] SNT-4A SNT-6A SNT-6A (H) SNT-8A SNT Package User s Guide Introduction This manual describes the features, dimensions, mountability, reliability,
(Small outline Non-leaded Thin package) [Target Packages] SNT-4A SNT-6A SNT-6A (H) SNT-8A SNT Package User s Guide Introduction This manual describes the features, dimensions, mountability, reliability,
IPC J-STD-001E TRAINING AND CERTIFICATION PROGRAM LESSON PLAN FOR TRAINING CERTIFIED IPC SPECIALIST (CIS)
 Review Questions 1. Minimum end joint width for castellated terminations on a Class 2 product is. A. 100% (W). B. 25% (W). C. 50% (W). D. 75% (W). C, Clause. 7.5.6 Table 7-6, Page 29 2. For Class 3, a
Review Questions 1. Minimum end joint width for castellated terminations on a Class 2 product is. A. 100% (W). B. 25% (W). C. 50% (W). D. 75% (W). C, Clause. 7.5.6 Table 7-6, Page 29 2. For Class 3, a
For details on Vishay Siliconix MOSFETs, visit
 SiXXXX For details on MOSFETs, visit /mosfets/ Revision: 6-Oct-09 Document Number: 65580 For technical questions, contact: pmostechsupport@vishay.com THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE.
SiXXXX For details on MOSFETs, visit /mosfets/ Revision: 6-Oct-09 Document Number: 65580 For technical questions, contact: pmostechsupport@vishay.com THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE.
Assembly Instructions for SCA6x0 and SCA10x0 series
 Technical Note 71 Assembly Instructions for SCA6x0 and SCA10x0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI'S DIL-8 and DIL-12 packages...2 3 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
Technical Note 71 Assembly Instructions for SCA6x0 and SCA10x0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI'S DIL-8 and DIL-12 packages...2 3 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
EMERGING SUBSTRATE TECHNOLOGIES FOR PACKAGING
 EMERGING SUBSTRATE TECHNOLOGIES FOR PACKAGING Henry H. Utsunomiya Interconnection Technologies, Inc. Suwa City, Nagano Prefecture, Japan henryutsunomiya@mac.com ABSTRACT This presentation will outline
EMERGING SUBSTRATE TECHNOLOGIES FOR PACKAGING Henry H. Utsunomiya Interconnection Technologies, Inc. Suwa City, Nagano Prefecture, Japan henryutsunomiya@mac.com ABSTRACT This presentation will outline
Silicon Interposers enable high performance capacitors
 Interposers between ICs and package substrates that contain thin film capacitors have been used previously in order to improve circuit performance. However, with the interconnect inductance due to wire
Interposers between ICs and package substrates that contain thin film capacitors have been used previously in order to improve circuit performance. However, with the interconnect inductance due to wire
FEATURES DESCRIPTION ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS. T AMB = +25 C ( Unless otherwise specified )
 Monolithic PIN SP5T Diode Switch FEATURES Ultra Broad Bandwidth: 50MHz to 26GHz 1.0 db Insertion Loss 30 db Isolation at 20GHz Reliable. Fully Monolithic Glass Encapsulated Construction DESCRIPTION The
Monolithic PIN SP5T Diode Switch FEATURES Ultra Broad Bandwidth: 50MHz to 26GHz 1.0 db Insertion Loss 30 db Isolation at 20GHz Reliable. Fully Monolithic Glass Encapsulated Construction DESCRIPTION The
BGA (Ball Grid Array)
 BGA (Ball Grid Array) National Semiconductor Application Note 1126 November 2002 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Package Overview... 3 PBGA (PLASTIC BGA) CONSTRUCTION... 3 TE-PBGA (THERMALLY ENHANCED
BGA (Ball Grid Array) National Semiconductor Application Note 1126 November 2002 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Package Overview... 3 PBGA (PLASTIC BGA) CONSTRUCTION... 3 TE-PBGA (THERMALLY ENHANCED
Silicon PIN Limiter Diodes V 5.0
 5 Features Lower Insertion Loss and Noise Figure Higher Peak and Average Operating Power Various P1dB Compression Powers Lower Flat Leakage Power Reliable Silicon Nitride Passivation Description M/A-COM
5 Features Lower Insertion Loss and Noise Figure Higher Peak and Average Operating Power Various P1dB Compression Powers Lower Flat Leakage Power Reliable Silicon Nitride Passivation Description M/A-COM
UMS User guide for bare dies GaAs MMIC. storage, pick & place, die attach and wire bonding
 UMS User guide for bare dies GaAs MMIC storage, pick & place, die attach and wire bonding Ref. : AN00014097-07 Apr 14 1/10 Specifications subject to change without notice United Monolithic Semiconductors
UMS User guide for bare dies GaAs MMIC storage, pick & place, die attach and wire bonding Ref. : AN00014097-07 Apr 14 1/10 Specifications subject to change without notice United Monolithic Semiconductors
DOES PCB PAD FINISH AFFECT VOIDING LEVELS IN LEAD-FREE ASSEMBLIES?
 DOES PCB PAD FINISH AFFECT VOIDING LEVELS IN LEAD-FREE ASSEMBLIES? David Bernard Dage Precision Industries Fremont, CA d.bernard@dage-group.com Keith Bryant Dage Precision Industries Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire,
DOES PCB PAD FINISH AFFECT VOIDING LEVELS IN LEAD-FREE ASSEMBLIES? David Bernard Dage Precision Industries Fremont, CA d.bernard@dage-group.com Keith Bryant Dage Precision Industries Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire,
Processes for Flexible Electronic Systems
 Processes for Flexible Electronic Systems Michael Feil Fraunhofer Institut feil@izm-m.fraunhofer.de Outline Introduction Single sheet versus reel-to-reel (R2R) Substrate materials R2R printing processes
Processes for Flexible Electronic Systems Michael Feil Fraunhofer Institut feil@izm-m.fraunhofer.de Outline Introduction Single sheet versus reel-to-reel (R2R) Substrate materials R2R printing processes
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com -800-83-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. HPND- 4005 Beam Lead PIN Diode Data Sheet Description The HPND-4005 planar
Distributed by: www.jameco.com -800-83-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. HPND- 4005 Beam Lead PIN Diode Data Sheet Description The HPND-4005 planar
SiP packaging technology of intelligent sensor module. Tony li
 SiP packaging technology of intelligent sensor module Tony li 2016.9 Contents What we can do with sensors Sensor market trend Challenges of sensor packaging SiP technology to overcome challenges Overview
SiP packaging technology of intelligent sensor module Tony li 2016.9 Contents What we can do with sensors Sensor market trend Challenges of sensor packaging SiP technology to overcome challenges Overview
Advanced High-Density Interconnection Technology
 Advanced High-Density Interconnection Technology Osamu Nakao 1 This report introduces Fujikura s all-polyimide IVH (interstitial Via Hole)-multi-layer circuit boards and device-embedding technology. Employing
Advanced High-Density Interconnection Technology Osamu Nakao 1 This report introduces Fujikura s all-polyimide IVH (interstitial Via Hole)-multi-layer circuit boards and device-embedding technology. Employing
MAAP Power Amplifier, 15 W GHz Rev. V1. Features. Functional Schematic. Description. Pin Configuration 2. Ordering Information
 Features 15 W Power Amplifier 42 dbm Saturated Pulsed Output Power 17 db Large Signal Gain P SAT >40% Power Added Efficiency Dual Sided Bias Architecture On Chip Bias Circuit 100% On-Wafer DC, RF and Output
Features 15 W Power Amplifier 42 dbm Saturated Pulsed Output Power 17 db Large Signal Gain P SAT >40% Power Added Efficiency Dual Sided Bias Architecture On Chip Bias Circuit 100% On-Wafer DC, RF and Output
Flip Chips. FA10-200x200 FA10-400x400 FA10-600x x 200 mils 400 x 400 mils
 Flip Chip FlipChip International Flip Chip describes the method of electrically connecting the die to the package carrier. The package carrier, either substrate or leadframe, then provides the connection
Flip Chip FlipChip International Flip Chip describes the method of electrically connecting the die to the package carrier. The package carrier, either substrate or leadframe, then provides the connection
Flip-Chip PBGA Package ConstructionÑ Assembly and Board-Level Reliability
 Order Number: AN1850/D Rev. 0, 5/2000 Application Note Flip-Chip PBGA Package ConstructionÑ Assembly and Motorola introduced the ßip-chip plastic ball grid array (FC PBGA) packages as an alternative to,
Order Number: AN1850/D Rev. 0, 5/2000 Application Note Flip-Chip PBGA Package ConstructionÑ Assembly and Motorola introduced the ßip-chip plastic ball grid array (FC PBGA) packages as an alternative to,
Advanced Packaging - Pulsed-laser Heating for Flip Chip Assembly
 Page 1 of 5 Pulsed-laser Heating for Flip Chip Assembly A stress-free alternative By Thorsten Teutsch, Ph.D., Pac Tech USA, Elke Zakel, Ph.D., and Ghassem Azdasht, Pac Tech GmbH As flip chip applications
Page 1 of 5 Pulsed-laser Heating for Flip Chip Assembly A stress-free alternative By Thorsten Teutsch, Ph.D., Pac Tech USA, Elke Zakel, Ph.D., and Ghassem Azdasht, Pac Tech GmbH As flip chip applications
Assembly/Packagng RF-PCB. Thick Film. Thin Film. Screening/Test. Design Manual
 Thick Film Thin Film RF-PCB Assembly/Packagng Screening/Test Design Manual RHe Design Manual The following rules are effective for the draft of circuit boards and hybrid assemblies. The instructions are
Thick Film Thin Film RF-PCB Assembly/Packagng Screening/Test Design Manual RHe Design Manual The following rules are effective for the draft of circuit boards and hybrid assemblies. The instructions are
BOARD DESIGN, SURFACE MOUNT ASSEMBLY AND BOARD LEVEL RELIABILITY ASPECTS OF FUSIONQUAD TM PACKAGES
 BOARD DESIGN, SURFACE MOUNT ASSEMBLY AND BOARD LEVEL RELIABILITY ASPECTS OF FUSIONQUAD TM PACKAGES Ahmer Syed 1, Sundar Sethuraman 2, WonJoon Kang 1, Gary Hamming 1, YeonHo Choi 1 1 Amkor Technology, Inc.
BOARD DESIGN, SURFACE MOUNT ASSEMBLY AND BOARD LEVEL RELIABILITY ASPECTS OF FUSIONQUAD TM PACKAGES Ahmer Syed 1, Sundar Sethuraman 2, WonJoon Kang 1, Gary Hamming 1, YeonHo Choi 1 1 Amkor Technology, Inc.
NPL Report MATC(A)92 An Review of Electronics Materials Deposition Techniques Including Solder Jetting and Relief Printing
 An Review of Electronics Materials Deposition Techniques Including Solder Jetting and Relief Printing Martin Wickham, Ling Zou, Milos Dusek & Christopher Hunt April 2002 SENSOR NPL Report MATC(A) 92 April
An Review of Electronics Materials Deposition Techniques Including Solder Jetting and Relief Printing Martin Wickham, Ling Zou, Milos Dusek & Christopher Hunt April 2002 SENSOR NPL Report MATC(A) 92 April
Chip Assembly on MID (Molded Interconnect Device) A Path to Chip Modules with increased Functionality
 T e c h n o l o g y Dr. Werner Hunziker Chip Assembly on MID (Molded Interconnect Device) A Path to Chip Modules with increased Functionality The MID (Molded Interconnect Device) technology enables the
T e c h n o l o g y Dr. Werner Hunziker Chip Assembly on MID (Molded Interconnect Device) A Path to Chip Modules with increased Functionality The MID (Molded Interconnect Device) technology enables the
An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging. Prof. G. V. Mahesh. Department of Electronic Systems Engineering
 An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 33 Reflow and Wave
An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 33 Reflow and Wave
MADP Solderable AlGaAs Flip Chip PIN. Features. Chip Dimensions. Description. Applications
 Features Low Series Resistance Ultra Low Capacitance Millimeter Wave Switching & Cutoff Frequency 2 Nanosecond Switching Speed Can be Driven by a Buffered TTL Silicon Nitride Passivation Polyimide Scratch
Features Low Series Resistance Ultra Low Capacitance Millimeter Wave Switching & Cutoff Frequency 2 Nanosecond Switching Speed Can be Driven by a Buffered TTL Silicon Nitride Passivation Polyimide Scratch
New Power MOSFET. 1. Introduction. 2. Application of Power MOSFETs. Naoto Fujisawa Toshihiro Arai Tadanori Yamada
 New Power MOSFET Naoto Fujisawa Toshihiro Arai Tadanori Yamada 1. Introduction Due to the finer patterns and higher integration of LSIs, functions that were used a few years ago in minicomputers have now
New Power MOSFET Naoto Fujisawa Toshihiro Arai Tadanori Yamada 1. Introduction Due to the finer patterns and higher integration of LSIs, functions that were used a few years ago in minicomputers have now
IC Packaging/Intro. ICs are at the core of a modern digital system Many systems fit entirely on a single IC (SOC)
 IC Packaging/Intro ICs are at the core of a modern digital system Many systems fit entirely on a single IC (SOC) a single (15-mm) 2 chip can hold several million gates (1997) a simple 32-bit CPU can be
IC Packaging/Intro ICs are at the core of a modern digital system Many systems fit entirely on a single IC (SOC) a single (15-mm) 2 chip can hold several million gates (1997) a simple 32-bit CPU can be
The Role of Flip Chip Bonding in Advanced Packaging David Pedder
 The Role of Flip Chip Bonding in Advanced Packaging David Pedder David Pedder Associates Stanford in the Vale Faringdon Oxfordshire The Role of Flip Chip Bonding in Advanced Packaging Outline Flip Chip
The Role of Flip Chip Bonding in Advanced Packaging David Pedder David Pedder Associates Stanford in the Vale Faringdon Oxfordshire The Role of Flip Chip Bonding in Advanced Packaging Outline Flip Chip
Compression Molding. Solutions for 3D TSV and other advanced packages as well as cost savings for standard package applications
 Compression Molding Solutions for 3D TSV and other advanced packages as well as cost savings for standard package applications 1. Company Introduction 2. Package Development Trend 3. Compression FFT Molding
Compression Molding Solutions for 3D TSV and other advanced packages as well as cost savings for standard package applications 1. Company Introduction 2. Package Development Trend 3. Compression FFT Molding
Applications of Solder Fortification with Preforms
 Applications of Solder Fortification with Preforms Carol Gowans Indium Corporation Paul Socha Indium Corporation Ronald C. Lasky, PhD, PE Indium Corporation Dartmouth College ABSTRACT Although many have
Applications of Solder Fortification with Preforms Carol Gowans Indium Corporation Paul Socha Indium Corporation Ronald C. Lasky, PhD, PE Indium Corporation Dartmouth College ABSTRACT Although many have
Our Top 10 Commonly Asked Soldering Questions This Year
 Our Top 10 Commonly Asked Soldering Questions This Year 1 Chip Component Shifting Can be related to components floating on the molten solder plus the equipment may have vibrations, which may not be felt
Our Top 10 Commonly Asked Soldering Questions This Year 1 Chip Component Shifting Can be related to components floating on the molten solder plus the equipment may have vibrations, which may not be felt
HOTBAR REFLOW SOLDERING
 HOTBAR REFLOW SOLDERING Content 1. Hotbar Reflow Soldering Introduction 2. Application Types 3. Process Descriptions > Flex to PCB > Wire to PCB 4. Design Guidelines 5. Equipment 6. Troubleshooting Guide
HOTBAR REFLOW SOLDERING Content 1. Hotbar Reflow Soldering Introduction 2. Application Types 3. Process Descriptions > Flex to PCB > Wire to PCB 4. Design Guidelines 5. Equipment 6. Troubleshooting Guide
3D TSV Micro Cu Column Chip-to-Substrate/Chip Assmbly/Packaging Technology
 3D TSV Micro Cu Column Chip-to-Substrate/Chip Assmbly/Packaging Technology by Seung Wook Yoon, *K. T. Kang, W. K. Choi, * H. T. Lee, Andy C. B. Yong and Pandi C. Marimuthu STATS ChipPAC LTD, 5 Yishun Street
3D TSV Micro Cu Column Chip-to-Substrate/Chip Assmbly/Packaging Technology by Seung Wook Yoon, *K. T. Kang, W. K. Choi, * H. T. Lee, Andy C. B. Yong and Pandi C. Marimuthu STATS ChipPAC LTD, 5 Yishun Street
High efficient heat dissipation on printed circuit boards
 High efficient heat dissipation on printed circuit boards Figure 1: Heat flux in a PCB Markus Wille Schoeller Electronics Systems GmbH www.schoeller-electronics.com Abstract This paper describes various
High efficient heat dissipation on printed circuit boards Figure 1: Heat flux in a PCB Markus Wille Schoeller Electronics Systems GmbH www.schoeller-electronics.com Abstract This paper describes various
SOLDERABLE ANISOTROPIC CONDUCTIVE ADHESIVES FOR 3D PACKAGE APPLICATIONS
 SOLDERABLE ANISOTROPIC CONDUCTIVE ADHESIVES FOR 3D PACKAGE APPLICATIONS ABSTRACT: Dr. Mary Liu and Dr. Wusheng Yin YINCAE Advanced Materials, LLC Albany, NY 3D packaging has recently become very attractive
SOLDERABLE ANISOTROPIC CONDUCTIVE ADHESIVES FOR 3D PACKAGE APPLICATIONS ABSTRACT: Dr. Mary Liu and Dr. Wusheng Yin YINCAE Advanced Materials, LLC Albany, NY 3D packaging has recently become very attractive
Webinar: Suppressing BGAs and/or multiple DC rails Keith Armstrong. 1of 5
 1of 5 Suppressing ICs with BGA packages and multiple DC rails Some Intel Core i5 BGA packages CEng, EurIng, FIET, Senior MIEEE, ACGI Presenter Contact Info email: keith.armstrong@cherryclough.com website:
1of 5 Suppressing ICs with BGA packages and multiple DC rails Some Intel Core i5 BGA packages CEng, EurIng, FIET, Senior MIEEE, ACGI Presenter Contact Info email: keith.armstrong@cherryclough.com website:
Line-Following Robot
 1 Line-Following Robot Printed Circuit Board Assembly Jeffrey La Favre October 5, 2014 After you have learned to solder, you are ready to start the assembly of your robot. The assembly will be divided
1 Line-Following Robot Printed Circuit Board Assembly Jeffrey La Favre October 5, 2014 After you have learned to solder, you are ready to start the assembly of your robot. The assembly will be divided
14.8 Designing Boards For BGAs
 exposure. Maintaining proper control of moisture uptake in components is critical to the prevention of "popcorning" of the package body or encapsulation material. BGA components, before shipping, are baked
exposure. Maintaining proper control of moisture uptake in components is critical to the prevention of "popcorning" of the package body or encapsulation material. BGA components, before shipping, are baked
TAIPRO Engineering. Speaker: M. Saint-Mard Managing director. TAIlored microsystem improving your PROduct
 TAIPRO Engineering MEMS packaging is crucial for system performance and reliability Speaker: M. Saint-Mard Managing director TAIPRO ENGINEERING SA Michel Saint-Mard Administrateur délégué m.saintmard@taipro.be
TAIPRO Engineering MEMS packaging is crucial for system performance and reliability Speaker: M. Saint-Mard Managing director TAIPRO ENGINEERING SA Michel Saint-Mard Administrateur délégué m.saintmard@taipro.be
Design and Development of True-CSP
 Design and Development of True-CSP *Kolan Ravi Kanth, Francis K.S. Poh, B.K. Lim, Desmond Y.R. Chong, Anthony Sun, H.B. Tan United Test & Assembly Center Ltd (UTAC) 5 Serangoon North Ave 5, Singapore 554916
Design and Development of True-CSP *Kolan Ravi Kanth, Francis K.S. Poh, B.K. Lim, Desmond Y.R. Chong, Anthony Sun, H.B. Tan United Test & Assembly Center Ltd (UTAC) 5 Serangoon North Ave 5, Singapore 554916
PMEG6002EB; PMEG6002TV
 Rev. 01 24 November 2006 Product data sheet 1. Product profile 1.1 General description Planar Maximum Efficiency General Application (MEGA) Schottky barrier rectifiers with an integrated guard ring for
Rev. 01 24 November 2006 Product data sheet 1. Product profile 1.1 General description Planar Maximum Efficiency General Application (MEGA) Schottky barrier rectifiers with an integrated guard ring for
Features. = 25 C, IF = 3 GHz, LO = +16 dbm
 mixers - i/q mixers / irm - CHIP Typical Applications This is ideal for: Point-to-Point Radios Test & Measurement Equipment SATCOM Radar Functional Diagram Features Wide IF Bandwidth: DC - 5 GHz High Image
mixers - i/q mixers / irm - CHIP Typical Applications This is ideal for: Point-to-Point Radios Test & Measurement Equipment SATCOM Radar Functional Diagram Features Wide IF Bandwidth: DC - 5 GHz High Image
Surface Mount RF PIN Low Distortion Attenuator Diodes. Technical Data. HSMP-381x Series and HSMP-481x Series. Features
 Surface Mount RF PIN Low Distortion Attenuator Diodes Technical Data HSMP-81x Series and HSMP-481x Series Features Diodes Optimized for: Low Distortion Attenuating Microwave Frequency Operation Surface
Surface Mount RF PIN Low Distortion Attenuator Diodes Technical Data HSMP-81x Series and HSMP-481x Series Features Diodes Optimized for: Low Distortion Attenuating Microwave Frequency Operation Surface
SMPP Series. Surface Mount Plastic PIN Diodes. Features. Description and Applications. Package Outlines. Rev. V22
 Features Industry Surface Mount Packages Lead-Free () Equivalents Available with 260 C Reflow Compatibility Low Loss, igh Isolation Switching Diodes Low Distortion Attenuator Diodes Single and Dual Diode
Features Industry Surface Mount Packages Lead-Free () Equivalents Available with 260 C Reflow Compatibility Low Loss, igh Isolation Switching Diodes Low Distortion Attenuator Diodes Single and Dual Diode
Features. Preliminary. = +25 C, IF = 1 GHz, LO = +13 dbm*
 Typical Applications Features The is ideal for: Test Equipment & Sensors Point-to-Point Radios Point-to-Multi-Point Radios Military & Space Functional Diagram Wide IF Bandwidth: DC - 17 GHz Input IP3:
Typical Applications Features The is ideal for: Test Equipment & Sensors Point-to-Point Radios Point-to-Multi-Point Radios Military & Space Functional Diagram Wide IF Bandwidth: DC - 17 GHz Input IP3:
Application Note. Soldering Guidelines for Module PCB Mounting Rev 13
 Application Note Soldering Guidelines for Module PCB Mounting Rev 13 OBJECTIVE The objective of this application note is to provide ANADIGICS customers general guidelines for PCB second level interconnect
Application Note Soldering Guidelines for Module PCB Mounting Rev 13 OBJECTIVE The objective of this application note is to provide ANADIGICS customers general guidelines for PCB second level interconnect
Pin Connections and Package Marking. GUx
 Surface Mount RF PIN Switch Diodes Technical Data HSMP-389x Series HSMP-89x Series Features Unique Configurations in Surface Mount Packages Add Flexibility Save Board Space Reduce Cost Switching Low Capacitance
Surface Mount RF PIN Switch Diodes Technical Data HSMP-389x Series HSMP-89x Series Features Unique Configurations in Surface Mount Packages Add Flexibility Save Board Space Reduce Cost Switching Low Capacitance
APPLICATION NOTE 6381 ORGANIC LAND GRID ARRAY (OLGA) AND ITS APPLICATIONS
 Keywords: OLGA, SMT, PCB design APPLICATION NOTE 6381 ORGANIC LAND GRID ARRAY (OLGA) AND ITS APPLICATIONS Abstract: This application note discusses Maxim Integrated s OLGA and provides the PCB design and
Keywords: OLGA, SMT, PCB design APPLICATION NOTE 6381 ORGANIC LAND GRID ARRAY (OLGA) AND ITS APPLICATIONS Abstract: This application note discusses Maxim Integrated s OLGA and provides the PCB design and
TOLERANCE FORGOTTEN: IMPACTS OF TODAY S COMPONENT PACKAGING AND COPPER ROUTING ON ELECTRONIC
 TOLERANCE FORGOTTEN: IMPACTS OF TODAY S COMPONENT PACKAGING AND COPPER ROUTING ON ELECTRONIC Presented By: Dale Lee E-mail: Dale.Lee@Plexus.Com April 2013 High Layer Counts Wide Range Of Component Package
TOLERANCE FORGOTTEN: IMPACTS OF TODAY S COMPONENT PACKAGING AND COPPER ROUTING ON ELECTRONIC Presented By: Dale Lee E-mail: Dale.Lee@Plexus.Com April 2013 High Layer Counts Wide Range Of Component Package
High Current Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) Uses DirectFET MOSFETs to Achieve Current Densities of 25A/in2 at 1MHz to Power 32-bit Servers
 High Current Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) Uses DirectFET MOSFETs to Achieve Current Densities of 25A/in2 at 1MHz to Power 32-bit Servers Ralph Monteiro, Carl Blake and Andrew Sawle, Arthur Woodworth
High Current Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) Uses DirectFET MOSFETs to Achieve Current Densities of 25A/in2 at 1MHz to Power 32-bit Servers Ralph Monteiro, Carl Blake and Andrew Sawle, Arthur Woodworth
Sectional Design Standard for High Density Interconnect (HDI) Printed Boards
 IPC-2226 ASSOCIATION CONNECTING ELECTRONICS INDUSTRIES Sectional Design Standard for High Density Interconnect (HDI) Printed Boards Developed by the HDI Design Subcommittee (D-41) of the HDI Committee
IPC-2226 ASSOCIATION CONNECTING ELECTRONICS INDUSTRIES Sectional Design Standard for High Density Interconnect (HDI) Printed Boards Developed by the HDI Design Subcommittee (D-41) of the HDI Committee
Low Thermal Resistance Flip-Chip Bonding of 850nm 2-D VCSEL Arrays Capable of 10 Gbit/s/ch Operation
 Low Thermal Resistance Flip-Chip Bonding of 85nm -D VCSEL Arrays Capable of 1 Gbit/s/ch Operation Hendrik Roscher In 3, our well established technology of flip-chip mounted -D 85 nm backside-emitting VCSEL
Low Thermal Resistance Flip-Chip Bonding of 85nm -D VCSEL Arrays Capable of 1 Gbit/s/ch Operation Hendrik Roscher In 3, our well established technology of flip-chip mounted -D 85 nm backside-emitting VCSEL
Enabling Parallel Testing at Sort for High Power Products
 Enabling Parallel Testing at Sort for High Power Products Abdel Abdelrahman Tim Swettlen 2200 Mission College Blvd. M/S SC2-07 Santa Clara, CA 94536 Abdel.Abdelrahman@intel.com Tim.Swettlen@intel.com Agenda
Enabling Parallel Testing at Sort for High Power Products Abdel Abdelrahman Tim Swettlen 2200 Mission College Blvd. M/S SC2-07 Santa Clara, CA 94536 Abdel.Abdelrahman@intel.com Tim.Swettlen@intel.com Agenda
Flip-Chip for MM-Wave and Broadband Packaging
 1 Flip-Chip for MM-Wave and Broadband Packaging Wolfgang Heinrich Ferdinand-Braun-Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik (FBH) Berlin / Germany with contributions by F. J. Schmückle Motivation Growing markets
1 Flip-Chip for MM-Wave and Broadband Packaging Wolfgang Heinrich Ferdinand-Braun-Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik (FBH) Berlin / Germany with contributions by F. J. Schmückle Motivation Growing markets
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit V DD supply voltage
 Rev. 01 5 February 2008 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features 3. Applications 4. Quick reference data The is a CMOS quartz oscillator optimized for low power consumption. The 32 khz output
Rev. 01 5 February 2008 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features 3. Applications 4. Quick reference data The is a CMOS quartz oscillator optimized for low power consumption. The 32 khz output
