It Was the Best of. My LITTLE Book. Tricks. of big Multiplication. Mike McCabe
|
|
|
- Posy Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 It Was the Best of TIMES My LITTLE Book of big Multiplication Tricks Mike McCabe
2 The Quick Response (QR) Code 1. You will need to download an app from your smartphone. 2. Once you have it downloaded, follow the instructions on your phone. Just scan the QR code and the link should appear on the smartphone. 3. Apps that you may consider are: iphone Scan (Free), Quickmark ($1), Optiscan ($2) BlackBerry Code Scanner Pro (Free) Android Barcode Scanner (Free) Scan here to access my website 1
3 Table of Contents Page Topic 3... Multiplying by Doubling and Halving 7...Multiplying by Multiplying by 4 11.Multiplying by 5 13.Multiplying an Even Number by Multiplying by 8 17.Multiplying by 9 20.Multiplying by 9 Using Finger Tricks 22.Fun Trick With x9 Facts 23.Multiplying Single Digits Finger Tricks (Dactylonomy) 25.Multiplying by x tables: Using Equivalent Fractions to ½ 29.Multiplying by Multiplying Two-Digit Numbers Where the Tens Digits arethesame and the Ones Digits Have a Sum of Ten 33.Multiplying Two-Digit Numbers that End in 1 35.Multiplying Two-Digit and Three-Digit Numbers by 7x11x13! 37.Difference of Squares 2
4 Multiplying by 2 Multiplying by 2 is the simplest concept of doubling. Students come to multiplying with an understanding of doubling. They have played clapping games, skipping games, they know rhymes and songs that reinforce these concepts. This is also the basis for a number of the strategies such as multiplying by 4 and 8). What should be reinforced: When the doubling requires regrouping, the students tend to have more difficulty i.e., 16 x 2 =?. We can assist students by providing more than one strategy (apart from the traditional method). We can have students say: Example: 1 Distributive: (10 x 2) + (6 x 2) = = 32 Or Using more common facts (15 x 2) + 2 = = 32 We can also reinforce the common doubles (such as 16 x 2 = 32 and 48 x 2 = 96) through repetition and the strategy mentioned above, namely, distributive: 48 x 2 = (40 x 2) + (8 x 2). 3
5 Practice: 9 x 2 27 x x 2 First strategy used (memory,distributiv e, using simpler facts, other ) Second strategy used (memory, distributive, using simpler facts, other ) 4
6 Doubling and Halving This strategy is used when multiplying numbers. It is done by halving one number and doubling another number and is especially good for circumstances when the half of a number is easily recognized. Example #1: 42 x 50 = Steps: A. Take the two numbers you are multiplying (e.g. 42 x 50) B. Think one-half of 42 is 21, and C. Think 50 doubled is 100. D. Now multiply the two new numbers. Therefore, 21 x 100 is 2,100. Example #2: 4.5 x 2.2 = A. Think double 4.5 to get 9 B. Think one-half of 2.2 is 1.1. C. Now multiply the two new numbers. Therefore 9 x 1.1 = 9.9 5
7 Practice Steps 36 x 4 22 x 35 A. Take the two numbers you are multiplying B. Double one of the numbers and half the other one. C. Now multiply the two new numbers. How it Works: Because we are doing opposite things to the two numbers (doubling one and halving the other), it keeps the question essentially the same. All we are doing ismanipulating the numbers to find numbers that are easier to work with mentally and on paper. 6
8 Multiplying by 3 (Are these numbers multiples of 3?) Steps: Add all up all the digits of the product until you have a single digit (This is called the digit sum). If that number is divisible by 3, so is the original number. Example #1: =? = = 3 3 is divisible by 3, therefore 8787 is also divisible by 3 Example #2: =? = = 7 7 is not divisible by 3, therefore is not divisible by 3 either Example #3: =? = 9 9 is divisible by 3, therefore 2340 is also divisible by 3 7
9 Practice: Are these numbers multiples of 3? Add digit sum Is the digit sum a multiple of three?. 8
10 Multiplying by 4 When multiplying by 4, it simply means multiply by 2 and then multiply by 2 again or double, double (The Tim Horton s strategy). Whenever we multiply by 4 take the number and double it, then double it again. Example #1: 16 x 4 = Double 16 = 32 Double 32 = 64 Example#2: 215 x 4 = Double 215 = 430 Double 430 = 860 Example # 3: 1546 x 4 = Double1546 = (2 x 1000) + (2 x (2 x 40) + (2 x 6) = (distributive property) 9
11 Practice: 26 x x 4 532x 4 Double Double again (Did you use the distributive property?) 10
12 Multiply by 5 To multiply by 5, you must understand that multiplying by 5 is the same as multiplying by 10 and dividing by = 5 or 2 x 10 = 5 Example #1: 88 x 5 = Steps: These steps can be done in reverse order depending upon the question = communicative property. A. Divide the number by two 88 2 = 44 B. Multiply by x 10 = 440 Example #2: 25 x 5 = Steps: Steps are reversed from above. A. Multiply by x 10 = 250. B. Divide the number by two =
13 Practice: 28 x x x 5 x 10 2 (or you could do these in reverse order) 12
14 Multiplying an Even Number by 6 This trick only works for multiplying 6 by even numbers. See note below for odd numbers Example #1: 6 x 8 = Steps: A. Take the second number in the equation (8) and move it to the one s column. 6 x 8 = 8 B. Half the second number in the equation (8 2 = 4) and move it to the ten s column 6 x 8 = 48 Example #2: 6 x 24 = Steps: A. Take the ones column from the second number in the equation (that s the 4 from 24) and move it to the one s column 6 x 24 = 4 A. Half the second number in the equation (24 2 = 12) and move it to the ten s column BUT you must add the 2 that is already in the tens column. Therefore, = 14 6 x 24 = 144 Note: To use an odd multiple of 6, i.e., 6 x 25, all you have to do is 6 x 24 then add 6. 13
15 Practice: 6 x 6 32 x 6 84 x 6 Write down the number you are multiplying by (if it is greater than 10, regroup the 10 s column) Take half of the number you just wrote down and put it in the tens column (add the regrouped number to this) 14
16 Multiplying by 8 8 = 2 x 2 x 2 When multiplying by 8, it simply means double, double, double. Whenever wemultiply by 8 take the number, double it, double it again then double it again. Example #1: 9 x 8 = double 9 = 18 double 18 = 36 double 36 = 72 As with the x4, you will need practice with some common double facts. This can be learned using distributive properties. Example #2: 16 x 8 = double 16 = 32 double 32 = 64 double 64 = (60 x 2) + (4 x 2) = =
17 Practice: 24 x x 8 431x 8 Double Double again (Did you use distributive property?) Double again (Did you use distributive property?) 16
18 Multiplying by 9 Multiplying by 9s provides so many opportunities for recognizing patterns. Pattern #1 When you add the digit sum of any multiple of 9, it always equals 9. So Example #1 1 x 9 = 09 2 x 9 = 18 3 x 9 = 27 4 x 9 = 36 5 x 9 = 45 6 x 9 = 54 7 x 9 = 63 8 x 9 = 72 9 x 9 = x 9 = x 9 = = 9 Example # x 9 = 29, = 18, and = = = = = = = = = = = 9 17
19 Practice: Multiply 16 x x 9 431x 9 Find the product sum Is the number a multiple of nine? 18
20 Multiplying by 9 Pattern #2 When you multiply a single digit by 9, simply write a number that is one less than the number you are multiplying by 9; i.e. 8 x 9 = 7? (because 7 is one less than 8). Now add whatever you need to the 7 to make a total of 9. i.e. 7 +? = = 9 Therefore, 8 x 9 = 72 1 x 9 = 09 2 x 9 = 18 3 x 9 = 27 4 x 9 = 36 5 x 9 = 45 6 x 9 = 54 7 x 9 = 63 8 x 9 = 72 9 x 9 = x 9 = 90 19
21 Multiplying by 9 Using Finger Tricks Because we need a digit sum of 9 when multiplying by 9, we can use our fingers. Steps: 1. Hold your two hands in front of you so you are looking at the back of your hands and your thumbs are touching. Counting from left to right, number your fingers 1,2,3, When you multiply, 3 x 9, fold down digit 3(that should be your left middle finger- see diagram below). 3. Count the number of fingers to the left of the downed finger. This is your 10 s column. In this case you should have 2 in the tens column = 2_. 4. Now count the fingers to the right of the downed finger. This is your ones column. In this case you should have 7 in the ones column = 27 20
22 Practice: Tens Column (Number of fingers to the left of the downed finger) Ones Column (Number of fingers to the right of the downed finger) 4 x 9 = 7 x 9 = 21
23 Fun Trick Here s a trick you can do using your x 9 facts. Steps: A. Choose a number between 1 and 10 (let s choose 7) B. Multiply that number by nine (9 x 7 = 63) C. Add the two digits of your number (63 = 6+3= 9) D. Subtract five (9 5 = 4) E. Find the corresponding letter of the alphabet (A=1; B=2; C=3; D=4 ) F. Think of a country that begins with that letter. (most people choose Denmark) G. Think of an animal that begins with the second letter of the country (most people choose Elelphant) H. Think of the colour of the animal (grey) Once your friends are finished, tell them that : GREY ELEPHANTS DO NOT LIVE IN DENMARK! 22
24 Multiplying Single DigitsFingerTricks (Dactylonomy) This strategy could be used for multiplying from 6 x 6 to 10 x 10. Please see accompanying diagram below. KEEP THUMBS AT THE PONTED DOWNWARD FOR ALL CALCULATIONS. Steps: A. Number thumbs = 6, Index fingers = 7, Tommy Tall = 8, Ring man = 9 Pinkie = 10 B. Put digits together for question, ex., 7 x 8, touch index finger on one hand to Tommy tall on the other hand (see line connecting the two below). C. For the tens column: Count the two touching fingers and any finger below them. In this example = 5_ D. For the ones column: Multiply the number of fingers above the touching fingers on the left hand x the number of fingers above the touching fingers on the right hand. In this example, 3 x 2 = 6Therefore, 7 x 8 =
25 Practice Steps 9 x 6 = 6 x 7 = Touch the two fingers together (remember, thumbs at the bottom) Tens Column: (Count the number of fingers touching and below the touching fingers) Ones Column: (Multiply the fingers above the touching fingers) 24
26 Multiplying by 11 You can use this to understand how to separate concepts. This can expand and be used for multiplying, ex., 11 X etc. Steps: A. Single digit answer Ex x 72 = (separate 7 2) Hundreds Ones B. Now add the numbers that are beside each other = 9 tens 11 x 72 = Ex x 5432 = 5 _ 2 Now add the numbers that are beside each other = = = 5 Therefore the answer is Regrouping 11 x 77 = (separate 7 7) Hundreds Ones (7 + 7) = 14 (regroup) (addthe 1 to hundreds) (tens) 11 x 77 = (7 +1 ) x 77 =
27 Practice 11 x 36 = 11 x 4532= 11 x 4785 = Separate the first and last digit Now add the numbers that are beside each other. (remember to regroup if necessary) Write the final answer 26
28 12 x Tables: Using Equivalent Fractions to ½ Steps: ex. 12 x 8 = A. When multiplying a number by 12, take the number that you are multiplying (ex. 8) and find its equivalent fraction to ½ (ex.. 8/16). B. Add the numerator to the tens column of the denominator (8 + 1 = 9). C. The answer in Step B. becomes the tens column and the ones in the denominator becomes the ones column. ( = 96). Therefore, 12 x 8 = 8/16 = = 9, followed by x 8 = 96 This can be used with three-digit denominators or numerators as well. Examples: 12 x 3 = 3/6 = x 6 = 6/12 = 72 (add the 6 & 1) 12 x 7 = 7 / 14 = 84 (add the 7 & 1) 12x11 = 11/ 22 = x12 = 12 /24 = x31 = 31 /62 = 372 (add the 31 & 6) 12x47 = 47 / 94 = x70 = 70/140 = 840 (add the 70 & 14) 27
29 Practice Steps 12 x x x 150 A. Find an equivalent fraction to ½ using the number you are multiplying as the numerator. B. Add the numerator to the tens column of the denominator. C. The answer in Step B. becomes the tens column and the ones in the denominator becomes the ones column. D. Write the final answer 28
30 Multiplying two numbers between 11 and 19 Example #1: 19 x 13 = Steps: A. Write the larger of the two numbers above the smaller number. 19 x 13 B. Add the larger number to the ones column of the smaller number. Multiply this sum by 10 (add a zero) = x 10 = 220 C. Next, multiply the two numbers in the ones column of the original question. 9 x 3 = 27 D. Add the solution of Step B to the solution found in Step C. This number is the answer to your original multiplication question =
31 Practice: Steps: A. Write the larger of the two numbers above the smaller number. 18 x 14 = 15 x 12 = B. Add the larger number to the ones column of the smaller number. Multiply this sum by 10 (add a zero). C. Next, multiply the two numbers in the ones column of the original question. D. Add the solution of Step B to the solution found in Step C. This number is the answer to your original multiplication question. 30
32 Multiplying Two- Digit Numbers Where the Tens Digits are the Same and the Ones Digits Have a Sum of Ten Example #1: 42 x 48 = (tens digits are the same and the ones add to ten) Steps: A. Multiply the number in the tens column by the next consecutive number (in the example above, 4 x 5 = 20). That makes the first two digits of your answer. 20 B. Check to make sure that the digits in the ones column, when added together, have a sum of 10 (2 + 8 = 10). Then multiply those two numbers together (2 x 8 = 16). - This makes the last two digits of your answer x 48 = 2016 Answer: 42 x 48 = 2016 Example #2: 64 x 66 = Steps: A = 7. Therefore 6 x 7 = 42 B = 10. Therefore 6 x 4 = 24 C. Answer: 4224 Practice 31
33 Steps 27 x 23 = 75 x 75 = A. Multiply the number in the tens column by the next consecutive number. That makes the first two digits of your answer. D. Check to make sure that the digits in the ones column, when added together, have a sum of 10 Then multiply those two numbers together. E. This makes the last two digits of your answer. ultiplying Two-Digit Numbers 32
34 that End in 1 Steps: A. Multiply the digits in the "tens" column together. B. Add a 0 (multiply by 10) after the product obtained in Step A. C. Add the digits in the "tens" columns together. D. Add the sum of the number obtained in Step C. to the number found in Step B. E. Put on a one (1) in the ones column. Example #1: 61 x 51 = A. 6 x 5 = 30 B. 300 C = 11 D = 311 E Example #2: 41 x 81 = A. 4 x 8 = 32 B. 320 C = 12 D = 332 E
35 Practice Steps 91 x 31 = 71 x 71 = A. Multiply the digits in the "tens" column together. B. Add a 0 (multiply by 10) after the product obtained in Step A. C. Add the digits in the "tens" columns together. D. Add the sum of the number obtained in Step C. to the number found in Step B. E. Put on a one (1) in the ones column. 34
36 Multiplying Two-Digit and Three-Digit Numbers by 7 x 11 x 13! This trick makes you look like your brain is a mega calculator! (And it is!) Three Digit Numbers: A. Ask a friend to write down ANY three digit number (e.g. 231 or 884) B. Ask them to multiply the number x 7 x 11 x 13 (e.g. 231 x 7 x 11 x 13) C. All you do is write out the beginning number twice! So 231 will become and 884 will become Two Digit Numbers: A. Ask a friend to write down ANY two digit number(e.g. 52 or 21) B. Ask them to multiply: number x 7 x 11 x 13 (e.g. 52 x 7 x 11 x 13) C. All you do is write out the starting number twice witha 0 in between! So 52 will become and 21 will become Practice 35
37 Steps A. Ask a friend to write down ANY three digit (or two digit) number B. Ask them to multiply the number x 7 x 11 x 13 C. All you do is write out the beginning number twice! (For the two digit number write out the starting number twice with a 0 in between) 36
38 Difference of Squares Soon, in algebra, you will be introduced to the Difference of Squares. It is described in short form below. Steps: A. Recognize two numbers that you are multiplying have a middle number, ex., 9 x 7, (the middle number is 8). Or 24 x 26, the middle number is 25. B. Take the middle number and multiply it by itself ex., 8 2 or 25 2 C. Subtract 1 from the answer. Example #1: 11 x 13 = Steps A. 12 is the middle number. B. 12 x 12 = 144 C = 143. Therefore, 11 x 13 = 143 Example #2: 199 x 201 = Steps A. 200 is the middle number. B. 200 x 200 = C =
39 Practice Steps A. Recognize two numbers that you are multiplying have a middle number. 8 x 6 = 99 x 101 = B. Take the middle number and multiply it by itself. C. Subtract 1 from the answer in step B. 38
The bottom number in the fraction is called the denominator. The top number is called the numerator.
 For Topics 8 and 9, the students should know: Fractions are a part of a whole. The bottom number in the fraction is called the denominator. The top number is called the numerator. Equivalent fractions
For Topics 8 and 9, the students should know: Fractions are a part of a whole. The bottom number in the fraction is called the denominator. The top number is called the numerator. Equivalent fractions
Fractions Presentation Part 1
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide / Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide / Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Fourth Grade. Adding Fractions with Common Denominators. Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111. Slide 4 / 111. Slide 3 / 111. Slide 6 / 111.
 Slide / Slide / Fourth Grade Fraction Computation 0-- www.njctl.org Slide / Slide / Table of Contents Click on a topic to go to that section. Adding Fractions with Common Denominators Adding Mixed Numbers
Slide / Slide / Fourth Grade Fraction Computation 0-- www.njctl.org Slide / Slide / Table of Contents Click on a topic to go to that section. Adding Fractions with Common Denominators Adding Mixed Numbers
Multiplication and Division MODELS
 Multiplication and Divion MODELS Multiplication groups and arrays When we put objects into rows and columns like th we call it an array. Arrays can make it easier to work out how many objects there are
Multiplication and Divion MODELS Multiplication groups and arrays When we put objects into rows and columns like th we call it an array. Arrays can make it easier to work out how many objects there are
Study Guide 3: Addition of Whole Numbers Category 2: Computation and Algebraic Relationships
 Study Guide 3: Addition of Whole Numbers Category 2: Computation and Algebraic Relationships Vocabulary Addition Addends Missing addend Sum Total Plus Number sentence Equation Regroup Estimate Estimation
Study Guide 3: Addition of Whole Numbers Category 2: Computation and Algebraic Relationships Vocabulary Addition Addends Missing addend Sum Total Plus Number sentence Equation Regroup Estimate Estimation
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS K-2 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS K-2 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Domain: Counting and Cardinality Know number names and the count
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS K-2 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Domain: Counting and Cardinality Know number names and the count
Whole Numbers. Whole Numbers. Curriculum Ready.
 Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Curriculum links Maths: working mathematically, number, algebra.
 A STEM learning and teaching resource that explores a variety of magical maths activities, from multiplication tips to card tricks. Curriculum links Maths: working mathematically, number, algebra. Mind
A STEM learning and teaching resource that explores a variety of magical maths activities, from multiplication tips to card tricks. Curriculum links Maths: working mathematically, number, algebra. Mind
Common Core State Standard I Can Statements 2 nd Grade
 CCSS Key: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) Measurement and Data (MD) Geometry (G) Common Core State Standard 2 nd Grade Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
CCSS Key: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) Measurement and Data (MD) Geometry (G) Common Core State Standard 2 nd Grade Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Study Material. For. Shortcut Maths
 N ew Shortcut Maths Edition 2015 Study Material For Shortcut Maths Regd. Office :- A-202, Shanti Enclave, Opp.Railway Station, Mira Road(E), Mumbai. bankpo@laqshya.in (Not For Sale) (For Private Circulation
N ew Shortcut Maths Edition 2015 Study Material For Shortcut Maths Regd. Office :- A-202, Shanti Enclave, Opp.Railway Station, Mira Road(E), Mumbai. bankpo@laqshya.in (Not For Sale) (For Private Circulation
CPM EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM
 CPM EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM SAMPLE LESSON: ALGEBRA TILES PART 1: INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRA TILES The problems in Part 1 introduce algebra tiles to students. These first eleven problems will probably span two
CPM EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM SAMPLE LESSON: ALGEBRA TILES PART 1: INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRA TILES The problems in Part 1 introduce algebra tiles to students. These first eleven problems will probably span two
DCSD Common Core State Standards Math Pacing Guide 2nd Grade Trimester 1
 Trimester 1 OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction. 1. Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve oneand two-step word problems involving
Trimester 1 OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction. 1. Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve oneand two-step word problems involving
Lesson 1 6. Algebra: Variables and Expression. Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions.
 Lesson 1 6 Algebra: Variables and Expression Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions. P1 Represent and analyze patterns, rules and functions with words, tables, graphs and simple variable
Lesson 1 6 Algebra: Variables and Expression Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions. P1 Represent and analyze patterns, rules and functions with words, tables, graphs and simple variable
NOTES: SIGNED INTEGERS DAY 1
 NOTES: SIGNED INTEGERS DAY 1 MULTIPLYING and DIVIDING: Same Signs (POSITIVE) + + = + positive x positive = positive = + negative x negative = positive Different Signs (NEGATIVE) + = positive x negative
NOTES: SIGNED INTEGERS DAY 1 MULTIPLYING and DIVIDING: Same Signs (POSITIVE) + + = + positive x positive = positive = + negative x negative = positive Different Signs (NEGATIVE) + = positive x negative
Multiplying Three Factors and Missing Factors
 LESSON 18 Multiplying Three Factors and Missing Factors Power Up facts count aloud Power Up C Count up and down by 5s between 1 and 51. Count up and down by 200s between 0 and 2000. mental math a. Number
LESSON 18 Multiplying Three Factors and Missing Factors Power Up facts count aloud Power Up C Count up and down by 5s between 1 and 51. Count up and down by 200s between 0 and 2000. mental math a. Number
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS
 MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring
 Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
Improper Fractions. An Improper Fraction has a top number larger than (or equal to) the bottom number.
 Improper Fractions (seven-fourths or seven-quarters) 7 4 An Improper Fraction has a top number larger than (or equal to) the bottom number. It is "top-heavy" More Examples 3 7 16 15 99 2 3 15 15 5 See
Improper Fractions (seven-fourths or seven-quarters) 7 4 An Improper Fraction has a top number larger than (or equal to) the bottom number. It is "top-heavy" More Examples 3 7 16 15 99 2 3 15 15 5 See
Simple Solutions Mathematics. Level 2. Help Pages & Who Knows?
 Simple Solutions Mathematics Level 2, 2nd semester Level 2 & Who Knows? 139 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Addition When you combine numbers, you add. The sign + means add. The answer to an addition
Simple Solutions Mathematics Level 2, 2nd semester Level 2 & Who Knows? 139 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Addition When you combine numbers, you add. The sign + means add. The answer to an addition
Grade 6 Math Circles March 1-2, Introduction to Number Theory
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 1-2, 2016 Introduction to Number Theory Being able to do mental math quickly
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 1-2, 2016 Introduction to Number Theory Being able to do mental math quickly
100 IDEAS FOR USING A HUNDRED SQUARE
 100 IDEAS FOR USING A HUNDRED SQUARE These ideas are in no particular order and can be adapted to any age range or ability. The objectives are for children to learn to recognise numbers, understand numbers
100 IDEAS FOR USING A HUNDRED SQUARE These ideas are in no particular order and can be adapted to any age range or ability. The objectives are for children to learn to recognise numbers, understand numbers
Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards. Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction
 Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.2.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100
Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.2.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100
Standards for Mathematical Practice
 Common Core State Standards Mathematics Student: Teacher: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Standards for Mathematical Practice 3. Construct
Common Core State Standards Mathematics Student: Teacher: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Standards for Mathematical Practice 3. Construct
Mastering Math Facts with Card Games!
 Mastering Math Facts with Card Games! Joan A. Cotter, Ph.D. JoanCotter@RightStartMath.com! Sioux Empire Christian Home Educators Homeschool Conference Sioux Falls, SD Saturday, May 2, 2015 11:30 a.m. 12:30
Mastering Math Facts with Card Games! Joan A. Cotter, Ph.D. JoanCotter@RightStartMath.com! Sioux Empire Christian Home Educators Homeschool Conference Sioux Falls, SD Saturday, May 2, 2015 11:30 a.m. 12:30
Times Tables. Games and strategies to help your child learn their times tables.
 Times Tables Games and strategies to help your child learn their times tables. I m sure we all remember standing up, chanting tables at school. Learning by rote is one strategy, but there are also other
Times Tables Games and strategies to help your child learn their times tables. I m sure we all remember standing up, chanting tables at school. Learning by rote is one strategy, but there are also other
1 /4. (One-Half) (One-Quarter) (Three-Eighths)
 LESSON 4: Fractions: A fraction is a part of a whole. Slice a pizza, and you will have fractions: 1 /2 1 /4 3 /8 (One-Half) (One-Quarter) (Three-Eighths) The top number tells how many slices you have and
LESSON 4: Fractions: A fraction is a part of a whole. Slice a pizza, and you will have fractions: 1 /2 1 /4 3 /8 (One-Half) (One-Quarter) (Three-Eighths) The top number tells how many slices you have and
Content Area: Mathematics- 3 rd Grade
 Unit: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Topic: Multiplication and Division Strategies Multiplication is grouping objects into sets which is a repeated form of addition. What are the different meanings
Unit: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Topic: Multiplication and Division Strategies Multiplication is grouping objects into sets which is a repeated form of addition. What are the different meanings
Number Fun December 3,
 Number Fun December 3, 2008 John L. Lehet jlehet@mathmaverick.com www.mathmaverick.com Numbers Fibonacci Numbers Digital Roots Vedic Math Original Puzzles MathMagic Tricks Predict the Sum? (PredictTheSum.xls)
Number Fun December 3, 2008 John L. Lehet jlehet@mathmaverick.com www.mathmaverick.com Numbers Fibonacci Numbers Digital Roots Vedic Math Original Puzzles MathMagic Tricks Predict the Sum? (PredictTheSum.xls)
Skill Builder. J. B. Wright A D VA N TA G E
 MATHS MATE Skill Builder 6 J. B. Wright THE EDUCATIONAL A D VA N TA G E THE EDUCATIONAL MATHS MATE /6 Skill Builder J. B. Wright Published by The Educational Advantage Pty Ltd PO Box 068 Echuca VIC 64
MATHS MATE Skill Builder 6 J. B. Wright THE EDUCATIONAL A D VA N TA G E THE EDUCATIONAL MATHS MATE /6 Skill Builder J. B. Wright Published by The Educational Advantage Pty Ltd PO Box 068 Echuca VIC 64
Time for Math. An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement!
 Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
NSCAS - Math Table of Specifications
 NSCAS - Math Table of Specifications MA 3. MA 3.. NUMBER: Students will communicate number sense concepts using multiple representations to reason, solve problems, and make connections within mathematics
NSCAS - Math Table of Specifications MA 3. MA 3.. NUMBER: Students will communicate number sense concepts using multiple representations to reason, solve problems, and make connections within mathematics
Grade 2 Mathematics Scope and Sequence
 Grade 2 Mathematics Scope and Sequence Common Core Standards 2.OA.1 I Can Statements Curriculum Materials & (Knowledge & Skills) Resources /Comments Sums and Differences to 20: (Module 1 Engage NY) 100
Grade 2 Mathematics Scope and Sequence Common Core Standards 2.OA.1 I Can Statements Curriculum Materials & (Knowledge & Skills) Resources /Comments Sums and Differences to 20: (Module 1 Engage NY) 100
Chapter 7 Math Guide
 I can write fractions as a sum Write as unit fractions This means the fractions are broken into each individual unit/1 single piece. The fraction is /6. The model shows that pieces are shaded in. If you
I can write fractions as a sum Write as unit fractions This means the fractions are broken into each individual unit/1 single piece. The fraction is /6. The model shows that pieces are shaded in. If you
MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 2
 MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 2 UTAH STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION 250 EAST 500 SOUTH P.O. BOX 144200 SALT LAKE CITY, UTAH 84114-4200 SYDNEE DICKSON, Ed.D., STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Operations
MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 2 UTAH STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION 250 EAST 500 SOUTH P.O. BOX 144200 SALT LAKE CITY, UTAH 84114-4200 SYDNEE DICKSON, Ed.D., STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Operations
Mathematics in your head the secrets of mental math
 Mathematics in your head the secrets of mental math 1. Fundamentals: mental addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, and gestimation. Addition: 42 + 3 = 45 42 + 30 = 72 42 + 300 = 342 42 + 3000
Mathematics in your head the secrets of mental math 1. Fundamentals: mental addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, and gestimation. Addition: 42 + 3 = 45 42 + 30 = 72 42 + 300 = 342 42 + 3000
Simple Solutions Mathematics Level 3. Level 3. Help Pages & Who Knows Drill
 Level 3 & Who Knows Drill 283 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and 1 is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication
Level 3 & Who Knows Drill 283 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and 1 is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication
The Factor Game (gr. 3-5) Product Game (gr. 3-5) Target Number (exponents) (gr. 4-5)
 The Factor Game (gr. 3-5) Product Game (gr. 3-5) Target Number (exponents) (gr. 4-5) The Factor Game ( Gr. 3-5) Player A chooses a number on the game board and circles it. Using a different color, Player
The Factor Game (gr. 3-5) Product Game (gr. 3-5) Target Number (exponents) (gr. 4-5) The Factor Game ( Gr. 3-5) Player A chooses a number on the game board and circles it. Using a different color, Player
An ordered collection of counters in rows or columns, showing multiplication facts.
 Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
GRADE 4. M : Solve division problems without remainders. M : Recall basic addition, subtraction, and multiplication facts.
 GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM.
 KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM. LOOKING AT THE NUMBER SYSTEM. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Our number
KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM. LOOKING AT THE NUMBER SYSTEM. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Our number
Addition and Subtraction
 Addition and Subtraction If any of your students don t know their addition and subtraction facts, teach them to add and subtract using their fi ngers by the methods taught below. You should also reinforce
Addition and Subtraction If any of your students don t know their addition and subtraction facts, teach them to add and subtract using their fi ngers by the methods taught below. You should also reinforce
Make Math Meaningful!
 Make Math Meaningful! I hear, and I forget. I see, and I remember. I do, and I understand. Knowledge comes easily to those who understand. Proverbs 14:6 B-A-T Place Value Game B = Brilliant; right number
Make Math Meaningful! I hear, and I forget. I see, and I remember. I do, and I understand. Knowledge comes easily to those who understand. Proverbs 14:6 B-A-T Place Value Game B = Brilliant; right number
Developing Algebraic Thinking
 Developing Algebraic Thinking DEVELOPING ALGEBRAIC THINKING Algebra is an important branch of mathematics, both historically and presently. algebra has been too often misunderstood and misrepresented as
Developing Algebraic Thinking DEVELOPING ALGEBRAIC THINKING Algebra is an important branch of mathematics, both historically and presently. algebra has been too often misunderstood and misrepresented as
Madison County Schools Suggested 2 nd Grade Math Pacing Guide,
 Madison County Schools Suggested 2 nd Grade Math Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 The following Standards have changes from the 2015-16 MS College- and Career-Readiness Standards: Significant Changes (ex: change
Madison County Schools Suggested 2 nd Grade Math Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 The following Standards have changes from the 2015-16 MS College- and Career-Readiness Standards: Significant Changes (ex: change
Powers and roots 6.1. Previous learning. Objectives based on NC levels and (mainly level ) Lessons 1 Squares, cubes and roots.
 N 6.1 Powers and roots Previous learning Before they start, pupils should be able to: use index notation and the index laws for positive integer powers understand and use the order of operations, including
N 6.1 Powers and roots Previous learning Before they start, pupils should be able to: use index notation and the index laws for positive integer powers understand and use the order of operations, including
1. Activities (from Guidelines in Number)
 Teach Early Years Number page 16 13 Count all to add (two collections) Targets Children usually start to add by recounting both numbers of objects as an entirely new set to be counted. The next step is
Teach Early Years Number page 16 13 Count all to add (two collections) Targets Children usually start to add by recounting both numbers of objects as an entirely new set to be counted. The next step is
Second Grade Mathematics Goals
 Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet
 Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet Target 1: Writing Repeating Decimals in Rational Form Remember the goal is to get rid of the repeating decimal so we can write the number in rational
Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet Target 1: Writing Repeating Decimals in Rational Form Remember the goal is to get rid of the repeating decimal so we can write the number in rational
Grade 7 Math notes Unit 5 Operations with Fractions
 Grade 7 Math notes Unit Operations with Fractions name: Using Models to Add Fractions We can use pattern blocks to model fractions. A hexagon is whole A trapezoid is of the whole. A parallelogram is of
Grade 7 Math notes Unit Operations with Fractions name: Using Models to Add Fractions We can use pattern blocks to model fractions. A hexagon is whole A trapezoid is of the whole. A parallelogram is of
FSA Math Review. **Rounding / Estimating** **Addition and Subtraction** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about
 FSA Math Review **Rounding / Estimating** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about 5 or more add one more-----round UP 0-4 just ignore-----stay SAME Find the number in the place value
FSA Math Review **Rounding / Estimating** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about 5 or more add one more-----round UP 0-4 just ignore-----stay SAME Find the number in the place value
Patterns and Relations
 Grade 7 - Unit One Patterns and Relations Name: In this section we will be looking at the Divisibility Rules for the numbers 2, 4, 5, 8 & 10. Divisible means that a number can be divided by a certain number.
Grade 7 - Unit One Patterns and Relations Name: In this section we will be looking at the Divisibility Rules for the numbers 2, 4, 5, 8 & 10. Divisible means that a number can be divided by a certain number.
MATHS WORKSHEETS FIRST TERM
 NAME: GRADE: MATHS WORKSHEETS FIRST TERM 2010 1 GRADE 4 MATHS SYLLABUS - FIRST TERM SYLLABUS INSTAMATHS WKBOOK 1-15 Basic Addition and Subtraction 1; 3; 5; 6; 10; 16; 17; 3 Number Sequences 15; 58 4 Place
NAME: GRADE: MATHS WORKSHEETS FIRST TERM 2010 1 GRADE 4 MATHS SYLLABUS - FIRST TERM SYLLABUS INSTAMATHS WKBOOK 1-15 Basic Addition and Subtraction 1; 3; 5; 6; 10; 16; 17; 3 Number Sequences 15; 58 4 Place
Third Grade: Mathematics. Unit 1: Math Strategies
 Third Grade: Mathematics Unit 1: Math Strategies Math Strategies for Addition Open Number Line (Adding Up) The example below shows 543 + 387 using the open number line. First, you need to draw a blank
Third Grade: Mathematics Unit 1: Math Strategies Math Strategies for Addition Open Number Line (Adding Up) The example below shows 543 + 387 using the open number line. First, you need to draw a blank
Modeling Addition of Fractions (12 1)
 Modeling Addition of Fractions ( ) Eight friends want to see a movie. Four of them want to see a comedy. Two want to see an action movie and two want to see a science-fiction movie. What fraction of the
Modeling Addition of Fractions ( ) Eight friends want to see a movie. Four of them want to see a comedy. Two want to see an action movie and two want to see a science-fiction movie. What fraction of the
DIVISION BY FRACTIONS
 DIVISION BY FRACTIONS 6.. 6.. Division by fractions introduces three methods to help students understand how dividing by fractions works. In general, think of division for a problem like 8 as, In 8, how
DIVISION BY FRACTIONS 6.. 6.. Division by fractions introduces three methods to help students understand how dividing by fractions works. In general, think of division for a problem like 8 as, In 8, how
Whole Numbers WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT.
 WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
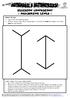 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
Based on CBSE, ICSE & GCSE Syllabus
 MATHEMAGIC ACTIVITY BOOK CLASS III Price : Rs. 60 Copyright reserved Second Edition : October 2007 Published by : Eduheal Foundation, 10, Ground Floor, Taj Apartment, Near VMMC & Safdarjung Hospital, New
MATHEMAGIC ACTIVITY BOOK CLASS III Price : Rs. 60 Copyright reserved Second Edition : October 2007 Published by : Eduheal Foundation, 10, Ground Floor, Taj Apartment, Near VMMC & Safdarjung Hospital, New
8 Fraction Book. 8.1 About this part. 8.2 Pieces of Cake. Name 55
 Name 8 Fraction Book 8. About this part This book is intended to be an enjoyable supplement to the standard text and workbook material on fractions. Understanding why the rules are what they are, and why
Name 8 Fraction Book 8. About this part This book is intended to be an enjoyable supplement to the standard text and workbook material on fractions. Understanding why the rules are what they are, and why
Intermediate A. Help Pages & Who Knows
 & Who Knows 83 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication problem.
& Who Knows 83 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication problem.
Turn your soroban into a foot inch calculator By Dino Marcantonio
 Turn your soroban into a foot inch calculator By Dino Marcantonio *a variation on this technique by Steve Treadwell: https://groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/sorobanabacus/conversations/messages/8590 The soroban
Turn your soroban into a foot inch calculator By Dino Marcantonio *a variation on this technique by Steve Treadwell: https://groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/sorobanabacus/conversations/messages/8590 The soroban
L_sson 9 Subtracting across zeros
 L_sson 9 Subtracting across zeros A. Here are the steps for subtracting 3-digit numbers across zeros. Complete the example. 7 10 12 8 0 2 2 3 8 9 1. Subtract the ones column. 2 8 requires regrouping. 2.
L_sson 9 Subtracting across zeros A. Here are the steps for subtracting 3-digit numbers across zeros. Complete the example. 7 10 12 8 0 2 2 3 8 9 1. Subtract the ones column. 2 8 requires regrouping. 2.
Diocese of Erie Mathematics Curriculum Third Grade August 2012
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 1 1. Interpret products of whole numbers. Interpret 5x7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups
Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 1 1. Interpret products of whole numbers. Interpret 5x7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups
Fractions! You can find much more about all these issues, and more, in the ebook Understanding Fractions [ibooks]. Ronit Bird
![Fractions! You can find much more about all these issues, and more, in the ebook Understanding Fractions [ibooks]. Ronit Bird Fractions! You can find much more about all these issues, and more, in the ebook Understanding Fractions [ibooks]. Ronit Bird](/thumbs/95/125593741.jpg) Fractions Some children whether or not they are dyscalculic or dyslexic find the whole idea of fractions very difficult and confusing. One reason for the difficulty is that classroom teaching often focuses
Fractions Some children whether or not they are dyscalculic or dyslexic find the whole idea of fractions very difficult and confusing. One reason for the difficulty is that classroom teaching often focuses
Grade 2: Mathematics Curriculum (2010 Common Core) Warren Hills Cluster (K 8)
 Focus Topic:OA Operations and Algebraic Thinking TSW = The Student Will TSW use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from,
Focus Topic:OA Operations and Algebraic Thinking TSW = The Student Will TSW use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from,
Logarithms ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Logarithms ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning History and Uses We noticed that when we multiply two numbers that are the same base raised to different exponents, that the result is the base raised
Logarithms ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning History and Uses We noticed that when we multiply two numbers that are the same base raised to different exponents, that the result is the base raised
Let's Play Math Games! Activities for Learning, Inc. 2017
 Let's Play Math Games! 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 142128354249566370 Games Games Math = Books Reading Games provide instant feedback. Games provide interesting repetition needed for automatic responses in a social
Let's Play Math Games! 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 142128354249566370 Games Games Math = Books Reading Games provide instant feedback. Games provide interesting repetition needed for automatic responses in a social
Mental Calculation Policy 2014
 Mental Calculation Policy 2014 RECEPTION Children count reliably with numbers from one to 20 and place them in order. Children can say which number is one more or one less than a given number up to 20
Mental Calculation Policy 2014 RECEPTION Children count reliably with numbers from one to 20 and place them in order. Children can say which number is one more or one less than a given number up to 20
I.G.C.S.E. Solving Linear Equations. You can access the solutions from the end of each question
 I.G.C.S.E. Solving Linear Equations Inde: Please click on the question number you want Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 You can access the solutions
I.G.C.S.E. Solving Linear Equations Inde: Please click on the question number you want Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 You can access the solutions
A few chessboards pieces: 2 for each student, to play the role of knights.
 Parity Party Returns, Starting mod 2 games Resources A few sets of dominoes only for the break time! A few chessboards pieces: 2 for each student, to play the role of knights. Small coins, 16 per group
Parity Party Returns, Starting mod 2 games Resources A few sets of dominoes only for the break time! A few chessboards pieces: 2 for each student, to play the role of knights. Small coins, 16 per group
Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 3/4, 2015 Arithmetic Aerobics Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 3/4, 2015 Arithmetic Aerobics Solutions Mental Math is Good For You! You
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 3/4, 2015 Arithmetic Aerobics Solutions Mental Math is Good For You! You
Hillhead High School. Fractions. What you need to know. S.O Grady 1
 Fractions What you need to know S.O Grady What is a fraction? A fraction is a part of a whole (). Fractions consist of two numbers, a numerator and a denominator. Top number How many parts we have Bottom
Fractions What you need to know S.O Grady What is a fraction? A fraction is a part of a whole (). Fractions consist of two numbers, a numerator and a denominator. Top number How many parts we have Bottom
RACE FOR A FLAT. Getting Ready. The Activity. 58 Base Ten Blocks Grades K 2 ETA/Cuisenaire. Overview. Introducing
 RACE FOR A FLAT NUMBER Counting Place value Addition Getting Ready What You ll Need Base Ten Blocks, 1 set per group Base Ten Blocks Place-Value Mat, 1 per pair Number cubes marked 1 to, 2 per group Units/Longs
RACE FOR A FLAT NUMBER Counting Place value Addition Getting Ready What You ll Need Base Ten Blocks, 1 set per group Base Ten Blocks Place-Value Mat, 1 per pair Number cubes marked 1 to, 2 per group Units/Longs
THE NUMBER WAR GAMES
 THE NUMBER WAR GAMES Teaching Mathematics Facts Using Games and Cards Mahesh C. Sharma President Center for Teaching/Learning Mathematics 47A River St. Wellesley, MA 02141 info@mathematicsforall.org @2008
THE NUMBER WAR GAMES Teaching Mathematics Facts Using Games and Cards Mahesh C. Sharma President Center for Teaching/Learning Mathematics 47A River St. Wellesley, MA 02141 info@mathematicsforall.org @2008
CONNECT: Divisibility
 CONNECT: Divisibility If a number can be exactly divided by a second number, with no remainder, then we say that the first number is divisible by the second number. For example, 6 can be divided by 3 so
CONNECT: Divisibility If a number can be exactly divided by a second number, with no remainder, then we say that the first number is divisible by the second number. For example, 6 can be divided by 3 so
Unit 1. Activity 1. Whole numbers. 1. Copy and complete each number pattern.
 1 2 Unit 1 Whole numbers Activity 1 1. Copy and complete each number pattern. 2 671 2 680 2 689 13 450 13 650 14 450 25 125 25 000 24 875 124 300 126 300 128 300 180 500 180 000 179 500 2. Write these
1 2 Unit 1 Whole numbers Activity 1 1. Copy and complete each number pattern. 2 671 2 680 2 689 13 450 13 650 14 450 25 125 25 000 24 875 124 300 126 300 128 300 180 500 180 000 179 500 2. Write these
Math Grade 2. Understand that three non-zero digits of a 3-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens and ones.
 Number Sense Place value Counting Skip counting Other names for numbers Comparing numbers Using properties or place value to add and subtract Standards to be addressed in Number Sense Standard Topic Term
Number Sense Place value Counting Skip counting Other names for numbers Comparing numbers Using properties or place value to add and subtract Standards to be addressed in Number Sense Standard Topic Term
Let s Play Math Games!
 Let s Play Math Games! July, at : pm Arizona Families for Home Education Conference presented by Kathleen Cotter Lawler based on the work of Dr. Joan A. Cotter // Games Math Games Games provide instant
Let s Play Math Games! July, at : pm Arizona Families for Home Education Conference presented by Kathleen Cotter Lawler based on the work of Dr. Joan A. Cotter // Games Math Games Games provide instant
Hundreds Grid. MathShop: Hundreds Grid
 Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Math at the Primary Level. Marian Small October 2015
 Math at the Primary Level Marian Small October 2015 Issues Using manipulatives effectively Building number sense (including mental math) Better consolidation of lessons Manipulatives of Value Counters
Math at the Primary Level Marian Small October 2015 Issues Using manipulatives effectively Building number sense (including mental math) Better consolidation of lessons Manipulatives of Value Counters
Multiplication and Division
 E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
How much effort did you put into math?
 Name: # I can: Math Topic 3: Using Place Value to Add and Subtract Study Guide Solve 3-digit addition problems using an expanded algorithm. (3-1) Add 3-digit numbers using place-value blocks or pictures
Name: # I can: Math Topic 3: Using Place Value to Add and Subtract Study Guide Solve 3-digit addition problems using an expanded algorithm. (3-1) Add 3-digit numbers using place-value blocks or pictures
Children to write number sentences Children to show jumps on laminated number line: Show the jumps on a number line as counting on e.
 Written Methods& Mental Methods & A D D I T I O N FOUNDATION STAGE YEAR 1 YEAR 2 Count with 1:1 correspondence Recognise numbers Count to 20 and beyond Write numbers Order numbers to 20 Know one more than
Written Methods& Mental Methods & A D D I T I O N FOUNDATION STAGE YEAR 1 YEAR 2 Count with 1:1 correspondence Recognise numbers Count to 20 and beyond Write numbers Order numbers to 20 Know one more than
Math Review Questions
 Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
SHAKUNTALA nevi. Figuring THE JOY OF NUMBERS HARPER & ROW, PUBLISHERS. New York, Hagerstown, San Francisco, London
 SHAKUNTALA nevi Figuring THE JOY OF NUMBERS HARPER & ROW, PUBLISHERS New York, Hagerstown, San Francisco, London FIGURING THE JOY OF NUMBERS. Copyright 1977 by Shakuntala Devi. All rights reserved. Printed
SHAKUNTALA nevi Figuring THE JOY OF NUMBERS HARPER & ROW, PUBLISHERS New York, Hagerstown, San Francisco, London FIGURING THE JOY OF NUMBERS. Copyright 1977 by Shakuntala Devi. All rights reserved. Printed
Place the First Digit
 Lesson 2. Place the First Digit When you divide, you can use estimation or place value to place the first digit of the quotient. Divide. 6q w,266 Estimate.,200 4 6 5 200, so the first digit of the quotient
Lesson 2. Place the First Digit When you divide, you can use estimation or place value to place the first digit of the quotient. Divide. 6q w,266 Estimate.,200 4 6 5 200, so the first digit of the quotient
copyright amberpasillas2010 What is Divisibility? Divisibility means that after dividing, there will be No remainder.
 What is Divisibility? Divisibility means that after dividing, there will be No remainder. 1 356,821 Can you tell by just looking at this number if it is divisible by 2? by 5? by 10? by 3? by 9? By 6? The
What is Divisibility? Divisibility means that after dividing, there will be No remainder. 1 356,821 Can you tell by just looking at this number if it is divisible by 2? by 5? by 10? by 3? by 9? By 6? The
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT
 MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
Focus on Mathematics
 Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
GRADE 3 TEKS ALIGNMENT CHART
 GRADE 3 TEKS ALIGNMENT CHART TEKS 3.2.A compose and decompose numbers up to,000 as the sum of so many ten thousands, so many thousands, so many hundreds, so many tens, and so many ones using objects, pictorial
GRADE 3 TEKS ALIGNMENT CHART TEKS 3.2.A compose and decompose numbers up to,000 as the sum of so many ten thousands, so many thousands, so many hundreds, so many tens, and so many ones using objects, pictorial
Removing the Fear of Fractions from Your Students Thursday, April 16, 2015: 9:30 AM-10:30 AM 157 A (BCEC) Lead Speaker: Joseph C.
 Removing the Fear of Fractions from Your Students Thursday, April 6, 20: 9:0 AM-0:0 AM 7 A (BCEC) Lead Speaker: Joseph C. Mason Associate Professor of Mathematics Hagerstown Community College Hagerstown,
Removing the Fear of Fractions from Your Students Thursday, April 6, 20: 9:0 AM-0:0 AM 7 A (BCEC) Lead Speaker: Joseph C. Mason Associate Professor of Mathematics Hagerstown Community College Hagerstown,
Contents. PART 1 Unit 1: Number Sense: Numbers to 10. Unit 2: Number Sense: Numbers to 20. Unit 3: Patterns and Algebra: Repeating Patterns
 Contents PART 1 Unit 1: Number Sense: Numbers to 10 NS2-1 Counting and Matching 1 NS2-2 One-to-One Correspondence 3 NS2-3 More, Fewer, and Less 5 NS2-4 How Many More? 7 NS2-5 Reading Number Words to Ten
Contents PART 1 Unit 1: Number Sense: Numbers to 10 NS2-1 Counting and Matching 1 NS2-2 One-to-One Correspondence 3 NS2-3 More, Fewer, and Less 5 NS2-4 How Many More? 7 NS2-5 Reading Number Words to Ten
Oaktree School Assessment MATHS: NUMBER P4
 MATHS: NUMBER P4 I can collect objects I can pick up and put down objects I can hold one object I can see that all the objects have gone I can help to count I can help to match things up one to one (ie.
MATHS: NUMBER P4 I can collect objects I can pick up and put down objects I can hold one object I can see that all the objects have gone I can help to count I can help to match things up one to one (ie.
Developing Conceptual Understanding of Number. Set D: Number Theory
 Developing Conceptual Understanding of Number Set D: Number Theory Carole Bilyk cbilyk@gov.mb.ca Wayne Watt wwatt@mts.net Vocabulary digit hundred s place whole numbers even Notes Number Theory 1 odd multiple
Developing Conceptual Understanding of Number Set D: Number Theory Carole Bilyk cbilyk@gov.mb.ca Wayne Watt wwatt@mts.net Vocabulary digit hundred s place whole numbers even Notes Number Theory 1 odd multiple
Part Mark Answer Further Information. Part Mark Answer Further Information Award 1 mark for 20, 15, 35 or. Part Mark Answer Further Information
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Checkpoint MATHEMATICS 1112/01 Paper 1 For Examination from 2014 SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 50 This document consists of 11 printed pages and 1 blank
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Checkpoint MATHEMATICS 1112/01 Paper 1 For Examination from 2014 SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 50 This document consists of 11 printed pages and 1 blank
Time for Math. An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement!
 Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
 Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 4th Grade THIRD GRADE GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS IN MATHMATICS When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 4th Grade THIRD GRADE GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS IN MATHMATICS When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Texas Go Math! Grade 4. correlated to MegaMath Video Activities Grades 3 6
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt 2015 correlated to Grades 3 6 Unit 1 Number and Operations: Place Value, Fraction Concepts, and Operations Module 1: Whole Number Place Value 1.1 Place Value and Patterns The
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt 2015 correlated to Grades 3 6 Unit 1 Number and Operations: Place Value, Fraction Concepts, and Operations Module 1: Whole Number Place Value 1.1 Place Value and Patterns The
