Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Memory Management (Stallings, chapter ) Next: continued. Self-Study Exercise #6. Project #4 (due 10/11)
|
|
|
- Kenneth Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture Topics Today: Memory Management (Stallings, chapter ) Next: continued 1 Announcements Self-Study Exercise #6 Project #4 (due 10/11) Project #5 (due 10/18) 2
2 Memory Hierarchy 3 Memory Hierarchy Trade-offs among types of storage Faster access time, greater cost per bit Greater capacity, smaller cost per bit Greater capacity, slower access speed Moving down the hierarchy: Slower access time, decreasing cost per bit Increasing capacity Decreasing frequency of access by CPU 4
3 Locality of Reference Memory references for both instructions and data values tend to cluster over time. Example: once a loop is entered, there is frequent access to a small set of instructions. Hence: once an instruction is referenced, it is likely that the instruction (and nearby instructions) will be referenced again in the near future. 5 Types of Locality Temporal locality: same address referenced repeatedly in the near-term future instructions: loops, functions data: variables Spatial locality: nearby addresses referenced in the near-term future instructions: sequential execution data: arrays, similar data structures 6
4 Example: C/C++ Program From int sum = 0; int main() { for( int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { sum = sum + i; } } 7 Equivalent ARM Assembly Language.global main.text main: push {lr} mov r0, #1 loop: cmp r0, #6 bgt end ldr r2, =sum ldr r1, [r2] add r1, r1, r0 str r1, [r2] add r0, r0, #1 b loop end: pop {lr} mov pc, lr 8
5 Equivalent ARM Machine Language.global main.text 0000 E52DE004 main: push {lr} 0004 E3A00001 mov r0, # E loop: cmp r0, #6 000c CA bgt end 0010 E59F2018 ldr r2, =sum 0014 E ldr r1, [r2] 0018 E add r1, r1, r0 001c E str r1, [r2] 0020 E add r0, r0, # EAFFFFF7 b loop 0028 E49DE004 end: pop {lr} 002c E1A0F00E mov pc, lr 9 Execution Trace Time PC IR E52DE004 * main: push {lr} E3A00001 mov r0, # E loop: cmp r0, # c CA bgt end E59F2018 * ldr r2, =sum E * ldr r1, [r2] E add r1, r1, r c E * str r1, [r2] E add r0, r0, # EAFFFFF7 b loop E loop: cmp r0, # c CA bgt end... 10
6 Exploiting Locality RAM (primary storage) is slow compared to CPU registers (by a factor of about 200): 0.5 ns to access registers 100 ns to access RAM Exploit locality of reference by keeping a subset of the instructions and data values in high-speed storage (with mechanism to change the subset of instructions and data values when necessary) 11 Cache Memory Cache: fast (and thus small and expensive) Main memory: slow (and thus large and cheap) Processor first checks cache for requested word If not found in cache, a block of memory containing the word is moved to the cache 12
7 The Hit Ratio Hit ratio: fraction of accesses where item is in cache T1: access time for fast memory T2: access time for slow memory T2 >> T1 When hit ratio is close to 1.0, average access time is close to T1 13 Average Memory Access Time Consider a two-level memory hierarchy, where M1 is faster then M2. The average memory access time can be calculated using: AMAT = H * T1 + (1-H) * (T1 + T2) = T1 + (1-H) * T2 H = hit ratio (fraction of references found in M1) T1 = access time for M1 T2 = access time for M2 14
8 Single Level of Cache 15 Example Processor configuration: cache access time is 1 clock cycle (1 ns) cache miss penalty is 100 clock cycles If the requested item is in cache, then it can be accessed in one clock cycle (no delay) If the requested item is not in cache, then the processor has to stall until the item can be fetched from RAM 16
9 Example (continued) For a particular instruction sequence, the hit rate is 97%. What is the average memory access time? AMAT = time for a hit + miss rate * miss penalty = 1 clock cycle * 100 clock cycles = 4 clock cycles (or 4 ns) 17 Example (continued) Assume the hit rate is 99% instead. What is the average memory access time? AMAT = time for a hit + miss rate * miss penalty = 1 clock cycle * 100 clock cycles = 2 clock cycles (or 2 ns) 18
10 Multiple Levels of Cache 19 Example Processor configuration: Level 1 cache access time is 1 clock cycle (1 ns) Level 2 cache access time is 10 clock cycles RAM access time is 100 clock cycles Check L1 cache If not found, check L2 cache If not found, fetch from RAM 20
11 Example (continued) For a particular instruction sequence L1 cache: 90% hit rate L2 cache: 80% hit rate for remaining references Fraction of references found at each level? Level 1: 90% of all references (0.9) Level 2: 80% of remaining 10% (0.08) RAM: 20% of remaining 10% (0.02) 21 Example (continued) For a particular instruction sequence L1 cache: 90% hit rate L2 cache: 80% hit rate for remaining references What is the average memory access time? AMAT = 1 clock cycle * 10 clock cycles * 100 clock cycles = clock cycles = 4 clock cycles (4 ns) 22
12 Example (continued) For a particular instruction sequence L1 cache: 95% hit rate L2 cache: 80% hit rate for remaining references What is the average memory access time? AMAT = 1 clock cycle * 10 clock cycles * 100 clock cycles = clock cycles = 2.5 clock cycles (2.5 ns) 23 Cache and RAM Configuration Unit of transfer between RAM and cache is one block Each cache slot holds one block RAM is viewed as being divided into fixed-size blocks 24
13 Read Operation Load instruction: copy data from RAM to CPU Check cache first if desired item is already present in the cache, simply copy item from cache to CPU If desired item is not already present in the cache, copy a block (item and its neighbors) from RAM to the cache and copy the item to the CPU 25 Read Operation 26
14 Write Operation Store instruction: copy data from CPU to RAM Check cache first if desired item is already present in the cache, simply copy item from CPU to cache If desired item is not already present in the cache, copy item (and its neighbors) from RAM to the cache and copy the item from the CPU 27 Write Policies After a store instruction, cache and RAM are inconsistent: contents of block in cache and RAM are different Two strategies: Write through Write back 28
15 Write Policies Write through: whenever a cache block is changed, the block is written (copied) to RAM Write back: cache block is only written (copied) to RAM when the cache line is evicted (replaced) multiple store instructions can occur before block has to be written to RAM modified bit used to indicate that block has been changed (and must be written to RAM) 29 Cache Organizations 30
7/11/2012. Single Cycle (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. Multi-Cycle Implementation. Single Cycle with Jump. Pipelining Analogy
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel
 Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
EE445L Fall 2015 Final Version B Page 1 of 7
 EE445L Fall 2015 Final Version B Page 1 of 7 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: This is the closed book section. You must put your answers in the boxes. When you are done, you turn in the closed-book part
EE445L Fall 2015 Final Version B Page 1 of 7 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: This is the closed book section. You must put your answers in the boxes. When you are done, you turn in the closed-book part
Introduction to co-simulation. What is HW-SW co-simulation?
 Introduction to co-simulation CPSC489-501 Hardware-Software Codesign of Embedded Systems Mahapatra-TexasA&M-Fall 00 1 What is HW-SW co-simulation? A basic definition: Manipulating simulated hardware with
Introduction to co-simulation CPSC489-501 Hardware-Software Codesign of Embedded Systems Mahapatra-TexasA&M-Fall 00 1 What is HW-SW co-simulation? A basic definition: Manipulating simulated hardware with
Efficient FDTD parallel processing on modern PC CPUs
 Efficient FDTD simulations 1 of 8 Efficient FDTD parallel processing on modern PC CPUs Efficient FDTD simulations W. Simon, A. Lauer, D. Manteuffel, A. Wien, I.Wolff IMST GmbH, Carl-Friedrich-Gauss-Str.
Efficient FDTD simulations 1 of 8 Efficient FDTD parallel processing on modern PC CPUs Efficient FDTD simulations W. Simon, A. Lauer, D. Manteuffel, A. Wien, I.Wolff IMST GmbH, Carl-Friedrich-Gauss-Str.
Hybrid QR Factorization Algorithm for High Performance Computing Architectures. Peter Vouras Naval Research Laboratory Radar Division
 Hybrid QR Factorization Algorithm for High Performance Computing Architectures Peter Vouras Naval Research Laboratory Radar Division 8/1/21 Professor G.G.L. Meyer Johns Hopkins University Parallel Computing
Hybrid QR Factorization Algorithm for High Performance Computing Architectures Peter Vouras Naval Research Laboratory Radar Division 8/1/21 Professor G.G.L. Meyer Johns Hopkins University Parallel Computing
BACHELOR IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (BIT) Term-End Examination December, 2011 CSI-01 : COMPUTER PLATFORMS
 No. of Printed Pages : 5 BACHELOR IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (BIT) Term-End Examination December, 2011 00 570 CSI-01 : COMPUTER PLATFORMS Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 75 Note : There are two sections
No. of Printed Pages : 5 BACHELOR IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (BIT) Term-End Examination December, 2011 00 570 CSI-01 : COMPUTER PLATFORMS Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 75 Note : There are two sections
Chapter 5: Signal conversion
 Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H ) Next: continued. Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2)
 Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
Fall 2015 COMP Operating Systems. Lab #7
 Fall 2015 COMP 3511 Operating Systems Lab #7 Outline Review and examples on virtual memory Motivation of Virtual Memory Demand Paging Page Replacement Q. 1 What is required to support dynamic memory allocation
Fall 2015 COMP 3511 Operating Systems Lab #7 Outline Review and examples on virtual memory Motivation of Virtual Memory Demand Paging Page Replacement Q. 1 What is required to support dynamic memory allocation
Performance Evaluation of Recently Proposed Cache Replacement Policies
 University of Jordan Computer Engineering Department Performance Evaluation of Recently Proposed Cache Replacement Policies CPE 731: Advanced Computer Architecture Dr. Gheith Abandah Asma Abdelkarim January
University of Jordan Computer Engineering Department Performance Evaluation of Recently Proposed Cache Replacement Policies CPE 731: Advanced Computer Architecture Dr. Gheith Abandah Asma Abdelkarim January
Game Architecture. 4/8/16: Multiprocessor Game Loops
 Game Architecture 4/8/16: Multiprocessor Game Loops Monolithic Dead simple to set up, but it can get messy Flow-of-control can be complex Top-level may have too much knowledge of underlying systems (gross
Game Architecture 4/8/16: Multiprocessor Game Loops Monolithic Dead simple to set up, but it can get messy Flow-of-control can be complex Top-level may have too much knowledge of underlying systems (gross
DSP Project. Reminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239).
 DSP Project eminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239). Budget: $150 for project. Free parts: Surplus parts from previous year s project are available on
DSP Project eminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239). Budget: $150 for project. Free parts: Surplus parts from previous year s project are available on
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on
 EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO. Architectures for Embedded Computing
 UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 23
UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 23
Parallelism Across the Curriculum
 Parallelism Across the Curriculum John E. Howland Department of Computer Science Trinity University One Trinity Place San Antonio, Texas 78212-7200 Voice: (210) 999-7364 Fax: (210) 999-7477 E-mail: jhowland@trinity.edu
Parallelism Across the Curriculum John E. Howland Department of Computer Science Trinity University One Trinity Place San Antonio, Texas 78212-7200 Voice: (210) 999-7364 Fax: (210) 999-7477 E-mail: jhowland@trinity.edu
January 11, 2017 Administrative notes
 January 11, 2017 Administrative notes Clickers Updated on Canvas as of people registered yesterday night. REEF/iClicker mobile is not working for everyone. Use at your own risk. If you are having trouble
January 11, 2017 Administrative notes Clickers Updated on Canvas as of people registered yesterday night. REEF/iClicker mobile is not working for everyone. Use at your own risk. If you are having trouble
Performance Metrics. CS356 Unit 8. The Memory Wall. Options for Improving Performance. Memory. Latency: Total time for a to complete
 7 7 Performance Metrics CS56 Unit 8 Memory Latency: Total time for a to complete Often hard to improve dramatically Example: Takes roughly 4 years to get your bachelor's degree From perspective of an Throughput/Bandwidth:
7 7 Performance Metrics CS56 Unit 8 Memory Latency: Total time for a to complete Often hard to improve dramatically Example: Takes roughly 4 years to get your bachelor's degree From perspective of an Throughput/Bandwidth:
Chapter 7: From Digital-to-Analog and Back Again
 Chapter 7: From Digital-to-Analog and Back Again Overview Often the information you want to capture in an experiment originates in the laboratory as an analog voltage or a current. Sometimes you want to
Chapter 7: From Digital-to-Analog and Back Again Overview Often the information you want to capture in an experiment originates in the laboratory as an analog voltage or a current. Sometimes you want to
Advanced Digital Logic Design
 \ / Advanced Digital Logic Design Using VHDL, State Machines, and Synthesis for FPGAs Sunggu Lee С ENGAGE 1% Learning" Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States Ф Ф ФФтшш»» '
\ / Advanced Digital Logic Design Using VHDL, State Machines, and Synthesis for FPGAs Sunggu Lee С ENGAGE 1% Learning" Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States Ф Ф ФФтшш»» '
Computer Hardware. Pipeline
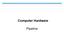 Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
Lecture 3, Handouts Page 1. Introduction. EECE 353: Digital Systems Design Lecture 3: Digital Design Flows, Simulation Techniques.
 Introduction EECE 353: Digital Systems Design Lecture 3: Digital Design Flows, Techniques Cristian Grecu grecuc@ece.ubc.ca Course web site: http://courses.ece.ubc.ca/353/ What have you learned so far?
Introduction EECE 353: Digital Systems Design Lecture 3: Digital Design Flows, Techniques Cristian Grecu grecuc@ece.ubc.ca Course web site: http://courses.ece.ubc.ca/353/ What have you learned so far?
Microcircuit Electrical Issues
 Microcircuit Electrical Issues Distortion The frequency at which transmitted power has dropped to 50 percent of the injected power is called the "3 db" point and is used to define the bandwidth of the
Microcircuit Electrical Issues Distortion The frequency at which transmitted power has dropped to 50 percent of the injected power is called the "3 db" point and is used to define the bandwidth of the
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques
 Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
Period/Pulse-Width Accumulator TPU Function (PPWA)
 SEMICONDUCTOR PROGRAMMING NOTE Order this document by TPUPN/D Period/Pulse-Width Accumulator TPU Function (PPWA) by Mark Maiolani and Sharon Darley Function Overview The period/pulse-width accumulator
SEMICONDUCTOR PROGRAMMING NOTE Order this document by TPUPN/D Period/Pulse-Width Accumulator TPU Function (PPWA) by Mark Maiolani and Sharon Darley Function Overview The period/pulse-width accumulator
COTSon: Infrastructure for system-level simulation
 COTSon: Infrastructure for system-level simulation Ayose Falcón, Paolo Faraboschi, Daniel Ortega HP Labs Exascale Computing Lab http://sites.google.com/site/hplabscotson MICRO-41 tutorial November 9, 28
COTSon: Infrastructure for system-level simulation Ayose Falcón, Paolo Faraboschi, Daniel Ortega HP Labs Exascale Computing Lab http://sites.google.com/site/hplabscotson MICRO-41 tutorial November 9, 28
Final Report: DBmbench
 18-741 Final Report: DBmbench Yan Ke (yke@cs.cmu.edu) Justin Weisz (jweisz@cs.cmu.edu) Dec. 8, 2006 1 Introduction Conventional database benchmarks, such as the TPC-C and TPC-H, are extremely computationally
18-741 Final Report: DBmbench Yan Ke (yke@cs.cmu.edu) Justin Weisz (jweisz@cs.cmu.edu) Dec. 8, 2006 1 Introduction Conventional database benchmarks, such as the TPC-C and TPC-H, are extremely computationally
Asanovic/Devadas Spring Pipeline Hazards. Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T.
 Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
7/19/2012. IF for Load (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. EX for Load (Review) ID for Load (Review) WB for Load (Review) MEM for Load (Review)
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance
 Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance Michael D. Powell, Arijit Biswas, Shantanu Gupta, and Shubu Mukherjee SPEARS Group, Intel Massachusetts EECS, University
Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance Michael D. Powell, Arijit Biswas, Shantanu Gupta, and Shubu Mukherjee SPEARS Group, Intel Massachusetts EECS, University
ECE251: Tuesday October 3 0
 ECE251: Tuesday October 3 0 Timer Module Continued Review Pulse Input Characterization Output Pulses Pulse Count Capture Homework #6 due Thursday Lab 7 (Maskable Interrupts/ SysTick Timer) this week. Significant
ECE251: Tuesday October 3 0 Timer Module Continued Review Pulse Input Characterization Output Pulses Pulse Count Capture Homework #6 due Thursday Lab 7 (Maskable Interrupts/ SysTick Timer) this week. Significant
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
Computer Architecture ( L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS
 Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Chapter 4. Pipelining Analogy. The Processor. Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution. Parallelism improves performance. Four loads: Non-stop:
 Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri. Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal. Instructor: Dr. Rajat Moona
 NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal Course Name: Department: Program Optimization for Multi-core Architecture Computer Science and Engineering IIT
NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal Course Name: Department: Program Optimization for Multi-core Architecture Computer Science and Engineering IIT
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Computer Architecture ECE 568
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Computer Architecture ECE 568 Part 14 Improving Performance: Interleaving Israel Koren ECE568/Koren Part.14.1 Background Performance
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Computer Architecture ECE 568 Part 14 Improving Performance: Interleaving Israel Koren ECE568/Koren Part.14.1 Background Performance
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
Embedded System Hardware - Reconfigurable Hardware -
 2 Embedded System Hardware - Reconfigurable Hardware - Peter Marwedel Informatik 2 TU Dortmund Germany GOPs/J Courtesy: Philips Hugo De Man, IMEC, 27 Energy Efficiency of FPGAs 2, 28-2- Reconfigurable
2 Embedded System Hardware - Reconfigurable Hardware - Peter Marwedel Informatik 2 TU Dortmund Germany GOPs/J Courtesy: Philips Hugo De Man, IMEC, 27 Energy Efficiency of FPGAs 2, 28-2- Reconfigurable
Lecture 4&5 CMOS Circuits
 Lecture 4&5 CMOS Circuits Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese566/ Worst-Case V OL 2 3 Outline Combinational Logic (Delay Analysis) Sequential Circuits
Lecture 4&5 CMOS Circuits Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese566/ Worst-Case V OL 2 3 Outline Combinational Logic (Delay Analysis) Sequential Circuits
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors
 6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
Pipelined Beta. Handouts: Lecture Slides. Where are the registers? Spring /10/01. L16 Pipelined Beta 1
 Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
Accelerated Impulse Response Calculation for Indoor Optical Communication Channels
 Accelerated Impulse Response Calculation for Indoor Optical Communication Channels M. Rahaim, J. Carruthers, and T.D.C. Little Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University, Boston,
Accelerated Impulse Response Calculation for Indoor Optical Communication Channels M. Rahaim, J. Carruthers, and T.D.C. Little Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University, Boston,
Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University
 Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University EE 224 Solid State Electronics II Lecture 3: Lattice and symmetry 1 Outline
Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University EE 224 Solid State Electronics II Lecture 3: Lattice and symmetry 1 Outline
Controlling a Solver Execution: the runsolver Tool
 Controlling a Solver Execution: the runsolver Tool Olivier ROUSSEL CRIL - CNRS UMR 8188 roussel@cril.univ-artois.fr http://www.cril.univ-artois.fr/ roussel/runsolver/ Controlling a Solver Execution: the
Controlling a Solver Execution: the runsolver Tool Olivier ROUSSEL CRIL - CNRS UMR 8188 roussel@cril.univ-artois.fr http://www.cril.univ-artois.fr/ roussel/runsolver/ Controlling a Solver Execution: the
A Static Power Model for Architects
 A Static Power Model for Architects J. Adam Butts and Guri Sohi University of Wisconsin-Madison {butts,sohi}@cs.wisc.edu 33rd International Symposium on Microarchitecture Monterey, California December,
A Static Power Model for Architects J. Adam Butts and Guri Sohi University of Wisconsin-Madison {butts,sohi}@cs.wisc.edu 33rd International Symposium on Microarchitecture Monterey, California December,
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Algorithms and Data Structures Self-Organizing Lists Marius Kloft Assumptions for Searching Until now, we implicitly assumed that every element of our list is searched with the same probability, i.e.,
Algorithms and Data Structures Self-Organizing Lists Marius Kloft Assumptions for Searching Until now, we implicitly assumed that every element of our list is searched with the same probability, i.e.,
EC4205 Microprocessor and Microcontroller
 EC4205 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Webcast link: https://sites.google.com/a/bitmesra.ac.in/aminulislam/home All announcement made through webpage: check back often Students are welcome outside the
EC4205 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Webcast link: https://sites.google.com/a/bitmesra.ac.in/aminulislam/home All announcement made through webpage: check back often Students are welcome outside the
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation
 SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
CS4617 Computer Architecture
 1/26 CS4617 Computer Architecture Lecture 2 Dr J Vaughan September 10, 2014 2/26 Amdahl s Law Speedup = Execution time for entire task without using enhancement Execution time for entire task using enhancement
1/26 CS4617 Computer Architecture Lecture 2 Dr J Vaughan September 10, 2014 2/26 Amdahl s Law Speedup = Execution time for entire task without using enhancement Execution time for entire task using enhancement
CMOS Process Variations: A Critical Operation Point Hypothesis
 CMOS Process Variations: A Critical Operation Point Hypothesis Janak H. Patel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign jhpatel@uiuc.edu Computer Systems
CMOS Process Variations: A Critical Operation Point Hypothesis Janak H. Patel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign jhpatel@uiuc.edu Computer Systems
Power Management in Multicore Processors through Clustered DVFS
 Power Management in Multicore Processors through Clustered DVFS A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Tejaswini Kolpe IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE
Power Management in Multicore Processors through Clustered DVFS A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Tejaswini Kolpe IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture An Introduction Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
Computer Architecture An Introduction Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
Challenges in Transition
 Challenges in Transition Keynote talk at International Workshop on Software Engineering Methods for Parallel and High Performance Applications (SEM4HPC 2016) 1 Kazuaki Ishizaki IBM Research Tokyo kiszk@acm.org
Challenges in Transition Keynote talk at International Workshop on Software Engineering Methods for Parallel and High Performance Applications (SEM4HPC 2016) 1 Kazuaki Ishizaki IBM Research Tokyo kiszk@acm.org
A Parallel Monte-Carlo Tree Search Algorithm
 A Parallel Monte-Carlo Tree Search Algorithm Tristan Cazenave and Nicolas Jouandeau LIASD, Université Paris 8, 93526, Saint-Denis, France cazenave@ai.univ-paris8.fr n@ai.univ-paris8.fr Abstract. Monte-Carlo
A Parallel Monte-Carlo Tree Search Algorithm Tristan Cazenave and Nicolas Jouandeau LIASD, Université Paris 8, 93526, Saint-Denis, France cazenave@ai.univ-paris8.fr n@ai.univ-paris8.fr Abstract. Monte-Carlo
Compiler Optimisation
 Compiler Optimisation 6 Instruction Scheduling Hugh Leather IF 1.18a hleather@inf.ed.ac.uk Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 2018 Introduction This
Compiler Optimisation 6 Instruction Scheduling Hugh Leather IF 1.18a hleather@inf.ed.ac.uk Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 2018 Introduction This
Digital Camera Sensors
 Digital Camera Sensors Agenda Basic Parts of a Digital Camera The Pixel Camera Sensor Pixels Camera Sensor Sizes Pixel Density CMOS vs. CCD Digital Signal Processors ISO, Noise & Light Sensor Comparison
Digital Camera Sensors Agenda Basic Parts of a Digital Camera The Pixel Camera Sensor Pixels Camera Sensor Sizes Pixel Density CMOS vs. CCD Digital Signal Processors ISO, Noise & Light Sensor Comparison
Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur
 NPTEL Online - IIT Bombay Course Name Parallel Computer Architecture Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur Instructor Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture1/main.html[6/13/2012
NPTEL Online - IIT Bombay Course Name Parallel Computer Architecture Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur Instructor Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture1/main.html[6/13/2012
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
Proc. IEEE Intern. Conf. on Application Specific Array Processors, (Eds. Capello et. al.), IEEE Computer Society Press, 1995, 76-84
 Proc. EEE ntern. Conf. on Application Specific Array Processors, (Eds. Capello et. al.), EEE Computer Society Press, 1995, 76-84 Session 2: Architectures 77 toning speed is affected by the huge amount
Proc. EEE ntern. Conf. on Application Specific Array Processors, (Eds. Capello et. al.), EEE Computer Society Press, 1995, 76-84 Session 2: Architectures 77 toning speed is affected by the huge amount
REVOLUTIONIZING THE COMPUTING LANDSCAPE AND BEYOND.
 December 3-6, 2018 Santa Clara Convention Center CA, USA REVOLUTIONIZING THE COMPUTING LANDSCAPE AND BEYOND. https://tmt.knect365.com/risc-v-summit @risc_v ACCELERATING INFERENCING ON THE EDGE WITH RISC-V
December 3-6, 2018 Santa Clara Convention Center CA, USA REVOLUTIONIZING THE COMPUTING LANDSCAPE AND BEYOND. https://tmt.knect365.com/risc-v-summit @risc_v ACCELERATING INFERENCING ON THE EDGE WITH RISC-V
PARALLEL ALGORITHMS FOR HISTOGRAM-BASED IMAGE REGISTRATION. Benjamin Guthier, Stephan Kopf, Matthias Wichtlhuber, Wolfgang Effelsberg
 This is a preliminary version of an article published by Benjamin Guthier, Stephan Kopf, Matthias Wichtlhuber, and Wolfgang Effelsberg. Parallel algorithms for histogram-based image registration. Proc.
This is a preliminary version of an article published by Benjamin Guthier, Stephan Kopf, Matthias Wichtlhuber, and Wolfgang Effelsberg. Parallel algorithms for histogram-based image registration. Proc.
Unit-6 PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS 8259A-PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (PIC) INTRODUCTION
 M i c r o p r o c e s s o r s a n d M i c r o c o n t r o l l e r s P a g e 1 PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS 8259A-PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (PIC) INTRODUCTION Microcomputer system design requires
M i c r o p r o c e s s o r s a n d M i c r o c o n t r o l l e r s P a g e 1 PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS 8259A-PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (PIC) INTRODUCTION Microcomputer system design requires
ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution
 ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2016-11-28-17-33 1 In-Order Dual-Issue
ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2016-11-28-17-33 1 In-Order Dual-Issue
Campus Fighter. CSEE 4840 Embedded System Design. Haosen Wang, hw2363 Lei Wang, lw2464 Pan Deng, pd2389 Hongtao Li, hl2660 Pengyi Zhang, pnz2102
 Campus Fighter CSEE 4840 Embedded System Design Haosen Wang, hw2363 Lei Wang, lw2464 Pan Deng, pd2389 Hongtao Li, hl2660 Pengyi Zhang, pnz2102 March 2011 Project Introduction In this project we aim to
Campus Fighter CSEE 4840 Embedded System Design Haosen Wang, hw2363 Lei Wang, lw2464 Pan Deng, pd2389 Hongtao Li, hl2660 Pengyi Zhang, pnz2102 March 2011 Project Introduction In this project we aim to
Why Modern Servicing Requires Complete Waveform & Circuit Analyzing!
 Why Modern Servicing Requires Complete Waveform & Circuit Analyzing! DC Bias Voltages DC Currents Resistance AC Signals Of Various Waveshapes & Amplitudes Continuity Of Circuit Paths & Components If you
Why Modern Servicing Requires Complete Waveform & Circuit Analyzing! DC Bias Voltages DC Currents Resistance AC Signals Of Various Waveshapes & Amplitudes Continuity Of Circuit Paths & Components If you
of the 1989 International Conference on Systolic Arrays, Killarney, Ireland Architectures using four state coding, a data driven technique for
 - Proceedings of the 1989 International Conference on Systolic Arrays, Killarney, Ireland EXPLOITING THE INHERENT FAULT ARRAYS. TOLERANCE OF ASYNCHRONOUS Rodney Me GoodmAn Anthony McAuley Kathleen Kramer
- Proceedings of the 1989 International Conference on Systolic Arrays, Killarney, Ireland EXPLOITING THE INHERENT FAULT ARRAYS. TOLERANCE OF ASYNCHRONOUS Rodney Me GoodmAn Anthony McAuley Kathleen Kramer
Electronics Design Laboratory Lecture #9. ECEN 2270 Electronics Design Laboratory
 Electronics Design Laboratory Lecture #9 Electronics Design Laboratory 1 Notes Finishing Lab 4 this week Demo requires position control using interrupts and two actions Rotate a given angle Move forward
Electronics Design Laboratory Lecture #9 Electronics Design Laboratory 1 Notes Finishing Lab 4 this week Demo requires position control using interrupts and two actions Rotate a given angle Move forward
CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lab 3 Report Abstract Pipelining is a process in which successive steps of an instruction sequence are executed in turn by a sequence of modules able to operate concurrently,
CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lab 3 Report Abstract Pipelining is a process in which successive steps of an instruction sequence are executed in turn by a sequence of modules able to operate concurrently,
EE241 - Spring 2004 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. Announcements. Borivoje Nikolic. Lecture 15 Low-Power Design: Supply Voltage Scaling
 EE241 - Spring 2004 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Borivoje Nikolic Lecture 15 Low-Power Design: Supply Voltage Scaling Announcements Homework #2 due today Midterm project reports due next Thursday
EE241 - Spring 2004 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Borivoje Nikolic Lecture 15 Low-Power Design: Supply Voltage Scaling Announcements Homework #2 due today Midterm project reports due next Thursday
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Pipelined Microprocessor
 ECE 2300 Digital ogic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 ore Pipelined icroprocessor ecture 18: 1 nnouncements No instructor office hour today Rescheduled to onday pril 16, 4:00-5:30pm Prelim 2 review
ECE 2300 Digital ogic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 ore Pipelined icroprocessor ecture 18: 1 nnouncements No instructor office hour today Rescheduled to onday pril 16, 4:00-5:30pm Prelim 2 review
Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS. Single Clock Cycle Length
 Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS Single Clock Cycle Length Suppose we have 2ns 2ns ister read 2ns ister write 2ns ory read 2ns ory write 2ns 2ns What is the clock cycle length? 1 Single Cycle Length Worst case
Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS Single Clock Cycle Length Suppose we have 2ns 2ns ister read 2ns ister write 2ns ory read 2ns ory write 2ns 2ns What is the clock cycle length? 1 Single Cycle Length Worst case
Computer Architecture and Organization:
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L03: Register transfer and System Bus By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU Outlines
Computer Architecture and Organization: L03: Register transfer and System Bus By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU Outlines
Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
Perception in Immersive Environments
 Perception in Immersive Environments Scott Kuhl Department of Computer Science Augsburg College scott@kuhlweb.com Abstract Immersive environment (virtual reality) systems provide a unique way for researchers
Perception in Immersive Environments Scott Kuhl Department of Computer Science Augsburg College scott@kuhlweb.com Abstract Immersive environment (virtual reality) systems provide a unique way for researchers
How Close Can You Get?
 How Close Can You Get? Group: Pairs Materials: calculator, How Close Can You Get Sheet, How Close Can You Get cards Give each pair a cut out set of the How Close Can You Get cards. Issue a How Close Can
How Close Can You Get? Group: Pairs Materials: calculator, How Close Can You Get Sheet, How Close Can You Get cards Give each pair a cut out set of the How Close Can You Get cards. Issue a How Close Can
NanoFabrics: : Spatial Computing Using Molecular Electronics
 NanoFabrics: : Spatial Computing Using Molecular Electronics Seth Copen Goldstein and Mihai Budiu Computer Architecture, 2001. Proceedings. 28th Annual International Symposium on 30 June-4 4 July 2001
NanoFabrics: : Spatial Computing Using Molecular Electronics Seth Copen Goldstein and Mihai Budiu Computer Architecture, 2001. Proceedings. 28th Annual International Symposium on 30 June-4 4 July 2001
DS Tap Silicon Delay Line
 www.dalsemi.com FEATURES All-silicon time delay taps equally spaced Delays are stable and precise Both leading and trailing edge accuracy Delay tolerance ±% or ± ns, whichever is greater Low-power CMOS
www.dalsemi.com FEATURES All-silicon time delay taps equally spaced Delays are stable and precise Both leading and trailing edge accuracy Delay tolerance ±% or ± ns, whichever is greater Low-power CMOS
CellSpecks: A Software for Automated Detection and Analysis of Calcium
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 115 Supplemental Information CellSpecks: A Software for Automated Detection and Analysis of Calcium Channels in Live Cells Syed Islamuddin Shah, Martin Smith, Divya Swaminathan,
Biophysical Journal, Volume 115 Supplemental Information CellSpecks: A Software for Automated Detection and Analysis of Calcium Channels in Live Cells Syed Islamuddin Shah, Martin Smith, Divya Swaminathan,
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) 2 1. DAC In an electronic circuit, a combination of high voltage (+5V) and low voltage (0V) is usually used to represent a binary
1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) 2 1. DAC In an electronic circuit, a combination of high voltage (+5V) and low voltage (0V) is usually used to represent a binary
Computer Elements and Datapath. Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA
 6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on LHC)
 Lecture 2 Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on LHC) Introduction Data handling requirements for LHC Design issues: Architectures Front-end, event selection levels Trigger Future evolutions Conclusion
Lecture 2 Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on LHC) Introduction Data handling requirements for LHC Design issues: Architectures Front-end, event selection levels Trigger Future evolutions Conclusion
GATE Online Free Material
 Subject : Digital ircuits GATE Online Free Material 1. The output, Y, of the circuit shown below is (a) AB (b) AB (c) AB (d) AB 2. The output, Y, of the circuit shown below is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) B (d) A 3.
Subject : Digital ircuits GATE Online Free Material 1. The output, Y, of the circuit shown below is (a) AB (b) AB (c) AB (d) AB 2. The output, Y, of the circuit shown below is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) B (d) A 3.
DS Tap Silicon Delay Line
 www.dalsemi.com FEATURES All-silicon time delay 10 taps equally spaced Delays are stable and precise Leading and trailing edge accuracy Delay tolerance ±5% or ±2 ns, whichever is greater Economical Auto-insertable,
www.dalsemi.com FEATURES All-silicon time delay 10 taps equally spaced Delays are stable and precise Leading and trailing edge accuracy Delay tolerance ±5% or ±2 ns, whichever is greater Economical Auto-insertable,
Objective Questions. (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these
 Objective Questions Module 1: Introduction 1. Which of the following is an analog quantity? (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these 2. Which of the following is a digital quantity? (a) Electrical
Objective Questions Module 1: Introduction 1. Which of the following is an analog quantity? (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these 2. Which of the following is a digital quantity? (a) Electrical
Chapter 5: Analog Input
 Chapter 5: Analog Input tw rev. 30.8.16 If you use or reference these slides or the associated textbook, please cite the original authors work as follows: Toulson, R. & Wilmshurst, T. (2016). Fast and
Chapter 5: Analog Input tw rev. 30.8.16 If you use or reference these slides or the associated textbook, please cite the original authors work as follows: Toulson, R. & Wilmshurst, T. (2016). Fast and
Software-based Microarchitectural Attacks
 SCIENCE PASSION TECHNOLOGY Software-based Microarchitectural Attacks Daniel Gruss April 19, 2018 Graz University of Technology 1 Daniel Gruss Graz University of Technology Whoami Daniel Gruss Post-Doc
SCIENCE PASSION TECHNOLOGY Software-based Microarchitectural Attacks Daniel Gruss April 19, 2018 Graz University of Technology 1 Daniel Gruss Graz University of Technology Whoami Daniel Gruss Post-Doc
Series Circuits and Kirchoff s Voltage Law
 ELEN 236 Series and Parallel Circuits www.okanagan.bc.ca/electronics Series Circuits and Kirchoff s Voltage Law Reference All About Circuits->DC->Chapter 5 and Chapter 6 Questions: CurrentVoltageResistance:
ELEN 236 Series and Parallel Circuits www.okanagan.bc.ca/electronics Series Circuits and Kirchoff s Voltage Law Reference All About Circuits->DC->Chapter 5 and Chapter 6 Questions: CurrentVoltageResistance:
Exploiting Resonant Behavior to Reduce Inductive Noise
 To appear in the 31st International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA 31), June 2004 Exploiting Resonant Behavior to Reduce Inductive Noise Michael D. Powell and T. N. Vijaykumar School of Electrical
To appear in the 31st International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA 31), June 2004 Exploiting Resonant Behavior to Reduce Inductive Noise Michael D. Powell and T. N. Vijaykumar School of Electrical
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining
 Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Advanced Digital Design
 Advanced Digital Design The Need for a Design Style by A. Steininger Vienna University of Technology Outline Skew versus consistency The need for a design style Hazards, Glitches & Runts Lecture "Advanced
Advanced Digital Design The Need for a Design Style by A. Steininger Vienna University of Technology Outline Skew versus consistency The need for a design style Hazards, Glitches & Runts Lecture "Advanced
Administrative Issues
 dministrative Issues Text book ($56.69 in mazon.com) Scanned problem set Email list Homework 1 announced, due 01/13/10 Quiz, 01/15/10 Graduate students meeting Relevant chapters in textbook? Technology
dministrative Issues Text book ($56.69 in mazon.com) Scanned problem set Email list Homework 1 announced, due 01/13/10 Quiz, 01/15/10 Graduate students meeting Relevant chapters in textbook? Technology
Cherry Picking: Exploiting Process Variations in the Dark Silicon Era
 Cherry Picking: Exploiting Process Variations in the Dark Silicon Era Siddharth Garg University of Waterloo Co-authors: Bharathwaj Raghunathan, Yatish Turakhia and Diana Marculescu # Transistors Power/Dark
Cherry Picking: Exploiting Process Variations in the Dark Silicon Era Siddharth Garg University of Waterloo Co-authors: Bharathwaj Raghunathan, Yatish Turakhia and Diana Marculescu # Transistors Power/Dark
An Efficient Low Power and High Speed carry select adder using D-Flip Flop
 Journal From the SelectedWorks of Journal April, 2016 An Efficient Low Power and High Speed carry select adder using D-Flip Flop Basavva Mailarappa Konnur M. Sharanabasappa This work is licensed under
Journal From the SelectedWorks of Journal April, 2016 An Efficient Low Power and High Speed carry select adder using D-Flip Flop Basavva Mailarappa Konnur M. Sharanabasappa This work is licensed under
Serial Addition. Lecture 29 1
 Serial Addition Operations in digital computers are usually done in parallel because that is a faster mode of operation. Serial operations are slower because a datapath operation takes several clock cycles,
Serial Addition Operations in digital computers are usually done in parallel because that is a faster mode of operation. Serial operations are slower because a datapath operation takes several clock cycles,
The Message Passing Interface (MPI)
 The Message Passing Interface (MPI) MPI is a message passing library standard which can be used in conjunction with conventional programming languages such as C, C++ or Fortran. MPI is based on the point-to-point
The Message Passing Interface (MPI) MPI is a message passing library standard which can be used in conjunction with conventional programming languages such as C, C++ or Fortran. MPI is based on the point-to-point
Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures
 Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Transistor: Building Block of Computers Microprocessors contain millions of transistors Intel Pentium 4 (2): 48 million IBM PowerPC 75FX (22): 38 million IBM/Apple PowerPC
Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Transistor: Building Block of Computers Microprocessors contain millions of transistors Intel Pentium 4 (2): 48 million IBM PowerPC 75FX (22): 38 million IBM/Apple PowerPC
ΕΠΛ 605: Προχωρημένη Αρχιτεκτονική
 ΕΠΛ 605: Προχωρημένη Αρχιτεκτονική Υπολογιστών Presentation of UniServer Horizon 2020 European project findings: X-Gene server chips, voltage-noise characterization, high-bandwidth voltage measurements,
ΕΠΛ 605: Προχωρημένη Αρχιτεκτονική Υπολογιστών Presentation of UniServer Horizon 2020 European project findings: X-Gene server chips, voltage-noise characterization, high-bandwidth voltage measurements,
