A COMPARISON STUDY OF 3G SYSTEM PROPOSALS: CDMA2000 VS. WCDMA
|
|
|
- Silas McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A COMPARISON STUDY OF 3G SYSTEM PROPOSALS: CDMA2000 VS. WCDMA Emre A. Yavuz and Dr. Victor Leung University of British Colombia, 2356 Main Mall, Vancouver, BC, CANADA, V6T 1Z4 ABSTRACT With the introduction of the third generation systems (IMT-2000), second generation capabilities (voice and low/medium rate data) are extended adding multimedia capabilities to second-generation platforms such as support for high bit rates and introduction of packet data/ip access. In this paper the technical features of the two IMT-2000 radio interface proposals, ARIB/ETSI s WCDMA and TIA s cdma2000, are discussed and a comparison is being made regarding their performances. After the similarities are given briefly, the study is more focused on the differences that are affecting the performance. Main issues of the differences are examined in detail to find out the benefits or the drawbacks that those issues bring to each proposal. KEY WORDS WCDMA, cdma2000, 3G Proposals, Standardization, radio access networks, IMT 2000, TIA TR45.5. I. Introduction Wireless communication is taking the lead role in the communication business, as Internet is growing explosively and the users of the services like data and multimedia are demanding that those services are also available on the move. Research has been going on for more than a decade to find enabling techniques to increase capacity, data rates and thus to introduce multimedia and new supported services into mobile communications. These research efforts have been aligned with efforts in the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and other bodies to find standards and recommendations to develop a mobile communication network which has an access to multimedia capabilities and service quality similar to the fixed network. With the introduction of the third generation systems (IMT-2000), second generation capabilities (voice and low/medium rate data) are extended adding multimedia capabilities to second generation platforms such as support for high bit rates and introduction of packet data/ip access. European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) / Special Mobile Group (SMG), has been responsible for UMTS standardization since the early 1990s. The wideband CDMA (WCDMA) scheme has been developed as a joint effort between ETSI and ARIB during the second half of 1997 and was chosen in January 1998 as the basic technology for the UMTS terrestrial radio access (UTRA) system. On the other hand, in the United States in March 1998, the TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) TR45.5 committee, adopted a framework for wideband CDMA, backward compatible with IS-95, which is called cdma2000. Originally under TIA TR45.5, the responsibility of the cdma2000 work has been moved to a newly formed organization called The Third Generation Partnership Project 2, or 3GPP2, thereby benefiting from the expertise of specialists from Chinese (CWTS), Japanese (ARIB and TTC), Korean (TTA), and North American (TIA) standards bodies. The ITU approved the cdma2000 radio access system as the CDMA Multi- Carrier (MC) member of the IMT-2000 family of standards. This paper will discuss the similarities and the differences between the two radio interface proposals, ARIB/ETSI s WCDMA and TIA s cdma2000, for future mobile multimedia communications (IMT-2000) by comparing the technical features of each proposal. After the similarities between the proposals are given briefly in the following section, the study will be focused on the differences that are affecting the performance and examining the main issues in detail to find out the benefits or the drawbacks that those issues bring to each proposal. Only the frequency division duplexing (FDD) mode will be considered in this paper. II. Similarities between cdma2000 and WCDMA Although they are developed by different organizations, there are many similarities between the two systems, since both employ key design concepts of IS-95. Below is a brief summary of the important similarities both systems have [3]: Coherent downlink and reverse link. Fast power control on forward (downlink) link as well as reverse (uplink) link. Variable length orthogonal Walsh sequences used for forward (downlink) and uplink channelization in order to separate users..
2 Complex QPSK spreading on downlink. Convolutional codes used as baseline (identical polynomials). Variable spreading factor to achieve higher data rates and to support blind rate estimation for simple services (e.g. voice). In current WCDMA systems this is done by TFIC (transport format Combination Indicator) Soft handover and mobile assisted inter-frequency hard handoff procedures. Turbo codes for higher data rates. It should be noted that while the concepts are similar, the details of the physical layers, which are going to be mentioned later, are different because of the separate standardization efforts. Nevertheless, although it is mentioned that both proposals employ key design concepts of IS-95, there are also differences in parameters like chip rate selection, pilot structure, base station synchronization, and frame length as well as the details of physical layers, procedures and etc. This is also due to another fact that WCDMA has to be compatible with GSM while cdma2000 has to be compatible with IS-95. III. Differences between WCDMA and cdma2000 Differences between the two systems include parameters like: a) Forward (downlink) link RF channel structure - beside the direct spread technique used for both channel structures, multicarrier cdma technique is also used for cdma2000. In this technique, multiple narrowband DS CDMA waveforms, each at a distinct carrier frequency, are combined to yield a composite wideband CDMA signal. Among the advantages of such an approach is the ability to achieve the same type of system performance that a conventional signal carrier, wideband CDMA signal, would provide, such as diversity enhancement over a multipath channel; however this is achieved without the need for a contiguous spectral band over which to spread. It also allows backward compatibility with IS-95 systems. On the other hand as it s indicated in the cdma2000 proposal [2] and shown in Table 1, DS is more spectrally efficient in the vehicular environment than the multicarrier method, whereas it s only slightly better or comparable in the pedestrian and indoor environments. b) Chip rates - the most discussed and debated parameter, which will be mentioned later in detail. c) Frame lengths - 10 ms/20 ms (optional) for WCDMA, 20 ms for data and control / 5 ms for control information on the fundamental and dedicated control channel of cdma2000. Coding operations are performed based on Tranmision Time Interval (TTI), 10 to 80 ms. This parameter will also be mentioned later in detail. TABLE 1. Spectrum efficiency comparison of MC and DS modes in cdma2000. Service Voice 9.6 kbps 1% FER Spectrum Efficiency (RL/FL) Environment (users/mhz/cell) for voice (Mbps/MHz/cell) for data Multicarrier Direct (MC) Spread (DS) Vehicular 29 / / 45.1 Pedestrian 42.1 / / 45.3 Indoor 38.9 / / 33.6 Mixed 34.1 / / 46.1 Vehicular / / Pedestrian / / Packet Data 76.8 kpbs 10% FER Indoor / / d) Coherent detection - while there is only common pilot for forward (downlink) link in WCDMA, there is a common continuous and common and dedicated auxiliary pilot for forward (downlink) link in cdma2000. This parameter will be discussed later in detail regarding the differences in the physical layer parameters of both systems. e) multiplexing in forward (downlink) link - A combined IQ and code multiplexing solution (dual channel QPSK) is used in WCDMA uplink to avoid electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) problems with discontinuous transmission (DTX)., pilot, fundamental and supplemental channels are also code multiplexed in cdma2000 uplink. However, in the downlink of WCDMA, the dedicated channels (DPDCH and DPCCH) are time multiplexed as the EMC problem caused by discontinuous transmission is not considered difficult because of the parallel transmitted signals to several users and having the base stations not so close to other electrical equipment, like hearing aids. Nevertheless, this last issue may also become a more important concern in the future when closer deployment of new base stations is considered. f) Power control - both systems have similar open and fast closed loops other than the rates that they are
3 FORWARD CDMA CHANNEL for Spreading Rates 1 and 3 (SR1 and SR3) Assignment Power Pilot s s Sync s Broadcast Paging s (SR1) Quick Paging Forward Pilot Transmit Diversity Pilot Aux. Pilot Auxiliary Transmit Diversity Pilot Fundamental Auxiliary Pilot Supplemental Code s (Radio Configurations 1-2) Figure 1. Forward channel structure of cdma2000. using: 1.5 khz for WCDMA vs. 800 Hz in cdma2000. g) Spreading for both forward (downlink) and reverse (uplink) link - variable length orthogonal sequences for channel separation and Gold sequences 2 18 for cell and user separation are used in downlink for WCDMA while variable length Walsh sequences for channel separation and M-sequence 2 15 (same sequence with time shift utilized in different cells, different sequence in I&Q channel) are used in downlink for cdma2000. In uplink variable length orthogonal sequences for channel separation and Gold sequences 2 24 for user separation (different time shifts in I and Q channel) are used for WCDMA while variable length orthogonal sequences for channel separation, M- sequence 2 15 (same sequence for all users, different sequences in I&Q channels) and M-sequence 2 41 for user separation (different time shifts for different users) are used for cdma2000. h) Base station synchronization - WCDMA utilizes asynchronous base station operation which is composed of 3 step parallel code search for base station detection and slot/ frame, while cdma2000 uses synchronous base station operation that is through time shifted PN correlation. IV. Selection of Chip Rates At first, a chip rate of Mbps was assigned for WCDMA, while a rate of Mbps was proposed for cdma2000. But then, despite the fact that was claimed by the WCDMA proponents that the lower cdma2000 rate degrades the performance, this rate has been changed to 3.84 Mbps after considering the inefficiencies that deteriorated the system capacity. The case of the deployment of scenarios, is mentioned in [4]. On the other hand, it has to be highlighted that, chip rate, alone does not determine the overall system capacity. V. Frame Length The WCDMA RTT uses a 10 ms frame length, however 20 ms is also considered as an optional frame length. While 5 and 10 ms frame lengths can be appropriate for certain type of control messages and low-delay data applications, 20 ms based frame length is considered as the basis for voice and data applications. Since one of the common objectives is to reduce the endto-end delay, it s the 10 ms frame length to be chosen to reduce it regarding the target set by ITU. Both frame lengths couldn t meet the original end-to-end delay of 40 ms set by ITU.
4 REVERSE CDMA CHANNEL for Spreading Rates 1 and 3 (SR1 and SR3) Phy. Data s (RC 1 or 2) Enhanced Pilot Fundamental Power Subchannel However the ITU requirement has been relaxed, taking the constraint on using the 20 ms frame length away, while the end-to-end delay with 10 ms frame length will still be less. In spite of this advantage, it has been demonstrated that 10 ms frame reduces time diversity and increases E b /N o requirements. At 30 km/h, up to 2 db additional E b /N o may be required, based on simulation results on RL, 800 bps PC, and two antennas per one path per antenna [3]. Another advantage of using 20 ms frames is the overhead percentage (convolutional tail bits, CRC etc.). While the overhead is 11% for 8.6 kbps voice services (per cdma2000 numerology) with a 20 ms frame length, it s 20% with a 10 ms frame length for 8kbps voice services (per WCDMA/NA numerology) [3]. Existing vocoders are widely deployed based on 20 ms frames, which seem to offer the best tradeoff between vocoder delay and interleaver depth. On the other hand, 5 ms frame length is also used for control information on the fundamental and dedicated control channel in cdma2000. VI. Physical Layers The forward and reverse channel structures of cdma2000 and WCDMA are given in figures 1,2,3 and 4. i. Pilot Structures Supplemental Code s Figure 2. channel structure of cdma2000. In the current WCDMA description, time multiplexed pilot symbols are used in the downlink as opposed to code multiplexed pilot symbols in the uplink. Time multiplexed common pilot channel (CPICH) of WCDMA has two types of channels named Primary and Secondary which are similar to forward pilot channel (F-PICH) and forward common auxiliary pilot channel (F- CAPICH) respectively in cdma2000. In addition to these, cdma2000 has forward dedicated auxiliary pilot channel (F-DAPICH) to increase the coverage or data rate towards a particular mobile station, forward transmit diversity pilot channel (F-TDPICH) to be used for transmit diversity coherent detection and forward auxiliary transmit diversity pilot channel (F- ATDPICH) to be used for transmit coherent detection for a group of users. In WCDMA, the pilot symbols are transmitted by the code multiplexed dedicated physical control channel (DPCCH) in the uplink. However, cdma2000 has a pilot channel (R- PICH), which consists of a fixed reference value (pilot symbol) and multiplexed forward power control (PC) information. Although this is time multiplexed, these pilot symbols and the muxed power symbols are all sent with the same power level in order not to arise EMC problems. ii. Synchronization channels WCDMA has a synchronization channel (SCH), which consists of two sub channels named primary and secondary corresponding to forward synchronization channel (F- SYNC) in cdma2000. The advantage of two subchannels is the limitation of the search of long codes to a subset of all the codes. The unmodulated primary SCH is used to acquire the timing for secondary SCH, while the modulated secondary SCH code carries information about the long code group, which the long code of the BS belongs to. iii. Broadcasting channels In WCDMA, broadcast channel (BCCH) has a fixed rate of 32 kbps whereas the broadcast channel (F- BCCH) of cdma2000 has a frame containing 744 bits, transmitted at 19.2, 9.6 or 4.8 kbps. The transmission of 744 bits for once, twice or four times has a benefit of reducing battery consumption since a terminal that is able to successfully receive the first copy of the broadcast frame can stop monitoring the channel after.
5 FORWARD WCDMA CHANNEL Sync Primary Downlink Shared s Page Indicator Secondary Acquisition Indicator Primary Pilot Broadcast Paging Secondary Pilot Forward Physical Data Physical (Pilot + Power control + Transport format) Figure 3. Forward channel structure of WCDMA. iv. Paging channels Paging channel (PCH) of WCDMA is carried by secondary common control physical channel (S-CCPCH) whose rate may be different for different cells and can be set to provide the required capacity for PCH and FACH in each specific environment. The correspondent paging channel in cdma2000 is F-PCH, which is backward compatible with IS- 95. In addition to that, cdma2000 has a quick paging channel (F-QPCH), which is used for informing mobiles to listen to the paging, or forward common control channels when it s necessary to save power and maximize battery life. Usage of quick paging channel is more advantageous when it s used with synchronized base stations. v. Other downlink channel structures With an exception of slight differences, dedicated physical control and data channels (DPCCH and DPDCH) in WCDMA correspond to forward dedicated control channel (F- DCCH) and fundamental channel (F-FCH) in cdma2000 respectively. Other than those above, there are some other proposed channels for both systems, which can t be directly corresponded to each other but have some functions in common. In WCDMA, there is physical downlink shared channel (PDSCH), which is shared by users based on code multiplexing and acquisition indication channel (AICH). In cdma2000, there are forward common power control channel (F-PCCH), which supports the transmission of multiple power control bits associated with various reverse common control channels (R-CCCH) and forward common control channel (F-CCCH) which is used for communication of layer 3 and MAC messages from BS to MS. In addition to those in cdma2000, there is another channel called forward common assignment channel (F-CACH), which can be related to forward access channel (FACH) in WCDMA. vi. Uplink channel structures In the uplink, dedicated physical data channel (DPDCH) in WCDMA correspond to both reverse fundamental and supplemental channels (R-FCH and R-SCH) of cdma2000. physical control channel (DPCCH) of WCDMA corresponds to reverse pilot and dedicated control channels (R- PICH and R-DCCH) of cdma2000. Physical random access channel (PRACH) and physical common packet channel (PCPCH) of WCDMA are correspondents for reverse access channel (R-ACH) and reverse common control channel (R-CCCH) of cdma2000, respectively. cdma2000 has an enhanced access channel (R-EACH) for random access control information. Although we ve used the term correspondence for the channels that are proposed for similar functions in both systems, it should also be noted that there are slight differences in their implementations and functioning. VII. Synchronization Base stations are synchronized in cdma2000 while WCDMA utilizes asynchronous BS operation. A comparison of asynchronous and synchronous base stations is given in [3] in detail and will be shortly
6 REVERSE WCDMA CHANNEL Random Physical Data Packet Physical discussed here: synchronized base stations with time -shifted common pilots permit fast one-step correlation resulting in quick acquisition and neighbor detection. Complexity in the mobile station is kept to a minimum since there is no need to adjust the timing of individual mobile in soft hand-off. experience with current commercial CDMA networks has shown that synchronized networks are reliable and efficient. Utilizing asynchronous BS operation, WCDMA requires highly stable timing references in the infrastructure for timing alignment. synchronized base stations permit the operation of common overhead and signaling channels (such as common control and paging channels) into soft handoff. Those techniques cannot be used in asynchronous networks without the expense of additional complexity and reduced performance that outweigh any benefits. MS terminal battery saving techniques such as Quick Paging channel work best with synchronized base stations whereas with asynchronous base stations, different cells are not time aligned and the MS must wake up multiple times and for larger periods to monitor the different base stations. performance issues like hard, inter-frequency handoff are still to be resolved regarding asynchronous operation. With asynchronous cells in WCDMA, it turns out that prior to handling off to the new frequency, the mobile has to shift to the new frequency channel for a delay of 40 ms, which is long and performance degrading, before decoding. although it s often claimed that an asynchronous system can be operated in synchronous mode and benefit from synchronous operation while it can operate asynchronously when timing reference is not available, this will lead to a higher mobile complexity, reduced capacity (due to non-orthogonal acquisition channels and large signaling overhead) and increased designed cycle. VIII. Conclusion This paper introduced a summary of comparison between the two dominant CDMA pro posals, cdma2000 and WCDMA for third generation systems. REFERENCES [1] 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Network; Physical channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD) (3G TS version 3.0.0). Pilot Subchannel Power Subchannel Transport Format Indicator Figure 4. channel structure of WCDMA [2] TIA/TR45.5, The cdma2000 ITU-R RTT Candidate Submission ( 1998). [3] Rao, Y.S. and Kripalani, A., cdma2000 Mobile Radio for IMT 2000, ICPWC, Jaipur, India, 1999, [4] CDG: 3G:Detailed Info: 3rd Generation Sy stems White Paper, asp [5] ETSI Tech. Rep , UMTS Terrestrial radio access: Concept evaluation (UMTS 30.06) (Version 3.0.0, Dec. 1997). [6] Willeneger, S., cdma2000 Physical Layer: An Overview, Journal of Communications and Networks, Vol.2, No: 1, March 2000, [7] Prasad Ramjee, Ojanpera Tero, An Overview of CDMA Evolution toward Wideband CDMA, IEEE Communication Surveys, [8] Dahlman E., Beming P., Knutsson J, Ovesjo, F., Persson, M., and Roobol, C., WCDMA The Radio Interface for Future Mobile Multimedia Communications, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 47, No 4, Nov. 1998, [9] Adachi, F., Sawahashi, M., Suda, H., Wideband DS-CDMA for Next Generation Mobile Communication Systems, IEEE Communications Magazine, Sep. 1998, [10] Dahlman E., Gudmundson B., Nilsson M, and Skold J. UMTS/IMT-2000 Based on Wideband CDMA, IEEE Communication Magazine, September 1998, [11] Knisely, D., N., Kumar, S., Laha, S., and Nanda, S., Evolution of Wireless Data Services : IS-95 to cdma2000, IEEE Communication Magazine, October 1998,
TELE4652 Mobile and Satellite Communications
 Mobile and Satellite Communications Lecture 12 UMTS W-CDMA UMTS W-CDMA The 3G global cellular standard set to supersede GSM Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) Slow on the uptake by mid-2008
Mobile and Satellite Communications Lecture 12 UMTS W-CDMA UMTS W-CDMA The 3G global cellular standard set to supersede GSM Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) Slow on the uptake by mid-2008
Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 14 CDMA2000
 Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 14 CDMA2000 1 CDMA2000 400 MHz, 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1700 MHz, 1800 MHz, 1900 MHz, and 2100 MHz Compatible with the cdmaone standard A set
Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 14 CDMA2000 1 CDMA2000 400 MHz, 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1700 MHz, 1800 MHz, 1900 MHz, and 2100 MHz Compatible with the cdmaone standard A set
Lauri Pirttiaho, NMP/Oulu
 Contents: General about radio communications systems 3GPP WCDMA L1, the physical layer structure Transmitting and receiving Channels Codings Procedures Not included: Lauri Pirttiaho, NMP/Oulu diversity
Contents: General about radio communications systems 3GPP WCDMA L1, the physical layer structure Transmitting and receiving Channels Codings Procedures Not included: Lauri Pirttiaho, NMP/Oulu diversity
RF Lecture Series Modulation Fundamentals Introduction to WCDMA
 RF Lecture Series Modulation Fundamentals Introduction to WCDMA Jeff Brenner Verigy Austin, TX 1. Introduction Second generation (2G) mobile communication standards were developed to provide higher bandwidth
RF Lecture Series Modulation Fundamentals Introduction to WCDMA Jeff Brenner Verigy Austin, TX 1. Introduction Second generation (2G) mobile communication standards were developed to provide higher bandwidth
Channelisation Codes (2)
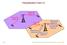 Channelisation Codes (2) Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #1 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 p. 51 Channelisation Codes (3)
Channelisation Codes (2) Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #1 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 p. 51 Channelisation Codes (3)
Lecture overview. UMTS concept UTRA FDD TDD
 Lecture overview 3G UMTS concept UTRA FDD TDD 3 rd Generation of Mobile Systems Goal to create a global system enabling global roaming International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT-2000) requirements: Throughput
Lecture overview 3G UMTS concept UTRA FDD TDD 3 rd Generation of Mobile Systems Goal to create a global system enabling global roaming International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT-2000) requirements: Throughput
RADIO LINK ASPECT OF GSM
 RADIO LINK ASPECT OF GSM The GSM spectral allocation is 25 MHz for base transmission (935 960 MHz) and 25 MHz for mobile transmission With each 200 KHz bandwidth, total number of channel provided is 125
RADIO LINK ASPECT OF GSM The GSM spectral allocation is 25 MHz for base transmission (935 960 MHz) and 25 MHz for mobile transmission With each 200 KHz bandwidth, total number of channel provided is 125
<3rd generation CDMA wireless systems>
 Page 1 Overview What is 3G? A brief overview of IS95 Key design choices for CDMA 3G systems. Bandwidth Modulation Coding Power Control
Page 1 Overview What is 3G? A brief overview of IS95 Key design choices for CDMA 3G systems. Bandwidth Modulation Coding Power Control
RFCD 202: Introduction to W-CDMA
 RFCD 202: Introduction to W-CDMA Technical data is subject to change Copyright@2003 Agilent Technologies Printed on Dec. 4, 2002 5988-8504ENA This paper examines the core concepts of one operating mode
RFCD 202: Introduction to W-CDMA Technical data is subject to change Copyright@2003 Agilent Technologies Printed on Dec. 4, 2002 5988-8504ENA This paper examines the core concepts of one operating mode
A Simulation Tool for Third Generation CDMA Systems Presentation to IEEE Sarnoff Symposium
 A Simulation Tool for Third Generation CDMA Systems Presentation to IEEE Sarnoff Symposium March 22, 2000 Fakhrul Alam, William Tranter, Brian Woerner Mobile and Portable Radio Research Group () e-mail:
A Simulation Tool for Third Generation CDMA Systems Presentation to IEEE Sarnoff Symposium March 22, 2000 Fakhrul Alam, William Tranter, Brian Woerner Mobile and Portable Radio Research Group () e-mail:
ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG 903 / 97. December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2. Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: System Description Summary
 ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG 903 / 97 Madrid, Spain Agenda item 4.1: UTRA December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: System Description Summary Concept Group Alpha -
ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG 903 / 97 Madrid, Spain Agenda item 4.1: UTRA December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: System Description Summary Concept Group Alpha -
WCDMA and cdma The Radio Interfaces for Future Mobile Multimedia Communications - Part II
 WCDMA and cdma2000 - The Radio Interfaces for Future Mobile Multimedia Communications - Part II Emre A. Yavuz 6.0 WCDMA The WCDMA scheme has been developed as a joint effort between ETSI and ARIB during
WCDMA and cdma2000 - The Radio Interfaces for Future Mobile Multimedia Communications - Part II Emre A. Yavuz 6.0 WCDMA The WCDMA scheme has been developed as a joint effort between ETSI and ARIB during
Chapter 5 3G Wireless Systems. Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar.
 Chapter 5 3G Wireless Systems Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. Upgrade paths for 2G Technologies 2G IS-95 GSM- IS-136 & PDC 2.5G IS-95B HSCSD GPRS EDGE Cdma2000-1xRTT W-CDMA 3G Cdma2000-1xEV,DV,DO EDGE Cdma2000-3xRTT
Chapter 5 3G Wireless Systems Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. Upgrade paths for 2G Technologies 2G IS-95 GSM- IS-136 & PDC 2.5G IS-95B HSCSD GPRS EDGE Cdma2000-1xRTT W-CDMA 3G Cdma2000-1xEV,DV,DO EDGE Cdma2000-3xRTT
CDMA Principle and Measurement
 CDMA Principle and Measurement Concepts of CDMA CDMA Key Technologies CDMA Air Interface CDMA Measurement Basic Agilent Restricted Page 1 Cellular Access Methods Power Time Power Time FDMA Frequency Power
CDMA Principle and Measurement Concepts of CDMA CDMA Key Technologies CDMA Air Interface CDMA Measurement Basic Agilent Restricted Page 1 Cellular Access Methods Power Time Power Time FDMA Frequency Power
Band Class Specification for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems
 GPP C.S00 Version.0 Date: February, 00 Band Class Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems Revision 0 COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual
GPP C.S00 Version.0 Date: February, 00 Band Class Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems Revision 0 COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual
Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations
 Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate
Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Cellular Networks: 2.5G and 3G 2.5G Data services over 2G networks GSM: High-speed
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Cellular Networks: 2.5G and 3G 2.5G Data services over 2G networks GSM: High-speed
Band Class Specification for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems
 GPP C.S00-B Version.0 Date: August, 00 Band Class Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems Revision B COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual
GPP C.S00-B Version.0 Date: August, 00 Band Class Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems Revision B COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual
Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA (WCDMA) EVALUATION DOCUMENT (3.0) Part 1: System Description Performance Evaluation
 ETSI SMG Tdoc SMG 905/97 Meeting no 24 Madrid, Spain 15-19 December 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA (WCDMA) EVALUATION DOCUMENT (3.0) Part 1: System Description Performance
ETSI SMG Tdoc SMG 905/97 Meeting no 24 Madrid, Spain 15-19 December 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA (WCDMA) EVALUATION DOCUMENT (3.0) Part 1: System Description Performance
CHAPTER 2 WCDMA NETWORK
 CHAPTER 2 WCDMA NETWORK 2.1 INTRODUCTION WCDMA is a third generation mobile communication system that uses CDMA technology over a wide frequency band to provide high-speed multimedia and efficient voice
CHAPTER 2 WCDMA NETWORK 2.1 INTRODUCTION WCDMA is a third generation mobile communication system that uses CDMA technology over a wide frequency band to provide high-speed multimedia and efficient voice
Transmit Diversity Schemes for CDMA-2000
 1 of 5 Transmit Diversity Schemes for CDMA-2000 Dinesh Rajan Rice University 6100 Main St. Houston, TX 77005 dinesh@rice.edu Steven D. Gray Nokia Research Center 6000, Connection Dr. Irving, TX 75240 steven.gray@nokia.com
1 of 5 Transmit Diversity Schemes for CDMA-2000 Dinesh Rajan Rice University 6100 Main St. Houston, TX 77005 dinesh@rice.edu Steven D. Gray Nokia Research Center 6000, Connection Dr. Irving, TX 75240 steven.gray@nokia.com
cdma2000 1x Rev. E Forward Link Voice Capacity
 cdma2 1x Rev. E Forward Link Voice Capacity Yucheun Jou, Peter Black, Qiang Wu, Rashid Attar, Wanlun Zhao, Bharat Ahuja, Junsheng Han Qualcomm Inc, San Diego, CA 92121, USA Abstract The forward link capacity
cdma2 1x Rev. E Forward Link Voice Capacity Yucheun Jou, Peter Black, Qiang Wu, Rashid Attar, Wanlun Zhao, Bharat Ahuja, Junsheng Han Qualcomm Inc, San Diego, CA 92121, USA Abstract The forward link capacity
Mobile Comms. Systems. Radio Interface
 Radio Interface Multiple Access Techniques MuAT (1/23) The transmission of bidirectional information in duplex systems (uplink - UL - and downlink - DL - channels) can be done by dividing in: frequency:
Radio Interface Multiple Access Techniques MuAT (1/23) The transmission of bidirectional information in duplex systems (uplink - UL - and downlink - DL - channels) can be done by dividing in: frequency:
ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG2 898 / 97 Madrid, Spain December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2. Concept Group Delta WB-TDMA/CDMA: Evaluation Summary
 ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG2 898 / 97 Madrid, Spain December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Delta WB-TDMA/CDMA: Evaluation Summary Introduction In the procedure to define the UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access
ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG2 898 / 97 Madrid, Spain December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Delta WB-TDMA/CDMA: Evaluation Summary Introduction In the procedure to define the UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access
IJPSS Volume 2, Issue 9 ISSN:
 INVESTIGATION OF HANDOVER IN WCDMA Kuldeep Sharma* Gagandeep** Virender Mehla** _ ABSTRACT Third generation wireless system is based on the WCDMA access technique. In this technique, all users share the
INVESTIGATION OF HANDOVER IN WCDMA Kuldeep Sharma* Gagandeep** Virender Mehla** _ ABSTRACT Third generation wireless system is based on the WCDMA access technique. In this technique, all users share the
CH 4. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System
 CH 4. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
CH 4. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
CH 5. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System
 CH 5. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
CH 5. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
Chapter 8: GSM & CDAMA Systems
 Chapter 8: GSM & CDAMA Systems Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Second Generation (Digital) Cellular System Operated in 900 MHz band GSM is also operated in 1800 MHz band and this version of
Chapter 8: GSM & CDAMA Systems Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Second Generation (Digital) Cellular System Operated in 900 MHz band GSM is also operated in 1800 MHz band and this version of
UMTS Radio Access Network Physical Layer. Fabrizio Tomatis
 UMTS Radio Access Network Physical Layer Fabrizio Tomatis Agenda 3G Standardization process 3GPP standardization committee ITU and frequency planning Physical layer principles Mapping of transport channels
UMTS Radio Access Network Physical Layer Fabrizio Tomatis Agenda 3G Standardization process 3GPP standardization committee ITU and frequency planning Physical layer principles Mapping of transport channels
IMPROVEMENT OF CALL BLOCKING PROBABILITY IN UMTS
 International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Vol.1,Issue 3 :Page No.299-303,September-October (2012) http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):2278-5299 IMPROVEMENT OF CALL
International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Vol.1,Issue 3 :Page No.299-303,September-October (2012) http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):2278-5299 IMPROVEMENT OF CALL
Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Stations
 Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate matching Interleaver
Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate matching Interleaver
Introduction to cdma2000 Standards for Spread Spectrum Systems Release C
 Version.0 Date: May 8, 00 Introduction to cdma000 Standards for Spread Spectrum Systems Release C GPP 00 GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
Version.0 Date: May 8, 00 Introduction to cdma000 Standards for Spread Spectrum Systems Release C GPP 00 GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
Performance Evaluation of 3G CDMA Networks with Antenna Arrays
 Jul. 2003 1 Performance Evaluation of 3G CDMA Networks with Antenna Arrays IEEE 4th Workshop on Applications and Services in Wireless Networks Dr. D. J. Shyy The Corporation Jin Yu and Dr. Yu-Dong Yao
Jul. 2003 1 Performance Evaluation of 3G CDMA Networks with Antenna Arrays IEEE 4th Workshop on Applications and Services in Wireless Networks Dr. D. J. Shyy The Corporation Jin Yu and Dr. Yu-Dong Yao
CDMA & WCDMA (UMTS) AIR INTERFACE. ECE 2526-WIRELESS & CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, June 25, 2018
 CDMA & WCDMA (UMTS) AIR INTERFACE ECE 2526-WIRELESS & CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, June 25, 2018 SPREAD SPECTRUM OPTIONS (1) Fast Frequency Hopping (FFSH) Advantages: Has higher anti-jamming
CDMA & WCDMA (UMTS) AIR INTERFACE ECE 2526-WIRELESS & CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, June 25, 2018 SPREAD SPECTRUM OPTIONS (1) Fast Frequency Hopping (FFSH) Advantages: Has higher anti-jamming
Introduction to WCDMA and WCDMA Dimensioning for UMTS
 Introduction to WCDMA and WCDMA Dimensioning for UMTS 1 internet Third generation services 2M 384K video conference video conference remote medical service video catalogue shopping video on demand mobile
Introduction to WCDMA and WCDMA Dimensioning for UMTS 1 internet Third generation services 2M 384K video conference video conference remote medical service video catalogue shopping video on demand mobile
CDMA Tutorial April 29, Michael Souryal April 29, 2006
 Michael Souryal April 29, 2006 Common Components Encoding, modulation, spreading Common Features/Functionality Power control, diversity, soft handoff System Particulars cdmaone (IS-95) cdma2000 Sources:
Michael Souryal April 29, 2006 Common Components Encoding, modulation, spreading Common Features/Functionality Power control, diversity, soft handoff System Particulars cdmaone (IS-95) cdma2000 Sources:
W-CDMA for UMTS Principles
 W-CDMA for UMTS Principles Introduction CDMA Background/ History Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Why CDMA? CDMA Principles / Spreading Codes Multi-path Radio Channel and Rake Receiver Problems to
W-CDMA for UMTS Principles Introduction CDMA Background/ History Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Why CDMA? CDMA Principles / Spreading Codes Multi-path Radio Channel and Rake Receiver Problems to
Chapter 6 Applications. Office Hours: BKD Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30
 Chapter 6 Applications 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Chapter 6 Applications 6.1 3G (UMTS and WCDMA) 2 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30
Chapter 6 Applications 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Chapter 6 Applications 6.1 3G (UMTS and WCDMA) 2 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VI: WCDMA Basics. Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 24.1.
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VI: WCDMA Basics Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 24.1.2008 Outline Network elements Physical layer Radio resource management
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VI: WCDMA Basics Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 24.1.2008 Outline Network elements Physical layer Radio resource management
CS 218 Fall 2003 October 23, 2003
 CS 218 Fall 2003 October 23, 2003 Cellular Wireless Networks AMPS (Analog) D-AMPS (TDMA) GSM CDMA Reference: Tanenbaum Chpt 2 (pg 153-169) Cellular Wireless Network Evolution First Generation: Analog AMPS:
CS 218 Fall 2003 October 23, 2003 Cellular Wireless Networks AMPS (Analog) D-AMPS (TDMA) GSM CDMA Reference: Tanenbaum Chpt 2 (pg 153-169) Cellular Wireless Network Evolution First Generation: Analog AMPS:
IS-95 /CdmaOne Standard. By Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar.
 IS-95 /CdmaOne Standard By Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. CDMA Classification of CDMA Systems CDMA SYSTEMS CDMA one CDMA 2000 IS95 IS95B JSTD 008 Narrow Band Wide Band CDMA Multiple Access in CDMA: Each user is assigned
IS-95 /CdmaOne Standard By Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. CDMA Classification of CDMA Systems CDMA SYSTEMS CDMA one CDMA 2000 IS95 IS95B JSTD 008 Narrow Band Wide Band CDMA Multiple Access in CDMA: Each user is assigned
HSDPA SYSTEM SIMULATION
 Thesis Number: MEE05:30 HSDPA SYSTEM SIMULATION Nguyen Kim Cuong Khan Muhammad Sohaib This thesis is presented as part of Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Blekinge Institute of Technology
Thesis Number: MEE05:30 HSDPA SYSTEM SIMULATION Nguyen Kim Cuong Khan Muhammad Sohaib This thesis is presented as part of Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Blekinge Institute of Technology
HSPA & HSPA+ Introduction
 HSPA & HSPA+ Introduction www.huawei.com Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic principle and features of HSPA and HSPA+ Page1 Contents 1. HSPA & HSPA+ Overview
HSPA & HSPA+ Introduction www.huawei.com Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic principle and features of HSPA and HSPA+ Page1 Contents 1. HSPA & HSPA+ Overview
5G Standardization Status in 3GPP
 As the radio interface of mobile phones has evolved, it has typically been changed about every ten years, and the 5G (5th Generation) interface is expected to start being used in the 2020s. Similar to
As the radio interface of mobile phones has evolved, it has typically been changed about every ten years, and the 5G (5th Generation) interface is expected to start being used in the 2020s. Similar to
Keysight Technologies Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations (Including Femtocells)
 Keysight Technologies Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations (Including Femtocells) Application Note DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder
Keysight Technologies Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations (Including Femtocells) Application Note DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder
ETSI TS V6.2.0 ( )
 TS 25 2 V6.2. (24-9) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Physical channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD) (3GPP TS 25.2 version 6.2.
TS 25 2 V6.2. (24-9) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Physical channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD) (3GPP TS 25.2 version 6.2.
Band Class Specification for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems
 GPP C.P00-C Version 0.0. Date: May 00Oct 00 Band Class Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
GPP C.P00-C Version 0.0. Date: May 00Oct 00 Band Class Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
CDMA is used to a limited extent on the 800-MHz band, but is much more common in the 1900-MHz PCS band. It uses code-division multiple access by
 IS-95 CDMA PCS CDMA Frequency Use CDMA Channels Forward Channel Reverse Channel Voice Coding Mobile Power Control Rake Receivers and Soft handoffs CDMA Security CDMA is used to a limited extent on the
IS-95 CDMA PCS CDMA Frequency Use CDMA Channels Forward Channel Reverse Channel Voice Coding Mobile Power Control Rake Receivers and Soft handoffs CDMA Security CDMA is used to a limited extent on the
ETSI TR V1.1.1 ( )
 TR 101 866 V1.1.1 (2001-07) Technical Report Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Satellite Component of UMTS/IMT-2000; Analysis and definition of the Packet Mode 2 TR 101 866 V1.1.1 (2001-07) Reference
TR 101 866 V1.1.1 (2001-07) Technical Report Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Satellite Component of UMTS/IMT-2000; Analysis and definition of the Packet Mode 2 TR 101 866 V1.1.1 (2001-07) Reference
Mobile Communication Systems. Part 7- Multiplexing
 Mobile Communication Systems Part 7- Multiplexing Professor Z Ghassemlooy Faculty of Engineering and Environment University of Northumbria U.K. http://soe.ac.uk/ocr Contents Multiple Access Multiplexing
Mobile Communication Systems Part 7- Multiplexing Professor Z Ghassemlooy Faculty of Engineering and Environment University of Northumbria U.K. http://soe.ac.uk/ocr Contents Multiple Access Multiplexing
Handover in IS-95, cdma2000, 1X-EV and WCDMA
 Chapter #8 Handover in IS-95, cdma2000, 1X-EV and WCDMA Key words: Abstract: Handover, handoff, soft handoff, intra-frequency handover, fast cell site selection This chapter introduces the concept of handover
Chapter #8 Handover in IS-95, cdma2000, 1X-EV and WCDMA Key words: Abstract: Handover, handoff, soft handoff, intra-frequency handover, fast cell site selection This chapter introduces the concept of handover
3G TECHNOLOGY WHICH CAN PROVIDE AUGMENTED DATA TRANSFER RATES FOR GSM STANDARTS AND THE MODULATION TECHNIQUES
 3G TECHNOLOGY WHICH CAN PROVIDE AUGMENTED DATA TRANSFER RATES FOR GSM STANDARTS AND THE MODULATION TECHNIQUES Mustafa ALKAN Ejder ORUÇ Nur ERZEN Özgür GENÇ malkan@tk.gov.tr eoruc@tk.gov.tr nerzen@tk.gov.tr
3G TECHNOLOGY WHICH CAN PROVIDE AUGMENTED DATA TRANSFER RATES FOR GSM STANDARTS AND THE MODULATION TECHNIQUES Mustafa ALKAN Ejder ORUÇ Nur ERZEN Özgür GENÇ malkan@tk.gov.tr eoruc@tk.gov.tr nerzen@tk.gov.tr
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOWNLINK POWER CONTROL IN WCDMA SYSTEM
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOWNLINK POWER CONTROL IN WCDMA SYSTEM Dr. M. Mahbubur Rahman, Md. Khairul Islam, Tarek Hassan-Al-Mahmud, A. R. Mahmud Abstract: WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) plays
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOWNLINK POWER CONTROL IN WCDMA SYSTEM Dr. M. Mahbubur Rahman, Md. Khairul Islam, Tarek Hassan-Al-Mahmud, A. R. Mahmud Abstract: WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) plays
CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cdma/questions_and_answers.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com 1. What is CDMA? CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a wireless technology
CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cdma/questions_and_answers.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com 1. What is CDMA? CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a wireless technology
ECE 476/ECE 501C/CS Wireless Communication Systems Winter Lecture 9: Multiple Access, GSM, and IS-95
 ECE 476/ECE 501C/CS 513 - Wireless Communication Systems Winter 2003 Lecture 9: Multiple Access, GSM, and IS-95 Outline: Two other important issues related to multiple access space division with smart
ECE 476/ECE 501C/CS 513 - Wireless Communication Systems Winter 2003 Lecture 9: Multiple Access, GSM, and IS-95 Outline: Two other important issues related to multiple access space division with smart
The Parametric Analysis of Gaussian Pulse Shaping Filter in WCDMA Network
 Abstract The Parametric Analysis of Gaussian Pulse Shaping Filter in WCDMA Network Shilpa Shukla*, Mr. Puran Gour,*Student, H.O.D, Department of Electronics & Comm., NIIST, Bhopal (M.P.) Digital Signal
Abstract The Parametric Analysis of Gaussian Pulse Shaping Filter in WCDMA Network Shilpa Shukla*, Mr. Puran Gour,*Student, H.O.D, Department of Electronics & Comm., NIIST, Bhopal (M.P.) Digital Signal
ETSI TS V2.1.1 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 85--2 V2.. (28-) Technical Specification Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Satellite Component of UMTS/IMT-2; Part : Physical channels and mapping of transport channels into physical channels;
TS 85--2 V2.. (28-) Technical Specification Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Satellite Component of UMTS/IMT-2; Part : Physical channels and mapping of transport channels into physical channels;
Abstract. Marío A. Bedoya-Martinez. He joined Fujitsu Europe Telecom R&D Centre (UK), where he has been working on R&D of Second-and
 Abstract The adaptive antenna array is one of the advanced techniques which could be implemented in the IMT-2 mobile telecommunications systems to achieve high system capacity. In this paper, an integrated
Abstract The adaptive antenna array is one of the advanced techniques which could be implemented in the IMT-2 mobile telecommunications systems to achieve high system capacity. In this paper, an integrated
An Overview of the QUALCOMM CDMA Digital Cellular Proposal
 An Overview of the QUALCOMM CDMA Digital Cellular Proposal Zeljko Zilic ELE 543S- Course Project Abstract.0 Introduction This paper describes a proposed Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) digital cellular
An Overview of the QUALCOMM CDMA Digital Cellular Proposal Zeljko Zilic ELE 543S- Course Project Abstract.0 Introduction This paper describes a proposed Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) digital cellular
Planning of LTE Radio Networks in WinProp
 Planning of LTE Radio Networks in WinProp AWE Communications GmbH Otto-Lilienthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblingen mail@awe-communications.com Issue Date Changes V1.0 Nov. 2010 First version of document V2.0
Planning of LTE Radio Networks in WinProp AWE Communications GmbH Otto-Lilienthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblingen mail@awe-communications.com Issue Date Changes V1.0 Nov. 2010 First version of document V2.0
CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT
 CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT 7.1 INTRODUCTION Originally developed to be used in GSM by the Europe Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), the AMR speech codec
CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT 7.1 INTRODUCTION Originally developed to be used in GSM by the Europe Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), the AMR speech codec
WCDMA / UMTS. Principle of Spectrum Spreading. Frequency used
 WCDMA / UMTS UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) is a new mobile standard. We talk about the third generation of telephony or 3G. Purists prefer the term W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple
WCDMA / UMTS UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) is a new mobile standard. We talk about the third generation of telephony or 3G. Purists prefer the term W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple
Harmonization of Global Third-Generation Mobile Systems
 3G SYSTEMS Harmonization of Global Third-Generation Mobile Systems M. Zeng, Motorola Inc. A. Annamalai, Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University Vijay K. Bhargava, University of Victoria Editorial
3G SYSTEMS Harmonization of Global Third-Generation Mobile Systems M. Zeng, Motorola Inc. A. Annamalai, Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University Vijay K. Bhargava, University of Victoria Editorial
Concept Group Alpha Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: Evaluation Summary
 ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG2 904 / 97 Madrid, Spain December 15-19, 1997 Agenda item 4.1: UTRA Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: Evaluation Summary Title: Summary of the Concept
ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG2 904 / 97 Madrid, Spain December 15-19, 1997 Agenda item 4.1: UTRA Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: Evaluation Summary Title: Summary of the Concept
3G/4G Mobile Communications Systems. Dr. Stefan Brück Qualcomm Corporate R&D Center Germany
 3G/4G Mobile Communications Systems Dr. Stefan Brück Qualcomm Corporate R&D Center Germany Chapter VI: Physical Layer of LTE 2 Slide 2 Physical Layer of LTE OFDM and SC-FDMA Basics DL/UL Resource Grid
3G/4G Mobile Communications Systems Dr. Stefan Brück Qualcomm Corporate R&D Center Germany Chapter VI: Physical Layer of LTE 2 Slide 2 Physical Layer of LTE OFDM and SC-FDMA Basics DL/UL Resource Grid
CS 6956 Wireless & Mobile Networks April 1 st 2015
 CS 6956 Wireless & Mobile Networks April 1 st 2015 The SIM Card Certain phones contain SIM lock and thus work only with the SIM card of a certain operator. However, this is not a GSM restriction introduced
CS 6956 Wireless & Mobile Networks April 1 st 2015 The SIM Card Certain phones contain SIM lock and thus work only with the SIM card of a certain operator. However, this is not a GSM restriction introduced
Chapter #4. An Overview of IS-95 and cdma INTRODUCTION
 Chapter #4 An Overview of IS-95 and cdma2000 Key words: Abstract: IS-95, cdma2000 The cdma2000 system is the third-generation extension of the existing IS-95 CDMA system currently deployed worldwide. This
Chapter #4 An Overview of IS-95 and cdma2000 Key words: Abstract: IS-95, cdma2000 The cdma2000 system is the third-generation extension of the existing IS-95 CDMA system currently deployed worldwide. This
Part 7. B3G and 4G Systems
 Part 7. B3G and 4G Systems p. 1 Roadmap HSDPA HSUPA HSPA+ LTE AIE IMT-Advanced (4G) p. 2 HSPA Standardization 3GPP Rel'99: does not manage the radio spectrum efficiently when dealing with bursty traffic
Part 7. B3G and 4G Systems p. 1 Roadmap HSDPA HSUPA HSPA+ LTE AIE IMT-Advanced (4G) p. 2 HSPA Standardization 3GPP Rel'99: does not manage the radio spectrum efficiently when dealing with bursty traffic
Technical Aspects of LTE Part I: OFDM
 Technical Aspects of LTE Part I: OFDM By Mohammad Movahhedian, Ph.D., MIET, MIEEE m.movahhedian@mci.ir ITU regional workshop on Long-Term Evolution 9-11 Dec. 2013 Outline Motivation for LTE LTE Network
Technical Aspects of LTE Part I: OFDM By Mohammad Movahhedian, Ph.D., MIET, MIEEE m.movahhedian@mci.ir ITU regional workshop on Long-Term Evolution 9-11 Dec. 2013 Outline Motivation for LTE LTE Network
Background: Cellular network technology
 Background: Cellular network technology Overview 1G: Analog voice (no global standard ) 2G: Digital voice (again GSM vs. CDMA) 3G: Digital voice and data Again... UMTS (WCDMA) vs. CDMA2000 (both CDMA-based)
Background: Cellular network technology Overview 1G: Analog voice (no global standard ) 2G: Digital voice (again GSM vs. CDMA) 3G: Digital voice and data Again... UMTS (WCDMA) vs. CDMA2000 (both CDMA-based)
Multiplexing Module W.tra.2
 Multiplexing Module W.tra.2 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA 1 Multiplexing W.tra.2-2 Multiplexing shared medium at
Multiplexing Module W.tra.2 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA 1 Multiplexing W.tra.2-2 Multiplexing shared medium at
3GPP Long Term Evolution LTE
 Chapter 27 3GPP Long Term Evolution LTE Slides for Wireless Communications Edfors, Molisch, Tufvesson 630 Goals of IMT-Advanced Category 1 2 3 4 5 peak data rate DL / Mbit/s 10 50 100 150 300 max DL modulation
Chapter 27 3GPP Long Term Evolution LTE Slides for Wireless Communications Edfors, Molisch, Tufvesson 630 Goals of IMT-Advanced Category 1 2 3 4 5 peak data rate DL / Mbit/s 10 50 100 150 300 max DL modulation
Page 1. Overview : Wireless Networks Lecture 9: OFDM, WiMAX, LTE
 Overview 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 9: OFDM, WiMAX, LTE Dina Papagiannaki & Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2009 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wireless09/
Overview 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 9: OFDM, WiMAX, LTE Dina Papagiannaki & Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2009 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wireless09/
3GPP TS V8.3.0 ( )
 TS 36.133 V8.3.0 (2008-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Requirements
TS 36.133 V8.3.0 (2008-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Requirements
Page 1. What is a Survey? : Wireless Networks Lecture 8: Cellular Networks. Deliverables. Surveys. Cell splitting.
 What is a Survey? 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 8: Cellular Networks Dina Papagiannaki & Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2009
What is a Survey? 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 8: Cellular Networks Dina Papagiannaki & Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2009
3G Technologies. Outline. WCDMA, TD-(S)CDMA and cdma2000 Janne Kurjenniemi. Background. 3G technologies WCDMA TD-(S)CDMA. cdma2000
 3G Technologies WCDMA, TD-(S)CDMA and cdma2000 Janne Kurjenniemi 1 Magister Solutions 2006-11-02 / JKu Outline Background Why new radio access Frequency allocation Spread spectrum 3G technologies WCDMA
3G Technologies WCDMA, TD-(S)CDMA and cdma2000 Janne Kurjenniemi 1 Magister Solutions 2006-11-02 / JKu Outline Background Why new radio access Frequency allocation Spread spectrum 3G technologies WCDMA
IMT-2000 members UTRA-TDD and UTRA-FDD
 IMT-2000 members UTRA-TDD and UTRA-FDD Dr. Christian Menzel, SIEMENS AG christian.menzel@icn.siemens.de Author Siemens AG, Munich Siemens AG 2000 IMT-2000_UTRA_TDD_FDD_1 UTRA (FDD + TDD)! IMT-2000 and
IMT-2000 members UTRA-TDD and UTRA-FDD Dr. Christian Menzel, SIEMENS AG christian.menzel@icn.siemens.de Author Siemens AG, Munich Siemens AG 2000 IMT-2000_UTRA_TDD_FDD_1 UTRA (FDD + TDD)! IMT-2000 and
Wireless Networks: An Introduction
 Wireless Networks: An Introduction Master Universitario en Ingeniería de Telecomunicación I. Santamaría Universidad de Cantabria Contents Introduction Cellular Networks WLAN WPAN Conclusions Wireless Networks:
Wireless Networks: An Introduction Master Universitario en Ingeniería de Telecomunicación I. Santamaría Universidad de Cantabria Contents Introduction Cellular Networks WLAN WPAN Conclusions Wireless Networks:
Simulation Software WinIQSIM
 Data sheet Version 04.00 Simulation Software WinIQSIM September 2004... ideal for the generation of digitally modulated signals Calculation of digitally modulated I/Q and IF signals For driving the internal
Data sheet Version 04.00 Simulation Software WinIQSIM September 2004... ideal for the generation of digitally modulated signals Calculation of digitally modulated I/Q and IF signals For driving the internal
System-Level Simulator for the W-CDMA Low Chip Rate TDD System y
 System-Level Simulator for the W-CDMA Low Chip Rate TDD System y Sung Ho Moon Λ, Jae Hoon Chung Λ, Jae Kyun Kwon Λ, Suwon Park Λ, Dan Keun Sung Λ, Sungoh Hwang ΛΛ, and Junggon Kim ΛΛ * CNR Lab., Dept.
System-Level Simulator for the W-CDMA Low Chip Rate TDD System y Sung Ho Moon Λ, Jae Hoon Chung Λ, Jae Kyun Kwon Λ, Suwon Park Λ, Dan Keun Sung Λ, Sungoh Hwang ΛΛ, and Junggon Kim ΛΛ * CNR Lab., Dept.
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Wireless and mobile communications
 9210-119 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Wireless and mobile communications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
9210-119 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Wireless and mobile communications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
Mobilné systémy 3. generácie UMTS
 Mobilné systémy 3. generácie UMTS Ing. Matúš Turcsány, PhD. turcsany@ktl.elf.stuba.sk KTL FEI STU 2009 Prehľad prednášok UMTS HSDPA, EUL HSPA evolution LTE LTE-Advanced Nasadené technológie GSM worldwide
Mobilné systémy 3. generácie UMTS Ing. Matúš Turcsány, PhD. turcsany@ktl.elf.stuba.sk KTL FEI STU 2009 Prehľad prednášok UMTS HSDPA, EUL HSPA evolution LTE LTE-Advanced Nasadené technológie GSM worldwide
EC 551 Telecommunication System Engineering. Mohamed Khedr
 EC 551 Telecommunication System Engineering Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr 1 Mohamed Khedr., 2008 Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week
EC 551 Telecommunication System Engineering Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr 1 Mohamed Khedr., 2008 Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week
Implementation of 3G WCDMA Systems Using Cyclic Hierarchical Code
 www.semargroups.org ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.02,Issue.05, May-2013, Pages:226-231 Implementation of 3G WCDMA Systems Using Cyclic Hierarchical Code D.PRASAD Associate Professor, ECE Dept, Ramanandatirtha Engineering
www.semargroups.org ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.02,Issue.05, May-2013, Pages:226-231 Implementation of 3G WCDMA Systems Using Cyclic Hierarchical Code D.PRASAD Associate Professor, ECE Dept, Ramanandatirtha Engineering
PERFORMANCE GAIN OF SMART DUAL ANTENNAS AT HANDSETS IN 3G CDMA SYSTEM
 PERFORMANCE GAIN OF SMART DUAL ANTENNAS AT HANDSETS IN 3G CDMA SYSTEM Suk Won Kim 1,DongSamHa 1,andJeongHoKim 2 1 VTVT (Virginia Tech VLSI for Telecommunications) Laboratory Department of Electrical and
PERFORMANCE GAIN OF SMART DUAL ANTENNAS AT HANDSETS IN 3G CDMA SYSTEM Suk Won Kim 1,DongSamHa 1,andJeongHoKim 2 1 VTVT (Virginia Tech VLSI for Telecommunications) Laboratory Department of Electrical and
Survey of Power Control Schemes for LTE Uplink E Tejaswi, Suresh B
 Survey of Power Control Schemes for LTE Uplink E Tejaswi, Suresh B Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering K L University, Guntur, India Abstract In multi user environment number of users
Survey of Power Control Schemes for LTE Uplink E Tejaswi, Suresh B Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering K L University, Guntur, India Abstract In multi user environment number of users
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF WCDMA RAKE RECEIVER USED IN 3G WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
 http:// DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF WCDMA RAKE RECEIVER USED IN 3G WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Kapil Sahu 1, Sarita Boolchandani 2, Brijesh Kumar 3 1,2,3 E & C Dept., Vivekananda Institute of Technology-East,
http:// DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF WCDMA RAKE RECEIVER USED IN 3G WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Kapil Sahu 1, Sarita Boolchandani 2, Brijesh Kumar 3 1,2,3 E & C Dept., Vivekananda Institute of Technology-East,
1X-Advanced: Overview and Advantages
 1X-Advanced: Overview and Advantages Evolution to CDMA2000 1X QUALCOMM INCORPORATED Authored by: Yallapragada, Rao 1X-Advanced: Overview and Advantages Evolution to CDMA2000 1X Introduction Since the first
1X-Advanced: Overview and Advantages Evolution to CDMA2000 1X QUALCOMM INCORPORATED Authored by: Yallapragada, Rao 1X-Advanced: Overview and Advantages Evolution to CDMA2000 1X Introduction Since the first
The 5th Smart Antenna Workshop 21 April 2003, Hanyang University, Korea Broadband Mobile Technology Fumiyuki Adachi
 The 5th Smart Antenna Workshop 21 April 2003, Hanyang University, Korea Broadband Mobile Technology Fumiyuki Adachi Dept. of Electrical and Communications Engineering, Tohoku University, Japan adachi@ecei.tohoku.ac.jp
The 5th Smart Antenna Workshop 21 April 2003, Hanyang University, Korea Broadband Mobile Technology Fumiyuki Adachi Dept. of Electrical and Communications Engineering, Tohoku University, Japan adachi@ecei.tohoku.ac.jp
ETSI TS V1.2.1 ( )
 TS 85- V.2. (26-) Technical Specification Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Satellite Component of UMTS/IMT2; G-family; Part : Physical channels and mapping of transport channels into physical
TS 85- V.2. (26-) Technical Specification Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Satellite Component of UMTS/IMT2; G-family; Part : Physical channels and mapping of transport channels into physical
SPREAD SPECTRUM (SS) SIGNALS FOR DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS
 Dr. Ali Muqaibel SPREAD SPECTRUM (SS) SIGNALS FOR DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS VERSION 1.1 Dr. Ali Hussein Muqaibel 1 Introduction Narrow band signal (data) In Spread Spectrum, the bandwidth W is much greater
Dr. Ali Muqaibel SPREAD SPECTRUM (SS) SIGNALS FOR DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS VERSION 1.1 Dr. Ali Hussein Muqaibel 1 Introduction Narrow band signal (data) In Spread Spectrum, the bandwidth W is much greater
References. What is UMTS? UMTS Architecture
 1 References 2 Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications Magazine, February
1 References 2 Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications Magazine, February
Difference Between. 1. Old connection is broken before a new connection is activated.
 Difference Between Hard handoff Soft handoff 1. Old connection is broken before a new connection is activated. 1. New connection is activated before the old is broken. 2. "break before make" connection
Difference Between Hard handoff Soft handoff 1. Old connection is broken before a new connection is activated. 1. New connection is activated before the old is broken. 2. "break before make" connection
Long Term Evolution (LTE)
 1 Lecture 13 LTE 2 Long Term Evolution (LTE) Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications
1 Lecture 13 LTE 2 Long Term Evolution (LTE) Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications
10EC81-Wireless Communication UNIT-6
 UNIT-6 The first form of CDMA to be implemented is IS-95, specified a dual mode of operation in the 800Mhz cellular band for both AMPS and CDMA. IS-95 standard describes the structure of wideband 1.25Mhz
UNIT-6 The first form of CDMA to be implemented is IS-95, specified a dual mode of operation in the 800Mhz cellular band for both AMPS and CDMA. IS-95 standard describes the structure of wideband 1.25Mhz
3GPP TS V6.6.0 ( )
 TS 25.106 V6.6.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; UTRA repeater radio transmission and reception (Release 6) The
TS 25.106 V6.6.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; UTRA repeater radio transmission and reception (Release 6) The
Contents. 1. HSPA & HSPA+ Overview. 2. HSDPA Introduction. 3. HSUPA Introduction. 4. HSPA+ Introduction
 Contents 1. HSPA & HSPA+ Overview 2. HSDPA Introduction 3. HSUPA Introduction 4. HSPA+ Introduction Page58 All the HSPA+ Features in RAN11 and RAN12 3GPP Version HSPA+ Technology RAN Version Release 7
Contents 1. HSPA & HSPA+ Overview 2. HSDPA Introduction 3. HSUPA Introduction 4. HSPA+ Introduction Page58 All the HSPA+ Features in RAN11 and RAN12 3GPP Version HSPA+ Technology RAN Version Release 7
Lecture 3 Cellular Systems
 Lecture 3 Cellular Systems I-Hsiang Wang ihwang@ntu.edu.tw 3/13, 2014 Cellular Systems: Additional Challenges So far: focus on point-to-point communication In a cellular system (network), additional issues
Lecture 3 Cellular Systems I-Hsiang Wang ihwang@ntu.edu.tw 3/13, 2014 Cellular Systems: Additional Challenges So far: focus on point-to-point communication In a cellular system (network), additional issues
S Postgraduate Course in Radiocommunications. WCDMA Radio Link Performance Indicators. Seminar Mervi Berner
 S-72.333 Postgraduate Course in Radiocommunications Seminar 21.01.2003 Mervi Berner Content Definitions of WCDMA Radio Link Performance Indicators Multipath Channel Conditions and Services Link-level Simulation
S-72.333 Postgraduate Course in Radiocommunications Seminar 21.01.2003 Mervi Berner Content Definitions of WCDMA Radio Link Performance Indicators Multipath Channel Conditions and Services Link-level Simulation
Multiple Access Schemes
 Multiple Access Schemes Dr Yousef Dama Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology An-Najah National University 2016-2017 Why Multiple access schemes Multiple access schemes are used to allow many
Multiple Access Schemes Dr Yousef Dama Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology An-Najah National University 2016-2017 Why Multiple access schemes Multiple access schemes are used to allow many
