Power supply circuits
|
|
|
- Elvin Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Power supply circuits Practical exercise in Analog Electronics Abstract In this lab some different power supply circuits should be characterized.
2
3 1 Introduction he four basic constituents of a power supply circuit are the transformer, the rectifier bridge and the electrolyte capacitor. In this laboration, we examine how these different parts influence the output voltage as well as the load s influence. Voltage stabilization with a Zener diode, as well as a Boost converter are also constructed. In all cases set the oscilloscope to dcmode to observe the general appearance of the output voltage. In case of a reasonably good rectification, the voltage is roughly constant with small variations, the ripple. Set the oscilloscope to ac-mode in order to observe the ripple voltage. Note that it is not possible to measure the MS-value using a conventional voltmeter, if the voltage is not sinusoidal. 2 Half wave rectifier Connect the diode 1N4002 between the output of the transformer and a 1k/5W resistor load (see figure 4.2). 1N4002 Figure 1. Half wave rectifier without capacitance Observe and measure the load voltage using the oscilloscope. Draw the observed waveform. Calculate the average and MS (root-mean-square) values. Calculate the output power in this case. urn the diode in the opposite direction. Observe and measure the load voltage using the oscilloscope. Draw the observed waveform. Calculate the average and MS (root-meansquare) values. Calculate the output power in this case. Summary: Draw U(t) as seen on the oscilloscope. Calculate U m and U MS. Do this with the diode in both directions. Calculate P out. 3 Half wave rectifier with filtering capacitance Connect the capacitance C = 100uF/50V (Observe the polarity and use a shielding box supplied by the laboratory teacher) in parallel to the load =1k/5W (as shown in figure 4.3). 1N4002 C Figure 2. Half wave rectifier with capacitance Summary: Draw U(t) as seen on the oscilloscope. Calculate U m and U MS. he signal can be approximated to ramp function in the calculations. Do this with and without the load. Calculate P out.
4 4 Full wave rectifier Connect the full wave rectifier (built using four diodes 1N4002) between the output of the transformer and the load =1k/5W (as in figure 4.4). - Figure 3. Full wave rectifier without capacitance Observe and measure the load voltage using the oscilloscope. Draw the observed waveform. Calculate the average and MS values as well as the load power. Summary: Draw U(t) as seen on the oscilloscope. Calculate U m and U MS. Calculate P out. 5 Full wave rectifier with filtering capacitance Connect the capacitance C=100F/50V (with SHIELD supplied by the laboratory instructor) in parallel to the load = 1k/5W (shown in figure 4.5). - C Figure 4. Full wave rectifier with capacitance Observe and measure the load voltage using the oscilloscope. Draw the observed waveform. Calculate the average and MS values as well as the load power. Summary: Draw U(t) as seen on the oscilloscope. Calculate U m and U MS. Calculate P out.
5 6 he Zener diode as a voltage stabilizer A Zener diode can be used as a voltage stabiliser to further improve the performance of the rectifying circuits. he serial resistance S in figure 4.6 needs to be chosen in such a way that the maximum power dissipation (1.3 W) of the Zener diode BZX85/C30, is not exceeded. Calculate S in such a way that the maximum power dissipation (which occurs when ) is 1 W. Calculate the maximal power dissipation in S when for the voltage where the stabilization stops working and select a resistor that fulfills the requirements. (Observe that the s in this way will not tolerate a short circuited load as the all of the input voltage will be dissipated in s ) s 230 V - C Figure 5. Zener diode voltage stabilizer Measure the Zener diode voltage and current for =. Use the oscilloscope for the measurement and measure the maximum ripple voltage. Connect the load =1k/5W. Measure the voltage and current as well as the maximum ripple voltage. Use the results to calculate the dynamic resistance of the diode. Summary: Determine s to limit power dissipation. Calculate P max for s. Draw U(t) as seen on the oscilloscope. Calculate U m and U MS. Do this with and without the load. Calculate d. 7 Formulas U U MS mean 1 U 1 U 0 0 u u t 2 dt t dt Hint: o simplify the integrals, the period of the functions can be chosen to: Sinusoidal functions: Use a period of 2 amp functions: Use a period of 1 his makes the calculations as simple as possible but will not affect the result. P U I U I d U I V Boost Out U I MS U I Vin 1 Duty MS 0 0
6 8 Documentation he lab should be documented in word or some other word-processor. All relevant graphs and calculations should be included in the report. he report should be submitted by to or within one week of the *second* lab session for this lab. Good Luck
Power supply circuits
 Power supply circuits Practical exercise in Analog Electronics Abstract In this lab some different power supply circuits should be characterized. 1. Introduction The four basic constituents of a power
Power supply circuits Practical exercise in Analog Electronics Abstract In this lab some different power supply circuits should be characterized. 1. Introduction The four basic constituents of a power
Diodes This week, we look at switching diodes, LEDs, and diode rectification. Be sure to bring a flash drive for recording oscilloscope traces.
 Diodes This week, we look at switching diodes, LEDs, and diode rectification. Be sure to bring a flash drive for recording oscilloscope traces. 1. Basic diode characteristics Build the circuit shown in
Diodes This week, we look at switching diodes, LEDs, and diode rectification. Be sure to bring a flash drive for recording oscilloscope traces. 1. Basic diode characteristics Build the circuit shown in
Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide Andras Meszaros, Mark Horvath
 Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide Andras Meszaros, Mark Horvath 3. Measurement: Diodes and rectifiers 2017.02.27. In this session we are going to measure forward and reverse characteristics of
Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide Andras Meszaros, Mark Horvath 3. Measurement: Diodes and rectifiers 2017.02.27. In this session we are going to measure forward and reverse characteristics of
Exercise 7 AC voltage measurements peak responding detectors
 Exercise 7 AC voltage measurements peak responding detectors 1. Aim of the exercise The aim of the exercise is to familiarize students with the AC voltage measurements by means of peak responding detectors.
Exercise 7 AC voltage measurements peak responding detectors 1. Aim of the exercise The aim of the exercise is to familiarize students with the AC voltage measurements by means of peak responding detectors.
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 2 - Semiconductor Diodes Overview: In this lab session students will investigate I-V characteristics
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 2 - Semiconductor Diodes Overview: In this lab session students will investigate I-V characteristics
EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes
 EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Dr. A.V. Radun Dr. K.D. Donohue (9/18/03) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Laboratory
EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Dr. A.V. Radun Dr. K.D. Donohue (9/18/03) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Laboratory
Exercise 6 AC voltage measurements average responding voltmeters
 Exercise 6 AC voltage measurements average responding voltmeters 1. Aim of the exercise The aim of the exercise is to familiarize students with the AC voltage measurements by means of rectified average
Exercise 6 AC voltage measurements average responding voltmeters 1. Aim of the exercise The aim of the exercise is to familiarize students with the AC voltage measurements by means of rectified average
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE
 EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (I max = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6V pp, 12.6 V RMS ) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (I max = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6V pp, 12.6 V RMS ) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier
 PURPOSE: ELECTRONICS 224 ETR620S Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier This laboratory session acquaints you with the operation of a diode power supply. You will study the operation of half-wave and the effect
PURPOSE: ELECTRONICS 224 ETR620S Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier This laboratory session acquaints you with the operation of a diode power supply. You will study the operation of half-wave and the effect
SKEU 3741 BASIC ELECTRONICS LAB
 Faculty: Subject Subject Code : SKEU 3741 FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING : 2 ND YEAR ELECTRONIC DESIGN LABORATORY Review Release Date Last Amendment Procedure Number : 1 : 2013 : 2013 : PK-UTM-FKE-(0)-10
Faculty: Subject Subject Code : SKEU 3741 FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING : 2 ND YEAR ELECTRONIC DESIGN LABORATORY Review Release Date Last Amendment Procedure Number : 1 : 2013 : 2013 : PK-UTM-FKE-(0)-10
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION
 EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
Basic DC Power Supply
 Basic DC Power Supply Equipment: 1. Analog Oscilloscope 2. Digital multimeter 3. Experimental board and connectors. Objectives: 1. To understand the basic DC power supply both half wave and full wave rectifier.
Basic DC Power Supply Equipment: 1. Analog Oscilloscope 2. Digital multimeter 3. Experimental board and connectors. Objectives: 1. To understand the basic DC power supply both half wave and full wave rectifier.
Topic Rectification. Draw and understand the use of diodes in half wave and full wave
 Topic 2.4.2 Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Draw and understand the use of diodes in half wave and full wave bridge rectifiers; Calculate the peak value of the output
Topic 2.4.2 Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Draw and understand the use of diodes in half wave and full wave bridge rectifiers; Calculate the peak value of the output
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT : 1 TITLE : Half-Wave Rectifier & Filter OUTCOME : Upon completion of this unit, the student should be able to: i. Construct
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT : 1 TITLE : Half-Wave Rectifier & Filter OUTCOME : Upon completion of this unit, the student should be able to: i. Construct
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE
 EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Equipment List Dual Channel Oscilloscope R, 330, 1k, 10k resistors P, Tri-Power Supply V, 2x Multimeters D, 4x 1N4004: I max = 1A, PIV = 400V Silicon Diode P 2 35.6V pp (12.6 V
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Equipment List Dual Channel Oscilloscope R, 330, 1k, 10k resistors P, Tri-Power Supply V, 2x Multimeters D, 4x 1N4004: I max = 1A, PIV = 400V Silicon Diode P 2 35.6V pp (12.6 V
Başkent University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EEM 214 Electronics I Experiment 2. Diode Rectifier Circuits
 Başkent University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EEM 214 Electronics I Experiment 2 Diode Rectifier Circuits Aim: The purpose of this experiment is to become familiar with the use
Başkent University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EEM 214 Electronics I Experiment 2 Diode Rectifier Circuits Aim: The purpose of this experiment is to become familiar with the use
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE
 EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting AC to DC
 EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10
 DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10 In this experiment we will measure the I vs V characteristics of Si, Ge, and Zener p-n junction diodes, and
DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10 In this experiment we will measure the I vs V characteristics of Si, Ge, and Zener p-n junction diodes, and
ECEG 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2017
 ECEG 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2017 Introduction Lab #4: Regulated DC Power Supply A simple DC power supply can be designed using only a transformer, a rectifier, and a filter capacitor. However,
ECEG 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2017 Introduction Lab #4: Regulated DC Power Supply A simple DC power supply can be designed using only a transformer, a rectifier, and a filter capacitor. However,
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers
 Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 204 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 204 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
3. Diode, Rectifiers, and Power Supplies
 3. Diode, Rectifiers, and Power Supplies Semiconductor diodes are active devices which are extremely important for various electrical and electronic circuits. Diodes are active non-linear circuit elements
3. Diode, Rectifiers, and Power Supplies Semiconductor diodes are active devices which are extremely important for various electrical and electronic circuits. Diodes are active non-linear circuit elements
transformer rectifiers
 Power supply mini-project This week, we finish up 201 lab with a short mini-project. We will build a bipolar power supply and use it to power a simple amplifier circuit. 1. power supply block diagram Figure
Power supply mini-project This week, we finish up 201 lab with a short mini-project. We will build a bipolar power supply and use it to power a simple amplifier circuit. 1. power supply block diagram Figure
Diode Applications Half-Wave Rectifying
 Lab 5 Diode Applications Half-Wave ectifying Objectives: Study the half-wave rectifying and smoothing with a capacitor for a simple diode circuit. Study the use of a Zener diode in a circuit with an AC
Lab 5 Diode Applications Half-Wave ectifying Objectives: Study the half-wave rectifying and smoothing with a capacitor for a simple diode circuit. Study the use of a Zener diode in a circuit with an AC
EE 2212 EXPERIMENT 3 3 October 2013 Diode I D -V D Measurements and Half Wave and Full Wave Bridge Rectifiers PURPOSE
 EE 2212 EXPERIMENT 3 3 October 2013 Diode I D -V D Measurements and Half Wave and Full Wave Bridge Rectifiers PURPOSE Use laboratory measurements to extract key diode model parameters including I S,n (also
EE 2212 EXPERIMENT 3 3 October 2013 Diode I D -V D Measurements and Half Wave and Full Wave Bridge Rectifiers PURPOSE Use laboratory measurements to extract key diode model parameters including I S,n (also
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL
 ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
After performing this experiment, you should be able to:
 Objectives: After performing this experiment, you should be able to: Demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of the two basic rectifier circuits. Draw the output waveforms for the two basic rectifier
Objectives: After performing this experiment, you should be able to: Demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of the two basic rectifier circuits. Draw the output waveforms for the two basic rectifier
Application of diodes
 Application of diodes Instructions for the practical exercises of subject AE4B34EM 1 Objective measurements 2 The purpose of this measure is the introduction to the features and applications of semiconductor
Application of diodes Instructions for the practical exercises of subject AE4B34EM 1 Objective measurements 2 The purpose of this measure is the introduction to the features and applications of semiconductor
Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits
 1. Learning Outcomes Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits At the end of this lab, the students should be able to compare the experimental data to the theoretical curve of the diodes. The students
1. Learning Outcomes Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits At the end of this lab, the students should be able to compare the experimental data to the theoretical curve of the diodes. The students
EXPERIMENT 6: THE ZENER DIODE AND REGULATION
 EXPERIMENT 6: THE ZENER DIODE AND REGULATION Equipment List P 3 Full Wave Bridge OR 4x 1N4004 Diodes. OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope 100 F Electrolytic capacitor I Watt 8.2V Zener Diode R 5 Cenco
EXPERIMENT 6: THE ZENER DIODE AND REGULATION Equipment List P 3 Full Wave Bridge OR 4x 1N4004 Diodes. OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope 100 F Electrolytic capacitor I Watt 8.2V Zener Diode R 5 Cenco
In-Class Exercises for Lab 2: Input and Output Impedance
 In-Class Exercises for Lab 2: Input and Output Impedance. What is the output resistance of the output device below? Suppose that you want to select an input device with which to measure the voltage produced
In-Class Exercises for Lab 2: Input and Output Impedance. What is the output resistance of the output device below? Suppose that you want to select an input device with which to measure the voltage produced
ECE 2274 Pre-Lab for Experiment # 4 Diode Basics and a Rectifier Completed Prior to Coming to Lab
 Part I I-V Characteristic Curve ECE 2274 Pre-Lab for Experiment # 4 Diode Basics and a Rectifier Completed Prior to Coming to Lab 1. Construct the circuit shown in figure 4-1. Using a DC Sweep, simulate
Part I I-V Characteristic Curve ECE 2274 Pre-Lab for Experiment # 4 Diode Basics and a Rectifier Completed Prior to Coming to Lab 1. Construct the circuit shown in figure 4-1. Using a DC Sweep, simulate
EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification
 Name & Surname: ID: Date: EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification Objective To calculate, compare, draw, and measure the DC output voltages of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. Tools
Name & Surname: ID: Date: EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification Objective To calculate, compare, draw, and measure the DC output voltages of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. Tools
EDUCATIONAL MODULES EDU-006. EDU-006. Rectifiers. pag. 1 / 8. pag. 8/ 8. pag. 4/ 8. pag. 5/ 8. For LEARNING and to PRACTISE the ELECTRONICS
 . Rectifiers. Practice. Medium Wave Rectifier. The current will have a specific behaviour if you operate with one or several diodes in determined circuits. One of the most common diode's applications is
. Rectifiers. Practice. Medium Wave Rectifier. The current will have a specific behaviour if you operate with one or several diodes in determined circuits. One of the most common diode's applications is
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING. Electrical Engineering Science. Laboratory Manual
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Experiment #1 OHM S LAW... 3 Experiment # 2 SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS... 8
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Experiment #1 OHM S LAW... 3 Experiment # 2 SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS... 8
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers
 EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2018 Contents Objective:...2 Discussion:...2 Components Needed:...2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier...2 Part 2 A Nonlinear Application...3
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2018 Contents Objective:...2 Discussion:...2 Components Needed:...2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier...2 Part 2 A Nonlinear Application...3
Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB Amplifiers
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) Instrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor Objectives This exercise is designed
Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) Instrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor Objectives This exercise is designed
Diode Characteristics and Applications
 Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Electronics 1 Lab (CME 2410)
 Electronics 1 Lab (CME 410) School of Informatics & Computing German Jordanian University Laboratory Experiment () 1. Objective: Half-Wave, Full-Wave Rectifiers o be familiar with the half-wave rectifier,
Electronics 1 Lab (CME 410) School of Informatics & Computing German Jordanian University Laboratory Experiment () 1. Objective: Half-Wave, Full-Wave Rectifiers o be familiar with the half-wave rectifier,
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
DC Power Supply Design
 Sopczynski 1 John Sopczynski EE 310 Section 4 DC Power Supply Design Introduction The goal of this experiment was to design a DC power supply. Our team would be receiving 120 Vrms oscillating at 60 Hz
Sopczynski 1 John Sopczynski EE 310 Section 4 DC Power Supply Design Introduction The goal of this experiment was to design a DC power supply. Our team would be receiving 120 Vrms oscillating at 60 Hz
INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I
 INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I Laboratory 4 Wave Shaping Diode Circuits Author: ID CoAuthors: 1. ID 2. ID 3. ID Experiment Date: Report received Date: Comments For Instructor Full Marks Pre
INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I Laboratory 4 Wave Shaping Diode Circuits Author: ID CoAuthors: 1. ID 2. ID 3. ID Experiment Date: Report received Date: Comments For Instructor Full Marks Pre
Lab Exercise # 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits
 Objectives: THEORY Lab Exercise # 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits 1. To understand how to use multiple power supplies in a circuit. 2. To understand the distinction between signals and power. 3. To understand
Objectives: THEORY Lab Exercise # 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits 1. To understand how to use multiple power supplies in a circuit. 2. To understand the distinction between signals and power. 3. To understand
AC Theory and Electronics
 AC Theory and Electronics An Alternating Current (AC) or Voltage is one whose amplitude is not constant, but varies with time about some mean position (value). Some examples of AC variation are shown below:
AC Theory and Electronics An Alternating Current (AC) or Voltage is one whose amplitude is not constant, but varies with time about some mean position (value). Some examples of AC variation are shown below:
Homework No. 2 Diodes Electronics I. Reading Assignment: Chapters 1 through 4 in Microelectronic Circuits, by Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C. Smith.
 Homework No. 2 Diodes Electronics I Homework Quiz: See website for quiz date. Reading Assignment: Chapters 1 through 4 in Microelectronic Circuits, by Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C. Smith. 1. Exercises 4.1
Homework No. 2 Diodes Electronics I Homework Quiz: See website for quiz date. Reading Assignment: Chapters 1 through 4 in Microelectronic Circuits, by Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C. Smith. 1. Exercises 4.1
Physics 310 Lab 4 Transformers, Diodes, & Power Supplies
 Physics 310 Lab 4 Transformers, Diodes, & Power Supplies Equipment: O scope, W02G Bridge Rectifier, 110 6.3V transformer, four 1N4004 diodes, 1k, 10µF, 100µF, 1N5231 Zeener diode, ½ - Watt 100 Ω, 270Ω,
Physics 310 Lab 4 Transformers, Diodes, & Power Supplies Equipment: O scope, W02G Bridge Rectifier, 110 6.3V transformer, four 1N4004 diodes, 1k, 10µF, 100µF, 1N5231 Zeener diode, ½ - Watt 100 Ω, 270Ω,
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers
 EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
EE320L Electronics I. Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #4. Diode Rectifiers and Power Supply Circuits. Angsuman Roy
 EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #4 Diode Rectifiers and Power Supply Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective:
EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #4 Diode Rectifiers and Power Supply Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective:
Chapter 1: Introduction
 1.1. Introduction to power processing 1.2. Some applications of power electronics 1.3. Elements of power electronics Summary of the course 2 1.1 Introduction to Power Processing Power input Switching converter
1.1. Introduction to power processing 1.2. Some applications of power electronics 1.3. Elements of power electronics Summary of the course 2 1.1 Introduction to Power Processing Power input Switching converter
ECE 2274 Diode Basics and a Rectifier Completed Prior to Coming to Lab
 ECE 2274 Diode Basics and a Rectifier Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Perlab: Part I I-V Characteristic Curve for the 1. Construct the circuit shown in figure 1. Using a DC Sweep, simulate in LTspice
ECE 2274 Diode Basics and a Rectifier Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Perlab: Part I I-V Characteristic Curve for the 1. Construct the circuit shown in figure 1. Using a DC Sweep, simulate in LTspice
EELE 201 Circuits I. Fall 2013 (4 Credits)
 EELE 201 Circuits I Instructor: Fall 2013 (4 Credits) Jim Becker 535 Cobleigh Hall 994-5988 Office hours: Monday 2:30-3:30 pm and Wednesday 3:30-4:30 pm or by appointment EMAIL: For EELE 201-related questions,
EELE 201 Circuits I Instructor: Fall 2013 (4 Credits) Jim Becker 535 Cobleigh Hall 994-5988 Office hours: Monday 2:30-3:30 pm and Wednesday 3:30-4:30 pm or by appointment EMAIL: For EELE 201-related questions,
Semiconductor theory predicts that the current through a diode is given by
 3 DIODES 3 Diodes A diode is perhaps the simplest non-linear circuit element. To first order, it acts as a one-way valve. It is important, however, for a wide variety of applications, and will also form
3 DIODES 3 Diodes A diode is perhaps the simplest non-linear circuit element. To first order, it acts as a one-way valve. It is important, however, for a wide variety of applications, and will also form
Diodes. Diodes, Page 1
 Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 204 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 204 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering -
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering - Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Safety Rules and Operating Procedures... 3 Troubleshooting Hints... 4 Experiment
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering - Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Safety Rules and Operating Procedures... 3 Troubleshooting Hints... 4 Experiment
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits
 EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture V James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Finished the diode conduction
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture V James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Finished the diode conduction
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 Name: MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.091 Hands-On Introduction to EE Lab Skills Laboratory No. 1 Oscilloscopes, Multimeter, Function Generator IAP 2008 1 Objective In this laboratory, you will
Name: MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.091 Hands-On Introduction to EE Lab Skills Laboratory No. 1 Oscilloscopes, Multimeter, Function Generator IAP 2008 1 Objective In this laboratory, you will
Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad Pakistan SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I
 SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Yousaf Hameed Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Yousaf Hameed Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
CENG4480 Embedded System Development and Applications The Chinese University of Hong Kong Laboratory 1: Op Amp (I)
 CENG4480 Embedded System Development and Applications The Chinese University of Hong Kong Laboratory 1: Op Amp (I) Student ID: 2018 Fall 1 Introduction This lab session introduces some very basic concepts
CENG4480 Embedded System Development and Applications The Chinese University of Hong Kong Laboratory 1: Op Amp (I) Student ID: 2018 Fall 1 Introduction This lab session introduces some very basic concepts
Power Supplies. Linear Regulated Supplies Switched Regulated Supplies Batteries
 Power Supplies Linear Regulated Supplies Switched Regulated Supplies Batteries Im Alternating Current The Power -Im π/2 π 2π π t Im Idc Direct Current Supply π/2 π 2 π πt -Im ٢ http://bkaragoz.kau.edu.sa
Power Supplies Linear Regulated Supplies Switched Regulated Supplies Batteries Im Alternating Current The Power -Im π/2 π 2π π t Im Idc Direct Current Supply π/2 π 2 π πt -Im ٢ http://bkaragoz.kau.edu.sa
Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region
 Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region The field effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device can be used in two extreme ways as an active element in a circuit. One is
Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region The field effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device can be used in two extreme ways as an active element in a circuit. One is
Experiment No.15 DC-DC Converters
 Experiment No.15 DC-DC Converters Experiment aim The aim of Experiment is to analyze the operation (Switching) of DC-DC converter with resistive load. Apparatus 1. Power electronic trainer 2. Connection
Experiment No.15 DC-DC Converters Experiment aim The aim of Experiment is to analyze the operation (Switching) of DC-DC converter with resistive load. Apparatus 1. Power electronic trainer 2. Connection
Industrial Electricity. Answer questions and/or record measurements in the spaces provided.
 Industrial Electricity Lab 10: Building a Basic Power Supply ame Due Friday, 3/16/18 Answer questions and/or record measurements in the spaces provided. Measure resistance (impedance actually) on each
Industrial Electricity Lab 10: Building a Basic Power Supply ame Due Friday, 3/16/18 Answer questions and/or record measurements in the spaces provided. Measure resistance (impedance actually) on each
EE283 Electrical Measurement Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #7: Digital Counter
 EE283 Electrical Measurement Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #7: al Counter Objectives: 1. To familiarize students with sequential digital circuits. 2. To show how digital devices can be used for measurement
EE283 Electrical Measurement Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #7: al Counter Objectives: 1. To familiarize students with sequential digital circuits. 2. To show how digital devices can be used for measurement
VOLTAGE REGULATORS. A simplified block diagram of series regulators is shown in the figure below.
 VOTAGE EGATOS Voltage regulators provide a constant DC output voltage which is almost completely unaffected by changes in the load current, the input voltage or the temperature. They form the basis of
VOTAGE EGATOS Voltage regulators provide a constant DC output voltage which is almost completely unaffected by changes in the load current, the input voltage or the temperature. They form the basis of
University of Minnesota. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EE 3105 Laboratory Manual. A Second Laboratory Course in Electronics
 University of Minnesota Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE 3105 Laboratory Manual A Second Laboratory Course in Electronics Introduction You will find that this laboratory continues in
University of Minnesota Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE 3105 Laboratory Manual A Second Laboratory Course in Electronics Introduction You will find that this laboratory continues in
1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier. (2 points)
 Exam 1 Name: Score /60 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier.
Exam 1 Name: Score /60 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier.
Figure 1: Diode Measuring Circuit
 Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS
 UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS II EKT 214 Semester II (2013/2014) EXPERIMENT # 4 OP-AMP (COMPARATOR BASICS) EXPERIMENT 4 Op-Amp (Comparator Basics) 1. OBJECTIVE: 1.1 To demonstrate the op-amp
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS II EKT 214 Semester II (2013/2014) EXPERIMENT # 4 OP-AMP (COMPARATOR BASICS) EXPERIMENT 4 Op-Amp (Comparator Basics) 1. OBJECTIVE: 1.1 To demonstrate the op-amp
Instructions for the final examination:
 School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Practice Problems for the Final Examination COURSE : ECS304 Basic Electrical
School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Practice Problems for the Final Examination COURSE : ECS304 Basic Electrical
ECE 303 ELECTRONICS LABORATORY SPRING No labs meet this week. Course introduction & lab safety
 ECE 303 ELECTRONICS LABORATORY SPRING 2018 Week of Jan. 8 Jan. 15 Jan. 22 Jan. 29 Feb. 5 Feb. 12 Feb. 19 Feb. 26 Mar. 5 Mar. 12 Mar. 19 Mar. 26 Apr. 2 Apr. 9 Apr. 16 Topic No labs meet this week Course
ECE 303 ELECTRONICS LABORATORY SPRING 2018 Week of Jan. 8 Jan. 15 Jan. 22 Jan. 29 Feb. 5 Feb. 12 Feb. 19 Feb. 26 Mar. 5 Mar. 12 Mar. 19 Mar. 26 Apr. 2 Apr. 9 Apr. 16 Topic No labs meet this week Course
Experiment #3: Solid State Diodes Applications II
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #3: Solid State Diodes Applications II COMPONENTS Type
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #3: Solid State Diodes Applications II COMPONENTS Type
Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme
 Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme Akanksha Mishra, Anamika Upadhyay Akanksha Mishra is a lecturer ABIT, Cuttack, India (Email: misakanksha@gmail.com) Anamika Upadhyay
Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme Akanksha Mishra, Anamika Upadhyay Akanksha Mishra is a lecturer ABIT, Cuttack, India (Email: misakanksha@gmail.com) Anamika Upadhyay
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
 Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual EDC-I For Second Year Students Manual made by A.A.Sayar Author JNEC, Aurangabad 1 MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College N-6, CIDCO, Aurangabad
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual EDC-I For Second Year Students Manual made by A.A.Sayar Author JNEC, Aurangabad 1 MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College N-6, CIDCO, Aurangabad
29:128 Homework Problems
 29:128 Homework Problems Revised 22 Feb 2012 29:128 Homework 1 (15 points) references: Sections 1.6-1.7 & 4.8, Meyer Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill, 2nd Edition (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9
29:128 Homework Problems Revised 22 Feb 2012 29:128 Homework 1 (15 points) references: Sections 1.6-1.7 & 4.8, Meyer Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill, 2nd Edition (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9
Applications of diodes
 Applications of diodes Learners should be able to: (a) describe the I V characteristics of a silicon diode (b) describe the use of diodes for component protection in DC circuits and half-wave rectification
Applications of diodes Learners should be able to: (a) describe the I V characteristics of a silicon diode (b) describe the use of diodes for component protection in DC circuits and half-wave rectification
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
Lab Report 2 Half, Full and clipping Circuits of Diodes
 Abu Dhabi University Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab Report 2 Half, Full and clipping Circuits of Diodes Author: Muhammad Obaidullah 1030313 Hezam Salem 1014191 Salem Mohammad 1012824 Supervisor: Dr.
Abu Dhabi University Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab Report 2 Half, Full and clipping Circuits of Diodes Author: Muhammad Obaidullah 1030313 Hezam Salem 1014191 Salem Mohammad 1012824 Supervisor: Dr.
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
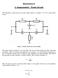 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Diode Bridges. Book page
 Diode Bridges Book page 450-454 Rectification The process of converting an ac supply into dc is called rectification The device that carries this out is called a rectifier Half wave rectifier only half
Diode Bridges Book page 450-454 Rectification The process of converting an ac supply into dc is called rectification The device that carries this out is called a rectifier Half wave rectifier only half
EE351 Laboratory Exercise 1 Diode Circuits
 revised July 19, 2009 The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to gain experience and understanding working with diodes. Focus on taking good data so that the plots and calculations you will do later
revised July 19, 2009 The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to gain experience and understanding working with diodes. Focus on taking good data so that the plots and calculations you will do later
Electrical and Electronic Principles in Engineering
 Unit 56: Electrical and Electronic Principles in Engineering Level: 3 Unit type: Optional Assessment type: Internal Guided learning: 60 Unit introduction The modern world relies on electrical and electronic
Unit 56: Electrical and Electronic Principles in Engineering Level: 3 Unit type: Optional Assessment type: Internal Guided learning: 60 Unit introduction The modern world relies on electrical and electronic
Each question is worth 2 points, except for problem 3, where each question is worth 5 points.
 Name: Date: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139 Spring Term 2007 Quiz 1 6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics
Name: Date: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139 Spring Term 2007 Quiz 1 6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics
Electronics. RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555
 Electronics RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555 0.1 Lab Ticket Each individual will write up his or her own Lab Report for this two-week experiment. You must also submit Lab Tickets individually. You are expected
Electronics RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555 0.1 Lab Ticket Each individual will write up his or her own Lab Report for this two-week experiment. You must also submit Lab Tickets individually. You are expected
Direct Current Waveforms
 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 20 DC and AC Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Direct Current (dc): o Direct current moves in only one direction in a circuit. o Though dc must
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 20 DC and AC Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Direct Current (dc): o Direct current moves in only one direction in a circuit. o Though dc must
Electric Circuit Fall 2017 Lab3 LABORATORY 3. Diode. Guide
 LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
ECEG 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2016
 EEG 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2016 Lab #4: Basic D Power Supply (Documentation requirements and scoring criteria revised 10/27/16) Introduction Because many types of electronic circuits are designed
EEG 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2016 Lab #4: Basic D Power Supply (Documentation requirements and scoring criteria revised 10/27/16) Introduction Because many types of electronic circuits are designed
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015
 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
Electronic I Lecture 3 Diode Rectifiers. By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood
 Electronic I Lecture 3 Diode Rectifiers By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood Diode Approximations 1- The Ideal Model When forward biased, act as a closed (on) switch When reverse biased, act as open (off)
Electronic I Lecture 3 Diode Rectifiers By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood Diode Approximations 1- The Ideal Model When forward biased, act as a closed (on) switch When reverse biased, act as open (off)
R 1 R 2. (3) Suppose you have two ac signals, which we ll call signals A and B, which have peak-to-peak amplitudes of 30 mv and 600 mv, respectively.
 29:128 Homework Problems 29:128 Homework 0 reference: Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9 V, R 1 = 1.5 kω, R 2 = 5.6 kω, (a) Calculate V out (b) Calculate the power
29:128 Homework Problems 29:128 Homework 0 reference: Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9 V, R 1 = 1.5 kω, R 2 = 5.6 kω, (a) Calculate V out (b) Calculate the power
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS TESTING OF HALF WAVE, FULL WAVE AND BRIDGE RECTIFIERS WITH AND WITHOUT CAPACITOR
 TESTING OF HALF WAVE, FULL WAVE AND BRIDGE RECTIFIERS WITH AND WITHOUT CAPACITOR Aim: To determine the ripple factor, efficiency and regulation of the half wave, full wave and bridge rectifier circuits
TESTING OF HALF WAVE, FULL WAVE AND BRIDGE RECTIFIERS WITH AND WITHOUT CAPACITOR Aim: To determine the ripple factor, efficiency and regulation of the half wave, full wave and bridge rectifier circuits
Examples to Power Supply
 Examples to Power Supply Example-1: A center-tapped full-wave rectifier connected to a transformer whose each secondary coil has a r.m.s. voltage of 1 V. Assume the internal resistances of the diode and
Examples to Power Supply Example-1: A center-tapped full-wave rectifier connected to a transformer whose each secondary coil has a r.m.s. voltage of 1 V. Assume the internal resistances of the diode and
Circuit operation Let s look at the operation of this single diode rectifier when connected across an alternating voltage source v s.
 Diode Rectifier Circuits One of the important applications of a semiconductor diode is in rectification of AC signals to DC. Diodes are very commonly used for obtaining DC voltage supplies from the readily
Diode Rectifier Circuits One of the important applications of a semiconductor diode is in rectification of AC signals to DC. Diodes are very commonly used for obtaining DC voltage supplies from the readily
Lab 2 Operational Amplifier
 Lab 2 Operational Amplifier Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Lab Section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday TA Signature: Note: The Pre-Lab section must be completed prior to the lab session.
Lab 2 Operational Amplifier Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Lab Section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday TA Signature: Note: The Pre-Lab section must be completed prior to the lab session.
UNIT V - RECTIFIERS AND POWER SUPPLIES
 UNIT V - RECTIFIERS AND POWER SUPPLIES OBJECTIVE On the completion of this unit the student will understand CLASSIFICATION OF POWER SUPPLY HALF WAVE, FULL WAVE, BRIDGE RECTIFER AND ITS RIPPLE FACTOR C,
UNIT V - RECTIFIERS AND POWER SUPPLIES OBJECTIVE On the completion of this unit the student will understand CLASSIFICATION OF POWER SUPPLY HALF WAVE, FULL WAVE, BRIDGE RECTIFER AND ITS RIPPLE FACTOR C,
Exercise 3: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE
 Exercise 3: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE voltage equal to double the peak ac input voltage by using a voltage doubler circuit. You will verify your results with a multimeter and an oscilloscope. DISCUSSION times
Exercise 3: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE voltage equal to double the peak ac input voltage by using a voltage doubler circuit. You will verify your results with a multimeter and an oscilloscope. DISCUSSION times
Week 12 Experiment 21. Design a Traffic Arrow
 Week 12 Experiment 21 Design a Traffic Arrow Just so it is clear This is it. Last official experiment for the semester. It is your option as to whether or not you do a make-up experiment. This is the last
Week 12 Experiment 21 Design a Traffic Arrow Just so it is clear This is it. Last official experiment for the semester. It is your option as to whether or not you do a make-up experiment. This is the last
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 2 BASIC CIRCUIT ELEMENTS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 2 BASIC CIRCUIT ELEMENTS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with
