The Application of EDA Technology in the Teaching of Communication Circuits
|
|
|
- Justina Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /jitae The Application of EDA Technology in the Teaching of Communication Circuits Jianfang YE 1, Jianwei YE* 2, Jiale TU 2 1 College of Information Science and Technology, Donghua University, No North Renmin Road, Shanghai , China 2 PLA South China Service Center for Computer Technology, Guangzhou , China leaf6411@dhu.edu.cn; *Yejianwei1@126.com Abstract With the design and simulation of single and double tuned amplifiers as an example, this paper discusses the application of NI Multisim, the advanced software, in the communication circuit teaching. Using the NI Multisim simulation platform, the parameters of various components in the circuit can be set freely. The relationship between the specific circuit parameters and the circuit performance can be investigated directly and in depth by referring to the simulation results. The proper combination of NI Multisim simulation software and the NI ELVIS platform can provide an effective training platform for improving the students comprehensive abilities in circuit design. Keywords EDA; Communication Circuits; Tuned Amplifier; NI ELVIS Introduction Electronic communication circuit is an engineering subject, for which practical training is very important for students to raise their abilities in system design and solve problems in practical engineering. In a laboratory, the software and hardware conditions are restricted, and therefore the experiments are mainly verification experiments; i.e., the students simply connect the wires on the developed circuit modules, measure the experimental data, conduct data analyses and finally submit experimental reports. By performing these experiments, the students can be trained to use the basic experimental instruments very skillfully. However, since the circuit modules have already been developed, the parameters of the components cannot be changed and the induced variations in circuit performance cannot be observed and measured. Correspondingly, the students are uncertain of the key components that can impose significant effects on circuit performance, and therefore their systematical design abilities cannot be refined by these experimental processes in which the data have been passively measured and recorded. The NI software Multisim has been introduced in the experimental teaching of electronic communication circuits with the aim of solving the above described problems (HOU Haipeng, 2006). Using this simulation platform, the parameters of circuit components can be flexibly adjusted and the effects of component parameters on the circuit performance can be directly investigated. For example, in a small signal tuned amplifier, by changing the load resistance, which is connected into the tuned network in parallel, the way that the load affects the Q value of the loop can be investigated, and further effects can be imposed on the frequency selecting characteristics of the amplifier (Sayre C., 2008). With regarding to a double tuned amplifier, by means of the simulation software Multisim, the parameters of coupling capacitance in the double tuned circuit can be scanned and then the variation process, from a single peak to the twin peak distribution of the frequency selecting characteristic, can be investigated. In experiments related to electronic communication circuits, through simulation and analysis using Multisim software and the construction of hardware circuits using ELVIS software, the physical properties of a circuit can be measured using the built in virtual instrument in the platform, and can then be compared with the simulation results. The procedure can greatly improve the efficiency and flexibility of experiments. As a consequence, the concept of design is integrated into the teaching process, and the objectives of ability training in innovation and engineering design are then effectively achieved. Communication Circuits Simulation A Single Tuned Amplifier A tuned amplifier is an amplifier loaded with the resonance circuit, which consists of a capacitor and inductor, whose gain varies with frequency. By using a 137
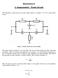
2 Journal of Information Technology and Application in Education Vol. 3 Iss. 4, December 2014 tuned amplifier, the high frequency signals within a certain frequency range can be magnified selectively. The resonance often tuned to the center frequencies of target signals. Due to the fact that the parallel resonance impedance of the tuned loop is quite large around the resonant frequency, a comparatively large voltage gain can be acquired in the amplifier (Gilmore R. and Besser L., 2006). When the circuit is at a frequency far away from the resonance point, the impedance of the loop decreases dramatically and the gain of the amplifier decreases accordingly. Conclusively, a tuned amplifier is a type of narrow band amplifier with high gains and favorable frequency selections. In this study, the focus was on the circuit of an intermediate frequency amplifier (IF AMP) in a frequency modulated receiver, as displayed in Fig By making use of the powerful circuit analysis ability of Multisim, the effects of emitter resistance on the gain of an amplifier, as well as the effects of the load resistor in an LC frequency selective network on the frequency selecting characteristics, were studied in this paper. FIG. 2.2 THE Re=500Ω INPUT AND OUTPUT WAVEFORM FIG. 2.3 THE Re=1KΩ INPUT AND OUTPUT WAVEFORM FIG. 2.4 THE Re=2KΩ INPUT AND OUTPUT WAVEFORM The cursor was shifted to the peak values of the input and output signals, and then the gain of amplifier (A) when Re was set as 500, 1000 and 2000Ω were calculated according to the simulation results in Fig The calculation results of the gain are listed as follows: A = V/ mv = db (Re = 500 Ω) A = V / mv = db (Re = 1000 Ω) A = V / mv = db (Re = 2000 Ω) FIG. 2.1 AN INTERMEDIATE FREQUENCY SINGLE TUNED AMPLIFIER 1) The Influence of an Emitter Resistor on the Gain of a Tuned Amplifier The frequency and amplitude of the input signals of Fig. 2.1, the simulated circuit constructed in Multisim, were set as 10.7 MHz and 25 mv, respectively. The CT of variable capacity was adjusted so that the amplifier was tuned at 10.7 MHz. The collector resistance was set as 10 KΩ, i.e., R=R0=10kΩ, while Re was assigned to be 500, 1000, and 2000 Ω. The oscilloscope, as showed in Fig. 2.1, was used for observing the input and output waveforms, with the simulation results showed in Fig As indicated in the simulation results, the voltage gain are reduced with the increase of Re, with the same input signals Vi. Theoretically, Re, which can provide negative current feedback, plays an important role in stabling the quiescent operating point of an amplifier. On the other hand, Re sacrifices the gain of an amplifier. The following problem was assigned to students as the after school training: as the bypass capacitance of emitter resistance in Fig. 2.1 is increased from 100 to 1000 nf, please perform simulations on the gain characteristics when Re is 500, 1000 and 2000 Ω, compare, and give reasonable explanations for the obtained simulation results. 2) The Effect of Load Resistance on the Frequency Selecting Characteristic of the Tuned Amplifier The frequency selecting characteristic of an amplifier is 138
3 referred as to its band pass properties. The signals within a bandwidth of 3dB can be amplified effectively by an amplifier, while the signals outside of the band present a rapidly decreasing gain. Set Re=1 KΩ, R=470, 2000 and 10000Ω, respectively, the amplitude frequency characteristic of the amplifier, was observed using the Bode Plotter, as shown in Fig. 2. The simulation results are displayed in Fig FIG. 2.5 THE AMPLITUDE VERSUS FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC WHEN R=470Ω FIG. 2.6 THE AMPLITUDE VERSUS FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC WHEN R=2 KΩ BW= ( ) MHz =0.452MHz (R = 2000 Ω) BW= ( ) MHz=0.145 MHz (R = Ω) The simulation results suggest that the amplitudefrequency characteristic of an amplifier is significantly affected by the load resistance R in the LC frequency selective network. The larger the R, the narrower the pass band of the amplifier, i.e., the more preferable the frequency selecting characteristic. As displayed in Figure 2.5, when the load resistance R is small, the frequency selecting characteristic and gain of the amplifier can be affected. Accordingly, when designing a tuned amplifier, if the given load resistance is small, an impedance transformation should be used by partly inserting the transformer coils in order to increase the load resistance in the tuned circuit. B Double Tuned Amplifier The load in a double tuned amplifier is comprised of two tuned circuits coupled by an inductor or capacitor. The double tuned amplifier is commonly used in the intermediate frequency amplifier (IF AMP) in a super heterodyne receiver (Rowan Gilmore, Les Besser, Yang Fang and Weng Muyun, 2006). Generally, the signal tuned amplifier has a simple circuit but several defects in its properties, such as a poor frequency selecting characteristic, uneven in band and slow out band attenuation. Moreover, there is a conflict between the selectivity and pass band in a single tuned circuit, which can be effectively solved by the double tuned amplifier (Gruenbacher D, Natarajan B and Kuhn W, 2006). In a double tuned amplifier, the rectangle coefficient is greatly improved. Fig. 2.8 displays the circuit of a double tuned amplifier, in which C4 is the coupling capacitor in two tuned circuits. When C4 was set as 5, 12, and 30pf, the amplitude frequency characteristic of the amplifier was observed using the Bode Plotter, and the simulation results are displayed in Fig FIG. 2.7 THE AMPLITUDE VERSUS FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC WHEN R=10KΩ Based on the simulated results as shown in Figures , the cursor was shifted to the upper and lower side frequencies, which were 3dB below the peak values, and then the 3dB bandwidth (BW) of the amplifier when the load resistance (R) was 470, 2000 and 10000Ω was calculated. Specifically: BW= ( ) MHz =1.539MHz(R = 470 Ω) FIG. 2.8 A DOUBLE TUNED AMPLIFIER 139
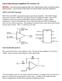
4 Journal of Information Technology and Application in Education Vol. 3 Iss. 4, December 2014 FIG. 2.9 THE AMPLITUDE VERSUS FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC WHEN C4=5PF Plotter, the amplitude frequency characteristic curve is twin peak distribution, and the pass band becomes broader, showing a concave between two peaks. As C4 continually increases, the concave between the two peaks becomes wider and deeper. Through simulation analyses, the coupling capacitance can be reasonably selected in accordance with the frequency selecting characteristic of the circuit, and therefore the design objective can be achieved quickly and accurately; i.e., the design efficiency can be greatly enhanced. The Circuit Implementation Based On NI ELVIS FIG THE AMPLITUDE VERSUS FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC WHEN C4=12PF FIG THE AMPLITUDE VERSUS FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC WHEN C4=30PF Similarly, according to the simulated amplitudefrequency characteristics in Figures , by shifting the cursor to the upper and lower side frequencies, which were 3dB below the peak values, the 3dB bandwidth (BW) of the amplifier when C4 was 5, 12, 30 pf can be calculated; specifically: The schematic circuit diagram, which had been simulated in Multisim, was constructed in the virtual ELVIS II+ platform, and thus the circuit components were connected in a virtual environment. Accordingly, it was possible to verify whether the electrical connection of the components was correct. Having been examined to be satisfactory, the hardware circuit was implemented on the physical ELVIS II+ platform, and the circuit performance was tested using the 12 kinds of ELVIS II+ built in virtual instruments. Moreover, the test results obtained by the virtual instruments could be compared with the simulation results from Multisim. Fig. 3.1 displays the constructed hardware circuit based on the platform of ELVIS II+, in which the left part displays the circuit constructed on the built in bread board of a prototyping board. If the circuit passed the test, i.e., the test results fitted well with the requirements, the PCB circuit as shown in the right part of Fig. 3.1 was then produced so that the stability of circuit performance could be ensured. BW= ( ) MHz =0.448MHz (C4 = 5 pf); BW= ( ) MHz = 1.004MHz (C4 = 12 pf) BW= ( ) MHz=1.863MHz. (C4 = 30 pf) As can be observed from the simulation results, the coupling state of the circuit is closely related to the coupling capacitance C4. When C4 is small, the circuit is weakly coupled, with a narrow pass band and small gain. This state should be avoided in the design of an amplifier. As the coupling capacitance C4 gradually increases, the circuit firstly changes to a critical coupling state while the amplitude frequency characteristic curve is single peaked; however, the pass band and the gain of the amplifier are more perfect compared to the situation of weakly coupled. When C4 is further increased, the circuit becomes strongly coupled. As can be observed by the Bode FIG. 3.1 THE IMPLEMENTATION OF A HARDWARE CIRCUIT BASED ON NI ELVISII+ The power supply and various input signals required by the circuit are provided by NI ELVIS II+. The 12 kinds of virtual instruments in ELVIS II+, with a USB interface, can be connected with the computer so that the circuit performance tests can be easily conducted and directly compared with the simulation results. Combined with fast and simple measurements and 140
5 displays, the design efficiency of communication circuits can be significantly improved (Mitchell J., Canavan B. and Smith J, 2010). The designer, whether a beginner or a veteran, can be trained on this hardware platform and complete the designs. Conclusions Compared with conventional cut and try designing methods, using Multisim to simulate circuit performance has a great advantage. Owing to the powerful simulation function of Multisim, circuit designers can change the component parameters as needed, and Multisim will provide an intuitive simulation result, which helps in knowing whether the design is suitable. If it is not, the component parameters can be optimized until the circuit performance is satisfactory. Finally, the hardware circuit is implemented on the NIELVIS II+, which integrates 12 common used virtual instruments within the platform, and makes the circuit performance testing very easy, without any of the limitations of laboratory equipment. The most important thing is that by means of Multisim simulation, the designer gets to know the key component parameters, which best suit the circuit performance. This paper discusses the influence of the load resistor s values on the amplitude versus the frequency characteristic of a single tuned amplifier, and the coupled capacitor s values on the amplitude versus the frequency characteristic of the double tuned amplifier. The analyses are taken as examples to show the methods of changing the component parameters and the resulting influences on the circuit performance with the use of Multisim. With the help of advanced EDA software, the efficiency and the possibility of successful circuit design are greatly enhanced. Incorporating performance simulation and a physical test platform make it possible to introduce comprehensive experiments into the teaching of Communication Circuits, which will help foster students ability as regard to both engineering problem solving and innovation. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The work of this paper is part of the project High quality engineering courses construction, funded by Shanghai Education Committee. REFERENCES Gilmore R. and Besser L. Modern Wireless RF Circuits Design. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, Gruenbacher D, Natarajan B, and Kuhn W. Work in Progress: An Integrated Laboratory Experience A New Environment for Teaching Communications. 36th ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, Oct 27 31, 2006; San Diego, CA, p Hou Haipeng. Simulation Application in Communication Circuits. Computer Technology Application, 2006, vol. 8. Mitchell J., Canavan B., and Smith J. Problem based learning in communication systems: student perceptions and achievement. IEEE Trans. Edu vol. 53, no.4, p Rowan Gilmore, Les Besser, Yang Fang, and Weng Muyun. Modern Wireless RF Circuits Design.. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, (In Chinese) Sayre C. Complete Wireless Design (2nd.). New York: McGraw Hill Professional,
Simulation of small signal resonant amplifier based on Multisim Dan Ren
 Simulation of small signal resonant amplifier based on Multisim Dan Ren College of engineering and technology, Eastern Liaoning University, Dandong Liaoning 118000, China ldxyrendan@163.com Abstract. In
Simulation of small signal resonant amplifier based on Multisim Dan Ren College of engineering and technology, Eastern Liaoning University, Dandong Liaoning 118000, China ldxyrendan@163.com Abstract. In
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name:
 ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206
 UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
14 MHz Single Side Band Receiver
 EPFL - LEG Laboratoires à options 8 ème semestre MHz Single Side Band Receiver. Objectives. The objective of this work is to calculate and adjust the key elements of an Upper Side Band Receiver in the
EPFL - LEG Laboratoires à options 8 ème semestre MHz Single Side Band Receiver. Objectives. The objective of this work is to calculate and adjust the key elements of an Upper Side Band Receiver in the
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator
 Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
University of Southern C alifornia School Of Engineering Department Of Electrical Engineering
 University of Southern alifornia School Of Engineering Department Of Electrical Engineering EE 348: Homework Assignment #02 Spring, 2001 (Due 02/01/2001) homa Problem #05: The amplifier module in Fig.
University of Southern alifornia School Of Engineering Department Of Electrical Engineering EE 348: Homework Assignment #02 Spring, 2001 (Due 02/01/2001) homa Problem #05: The amplifier module in Fig.
PURPOSE: NOTE: Be sure to record ALL results in your laboratory notebook.
 EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
Design and Implementation of a New Gain Control RF Amplifier
 2016 3 rd International Conference on Materials Science and Mechanical Engineering (ICMSME 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-391-5 Design and Implementation of a New Gain Control RF Amplifier Qingtian Wang, Yu Yan
2016 3 rd International Conference on Materials Science and Mechanical Engineering (ICMSME 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-391-5 Design and Implementation of a New Gain Control RF Amplifier Qingtian Wang, Yu Yan
Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter
 SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
 168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator
 Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Lab 2: Discrete BJT Op-Amps (Part I)
 Lab 2: Discrete BJT Op-Amps (Part I) This is a three-week laboratory. You are required to write only one lab report for all parts of this experiment. 1.0. INTRODUCTION In this lab, we will introduce and
Lab 2: Discrete BJT Op-Amps (Part I) This is a three-week laboratory. You are required to write only one lab report for all parts of this experiment. 1.0. INTRODUCTION In this lab, we will introduce and
Core Technology Group Application Note 6 AN-6
 Characterization of an RLC Low pass Filter John F. Iannuzzi Introduction Inductor-capacitor low pass filters are utilized in systems such as audio amplifiers, speaker crossover circuits and switching power
Characterization of an RLC Low pass Filter John F. Iannuzzi Introduction Inductor-capacitor low pass filters are utilized in systems such as audio amplifiers, speaker crossover circuits and switching power
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
PHYSICS 330 LAB Operational Amplifier Frequency Response
 PHYSICS 330 LAB Operational Amplifier Frequency Response Objectives: To measure and plot the frequency response of an operational amplifier circuit. History: Operational amplifiers are among the most widely
PHYSICS 330 LAB Operational Amplifier Frequency Response Objectives: To measure and plot the frequency response of an operational amplifier circuit. History: Operational amplifiers are among the most widely
Filters And Waveform Shaping
 Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Application Note SAW-Components
 Application Note SAW-Components Comparison between negative impedance oscillator (Colpitz oscillator) and feedback oscillator (Pierce structure) App.: Note #13 Author: Alexander Glas EPCOS AG Updated:
Application Note SAW-Components Comparison between negative impedance oscillator (Colpitz oscillator) and feedback oscillator (Pierce structure) App.: Note #13 Author: Alexander Glas EPCOS AG Updated:
Theory: The idea of this oscillator comes from the idea of positive feedback, which is described by Figure 6.1. Figure 6.1: Positive Feedback
 Name1 Name2 12/2/10 ESE 319 Lab 6: Colpitts Oscillator Introduction: This lab introduced the concept of feedback in combination with bipolar junction transistors. The goal of this lab was to first create
Name1 Name2 12/2/10 ESE 319 Lab 6: Colpitts Oscillator Introduction: This lab introduced the concept of feedback in combination with bipolar junction transistors. The goal of this lab was to first create
A Simple Bandpass Filter with Independently Tunable Center Frequency and Bandwidth
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 69, 3 8, 27 A Simple Bandpass Filter with Independently Tunable Center Frequency and Bandwidth Bo Zhou *, Jing Pan Song, Feng Wei, and Xiao Wei Shi Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 69, 3 8, 27 A Simple Bandpass Filter with Independently Tunable Center Frequency and Bandwidth Bo Zhou *, Jing Pan Song, Feng Wei, and Xiao Wei Shi Abstract
3-Stage Transimpedance Amplifier
 3-Stage Transimpedance Amplifier ECE 3400 - Dr. Maysam Ghovanloo Garren Boggs TEAM 11 Vasundhara Rawat December 11, 2015 Project Specifications and Design Approach Goal: Design a 3-stage transimpedance
3-Stage Transimpedance Amplifier ECE 3400 - Dr. Maysam Ghovanloo Garren Boggs TEAM 11 Vasundhara Rawat December 11, 2015 Project Specifications and Design Approach Goal: Design a 3-stage transimpedance
Tuned circuits. Introduction - Tuned Circuits
 Tuned circuits Introduction - Tuned Circuits Many communication applications use tuned circuits. These circuits are assembled from passive components (that is, they require no power supply) in such a way
Tuned circuits Introduction - Tuned Circuits Many communication applications use tuned circuits. These circuits are assembled from passive components (that is, they require no power supply) in such a way
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 FILTER NETWORKS OBJECTIVES In this lab session the student will investigate passive low-pass and
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 FILTER NETWORKS OBJECTIVES In this lab session the student will investigate passive low-pass and
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS. Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi
 EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
The Hartley Oscillator
 The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
Chapter 2. The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review
 Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks)
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
DESIGN AND INVESTIGATION OF BROADBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA LOADED WITH NON-FOSTER CIRCUIT
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 17, 245 255, 21 DESIGN AND INVESTIGATION OF BROADBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA LOADED WITH NON-FOSTER CIRCUIT F.-F. Zhang, B.-H. Sun, X.-H. Li, W. Wang, and J.-Y.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 17, 245 255, 21 DESIGN AND INVESTIGATION OF BROADBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA LOADED WITH NON-FOSTER CIRCUIT F.-F. Zhang, B.-H. Sun, X.-H. Li, W. Wang, and J.-Y.
Designing and Application of -type Miniaturized Lumped Equalizer
 016 International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Intellectualization (ICEITI 016) IBN: 978-1-60595-364-9 Designing and Application of -type Miniaturized Lumped Equalizer Yi Wang, Yuntao
016 International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Intellectualization (ICEITI 016) IBN: 978-1-60595-364-9 Designing and Application of -type Miniaturized Lumped Equalizer Yi Wang, Yuntao
Experiment No. 9 DESIGN AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMON BASE AND COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIERS
 Experiment No. 9 DESIGN AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMON BASE AND COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIERS 1. Objective: The objective of this experiment is to explore the basic applications of the bipolar junction transistor
Experiment No. 9 DESIGN AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMON BASE AND COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIERS 1. Objective: The objective of this experiment is to explore the basic applications of the bipolar junction transistor
Low Pass Filter Introduction
 Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter
 EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design
 Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design Switched Mode Power Supply Measurements AC Input Power measurements Safe operating area Harmonics and compliance Efficiency Switching Transistor Losses
Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design Switched Mode Power Supply Measurements AC Input Power measurements Safe operating area Harmonics and compliance Efficiency Switching Transistor Losses
An Oscillator Scheme for Quartz Crystal Characterization.
 An Oscillator Scheme for Quartz Crystal Characterization. Wes Hayward, 15Nov07 The familiar quartz crystal is modeled with the circuit shown below containing a series inductor, capacitor, and equivalent
An Oscillator Scheme for Quartz Crystal Characterization. Wes Hayward, 15Nov07 The familiar quartz crystal is modeled with the circuit shown below containing a series inductor, capacitor, and equivalent
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) NOISE MEASUREMENTS 1
 4. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) NOISE MEASUREMENTS 4.1 Object The objective of this experiment is to measure the mean-square equivalent input noise, v 2 ni, and base spreading resistance, r x, of
4. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) NOISE MEASUREMENTS 4.1 Object The objective of this experiment is to measure the mean-square equivalent input noise, v 2 ni, and base spreading resistance, r x, of
Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 Introduction to Active Filters
 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 Introduction to Active Filters i-1 Preface: Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually. Laboratory hardware exercises are to be done in groups. This laboratory
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 Introduction to Active Filters i-1 Preface: Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually. Laboratory hardware exercises are to be done in groups. This laboratory
ITT Technical Institute. ET275 Electronic Communications Systems I Onsite Course SYLLABUS
 ITT Technical Institute ET275 Electronic Communications Systems I Onsite Course SYLLABUS Credit hours: 4 Contact/Instructional hours: 50 (30 Theory Hours, 20 Lab Hours) Prerequisite(s) and/or Corequisite(s):
ITT Technical Institute ET275 Electronic Communications Systems I Onsite Course SYLLABUS Credit hours: 4 Contact/Instructional hours: 50 (30 Theory Hours, 20 Lab Hours) Prerequisite(s) and/or Corequisite(s):
Intruder Alarm Name Mohamed Alsubaie MMU ID Supervisor Pr. Nicholas Bowring Subject Electronic Engineering Unit code 64ET3516
 Intruder Alarm Name MMU ID Supervisor Subject Unit code Course Mohamed Alsubaie 09562211 Pr. Nicholas Bowring Electronic Engineering 64ET3516 BEng (Hons) Computer and Communication Engineering 1. Introduction
Intruder Alarm Name MMU ID Supervisor Subject Unit code Course Mohamed Alsubaie 09562211 Pr. Nicholas Bowring Electronic Engineering 64ET3516 BEng (Hons) Computer and Communication Engineering 1. Introduction
Module 4 Unit 4 Feedback in Amplifiers
 Module 4 Unit 4 Feedback in mplifiers eview Questions:. What are the drawbacks in a electronic circuit not using proper feedback? 2. What is positive feedback? Positive feedback is avoided in amplifier
Module 4 Unit 4 Feedback in mplifiers eview Questions:. What are the drawbacks in a electronic circuit not using proper feedback? 2. What is positive feedback? Positive feedback is avoided in amplifier
Chapter 3 Electronic Circuit for MWCNT Ethylene Sensor
 Chapter Electronic Circuit for MWCNT Ethylene Sensor This chapter deals with design and prototype development of electronic circuits required for MWCNT ethylene sensor application. The customized potentiostat
Chapter Electronic Circuit for MWCNT Ethylene Sensor This chapter deals with design and prototype development of electronic circuits required for MWCNT ethylene sensor application. The customized potentiostat
EXPERIMENT 1: Characteristics of Passive and Active Filters
 Kathmandu University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering ELECTRONICS AND ANALOG FILTER DESIGN LAB EXPERIMENT : Characteristics of Passive and Active Filters Objective: To understand the
Kathmandu University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering ELECTRONICS AND ANALOG FILTER DESIGN LAB EXPERIMENT : Characteristics of Passive and Active Filters Objective: To understand the
Discrete Op-Amp Kit MitchElectronics 2019
 Discrete Op-Amp Kit MitchElectronics 2019 www.mitchelectronics.co.uk CONTENTS Introduction 3 Schematic 4 How It Works 5 Materials 9 Construction 10 Important Information 11 Page 2 INTRODUCTION Even if
Discrete Op-Amp Kit MitchElectronics 2019 www.mitchelectronics.co.uk CONTENTS Introduction 3 Schematic 4 How It Works 5 Materials 9 Construction 10 Important Information 11 Page 2 INTRODUCTION Even if
Testing Power Factor Correction Circuits For Stability
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, switching power supply, PFC, boost converter, flyback converter,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, switching power supply, PFC, boost converter, flyback converter,
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
Fig. 1. NI Elvis System
 Lab 2: Introduction to I Elvis Environment. Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to provide an introduction to the NI Elvis design and prototyping environment. Basic operations provided by Elvis
Lab 2: Introduction to I Elvis Environment. Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to provide an introduction to the NI Elvis design and prototyping environment. Basic operations provided by Elvis
Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
Design of a Wideband Band-Pass Filter Using Semi-lumped and Semi-distributed Technology
 3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) Design of a Wideband Band-Pass Filter Using Semi-lumped and Semi-distributed Technology Ying Liu 1, Jiayu Xie 1, Junling Huang 1
3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) Design of a Wideband Band-Pass Filter Using Semi-lumped and Semi-distributed Technology Ying Liu 1, Jiayu Xie 1, Junling Huang 1
Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Systems Using Open-loop Square Microstrip Resonators
 International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications 2016, 6(1): 7-12 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijea.20160601.02 Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Charles U. Ndujiuba 1,*, Samuel N. John 1, Taofeek
International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications 2016, 6(1): 7-12 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijea.20160601.02 Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Charles U. Ndujiuba 1,*, Samuel N. John 1, Taofeek
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
HOME ASSIGNMENT. Figure.Q3
 HOME ASSIGNMENT 1. For the differential amplifier circuit shown below in figure.q1, let I=1 ma, V CC =5V, v CM = -2V, R C =3kΩ and β=100. Assume that the BJTs have v BE =0.7 V at i C =1 ma. Find the voltage
HOME ASSIGNMENT 1. For the differential amplifier circuit shown below in figure.q1, let I=1 ma, V CC =5V, v CM = -2V, R C =3kΩ and β=100. Assume that the BJTs have v BE =0.7 V at i C =1 ma. Find the voltage
his report is my recent analysis of the EH antenna using the Pspice program and considering the antenna as a set of circuit elements.
 his report is my recent analysis of the EH antenna using the Pspice program and considering the antenna as a set of circuit elements. The antenna can be considered as a set of circuit elements because
his report is my recent analysis of the EH antenna using the Pspice program and considering the antenna as a set of circuit elements. The antenna can be considered as a set of circuit elements because
ET275P Electronic Communications Systems I [Onsite]
![ET275P Electronic Communications Systems I [Onsite] ET275P Electronic Communications Systems I [Onsite]](/thumbs/85/92760903.jpg) ET275P Electronic Communications Systems I [Onsite] Course Description: In this course, several methods of signal transmission and reception are covered, including such techniques as mixing, modulating
ET275P Electronic Communications Systems I [Onsite] Course Description: In this course, several methods of signal transmission and reception are covered, including such techniques as mixing, modulating
Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 4929 Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI APPLICATION NOTE 4929 Adapting
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 4929 Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI APPLICATION NOTE 4929 Adapting
ELEC 351L Electronics II Laboratory Spring 2014
 ELEC 351L Electronics II Laboratory Spring 2014 Lab #5: Amplifier with Specified Frequency Response Introduction The focus of this three-week lab exercise will be to design and build a common-emitter amplifier
ELEC 351L Electronics II Laboratory Spring 2014 Lab #5: Amplifier with Specified Frequency Response Introduction The focus of this three-week lab exercise will be to design and build a common-emitter amplifier
New Technique Accurately Measures Low-Frequency Distortion To <-130 dbc Levels by Xavier Ramus, Applications Engineer, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 New Technique Accurately Measures Low-Frequency Distortion To
New Technique Accurately Measures Low-Frequency Distortion To
CONDUCTIVITY sensors are required in many application
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 54, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2005 2433 A Low-Cost and Accurate Interface for Four-Electrode Conductivity Sensors Xiujun Li, Senior Member, IEEE, and Gerard
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 54, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2005 2433 A Low-Cost and Accurate Interface for Four-Electrode Conductivity Sensors Xiujun Li, Senior Member, IEEE, and Gerard
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Homework Assignment 11
 Homework Assignment 11 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
Homework Assignment 11 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
AN-1098 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Methodology for Narrow-Band Interface Design Between High Performance
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Methodology for Narrow-Band Interface Design Between High Performance
RF Amplifier with Mirror Frequency Filter
 Radio Project ETI 041 RF Amplifier with Mirror Frequency Filter Qiran Zhou 07SOC Lunds tekniska högskola Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract When using traditional RF filter, we usually need 7 to 8 orders
Radio Project ETI 041 RF Amplifier with Mirror Frequency Filter Qiran Zhou 07SOC Lunds tekniska högskola Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract When using traditional RF filter, we usually need 7 to 8 orders
Lab 1. Resonance and Wireless Energy Transfer Physics Enhancement Programme Department of Physics, Hong Kong Baptist University
 Lab 1. Resonance and Wireless Energy Transfer Physics Enhancement Programme Department of Physics, Hong Kong Baptist University 1. OBJECTIVES Introduction to the concept of resonance Observing resonance
Lab 1. Resonance and Wireless Energy Transfer Physics Enhancement Programme Department of Physics, Hong Kong Baptist University 1. OBJECTIVES Introduction to the concept of resonance Observing resonance
A New Topology of Load Network for Class F RF Power Amplifiers
 A New Topology of Load Network for Class F RF Firas Mohammed Ali Al-Raie Electrical Engineering Department, University of Technology/Baghdad. Email: 30204@uotechnology.edu.iq Received on:12/1/2016 & Accepted
A New Topology of Load Network for Class F RF Firas Mohammed Ali Al-Raie Electrical Engineering Department, University of Technology/Baghdad. Email: 30204@uotechnology.edu.iq Received on:12/1/2016 & Accepted
CHAPTER 4 MEASUREMENT OF NOISE SOURCE IMPEDANCE
 69 CHAPTER 4 MEASUREMENT OF NOISE SOURCE IMPEDANCE 4.1 INTRODUCTION EMI filter performance depends on the noise source impedance of the circuit and the noise load impedance at the test site. The noise
69 CHAPTER 4 MEASUREMENT OF NOISE SOURCE IMPEDANCE 4.1 INTRODUCTION EMI filter performance depends on the noise source impedance of the circuit and the noise load impedance at the test site. The noise
Code: 9A Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
 II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
1) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz
 ) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology
 Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology Renbin Dai, and Rana Arslan Ali Khan Abstract The design of Class A and Class AB 2-stage X band Power Amplifier is described in
Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology Renbin Dai, and Rana Arslan Ali Khan Abstract The design of Class A and Class AB 2-stage X band Power Amplifier is described in
Introduction (cont )
 Active Filter 1 Introduction Filters are circuits that are capable of passing signals within a band of frequencies while rejecting or blocking signals of frequencies outside this band. This property of
Active Filter 1 Introduction Filters are circuits that are capable of passing signals within a band of frequencies while rejecting or blocking signals of frequencies outside this band. This property of
AN1996 Demodulating at 10.7MHz IF with the SA605/625
 RF COMMUNICATIONS PRODUCTS Demodulating at 10.7MHz IF with the 605/625 Alvin K. Wong 1997 Oct 23 Philips Semiconductors Demodulating at 10.7MHz IF with the 605/625 Author: Alvin K. Wong INTRODUCTION The
RF COMMUNICATIONS PRODUCTS Demodulating at 10.7MHz IF with the 605/625 Alvin K. Wong 1997 Oct 23 Philips Semiconductors Demodulating at 10.7MHz IF with the 605/625 Author: Alvin K. Wong INTRODUCTION The
RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link
 Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF R, L AND C ELEMENTS
 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF R, L AND C ELEMENTS Marking scheme : Methods & diagrams : 3 Graph plotting : - Tables & analysis : 2 Questions & discussion : 3 Performance : 2 Aim: This experiment will investigate
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF R, L AND C ELEMENTS Marking scheme : Methods & diagrams : 3 Graph plotting : - Tables & analysis : 2 Questions & discussion : 3 Performance : 2 Aim: This experiment will investigate
2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS
 2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS I. Objectives and Contents The goal of this experiment is to become familiar with BJT as an amplifier and to evaluate the basic configurations
2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS I. Objectives and Contents The goal of this experiment is to become familiar with BJT as an amplifier and to evaluate the basic configurations
Chapter.8: Oscillators
 Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
for use Supervisor: on chip
 Local Oscillator for use in FM Broadcast Radio Receiver ETI 041: Radio Project Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Student: Yelin Wang and Hao Cai Master Program: System on chip Lund University Abstract Oscillator
Local Oscillator for use in FM Broadcast Radio Receiver ETI 041: Radio Project Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Student: Yelin Wang and Hao Cai Master Program: System on chip Lund University Abstract Oscillator
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
Chapter 4 4. Optoelectronic Acquisition System Design
 4. Optoelectronic Acquisition System Design The present chapter deals with the design of the optoelectronic (OE) system required to translate the obtained optical modulated signal with the photonic acquisition
4. Optoelectronic Acquisition System Design The present chapter deals with the design of the optoelectronic (OE) system required to translate the obtained optical modulated signal with the photonic acquisition
Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
AUDIO OSCILLATOR DISTORTION
 AUDIO OSCILLATOR DISTORTION Being an ardent supporter of the shunt negative feedback in audio and electronics, I would like again to demonstrate its advantages, this time on the example of the offered
AUDIO OSCILLATOR DISTORTION Being an ardent supporter of the shunt negative feedback in audio and electronics, I would like again to demonstrate its advantages, this time on the example of the offered
CHAPTER 2 THE DESIGN OF ACTIVE POLYPHASE FILTER
 CHAPTER 2 THE DESIGN OF ACTIVE POLYPHASE FILTER 2.1 INTRODUCTION The fast growth of wireless applications in recent years has driven intense efforts to design highly integrated, high-performance, low-cost
CHAPTER 2 THE DESIGN OF ACTIVE POLYPHASE FILTER 2.1 INTRODUCTION The fast growth of wireless applications in recent years has driven intense efforts to design highly integrated, high-performance, low-cost
IC Preamplifier Challenges Choppers on Drift
 IC Preamplifier Challenges Choppers on Drift Since the introduction of monolithic IC amplifiers there has been a continual improvement in DC accuracy. Bias currents have been decreased by 5 orders of magnitude
IC Preamplifier Challenges Choppers on Drift Since the introduction of monolithic IC amplifiers there has been a continual improvement in DC accuracy. Bias currents have been decreased by 5 orders of magnitude
Experiment #10: Passive Filter Design
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEEING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPATMENT OF ELECTICAL AND COMPUTE ENGINEEING ECE 2110: CICUIT THEOY LABOATOY Experiment #10: Passive Filter Design EQUIPMENT Lab Equipment Equipment Description
SCHOOL OF ENGINEEING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPATMENT OF ELECTICAL AND COMPUTE ENGINEEING ECE 2110: CICUIT THEOY LABOATOY Experiment #10: Passive Filter Design EQUIPMENT Lab Equipment Equipment Description
ANADOLU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 ANADOLU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EEM 206 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT#3 RESONANT CIRCUITS 1 RESONANT CIRCUITS
ANADOLU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EEM 206 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT#3 RESONANT CIRCUITS 1 RESONANT CIRCUITS
Impact of the Output Capacitor Selection on Switching DCDC Noise Performance
 Impact of the Output Capacitor Selection on Switching DCDC Noise Performance I. Introduction Most peripheries in portable electronics today tend to systematically employ high efficiency Switched Mode Power
Impact of the Output Capacitor Selection on Switching DCDC Noise Performance I. Introduction Most peripheries in portable electronics today tend to systematically employ high efficiency Switched Mode Power
ECEN Network Analysis Section 3. Laboratory Manual
 ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
High Frequency Amplifiers
 EECS 142 Laboratory #3 High Frequency Amplifiers A. M. Niknejad Berkeley Wireless Research Center University of California, Berkeley 2108 Allston Way, Suite 200 Berkeley, CA 94704-1302 October 27, 2008
EECS 142 Laboratory #3 High Frequency Amplifiers A. M. Niknejad Berkeley Wireless Research Center University of California, Berkeley 2108 Allston Way, Suite 200 Berkeley, CA 94704-1302 October 27, 2008
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
Exercise 2: Q and Bandwidth of a Series RLC Circuit
 Series Resonance AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 2: Q and Bandwidth of a Series RLC Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to calculate the bandwidth and Q of a series
Series Resonance AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 2: Q and Bandwidth of a Series RLC Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to calculate the bandwidth and Q of a series
A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity
 A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity Johan Karlsson Mikael Grudd Radio project 2008 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract This report
A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity Johan Karlsson Mikael Grudd Radio project 2008 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract This report
R 1 R 2. (3) Suppose you have two ac signals, which we ll call signals A and B, which have peak-to-peak amplitudes of 30 mv and 600 mv, respectively.
 29:128 Homework Problems 29:128 Homework 0 reference: Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9 V, R 1 = 1.5 kω, R 2 = 5.6 kω, (a) Calculate V out (b) Calculate the power
29:128 Homework Problems 29:128 Homework 0 reference: Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9 V, R 1 = 1.5 kω, R 2 = 5.6 kω, (a) Calculate V out (b) Calculate the power
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
California Eastern Laboratories
 California Eastern Laboratories AN143 Design of Power Amplifier Using the UPG2118K APPLICATION NOTE I. Introduction Renesas' UPG2118K is a 3-stage 1.5W GaAs MMIC power amplifier that is usable from approximately
California Eastern Laboratories AN143 Design of Power Amplifier Using the UPG2118K APPLICATION NOTE I. Introduction Renesas' UPG2118K is a 3-stage 1.5W GaAs MMIC power amplifier that is usable from approximately
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: Coil Losses:
 TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB Amplifiers
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
