SPATIAL BEAM COMPRESSION AND EFFECTIVE BEAM INJECTION USING TRIANGULAR GRADIENT INDEX PROFILE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
|
|
|
- Grace Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, 51 67, 2012 SPATIAL BEAM COMPRESSION AND EFFECTIVE BEAM INJECTION USING TRIANGULAR GRADIENT INDEX PROFILE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS N. Yogesh and V. Subramanian * Microwave Laboratory, Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai , India Abstract Spatial beam compression of an electromagnetic wave is one of the fundamental techniques employed in microwaves and optics. As there are many ways to achieve this task using the combination of prisms and lenses, recent research suggests the parabolic gradient index photonic crystals (GRIN PC) for the design of spatial beam compressor owing to its functionalities. However, the fabrication of a graded media with the parabolic profile is a difficult challenge in practical realization. As an alternative, present work attempts this problem with respect to the triangular gradient index profile. The performance and aspects of the beam compression are investigated experimentally using the pillar type GRIN PC at the microwave length-scales. The utility of the device for an effective beam injection to the photonic-waveguide component is further demonstrated experimentally. 1. INTRODUCTION Photonic crystals (PCs) are the periodic arrangement of dielectric constituents in one, two, and three dimensions that show various electromagnetic (e-m) phenomena including ultra-divergence, selfcollimation, and negative refraction [1 5]. Gradient variations introduced in the lattice period, filling factor, and dielectric constant of these periodic media (referred as Gradient Index Photonic Crystals (GRIN PC) [6]) can provide efficient light molding applications such as spatial beam compression [7, 8], effective control over light propagation [9], optical absorbers [10], directional cloaking [11] etc. Among several applications, spatial beam compression of an e-m wave is paid much attention, as it would be the fundamental principle Received 2 May 2012, Accepted 27 May 2012, Scheduled 13 June 2012 * Corresponding author: Venkatachalam Subramanian (manianvs@iitm.ac.in).
2 52 Yogesh and Subramanian for the realization of couplers in integrated and transformational electromagnetics [12 14]. The recent investigation [8] reveals the beam compression aspect of the parabolic GRIN PC lens with the index profile given as n(r) = n 0 (1 α2 2 r2 ), where n 0 is the refractive index along the optical axis of the GRIN PC lens, α is the gradient coefficient (m 1 ), and r is the geometrical coordinate (m)). The design principle of the beam compressor involves the combination of two GRIN PC lenses with different focal lengths, where the first PC focuses the parallel beam into a minimum spot size and the second lens will either collimate or diverge the minimum spot size according to the frequency dispersion. This approach guarantees a larger beam compression ratio (input beam width to the output beam width) with respect to the frequency dependent focal lengths. However, for practical realization, one has to fabricate the parabolic graded media with the greatest precision. For example, to produce a quadratic change in the refractive index (parabolic profile), one has to produce similar change in the dimension of the PC pillars. This would be a challenging task, as the fabricating errors are larger than the actual gradation required [15]. To overcome this constraint, beam compression aspect can be studied with respect to the linear index distribution such as the triangular index profile. In a periodic media, this profile can be easily created through the linear variations in the dimension of the PC pillars. This paper reveals the aspects of the triangular index profile for the spatial beam compression and experimental investigations are carried out at the microwave length-scales. Moreover, the compressing ability of the device is utilized for the realization of effective beam injector and it is demonstrated experimentally owing to its microwave photonics applications. 2. DESIGN PARAMETERS AND NUMERICAL RESULT 2.1. Group Index Calculations Pillar type photonic crystals consisting of square lattice arrangement of PTFE (polytetra fluoro ethylene relative dielectric permittivity is 2.1) rods arranged in an air background is considered for the realization of the beam compressor. The investigation is done with the transverse magnetic (TM) polarization, where E-field is parallel to the axis of the pillars. To form the graded index profile, one has to compute the group index for various filling fractions. This is done with the help of plane wave expansion based open-source solver MPB [16]. The procedure is to solve for the band structure of the periodic media,
3 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, (a) (b) Figure 1. (a) Group index as a function of the pillar radius at a normalized angular frequency of (2πc/a) for TM (E z ) mode polarization. (b) Triangular index profiles for various gradient coefficients at ω = (2πc/a). The diamond (α 1 = a 1 ), circle (α 2 = a 1 ), and square (α 3 = a 1 ) markers represent the group index for the available pillar radius. For a given α, the gradation introduced along the individual vertical photonic layer is also shown in the plot. and the group index at a given frequency is calculated through the Hellman-Feynman theorem [17]. In Figure 1(a), the group index is plotted as a function of the radius of the pillars at a normalized angular frequency of (2πc/a). This frequency is chosen within the homogenous response of the GRIN PC (Eigen frequency contours are circular for the pillar radius varies from a to a) ranging from 0.18 to 0.34 (2πc/a). If a = 1.2 cm, then the radius varies from 0.05 cm to 0.5 cm and the frequency range varies within 4.5 to 8.5 GHz. The computed group indices are fitted with the triangular index profile given as n (r) = n 0 ( 1 α 2 r ) where n(r) is the position dependent refractive index, r is chosen along the vertical direction of the PC, and α is the gradient coefficient (m 1 ). It may be noted that Eq. (1) is a representative of the triangular profile for a periodic media but for the modal dispersion analysis, one may need to redefine it to the other form of expressions, as discussed in fiber optics [18]. Figure 1(b) shows the triangular index fit for three different α s. Along with the theoretical fit, group indices for (1)
4 54 Yogesh and Subramanian the commercially available pillar radius at a given α are also shown in Figure 1(b) with the solid circles, squares and diamond markers. It may be noted that in all the three cases, the center pillar radius is taken to be 0.5 cm, which has the maximum group index value of Design Parameters The result of Figure 1 is used for the formation of beam compressor. It may be noted that Ref. [8] derives the design of the parabolic GRIN PC according to the Gaussian optics approximations [19]. For example, the focal length of the parabolic GRIN PC lens is approximated to the 1/4th of the pitch length of the GRIN medium given as f = π 2α, where f is the self-focusing length of the GRIN medium and α is the gradient coefficient. This approximation is also adopted for the GRIN PC lens with the triangular index profile. It is necessary to verify the validity of such approximations for a triangular index profile. Hence, focusing length of the GRIN medium with parabolic and triangular index profile is evaluated using finite-difference time-domain based e-m solver CST MWS [20]. Figure 2 shows the focusing effect of the GRIN medium formed by the parabolic and triangular index profiles with respect to the common α = a 1 at the frequency of 7.1 GHz. In both the cases, the GRIN medium has 31 rows with the lattice period of a = 1.2 cm. Plane wave excitation is used for the computation and perfectly matched boundary condition [21] is employed around the computational domain to terminate the open space. Figures 2(a) and (b) show the focusing effect for the parabolic GRIN medium at 7.1 GHz, where the focal length calculated from the electric field intensity profile is found to be around 15.9 cm. Similarly, for the triangular GRIN medium (given in 2(c) and (d)) the focal length is found to be around 17.1 cm. Both these values are closer to the theoretical value (f = π 2α ) of cm for a given α = a 1, where a is taken to be 1.2 cm. Hence, the focal length approximation used for the parabolic GRIN PC may also be taken for the triangular GRIN PC for further analysis. The beam compressor investigated in this work is shown in Figure 3. It involves a combination of two GRIN PC lenses, where PC1 is graded with the α P C1 = a 1 and PC2 is graded with the α P C2 = 0.175a 1. The explicit position of the pillar radius and its variation is also given in Figure 3. The lengths of the PC1 and PC2 are chosen using f = π 2α, where PC1 has a length of 13a and PC2 has a length of 9a respectively.
5 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, Numerical Results The beam compression aspect of the design given in Figure 3 is studied using the finite-element method (FEM) based e-m solver FEMLAB [22]. Figure 4 shows the results of the frequency dependent beam compressibility with respect to the different input beam apertures. For the first case, the compression is probed for a finite aperture size of 7.2 cm (an arbitrary choice). The E z field map given at 4.8 GHz in Figure 4(a) and full-width half-maximum (FWHM) values of the (a) (c) (b) (d) Figure 2. (a) and (b) show the focusing and the corresponding scanning plot of the parabolic GRIN medium. (c) and (d) show the focusing and the scanning plot for the triangular index GRIN medium. Both use a gradient coefficient of α = a 1 at 7.1 GHz. Figure 3. Design of beam-aperture modifier with respect to the triangular index profile. Explicit position of the pillars and its radius variation is given in the inset.
6 56 Yogesh and Subramanian (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Figure 4. (a) E z field map at 4.8 GHz for the finite aperture size of 7.2 cm and (b) shows the corresponding electric field intensity profiles at the input (i/p)/output (o/p) planes. (c) E z field map at 7.1 GHz for the aperture size of 7.2 cm and (d) shows the corresponding E 2 profiles of the i/p and o/p beams. (e) E z field map at 7.1 GHz for the aperture size of 4 cm and (f) shows the corresponding E 2 profiles of the i/p and o/p beams. input/output electric field intensity ( E 2 ) profiles shown in Figure 4(b) reveal the spatial beam compression ratio around 2 : 1. On the other hand, for the same aperture size, the E z field map given at 7.1 GHz in Figure 4(c) and FWHM of the input/output E 2 profiles (Figure 4(d)) show the compression ratio around 4 : 1. According to Ref. [8], for the given gradient coefficients (α P C1 = a 1 and = 0.175a 1 ), one should expect the beam compression ratio α( P C2 ) αp C2 α P C1 around 1.5 : 1. However, this empirical ratio does not taken into account of the frequency dispersion condition, where the effective focal length of the system is frequency dependent. For example, as per the Gaussian optics approximations, GRIN lens with the focal length f will change the incident beam width (W 0 )
7 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, into the output beam width of W 1 as W 1 = λf πw 0 (2) here λ is the applied wavelength. By substituting the values of W 1 and W 0, one can retrieve the effective focal length of the configuration as 8.1 cm at 4.8 GHz and 7.3 cm at 7.1 GHz respectively. On the other hand, the frequency independent equation for the combined focal length of the configuration can be written as f = f 1f 2 f 1 + f 2 (3) Here f 1 and f 2 are the focal lengths of the GRIN PC1 and GRIN PC2 defined according to the plane wave (no finite aperture) approximation as f = π 2α, where α is the gradient coefficient. The approximated value of f 1 = 13a and f 2 = 9a yields the combined focal length of 6.4 cm as per Eq. (3). This comparison reveals the frequency dependent characteristic of the GRIN PC lens and the higher beam compressibility is attributed to the entrance aperture effect. For the second case, the beam compression is probed with respect to size of the input beam aperture. The E z field map given in Figure 4(e) at 7.1 GHz reveals the compression effect for a smaller beam aperture of size 4 cm. Unlike in Figure 4(c), the focusing effect is not dominant in Figure 4(e) and this will result in reduced beam compression ratio of 1.76 (Figure 4(f)). This is in accordance with the Eq. (3), where input beam width plays major role in the beam compression aspect. To verify the above numerical results, two different microwave apertures are considered in the experimental demonstration. J-band (4.5 to 8.2 GHz) and the X-band (6.8 to 8.5 GHz) horn antennas are used for the excitation of larger input beam-widths. Passive waveguides are considered as the sources for the smaller beam apertures. 3. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS Beam compressor design given in Figure 3 is fabricated using PTFE rods and the experimental set up is given in Figure 5. The measured (using Transmission-Reflection line method [23]) dielectric constant of the PTFE is ε r = j Height of the rods is taken to be 10 cm and this choice ensures the reduction in the out-of-plane radiation losses due to the finite third dimension of the PC (It may be noted that in optical length-scales, reasonable estimation on the
8 58 Yogesh and Subramanian choice of the height of the PC slab is available for effective vertical confinement mechanisms [24]). The rods were arranged in a square lattice symmetry with the periodicity of a = 1.2 cm. The beam scanning measurements are carried out with vector network analyzer (N5230A). The beam coming from the J-band horn antenna is given as an input to the GRIN PC and the antenna is placed behind the beam compressor as shown in Figure 5(a). Monopole attached to the coaxial cable is used as the detector and it is mounted on a Vernier microscope for beam scanning. The beam compression aspect for a larger beam aperture given in Figure 5(b) shows the input/output FWHM profiles for GHz. It is evident that the ratio of the input beam width (8.370 cm) to the output beam width (2.640 cm) is around 3.2 at GHz. The beam compression ratio for other range of frequencies (4.5 to 8 GHz) is given in Figure 5(c). It is clear that for a larger beam aperture (given with blue open circles), the compression ratio is found (b) (a) (c) Figure 5. (a) Experimental setup for the beam compression studies. (b) Transmitted intensity profiles of the input and output beam scanned at GHz. (c) Beam compression ratio over a working frequency range of 4.5 to 8 GHz. Blue circled line corresponds to a larger beam aperture (J-band horn) and the red squared line corresponds to a smaller beam aperture (J-band waveguide).
9 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, in-between 2 : 1 to 4 : 1. The larger value obtained at the higher frequencies reveals the entrance aperture effect and importantly the frequency dispersive characteristics of the GRIN PC lens. On the other hand, for a smaller beam aperture (given with red open squares), the compression ratio is found to be around 1 : 1 for the range 4.5 to 5.5 GHz and 2 : 1 for the range 6 to 6.9 GHz. In case, if an input beam width matches to that of the GRIN PC mode, one can expect the self-collimation phenomenon, where the beam width is undistorted over the entire device [7]. The beam compression ratio of 1 : 1 observed in Figure 5(c) reveals the domination of collimation effect, where the e-m beam is confined and guided along the optical axis due to the higher refractive index. 4. APPLICATION ELECTROMAGNETIC BEAM INJECTOR The utility of this beam compression aspect can be explored with respect to an effective beam injection in microwave photonic devices. Injecting an e-m beam from free space or from a source component to any guiding medium is an inevitable task in many branches of microwave and optics. The common objective is to improve the coupling efficiency, reducing the return losses and increasing the operational bandwidth. There have been different mechanisms to achieve the above task and in particular, the following three are reported based on the photonic crystals; 1 PC concave lens configuration [12] This approach utilizes the negative refraction concept in PC concave lens so that the larger size beam width can be focused on to a waveguide device with the sub-wavelength focusing. Disadvantages are the limited bandwidth of negative refraction and aberrations due to the geometrical curvature. 2 Tapered Waveguide [13] It accompanies the introduction of gradient tapers in the PC waveguides for the effective coupling of an input beam. This approach has a constraint on the nature of the source and its beam width, but for most of the laser applications, this approach is sufficient. 3 GRIN PC coupler [14] This approach is based on the concept of strong focusing effect of the single gradient lens for the effective coupling in a waveguide device. Among the three different approaches, the graded index approach gives the promising features of a coupling element. It is important to note that as in Ref. [14], single graded lens itself suffices to show
10 60 Yogesh and Subramanian (a) (b) Figure 6. The role of source aperture for an effective-beam injection in a photonic crystal waveguide. (a) E z field map at 7.5 GHz corresponds to the source s aperture of 6 cm. (b) E z field map at 7.5 GHz to the source aperture of 3 cm. The PC waveguide is formed by the removal of center of row of rods in a layers of triangular lattice photonic crystal (defect spacing is d = 3a 2, where a 2 is the lattice constant taken to be 1.8 cm). the effective beam injection, but it is specially targeted for a single frequency operation. On the other hand, the aperture modifier dealt in this work is looked for the effective beam injection over a range of beam-compressing frequencies and their functionalities are probed experimentally at the microwave length-scales Numerical Results To demonstrate the coupling aspect of the beam compressor, PC waveguide shown in Figure 6(a) is considered. It is made of triangular lattice arrangement of glass rods (relative dielectric constant of ε r = 5.5) of radius r = 0.4 cm and with the lattice periodicity of a 2 = 1.8 cm. Removing the center row of rods will form the waveguide with the defect spacing of 3a 2 and confines the e-m wave corresponding to the defect-band frequencies ranging from 6.38 to 8.33 GHz. Figure 6 reveals the importance of the problem, as it shows the E z field map at 7.5 GHz (a) for a larger beam aperture of 6 cm and (b) for a smaller aperture of 3 cm. It is evident that the larger beam width does not couple to the PC waveguide, as most of the power is reflected back from the PC waveguide itself. On the other hand, when an incident beam width matches to that of PC waveguide width, the e-m beam is steered in to the waveguide. Hence, it is clear that the source with larger aperture cannot be integrated to any photonic device unless its spatial width is compressed. For an example, the
11 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, (a) (b) Figure 7. Numerical result of an effective beam injection. (a) E z field map at 7.5 GHz shows the effective coupling provided by the beam compressor for a source aperture of 6 cm. (b) Time-averaged power flow norm is plotted for the configurations of empty PC waveguide with source apertures of 6 and 3 cm (given in the inset), and the PC waveguide with the beam compressor for the source aperture of 6 cm. directional cloaking device discussed in Ref. [25] is functional only with the introduction of a beam compressor. Otherwise, the concept of invisibility or transparency is lost due to the under coupling effect of the incident e-m wave to the PC waveguide. The role of beam compressor in effective beam injection is given in Figure 7. The E z field map given at 7.5 GHz for a larger beam aperture (6 cm) (Figure 7(a)) shows the smooth steering of e-m beam into the PC waveguide. In Figure 7(b), the transmitted time-averaged power flow norm (It is the modulus value of the Poynting vector) is plotted for all the three cases (PC waveguide without the beam compressor for larger and smaller beam apertures (given in inset of Figure 7(b)) and PC waveguide with the beam compressor for a larger beam aperture).
12 62 Yogesh and Subramanian It is witnessed that the insertion of beam compressor between the source and the PC waveguide results in enhanced power flow, as the compressor produce the light transformation with the compressed beam width. In order to have further information on the effective coupling result, an experiment is conducted at the microwave lengthscales Experimental Setup and Measurements The PC waveguide part is fabricated using the glass rods with the radius of 0.4 cm arranged in triangular lattice symmetry with the periodicity of 1.8 cm. The measured dielectric permittivity of glass rods is found to be ε r = j Height of the glass rods is taken to be 10 cm. The complete experimental setup is shown in Figure 8 and the scattering parameters (relative reflection and relative transmission) are measured using the vector network analyzer (N5230A). The relative scattering parameters are defined as follows (S 21 ) relative = (S 21 ) structure (S 21 ) freespace (S 11 ) relative = (S 11 ) structure (S 11 ) freespace Figure 8. Experimental setup for an effective beam injection. The beam compressor has a length of 26.4 cm, and the PC waveguide has a length of 14.4 cm. This picture shows the X-band horn as the transmitter and receiver. Inset of the figure shows the setup for an empty PC waveguide.
13 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, ( ) Etransmitted S 21 = 20 log 10 E incident ( ) (4) Ereflected S 11 = 20 log 10 E incident In Eq. (4), (S 21 ) strucuture is the measured transmitted power (db scale) in the presence of photonic structure, (S 21 ) freespace is the measured transmitted power (db scale) in the free space, and S 21 and S 11 are the general definition of the transmitted and reflected power (db scale) respectively. Figure 9 shows the plot of relative parameters for various available beam apertures such as X-band horn antenna, X-band waveguide, and J-band horn antenna Results and Discussions The first part of the result (given in Figures 9(a) and 9(d)) shows the relative parameters for the beam injection from a X-band horn antenna. The beam width of an input beam measured at 2 cm away from the X- band horn is found to be around 4 5 cm in the frequency range of 7 to 8 GHz. By comparing the relative transmission of PC waveguide with ((blue solid line in Figure 9(a)) and without the beam compressor (red dashed line in Figure 9(a)), an improvement of 5 to 15 db transmission is observed in the frequency range of 7 to 8 GHz. In order to have clear idea about the beam injection, one can take one of the frequencies in Figure 9(a) and Figure 9(d) (indicated by arrows). At GHz, PC waveguide shows the transmission loss of around 17 db with respect to free space, whereas with the introduction of the beam compressor, the transmission loss is only around 5 db with respect to the free space. For the return loss part (in Figure 9(d)), it is found that the PC waveguide without the beam compressor is approximately 13 db more reflective than the PC waveguide with the beam compressor at GHz. The second part of the result (given in Figures 9(b) and 9(e)) considers the beam injection with respect to the larger beam aperture (J-band horn). Since the investigated beam compressor is not sufficient to accommodate the entire wavefront, an improved transmission of 8 to 12 db is observed only in the shaded regimes. Moreover, the relative reflected spectrum given in Figure 9(e) reveals the higher reflectivity with respect to the free space. It is useful to mention that the beam compressor is designed only based on the commercially available rod s diameters. In case, if one further increases the rod layers along the transverse direction, the entire wavefront can be accommodated within the GRIN PC and this will also ensure the accurate representation of the triangular-index profile (one can compare the theoretical and practically realizable profiles in Figure 1(b)).
14 64 Yogesh and Subramanian (a) (d) (b) (e) (c) (f) Figure 9. (a) (c) shows the relative transmission parameter and (d) (f) shows the relative reflective parameter for the PC waveguide with (blue solid line) and without (red dashed line) the beam compressor for the apertures of X-band horn antenna, J-band horn antenna, and X-band waveguide. The term relative refers to the comparative transmission/reflection value between the structure and an air background. The third part of the result considers the effect of a smaller beam aperture. Though the device is not efficient for a smaller beam aperture, the collimation effect may be sought for the beam injection owing to its divergence less beam propagation. Figures 9(c) and 9(f) shows an effective beam injection with an improved transmission of around 10 db within the frequency range of 6.8 to 8 GHz. However, it is important to mention that for a smaller beam-aperture, the empty PC waveguide may be sufficient, when the source aperture matches to that of PC waveguide mode.
15 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, CONCLUSIONS AND PERSPECTIVES Triangular index profile GRIN PC is emphasized for the design of spatial beam compressor, as the parabolic profile is difficult to realize practically. Focusing characteristics of the triangular index GRIN PC is evaluated numerically. It is demonstrated that the frequency dependent focal lengths and the finite beam aperture play major roles in the beam compression aspect. The following results are verified experimentally at the microwave length-scales using the PTFE pillar type PC. For a larger beam-aperture, the beam compression ratio of 2 : 1 is observed at the J-band frequencies. Higher beam compression is attributed to the frequency dispersion characteristics and entrance aperture effect of the GRIN PC lens. The beam compression ratio 1 : 1 suggests the collimation effect, as the light beam is guided and undistorted over the entire device. This will happen, when an incident beam width is matched to that of the GRIN PC mode. The utility of the device for effective beam injection is investigated both numerically and experimentally. The experimental results reveal the promising features of the beam compressor, where it injects the larger spatial width e-m beams into the photonic waveguide devices with an improved transmission of 10 db. It is observed that the investigated design also has some limitations with respect to the wavefront size, out-of-plane radiation losses, approximated triangular index profile due to the non-availability of the rods etc. It is expected that the optimization of this effective beam injector will be useful for some of the transformational and integrated electromagnetic applications such as directional cloaking, inter-connectors, transitions etc. REFERENCES 1. Yablonovitch, E., Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid state physics and electronics, Phys. Rev. Lett., Vol. 58, No. 20, , Kosaka, H., T. Kawashima, A. Tomita, M. Notomi, T. Tamamura, T. Sato, and S. Kawakami, Superprism phenomena in photonic crystals, Phys. Rev. B, Vol. 58, No. 16, R10096, Kosaka, H., T. Kawashima, A. Tomita, M. Notomi, T. Tamamura, T. Sato, and S. Kawakami, Self-collimating phenomena in photonic crystals, Appl. Phys. Lett., Vol. 74, No. 9, 1212, Yogesh, N. and V. Subramanian, Analysis of self-collimation based cavity resonator formed by photonic crystal, Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 12, , Luo, C., S. G. Johnson, J. D. Joannopoulos, and J. B. Pendry,
16 66 Yogesh and Subramanian All-angle negative refraction without negative effective index, Phys. Rev. B, Vol. 65, No. 20, (R), Centeno, E. and D. Cassagne, Graded photonic crystals, Opt. Lett., Vol. 30, No. 17, , Kurt, H. and D. S. Citrin, Graded index photonic crystals, Opt. Exp., Vol. 15, No. 3, , Lu, M., B. K. Juluri, S.-C. S. Lin, B. Kiraly, T. Gao, and T. J. Huang, Beam aperture modifier and beam deflector using gradient-index photonic crystals, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 108, No. 10, , 2010, Supplementary material at 9. Ren, K. and X. Ren, Controlling light transport by using a graded photonic crystal, Appl. Opt., Vol. 50, No. 15, , Wang, H.-W. and L.-W. Chen, A cylindrical optical black hole using graded index photonic crystals, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 109, No. 10, , Vasi, B. and R. Gaji, Self-focusing media using graded photonic crystals: Focusing, fourier transforming and imaging, directive emission, and directional cloaking, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 110, No. 5, , AbdelMalek, F., W. Belhadj, S. Haxha, and H. Bouchriha, Realization of a high coupling efficiency by employing a concave lens based on two-dimensional photonic crystals with a negative refractive index, J. Lightw. Technol., Vol. 25, No. 10, , Chien, H.-T., C. Lee, H.-K. Chiu, K.-C. Hsu, C.-C. Chen, J. A. Ho, and C. Chou, The Comparison between the graded photonic crystal coupler and various couplers, J. Lightw. Technol., Vol. 27, No. 14, , Cakmak, A. O., E. Colak, H. Caglayan, H. Kurt, and E. Ozbay, High efficiency of graded index photonic crystal as an input coupler, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 105, No. 14, , Moore, D. T., Gradient-index optics: A review, Appl. Opt., Vol. 19, No. 7, , Johnson, S. G. and J. D. Joannopoulos, Block-iterative frequency-domain methods for Maxwell s equations in a plane wave basis, Opt. Exp., Vol. 8, No. 3, , 2001, Sakoda, K., Opitcal Properties of Photonic Crystals, Chapter 2.5, 30 34, Springer, Chen, C.-L., Foundations for Guided-wave Optics, Chapter 9, 226,
17 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, Wiley, Roux, F. S. and I. De Leon, Planar photonic crystal gradient index lens, simulated with a finite difference time domain method, Phys. Rev. B., Vol. 74, No. 11, , More information can be found at Taflove, A. and S. C. Hagness, Computational Electrodynamics the Finite-difference Time-domain Method, 3rd Edition, Chapter 7, , Artech House, Boston, Whiteman, J. R., The Mathematics of Finite Elements and Applications, John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1998, Jarvis, J. B., E. J. Vanzura, and W. A. Kissick, Improved technique for determining complex permittivity with the transmission/reflection method, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech., Vol. 38, No. 8, , Johnson, S. G., S. Fan, P. R. Villeneuve, and J. D. Joannopoulos, Guided modes in photonic crystal slabs, Phys. Rev. B, Vol. 60, No. 8, , Yogesh, N. and V. Subramanian, Directional Cloaking Formed by Photonic Crystal Waveguides, accepted for presentation in International Microwave Symposium 2012, Montreal, Canada, Jun , 2012.
ANALYSIS OF SELF-COLLIMATION BASED CAVITY RESONATOR FORMED BY PHOTONIC CRYSTAL
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 12, 115 130, 2010 ANALYSIS OF SELF-COLLIMATION BASED CAVITY RESONATOR FORMED BY PHOTONIC CRYSTAL N. Yogesh and V. Subramanian Microwave Laboratory, Department
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 12, 115 130, 2010 ANALYSIS OF SELF-COLLIMATION BASED CAVITY RESONATOR FORMED BY PHOTONIC CRYSTAL N. Yogesh and V. Subramanian Microwave Laboratory, Department
Title. Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori. CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights.
 Title Wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): 1970-1975 Issue Date 2001-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5582
Title Wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): 1970-1975 Issue Date 2001-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5582
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL
 SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal Power Splitter
 Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 13-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32a002 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal
Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 13-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32a002 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal
Experimental demonstration of negative refraction imaging in both amplitude and phase
 Experimental demonstration of negative refraction imaging in both amplitude and phase Zhaolin Lu, Shouyuan Shi, Christopher A. Schuetz, and Dennis W. Prather Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Experimental demonstration of negative refraction imaging in both amplitude and phase Zhaolin Lu, Shouyuan Shi, Christopher A. Schuetz, and Dennis W. Prather Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
 43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
Engineering the light propagating features through the two-dimensional coupled-cavity photonic crystal waveguides
 Engineering the light propagating features through the two-dimensional coupled-cavity photonic crystal waveguides Feng Shuai( ) and Wang Yi-Quan( ) School of Science, Minzu University of China, Bejiing
Engineering the light propagating features through the two-dimensional coupled-cavity photonic crystal waveguides Feng Shuai( ) and Wang Yi-Quan( ) School of Science, Minzu University of China, Bejiing
Band-dropping via coupled photonic crystal waveguides
 and-dropping via coupled photonic crystal waveguides Mehmet ayindir and Ekmel Ozbay Department of Physics, ilkent University, ilkent, 6533 nkara, Turkey bayindir@fen.bilkent.edu.tr http://www.fen.bilkent.edu.tr/
and-dropping via coupled photonic crystal waveguides Mehmet ayindir and Ekmel Ozbay Department of Physics, ilkent University, ilkent, 6533 nkara, Turkey bayindir@fen.bilkent.edu.tr http://www.fen.bilkent.edu.tr/
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves Bilinear Transformations Figure 1 Graphical depiction of the bilinear transformation and derived material parameters. (a) The transformation
A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves Bilinear Transformations Figure 1 Graphical depiction of the bilinear transformation and derived material parameters. (a) The transformation
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005](/thumbs/91/105523130.jpg) Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays
 Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
COAXIAL / CIRCULAR HORN ANTENNA FOR A STANDARD
 COAXIAL / CIRCULAR HORN ANTENNA FOR 802.11A STANDARD Petr Všetula Doctoral Degree Programme (1), FEEC BUT E-mail: xvsetu00@stud.feec.vutbr.cz Supervised by: Zbyněk Raida E-mail: raida@feec.vutbr.cz Abstract:
COAXIAL / CIRCULAR HORN ANTENNA FOR 802.11A STANDARD Petr Všetula Doctoral Degree Programme (1), FEEC BUT E-mail: xvsetu00@stud.feec.vutbr.cz Supervised by: Zbyněk Raida E-mail: raida@feec.vutbr.cz Abstract:
Projects in microwave theory 2017
 Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2017 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2017 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 62, 17 22, 2016 A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency Ning Liu 1, *, Xian-Jun Sheng 2, and Jing-Jing Fan
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 62, 17 22, 2016 A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency Ning Liu 1, *, Xian-Jun Sheng 2, and Jing-Jing Fan
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Performance Analysis of Different Ultra Wideband Planar Monopole Antennas as EMI sensors
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 09742166 Volume 5, Number 4 (2012), pp. 435445 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Analysis
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 09742166 Volume 5, Number 4 (2012), pp. 435445 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Analysis
Negative refraction in photonic crystals
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 55 (28) pp 91-1 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Negative refraction in photonic crystals
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 55 (28) pp 91-1 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Negative refraction in photonic crystals
Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and
 Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and optics p. 4 Communication systems p. 6 Radar systems p.
Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and optics p. 4 Communication systems p. 6 Radar systems p.
ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/82/85804846.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY DESIGN OF A WIDEBAND 1 2 Y-BRANCH OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTER USING GaAs BASED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL Md. Shoaib Akther 1, Md. Rupam Khandkar
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY DESIGN OF A WIDEBAND 1 2 Y-BRANCH OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTER USING GaAs BASED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL Md. Shoaib Akther 1, Md. Rupam Khandkar
Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals
 Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals Binglin Miao, Caihua Chen, Ahmed Sharkway, Shouyuan Shi, and Dennis W. Prather University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 976 binglin@udel.edu
Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals Binglin Miao, Caihua Chen, Ahmed Sharkway, Shouyuan Shi, and Dennis W. Prather University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 976 binglin@udel.edu
ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 14, 113 121, 21 ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS J. Bai, S. Shi, and D. W. Prather
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 14, 113 121, 21 ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS J. Bai, S. Shi, and D. W. Prather
Principles of Optics for Engineers
 Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
Two compact structures for perpendicular coupling of optical signals between dielectric and photonic crystal waveguides
 Two compact structures for perpendicular coupling of optical signals between dielectric and photonic crystal waveguides Michael E. Potter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of
Two compact structures for perpendicular coupling of optical signals between dielectric and photonic crystal waveguides Michael E. Potter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING
 KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION LABORATORY (ECE 4103) EXPERIMENT NO 3 RADIATION PATTERN AND GAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DISH (PARABOLIC)
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION LABORATORY (ECE 4103) EXPERIMENT NO 3 RADIATION PATTERN AND GAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DISH (PARABOLIC)
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 235 247, 2011 BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS B. Zhou, H. Li, X. Y. Zou, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 235 247, 2011 BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS B. Zhou, H. Li, X. Y. Zou, and
1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems
 OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
Two Dimensional Photonic Crystal based Four Channel Demultiplexer for ITU.T.G CWDM Systems
 Two Dimensional Photonic Crystal based Four Channel Demultiplexer for ITU.T.G 694.2 CWDM Systems K. Venkatachalam *, S. Robinson, S. Umamaheswari Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Two Dimensional Photonic Crystal based Four Channel Demultiplexer for ITU.T.G 694.2 CWDM Systems K. Venkatachalam *, S. Robinson, S. Umamaheswari Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES
 EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES OBJECTIVES In this lab, firstly you will learn to couple semiconductor sources, i.e., lightemitting diodes (LED's), to optical fibers. The coupling
EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES OBJECTIVES In this lab, firstly you will learn to couple semiconductor sources, i.e., lightemitting diodes (LED's), to optical fibers. The coupling
Reflectionless Multichannel Wavelength Demultiplexer in a Transmission Resonator Configuration
 160 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 39, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 Reflectionless Multichannel Wavelength Demultiplexer in a Transmission Resonator Configuration Chongjun Jin, Shanhui Fan, Shouzhen
160 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 39, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 Reflectionless Multichannel Wavelength Demultiplexer in a Transmission Resonator Configuration Chongjun Jin, Shanhui Fan, Shouzhen
Wideband Bow-Tie Slot Antennas with Tapered Tuning Stubs
 Wideband Bow-Tie Slot Antennas with Tapered Tuning Stubs Abdelnasser A. Eldek, Atef Z. Elsherbeni and Charles E. Smith. atef@olemiss.edu Center of Applied Electromagnetic Systems Research (CAESR) Department
Wideband Bow-Tie Slot Antennas with Tapered Tuning Stubs Abdelnasser A. Eldek, Atef Z. Elsherbeni and Charles E. Smith. atef@olemiss.edu Center of Applied Electromagnetic Systems Research (CAESR) Department
RECENTLY, using near-field scanning optical
 1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
A COMPACT MULTIBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA FOR WLAN/WIMAX APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 23, 147 155, 2011 A COMPACT MULTIBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA FOR WLAN/WIMAX APPLICATIONS Z.-N. Song, Y. Ding, and K. Huang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 23, 147 155, 2011 A COMPACT MULTIBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA FOR WLAN/WIMAX APPLICATIONS Z.-N. Song, Y. Ding, and K. Huang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity
 263 Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity Victor Dmitriev and Marcelo N. Kawakatsu Department of Electrical Engineering, Federal
263 Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity Victor Dmitriev and Marcelo N. Kawakatsu Department of Electrical Engineering, Federal
1500 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST 1999
 1500 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST 1999 Analysis of Finite 2-D Photonic Crystals of Columns and Lightwave Devices Using the Scattering Matrix Method Jun Yonekura, Mitsutaka Ikeda,
1500 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST 1999 Analysis of Finite 2-D Photonic Crystals of Columns and Lightwave Devices Using the Scattering Matrix Method Jun Yonekura, Mitsutaka Ikeda,
Using Pcb-Techniques And Dielectric Design Band Pass Filter Resonators For Ku - Band Applications
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 2, ISSUE 5 149 Using Pcb-Techniques And Dielectric Design Band Pass Filter Resonators For Ku - Band Applications
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 2, ISSUE 5 149 Using Pcb-Techniques And Dielectric Design Band Pass Filter Resonators For Ku - Band Applications
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
FIVE-PORT POWER SPLITTER BASED ON PILLAR PHOTONIC CRYSTAL *
 IJST, Transactions of Electrical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. E1, pp 93-100 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shiraz University FIVE-PORT POWER SPLITTER BASED ON PILLAR PHOTONIC CRYSTAL * M. MOHAMMADI
IJST, Transactions of Electrical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. E1, pp 93-100 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shiraz University FIVE-PORT POWER SPLITTER BASED ON PILLAR PHOTONIC CRYSTAL * M. MOHAMMADI
Projects in microwave theory 2009
 Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Zero Focal Shift in High Numerical Aperture Focusing of a Gaussian Laser Beam through Multiple Dielectric Interfaces. Ali Mahmoudi
 1 Zero Focal Shift in High Numerical Aperture Focusing of a Gaussian Laser Beam through Multiple Dielectric Interfaces Ali Mahmoudi a.mahmoudi@qom.ac.ir & amahmodi@yahoo.com Laboratory of Optical Microscopy,
1 Zero Focal Shift in High Numerical Aperture Focusing of a Gaussian Laser Beam through Multiple Dielectric Interfaces Ali Mahmoudi a.mahmoudi@qom.ac.ir & amahmodi@yahoo.com Laboratory of Optical Microscopy,
Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
Optics Communications
 Optics Communications 282 (2009) 3172 3176 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Polarization insensitive self-collimation waveguide
Optics Communications 282 (2009) 3172 3176 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Polarization insensitive self-collimation waveguide
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Schematic of the proposed structure where within a two dimensional photonic crystal an input air waveguide is carved that feeds an EMNZ region that
Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Schematic of the proposed structure where within a two dimensional photonic crystal an input air waveguide is carved that feeds an EMNZ region that
Design of Rotman Lens Antenna at Ku-Band Based on Substrate Integrated Technology
 Journal of Communication Engineering, Vol. 3, No.1, Jan.- June 2014 33 Design of Rotman Lens Antenna at Ku-Band Based on Substrate Integrated Technology S. A. R. Hosseini, Z. H. Firouzeh and M. Maddahali
Journal of Communication Engineering, Vol. 3, No.1, Jan.- June 2014 33 Design of Rotman Lens Antenna at Ku-Band Based on Substrate Integrated Technology S. A. R. Hosseini, Z. H. Firouzeh and M. Maddahali
Improvement of Radiation Characteristics of Balanced Antipodal Vivaldi Antenna Using Transformation Optics
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 56, 189 196, 2017 Improvement of Radiation Characteristics of Balanced Antipodal Vivaldi Antenna Using Transformation Optics Fatemeh Etesami 1, *, Shapur Khorshidi
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 56, 189 196, 2017 Improvement of Radiation Characteristics of Balanced Antipodal Vivaldi Antenna Using Transformation Optics Fatemeh Etesami 1, *, Shapur Khorshidi
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
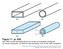 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 62, 131 137, 2016 A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation Ayed R. AlAjmi and Mohammad A. Saed * Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 62, 131 137, 2016 A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation Ayed R. AlAjmi and Mohammad A. Saed * Abstract
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
New Design of Optical Add-Drop Filter Based on Triangular Lattice Photonic Crystal Ring Resonator
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (4): 985-989 Science Explorer Publications New Design of Optical Add-Drop Filter
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (4): 985-989 Science Explorer Publications New Design of Optical Add-Drop Filter
A HIGH-POWER LOW-LOSS MULTIPORT RADIAL WAVEGUIDE POWER DIVIDER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 31, 189 198, 2012 A HIGH-POWER LOW-LOSS MULTIPORT RADIAL WAVEGUIDE POWER DIVIDER X.-Q. Li *, Q.-X. Liu, and J.-Q. Zhang School of Physical Science and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 31, 189 198, 2012 A HIGH-POWER LOW-LOSS MULTIPORT RADIAL WAVEGUIDE POWER DIVIDER X.-Q. Li *, Q.-X. Liu, and J.-Q. Zhang School of Physical Science and
A broadband achromatic metalens for focusing and imaging in the visible
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-017-0034-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. A broadband achromatic metalens for focusing and imaging in the visible
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-017-0034-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. A broadband achromatic metalens for focusing and imaging in the visible
Design and Simulation of Microstrip Rectangular Patch Antenna for Bluetooth Application
 Design and Simulation of Microstrip Rectangular Patch Antenna for Bluetooth Application Tejal B. Tandel, Nikunj Shingala Abstract A design of small sized, low profile patch antenna is proposed for BLUETOOTH
Design and Simulation of Microstrip Rectangular Patch Antenna for Bluetooth Application Tejal B. Tandel, Nikunj Shingala Abstract A design of small sized, low profile patch antenna is proposed for BLUETOOTH
Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon. photonic crystals
 Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals Daryl M. Beggs 1, *, Thomas P. White 1, Liam O Faolain 1 and Thomas F. Krauss 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, University
Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals Daryl M. Beggs 1, *, Thomas P. White 1, Liam O Faolain 1 and Thomas F. Krauss 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, University
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
Fiber Optic Communications Communication Systems
 INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
A COMPACT CPW-FED UWB SLOT ANTENNA WITH CROSS TUNING STUB
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 13, 159 170, 2010 A COMPACT CPW-FED UWB SLOT ANTENNA WITH CROSS TUNING STUB J. William and R. Nakkeeran Department of ECE Pondicherry Engineering College Puducherry-605
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 13, 159 170, 2010 A COMPACT CPW-FED UWB SLOT ANTENNA WITH CROSS TUNING STUB J. William and R. Nakkeeran Department of ECE Pondicherry Engineering College Puducherry-605
Design of Low-Index Metamaterial Lens Used for Wideband Circular Polarization Antenna
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 68, 93 98, 2017 Design of Low-Index Metamaterial Lens Used for Wideband Circular Polarization Antenna Yong Wang and Yanlin Zou * Abstract A novel low-index
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 68, 93 98, 2017 Design of Low-Index Metamaterial Lens Used for Wideband Circular Polarization Antenna Yong Wang and Yanlin Zou * Abstract A novel low-index
Tuning of Photonic Crystal Ring Resonators for Application in Analog to Digital Converter Systems
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (12): 4242-4247 Science Explorer Publications Tuning of Photonic Crystal Ring
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (12): 4242-4247 Science Explorer Publications Tuning of Photonic Crystal Ring
Lecture 10. Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers
 Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
Slot waveguide-based splitters for broadband terahertz radiation
 Slot waveguide-based splitters for broadband terahertz radiation Shashank Pandey, Gagan Kumar, and Ajay Nahata* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah
Slot waveguide-based splitters for broadband terahertz radiation Shashank Pandey, Gagan Kumar, and Ajay Nahata* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah
Susceptibility of an Electromagnetic Band-gap Filter
 1 Susceptibility of an Electromagnetic Band-gap Filter Shao Ying Huang, Student Member, IEEE and Yee Hui Lee, Member, IEEE, Abstract In a compact dual planar electromagnetic band-gap (EBG) microstrip structure,
1 Susceptibility of an Electromagnetic Band-gap Filter Shao Ying Huang, Student Member, IEEE and Yee Hui Lee, Member, IEEE, Abstract In a compact dual planar electromagnetic band-gap (EBG) microstrip structure,
Aperture Antennas. Reflectors, horns. High Gain Nearly real input impedance. Huygens Principle
 Antennas 97 Aperture Antennas Reflectors, horns. High Gain Nearly real input impedance Huygens Principle Each point of a wave front is a secondary source of spherical waves. 97 Antennas 98 Equivalence
Antennas 97 Aperture Antennas Reflectors, horns. High Gain Nearly real input impedance Huygens Principle Each point of a wave front is a secondary source of spherical waves. 97 Antennas 98 Equivalence
ANTENNAS FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE WILEY. Yi Huang University of Liverpool, UK. Kevin Boyle NXP Semiconductors, UK
 ANTENNAS FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE Yi Huang University of Liverpool, UK Kevin Boyle NXP Semiconductors, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents Preface Acronyms and Constants xi xiii 1
ANTENNAS FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE Yi Huang University of Liverpool, UK Kevin Boyle NXP Semiconductors, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents Preface Acronyms and Constants xi xiii 1
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Analysis of Crack Detection in Metallic and Non-metallic Surfaces Using FDTD Method
 ECNDT 26 - We.4.3.2 Analysis of Crack Detection in Metallic and Non-metallic Surfaces Using FDTD Method Faezeh Sh.A.GHASEMI 1,2, M. S. ABRISHAMIAN 1, A. MOVAFEGHI 2 1 K. N. Toosi University of Technology,
ECNDT 26 - We.4.3.2 Analysis of Crack Detection in Metallic and Non-metallic Surfaces Using FDTD Method Faezeh Sh.A.GHASEMI 1,2, M. S. ABRISHAMIAN 1, A. MOVAFEGHI 2 1 K. N. Toosi University of Technology,
SYMMETRICAL PYRAMIDAL HORN ANTENNAS BASED ON EBG STRUCTURES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 29, 1 22, 2011 SYMMETRICAL PYRAMIDAL HORN ANTENNAS BASED ON EBG STRUCTURES I. Khromova, I. Ederra, and R. Gonzalo Antenna Group Public University of Navarra,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 29, 1 22, 2011 SYMMETRICAL PYRAMIDAL HORN ANTENNAS BASED ON EBG STRUCTURES I. Khromova, I. Ederra, and R. Gonzalo Antenna Group Public University of Navarra,
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. FOUR 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. FOUR 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2
 angle VIRTUAL TRANSMISSION LINE OF CONICAL TYPE COAXIALOPEN-ENDED PROBE FOR DIELECTRIC MEASUREMENT H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2 ABSTRACT 1,2 Ecole Polytechnique of Montreal, Canada An improved virtually conical
angle VIRTUAL TRANSMISSION LINE OF CONICAL TYPE COAXIALOPEN-ENDED PROBE FOR DIELECTRIC MEASUREMENT H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2 ABSTRACT 1,2 Ecole Polytechnique of Montreal, Canada An improved virtually conical
TAPERED MEANDER SLOT ANTENNA FOR DUAL BAND PERSONAL WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 are closer to grazing, where 50. However, once the spectral current distribution is windowed, and the level of the edge singularity is reduced by this process, the computed RCS shows a much better agreement
are closer to grazing, where 50. However, once the spectral current distribution is windowed, and the level of the edge singularity is reduced by this process, the computed RCS shows a much better agreement
Index. Cambridge University Press Silicon Photonics Design Lukas Chrostowski and Michael Hochberg. Index.
 absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
Microstrip Antenna Using Dummy EBG
 www.ijsrnsc.org Available online at www.ijsrnsc.org IJSRNSC Volume-1, Issue-2, June- 2013 Research Paper Int. J. Sci. Res. in Network Security and Communication ISSN: 2321-3256 Microstrip Antenna Using
www.ijsrnsc.org Available online at www.ijsrnsc.org IJSRNSC Volume-1, Issue-2, June- 2013 Research Paper Int. J. Sci. Res. in Network Security and Communication ISSN: 2321-3256 Microstrip Antenna Using
Analysis of Microstrip Circuits Using a Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method
 Analysis of Microstrip Circuits Using a Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method M.G. BANCIU and R. RAMER School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications University of New South Wales Sydney 5 NSW
Analysis of Microstrip Circuits Using a Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method M.G. BANCIU and R. RAMER School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications University of New South Wales Sydney 5 NSW
Rectangular Patch Antenna to Operate in Flame Retardant 4 Using Coaxial Feeding Technique
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 3 (2017) pp. 399-407 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Rectangular Patch Antenna to Operate
International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 3 (2017) pp. 399-407 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Rectangular Patch Antenna to Operate
RCS Reduction of Patch Array Antenna by Complementary Split-Ring Resonators Structure
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 51, 95 101, 2014 RCS Reduction of Patch Array Antenna by Complementary Split-Ring Resonators Structure Jun Zheng 1, 2, Shaojun Fang 1, Yongtao Jia 3, *, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 51, 95 101, 2014 RCS Reduction of Patch Array Antenna by Complementary Split-Ring Resonators Structure Jun Zheng 1, 2, Shaojun Fang 1, Yongtao Jia 3, *, and
ENHANCEMENT OF PRINTED DIPOLE ANTENNAS CHARACTERISTICS USING SEMI-EBG GROUND PLANE
 J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 2, No. 8, 993 16, 26 ENHANCEMENT OF PRINTED DIPOLE ANTENNAS CHARACTERISTICS USING SEMI-EBG GROUND PLANE F. Yang, V. Demir, D. A. Elsherbeni, and A. Z. Elsherbeni
J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 2, No. 8, 993 16, 26 ENHANCEMENT OF PRINTED DIPOLE ANTENNAS CHARACTERISTICS USING SEMI-EBG GROUND PLANE F. Yang, V. Demir, D. A. Elsherbeni, and A. Z. Elsherbeni
Monoconical RF Antenna
 Page 1 of 8 RF and Microwave Models : Monoconical RF Antenna Monoconical RF Antenna Introduction Conical antennas are useful for many applications due to their broadband characteristics and relative simplicity.
Page 1 of 8 RF and Microwave Models : Monoconical RF Antenna Monoconical RF Antenna Introduction Conical antennas are useful for many applications due to their broadband characteristics and relative simplicity.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
HIGH GAIN AND LOW CROSS-POLAR COMPACT PRINTED ELLIPTICAL MONOPOLE UWB ANTENNA LOADED WITH PARTIAL GROUND AND PARASITIC PATCHES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 43, 151 167, 2012 HIGH GAIN AND LOW CROSS-POLAR COMPACT PRINTED ELLIPTICAL MONOPOLE UWB ANTENNA LOADED WITH PARTIAL GROUND AND PARASITIC PATCHES G. Shrikanth
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 43, 151 167, 2012 HIGH GAIN AND LOW CROSS-POLAR COMPACT PRINTED ELLIPTICAL MONOPOLE UWB ANTENNA LOADED WITH PARTIAL GROUND AND PARASITIC PATCHES G. Shrikanth
DESIGN OF SEVERAL POWER DIVIDERS USING CPW- TO-MICROSTRIP TRANSITION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 41, 125 134, 2013 DESIGN OF SEVERAL POWER DIVIDERS USING CPW- TO-MICROSTRIP TRANSITION Maoze Wang *, Fushun Zhang, Jian Sun, Ke Chen, and Bin Wen National
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 41, 125 134, 2013 DESIGN OF SEVERAL POWER DIVIDERS USING CPW- TO-MICROSTRIP TRANSITION Maoze Wang *, Fushun Zhang, Jian Sun, Ke Chen, and Bin Wen National
Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Performance Analysis of a Patch Antenna Array Feed For A Satellite C-Band Dish Antenna
 Cyber Journals: Multidisciplinary Journals in Science and Technology, Journal of Selected Areas in Telecommunications (JSAT), November Edition, 2011 Performance Analysis of a Patch Antenna Array Feed For
Cyber Journals: Multidisciplinary Journals in Science and Technology, Journal of Selected Areas in Telecommunications (JSAT), November Edition, 2011 Performance Analysis of a Patch Antenna Array Feed For
Wideband Double-Layered Dielectric-Loaded Dual-Polarized Magneto-Electric Dipole Antenna
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 63, 23 28, 2016 Wideband Double-Layered Dielectric-Loaded Dual-Polarized Magneto-Electric Dipole Antenna Changqing Wang 1, Zhaoxian Zheng 2,JianxingLi
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 63, 23 28, 2016 Wideband Double-Layered Dielectric-Loaded Dual-Polarized Magneto-Electric Dipole Antenna Changqing Wang 1, Zhaoxian Zheng 2,JianxingLi
Assembly and Experimental Characterization of Fiber Collimators for Low Loss Coupling
 Assembly and Experimental Characterization of Fiber Collimators for Low Loss Coupling Ruby Raheem Dept. of Physics, Heriot Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland EH14 4AS, UK ABSTRACT The repeatability of
Assembly and Experimental Characterization of Fiber Collimators for Low Loss Coupling Ruby Raheem Dept. of Physics, Heriot Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland EH14 4AS, UK ABSTRACT The repeatability of
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform
 Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform Muhammad Alam,* J. Stewart Aitchsion, and Mohammad Mojahedi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto,
Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform Muhammad Alam,* J. Stewart Aitchsion, and Mohammad Mojahedi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information "Large-scale integration of wavelength-addressable all-optical memories in a photonic crystal chip" SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Eiichi Kuramochi*, Kengo Nozaki, Akihiko Shinya,
Supplementary Information "Large-scale integration of wavelength-addressable all-optical memories in a photonic crystal chip" SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Eiichi Kuramochi*, Kengo Nozaki, Akihiko Shinya,
RF AND MICROWAVE ENGINEERING
 RF AND MICROWAVE ENGINEERING FUNDAMENTALS OF WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Frank Gustrau Dortmund University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Germany WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Preface List of
RF AND MICROWAVE ENGINEERING FUNDAMENTALS OF WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Frank Gustrau Dortmund University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Germany WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Preface List of
Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b,
 Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b, a Photonics Research Group, Ghent University-imec, Technologiepark-Zwijnaarde
Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b, a Photonics Research Group, Ghent University-imec, Technologiepark-Zwijnaarde
Analysis of the Focusing Characteristics of Double Negative Binary Diffractive Lens
 J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 1,, 557-56 doi:1.36/jemaa.1.97 Published Online September 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 557 Analysis of the Focusing Characteristics of Double Negative
J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 1,, 557-56 doi:1.36/jemaa.1.97 Published Online September 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 557 Analysis of the Focusing Characteristics of Double Negative
MITER BEND MIRROR DESIGN FOR CORRUGATED WAVEGUIDES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol., 57 6, 9 MITER BED MIRROR DESIG FOR CORRUGATED WAVEGUIDES S. Liao Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison 45 Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol., 57 6, 9 MITER BED MIRROR DESIG FOR CORRUGATED WAVEGUIDES S. Liao Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison 45 Engineering
Design of Six Channel Demultiplexer by Heterostructure Photonic Crystal Resonant Cavity
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (4): 976-984 Science Explorer Publications Design of Six Channel Demultiplexer
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (4): 976-984 Science Explorer Publications Design of Six Channel Demultiplexer
UNIT Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion?
 UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
Experimental Competition
 37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
2008 IEEE. Reprinted with permission.
 Pekka Alitalo, Olli Luukkonen, Joni Vehmas, and Sergei A. Tretyakov. 2008. Impedance matched microwave lens. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, volume 7, pages 187 191. 2008 IEEE Reprinted
Pekka Alitalo, Olli Luukkonen, Joni Vehmas, and Sergei A. Tretyakov. 2008. Impedance matched microwave lens. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, volume 7, pages 187 191. 2008 IEEE Reprinted
ANALYSIS OF A HIGH-GAIN FABRY-PÉROT CAVITY ANTENNA WITH AN FSS SUPERSTRATE: EFFECTIVE MEDIUM APPROACH
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 59 68, 29 ANALYSIS OF A HIGH-GAIN FABRY-PÉROT CAVITY ANTENNA WITH AN FSS SUPERSTRATE: EFFECTIVE MEDIUM APPROACH D. Kim and J. I. Choi Electromagnetic
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 59 68, 29 ANALYSIS OF A HIGH-GAIN FABRY-PÉROT CAVITY ANTENNA WITH AN FSS SUPERSTRATE: EFFECTIVE MEDIUM APPROACH D. Kim and J. I. Choi Electromagnetic
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
