Experimental demonstration of negative refraction imaging in both amplitude and phase
|
|
|
- Neil Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Experimental demonstration of negative refraction imaging in both amplitude and phase Zhaolin Lu, Shouyuan Shi, Christopher A. Schuetz, and Dennis W. Prather Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 976,USA Abstract: We studied a two-dimensional square-lattice photonic crystal with all-angle negative refraction at its first band. Using this photonic crystal, we designed and fabricated a flat lens functioning as a cylindrical lens by increasing the vertical dimension of the photonic crystal. Twodimensional finite-difference time-domain simulation validated negative refraction imaging. To perform the experiment, a microwave imaging system was built based on a vector network analyzer. Field distributions were acquired by scanning the imaging plane and object plane. The experiment demonstrated negative refraction imaging in both amplitude and phase, and obtained an image with feature size,.77λ. 5 Optical Society of America OCIS codes: ( ) Negative refraction, ( ) Photonic Crystal, ( ) Flat lens, (.99) Image formation theory, (.664) Super resolution, (.6) Lens design, (.55) Phase measurement References and links. V.G. Veselago, The electrodynamics of substances with simultaneously negative values of permittivity and permeability. Sov. Phys. Usp.,59-54(968).. J.B. Pendry, A.J. Holden, W.J. Stewart and I. Youngs, Extremely low frequency plasmons in metallic mesostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, (996).. J.B. Pendry, A.J. Holden, D.J. Robbins, and W.J. Stewart, Magnetism from conductors and enhanced nonlinear phenomena. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techniques. 47, (999). 4. R.A. Shelby, D.R. Smith, and S. Schultz, Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction. Science, 9, (). 5. M. Notomi, Theory of light propagation in strongly modulated photonic crystals: refractionlike behavior in the vicinity of the photonic band gap. Phys. Rev. B. 6, (). 6. P.V. Parimi, W.T. Lu, P. Vodo, J. Sokoloff, J.S. Derov, and S. Sridhar, Negative refraction and left-handed electromagnetism in microwave photonic crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 9, 74(4) (4). 7. E. Cubukcu, K. Aydin, E. Ozbay, S. Foteinopoulou, and C.M. Soukoulis, Electromagnetic wave: negative refraction by photonic crystals. Nature, 4, (). 8. J.B., Pendry, Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, (). 9. N. Garcia, and M. Nieto-Vesperinas, Left-handed materials do not make a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 74(4) ().. P.M. Valanju, R. M. Walser, and A. P. Valanju, Wave refraction in negative-index media: always positive and very inhomogeneous. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 874(4) ().. N. Garcia, and M. Nieto-Vesperinas, Is there an experimental verification of a negative index of refraction yet? Opt. Lett., 7, ().. J. B. Pendry, Positively negative. Nature, 4, ().. C. Luo, S.G. Johnson, J.D. Joannopoulos, and J.B. Pendry, All-angle negative refraction without negative effective index. Phys. Rev. B, 65, 4(R) (). 4. P.V. Parimi, W.T. Lu, P. Vodo, and S. Sridhar, Photonic crystals: imaging by flat lens using negative refraction. Nature, 46, 44 (). 5. H. Kosaka, T. Kawashima, A. Tomita, M. Notomi, T. Tamamura, T. Sato, and S. Kawakamib, Self-collimating phenomena in photonic crystals, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, -4 (999). # $5. US Received 8 February 5; revised 7 March 5; accepted 7 March 5 (C) 5 OSA March 5 / Vol., No. 6 / OPTICS EXPRESS 7
2 6. C. Luo, S.G. Johson, J.D. Joannopoulos, and J.B. Pendry, All-angle negative refraction in a threedimensionally periodic photonic crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 8, 5-54 (). 7. X. Ao and S. He, Three-dimensional photonic crystal of negative refraction achieved by interference lithography. Opt. Lett., 9, (4).. Introduction In 968, V.G. Veselago argued that if both permittivity and permeability were negative, it follows that the refractive index of the material would also be negative []. In this material, the electric field E, magnetic field H, and the propagation constant k are not composed of a set of right-handed coordinates, but left-handed coordinates. Therefore, he called this material left-handed material (LHM). The most remarkable thing for a LHM is that the group velocity is opposite to the phase velocity when electromagnetic waves propagate in it. Also, since the refractive index is negative, the refracted beam will bend to the wrong way when a beam is incident into this material from a common material (right-handed material). This phenomenon is negative refraction. Using negative refraction, one could make a lens with flat surface. Veselago also suggested that it was possible to find this material in plasmas. Pendry et al [] studied interlaced wire structure and concluded that their structure resembles plasma, but has very low effective electron density and very high effective electron mass, resulting in a plasma frequency as low as GHz s. In particular, it is possible to achieve negative permittivity at microwave regime by tuning its period. Based on the same philosophy, they proposed another structure made of periodic metal rings and showed negative permeability can also be achieved []. Shelby et al experimentally demonstrated negative refraction by a structure combining the interlaced wires and the periodic rings [4]. Meanwhile, Notomi [5] studied the dispersion behavior in the vicinity of the photonic band gap and simulated that negative refraction can also be achieved in a dielectric photonic crystal(phc). Parimi et al [6] and Cubukcu et al [7] experimentally demonstrated the negative refraction in dielectric photonic crystals. Pendry s another work sparked significant interest in negative refraction and the flat lens Negative refraction makes a perfect lens [8]. He explained that negative refraction amplifies evanescent waves, and both propagating and evanescent waves contribute to the resolution of the image. Garcia et al argued that negative refraction does not make a perfect lens because the finite thickness of a lens prevents the restoration of evanescent waves and perfect focusing [9]. In fact, there are more debates ever since the concept of negative refraction was proposed. Several years ago, negative refraction as a basic physical phenomenon was discussed intensely in physics and optics. The debates among scientists were then focused on whether negative refraction is possible and how it would work [-]. Nowadays, more interest in imaging by negative refraction has arisen in material science, RF engineering, electrical engineering, optical communication, and medical engineering. A key problem is whether a perfect lens can be achieved by negative refraction. Our work is aimed at answering this question.. Flat cylindrical lens In our work, we use a two-dimensional (D) photonic crystal to demonstrate negative refraction imaging. The key distinctions of this work lie in designing the photonic crystal at the first band [], increasing the vertical dimension of the flat lens, and validating the imaging in both amplitude and phase. Although imaging by a flat lens using negative refraction has been demonstrated in D photonic crystals formed by arranging alumina rods in the air [4], the phase distribution has not been reported yet, which is a very important and convenient criterion to validate the imaging when a point object is used. In addition, the assembled rods-in-air flat lens is not convenient for fabrication and applications. Its small dimension on vertical direction also limits its practical applications. Instead of fabricating holes in a thin dielectric slab or assembling short rods between two metal plates to form a photonic crystal allowing only single mode on the vertical direction, we increased the vertical dimension of the photonic crystal until this dimension can be treated as # $5. US Received 8 February 5; revised 7 March 5; accepted 7 March 5 (C) 5 OSA March 5 / Vol., No. 6 / OPTICS EXPRESS 8
3 infinite to avoid the reflection on vertical direction, as shown in Fig.. As a result, we proposed a lens with flat surfaces and functioning as a cylindrical lens, namely flat cylindrical lens. For designing a planar photonic crystal, a widely used method is to apply an effective index into D calculations and simulations. However, the effective index is always smaller than the bulk material refractive index. Thus, a poor index contrast results, which is often a problem for designing photonic crystal flat lens. In contrast, our approach has the advantage in that larger index contrast is available because we applied the bulk refractive index, instead of the effective index, to calculate the equi-frequency contours (EFC) and simulate the behavior of the electromagnetic wave in the horizontal plane (the zero-spatial frequency component) using the D finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method. Theoretically, this approach is a better approximation to the D configuration as the device has no limitation on the vertical direction, and the wave propagating on the vertical direction is excluded. (c) Source Detector y x Source Detector Flat lens Flat lens Fig.. Picture of the fabricated flat lens. Illustration of the experimental setup. The source is located at x= -. (c) Picture of the experimental setup.. Negative refraction at the first photonic band A square-lattice of air holes in dielectric ε=5, with lattice constant a, and hole diameter r=.7a is employed in our work. C. Luo, et al have theoretically investigated the dispersion properties of a similar photonic crystal and numerically simulated negative refraction imaging by the photonic crystal []. Our work is focused on experimental demonstration. However, we summarize some key points of the theoretical analysis for understanding the imaging mechanism and experimental results. We used the plane wave expansion method to solve the corresponding eigen frequencies for a given wave vector. Figures, and (c) show the photonic band diagram, photonic band structure and equi-frequency contours, respectively. By observing the EFCs, we can see that all-angle negative refraction in the first band occurs at normalized frequencies of ω n =.7~. because at these frequencies the EFCs are allconvex. By its definition, the excited mode will propagate with group velocity v g = k ω( k) [5], which means the group velocity is always perpendicular to the EFC. As a result, the group velocity is not opposite to its phase velocity in our case. However, negative refraction # $5. US Received 8 February 5; revised 7 March 5; accepted 7 March 5 (C) 5 OSA March 5 / Vol., No. 6 / OPTICS EXPRESS 9
4 still occurs at its first band. C. Luo et al attributed this to its negative-definite photon effective mass[]. Frequency (ω a/π c) Γ X M Γ PhC Air rd band Refracted beam ω n nd band ky PhC st band Air k nx k ny kx Incident beam (c) Fig.. TE mode dispersion diagram of the square-lattice PhC. TE mode photonic band structure of the square-lattice PhC. (c)te mode EFCs of the square-lattice PhC at the vicinity of the first bandgap. Fig.. Illustration of propagation of the incident beam and refracted beam in k-space. Illustration of propagation of the incident beam and refracted beam in real space. Figure shows how this occurs in k-space: when a light beam is incident from the air into the photonic crystal, the tangential component of the wave vector (phase velocity) is continuous at the interface and the group velocity is perpendicular to the EFC. As a result, k x component bends to reverse direction and k y component keeps its direction. The group velocity is only partially opposite to its phase velocity. However, the light beam still bends to a wrong direction, which is negative refraction. Figure shows how negative refraction occurs in the real space. In addition, the EFCs at ω n =.7~. are all-convex, which means the photonic crystal can gather incident beams from all direction and form an image. Based on these observations, we simulated a flat lens made of this photonic crystal: the hole diameter is r=.6mm, the lattice constant is a=.6/.7=.mm, the thickness of the lens is 4.5mm, and the working frequency is f=4.6ghz(λ =.mm), which corresponds to normalized frequency ω n =.9. The flat lens works at the first band and the optical axis is designed along (,). Figures 4a and 4b show the simulated phase and amplitude distributions. From Fig. 4, we can see that an image is really formed by the negative refraction using this flat lens. The lateral size of the simulated image is 9mm or.7λ. 4. Experiment In our work, a computer numerically controlled (CNC) micro-milling machine is used to fabricate the flat lens. Figure a shows the photonic crystal lens we fabricated. The squarelattice photonic crystal, as a flat lens, is fabricated in a low loss material with dielectric # $5. US Received 8 February 5; revised 7 March 5; accepted 7 March 5 (C) 5 OSA March 5 / Vol., No. 6 / OPTICS EXPRESS
5 constant 5. It has the same parameters as the flat lens we simulated, i.e., r=.6mm, a=.6/.7=.mm, the thickness of the lens=4.5mm. In addition, its dimension at vertical direction is 6.5mm, which is much larger than the lens thickness. We have built a microwave imaging setup, as illustrated and shown in Fig. and (c), based on an Agilent 856D vector network analyzer, which encompasses a test and measurement capability spanning 45MHz through GHz. A particularly attractive feature of this system is its ability to measure results in both amplitude and phase. The source is a dipole antenna connected to the network analyzer, and the detector is another dipole antenna fed back to the network analyzer. The detector is mounted on an X-Y scanner to map the electric field. The field distribution is acquired by scanning the object plane and image plane. A custom program was developed to synchronize the scanning and measurement. Once a scanning and measurement is finished, we depict the S-parameter value, S in our case, with regard to the position as an image. Consequently, each pixel in the image corresponds to the S-parameter value at a scanning position. In addition, in the network analyzer the S-parameter is given as complex values, so we can obtain both amplitude and phase distributions, which is impractical for near infrared or visible light measurement y (mm) y (mm) x e x (mm) x (mm) Fig. 4. Simulated phase distribution (unit: radian) when a dipole is placed at object distance mm: TE mode at 4.6GHz. Simulated amplitude distribution when a dipole is placed at object distance mm: TE mode at 4.6GHz. 4 x e y (mm) - -5 x y(mm) x(mm) x (mm) x(mm) x(mm) Fig. 5. The measured phase distributions (in degrees) at.ghz for the source (left) and the image (right). The flat lens (photonic crystal) is depicted between the source and the image. The measured amplitude distributions at.ghz. The flat lens (photonic crystal) is depicted between the source and the image x To perform the experiment, we placed the source dipole mm away from the lens, with the electric component polarizing along y-axis to stimulate a transverse-electric mode, and mapped the field distribution using the X-Y robot, meanwhile spanning the frequencies from GHz to 6GHz with spacing.ghz. Consequently, we observed good images in the frequency range of.±.6ghz. Figures 5 and 5 show the measured phase and amplitude distributions for.ghz. From the measured amplitude distribution, we can see that a high amplitude spot appears on the image plane. From the measured phase distribution, we can see that a closed circle appears on the image plane, which precludes the possibility that the small spot is observed because the detector is close to the source. According to this point, our result more strongly supports negative refraction imaging than the result reported [4]. Therefore, from the amplitude distribution and particularly from the phase distribution, we validate that waves converge to form an image at 7mm away from the lens at the imaging side, and then diverge into far field. The lateral size of the image is about mm, which is 77% of the corresponding wavelength, mm. In contrast, it is well known that a conventional # $5. US Received 8 February 5; revised 7 March 5; accepted 7 March 5 (C) 5 OSA March 5 / Vol., No. 6 / OPTICS EXPRESS
6 lens cannot focus microwave or light on an area smaller than a square wavelength [8]. The reduction of the intensity between the image and object may be attributed to the divergence on vertical direction and back reflection. In addition, there is little change with the image when we shifted the detector ±mm along the vertical direction. Although this is far from obtaining D imaging, the large vertical dimension of the flat lens opens the door for another dimension, as well as practical applications. Without another dimension, the flat lens can have few practical applications. Once another dimension is introduced, the photonic crystal flat lens can be directly used in microwave imaging, and optical imaging systems. This issue can be resolved by fabricating D photonic crystals [6,7]. 5. Conclusions To summarize, we designed, simulated, fabricated and characterized a flat lens, which works by negative refraction and functions as a cylindrical lens. For the first time, the experiment demonstrated the negative refraction image of a point source in both amplitude and phase. By analyzing the image field distribution, we measured the image feature size to be.77λ. However, as we claimed in section 4 the group velocity is not opposite to its phase velocity in our case. Effective index n eff = cannot be achieved in our structure. As a result, index matching and aberration are exacerbated in negative refraction imaging. Our recent experiment on a triangular-lattice PhC demonstrated negative refraction imaging with n eff =. We will report it in the future. # $5. US Received 8 February 5; revised 7 March 5; accepted 7 March 5 (C) 5 OSA March 5 / Vol., No. 6 / OPTICS EXPRESS
Resonance-induced wave penetration through electromagnetic opaque object
 Resonance-induced wave penetration through electromagnetic opaque object He Wen a,c), Bo Hou b), Yang Leng a), Weijia Wen b,d) a) Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Hong Kong University of Science
Resonance-induced wave penetration through electromagnetic opaque object He Wen a,c), Bo Hou b), Yang Leng a), Weijia Wen b,d) a) Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Hong Kong University of Science
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005](/thumbs/91/105523130.jpg) Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL
 SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
Rectangular Patch Antenna Using ARRAY OF HEXAGONAL RINGS Structure in L-band
 Rectangular Patch Antenna Using ARRAY OF HEXAGONAL RINGS Structure in L-band Anamika Verma, Dr.Sarita Singh Bhadauria Department of Electronics Engineering, Madhav Institute of Technology and Science,
Rectangular Patch Antenna Using ARRAY OF HEXAGONAL RINGS Structure in L-band Anamika Verma, Dr.Sarita Singh Bhadauria Department of Electronics Engineering, Madhav Institute of Technology and Science,
Determination of Transmission and Reflection Parameters by Analysis of Square Loop Metasurface
 Determination of Transmission and Reflection Parameters by Analysis of Square Loop Metasurface Anamika Sethi #1, Rajni *2 #Research Scholar, ECE Department, MRSPTU, INDIA *Associate Professor, ECE Department,
Determination of Transmission and Reflection Parameters by Analysis of Square Loop Metasurface Anamika Sethi #1, Rajni *2 #Research Scholar, ECE Department, MRSPTU, INDIA *Associate Professor, ECE Department,
Negative refraction in photonic crystals
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 55 (28) pp 91-1 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Negative refraction in photonic crystals
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 55 (28) pp 91-1 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Negative refraction in photonic crystals
Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals
 Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals Binglin Miao, Caihua Chen, Ahmed Sharkway, Shouyuan Shi, and Dennis W. Prather University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 976 binglin@udel.edu
Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals Binglin Miao, Caihua Chen, Ahmed Sharkway, Shouyuan Shi, and Dennis W. Prather University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 976 binglin@udel.edu
Magnetic Response of Rectangular and Circular Split Ring Resonator: A Research Study
 Magnetic Response of Rectangular and Circular Split Ring Resonator: A Research Study Abhishek Sarkhel Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur Sekhar Ranjan Bhadra Chaudhuri Bengal Engineering
Magnetic Response of Rectangular and Circular Split Ring Resonator: A Research Study Abhishek Sarkhel Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur Sekhar Ranjan Bhadra Chaudhuri Bengal Engineering
Band-dropping via coupled photonic crystal waveguides
 and-dropping via coupled photonic crystal waveguides Mehmet ayindir and Ekmel Ozbay Department of Physics, ilkent University, ilkent, 6533 nkara, Turkey bayindir@fen.bilkent.edu.tr http://www.fen.bilkent.edu.tr/
and-dropping via coupled photonic crystal waveguides Mehmet ayindir and Ekmel Ozbay Department of Physics, ilkent University, ilkent, 6533 nkara, Turkey bayindir@fen.bilkent.edu.tr http://www.fen.bilkent.edu.tr/
Low-Loss, Broadband and Tunable Negative Refractive Index Metamaterial
 J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 21, 2: 14-11 doi:1.4236/jemaa.21.2215 Published Online February 21 (www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) Low-Loss, Broadband and Tunable Negative Refractive Index Metamaterial
J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 21, 2: 14-11 doi:1.4236/jemaa.21.2215 Published Online February 21 (www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) Low-Loss, Broadband and Tunable Negative Refractive Index Metamaterial
Engineering the light propagating features through the two-dimensional coupled-cavity photonic crystal waveguides
 Engineering the light propagating features through the two-dimensional coupled-cavity photonic crystal waveguides Feng Shuai( ) and Wang Yi-Quan( ) School of Science, Minzu University of China, Bejiing
Engineering the light propagating features through the two-dimensional coupled-cavity photonic crystal waveguides Feng Shuai( ) and Wang Yi-Quan( ) School of Science, Minzu University of China, Bejiing
MICROSTRIP ANTENNA S GAIN ENHANCEMENT US- ING LEFT-HANDED METAMATERIAL STRUCTURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 8, 235 247, 29 MICROSTRIP ANTENNA S GAIN ENHANCEMENT US- ING LEFT-HANDED METAMATERIAL STRUCTURE H. A. Majid, M. K. A. Rahim, and T. Masri Faculty of Electrical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 8, 235 247, 29 MICROSTRIP ANTENNA S GAIN ENHANCEMENT US- ING LEFT-HANDED METAMATERIAL STRUCTURE H. A. Majid, M. K. A. Rahim, and T. Masri Faculty of Electrical
STUDY OF ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC MATERIAL FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS
 International Journal of Advances in Materials Science and Engineering (IJAMSE) Vol., No.,July 3 STUDY OF ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC MATERIAL FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS H. Benosman, N.Boukli Hacene Department
International Journal of Advances in Materials Science and Engineering (IJAMSE) Vol., No.,July 3 STUDY OF ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC MATERIAL FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS H. Benosman, N.Boukli Hacene Department
SPATIAL BEAM COMPRESSION AND EFFECTIVE BEAM INJECTION USING TRIANGULAR GRADIENT INDEX PROFILE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, 51 67, 2012 SPATIAL BEAM COMPRESSION AND EFFECTIVE BEAM INJECTION USING TRIANGULAR GRADIENT INDEX PROFILE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS N. Yogesh and V. Subramanian
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 129, 51 67, 2012 SPATIAL BEAM COMPRESSION AND EFFECTIVE BEAM INJECTION USING TRIANGULAR GRADIENT INDEX PROFILE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS N. Yogesh and V. Subramanian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves Bilinear Transformations Figure 1 Graphical depiction of the bilinear transformation and derived material parameters. (a) The transformation
A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves Bilinear Transformations Figure 1 Graphical depiction of the bilinear transformation and derived material parameters. (a) The transformation
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF λ/4 MONOPOLE ANTENNAS IN A LEFT-HANDED META-MATERIAL
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 51, 281 293, 2005 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF λ/4 MONOPOLE ANTENNAS IN A LEFT-HANDED META-MATERIAL Q. Sui, C. Li, L. L. Li, and F. Li Institute of Electrics Chinese
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 51, 281 293, 2005 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF λ/4 MONOPOLE ANTENNAS IN A LEFT-HANDED META-MATERIAL Q. Sui, C. Li, L. L. Li, and F. Li Institute of Electrics Chinese
ANALYSIS OF SELF-COLLIMATION BASED CAVITY RESONATOR FORMED BY PHOTONIC CRYSTAL
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 12, 115 130, 2010 ANALYSIS OF SELF-COLLIMATION BASED CAVITY RESONATOR FORMED BY PHOTONIC CRYSTAL N. Yogesh and V. Subramanian Microwave Laboratory, Department
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 12, 115 130, 2010 ANALYSIS OF SELF-COLLIMATION BASED CAVITY RESONATOR FORMED BY PHOTONIC CRYSTAL N. Yogesh and V. Subramanian Microwave Laboratory, Department
Design of Voltage control Oscillator using Nonlinear Composite Right/Left-Handed Transmission Line
 ADVANCED ELECTROMAGNETICS, VOL. 5, NO. 1, MARCH 2016 Design of Voltage control Oscillator using Nonlinear Composite Right/Left-Handed Transmission Line Hala J. El-Khozondar 1, Mahmoud Abu-Marasa 1, Rifa
ADVANCED ELECTROMAGNETICS, VOL. 5, NO. 1, MARCH 2016 Design of Voltage control Oscillator using Nonlinear Composite Right/Left-Handed Transmission Line Hala J. El-Khozondar 1, Mahmoud Abu-Marasa 1, Rifa
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF DISPERSION-ENGINEERED PHOTONIC CRYSTALS FOR APPLICATIONS IN THE MICROWAVE REGIME. Jerico N. Sabas
 DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF DISPERSION-ENGINEERED PHOTONIC CRYSTALS FOR APPLICATIONS IN THE MICROWAVE REGIME by Jerico N. Sabas A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF DISPERSION-ENGINEERED PHOTONIC CRYSTALS FOR APPLICATIONS IN THE MICROWAVE REGIME by Jerico N. Sabas A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial
A NOVEL EPSILON NEAR ZERO (ENZ) TUNNELING CIRCUIT USING MICROSTRIP TECHNOLOGY FOR HIGH INTEGRABILITY APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 65 74, 2010 A NOVEL EPSILON NEAR ZERO (ENZ) TUNNELING CIRCUIT USING MICROSTRIP TECHNOLOGY FOR HIGH INTEGRABILITY APPLICATIONS D. V. B. Murthy, A. Corona-Chávez
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 65 74, 2010 A NOVEL EPSILON NEAR ZERO (ENZ) TUNNELING CIRCUIT USING MICROSTRIP TECHNOLOGY FOR HIGH INTEGRABILITY APPLICATIONS D. V. B. Murthy, A. Corona-Chávez
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 4 Aug 2006
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 4 Aug 2006 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 4 Aug 2006](/thumbs/94/120580783.jpg) Tunable split-ring resonators for nonlinear negative-index metamaterials arxiv:physics/0608044v1 [physics.optics] 4 Aug 2006 Ilya V. Shadrivov, Steven K. Morrison, and Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics
Tunable split-ring resonators for nonlinear negative-index metamaterials arxiv:physics/0608044v1 [physics.optics] 4 Aug 2006 Ilya V. Shadrivov, Steven K. Morrison, and Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics
ELECTRICALLY CONTROLLABLE PCs & METAMATERIALS and THEIR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS. Frédérique GADOT
 ELECTRICALLY CONTROLLABLE PCs & METAMATERIALS and THEIR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS. Frédérique GADOT Université Paris Sud --IEF, Bât. Bât. 220, 220, 91405 Orsay, FRANCE 1 Outline 1. Brief summary on «left
ELECTRICALLY CONTROLLABLE PCs & METAMATERIALS and THEIR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS. Frédérique GADOT Université Paris Sud --IEF, Bât. Bât. 220, 220, 91405 Orsay, FRANCE 1 Outline 1. Brief summary on «left
Title. Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori. CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights.
 Title Wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): 1970-1975 Issue Date 2001-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5582
Title Wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): 1970-1975 Issue Date 2001-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5582
Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 Prerna Saxena,, 2013; Volume 1(8): 46-53 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK STUDY OF PATCH ANTENNA ARRAY USING SINGLE
Prerna Saxena,, 2013; Volume 1(8): 46-53 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK STUDY OF PATCH ANTENNA ARRAY USING SINGLE
Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna for Wireless Applications Using Metamaterial
 Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna for Wireless Applications Using Metamaterial Shalina Garg, Ratish Kumar Abstract A U-slot microstrip patch antenna loaded with metamaterial substrate is presented. The
Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna for Wireless Applications Using Metamaterial Shalina Garg, Ratish Kumar Abstract A U-slot microstrip patch antenna loaded with metamaterial substrate is presented. The
Metallic Coil-Polymer Braid Composites: I. The Numerical Modeling and Chirality
 Metallic Coil-Polymer Braid Composites: I. The Numerical Modeling and Chirality Alireza V. Amirkhizi, Thomas Plaisted, Syrus C. Nemat-Nasser, and Sia Nemat-Nasser Center of Excellence for Advanced Materials
Metallic Coil-Polymer Braid Composites: I. The Numerical Modeling and Chirality Alireza V. Amirkhizi, Thomas Plaisted, Syrus C. Nemat-Nasser, and Sia Nemat-Nasser Center of Excellence for Advanced Materials
MINIATURIZED ANTENNAS FOR COMPACT SOLDIER COMBAT SYSTEMS
 MINIATURIZED ANTENNAS FOR COMPACT SOLDIER COMBAT SYSTEMS Iftekhar O. Mirza 1*, Shouyuan Shi 1, Christian Fazi 2, Joseph N. Mait 2, and Dennis W. Prather 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
MINIATURIZED ANTENNAS FOR COMPACT SOLDIER COMBAT SYSTEMS Iftekhar O. Mirza 1*, Shouyuan Shi 1, Christian Fazi 2, Joseph N. Mait 2, and Dennis W. Prather 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Analysis of the Focusing Characteristics of Double Negative Binary Diffractive Lens
 J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 1,, 557-56 doi:1.36/jemaa.1.97 Published Online September 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 557 Analysis of the Focusing Characteristics of Double Negative
J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 1,, 557-56 doi:1.36/jemaa.1.97 Published Online September 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 557 Analysis of the Focusing Characteristics of Double Negative
Microstrip Antenna Using Dummy EBG
 www.ijsrnsc.org Available online at www.ijsrnsc.org IJSRNSC Volume-1, Issue-2, June- 2013 Research Paper Int. J. Sci. Res. in Network Security and Communication ISSN: 2321-3256 Microstrip Antenna Using
www.ijsrnsc.org Available online at www.ijsrnsc.org IJSRNSC Volume-1, Issue-2, June- 2013 Research Paper Int. J. Sci. Res. in Network Security and Communication ISSN: 2321-3256 Microstrip Antenna Using
CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
 43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
Experimental verification of backward-wave radiation from a negative refractive index metamaterial
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 10 15 NOVEMBER 2002 Experimental verification of backward-wave radiation from a negative refractive index metamaterial Anthony Grbic and George V. Eleftheriades
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 10 15 NOVEMBER 2002 Experimental verification of backward-wave radiation from a negative refractive index metamaterial Anthony Grbic and George V. Eleftheriades
Double Negative Left-Handed Metamaterials for Miniaturization of Rectangular Microstrip Antenna
 J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 2010, 2, 347-351 doi:10.4236/jemaa.2010.26044 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 347 Double Negative Left-Handed Metamaterials for
J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 2010, 2, 347-351 doi:10.4236/jemaa.2010.26044 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 347 Double Negative Left-Handed Metamaterials for
Projects in microwave theory 2009
 Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Projects in microwave theory 2017
 Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2017 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2017 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays
 Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
Study on Transmission Characteristic of Split-ring Resonator Defected Ground Structure
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 2, NO. 6, 26 71 Study on Transmission Characteristic of Split-ring Resonator Defected Ground Structure Bian Wu, Bin Li, Tao Su, and Chang-Hong Liang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 2, NO. 6, 26 71 Study on Transmission Characteristic of Split-ring Resonator Defected Ground Structure Bian Wu, Bin Li, Tao Su, and Chang-Hong Liang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
Size Reduction of Microstrip Patch Antenna by Using Meta-Fractal Technique
 Size Reduction of Microstrip Patch Antenna by Using Meta-Fractal Technique Ammar Nadal Shareef 1, Amer Basim Shaalan 2 1 (Department of Sciences, College of Basic Education/Muthanna University, Iraq) 2
Size Reduction of Microstrip Patch Antenna by Using Meta-Fractal Technique Ammar Nadal Shareef 1, Amer Basim Shaalan 2 1 (Department of Sciences, College of Basic Education/Muthanna University, Iraq) 2
Keywords: Array antenna; Metamaterial structure; Microstrip antenna; Split ring resonator
 International Journal of Technology (2016) 4: 683-690 ISSN 2086-9614 IJTech 2016 LEFT-HANDED METAMATERIAL (LHM) STRUCTURE STACKED ON A TWO- ELEMENT MICROSTRIP ANTENNA ARRAY Fitri Yuli Zulkifli 1*, Nugroho
International Journal of Technology (2016) 4: 683-690 ISSN 2086-9614 IJTech 2016 LEFT-HANDED METAMATERIAL (LHM) STRUCTURE STACKED ON A TWO- ELEMENT MICROSTRIP ANTENNA ARRAY Fitri Yuli Zulkifli 1*, Nugroho
On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers
 On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers Yasha Yi, Shoji Akiyama, Peter Bermel, Xiaoman Duan, and L. C. Kimerling Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts
On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers Yasha Yi, Shoji Akiyama, Peter Bermel, Xiaoman Duan, and L. C. Kimerling Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts
6 Electromagnetic Field Distribution Measurements using an Optically Scanning Probe System
 6 Electromagnetic Field Distribution Measurements using an Optically Scanning Probe System TAKAHASHI Masanori, OTA Hiroyasu, and ARAI Ken Ichi An optically scanning electromagnetic field probe system consisting
6 Electromagnetic Field Distribution Measurements using an Optically Scanning Probe System TAKAHASHI Masanori, OTA Hiroyasu, and ARAI Ken Ichi An optically scanning electromagnetic field probe system consisting
Slot waveguide-based splitters for broadband terahertz radiation
 Slot waveguide-based splitters for broadband terahertz radiation Shashank Pandey, Gagan Kumar, and Ajay Nahata* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah
Slot waveguide-based splitters for broadband terahertz radiation Shashank Pandey, Gagan Kumar, and Ajay Nahata* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah
Study of Microstrip Antenna Behavior with Metamaterial Substrate of SRR Type Combined with TW
 Study of Microstrip Antenna Behavior with Metamaterial Substrate of SRR Type Combined with TW JOSÉ LUCAS DA SILVA 1, HUMBERTO CÉSAR CHAVES FERNANDES, HUMBERTO DIONÍSIO DE ANDRADE 3 1, Department of Electrical
Study of Microstrip Antenna Behavior with Metamaterial Substrate of SRR Type Combined with TW JOSÉ LUCAS DA SILVA 1, HUMBERTO CÉSAR CHAVES FERNANDES, HUMBERTO DIONÍSIO DE ANDRADE 3 1, Department of Electrical
Enhanced transmission of electromagnetic waves through metamaterials w. wen 1,
 Appl. Phys. A 87, 217 221 (2007) DOI: 10.1007/s00339-006-3824-5 Applied Physics A Materials Science & Processing b. hou 1 h. wen 2 y. leng 3 Enhanced transmission of electromagnetic waves through metamaterials
Appl. Phys. A 87, 217 221 (2007) DOI: 10.1007/s00339-006-3824-5 Applied Physics A Materials Science & Processing b. hou 1 h. wen 2 y. leng 3 Enhanced transmission of electromagnetic waves through metamaterials
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 8 Jul 2010
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 8 Jul 2010 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 8 Jul 2010](/thumbs/88/117898724.jpg) Broadband Extraordinary Transmission in a Single Sub-wavelength Aperture arxiv:17.1349v1 [physics.optics] 8 Jul 21 Wenxuan Tang, 1 Yang Hao, 1, and Francisco Medina 2 1 Department of Electronic Engineering,
Broadband Extraordinary Transmission in a Single Sub-wavelength Aperture arxiv:17.1349v1 [physics.optics] 8 Jul 21 Wenxuan Tang, 1 Yang Hao, 1, and Francisco Medina 2 1 Department of Electronic Engineering,
Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform
 Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform Muhammad Alam,* J. Stewart Aitchsion, and Mohammad Mojahedi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto,
Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform Muhammad Alam,* J. Stewart Aitchsion, and Mohammad Mojahedi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto,
ENHANCEMENT OF PRINTED DIPOLE ANTENNAS CHARACTERISTICS USING SEMI-EBG GROUND PLANE
 J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 2, No. 8, 993 16, 26 ENHANCEMENT OF PRINTED DIPOLE ANTENNAS CHARACTERISTICS USING SEMI-EBG GROUND PLANE F. Yang, V. Demir, D. A. Elsherbeni, and A. Z. Elsherbeni
J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 2, No. 8, 993 16, 26 ENHANCEMENT OF PRINTED DIPOLE ANTENNAS CHARACTERISTICS USING SEMI-EBG GROUND PLANE F. Yang, V. Demir, D. A. Elsherbeni, and A. Z. Elsherbeni
ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 14, 113 121, 21 ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS J. Bai, S. Shi, and D. W. Prather
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 14, 113 121, 21 ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS J. Bai, S. Shi, and D. W. Prather
Design of a compact dual-band-rejection microwave filter based on metamaterials transmission lines.
 Design of a compact dual-band-rejection microwave filter based on metamaterials transmission lines. BACHIR BELKADI 1, ZOUBIR MAHDJOUB 1 1 Communication networks, structures and multi-media laboratory.
Design of a compact dual-band-rejection microwave filter based on metamaterials transmission lines. BACHIR BELKADI 1, ZOUBIR MAHDJOUB 1 1 Communication networks, structures and multi-media laboratory.
Planar Inverted L (PIL) Patch Antenna for Mobile Communication
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 4, Number 1 (2011), pp.117-122 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Planar Inverted L (PIL)
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 4, Number 1 (2011), pp.117-122 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Planar Inverted L (PIL)
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 62, 17 22, 2016 A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency Ning Liu 1, *, Xian-Jun Sheng 2, and Jing-Jing Fan
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 62, 17 22, 2016 A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency Ning Liu 1, *, Xian-Jun Sheng 2, and Jing-Jing Fan
Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity
 263 Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity Victor Dmitriev and Marcelo N. Kawakatsu Department of Electrical Engineering, Federal
263 Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity Victor Dmitriev and Marcelo N. Kawakatsu Department of Electrical Engineering, Federal
Resonant guided wave networks
 Resonant guided wave networks Eyal Feigenbaum * and Harry A. Atwater Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, * eyalf@caltech.edu Abstract A resonant guided wave network
Resonant guided wave networks Eyal Feigenbaum * and Harry A. Atwater Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, * eyalf@caltech.edu Abstract A resonant guided wave network
Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal Power Splitter
 Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 13-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32a002 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal
Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 13-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32a002 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal
ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/82/85804846.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY DESIGN OF A WIDEBAND 1 2 Y-BRANCH OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTER USING GaAs BASED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL Md. Shoaib Akther 1, Md. Rupam Khandkar
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY DESIGN OF A WIDEBAND 1 2 Y-BRANCH OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTER USING GaAs BASED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL Md. Shoaib Akther 1, Md. Rupam Khandkar
Coupling of small, low-loss hexapole mode with photonic crystal slab waveguide mode
 Coupling of small, low-loss hexapole mode with photonic crystal slab waveguide mode Guk-Hyun Kim and Yong-Hee Lee Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon 35-71,
Coupling of small, low-loss hexapole mode with photonic crystal slab waveguide mode Guk-Hyun Kim and Yong-Hee Lee Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon 35-71,
Photonic band gap effect, localization, and waveguiding in two-dimensional Quasicrystals
 Photonic band gap effect, localization, and waveguiding in two-dimensional Quasicrystals Mehmet Bayındır Ertugrul Cubukcu Irfan Bulu Ekmel Özbay M. Bayindir et al., Phys. Rev. B 63, 16114(R) (21) M. Bayindir
Photonic band gap effect, localization, and waveguiding in two-dimensional Quasicrystals Mehmet Bayındır Ertugrul Cubukcu Irfan Bulu Ekmel Özbay M. Bayindir et al., Phys. Rev. B 63, 16114(R) (21) M. Bayindir
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, , 2010
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 115 123, 2010 TUNABLE TRAPPED MODE IN SYMMETRIC RESONATOR DESIGNED FOR METAMATERIALS A. Ourir, R. Abdeddaim, and J. de Rosny Institut Langevin, ESPCI ParisTech,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 115 123, 2010 TUNABLE TRAPPED MODE IN SYMMETRIC RESONATOR DESIGNED FOR METAMATERIALS A. Ourir, R. Abdeddaim, and J. de Rosny Institut Langevin, ESPCI ParisTech,
Optics Communications
 Optics Communications 282 (2009) 3172 3176 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Polarization insensitive self-collimation waveguide
Optics Communications 282 (2009) 3172 3176 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Polarization insensitive self-collimation waveguide
Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Frequency Switching of PIFA Using Split Ring Resonator
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 7 (July 2014), PP.01-09 Frequency Switching of PIFA Using Split Ring Resonator
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 7 (July 2014), PP.01-09 Frequency Switching of PIFA Using Split Ring Resonator
Analysis and applications of 3D rectangular metallic waveguides
 Analysis and applications of 3D rectangular metallic waveguides Mohamed A. Swillam, and Amr S. Helmy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, M5S 3G4, Canada.
Analysis and applications of 3D rectangular metallic waveguides Mohamed A. Swillam, and Amr S. Helmy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, M5S 3G4, Canada.
Research Article A High Gain Omnidirectional Antenna Using Negative Permeability Metamaterial
 Antennas and Propagation Volume 213, Article ID 57562, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/57562 Research Article A High Gain Omnidirectional Antenna Using Negative Permeability Metamaterial Hangfei Tang,
Antennas and Propagation Volume 213, Article ID 57562, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/57562 Research Article A High Gain Omnidirectional Antenna Using Negative Permeability Metamaterial Hangfei Tang,
Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
Final Project Report
 DALHM IST 2001-35511 Development and Analysis of Left-Handed Materials Final Project Report Project period 1.9.2002-28.2.2006 Web-page: http://esperia.iesl.forth.gr/~ppm/dalhm Project Co-ordinator: Costas
DALHM IST 2001-35511 Development and Analysis of Left-Handed Materials Final Project Report Project period 1.9.2002-28.2.2006 Web-page: http://esperia.iesl.forth.gr/~ppm/dalhm Project Co-ordinator: Costas
Application of Metamaterials for the Microwave Antenna Realisations*
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 9, No. 1, February 01, 1-7 UDK: 61.396.67:66.017 DOI: 10.98/SJEE101001A Application of Metamaterials for the Microwave Antenna Realisations* Tatjana Asenov
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 9, No. 1, February 01, 1-7 UDK: 61.396.67:66.017 DOI: 10.98/SJEE101001A Application of Metamaterials for the Microwave Antenna Realisations* Tatjana Asenov
OPTICS DIVISION B. School/#: Names:
 OPTICS DIVISION B School/#: Names: Directions: Fill in your response for each question in the space provided. All questions are worth two points. Multiple Choice (2 points each question) 1. Which of the
OPTICS DIVISION B School/#: Names: Directions: Fill in your response for each question in the space provided. All questions are worth two points. Multiple Choice (2 points each question) 1. Which of the
A New Hyperthermia Scheme with a Cylindrical LHM Lens
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect APCBEE Procedia 7 (3 ) 3 36 ICBET 3: May 9-, 3, Copenhagen, Denmark A New Hyperthermia Scheme with a Cylindrical LHM Lens Yonghui Tao and Gang Wang
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect APCBEE Procedia 7 (3 ) 3 36 ICBET 3: May 9-, 3, Copenhagen, Denmark A New Hyperthermia Scheme with a Cylindrical LHM Lens Yonghui Tao and Gang Wang
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Splice losses in holey optical fibers
 Splice losses in holey optical fibers J.T. Lizier and G.E. Town School of Electrical and Information Engineering (J03), University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia. Tel: +612-9351-2110, Fax: +612-9351-3847,
Splice losses in holey optical fibers J.T. Lizier and G.E. Town School of Electrical and Information Engineering (J03), University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia. Tel: +612-9351-2110, Fax: +612-9351-3847,
Optical Isolation Can Occur in Linear and Passive Silicon Photonic Structures
 Optical Isolation Can Occur in Linear and Passive Silicon Photonic Structures Chen Wang and Zhi-Yuan Li Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. O. Box 603,
Optical Isolation Can Occur in Linear and Passive Silicon Photonic Structures Chen Wang and Zhi-Yuan Li Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. O. Box 603,
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
DUAL-WIDEBAND MONOPOLE LOADED WITH SPLIT RING FOR WLAN APPLICATION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 21, 11 18, 2011 DUAL-WIDEBAND MONOPOLE LOADED WITH SPLIT RING FOR WLAN APPLICATION W.-J. Wu, Y.-Z. Yin, S.-L. Zuo, Z.-Y. Zhang, and W. Hu National Key
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 21, 11 18, 2011 DUAL-WIDEBAND MONOPOLE LOADED WITH SPLIT RING FOR WLAN APPLICATION W.-J. Wu, Y.-Z. Yin, S.-L. Zuo, Z.-Y. Zhang, and W. Hu National Key
Electromagnetic Radiation
 Electromagnetic Radiation EMR Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle - superposition,
Electromagnetic Radiation EMR Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle - superposition,
Reflectionless Multichannel Wavelength Demultiplexer in a Transmission Resonator Configuration
 160 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 39, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 Reflectionless Multichannel Wavelength Demultiplexer in a Transmission Resonator Configuration Chongjun Jin, Shanhui Fan, Shouzhen
160 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 39, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 Reflectionless Multichannel Wavelength Demultiplexer in a Transmission Resonator Configuration Chongjun Jin, Shanhui Fan, Shouzhen
WIRELESS power transfer through coupled antennas
 3442 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2010 Fundamental Aspects of Near-Field Coupling Small Antennas for Wireless Power Transfer Jaechun Lee, Member, IEEE, and Sangwook
3442 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2010 Fundamental Aspects of Near-Field Coupling Small Antennas for Wireless Power Transfer Jaechun Lee, Member, IEEE, and Sangwook
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs
 Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Schematic of the proposed structure where within a two dimensional photonic crystal an input air waveguide is carved that feeds an EMNZ region that
Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Schematic of the proposed structure where within a two dimensional photonic crystal an input air waveguide is carved that feeds an EMNZ region that
BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 235 247, 2011 BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS B. Zhou, H. Li, X. Y. Zou, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 235 247, 2011 BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS B. Zhou, H. Li, X. Y. Zou, and
THE WIDE USE of optical wavelength division multiplexing
 1322 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 35, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1999 Coupling of Modes Analysis of Resonant Channel Add Drop Filters C. Manolatou, M. J. Khan, Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, H.
1322 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 35, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1999 Coupling of Modes Analysis of Resonant Channel Add Drop Filters C. Manolatou, M. J. Khan, Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, H.
Photonic band gaps and localization in two-dimensional metallic quasicrystals
 EUROPHYSIS LETTERS 1 October 2001 Europhys. Lett., 56 (1), pp. 41 46 (2001) Photonic band gaps and localization in two-dimensional metallic quasicrystals M. ayindir, E. ubukcu, I. ulu and E. Ozbay Department
EUROPHYSIS LETTERS 1 October 2001 Europhys. Lett., 56 (1), pp. 41 46 (2001) Photonic band gaps and localization in two-dimensional metallic quasicrystals M. ayindir, E. ubukcu, I. ulu and E. Ozbay Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Silver permittivity used in the simulations Silver permittivity values are obtained from Johnson & Christy s experimental data 31 and are fitted with a spline interpolation in order to estimate the permittivity
Silver permittivity used in the simulations Silver permittivity values are obtained from Johnson & Christy s experimental data 31 and are fitted with a spline interpolation in order to estimate the permittivity
A Circular Split Ringdouble Negative Metamaterial Having Simultaneous Negative Permittivity and Permeability
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 2 Ver. VII (Mar Apr. 2014), PP 34-38 A Circular Split Ringdouble Negative Metamaterial
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 2 Ver. VII (Mar Apr. 2014), PP 34-38 A Circular Split Ringdouble Negative Metamaterial
Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
Antenna Gain Enhancement and Beamshaping using a Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) Lens
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 214 Antenna Gain Enhancement and Beamshaping using a Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) Lens Christopher Torbitt
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 214 Antenna Gain Enhancement and Beamshaping using a Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) Lens Christopher Torbitt
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
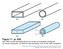 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Compact Broadband End-Fire Antenna with Metamaterial Transmission Line
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 73, 37 44, 2018 Compact Broadband End-Fire Antenna with Metamaterial Transmission Line Liang-Yuan Liu * and Jing-Qi Lu Abstract A broadband end-fire
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 73, 37 44, 2018 Compact Broadband End-Fire Antenna with Metamaterial Transmission Line Liang-Yuan Liu * and Jing-Qi Lu Abstract A broadband end-fire
Proposal and Characterization of Ring Resonator with Sharp U-Turns Using an SOI-Based Photonic Crystal Waveguide
 102 YASUHISA OMURA : PROPOSAL AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RING RESONATOR WITH ~ Proposal and Characterization of Ring Resonator with Sharp U-Turns Using an SOI-Based Photonic Crystal Waveguide Yasuhisa Omura,
102 YASUHISA OMURA : PROPOSAL AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RING RESONATOR WITH ~ Proposal and Characterization of Ring Resonator with Sharp U-Turns Using an SOI-Based Photonic Crystal Waveguide Yasuhisa Omura,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2015.137 Controlled steering of Cherenkov surface plasmon wakes with a one-dimensional metamaterial Patrice Genevet *, Daniel Wintz *, Antonio Ambrosio *, Alan
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2015.137 Controlled steering of Cherenkov surface plasmon wakes with a one-dimensional metamaterial Patrice Genevet *, Daniel Wintz *, Antonio Ambrosio *, Alan
THE PROBLEM of electromagnetic interference between
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY, VOL. 50, NO. 2, MAY 2008 399 Estimation of Current Distribution on Multilayer Printed Circuit Board by Near-Field Measurement Qiang Chen, Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY, VOL. 50, NO. 2, MAY 2008 399 Estimation of Current Distribution on Multilayer Printed Circuit Board by Near-Field Measurement Qiang Chen, Member, IEEE,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Two-dimensional beam steering array using planar eight-element composite right/left-handed leaky-wave antennas
 RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 43,, doi:10.1029/2007rs003800, 2008 Two-dimensional beam steering array using planar eight-element composite right/left-handed leaky-wave antennas Atsushi Sanada 1 Received 4 December
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 43,, doi:10.1029/2007rs003800, 2008 Two-dimensional beam steering array using planar eight-element composite right/left-handed leaky-wave antennas Atsushi Sanada 1 Received 4 December
FDTD CHARACTERIZATION OF MEANDER LINE ANTENNAS FOR RF AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 4, 85 99, 999 FDTD CHARACTERIZATION OF MEANDER LINE ANTENNAS FOR RF AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS C.-W. P. Huang, A. Z. Elsherbeni, J. J. Chen, and C. E. Smith
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 4, 85 99, 999 FDTD CHARACTERIZATION OF MEANDER LINE ANTENNAS FOR RF AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS C.-W. P. Huang, A. Z. Elsherbeni, J. J. Chen, and C. E. Smith
Printed Large-Area Single-Mode Photonic Crystal Bandedge Surface- Emitting Lasers on Silicon
 Printed Large-Area Single-Mode Photonic Crystal Bandedge Surface- Emitting Lasers on Silicon Deyin Zhao a, Shihchia Liu a, Hongjun Yang, Zhenqiang Ma, Carl Reuterskiöld-Hedlund 3, Mattias Hammar 3, and
Printed Large-Area Single-Mode Photonic Crystal Bandedge Surface- Emitting Lasers on Silicon Deyin Zhao a, Shihchia Liu a, Hongjun Yang, Zhenqiang Ma, Carl Reuterskiöld-Hedlund 3, Mattias Hammar 3, and
InGaAsP photonic band gap crystal membrane microresonators*
 InGaAsP photonic band gap crystal membrane microresonators* A. Scherer, a) O. Painter, B. D Urso, R. Lee, and A. Yariv Caltech, Laboratory of Applied Physics, Pasadena, California 91125 Received 29 May
InGaAsP photonic band gap crystal membrane microresonators* A. Scherer, a) O. Painter, B. D Urso, R. Lee, and A. Yariv Caltech, Laboratory of Applied Physics, Pasadena, California 91125 Received 29 May
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
ANTENNAS ON HIGH IMPEDANCE GROUND PLANES: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF THE ANTENNA ISOLATION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 41, 237 255, 2003 ANTENNAS ON HIGH IMPEDANCE GROUND PLANES: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF THE ANTENNA ISOLATION G. Poilasne University of California at Los Angeles, CA
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 41, 237 255, 2003 ANTENNAS ON HIGH IMPEDANCE GROUND PLANES: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF THE ANTENNA ISOLATION G. Poilasne University of California at Los Angeles, CA
Silicon-based photonic crystal nanocavity light emitters
 Silicon-based photonic crystal nanocavity light emitters Maria Makarova, Jelena Vuckovic, Hiroyuki Sanda, Yoshio Nishi Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Silicon-based photonic crystal nanocavity light emitters Maria Makarova, Jelena Vuckovic, Hiroyuki Sanda, Yoshio Nishi Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Research Article Miniaturized Circularly Polarized Microstrip RFID Antenna Using Fractal Metamaterial
 Antennas and Propagation Volume 3, Article ID 7357, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/7357 Research Article Miniaturized Circularly Polarized Microstrip RFID Antenna Using Fractal Metamaterial Guo Liu, Liang
Antennas and Propagation Volume 3, Article ID 7357, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/7357 Research Article Miniaturized Circularly Polarized Microstrip RFID Antenna Using Fractal Metamaterial Guo Liu, Liang
