A Novel High-Frequency Voltage Standing-Wave Ratio-Based Grounding Electrode Line Fault Supervision in Ultra-High Voltage DC Transmission Systems
|
|
|
- Alice West
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 energies Article A Novel High-Frequency Voltage Sting-Wave Ratio-Based Grounding Electrode ine Fault Supervion in Ultra-High Voltage DC Transsion Systes Yufei Teng 1, Xiaopeng i 1, Qi Huang, *, Yifei Wang 3, Shi Jing, henchao Jiang 1 Wei hen 1 1 State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Research Institute, Chengdu 617, China; yfteng11@163co (YT); clxpbsd@163co (X); jiangzhenchao@16co (J); zhenwei34156@163co (W) School Energy Science Engineering, University Electronic Science Technology China, Chengdu , China; elitejs@163co 3 Departent Electrical Engineering, Xi an Jiaotong University, Xi an 7149, China; wyf93117@163co * Correspondence: hwong@uestceducn Acadeic Editor: Silvio Siani Received: 8 Deceber 16; Accepted: 8 February 17; Publhed: 5 March 17 Abstract: In order to iprove onitoring perforance grounding electrode lines in ultra-high voltage DC (UHVDC) transsion systes, a novel onitoring approach based on high-frequency voltage sting-wave ratio () proposed in th paper defined considering a lossless transsion line, charactertics under different conditions are analyzed It shown that equals 1 when terinal copletely atches charactertic ipedance line, when a short circuit occurs on grounding electrode line, will be greater than 1 will approach positive infinity under etallic earth conditions, whereas in non-etallic earth s will be saller Based on se analytical results, a supervion criterion forulated effectiveness proposed -based supervion technique verified with a typical UHVDC project establhed in Power Systes Coputer Aided Design/Electroagnetic Transients including DC(PSCAD/EMTDC) Siulation results indicate that proposed strategy can reliably identify grounding electrode line has strong anti- capability Keywords: UHVDC transsion syste; grounding electrode line; supervion; voltage sting-wave ratio; injected current source 1 Introduction UHVDC projects play an iportant role in odern long-dtance electrical power delivery [1,] because ir capability delivering assive electricity transsion capacity over long dtances in a controllable way [3,4] grounding electrode an essential part in UHVDC project in that it provides current loop fro pole to earth acts as an unbalance reference between two poles In practice, grounding electrode sited far fro converter station via two parallel grounding wires, to avoid ipact DC agnetic bias at converter stations [5,6] refore, protection strategies supervion devices for grounding electrode line s are very iportant in practical UHVDC projects A typical UHVDC earth electrode design can be found in [7] Norally, grounding electrode line copres two parallel lines without separate switches, refore, two parallel lines always function as one line in practice unbalanced current protection generally equipped for earth Energies 17, 1, 39; doi:1339/en1339 wwwdpico/journal/energies
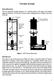
2 Energies 17, 1, electrode line, iproveent easures were proposed to enhance reliability exting unbalanced current protection strategy [8] authors in [9] proposed a fast tripping schee by inserting DC breakers into both grounding electrode lines control protection strategies were reved, in order to avoid blockage or pole if one pole was blocked failed to restart In [1], by considering charactertics grounding electrode line s, it was suggested that unbalanced current protection syste should adopt location inverse-tie function authors in [11] proposed to integrate differential current protections with exting unbalanced current protection to realize fast accurate location electrode grounding line s However, proposed current-based protection strategy can only be used in onopolar earth return ode cannot work under conditions where UHVDC syste operates in bipolar earth return ode or onopolar etallic return ode, because re no current in grounding electrode line under se operation odes It also noted that onopolar earth return configuration not coonly used because return current via earth ay endanger surrounding huan beings or anials [1] refore, current-based protection techniques are not applicable for grounding electrode lines in practical UHVDC projects In order to solve grounding electrode line proble in bipolar balanced operation ode, a high-frequency ipedance easureent technique for grounding electrode line supervion, in which ipedance was detected by injecting a high-frequency current source, was proposed in [13] In such ethods, voltage variation can also be used as indication or not [14] Th approach widely adopted in UHVDC projects because it applicable for all operation odes However, in practice it found that such schees ay fail to operate under conditions earth s via incorrect operation grounding electrode lines, due to defects in protection syste, has caused any s in practical UHVDC projects in recent years, leading to great econoic losses, so it great iportance to develop an electrode grounding line detection syste with better perforance In th paper, a novel onitoring algorith based on high-frequency voltage sting-wave ratio () principle proposed, by cobining high-frequency signal injection traveling wave detection technique traveling wave based detection widely utilized because it has ability to operate fast overcoes challenge fro earth via high charactertics on long-dtance lossless transsion line are investigated, perforance proposed approach studied by coparing with exting grounding electrode line detection systes under various operation conditions rest th paper organized as follows: Section briefly introduces principle evaluates perforance exting high-frequency ipedance detection ethod n Section 3 ainly presents definition calculation high-frequency charactertics high-frequency analyzed, n a novel grounding electrode line supervion ethodology based on high-frequency proposed proposed ethod verified by conducting siulations on PSCAD/EMTDC platfor in Section 4 Finally, conclusions are presented in Section 5 Overview High-Frequency Ipedance Supervion Technique for Grounding Electrode ine Fault 1 Operation Principle Figure 1 illustrates a typical grounding electrode line ipedance supervion (EIS) syste configured within a UHVDC syste EIS used to continuously onitor status electrode line A high-frequency AC current injected into electrode line voltage to ground at injection point easured Following practice in all HVDC projects Chinese state grid, frequency injected signal chosen as 1395 khz [15] ipedance calculated fro current voltage used as a easure conditions electrode line At two terinals grounding electrode line, a blocking filter installed to block injected
3 Energies 17, 1, Energies 17, 1, Energies 17, 1, high-frequency current At electrode station side terinal blocking filter also provided high-frequency current At electrode station side side terinal blocking blocking filter filter also also provided provided with with a restor, whose corresponds to charactertic ipedance electrode line with a restor, a restor, whose whose corresponds corresponds to to charactertic charactertic ipedance ipedance electrode electrode line Such line Such a configuration ensures a reflection free terination With less reflection at line Such a configuration a configuration ensures ensures a reflection a reflection free terination free terination With less With reflection less at reflection line terinations, line terinations, ipedance shifts caused by a can be better defined, aking detection ore terinations, ipedance shifts ipedance causedshifts by acaused can by be a better can defined, be better aking defined, aking detection detection ore accurate, ore accurate, especially for s close to electrode accurate, especially especially for sfor close s to close electrode to electrode Converter Converter DC ine DC ine AC Side AC Side Neutral Neutral Bus Bus Blocking Blocking Filter Filter Signal injection Signal TA injection TA TV TV Electrode line Electrode line restor restor Blocking Blocking Filter Filter Figure 1 EIS device in a typical bipolar UHVDC syste Figure Figure 1 1 EIS EIS device device in in a a typical typical bipolar bipolar UHVDC UHVDC syste syste A sudden change easured ipedance value criterion for an electrode line A sudden change easured ipedance value criterion for an electrode line (open Acircuit sudden or change grounding ) easured EIS ay ipedance alar if value change criterion greater for than ana electrode certain value line (open circuit or grounding ) EIS ay alar if change greater than a certain value (open voltage circuit current or grounding at converter ) EIS end ay alar grounding if electrode change line greater are easured than a certain to calculate value voltage current at converter end grounding electrode line are easured to calculate voltage high-frequency current ipedance at converter It found end that grounding easured electrode high-frequency line are easured ipedance to calculate a high-frequency ipedance It found that easured high-frequency ipedance a periodic high-frequency function ipedance dtance It found [1] that refore, easured operation high-frequency EIS ipedance different afro periodic periodic function dtance [1] refore, operation EIS different fro dtance function relay Equation dtance (1) defines [1] refore, operation operation condition EIS, which different illustrated fro dtance in Figure relay : dtance relay Equation (1) defines operation condition EIS, which illustrated in Figure : Equation (1) defines operation condition EIS, which illustrated in Figure : ref set ref set,, (1) (1) Ż where Ż re f set, (1) where represents calculated high-frequency ipedance based on voltage current at represents calculated high-frequency ipedance based on voltage current at where Ż represents ref converter end calculated high-frequency ipedance based on voltage current at ref reference ipedance calculated with electrode line paraeters under converter converter end end re f reference reference ipedance ipedance calculated calculated with electrode with electrode line paraeters line paraeters under noral under noral noral operation operation set operation set set threshold threshold threshold setting, usually setting, setting, 3usually usually Ω [15] 3 Ω [15] 3 Ω [15] jx jx R Figure Typical operation charactertics EIS in UHVDC syste Figure Typical operation charactertics EIS in UHVDC syste
4 Energies 17, 1, Perforance Evaluation Conventional EIS Technique It can be seen that Ż re f related to electrode line paraeters, such as, inductance capacitance In reality, values, inductance, capacitance grounding electrode line are easured at fundaental frequency, while injected high-frequency current 1395 khz Furrore, paraeters change with teperature, aging processes, huidity or factors Thus easured grounding electrode line paraeters are not guaranteed to be equal to actual values, so that high-frequency ipedance based syste ay operate erroneously Assue re f real re f eas are, respectively, reference ipedance calculated with actual electrode line paraeters easured electrode line paraeters Obviously, reference ipedance a function line inductance line capacitance C difference between re f real re f eas caused by variation C can be represented as follows after neglecting third higher order ters: re f eas re f real = + 1 re f real ( r,c r ) + 1 re f real ( r,c r ) (C C C r ) re f real ( r,c r ) ( r ) + re f real ( r,c r ) C (C C r ) ( r ) + re f real ( r,c r ) C ( r )(C C r ) () where, r C r are real line paraeter values C are easured line paraeter values According to (), we can obtain effect line paraeter variations on reference ipedance, as shown in Figure 3 It can be seen in Figure 3 that a 5% deviation inductance or capacitance will result in ore than 15% deviation reference ipedance ref That to say, reference ipedance ref sensitive to line paraeters traditional EIS technique subject to al-operation due to variations line paraeters easured values lted in Table 1 are per-unit length values, inductance capacitance electrode line for Yibin-Jinhua ±8 kv DC transsion project in China easured values are obtained using easuring ethods described in [16] real values line paraeters are unknown In order to illustrate perforance conventional EIS, real capacitance value considered to be 1% deviation fro easured one, as lted in Table 1 reference ipedance re f real re f eas are [14]: re f real = j7399 Ω re f eas = j17853 Ω (3) Table 1 real values easured values on grounding electrode line Values (H/k) R (oh/k) C (uf/k) Real value Measured value
5 Deviation reference ipedance ref / % Deviation reference ipedance ref / % Energies 17, 1, Energies 17, 1, Deviation inductance / % Deviation capacitance C/ % Figure 3 effect line paraeters variation on reference ipedance Effect inductance Figure 3 effect line paraeters variation on reference ipedance Effect inductance variation on ; Effect capacitance variation on variation on ; Effect capacitance variation on Suppose that a etallic short circuit occurs on grounding electrode line at 4 k away fro Suppose converter that a etallic end short easured circuit high-frequency occurs on ipedance grounding under electrode line condition at 4 k away fro converter end easured high-frequency ipedance under condition 4934 j Thus operation conditions EIS with actual reference = j44819ω Thus operation conditions EIS with actual reference ipedance ipedance easured reference easured ipedance reference are: ipedance are: ref real 3514 re f real = 3514 Ω (4) ref eas 53 (4) re f eas = 53 Ω Th shows that difference between calculated high-frequency ipedance under Th conditions shows that actual difference reference between ipedance calculated high-frequency ref real greater than ipedance threshold under EIS conditions actual reference ipedance re f real greater than threshold EIS should send should alar send inforation alar inforation under such under conditions such conditions However, However, difference difference between between calculated high-frequency calculated high-frequency ipedance ipedance reference ipedance ref eas less than reference ipedance re f eas less than threshold threshold EIS will not EIS take will any not actions take any actions
6 Energies 17, 1, Energies 17, 1, Technique for Grounding Electrode ine Fault 31 on a ossless Transsion ine 3 Technique for Grounding Electrode ine Fault Generally, sting waves are fored by overlap two waves with sae frequency 31 but opposite ondirections a ossless Transsion axiu ineaplitude appears at position tered as wave peak whereas Generally, iniu sting aplitude waves are fored position by called overlap wave valley two waves Under with noral sae operation, frequency but sting opposite wave directions effect can be neglected axiubecause aplitude wavelength appears at position fundaental teredfrequency as wave wave peak whereas far greater than iniu length aplitude position transsion calledlines wavefor valley Under injected noral high operation, frequency current, sting wave sting effect waves can be can neglected be utilized because in grounding wavelength electrode fundaental line supervion frequencytechniques wave far greater than Figure length 4 a typical transsion dtributed lines circuit Forodel injected a lossless high frequency transsion current, line sting charactertic waves can equations be utilized voltage in grounding current, electrode which will linebe used supervion for later derivation, techniques are rewritten below: Figure 4 a typical dtributed circuit odel x a lossless x transsion line charactertic U A1 e Ae equations voltage current, which will be used for later derivation, are rewritten below: A A, (5) I 1 e x U = A 1 ec γx + A ce γx, (5) I = A 1 c e γx A where γ transsion propagation c e γx constant, j C where γ transsion propagation constant, γ = jω C c = c z1 / y1 ( r1 jl1 ) /( g1 jc1 ) charactertic ipedance transsion z 1 /y 1 line = For (r1 + jωl lossless 1 )/(g transsion 1 + jωc 1 ) line, charactertic ipedance transsion line For lossless r1 g1 are set to transsion line, r 1 g 1 are set to zero, thus c = zero, thus z 1 /y 1 = c z1 / y1 l1 / c1 A1 A l 1 /c 1 A 1 A are coefficient are coefficient deterined by voltage current at two ends line deterined by voltage current at two ends line e x Figure 4 Dtributed paraeter circuit a power transsion line Assuing that end point transsion line x =, voltage at end transsion line UU,, load ipedance voltage current at position x on transsion line : U(x) = U (e γx + x Γ e γx ) x U ( x) U ( e e ) I(x) = U c U(e γx Γ x e γx ), (6) x, (6) I( x) ( e e ) where, Γ reflection coefficient at load side: c where, reflection coefficient at load side: Γ = c = / c 1 + c / c + 1 = n 1 n + 1, (7) c / c 1 n 1 where, n noralized load ipedance, (7) c / c 1 n 1 high-frequency defined as ratio voltage aplitudes at wave peak adjacent where, n wave valley noralized on transsion load ipedance line, as follows: high-frequency defined as ratio voltage aplitudes at wave peak adjacent wave valley on transsion = U(x) line, as axfollows: = 1 + Γ U(x) in 1 Γ, (8) U( x) 1 ax 3 Calculation, (8) U( x) 1 in In practice, on grounding electrode line easily obtained if terinal voltage current are given Assue that voltage current at converter station end grounding
7 Energies 17, 1, electrode line, U 1 İ 1, are easured, n voltage current at point x can be calculated as follows, fro (5): U(x) = 1 ( U 1 + c İ 1 )e γx + 1 ( U 1 c İ 1 )e γx I(x) = 1 ( U 1 c + İ 1)e γx 1, (9) ( U 1 c İ 1)e γx For a lossless transsion line, transsion propagation constant γ = jω C a pure iaginary nuber refore, (9) can be rewritten as: U(x) = U 1 cos βx j c İ 1 sin βx U 1 I(x) = İ 1 cos βx j c sin βx, (1) where, β = ω C phase constant Assuing that phase angle current at converter station end zero, n voltage easured at th point : U 1 = U s (cos ϕ u1 + j sin ϕ u1 ) I 1 = I s, (11) where, U S I S are aplitudes easured voltage current at converter station end on grounding electrode line, respectively ϕ u1 phase difference between U 1 İ 1 Substituting into (1), one has: U(x) = U s cos ϕ u1 cos βx + j(u s sin ϕ u1 cos βx c I s sin βx), (1) U(x) = 1 (U s + c Is ) + ( 1 U s 1 c Is ) cos βx U s c I s sin ϕ u1 sin βx (13) et: A c = ( 1 U s 1 c I s ) + U s c I s sin ϕ u1, (14) axiu iniu voltage aplitude can be calculated: U(x) = 1 ax (U s + c Is ) + A c U(x), (15) = 1 in (U s + c Is ) A c = 1 (U s + c Is ) + A c, (16) 1 (U s + c Is ) A c refore, once transsion paraeters grounding electrode line are known, can be easily calculated using easured voltage aplitudes, current aplitudes, phase angles Equation (16) shows that along transsion line independent dtance x, but only deterined by voltage U S current I S, ir phase angle ϕ u1, internal charactertics grounding line, such as c 33 Charactertics under Various Fault Conditions ay be subject to change, depending on restor installed at end grounding line, including conditions coplete atching terinal restor incoplete atching terinal restor If restor copletely atches charactertic ipedance, re no reflection at end grounding line equals 1 Orwe will be greater
8 33 Charactertics under Various Fault Conditions ay be subject to change, depending on restor installed at end grounding line, including conditions coplete atching terinal restor incoplete atching terinal restor If restor copletely atches charactertic Energies ipedance, 17, 1, re 39 no reflection at end grounding line equals 1 Orwe 8 17 will be greater than 1 In ters earth on grounding electrode line, equivalent restor should be considered to deterine wher equivalent restor atches than 1 In ters earth on grounding electrode line, equivalent restor should be charactertic ipedance or not considered to deterine wher equivalent restor atches charactertic ipedance or not (1) Noral operation with atching terinal restor (1) Noral operation with atching terinal restor If If end end restor restor equals equals to to charactertic ipedance C,, as as illustrated illustrated in in Figure 5 5 reflection coefficient voltage sting wave ratio can be calculated as: { Γ = = 1 1, (17) It It shown that that that re no no reflection at at end end grounding line line voltage aplitude reains constant along along whole whole grounding line line Figure 5 Matching terinal restor at earth end () Noral operation with atching terinal restor () Noral operation with atching terinal restor If end restor does not equal to charactertic ipedance C, ie, terinal If end restor restor atches does not equal to charactertic ipedance charactertic ipedance, reflection coefficient C, ie, terinal restor voltage sting atches charactertic ipedance, reflection coefficient voltage sting wave ratio wave ratio can be calculated as: can be calculated as: { Γ = > 1, (18) (18) 1 et V real V eas be s calculated with actual line paraeters easured line paraeters V et real V difference eas be between s V eas calculated V real with caused byactual variation line paraeters C can be represented as follows after neglecting third V higher order easured line paraeters difference between eas V ters real caused by variation C can be represented Vas eas follows V after neglecting third higher order ters real = V real( r,c r ) ( r ) + V real( r,c r ) C (C C r ) Vreal ( r, Cr ) Vreal ( r, Cr ) + 1 V V real eas ( V r,c r real ) ( r ) ( C Cr ) ( r ) + V real ( r,c r ) C ( C r )(C C r ) (19) + 1 1V real V( real r,c( r ) r, Cr ) Vreal ( r, Cr ) (C C ( ) ( )( ) r r C Cr (19) C r ) C According to (19), we1 Vreal ( r, Cr ) can obtain ( ) C effect C line paraeters variation on, as shown in r Figure 6 It can be seen in Figure C6 that a 5% deviation inductance or capacitance will result in less than 6% deviation That to say, insensitive to line paraeters based electrode line supervion technique ore robust
9 Energies 17, 1, Deviation / % Deviation / % According to (19), we can obtain effect line paraeters variation on, as shown in Figure 6 It can be seen in Figure 6 that a 5% deviation inductance or capacitance will result in less Energies than 6% 17, deviation 1, 39 That to say, insensitive to line paraeters 9 17 based electrode line supervion technique ore robust Deviation inductance / % Deviation capacitance C/ % Figure Figure 6 6 effect effect line line paraeters paraeters variation variation on on Effect Effect inductance inductance variation variation on ; on ; Effect Effect capacitance capacitance variation variation on on Assuing that axiu deviation between terinal restor charactertic Assuing that axiu deviation between terinal restor charactertic ipedance less than 1%, reflection coefficient voltage sting wave ratio are within ipedance less than 1%, reflection coefficient voltage sting wave ratio are within following range: following range: { Γ ( 56, 56,47 47),, () [1, 1, ) It It shown shown that that when when re re a reflection reflection at at end end terinal terinal grounding grounding line, line, atching atching degree degree less less than than 1%, 1%, axiu axiu only only (3) (3) Metallic Metallic short short circuit circuit condition condition When When a a etallic etallic short short circuit circuit occurs occurs at any at position any position grounding grounding electrode electrode line, equivalent line, equivalent restor zero restor According zero to According Equations to (7) Equations (8), (7) reflection (8), coefficient reflection coefficient (approaching (approaching infinity) are: infinity) are: { Γ = 1, (1)
10 Energies 17, 1, Energies 17, 1, (4) Non-etallic short circuit with atching terinal, restor (1) Under th condition, ground via occurs with atching terinal restor, (4) Non-etallic as shown inshort Figure circuit 7 Because with atching terinal load restor equal to charactertic ipedance, equivalent Under th ipedance condition, seen fro ground position via to end terinal occurs eq can with be calculated atching terinal restor, as shown in Figure 7 Because eq = terinal load equal to charactertic c f ipedance, equivalent ipedance seen fro, position to end terinal eq can be () c + f calculated Figure 7 7 Non-etallic short circuit with atching terinal restor Norally, charactertic ipedance C about c 5 Ω, if f in range 5 Ω, range reflection eq coefficient, would be in () c f following range: Norally, charactertic ipedance eq [, C 5 about c ] 5, Ω, if (3) in range 5 Ω, range = reflection c coefficient would be in { following range: Γ (1, 3333) (4) [ ] eq, [, 5 ) c, (3) Equation (4) indicates that if c equal to charactertic ipedance, equivalent ipedance half charactertic ipedance, under th condition, whereas if a etallic earth occurs at ( end 1, 3333 ) grounding line, will approach infinity, which siilar to above condition (4) [, ) (5) Non-etallic short circuit with atching terinal restor Equation (4) indicates that if equal to charactertic ipedance, In case that an equivalent earth ipedance via half charactertic occurs atipedance, iddle line, say, under x = l f (th total condition length, whereas grounding if a etallic line l), earth as shown occurs in Figure at 8 end Under such grounding condition, line, equivalent load will ipedance approach seen infinity, frowhich siilar position to toabove end condition terinal eq : (5) Non-etallic short circuit with atching terinal restor e γ(l l f ) + Γ In case that an earth via eq = e γ(l l f ) c e γ(l l occurs at iddle line, say, x = l f ) Γ e γ(l l f ), (5) Energies 17, 1, f ( total length grounding line l), as shown in Figure 8 Under such condition, equivalent load ipedance seen fro position to end terinal : eq eq c e ( ll f ) e ( ll f ) ( ll f ) e ( ll f ) e, (5) Figure 8 Non-etallic short circuit with atching terinal restor Figure 8 Non-etallic short circuit with atching terinal restor : Taking ipedance f into consideration, equivalent ipedance (1 ) j sin ( l l f ) eq
11 Energies 17, 1, Taking ipedance f into consideration, equivalent ipedance eq : eq = f c (1 Γ ) jγ sin β(l l f ) 1+Γ Γ cos β(l l f ) f + c (1 Γ ) jγ sin β(l l f ) 1+Γ Γ cos β(l l f ), (6) Thus reflection coefficient at converter station : Γ = ( f c ) (1 Γ ) jγ sin β(l l f ) 1+Γ Γ cos β(l l f ) ( f + c ) (1 Γ ) jγ sin β(l l f ) 1+Γ Γ cos β(l l f ) f + f, (7) It shows that when position not at end terinal grounding electrode line, equivalent ipedance no longer pure Hence, reflection coefficient presents coplex nuber charactertics aplitude reflection coefficient varies periodically with position dtance l f refore, varies periodically with position dtance l f as well 34 High Frequency -Based Grounding Electrode ine Fault Supervion -based technique for grounding electrode line onitoring systes has a siilar structure as shown in Figure 1, can be ipleented on an exting EIS syste devices, including injected current source, blocking filter on both ends grounding line, restor equal to charactertic ipedance electrode line, can be used voltage current at converter station end grounding electrode line are easured by installed PT CT Fro above analys, it can be safely concluded that close to 1 when electrode line under noral operation, whereas will increase if re are earth s on grounding electrode line Based on different values under noral y condition, criteria for judgeent can be developed: = 1 (U s + c Is ) + A c > 1 (U s + c Is set, (8) ) A c where set setting value for alar in proposed supervion schee Since end terinal restor ay not atch copletely with charactertics ipedance, ay be greater than 1 even under noral operation Thus setting value should be greater than 1 Assue that axiu deviation between terinal restor charactertic ipedance less than 1%, axiu value 11 following setting value suggested: set = k I ax_noral, (9) where, ax_noral axiu value under noral operation, k I reliable coefficient, taking 111 refore, setting value equals to 1 4 Case Study 41 Siulation Model verification proposed schee conducted on a ±8 kv UHVDC project in south-west China with PSCAD/EMTDC siulation transsion capacity th UHVDC project 8 MW length transsion line 165 k grounding electrode line th UHVDC
12 Energies 17, 1, project adopts parallel line length grounding line 1 k paraeters grounding electrode line are lted in Table high frequency current source with a frequency 1395 khz configured at converter station end to inject current into grounding electrode line blocking filter installed on both ends grounding line to reduce sting wave effect in high-frequency inflection Table Paraeters single grounding electrode line in case study Paraeters (H/k) R (oh/k) C (uf/k) Values charactertic ipedance double electrode lines c = 1 = Ω setting value follows (9) To verify charactertics under various operation conditions, case study perfored considering two scenarios: end terinal restor copletely atches charactertic ipedance; terinal restor does not atch charactertic ipedance Each scenario includes three kinds operation conditions: noral operation, double-line earth, single-line earth For earth, three different values ipedance are considered, which are 1 Ω, 1 Ω, Ω Table 3 lts siulation scenarios Table 3 Siulation scenarios in case study C Siulation Scenarios With Matched terinal restor With atched terinal restor Noral operation Noral operation Operation Conditions Double-line earth Single-line earth 1 Ω/1 Ω/ Ω 1 Ω/1 Ω/ Ω Double-line earth Single-line earth 1 Ω/1 Ω/ Ω 1 Ω/1 Ω/ Ω 4 With Matched Terinal Restor When terinal 7748 Ω, end restor atches with charactertic ipedance double grounding electrode line (1) Noral operation condition Under noral operation condition, voltage current at converter station end are easured to calculate : = 1 < set, (3) keeps around 1, which less than thresholds, thus proposed based schee works correctly () Double-line earth condition Figure 9 shows siulated results under double-line earth condition with a atched terinal restor double-line earth with etallic earth (1 Ω), via 1 Ω ipedance, via Ω ipedance are all plotted horizontal ax represents dtance fro converter station to position, on grounding electrode line
13 Figure 9 shows siulated results under double-line earth condition with a atched terinal restor double-line earth with etallic earth (1Ω), via 1 Ω ipedance, via Ω ipedance are all plotted horizontal ax represents Energies 17, 1, 39 dtance fro converter station to position, on grounding electrode line set Partial enlarged view Fault dtance / k Fault 1 oh Fault oh 15 set Fault dtance / k Figure 9 for different position double-line earth with atched terinal Figure 9 for different position double-line earth with atched terinal restor restor 1 Ω; are 1 Ω Ω, 1 Ω; are 1 Ω Ω, respectively respectively It It can can be be observed observed fro fro Figure Figure 9 that that when when non-etallic non-etallic earth earth occurs occurs on on grounding grounding electrode electrode line, line, decreases decreases with with increase increase will will also also reduce reduce when when dtance dtance res res refore, refore, double-line double-line earth earth via via a Ω Ω on on end end terinal terinal grounding grounding line line results results in in lowest lowest However, However, under th under worst th condition worst condition still greater still than greater than threshold, threshold, as shown as in shown Figure in 9b Figure Hence 9b Hence proposed proposed based technique based technique can perfor can correctly perfor correctly reliably under reliably th under condition th condition (3) (3) Single-line Single-line earth earth condition condition Figure 1 shows results under single-line earth condition with atched terinal Figure 1 shows results under single-line earth condition with atched terinal restor single-line earth also includes etallic earth (1 Ω), earth via 1 Ω restor, single-line earth via Ω also includes etallic earth (1 Ω), earth via 1 Ω Figure, 1 shows that via Ω in single-line earth with atched terinal restor condition a periodical function dtance because currents on each grounding electrode line are no longer equal to each or However, current voltage are easured at station end grounding electrode line, equivalent can be calculated following (16) equivalent s are still greater than thresholds, so that proposed based technique can operate correctly under such case
14 Energies 17, 1, Energies 17, 1, Fault 1 oh Fault oh Partial enlarged view set Fault dtance / k set Partial enlarged view 4 6 Fault dtance / k 8 1 Figure Figure 1 1 for for different different position position single-line single-line earth earth with with atched atched terinal terinal restor restor are are 1 1 Ω Ω Ω, Ω, respectively; respectively; 1 1Ω Ω Figure 1 shows that in single-line earth with atched terinal restor 43 With Matched Terinal condition a periodical function dtance because currents on each grounding electrode In th line case, are no longer terinal equal to each or assued However, to be 5 current Ω, which voltage about are 95% easured at charactertic station end ipedance grounding electrode line, equivalent can be calculated following (1) Noral (16) operation equivalent condition s are still greater than thresholds, so that proposed based technique can operate correctly under such case Under noral condition, voltage current at station end are easured to calculate 43 With : Matched Terinal = 118 < set (31) In th case, terinal assued to be 5 Ω, which about 95% charactertic It concluded ipedance that slightly greater than 1 because end terinal restor not copletely equal to charactertic ipedance Th result confors with analys in Section 3 (1) Noral operation condition However, still less than setting threshold 1 refore, -based supervion Under noral device will condition, be operating voltage correctly current at station end are easured to calculate : () Double-line earth condition 1 18 set, Figure 11 shows under double-line earth condition with atched terinal (31) restor It Siilar concluded to that double-line slightly with atched greater than terinal 1 because restor, end double-line terinal earth restor with not copletely atchedequal terinal to restor charactertic also includes ipedance etallic Th result earthconfors (1with Ω), analys earth in Section via 1 3 Ω However,, still vialess Ωthan setting threshold 1 refore, -based supervion device will be operating correctly
15 () Double-line earth condition Figure 11 shows under double-line earth condition with atched terinal restor Siilar to double-line with atched terinal restor, double-line earth with atched terinal restor also includes etallic earth (1 Ω), earth via Energies 17, 1, Ω, via Ω 4 35 Fault 1 oh 3 5 Fault oh set Fault dtance / k set Fault 1 oh Partial enlarged view Fault dtance / k Figure 11 for different position double-line earth with atched terinal Figure 11 for different position double-line earth with atched terinal restor restor are 1 are Ω 1 Ω Ω, respectively; Ω, respectively; 1 Ω 1 Ω Figure 11 indicates that with atched terinal, decreases with Figure 11 indicates that with atched terinal, decreases with rae rae, with rae dtance When non-etallic short, with rae dtance When non-etallic short circuit circuit occurs, varies periodically with dtance, which in accordance occurs, varies periodically with dtance, which in accordance with above with above analys in Section III under non-etallic earth with Ω analys in Section 3 under non-etallic earth with Ω at at end terinal grounding electrode line still greater than end terinal grounding electrode line still greater than threshold value 1 proposed threshold value 1 proposed technique will operate correctly technique will operate correctly (3) Single-line earth condition (3) Single-line earth condition Figure 1 presents siulated for different positions under single-line earth Figure 1 presents siulated for different positions under single-line earth condition with atched terinal Siilarly, single-line earth includes condition with atched terinal Siilarly, single-line earth includes etallic etallic earth (1 Ω), earth via 1 Ω, via Ω earth (1 Ω), earth via 1 Ω, via Ω It can be seen fro Figure 1 that also varies periodically with dtance l f s in different conditions are still greater than setting thresholds refore proposed schee works correctly
16 Energies 17, 1, It can be seen fro Figure 1 that also varies periodically with dtance s in different conditions are still greater than setting thresholds refore proposed schee works correctly Energies 17, 1, l f Fault 1 oh Partial enlarged view Fault oh set Fault dtance / k set Partial enlarged view Fault dtance / k Figure 1 for different position single-line earth with atched terinal Figure 1 for different position single-line earth with atched terinal restor restor are are 1 1 Ω Ω Ω, Ω, respectively; respectively; 1 1 Ω Ω 44 Suary 44 Suary Fro siulations above, it can be concluded that proposed -based technique for Fro siulations above, it can be concluded that proposed -based technique for grounding electrode line supervion will not act under noral operation condition no atter grounding electrode line supervion will not act under noral operation condition no atter wher terinal restor atched or not proposed technique can reliably identify both wher terinal restor atched or not proposed technique can reliably identify both etallic short circuit s non-etallic short circuit s protection range covers etallic short circuit s non-etallic short circuit s protection range covers total total length grounding electrode line length grounding electrode line 5 Conclusions Th paper proposes a novel electrode line supervion strategy based on high-frequency for for UHVDC transsion projects Siilar to exting high-frequency ipedance technique devices, high highfrequency frequencycurrent current injected injectedto to electrode electrode line line at at converter converter station station end end By easuring By easuring voltage voltage current, current, can can be calculated be calculated oretical oretical analys analys indicates indicates that that grounding grounding line line equals equals to to 1 under 1 under noral noral operation operationwith with atching terinal When When ashort shortcircuit circuitoccurs occurson on grounding groundingline, will willbe be greater greater than than 1 1 Siulation results indicate that proposed technique can can reliably identify grounding electrode line s has great anti- ipedance capability Meanwhile, under noral operation, proposed strategy will work reliably, even with atching terinal restors
17 Energies 17, 1, Acknowledgents: Th work presented in th paper was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation: No 15M58543 by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation: No 16M59659 Author Contributions: All authors have contributed equally to th anuscript More specifically, Yufei Teng designed ethodology wrote part paper Xiaopeng i Qi Huang perfored siulations reved paper Yifei Wang Shi Jing contributed specifically to introduction conclusion sections paper henchao Jiang Wei hen provided iportant coents on paper s structure Conflicts Interest: authors declare no conflict interest References 1 Akhatov, V; Callavik, M; Franck, CM; Rye, SE; Ahndorf, T; Bucher, MK; Muller, H; Schettler, F; Wiget, R Technical guidelines prestardization work for first HVDC grids IEEE Trans Power Deliv 14, 9, [CrossRef] Haons, TJ; Woodford, D; oughtan, M; Chaia, M Role HVDC transsion in future energy developent IEEE Power Eng Rev,, 1 5 [CrossRef] 3 Wei, ; Yuan, Y; ei, X; Wang, H; Sun, G; Sun, Y Direct-current predictive control strategy for inhibiting coutation failure in HVDC converter IEEE Trans Power Syst 14, 9, [CrossRef] 4 i, S; Haskew, TA; Xu, Control HVDC light syste using conventional direct current vector control approaches IEEE Trans Power Electr 1, 5, Pan, ; Wang, X; Tan, B; hu, ; iu, Y; iu, Y; Wen, X Potential copensation ethod for restraining DC bias transforers during HVDC onopolar operation IEEE Trans Power Deliv 14, 31, [CrossRef] 6 i, W; iu, ; heng, T; Huang, G; Shi, H Research on effects transforer DC bias on negative sequence protection In Proceedings 11 International Conference on Advanced Power Syste Autoation Protection (APAP), Beijing, China, 16 October 11; pp Yuan, S; Gong, X; uo, Y Design UHVDC earth electrode In Proceedings 14 International Conference on Power Syste Technology, Chengdu, China, October 14; pp 17 8 Yang, G; hu, T; Wei, ; i, Research on s electrode line HVDC transsion syste in onopolar ground return operation Power Syst Prot Control 9, 37, Xiao, Y; Niu, B; Shang, C; in, ; u, Y; Fan, ; i, S A proposal for fast tripping grounding electrode line HVDC Auto Electr Power Syst 9, 33, Cheng, J; Xu, Protection charactertics HVDC coon grounding electrode lines Auto Electr Power Syst 1, 36, eng, X; hang, X; Yang, T; Deng, S Iproveent easures electrodes line unbalance protection for HVDC syste Power Syst Prot Control 14, 4, Wang, W; Gerva, Y; Mukhedkar, D Probabiltic evaluation huan safety near HVDC ground electrode IEEE Trans Power Deliv 1986, 1, [CrossRef] 13 Teng, Y; Wang, Y; Jiao, ; hang, C; Pang, G Ipedance onitoring schee for ground electrode line ultra-high voltage DC transsion syste Trans China Electrotech Soc 16, 31, Teng, Y; Tang, Y; hou, B; Jiao, ; Pang, G Monitoring schee for UHVDC ground electrode line on bas high-frequency voltage variation High Volt Eng 16, 4, ABB 1JN , Electrode ine Ipedance Supervion; ABB: Vasteras, Sweden, 16 IEEE Stard 1893 TM -15 IEEE Guide for Measureent DC Transsion ine Earth Electrode ine Paraeters; Institute Electrical Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Pcataway, NJ, USA, by authors icensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerl Th article an open access article dtributed under ters conditions Creative Coons Attribution (CC BY) license (
Adaptive Harmonic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor
 Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF SINUSOIDAL APPROXIMATION IN ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE TWELVE-PULSE OUTPUT VOLTAGE TYPE RECTIFIERS
 th INTERNATIONAL SYPOSIU on POWER ELECTRONICS - Ee 9 XV eđunarodni sipoziju Energetska elektronika Ee 9 NOVI SAD, REPUBLIC OF SERBIA, October 8 th - th, 9 EXPERIENTAL VERIFICATION OF SINUSOIDAL APPROXIATION
th INTERNATIONAL SYPOSIU on POWER ELECTRONICS - Ee 9 XV eđunarodni sipoziju Energetska elektronika Ee 9 NOVI SAD, REPUBLIC OF SERBIA, October 8 th - th, 9 EXPERIENTAL VERIFICATION OF SINUSOIDAL APPROXIATION
UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Commutated AC to DC converters) Line Commutated Converter
 UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Coutated AC to DC converters) INTRODUCTION TO CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS Controlled rectifiers are line coutated ac to power converters which are used to convert a fixed
UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Coutated AC to DC converters) INTRODUCTION TO CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS Controlled rectifiers are line coutated ac to power converters which are used to convert a fixed
AccuBridge TOWARDS THE DEVELOPMENT OF A DC CURRENT COMPARATOR RATIO STANDARD
 AccuBridge TOWARD THE DEVELOPMENT OF A DC CURRENT COMPARATOR RATO TANDARD Duane Brown,Andrew Wachowicz, Dr. hiping Huang 3 Measureents nternational, Prescott Canada duanebrown@intl.co, Measureents nternational,
AccuBridge TOWARD THE DEVELOPMENT OF A DC CURRENT COMPARATOR RATO TANDARD Duane Brown,Andrew Wachowicz, Dr. hiping Huang 3 Measureents nternational, Prescott Canada duanebrown@intl.co, Measureents nternational,
] (1) Problem 1. University of California, Berkeley Fall 2010 EE142, Problem Set #9 Solutions Prof. Jan Rabaey
![] (1) Problem 1. University of California, Berkeley Fall 2010 EE142, Problem Set #9 Solutions Prof. Jan Rabaey ] (1) Problem 1. University of California, Berkeley Fall 2010 EE142, Problem Set #9 Solutions Prof. Jan Rabaey](/thumbs/81/84143587.jpg) University of California, Berkeley Fall 00 EE4, Proble Set #9 Solutions Ain Arbabian Prof. Jan Rabaey Proble Since the ixer is a down-conversion type with low side injection f LO 700 MHz and f RF f IF
University of California, Berkeley Fall 00 EE4, Proble Set #9 Solutions Ain Arbabian Prof. Jan Rabaey Proble Since the ixer is a down-conversion type with low side injection f LO 700 MHz and f RF f IF
Impact of the Reactive Power Compensation on Harmonic Distortion Level
 pact of the Reactive Power Copensation on Haronic Distortion Level J. A. M. eto,. C. Jesus, L. L. Piesanti Departaento de Tecnologia Universidade Regional do oroeste do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul juí
pact of the Reactive Power Copensation on Haronic Distortion Level J. A. M. eto,. C. Jesus, L. L. Piesanti Departaento de Tecnologia Universidade Regional do oroeste do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul juí
Power Improvement in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Embedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3
 Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
An improved Active Islanding Detection Technology for Grid-connected Solar Photovoltaic System
 An iproved Active Islanding Detection Technology for Grid-connected Solar Photovoltaic Syste H. T. Yang, P. C. Peng, T. Y. Tsai, and Y. Y. Hong Abstract--Solar photovoltaic (PV) generation has drawn ore
An iproved Active Islanding Detection Technology for Grid-connected Solar Photovoltaic Syste H. T. Yang, P. C. Peng, T. Y. Tsai, and Y. Y. Hong Abstract--Solar photovoltaic (PV) generation has drawn ore
New Adaptive Linear Combination Structure for Tracking/Estimating Phasor and Frequency of Power System
 28 Journal of Electrical Engineering & echnology Vol. 5, No., pp. 28~35, 2 New Adaptive Linear Cobination Structure for racking/estiating Phasor and Frequency of Power Syste Choowong-Wattanasakpubal and
28 Journal of Electrical Engineering & echnology Vol. 5, No., pp. 28~35, 2 New Adaptive Linear Cobination Structure for racking/estiating Phasor and Frequency of Power Syste Choowong-Wattanasakpubal and
ELEC2202 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Modulation (FM)
 ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
Amplifiers and Feedback
 6 A Textbook of Operational Transconductance Aplifier and AIC Chapter Aplifiers and Feedback. INTRODUCTION Practically all circuits using Operational Transconductance Aplifiers are based around one of
6 A Textbook of Operational Transconductance Aplifier and AIC Chapter Aplifiers and Feedback. INTRODUCTION Practically all circuits using Operational Transconductance Aplifiers are based around one of
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK
 PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
New Characteristics Analysis Considering Transmission Distance and Load Variation in Wireless Power Transfer via Magnetic Resonant Coupling
 New Characteristics nalysis Considering Transission Distance and oad Variation in Wireless Power Transfer via Magnetic Resonant Coupling Masaki Kato, Takehiro ura, Yoichi Hori The Departent of dvanced
New Characteristics nalysis Considering Transission Distance and oad Variation in Wireless Power Transfer via Magnetic Resonant Coupling Masaki Kato, Takehiro ura, Yoichi Hori The Departent of dvanced
Keywords: Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance, Finite Element, Inrush Current.
 Discriination of Inrush fro Fault Currents in Power Transforers Based on Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance Technique Coupled with Finite Eleent Method Downloaded fro ijeee.iust.ac.ir at 5:47 IRST on
Discriination of Inrush fro Fault Currents in Power Transforers Based on Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance Technique Coupled with Finite Eleent Method Downloaded fro ijeee.iust.ac.ir at 5:47 IRST on
Research Article Novel Design for Reduction of Transformer Size in Dynamic Voltage Restorer
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 8(19): 057-063, 014 DOI:10.1906/rjaset.8.1198 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 014 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Subitted: April
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 8(19): 057-063, 014 DOI:10.1906/rjaset.8.1198 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 014 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Subitted: April
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick. Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al.
 Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS
 Latin Aerican Applied Research 39:187-192 (2009) SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS L. ARNONE, C. GONZÁLEZ, C. GAYOSO, J. CASTIÑEIRA MOREIRA and M. LIBERATORI
Latin Aerican Applied Research 39:187-192 (2009) SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS L. ARNONE, C. GONZÁLEZ, C. GAYOSO, J. CASTIÑEIRA MOREIRA and M. LIBERATORI
ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS
 XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in 3rd Millenniu June 22 27, 2003, Dubrovnik, Croatia ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS Ch. Papageorgiou
XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in 3rd Millenniu June 22 27, 2003, Dubrovnik, Croatia ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS Ch. Papageorgiou
A HIGH POWER FACTOR THREE-PHASE RECTIFIER BASED ON ADAPTIVE CURRENT INJECTION APPLYING BUCK CONVERTER
 9th International onference on Power Electronics Motion ontrol - EPE-PEM Košice A HIGH POWER FATOR THREE-PHASE RETIFIER BASE ON AAPTIVE URRENT INJETION APPYING BUK ONVERTER Žarko Ja, Predrag Pejović EE
9th International onference on Power Electronics Motion ontrol - EPE-PEM Košice A HIGH POWER FATOR THREE-PHASE RETIFIER BASE ON AAPTIVE URRENT INJETION APPYING BUK ONVERTER Žarko Ja, Predrag Pejović EE
Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorithm Zhong Danmei 1, a, Wang zhan 1, a, Cheng zhu 1, a, Huang Da 1, a
 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT
 ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
Improvement of Power System Transient Stability using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volue 3 Issue 01 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Iproveent of Power Syste Transient Stability using Static Synchronous Series opensator
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volue 3 Issue 01 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Iproveent of Power Syste Transient Stability using Static Synchronous Series opensator
A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS
 A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS Jaal Moshtagh University of Bath, UK oshtagh79@yahoo.co Abstract
A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS Jaal Moshtagh University of Bath, UK oshtagh79@yahoo.co Abstract
Detection of Faults in Power System Using Wavelet Transform and Independent Component Analysis
 Detection of Faults in Power Syste Using Wavelet Transfor and Independent Coponent Analysis 1 Prakash K. Ray, 2 B. K. Panigrahi, 2 P. K. Rout 1 Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, IIIT, Bhubaneswar,
Detection of Faults in Power Syste Using Wavelet Transfor and Independent Coponent Analysis 1 Prakash K. Ray, 2 B. K. Panigrahi, 2 P. K. Rout 1 Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, IIIT, Bhubaneswar,
Ignition and monitoring technique for plasma processing of multicell superconducting radio frequency cavities
 Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
Part 9: Basic AC Theory
 Part 9: Basic AC Theory 9.1 Advantages Of AC Systes Dealing with alternating current (AC) supplies is on the whole ore coplicated than dealing with DC current, However there are certain advantages of AC
Part 9: Basic AC Theory 9.1 Advantages Of AC Systes Dealing with alternating current (AC) supplies is on the whole ore coplicated than dealing with DC current, However there are certain advantages of AC
5 Constellation for Digital Modulation Schemes
 5 Constellation for Digital Modulation Schees 5.1 PAM Definition 5.1. Recall, fro 3.6, that PAM signal wavefors are represented as s (t) = A p(t), 1 M where p(t) is a pulse and A A. 5.2. Clearly, PAM signals
5 Constellation for Digital Modulation Schees 5.1 PAM Definition 5.1. Recall, fro 3.6, that PAM signal wavefors are represented as s (t) = A p(t), 1 M where p(t) is a pulse and A A. 5.2. Clearly, PAM signals
Keywords: International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT) Systems, evaluating the usage of frequency bands, evaluation indicators
 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Inforatics (AMEII 206) Entropy Method based Evaluation for Spectru Usage Efficiency of International Mobile Telecounication
2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Inforatics (AMEII 206) Entropy Method based Evaluation for Spectru Usage Efficiency of International Mobile Telecounication
Real Time Etch-depth Measurement Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, (8): -7, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Real Tie Etch-depth Measureent Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor 1 Reza Hosseini, Navid Rahany, 3 Behrad Soltanbeigi, Rouzbeh
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, (8): -7, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Real Tie Etch-depth Measureent Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor 1 Reza Hosseini, Navid Rahany, 3 Behrad Soltanbeigi, Rouzbeh
Secondary-side-only Simultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer System
 069060 Secondary-side-only Siultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynaic Wireless Power Transfer Syste 6 Giorgio ovison ) Daita Kobayashi ) Takehiro Iura ) Yoichi Hori ) ) The University of Tokyo,
069060 Secondary-side-only Siultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynaic Wireless Power Transfer Syste 6 Giorgio ovison ) Daita Kobayashi ) Takehiro Iura ) Yoichi Hori ) ) The University of Tokyo,
General Smith Chart Matching
 General Sith Chart Matching Table of Contents I. General Ipedance Matching II. Ipedance Transforation for Power Aplifiers III. Ipedance Matching with a Sith Chart IV. Inputs V. Network Eleents VI. S-Paraeter
General Sith Chart Matching Table of Contents I. General Ipedance Matching II. Ipedance Transforation for Power Aplifiers III. Ipedance Matching with a Sith Chart IV. Inputs V. Network Eleents VI. S-Paraeter
Switching Transients of Low Cost Two Speed Drive for Single-Phase Induction Machine
 Switching Transients of Low Cost Two Speed Drive for Single-Phase Induction Machine L. Woods, A. Hoaifar, F. Fatehi M. Choat, T. Lipo CA&T State University University of Wisconsin-Madison Greensboro, C
Switching Transients of Low Cost Two Speed Drive for Single-Phase Induction Machine L. Woods, A. Hoaifar, F. Fatehi M. Choat, T. Lipo CA&T State University University of Wisconsin-Madison Greensboro, C
A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and peak-factor reduction in OFDM
 A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and pea-factor reduction in OFDM Yves LOUET *, Annic LE GLAUNEC ** and Pierre LERAY ** * PhD Student and ** Professors, Departent
A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and pea-factor reduction in OFDM Yves LOUET *, Annic LE GLAUNEC ** and Pierre LERAY ** * PhD Student and ** Professors, Departent
High Impedance Fault Detection in Electrical Power Feeder by Wavelet and GNN
 International Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences (IJEAS) ISSN: 2394-3661, Volue-2, Issue-3, March 2015 High Ipedance Fault Detection in Electrical Power Feeder by Wavelet and GNN Majid Jail, Rajveer
International Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences (IJEAS) ISSN: 2394-3661, Volue-2, Issue-3, March 2015 High Ipedance Fault Detection in Electrical Power Feeder by Wavelet and GNN Majid Jail, Rajveer
A New Localization and Tracking Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things
 Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
Block Diagram of FM Receiver
 FM Receivers FM receivers, like AM receivers, utilize the superheterodyne principle, but they operate at uch higher frequencies (88-108 MHz). A liiter is often used to ensure the received signal is constant
FM Receivers FM receivers, like AM receivers, utilize the superheterodyne principle, but they operate at uch higher frequencies (88-108 MHz). A liiter is often used to ensure the received signal is constant
Session Eleven: An On-Line Technique to Detect Winding Deformation within Power Transformers
 Session Eleven: An On-Line Technique to Detect Winding Deforation within Power Transforers A. Abu-Siada Senior Lecturer, Curtin University Abstract Frequency Response Analysis (FRA) has been growing in
Session Eleven: An On-Line Technique to Detect Winding Deforation within Power Transforers A. Abu-Siada Senior Lecturer, Curtin University Abstract Frequency Response Analysis (FRA) has been growing in
Definition Recall, from 6.7, that PAM signal waveforms are represented
 6.4 Constellations for Digital Modulation Schees 6.4.1 PAM Definition 6.45. Recall, fro 6.7, that PAM signal wavefors are represented as s (t) = A p(t), 1 M where p(t) is a pulse and A A. 6.46. Clearly,
6.4 Constellations for Digital Modulation Schees 6.4.1 PAM Definition 6.45. Recall, fro 6.7, that PAM signal wavefors are represented as s (t) = A p(t), 1 M where p(t) is a pulse and A A. 6.46. Clearly,
Characteristics of a Stand-Alone Induction Generator in Small Hydroelectric Plants
 Characteristics of a Stand-Alone nduction Generator in Sall Hydroelectric Plants M. H. Haque School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore 69798 Abstract-This
Characteristics of a Stand-Alone nduction Generator in Sall Hydroelectric Plants M. H. Haque School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore 69798 Abstract-This
A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless Positioning System
 2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
A Novel Control Scheme to Reduce Storage Capacitor of Flyback PFC Converter
 International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Vol. 4, No., April 6 A Novel Control Schee to Reduce Storage Capacitor of Flyback PFC Converter Boyang Chen and Lei Li College of Autoation,
International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Vol. 4, No., April 6 A Novel Control Schee to Reduce Storage Capacitor of Flyback PFC Converter Boyang Chen and Lei Li College of Autoation,
A simple charge sensitive preamplifier for experiments with a small number of detector channels
 A siple charge sensitive preaplifier for experients with a sall nuber of detector channels laudio Arnaboldi and Gianluigi Pessina Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) Università degli Studi di
A siple charge sensitive preaplifier for experients with a sall nuber of detector channels laudio Arnaboldi and Gianluigi Pessina Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) Università degli Studi di
ANALOGUE & DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
 1 ANALOGUE & DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Syed M. Zafi S. Shah & Uair Mujtaba Qureshi Lectures 5-6: Aplitude Modulation Part 1 Todays topics Recap of Advantages of Modulation Analog Modulation Defining Generation
1 ANALOGUE & DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Syed M. Zafi S. Shah & Uair Mujtaba Qureshi Lectures 5-6: Aplitude Modulation Part 1 Todays topics Recap of Advantages of Modulation Analog Modulation Defining Generation
a 2 R ja 2 x l2 R c jx m1
 Electric Machinery Labs NQN_version.0 Lab Exercise 6: Siulation of Inrush Currents in Three-Phase Transforers Students ID Group Date I. Introduction: Transforer plays an iportant role in the power transission
Electric Machinery Labs NQN_version.0 Lab Exercise 6: Siulation of Inrush Currents in Three-Phase Transforers Students ID Group Date I. Introduction: Transforer plays an iportant role in the power transission
Kalman Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environment
 16 Kalan Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environent Chin-Der Wann National Sun Yat-Sen University Taiwan 1. Introduction Kalan filter and its nonlinear extension, extended
16 Kalan Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environent Chin-Der Wann National Sun Yat-Sen University Taiwan 1. Introduction Kalan filter and its nonlinear extension, extended
Precise Indoor Localization System For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorithm
 Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
LUENBERGER ALGORITHM BASED HARMONICS ESTIMATOR FOR FRONT END RECTIFIER AND PWM-VSI
 LUENBERGER ALGORITHM BASED HARMONICS ESTIMATOR FOR FRONT END RECTIFIER AND PWM-VSI P Ajay-D-Vial Raj R.Sundaraurthy S Jeevananthan M.Sudhakaran Departent of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Pondicherry
LUENBERGER ALGORITHM BASED HARMONICS ESTIMATOR FOR FRONT END RECTIFIER AND PWM-VSI P Ajay-D-Vial Raj R.Sundaraurthy S Jeevananthan M.Sudhakaran Departent of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Pondicherry
Energy-Efficient Cellular Communications Powered by Smart Grid Technology
 Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
A Hybrid Method for Fault Location in EHV Multi-Terminal Circuits
 6th ATOAL POWER SYSTEMS COFERECE, 5th-7th DECEMBER, 754 A Hybrid Method for Fault Location in EHV Multi-Terinal Circuits B R K Vara, Research Scholar Departent of Electrical Engineering ational nstitute
6th ATOAL POWER SYSTEMS COFERECE, 5th-7th DECEMBER, 754 A Hybrid Method for Fault Location in EHV Multi-Terinal Circuits B R K Vara, Research Scholar Departent of Electrical Engineering ational nstitute
Clamping of Switch Peak Voltage with Diode and Transformer at Output of Class E Amplifier for Renewable Energy Applications
 adashi Suetsugu et al., Vol.3, No., 013 Claping of Switch Peak Voltage with Diode and ransforer at Output of Class E Aplifier for enewable Energy Applications adashi Suetsugu*, Xiuqin Wei * *Departent
adashi Suetsugu et al., Vol.3, No., 013 Claping of Switch Peak Voltage with Diode and ransforer at Output of Class E Aplifier for enewable Energy Applications adashi Suetsugu*, Xiuqin Wei * *Departent
Travelling waves for finding the fault location in transmission lines
 Journal Electrical and Electronic Engineering 3; (): -9 Published online April, 3 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.co/j/jeee) doi:.648/j.jeee.3. Travelling waves for finding the fault location in transission
Journal Electrical and Electronic Engineering 3; (): -9 Published online April, 3 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.co/j/jeee) doi:.648/j.jeee.3. Travelling waves for finding the fault location in transission
Introduction Traditionally, studying outage or cellular systes has been based on the signal-to-intererence ratio (SIR) dropping below a required thres
 Miniu Duration Outages in Rayleigh Fading Channels Jie Lai and Narayan B. Mandaya WINLAB, Rutgers University 73 Brett Rd., Piscataway, NJ 8854-86 Eail: jlai@winlab.rutgers.edu, narayan@winlab.rutgers.edu
Miniu Duration Outages in Rayleigh Fading Channels Jie Lai and Narayan B. Mandaya WINLAB, Rutgers University 73 Brett Rd., Piscataway, NJ 8854-86 Eail: jlai@winlab.rutgers.edu, narayan@winlab.rutgers.edu
Radar Imaging of Non-Uniformly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Component AM-FM Signal Parameter Estimation
 Sensors 5, 5, 695-693; doi:.339/s53695 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 44-8 www.dpi.co/journal/sensors Radar Iaging of Non-Uniforly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Coponent AM-FM Signal
Sensors 5, 5, 695-693; doi:.339/s53695 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 44-8 www.dpi.co/journal/sensors Radar Iaging of Non-Uniforly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Coponent AM-FM Signal
Design and Implementation of Piezoelectric Transducer Driving System with MPPT and ZVS Features
 Volue 02 Issue 05, October 2014 Design and Ipleentation of Piezoelectric Transducer Driving Syste with MPPT and ZVS Features Yu-Kai Chen, Chau-Chung Song and Chih-Ying Chen Departent of Aeronautical Engineering,
Volue 02 Issue 05, October 2014 Design and Ipleentation of Piezoelectric Transducer Driving Syste with MPPT and ZVS Features Yu-Kai Chen, Chau-Chung Song and Chih-Ying Chen Departent of Aeronautical Engineering,
Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectrum Based on EM Algorithm. Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b
 nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS
 NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
Distributed Power Delivery for Energy Efficient and Low Power Systems
 Distributed Power Delivery for Energy Efficient and Low Power Systes Selçuk Köse Departent of Electrical Engineering University of South Florida Tapa, Florida 33620 kose@usf.edu Eby G. Friedan Departent
Distributed Power Delivery for Energy Efficient and Low Power Systes Selçuk Köse Departent of Electrical Engineering University of South Florida Tapa, Florida 33620 kose@usf.edu Eby G. Friedan Departent
Design and Implementation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measurement System Based on STC12 Jian Huang
 International Conference on Education, Manageent and Coputer Science (ICEMC 2016) Design and Ipleentation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measureent Syste Based on STC12 Jian Huang Xijing University,
International Conference on Education, Manageent and Coputer Science (ICEMC 2016) Design and Ipleentation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measureent Syste Based on STC12 Jian Huang Xijing University,
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaker Arrays
 Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
DESIGN OF TRANSFORMER BASED CMOS ACTIVE INDUCTANCES
 roceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on Microelectronics, Nanoelectronics, Optoelectronics, rague, Czech epublic, March -4, 6 (pp64-69) DESIGN OF TANSFOME BASED CMOS ACTIVE INDUCTANCES G.SCANDUA, C.CIOFI
roceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on Microelectronics, Nanoelectronics, Optoelectronics, rague, Czech epublic, March -4, 6 (pp64-69) DESIGN OF TANSFOME BASED CMOS ACTIVE INDUCTANCES G.SCANDUA, C.CIOFI
AC Fundamental. Simple Loop Generator: Whenever a conductor moves in a magnetic field, an emf is induced in it.
 A Fundaental Siple oop Generator: Whenever a conductor oves in a agnetic field, an ef is induced in it. Fig.: Siple oop Generator The aount of EMF induced into a coil cutting the agnetic lines of force
A Fundaental Siple oop Generator: Whenever a conductor oves in a agnetic field, an ef is induced in it. Fig.: Siple oop Generator The aount of EMF induced into a coil cutting the agnetic lines of force
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
 Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Intermediate-Node Initiated Reservation (IIR): A New Signaling Scheme for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion
 Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Fundamental study for measuring microflow with Michelson interferometer enhanced by external random signal
 Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
A Novel Frequency Independent Simultaneous Matching Technique for Power Gain and Linearity in BJT amplifiers
 A Novel requency Independent iultaneous Matching Technique for Power Gain and Linearity in BJT aplifiers Mark P. van der Heijden, Henk. de Graaff, Leo. N. de Vreede Laboratory of Electronic oponents, Technology
A Novel requency Independent iultaneous Matching Technique for Power Gain and Linearity in BJT aplifiers Mark P. van der Heijden, Henk. de Graaff, Leo. N. de Vreede Laboratory of Electronic oponents, Technology
A Wireless Transmission Technique for Remote Monitoring and Recording System on Power Devices by GPRS Network
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Instruentation, Measureent, Circuits & Systes, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 007 13 A Wireless Transission Technique for Reote Monitoring and Recording
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Instruentation, Measureent, Circuits & Systes, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 007 13 A Wireless Transission Technique for Reote Monitoring and Recording
A Decoupling Structure of Controllable Reactor of Transformer Type
 TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol., No., January 5, pp. ~ 5 DOI:.59/telkonika.vi.67 A Decoupling Structure of Controllable Reactor of Transforer Type Yu He*, Huatai Chen Power
TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol., No., January 5, pp. ~ 5 DOI:.59/telkonika.vi.67 A Decoupling Structure of Controllable Reactor of Transforer Type Yu He*, Huatai Chen Power
Chapter 6. POWER AMPLIFIERS
 hapter 6. OWER AMFERS An aplifying syste usually has several cascaded stages. The input and interediate stages are sall signal aplifiers. Their function is only to aplify the input signal to a suitable
hapter 6. OWER AMFERS An aplifying syste usually has several cascaded stages. The input and interediate stages are sall signal aplifiers. Their function is only to aplify the input signal to a suitable
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops October 11, 2006
 Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
OTC Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker. sensitive to lateral loading such as the SAL5 and
 OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
A Novel Low Power UWB Cascode SiGe BiCMOS LNA with Current Reuse and Zero-Pole Cancellation
 A Novel Low Power UWB Cascode SiGe BiCMOS LNA with Current Reuse and Zero-Pole Cancellation Chunbao Ding, Wanrong Zhang, Dongyue Jin, Hongyun Xie, Pei Shen, Liang Chen, School of Electronic Inforation
A Novel Low Power UWB Cascode SiGe BiCMOS LNA with Current Reuse and Zero-Pole Cancellation Chunbao Ding, Wanrong Zhang, Dongyue Jin, Hongyun Xie, Pei Shen, Liang Chen, School of Electronic Inforation
EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM Guangrong Zou, Maro Antila, Antti Lanila and Jari Kataja Sart Machines, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland P.O. Box 00, FI-0 Tapere,
EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM Guangrong Zou, Maro Antila, Antti Lanila and Jari Kataja Sart Machines, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland P.O. Box 00, FI-0 Tapere,
An Automatic Control Strategy of Strip Width in Cold Rolling
 Advanced Materials Research Subitted: 204-06-04 ISSN: 662-8985, Vols. 004-005, pp 22-225 Accepted: 204-06-08 doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.004-005.22 Online: 204-08-3 204 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland
Advanced Materials Research Subitted: 204-06-04 ISSN: 662-8985, Vols. 004-005, pp 22-225 Accepted: 204-06-08 doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.004-005.22 Online: 204-08-3 204 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland
Torsion System. Encoder #3 ( 3 ) Third encoder/disk for Model 205a only. Figure 1: ECP Torsion Experiment
 Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Multitarget Direction Measurement Based on Bistatic Radar
 Sensors & ransducers Vol. 70 Issue 5 May 204 pp. 65-70 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Multitarget Direction Measureent Based on Bistatic Radar Yubao ou School
Sensors & ransducers Vol. 70 Issue 5 May 204 pp. 65-70 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Multitarget Direction Measureent Based on Bistatic Radar Yubao ou School
A new scheme based on correlation technique for generator stator fault detection-part І
 International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 04; 3(3): 64 Published online May 30, 04 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.co/j/ijepe) doi: 0.648/j.ijepe.040303. A new schee based on correlation
International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 04; 3(3): 64 Published online May 30, 04 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.co/j/ijepe) doi: 0.648/j.ijepe.040303. A new schee based on correlation
Comparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls
 Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition
 International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
POWER QUALITY ASSESSMENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIMATION NUMERICAL ALGORITHM
 POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
Hand Gesture Recognition and Its Application in Robot Control
 IJCSI International Journal of Coputer Science Issues, Volue 13, Issue 1, January 016 www.ijcsi.org 10 Hand Gesture Recognition and Its Application in Robot Control Pei-Guo Wu 1 and Qing-Hu Meng 1 Inforation
IJCSI International Journal of Coputer Science Issues, Volue 13, Issue 1, January 016 www.ijcsi.org 10 Hand Gesture Recognition and Its Application in Robot Control Pei-Guo Wu 1 and Qing-Hu Meng 1 Inforation
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, 2
 Subission International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ) PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS FOR MAPPING AIR FLOW IN THE EAR-CANALTO TONGUE MOVEMENT: A NEW STRATEGY
Subission International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ) PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS FOR MAPPING AIR FLOW IN THE EAR-CANALTO TONGUE MOVEMENT: A NEW STRATEGY
A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz amplifier.
 University of Michigan, EECS413 Final project. A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. 1 A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. Mark Ferriss, Junghwan Han, Joshua Jaeyoung Kang, University of Michigan. Abstract
University of Michigan, EECS413 Final project. A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. 1 A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. Mark Ferriss, Junghwan Han, Joshua Jaeyoung Kang, University of Michigan. Abstract
Performance Analysis of Atmospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays
 Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF PULSE TRANSFORMER CONSIDERING LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCE
 ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF PULSE TRANSFORMER CONSIDERING LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCE ABOLFAZL VAHEDI, HOSSEIN HEYDARI, and FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Electrical Engineering Departent, High Voltage & Magnetic
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF PULSE TRANSFORMER CONSIDERING LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCE ABOLFAZL VAHEDI, HOSSEIN HEYDARI, and FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Electrical Engineering Departent, High Voltage & Magnetic
HÉDIO TATIZAWA 1, ERASMO SILVEIRA NETO 2, GERALDO F. BURANI 1, ANTÔNIO A. C. ARRUDA 1, KLEIBER T. SOLETTO 1, NELSON M. MATSUO 1
 Application of odelling and coputer siulation for the developent of a test setup for calibration of power quality easureent transducers for high voltage networks HÉDIO TATIZAWA 1, ERASMO SILVEIRA NETO
Application of odelling and coputer siulation for the developent of a test setup for calibration of power quality easureent transducers for high voltage networks HÉDIO TATIZAWA 1, ERASMO SILVEIRA NETO
Unit 9. Alternating current
 nit 9 Alternating current 9. ntroduction 9. Features of an A.C. 9.3 Behaviour of basic dipoles facing an A.C. 9.4 RLC series circuit. pedance and phase lag. 9.5 Power on A.C. 9.6 Questions and probles
nit 9 Alternating current 9. ntroduction 9. Features of an A.C. 9.3 Behaviour of basic dipoles facing an A.C. 9.4 RLC series circuit. pedance and phase lag. 9.5 Power on A.C. 9.6 Questions and probles
SEVERAL benchmark tests for beam propagation methods
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1921 A COST 240 Benchark Test for Bea Propagation Methods Applied to an Electrooptical Modulator Based on Surface Plasons H. J. W. M. Hoekstra,
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1921 A COST 240 Benchark Test for Bea Propagation Methods Applied to an Electrooptical Modulator Based on Surface Plasons H. J. W. M. Hoekstra,
Air Absorption Error in Room Acoustical Modeling
 Air Absorption Error in Roo Acoustical Modeling Wenaekers, R.H.C.; Hak, C.C.J.M.; Martin, H.J.; van Luxeburg, L.C.J. Published in: Proceedings of the 155th ASA conference, Paris 2008 Published: 01/01/2008
Air Absorption Error in Roo Acoustical Modeling Wenaekers, R.H.C.; Hak, C.C.J.M.; Martin, H.J.; van Luxeburg, L.C.J. Published in: Proceedings of the 155th ASA conference, Paris 2008 Published: 01/01/2008
Equal Area Criterion Scheme to Reduce DC Bus Voltage Stress of Single Stage Single Switch Power Factor Corrected Converter
 Aerican nternational Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Matheatics Available online at http://www.iasir.net SSN (Print): 38-349, SSN (Online): 38-3580, SSN (CD-ROM): 38-369 AJRSTEM
Aerican nternational Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Matheatics Available online at http://www.iasir.net SSN (Print): 38-349, SSN (Online): 38-3580, SSN (CD-ROM): 38-369 AJRSTEM
Overlapped frequency-time division multiplexing
 April 29, 16(2): 8 13 www.sciencedirect.co/science/journal/158885 he Journal of China Universities of Posts and elecounications www.buptjournal.cn/xben Overlapped frequency-tie division ultiplexing JIANG
April 29, 16(2): 8 13 www.sciencedirect.co/science/journal/158885 he Journal of China Universities of Posts and elecounications www.buptjournal.cn/xben Overlapped frequency-tie division ultiplexing JIANG
Evolutionary Computing Based Antenna Array Beamforming with Low Probabality of Intercept Property
 World Applied Sciences Journal 23 (): 57-575, 23 ISSN 88-4952 IDOSI Publications, 23 DOI:.5829/idosi.wasj.23.23..89 Evolutionary Coputing Based Antenna Array Beaforing with Low Probabality of Intercept
World Applied Sciences Journal 23 (): 57-575, 23 ISSN 88-4952 IDOSI Publications, 23 DOI:.5829/idosi.wasj.23.23..89 Evolutionary Coputing Based Antenna Array Beaforing with Low Probabality of Intercept
Performance Analysis of an AMC System with an Iterative V-BLAST Decoding Algorithm
 I. J. Counications, Network and Syste Sciences, 008,, 105-06 Published Online May 008 in SciRes (http://www.srpublishing.org/journal/ijcns/). Perforance Analysis of an AMC Syste with an Iterative V-BLAST
I. J. Counications, Network and Syste Sciences, 008,, 105-06 Published Online May 008 in SciRes (http://www.srpublishing.org/journal/ijcns/). Perforance Analysis of an AMC Syste with an Iterative V-BLAST
Evolutionary Computing Based Antenna Array Beamforming with Low Probabality of Intercept Property
 World Applied Sciences Journal 23 (): 57-575, 23 ISSN 88-4952 IDOSI Publications, 23 DOI:.5829/idosi.wasj.23.23..89 Evolutionary Coputing Based Antenna Array Beaforing with Low Probabality of Intercept
World Applied Sciences Journal 23 (): 57-575, 23 ISSN 88-4952 IDOSI Publications, 23 DOI:.5829/idosi.wasj.23.23..89 Evolutionary Coputing Based Antenna Array Beaforing with Low Probabality of Intercept
A Novel Sine Duty-Cycle Modulation Control Scheme for Photovoltaic Single-Phase Power Inverters
 Leandre Nnee Nnee, Jean Mbihi A Novel Sine Duty-Cycle Modulation Control Schee for Photovoltaic Single-Phase Power Inverters ARNAUD OBONO BIYOBO Research Laboratory of Coputer Science Engineering and Autoation
Leandre Nnee Nnee, Jean Mbihi A Novel Sine Duty-Cycle Modulation Control Schee for Photovoltaic Single-Phase Power Inverters ARNAUD OBONO BIYOBO Research Laboratory of Coputer Science Engineering and Autoation
A.C. FUNDA- MENTALS. Learning Objectives
 C H A P T E R Learning Objectives Generation of Alternating Voltages and Currents Alternate Method for the Equations of Alternating Voltages and currents Siple Wavefors Cycle Different Fors of E.M.F. Equation
C H A P T E R Learning Objectives Generation of Alternating Voltages and Currents Alternate Method for the Equations of Alternating Voltages and currents Siple Wavefors Cycle Different Fors of E.M.F. Equation
LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES
 Page 1 of 10 LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES Hugh McPherson Spectral Line Systes Ltd, Units 1,2&3 Scott Road, Tarbert, Isle of Harris. www.spectral-line-systes.co.uk
Page 1 of 10 LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES Hugh McPherson Spectral Line Systes Ltd, Units 1,2&3 Scott Road, Tarbert, Isle of Harris. www.spectral-line-systes.co.uk
Parameter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB
 Paraeter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB Mato Fruk, Goran Vujisić, Toislav Špoljarić Departent of Electrical Engineering The Polytechnic of Zagreb Konavoska, Zagreb, Croatia ato.fruk@tvz.hr,
Paraeter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB Mato Fruk, Goran Vujisić, Toislav Špoljarić Departent of Electrical Engineering The Polytechnic of Zagreb Konavoska, Zagreb, Croatia ato.fruk@tvz.hr,
Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity
 Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity Aravind Kailas School of Electrical and Coputer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 3033-050,
Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity Aravind Kailas School of Electrical and Coputer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 3033-050,
Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynamic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
 Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
Tesla Coil Theoretical Model and its Experimental Verification
 Electrical, ontrol and ounication Engineering 4/7 Tesla oil Theoretical Model and its Experiental Verification doi: 55/ecce-4-8 Janis Voitkans (Researcher, Riga Technical niversity, Arnis Voitkans (Researcher,
Electrical, ontrol and ounication Engineering 4/7 Tesla oil Theoretical Model and its Experiental Verification doi: 55/ecce-4-8 Janis Voitkans (Researcher, Riga Technical niversity, Arnis Voitkans (Researcher,
