Low Latitude - Sferics, Tweeks and Whistlers: Present Understanding and Future Prospective. B. Veenadhari, Rajesh Singh, SushilKumar and Ajeet Maurya
|
|
|
- Diane Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Low Latitude - Sferics, Tweeks and Whistlers: Present Understanding and Future Prospective B. Veenadhari, Rajesh Singh, SushilKumar and Ajeet Maurya Sharjah-Stanford AWESOME VLF workshop University of Sharjah, Sharjah, U.A.E February 22 24, 2010
2 Space weather : Interdisciplinary field gained lot of interest Refers to the time variable conditions in the space environment that may effect space-borne or ground based technological systems According to US National Space Weather Programme, Conditions on the Sun and in the solar wind, magnetoshere, ionosphere and thermosphere that can influence the performance and reliability of space-borne and ground based technological systems and can endanger human life or health.
3 Why do we care about Space Weather? Analogous to violent terrestrial weather such as during a hurricane can disrupt satellite communications, destroy spacecraft, and expose astronauts and occupants of high-flying aircraft to high amounts of radiation Storms can result in power outage, pipeline and railroad disruptions Interesting science to understand the mass and electromagnetic output and variability of the Sun
4
5 Sources of geomagnetic storms CMEs Magnetic Clouds Corotating high speed plasma streams This composite image illustrates the different phenomena that can result in geomagnetic activity on Earth.
6 A magnetosphere has many parts, such as the bow shock, magnetosheath, magnetotail, plasmasheet, lobes, plasmasphere, radiation belts and many electric currents. It is composed of charged particles and magnetic flux. These particles are responsible for many wonderful natural phenomena such as the aurora and natural radio emissions such as lion roars and whistler waves.
7 From Otto, 2004
8 Coronal mass ejections or CMEs carry enormous amounts of the Sun s magnetic field with them. Often loop-like or bubble-like in appearance, when a CME plows into the solar wind, it can create a shock wave that accelerates particles to high energies. Behind that shock wave, the CME expands into a huge cloud that travels through the interplanetary medium and engulfs planets in its path. Out of these few CMEs are aimed at Earth, and carry strong southward magnetic fields of long duration. These southward field merge with the earth s northward fields at the dayside boundary of the magnetosphere as allow transfer of solar wind energy, momentum and mass to the magnetosphere.
9 Example of Dstindex Dst index for April 2000 Major storms (Dst <-100 nt) Minor storms (Dst <-50 nt) Quiet Period (no storm) Main Phase Recovery Phase
10
11
12
13 Space Weather
14 Space Weather: Ionosphere/Magnetosphere studies using ELF/VLF Electro-magnetic Waves
15 L-Shell Given as L=R/Ro where Ro=radius of Earth, R= distance along the equator form the Center of Earth. Indicates the height at which magnetic field lines crosses the magnetic equator. Describes a particular set of planetary magnetic field lines. We will often specifies the geospace locations in terms of L-shell. Field lines are horizontal at the magnetic equator & vertical at the magnetic poles
16 Low Mid - High Latitude Low latitude: 0-30 o, L<2 Middle latitude: o, 2<L<5 High latitude: o, L>5
17 Extremely Low & Very Low Frequency waves ELF/VLF Band of Spectrum ELF: 30 Hz 3000 Hz VLF: 3 khz 30 khz ELF-VLF: 30 Hz 30 khz
18 Sources of ELF / VLF waves ELF/VLF waves has various Natural and Artificial origin : Natural sources of ELF/VLF waves: Includes Lightning discharge from thunder storms, volcanic eruptions, dust storm and tornadoes, Earthquake, etc Man Made Sources of ELF and VLF Radio Waves: HF heating Fixed frequency VLF transmitters Nuclear explosions However, on a global basis, by far the most significant source of wave at ELF/VLF is that generated by lightning discharges from thunderstorms.
19 VLF Study Broad band Narrow band Covers entire VLF Spectrum 300Hz- 47.5kHz Example: Sferics Tweeks Whistlers ELF/VLF Emissions Fixed Frequency transmitter signals (Amplitude & Phase) Example: Solar Flayer Geomagnetic storm Earthquake Sprites, Elves, Blue jets
20 Low latitude Whistlers
21 Whistler Some part of radiated energy in the VLF range penetrates the lower boundary of ionosphere and guided through the magnetosphere along the geomagnetic field lines. This is called magneto-ionic mode propagation These waves are received on earth surface without any appreciable attenuation and called whistler waves. The sound of a whistler is a musical descending tone that lasts for a second or more which gives its name.
22 Whistler mode The terminology 'whistler mode' is widely used because lightning generated whistlers waves propagate in this mode. Whistler mode waves include waves having right hand polarization, and whose upper frequency cutoff is either the local electron plasma frequency or gyrofrequency, which ever is less (Stix, 1992).
23 Whistler at High & Low latitude The occurrence of whistler in low latitude is poorly understood, and it remains the focus of intense research activity.
24 ( a) WB dat Whistl er 22 nd Spectrogram t o = s x 10 4 F re q u e nc y (x H z) Frequency Whistle rs B A x 10 4 Time 2 ( b) (c ) WB dat 26 th Spectrogram WB dat Frequency t oa = s Whistlers 15 th Spectrogram t ob = s A B Time Time (s)
25 x 10 4 (d) WB dat 2 Fr equ enc y (x10 Frequency 4 Hz) t o = Whistler 7 th Spectrogram Time (e) WB dat 17 th Spectrogram Whistler t o =0.679 s Time (s)
26 Probing Potentiality of the Magnetospheric Parameters: Early 1950 s when it was understood that these radiations from lightning had traveled several earth radii out in space, so it carries subtle information about the medium through which they travel. Thus analyzing the received wave-features, it is possible to derive information about the magnetospheric medium properties such as - Electron and proton density, - Electric and magnetic field distribution in the medium - Flow of plasma between magnetosphere and ionosphere -Irregularity patches in the ionosphere The most important contribution discovery of PLASMAPAUSE by whistler waves observation (Carpenter D.L., 1964). - Equatorial electron density drops by a factor of 10 to 100
27 Their dynamic spectra reveal a long sweeping arc that illustrates how the high frequencies arrive first, followed by lower ones. Whistler The group velocity for whistler υ g αω 1/2 There dispersion is because of the great distances traveled by them through magnetosphere, which is strongly dispersive media
28 Wave Propagation in Magnetosphere Ducted and Non Ducted Propagation Waves in magnetosphere follows complex trajectory. One type of field aligned irregularities serve as guiding structure for these waves known as Duct. Waves traveling in ducts maintain direction along magnetic field lines. In Non-Ducted propagation, waves are influenced by smoothly varying ionization in the ionosphere.
29 DUCTED Whistlers The key step involved in generation and propagation mechanism of whistlers is the ducting of electromagnetic waves radiated by lightning discharge in electron density ducts aligned along geomagnetic field lines and its propagation over the path. A Duct may either be density enhancement ( Crest ) or density depletion ( Trough ). The Existence of duct is still only a theory but experimental evidence agree well. All whistlers observed on the ground have propagates in ducts????
30 For effective ducting wave normal angle should be less than 4 0 Waves with wave-normal angles greater than 4 0 do not reach the earth surface and hence cannot be observed by the ground based equipments. Equipments on board rockets and satellites usually observe them.
31 Types of Whistlers Various types of whistlers: 1. Short 2. Multiflash 3. Multipath 4. Sharp 5. Diffuse 6. Riser 7. Twin 8. low dispersion, high dispersion 9. banded, hooks, etc. and many more types have been observed at high and low latitude stations
32 Spectrogram of different type of Whistlers observed in India
33 Whistler Occurrence Rate The whistler occurrence rate depends on the local time, season and location Whistlers are more common during the night than day, because of high absorption in the daytime ionosphere. The are more frequent at location where lightning storms are common, or at points magnetically conjugate to regions of lightning activity The latitudinal dependence of whistler occurrence rate shows a maximum around geomagnetic latitudes ~ 45 o The lower latitude cut-off of whistler is found to be ~10 o? The occurrence rate exhibits a strong dependence on geomagnetic activity
34 Radio Atmospherics Sferics
35 Radio Atmospherics Also called as Earth Songs Natural source of these Electromagnetic pulses are lightning discharge form thunder storm. The energy radiated by these waves lies in the ELF/VLF frequency range ( Hz and 3-30kHz). The maximum energy lies in audio frequency range. Radio engineers referred these waves as Radio noise because these waves limits the system performance of radio transmission lines. They have many kinds depending on the sounds produced by them, The most common are: -Sferics -Tweeks -Whistlers For the first two signals it is waveguide mode propagation and for the third signal it s the magneto-ionic mode propagation
36 Sferics The natural lightning impulse radiates energy in the ELF/ VLF range travel over thousand of km through the conducting boundary of the earth-ionosphere waveguide,to be received as signals which do not exhibit dispersion are called sferics.
37 sferic The dynamic spectra of sferics are characterized by vertical lines indicating the simultaneous arrival of all frequencies. On spectrogram it may extend from a few khz to several tens of khz. It produces crisp sharp clicking sound. when signal presented to loudspeaker. Why these waves do not show dispersion????
38 D-region remote sensing by Sferics observations Cummer et al 1998-Assumption: D-region electron density can be described by a two parameter exponential profile, Here h is reference height in km and β is sharpness factor in km-1 By the use of LWPC model on sferic spectrum for different combinations of h and β have been calculated to find out most closely match for the observed sferic spectrum.
39 The observed and best fit modeled sferic spectrum: The measured D-region electron density profile For this type of study we need a good understanding of LWPC propagation model
40 Tweek Radio Atmospherics
41 Tweek Atmospherics Propagation Sky waves Ground wave Tweeks are VLF/ELF electromagnetic waves originated in the distant lightning and propagates in the Earth-ionosphere waveguide over long distances (> 1000 km ) with very low attenuation (2-3 3 db/1000km) through multiple reflections (Wood( and Inan,2002). Also called as guided waves. It sound like tweet when the signal is presented to loudspeaker. These signals shows the strong dispersion near the cutoff frequency of the waveguide ~ 1.8 khz (Mikhaylova,1988( Mikhaylova,1988).
42 Tweek The dynamic spectra of a tweek shows a vertical line at the higher frequencies with a curved section ( called hook ) appearing at ~ 2 KHz The tweek duration is roughly proportional to its path the longer the path in EIWG the longer will be the tweek.
43 Tweek Dispersion: A important features of tweeks and a reason for its distinct sound from other radio atmospherics. Why Dispersion in tweeks? Tweeks traveling via multiple reflection in the Earth-Ionosphere Waveguide. Every waveguide has a cutoff frequency because of its physical size, the closer wave to its cutoff, the slower it travels. So its shows dispersion. Waveguide Propagation In waveguide EM waves appears as modes. The three types of mode specifying the polarization of Electric and magnetic fields are: TE, TM,TEM TE and TM also has higher order modes like TE2, TM 2. Distinct modes are function of frequency, boundary reflection and having different cutoff frequency and attenuation rate. As Earth-Ionosphere waveguide is not a perfect conductor so modes are not pure Modes in real EIWG are: qte, qtm, qtem.
44 Radial direction The group velocity υ gn for the different modes of propagation is given by (Ohtsu,, 1960) : ν gn = c f 2 cn 1 2 f 1 2 Where f cn is cutoff frequency of nth mode and f is wave frequency The night time ionospeheric cutoff frequency of first mode~1.8 khz
45 Tweek Modes Mostly tweeks generated from vertical lightning discharges which preferentially excite qtm and qtem waveguide modes (Cummer,, 1997). QTM 2 QTM 1
46 By analyzing the dispersive part of tweeks we can estimate : A. Reflection height (h) of lower region (D-region) of ionosphere B. Night time Electron density (N) C. Propagation distance (d) in Earth-Ionosphere wave-guide
47 Set of Equations used in study of lower ionosphere 1. Electron density : N=1.66 x 10-2 f c [el/cm 3 ] Here f c is the cutoff frequency for first mode 2. Reflection height h = nc 2 f c [km] 3. distance d f = dtc f 2 cn [km] Here dt is the dispersion time measured from tweek
48 How to measure dispersion time dt? dt Tweek dt= t d - t o t o t d dt = Dispersion time t o = t d = Arrival time of tweek before dispersion Arrival time of tweek after dispersion
49 Tweek Applications Calculation of lower Ionospheric height, Electron density based on tweek measurements. Identification of source location of causative Lighting Discharges based on tweek study. Ionospheric diagnostics based on tweek measurements.
50 Whole night variations of D-region electron density,reflection height, and propagation distance of tweeks (Maurya et al 2009)
51 TWEEK EXAMPLES During March-May, 2007 (a) (b) (c) Reflection height & propagation distance for each mode in the example has been calculated and given in table (d)
52 Tweek Mode Cut-off Mean Reflection Frequency Frequency (f cn /n) Height (n) (khz) (khz) (Km) a b c d
53 One contradiction form the table is Mean cutoff frequency is increases with mode no and this causes decrease in reflection height for higher modes This observation is also supported by Singh & Singh 1996, Ohya et al, S Kumar et al 2009 has shown Mean cutoff frequency decreases with mode and reflection height is high for higher modes
54 Source location/direction finding of Causative Lightning
55 From the simultaneous observation of Tweeks at Indian station Allahabad Geomag. Lat.16.49N Geomag.Long E Nainital Geomag. Lat N Geomag. Long E Date: June 13, 2007; Time:15:00:00 19:00:00 UT Local Night time: 20:30:00 00:30:00 LT Analysis of 526 pairs (1052 total) of tweeks observed simultaneously at both sites during the period
56 Examples of Tweek atmospherics Analysed
57 for ALLAHABAD site Reflection Height Electron Density
58 for NAINITAL site Reflection Height Electron Density
59 Distance traveled by tweeks from source lightning discharge w.r.t. ALLAHABAD site (Geomag. Lat.16.49N; Geomag. Long E)
60 Distance traveled by tweeks from source lightning discharge w.r.t. NAINITAL site (Geomag. Lat.20.48N Geomag. Long E)
61 The calculated distance traveled were then used to locate the source position of causative lightning discharge of Tweeks This is fixed by the intersection of two circles drawn by the distance traveled (propagation distance) from Allahabad and Nainital stations. Ohya et al., 55, 627, 2003, Earth Planets Space
62 Causative Lightning Source location The location of the tweek atmospherics were confirmed by looking into WWLLN Lightning data.
63
64
65 Lightning generated tweek atmospherics has the unique advantage of being capable of estimating lower ionosphere electron densities (reflection heights) in a wide area surrounding observation site (~ km) The method is useful for detecting changes in reflection heights, electron density in the D-region ionosphere, which could correspond to abnormal geophysical conditions.
66 Morphological features VLF emissions are observed in the low latitude ground stations mostly during night time due to heavy absorption in the D region ionosphere during daytime. Emissions occur during winter season between November and March. VLF emissions at low latitude is very low as compared to middle and high latitudes. The activity is enhanced during the period of magnetic storms. Applications of VLF emissions alongwith Whistlers Electron density distributions in the outer ionosphere Ionosphere-protonosphere coupling Magnetospheric electric field Dyanmics of the earth s magnetosphere Explorations of other planetary atmospheres Distance and directions of lightening using spherics and tweeks
67 How Important is VLF study in Indian Low latitude region?
68 India is a very interesting location for several reasons like: - conjugate region of the India lies in Indian Ocean less lightning activity expected - Also the height of the magnetic field lines (~ 800 km max.) connecting conjugate regions lies in the ionosphere Probable absorption of signals Indian Conjugate Region Not enough VLF activity expected
69 Concluding remark: Continuous monitoring of these waves allow for the quantitative physical analysis of electromagnetic phenomena in the ionosphere and magnetosphere such as: - Radio atmospheric, - Whistlers, - VLF emissions, - Lightning induced electron precipitation (LEP), - Cosmic gamma-ray flares, - Solar flares - Geomagnetic storms, etc., - VLF waves as precursors to Earthquakes
70
71
72 1. Hiss 2. Discrete Emissions Rising tones Falling tones Hook. Combinations. Spectral forms of Emissions apart from Whistler 3. Periodic emissions Dispersive Non-dispersive Multiphase Drifting 4. Chorus 5. Quasi-periodic Emissions 6. Triggered Emissions
73 Spectrogram of different type of Emissions observed in India Generation mechanism of VLF emissions are poorly understood, and they remain the focus of intense research activity.
74 Some examples of observation Spectrogram of Hissler (Ref: Singh et al., GRL, 2004)
75 Non-Ducted Whistlers With the advent of the Satellites, VLF receivers were placed on rockets and satellites. These space borne receivers detected whistlers whose paths deviated from the Earths magnetic field line. Such whistlers are called as unducted or nonducted whistlers By nature of their propagation mode, these are mainly observed by satellites
76 Whistler observed onboard DE 1 satellite These observations have led to new understanding of whistler-mode propagation and to the deduction of important plasma parameters in space Two mode of Propagation: Pro-resonance (PR) mode of propagation: It is characterized by large wave normal angles along the propagation path. The wave normal angle increases rapidly along the ray path and reaches the resonance cone. Pro-longitudinal (PL) mode of propagation: It is characterized by propagation with the wave normals of the waves inside a characteristic cone relative to the geomagnetic field.
77 Low Mid - High Latitude
VLF Research in India and setup of AWESOME Receivers
 VLF Research in India and setup of AWESOME Receivers B. Veenadhari, Rajesh Singh, P. Vohat and A. Maurya Indian Institute of Geomagnetism, Navi Mumbai, India P. Pant, ARIES, Nainital, Uttrakhand, India
VLF Research in India and setup of AWESOME Receivers B. Veenadhari, Rajesh Singh, P. Vohat and A. Maurya Indian Institute of Geomagnetism, Navi Mumbai, India P. Pant, ARIES, Nainital, Uttrakhand, India
NON-TYPICAL SERIES OF QUASI-PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS
 NON-TYPICAL SERIES OF QUASI-PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS J. Manninen 1, N. Kleimenova 2, O. Kozyreva 2 1 Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory, Finland, e-mail: jyrki.manninen@sgo.fi; 2 Institute of Physics of the
NON-TYPICAL SERIES OF QUASI-PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS J. Manninen 1, N. Kleimenova 2, O. Kozyreva 2 1 Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory, Finland, e-mail: jyrki.manninen@sgo.fi; 2 Institute of Physics of the
Nighttime D-region equivalent electron density determined from tweek sferics observed in the South Pacific Region
 Earth Planets Space, 61, 905 911, 2009 Nighttime D-region equivalent electron density determined from tweek sferics observed in the South Pacific Region Sushil Kumar 1, Anil Deo 2, and V. Ramachandran
Earth Planets Space, 61, 905 911, 2009 Nighttime D-region equivalent electron density determined from tweek sferics observed in the South Pacific Region Sushil Kumar 1, Anil Deo 2, and V. Ramachandran
Study of Very Low Frequency (VLF) Phenomena at Maitri, Antarctica
 Nineteenth Indian Expedition to Antarctica, Scientific Report, 2004 Department of Ocean Development, Technical Publication No. 17, pp 107-114 Study of Very Low Frequency (VLF) Phenomena at Maitri, Antarctica
Nineteenth Indian Expedition to Antarctica, Scientific Report, 2004 Department of Ocean Development, Technical Publication No. 17, pp 107-114 Study of Very Low Frequency (VLF) Phenomena at Maitri, Antarctica
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION The dependence of society to technology increased in recent years as the technology has enhanced. increased. Moreover, in addition to technology, the dependence of society to nature
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION The dependence of society to technology increased in recent years as the technology has enhanced. increased. Moreover, in addition to technology, the dependence of society to nature
Modeling and Subionospheric VLF perturbations caused by direct and indirect effects of lightning
 Modeling and Subionospheric VLF perturbations caused by direct and indirect effects of lightning Prepared by Benjamin Cotts Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global
Modeling and Subionospheric VLF perturbations caused by direct and indirect effects of lightning Prepared by Benjamin Cotts Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global
SPACE WEATHER SIGNATURES ON VLF RADIO WAVES RECORDED IN BELGRADE
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 80 (2006), 191-195 Contributed paper SPACE WEATHER SIGNATURES ON VLF RADIO WAVES RECORDED IN BELGRADE DESANKA ŠULIĆ1, VLADIMIR ČADEŽ2, DAVORKA GRUBOR 3 and VIDA ŽIGMAN4
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 80 (2006), 191-195 Contributed paper SPACE WEATHER SIGNATURES ON VLF RADIO WAVES RECORDED IN BELGRADE DESANKA ŠULIĆ1, VLADIMIR ČADEŽ2, DAVORKA GRUBOR 3 and VIDA ŽIGMAN4
Precipitation of Energetic Protons from the Radiation Belts. using Lower Hybrid Waves
 Precipitation of Energetic Protons from the Radiation Belts using Lower Hybrid Waves Lower hybrid waves are quasi-electrostatic whistler mode waves whose wave normal direction is very close to the whistler
Precipitation of Energetic Protons from the Radiation Belts using Lower Hybrid Waves Lower hybrid waves are quasi-electrostatic whistler mode waves whose wave normal direction is very close to the whistler
The Earth s Atmosphere
 ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 May 5 and 7, 2010 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 May 5 and 7, 2010 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers & Antennas - Listening to the sounds of the atmosphere
 VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers & Antennas - Listening to the sounds of the atmosphere A presentation to Manly-Warringah Radio Society from Geoff Osborne VK2TGO VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers and Antennas 1.
VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers & Antennas - Listening to the sounds of the atmosphere A presentation to Manly-Warringah Radio Society from Geoff Osborne VK2TGO VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers and Antennas 1.
A generation mechanism of chorus emissions using BWO theory
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series A generation mechanism of chorus emissions using BWO theory To cite this article: Ashutosh K Singh et al 2010 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 208 012067 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series A generation mechanism of chorus emissions using BWO theory To cite this article: Ashutosh K Singh et al 2010 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 208 012067 View the article online
AWESOME for educational and research use
 SuperSID - a small-version AWESOME for educational and research use By Deborah Scherrer Tim Huynh Stanford University Solar Center 1 What I am going to talk about What is this project? What can the instrument
SuperSID - a small-version AWESOME for educational and research use By Deborah Scherrer Tim Huynh Stanford University Solar Center 1 What I am going to talk about What is this project? What can the instrument
Study of the morphology of the low-latitude D region ionosphere using the method of tweeks observed at Buon Ma Thuot, Dak Lak
 Vietnam Journal of Earth Sciences, 38(4), 37-338, DOI: 10.1565/0866-7187/38/4/8794 (VAST) Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology Vietnam Journal of Earth Sciences http://www.vjs.ac.vn/index.php/jse
Vietnam Journal of Earth Sciences, 38(4), 37-338, DOI: 10.1565/0866-7187/38/4/8794 (VAST) Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology Vietnam Journal of Earth Sciences http://www.vjs.ac.vn/index.php/jse
ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 November 3 and 5, The Atmosphere and Ionosphere
 ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 November 3 and 5, 2008 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 November 3 and 5, 2008 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
Near Earth space monitoring with LOFAR PL610 station in Borówiec
 Near Earth space monitoring with LOFAR PL610 station in Borówiec Hanna Rothkaehl 1, Mariusz Pożoga 1, Marek Morawski 1, Barbara Matyjasiak 1, Dorota Przepiórka 1, Marcin Grzesiak 1 and Roman Wronowski
Near Earth space monitoring with LOFAR PL610 station in Borówiec Hanna Rothkaehl 1, Mariusz Pożoga 1, Marek Morawski 1, Barbara Matyjasiak 1, Dorota Przepiórka 1, Marcin Grzesiak 1 and Roman Wronowski
World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology WJERT
 wjert, 2018, Vol. 4, Issue 2, 505-516. Original Article ISSN 2454-695X WJERT www.wjert.org SJIF Impact Factor: 5.218 OBSERVATION OF PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS AND WHISTLER- TRIGGERED PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS
wjert, 2018, Vol. 4, Issue 2, 505-516. Original Article ISSN 2454-695X WJERT www.wjert.org SJIF Impact Factor: 5.218 OBSERVATION OF PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS AND WHISTLER- TRIGGERED PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS
ALTITUDE PROFILES OF ELECTRON DENSITY DURING LEP EVENTS FROM VLF MONITORING OF THE LOWER IONOSPHERE
 The Sharjah-Stanford AWESOME VLF Workshop Sharjah, UAE, Feb 22-24, 2010. ALTITUDE PROFILES OF ELECTRON DENSITY DURING LEP EVENTS FROM VLF MONITORING OF THE LOWER IONOSPHERE Desanka Šulić 1 and Vladimir
The Sharjah-Stanford AWESOME VLF Workshop Sharjah, UAE, Feb 22-24, 2010. ALTITUDE PROFILES OF ELECTRON DENSITY DURING LEP EVENTS FROM VLF MONITORING OF THE LOWER IONOSPHERE Desanka Šulić 1 and Vladimir
HAARP Generated ELF/VLF Waves for Magnetospheric Probing. Mark Gołkowski
 HAARP Generated ELF/VLF Waves for Magnetospheric Probing Mark Gołkowski University of Colorado Denver M.B. Cohen, U. S. Inan, D. Piddyachiy Stanford University RF Ionospheric Workshop 20 April 2010 Outline
HAARP Generated ELF/VLF Waves for Magnetospheric Probing Mark Gołkowski University of Colorado Denver M.B. Cohen, U. S. Inan, D. Piddyachiy Stanford University RF Ionospheric Workshop 20 April 2010 Outline
Abstract. Introduction
 Subionospheric VLF measurements of the effects of geomagnetic storms on the mid-latitude D-region W. B. Peter, M. Chevalier, and U. S. Inan Stanford University, 350 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305 Abstract
Subionospheric VLF measurements of the effects of geomagnetic storms on the mid-latitude D-region W. B. Peter, M. Chevalier, and U. S. Inan Stanford University, 350 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305 Abstract
Some studies of solar flare effects on the propagation of sferics and a transmitted signal
 Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 38, October 2009, pp. 260-265 Some studies of solar flare effects on the propagation of sferics and a transmitted signal B K De 1, S S De 2,*, B Bandyopadhyay
Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 38, October 2009, pp. 260-265 Some studies of solar flare effects on the propagation of sferics and a transmitted signal B K De 1, S S De 2,*, B Bandyopadhyay
The Ionosphere and Thermosphere: a Geospace Perspective
 The Ionosphere and Thermosphere: a Geospace Perspective John Foster, MIT Haystack Observatory CEDAR Student Workshop June 24, 2018 North America Introduction My Geospace Background (Who is the Lecturer?
The Ionosphere and Thermosphere: a Geospace Perspective John Foster, MIT Haystack Observatory CEDAR Student Workshop June 24, 2018 North America Introduction My Geospace Background (Who is the Lecturer?
Chapter 6 Propagation
 Chapter 6 Propagation Al Penney VO1NO Objectives To become familiar with: Classification of waves wrt propagation; Factors that affect radio wave propagation; and Propagation characteristics of Amateur
Chapter 6 Propagation Al Penney VO1NO Objectives To become familiar with: Classification of waves wrt propagation; Factors that affect radio wave propagation; and Propagation characteristics of Amateur
Storms in Earth s ionosphere
 Storms in Earth s ionosphere Archana Bhattacharyya Indian Institute of Geomagnetism IISF 2017, WSE Conclave; Anna University, Chennai Earth s Ionosphere Ionosphere is the region of the atmosphere in which
Storms in Earth s ionosphere Archana Bhattacharyya Indian Institute of Geomagnetism IISF 2017, WSE Conclave; Anna University, Chennai Earth s Ionosphere Ionosphere is the region of the atmosphere in which
IONOSPHERIC SIGNATURES OF SEISMIC EVENTS AS OBSERVED BY THE DEMETER SATELLITE
 IONOSPHERIC SIGNATURES OF SEISMIC EVENTS AS OBSERVED BY THE DEMETER SATELLITE M. Parrot and F. Lefeuvre LPC2E/CNRS, 3 A Av Recherche Scientifique 45071 Orleans cedex 2 France lefeuvre@cnrs-orleans.fr URSI
IONOSPHERIC SIGNATURES OF SEISMIC EVENTS AS OBSERVED BY THE DEMETER SATELLITE M. Parrot and F. Lefeuvre LPC2E/CNRS, 3 A Av Recherche Scientifique 45071 Orleans cedex 2 France lefeuvre@cnrs-orleans.fr URSI
Study of small scale plasma irregularities. Đorđe Stevanović
 Study of small scale plasma irregularities in the ionosphere Đorđe Stevanović Overview 1. Global Navigation Satellite Systems 2. Space weather 3. Ionosphere and its effects 4. Case study a. Instruments
Study of small scale plasma irregularities in the ionosphere Đorđe Stevanović Overview 1. Global Navigation Satellite Systems 2. Space weather 3. Ionosphere and its effects 4. Case study a. Instruments
SMART SENSING OF MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA BY MEANS OF WHISTLER MODE SIGNALS OBSERVED AT A LOW LATITUDE INDIAN GROUND STATION SRINAGAR (L = 1.
 International Journal of Physics and Research (IJPR) ISSN 2250-0030 Vol. 3, Issue 1, Mar 2013, 11-16 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SMART SENSING OF MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA BY MEANS OF WHISTLER MODE SIGNALS OBSERVED AT
International Journal of Physics and Research (IJPR) ISSN 2250-0030 Vol. 3, Issue 1, Mar 2013, 11-16 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SMART SENSING OF MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA BY MEANS OF WHISTLER MODE SIGNALS OBSERVED AT
Scientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and ElectroDynamics - Data Assimilation (IDED-DA) Model
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Scientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and ElectroDynamics - Data Assimilation
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Scientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and ElectroDynamics - Data Assimilation
Research Letter Waveguide Parameters of 19.8 khz Signal Propagating over a Long Path
 Research Letters in Physics Volume 29, Article ID 216373, 4 pages doi:1.1155/29/216373 Research Letter Waveguide Parameters of 19.8 khz Signal Propagating over a Long Path Sushil Kumar School of Engineering
Research Letters in Physics Volume 29, Article ID 216373, 4 pages doi:1.1155/29/216373 Research Letter Waveguide Parameters of 19.8 khz Signal Propagating over a Long Path Sushil Kumar School of Engineering
The Effect of Geomagnetic Storm in the Ionosphere using N-h Profiles.
 The Effect of Geomagnetic Storm in the Ionosphere using N-h Profiles. J.C. Morka * ; D.N. Nwachuku; and D.A. Ogwu. Physics Department, College of Education, Agbor, Nigeria E-mail: johnmorka84@gmail.com
The Effect of Geomagnetic Storm in the Ionosphere using N-h Profiles. J.C. Morka * ; D.N. Nwachuku; and D.A. Ogwu. Physics Department, College of Education, Agbor, Nigeria E-mail: johnmorka84@gmail.com
Ionospheric Absorption
 Ionospheric Absorption Prepared by Forrest Foust Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global AWESOME Network VLF Injection Into the Magnetosphere Earth-based VLF
Ionospheric Absorption Prepared by Forrest Foust Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global AWESOME Network VLF Injection Into the Magnetosphere Earth-based VLF
Using the Radio Spectrum to Understand Space Weather
 Using the Radio Spectrum to Understand Space Weather Ray Greenwald Virginia Tech Topics to be Covered What is Space Weather? Origins and impacts Analogies with terrestrial weather Monitoring Space Weather
Using the Radio Spectrum to Understand Space Weather Ray Greenwald Virginia Tech Topics to be Covered What is Space Weather? Origins and impacts Analogies with terrestrial weather Monitoring Space Weather
PoS(2nd MCCT -SKADS)003
 The Earth's ionosphere: structure and composition. Dispersive effects, absorption and emission in EM wave propagation 1 Observatorio Astronómico Nacional Calle Alfonso XII, 3; E-28014 Madrid, Spain E-mail:
The Earth's ionosphere: structure and composition. Dispersive effects, absorption and emission in EM wave propagation 1 Observatorio Astronómico Nacional Calle Alfonso XII, 3; E-28014 Madrid, Spain E-mail:
4/18/2012. Supplement T3. 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups. Amateur Radio Technician Class
 Amateur Radio Technician Class Element 2 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 2 SUB-ELEMENTS Technician Licensing Class Supplement T3 Radio Wave Characteristics 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups T1 - FCC Rules, descriptions
Amateur Radio Technician Class Element 2 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 2 SUB-ELEMENTS Technician Licensing Class Supplement T3 Radio Wave Characteristics 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups T1 - FCC Rules, descriptions
The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave Science Instrument
 The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave Science Instrument Roger Karlsson Space Research Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Graz Graz in Space, September 7, 2006 The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave
The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave Science Instrument Roger Karlsson Space Research Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Graz Graz in Space, September 7, 2006 The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave
IONOSPHERE EFFECTS ON GPS/RF COMMUNICATION, ELECTRIC, METAL NETWORKS AND SPACECRAFTS OSMAN AKGÜN
 IONOSPHERE EFFECTS ON GPS/RF COMMUNICATION, ELECTRIC, METAL NETWORKS AND SPACECRAFTS 2119212 OSMAN AKGÜN IONOSPHERE IONOSPHERE EFFECTS POSSIBLE EFFECTS GPS errors Atomic oxygen attack Spacecraft charging
IONOSPHERE EFFECTS ON GPS/RF COMMUNICATION, ELECTRIC, METAL NETWORKS AND SPACECRAFTS 2119212 OSMAN AKGÜN IONOSPHERE IONOSPHERE EFFECTS POSSIBLE EFFECTS GPS errors Atomic oxygen attack Spacecraft charging
What is Space Weather? THE ACTIVE SUN
 Aardvark Roost AOC Space Weather in Southern Africa Hannes Coetzee 1 What is Space Weather? THE ACTIVE SUN 2 The Violant Sun 3 What is Space Weather? Solar eruptive events (solar flares, coronal Mass Space
Aardvark Roost AOC Space Weather in Southern Africa Hannes Coetzee 1 What is Space Weather? THE ACTIVE SUN 2 The Violant Sun 3 What is Space Weather? Solar eruptive events (solar flares, coronal Mass Space
CONSTRUCTING A LOW-COST ELF/VLF REMOTE SENSING TO OBSERVE TWEEK SFERICS GENERATED BY LIGHTNING DISCHARGES
 CONSTRUCTING A LOW-COST ELF/VLF REMOTE SENSING TO OBSERVE TWEEK SFERICS GENERATED BY LIGHTNING DISCHARGES Le MINH TAN, Marjan MARBOUTI and Keyvan GHANBARI Department of Physics, Faculty of Natural Science
CONSTRUCTING A LOW-COST ELF/VLF REMOTE SENSING TO OBSERVE TWEEK SFERICS GENERATED BY LIGHTNING DISCHARGES Le MINH TAN, Marjan MARBOUTI and Keyvan GHANBARI Department of Physics, Faculty of Natural Science
Introduction To The Ionosphere
 Introduction To The Ionosphere John Bosco Habarulema Radar School 12 13 September 2015, SANSA, What is a radar? This being a radar school... RAdio Detection And Ranging To determine the range, R, R=Ct/2,
Introduction To The Ionosphere John Bosco Habarulema Radar School 12 13 September 2015, SANSA, What is a radar? This being a radar school... RAdio Detection And Ranging To determine the range, R, R=Ct/2,
Ionospheric Propagation
 Ionospheric Nick Massey VA7NRM 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio Waves are a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Visible Light is also a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Radio Waves behave a lot like light
Ionospheric Nick Massey VA7NRM 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio Waves are a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Visible Light is also a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Radio Waves behave a lot like light
Radiation and Particles from the. Sun
 2017 Radiation and Particles from the Photons Sun Photons (300000km/s ~ 8m 20s) radio waves, infra red, visible light, ultra violet, x-ray, x galactic waves, Solar Flux (30000km/s ~ 8m 20s) The 10.7 cm
2017 Radiation and Particles from the Photons Sun Photons (300000km/s ~ 8m 20s) radio waves, infra red, visible light, ultra violet, x-ray, x galactic waves, Solar Flux (30000km/s ~ 8m 20s) The 10.7 cm
4/29/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Radio Wave Propagation. Radio Wave Propagation. Radio Wave Propagation.
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G3 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 G4 Amateur Radio
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G3 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 G4 Amateur Radio
RemoteSensingofMidUpperAtmosphereusingELFVLFWaves Strictly as per the compliance and regulations of:
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: A Physics and Space Science Volume 18 Issue 10 Version 1.0 Year 2018 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: A Physics and Space Science Volume 18 Issue 10 Version 1.0 Year 2018 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Influence of Major Geomagnetic Storms Occurred in the Year 2011 On TEC Over Bangalore Station In India
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 105-110 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Influence of Major
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 105-110 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Influence of Major
The Newly Formed LoCSST
 The Newly Formed LoCSST Lowell Center for Space Science and Technology 3 rd floor, Wannalancit Mill LoCSST Older Research Institutions UMLCAR (Center for Atmospheric Research) SSL (Space Sciences Lab)
The Newly Formed LoCSST Lowell Center for Space Science and Technology 3 rd floor, Wannalancit Mill LoCSST Older Research Institutions UMLCAR (Center for Atmospheric Research) SSL (Space Sciences Lab)
Plasma in the ionosphere Ionization and Recombination
 Plasma in the ionosphere Ionization and Recombination Jamil Muhammad Supervisor: Professor kjell Rönnmark 1 Contents: 1. Introduction 3 1.1 History.3 1.2 What is the ionosphere?...4 2. Ionization and recombination.5
Plasma in the ionosphere Ionization and Recombination Jamil Muhammad Supervisor: Professor kjell Rönnmark 1 Contents: 1. Introduction 3 1.1 History.3 1.2 What is the ionosphere?...4 2. Ionization and recombination.5
Observation of discrete VLF emissions at low latitudes and their generation mechanism
 Earth Planets Space, 56, 1067 1074, 2004 Observation of discrete VLF emissions at low latitudes and their generation mechanism Abhay Kumar Singh 1 and R. P. Singh 2 1 Department of Physics, Maharaja College,
Earth Planets Space, 56, 1067 1074, 2004 Observation of discrete VLF emissions at low latitudes and their generation mechanism Abhay Kumar Singh 1 and R. P. Singh 2 1 Department of Physics, Maharaja College,
Anomalistic wave propagation phenomena in whistler waveforms detected on wide-band VLF recordings of the DEMETER satellite
 International Symposium DEMETER. Results of the DEMETER project and of the recent advances in the seismo-electromagnetic effects and the ionospheric physic CNES, Toulouse-Labege, 14-16 June 2006 Anomalistic
International Symposium DEMETER. Results of the DEMETER project and of the recent advances in the seismo-electromagnetic effects and the ionospheric physic CNES, Toulouse-Labege, 14-16 June 2006 Anomalistic
The Ionosphere and its Impact on Communications and Navigation. Tim Fuller-Rowell NOAA Space Environment Center and CIRES, University of Colorado
 The Ionosphere and its Impact on Communications and Navigation Tim Fuller-Rowell NOAA Space Environment Center and CIRES, University of Colorado Customers for Ionospheric Information High Frequency (HF)
The Ionosphere and its Impact on Communications and Navigation Tim Fuller-Rowell NOAA Space Environment Center and CIRES, University of Colorado Customers for Ionospheric Information High Frequency (HF)
RESONANCE Project for Studies of Wave-Particle Interactions in the Inner Magnetosphere. Anatoly Petrukovich and Resonance team
 RESONANCE Project for Studies of Wave-Particle Interactions in the Inner Magnetosphere Ω Anatoly Petrukovich and Resonance team РЕЗОНАНС RESONANCE Resonance Inner magnetospheric mission Space weather Ring
RESONANCE Project for Studies of Wave-Particle Interactions in the Inner Magnetosphere Ω Anatoly Petrukovich and Resonance team РЕЗОНАНС RESONANCE Resonance Inner magnetospheric mission Space weather Ring
Perturbations of midlatitude subionospheric VLF signals associated with lower ionospheric disturbances during major geomagnetic storms
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005ja011346, 2006 Perturbations of midlatitude subionospheric VLF signals associated with lower ionospheric disturbances during major geomagnetic
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005ja011346, 2006 Perturbations of midlatitude subionospheric VLF signals associated with lower ionospheric disturbances during major geomagnetic
The relationship between median intensities of electromagnetic emissions in the VLF range and lightning activity
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, The relationship between median intensities of electromagnetic emissions in the VLF range and lightning activity F. Němec 1,2,3, O. Santolík
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, The relationship between median intensities of electromagnetic emissions in the VLF range and lightning activity F. Němec 1,2,3, O. Santolík
Ionospheric and cosmic ray monitoring: Recent developments at the RMI
 Solar Terrestrial Centre of Excellence Ionospheric and cosmic ray monitoring: Recent developments at the RMI Danislav Sapundjiev, Stan Stankov, Tobias Verhulst, Jean-Claude Jodogne Royal (RMI) Ringlaan
Solar Terrestrial Centre of Excellence Ionospheric and cosmic ray monitoring: Recent developments at the RMI Danislav Sapundjiev, Stan Stankov, Tobias Verhulst, Jean-Claude Jodogne Royal (RMI) Ringlaan
Role of VLF power line harmonic radiation in precipitating energetic electrons at high latitude
 Indian Journal of adio & Space Physics Vol. 38, April 009, pp. 74-79 ole of VLF power line harmonic radiation in precipitating energetic electrons at high latitude am Prakash *, D D Gupta & Manoj Kumar
Indian Journal of adio & Space Physics Vol. 38, April 009, pp. 74-79 ole of VLF power line harmonic radiation in precipitating energetic electrons at high latitude am Prakash *, D D Gupta & Manoj Kumar
DEVELOPMENT OF THE NEW ELF/VLF RECEIVER FOR DETECTING THE SUDDEN IONOSPHERIC DISTURBANCES
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE NEW ELF/VLF RECEIVER FOR DETECTING THE SUDDEN IONOSPHERIC DISTURBANCES Le MINH TAN 1, Keyvan GHANBARI 2 1 Department of Physics, Faculty of Natural Science and Technology, Tay Nguyen
DEVELOPMENT OF THE NEW ELF/VLF RECEIVER FOR DETECTING THE SUDDEN IONOSPHERIC DISTURBANCES Le MINH TAN 1, Keyvan GHANBARI 2 1 Department of Physics, Faculty of Natural Science and Technology, Tay Nguyen
Ground based measurements of ionospheric turbulence manifestations induced by the VLF transmitter ABSTRACT
 Ground based measurements of ionospheric turbulence manifestations induced by the VLF transmitter Dmitry S. Kotik, 1 Fedor I. Vybornov, 1 Alexander V. Ryabov, 1 Alexander V. Pershin 1 and Vladimir A. Yashnov
Ground based measurements of ionospheric turbulence manifestations induced by the VLF transmitter Dmitry S. Kotik, 1 Fedor I. Vybornov, 1 Alexander V. Ryabov, 1 Alexander V. Pershin 1 and Vladimir A. Yashnov
V-shaped VLF streaks recorded on DEMETER above powerful thunderstorms
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013336, 2008 V-shaped VLF streaks recorded on DEMETER above powerful thunderstorms M. Parrot, 1,2 U. S. Inan, 3
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013336, 2008 V-shaped VLF streaks recorded on DEMETER above powerful thunderstorms M. Parrot, 1,2 U. S. Inan, 3
Relationship between median intensities of electromagnetic emissions in the VLF range and lightning activity
 Relationship between median intensities of electromagnetic emissions in the VLF range and lightning activity F Němec, O Santolík, Michel Parrot, C.J. Rodger To cite this version: F Němec, O Santolík, Michel
Relationship between median intensities of electromagnetic emissions in the VLF range and lightning activity F Němec, O Santolík, Michel Parrot, C.J. Rodger To cite this version: F Němec, O Santolík, Michel
Regional ionospheric disturbances during magnetic storms. John Foster
 Regional ionospheric disturbances during magnetic storms John Foster Regional Ionospheric Disturbances John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory Regional Disturbances Meso-Scale (1000s km) Storm Enhanced Density
Regional ionospheric disturbances during magnetic storms John Foster Regional Ionospheric Disturbances John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory Regional Disturbances Meso-Scale (1000s km) Storm Enhanced Density
Sub-HF Search and Acquisition
 SECRET SP9KE Sub-HF Search and Acquisition (U) This report summarizes the history ofsub-hf search and discusses its present value to and future needs by SIGINT. The report concludes that a small automated
SECRET SP9KE Sub-HF Search and Acquisition (U) This report summarizes the history ofsub-hf search and discusses its present value to and future needs by SIGINT. The report concludes that a small automated
MIDLATITUDE D REGION VARIATIONS MEASURED FROM BROADBAND RADIO ATMOSPHERICS
 MIDLATITUDE D REGION VARIATIONS MEASURED FROM BROADBAND RADIO ATMOSPHERICS by Feng Han Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Steven A. Cummer, Advisor David
MIDLATITUDE D REGION VARIATIONS MEASURED FROM BROADBAND RADIO ATMOSPHERICS by Feng Han Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Steven A. Cummer, Advisor David
Space-born system for on-line precursors monitoring of eathquakes,, natural and man-made made catastrophes
 Space-born system for on-line precursors monitoring of eathquakes,, natural and man-made made catastrophes The main goal of the Project In my brief report, I would like to inform about the work on developing
Space-born system for on-line precursors monitoring of eathquakes,, natural and man-made made catastrophes The main goal of the Project In my brief report, I would like to inform about the work on developing
Ionospheric Effects on Aviation
 Ionospheric Effects on Aviation Recent experience in the observation and research of ionospheric irregularities, gradient anomalies, depletion walls, etc. in USA and Europe Stan Stankov, René Warnant,
Ionospheric Effects on Aviation Recent experience in the observation and research of ionospheric irregularities, gradient anomalies, depletion walls, etc. in USA and Europe Stan Stankov, René Warnant,
1. Terrestrial propagation
 Rec. ITU-R P.844-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.844-1 * IONOSPHERIC FACTORS AFFECTING FREQUENCY SHARING IN THE VHF AND UHF BANDS (30 MHz-3 GHz) (Question ITU-R 218/3) (1992-1994) Rec. ITU-R PI.844-1 The ITU
Rec. ITU-R P.844-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.844-1 * IONOSPHERIC FACTORS AFFECTING FREQUENCY SHARING IN THE VHF AND UHF BANDS (30 MHz-3 GHz) (Question ITU-R 218/3) (1992-1994) Rec. ITU-R PI.844-1 The ITU
The Global Atmospheric Electric Circuit
 The Global Atmospheric Electric Circuit Colin Price Department of Geophysics and Planetary Sciences Tel Aviv University Israel cprice@flash.tau.ac.il Historical Background 1752 Lemonnier discovered that
The Global Atmospheric Electric Circuit Colin Price Department of Geophysics and Planetary Sciences Tel Aviv University Israel cprice@flash.tau.ac.il Historical Background 1752 Lemonnier discovered that
Ionospheric effects of whistler waves from rocket-triggered lightning
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049869, 2011 Ionospheric effects of whistler waves from rocket-triggered lightning B. R. T. Cotts, 1 M. Gołkowski, 1 and R. C. Moore 2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049869, 2011 Ionospheric effects of whistler waves from rocket-triggered lightning B. R. T. Cotts, 1 M. Gołkowski, 1 and R. C. Moore 2 Received
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 4 Transmission Media
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 4 Transmission Media Ninth Edition by William Stallings Data and Computer Communications, Ninth Edition by William Stallings, (c) Pearson Education - Prentice Hall,
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 4 Transmission Media Ninth Edition by William Stallings Data and Computer Communications, Ninth Edition by William Stallings, (c) Pearson Education - Prentice Hall,
Analysis of Ionospheric Anomalies due to Space Weather Conditions by using GPS-TEC Variations
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Analysis of Ionospheric Anomalies due to Space Weather Conditions by using GPS-TEC Variations Asst. Prof. Dr. Mustafa ULUKAVAK 1,
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Analysis of Ionospheric Anomalies due to Space Weather Conditions by using GPS-TEC Variations Asst. Prof. Dr. Mustafa ULUKAVAK 1,
Dartmouth College SuperDARN Radars
 Dartmouth College SuperDARN Radars Under the guidance of Thayer School professor Simon Shepherd, a pair of backscatter radars were constructed in the desert of central Oregon over the Summer and Fall of
Dartmouth College SuperDARN Radars Under the guidance of Thayer School professor Simon Shepherd, a pair of backscatter radars were constructed in the desert of central Oregon over the Summer and Fall of
Models of ionospheric VLF absorption of powerful ground based transmitters
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl054437, 2012 Models of ionospheric VLF absorption of powerful ground based transmitters M. B. Cohen, 1 N. G. Lehtinen, 1 and U. S. Inan 1,2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl054437, 2012 Models of ionospheric VLF absorption of powerful ground based transmitters M. B. Cohen, 1 N. G. Lehtinen, 1 and U. S. Inan 1,2 Received
Space Weather and Propagation JANUARY 14, 2017
 Space Weather and Propagation MARTIN BUEHRING -KB4MG ELEC T R ICAL ENGINEER, A M AT EUR EXTRA CLASS LICENSE HOLDER JANUARY 14, 2017 Why know about Space Weather? Our SUN has an enormous affect not only
Space Weather and Propagation MARTIN BUEHRING -KB4MG ELEC T R ICAL ENGINEER, A M AT EUR EXTRA CLASS LICENSE HOLDER JANUARY 14, 2017 Why know about Space Weather? Our SUN has an enormous affect not only
Estimation of magnetospheric plasma parameters from whistlers observed at low latitudes
 Estimation of magnetospheric plasma parameters from whistlers observed at low latitudes M. Altaf* and M. M. Ahmad Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Hazratbal, Srinagar 190 006, India
Estimation of magnetospheric plasma parameters from whistlers observed at low latitudes M. Altaf* and M. M. Ahmad Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Hazratbal, Srinagar 190 006, India
Daytime modelling of VLF radio waves over land and sea, comparison with data from DEMETER Satellite
 Daytime modelling of VLF radio waves over land and sea, comparison with data from DEMETER Satellite S. G. Meyer 1,2, A. B. Collier 1,2, C. J. Rodger 3 1 SANSA Space Science, Hermanus, South Africa 2 School
Daytime modelling of VLF radio waves over land and sea, comparison with data from DEMETER Satellite S. G. Meyer 1,2, A. B. Collier 1,2, C. J. Rodger 3 1 SANSA Space Science, Hermanus, South Africa 2 School
ESS 7. Lectures 18, 19 and 20 November 14, 17 and 19. Technology and Space Weather
 ESS 7 Lectures 18, 19 and 20 November 14, 17 and 19 Technology and Space Weather Space Weather Effects on Satellite Lifetimes: Atmospheric Drag A satellite would orbit forever if gravity was the only force
ESS 7 Lectures 18, 19 and 20 November 14, 17 and 19 Technology and Space Weather Space Weather Effects on Satellite Lifetimes: Atmospheric Drag A satellite would orbit forever if gravity was the only force
C4: Collaborative Work on Novel Approaches to ELF/VLF Generation
 C4: Collaborative Work on Novel Approaches to ELF/VLF Generation Mark Golkowski University of Colorado Denver Robb Moore, Umran Inan, Morris Cohen, Ray Ingram, Tom Lee, Ed Kennedy, Paul Kossey C4: Collaborative
C4: Collaborative Work on Novel Approaches to ELF/VLF Generation Mark Golkowski University of Colorado Denver Robb Moore, Umran Inan, Morris Cohen, Ray Ingram, Tom Lee, Ed Kennedy, Paul Kossey C4: Collaborative
Comparing the Low-- and Mid Latitude Ionosphere and Electrodynamics of TIE-GCM and the Coupled GIP TIE-GCM
 Comparing the Low-- and Mid Latitude Ionosphere and Electrodynamics of TIE-GCM and the Coupled GIP TIE-GCM Clarah Lelei Bryn Mawr College Mentors: Dr. Astrid Maute, Dr. Art Richmond and Dr. George Millward
Comparing the Low-- and Mid Latitude Ionosphere and Electrodynamics of TIE-GCM and the Coupled GIP TIE-GCM Clarah Lelei Bryn Mawr College Mentors: Dr. Astrid Maute, Dr. Art Richmond and Dr. George Millward
D region ionosphere response to the total solar eclipse of 22 July 2009 deduced from ELF VLF tweek observations in the Indian sector
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011ja016641, 2011 D region ionosphere response to the total solar eclipse of 22 July 2009 deduced from ELF VLF tweek observations in the Indian
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011ja016641, 2011 D region ionosphere response to the total solar eclipse of 22 July 2009 deduced from ELF VLF tweek observations in the Indian
Monitoring the polar cap/ auroral ionosphere: Industrial applications. P. T. Jayachandran Physics Department University of New Brunswick Fredericton
 Monitoring the polar cap/ auroral ionosphere: Industrial applications P. T. Jayachandran Physics Department University of New Brunswick Fredericton Outline Ionosphere and its effects on modern and old
Monitoring the polar cap/ auroral ionosphere: Industrial applications P. T. Jayachandran Physics Department University of New Brunswick Fredericton Outline Ionosphere and its effects on modern and old
Study of the Ionosphere Irregularities Caused by Space Weather Activity on the Base of GNSS Measurements
 Study of the Ionosphere Irregularities Caused by Space Weather Activity on the Base of GNSS Measurements Iu. Cherniak 1, I. Zakharenkova 1,2, A. Krankowski 1 1 Space Radio Research Center,, University
Study of the Ionosphere Irregularities Caused by Space Weather Activity on the Base of GNSS Measurements Iu. Cherniak 1, I. Zakharenkova 1,2, A. Krankowski 1 1 Space Radio Research Center,, University
A generic description of planetary aurora
 A generic description of planetary aurora J. De Keyser, R. Maggiolo, and L. Maes Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, Brussels, Belgium Johan.DeKeyser@aeronomie.be Context We consider a rotating planetary
A generic description of planetary aurora J. De Keyser, R. Maggiolo, and L. Maes Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, Brussels, Belgium Johan.DeKeyser@aeronomie.be Context We consider a rotating planetary
Ionospheric Propagation
 Ionospheric Propagation Page 1 Ionospheric Propagation The ionosphere exists between about 90 and 1000 km above the earth s surface. Radiation from the sun ionizes atoms and molecules here, liberating
Ionospheric Propagation Page 1 Ionospheric Propagation The ionosphere exists between about 90 and 1000 km above the earth s surface. Radiation from the sun ionizes atoms and molecules here, liberating
General Classs Chapter 7
 General Classs Chapter 7 Radio Wave Propagation Bob KA9BHD Eric K9VIC Learning Objectives Teach you enough to get all the propagation questions right during the VE Session Learn a few things from you about
General Classs Chapter 7 Radio Wave Propagation Bob KA9BHD Eric K9VIC Learning Objectives Teach you enough to get all the propagation questions right during the VE Session Learn a few things from you about
The Association Between VLF and ELF Chorus Emissions and Electron Precipitation
 The Association Between VLF and ELF Chorus Emissions and Electron Precipitation Remmy Musumpuka A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the academic requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the
The Association Between VLF and ELF Chorus Emissions and Electron Precipitation Remmy Musumpuka A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the academic requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the
May 2012 Solar Activity ~ Radio and Geomagnetic Effects Whitham D. Reeve ( 2012 W. Reeve)
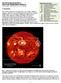 May 2012 Solar Activity ~ Radio and Geomagnetic Effects Whitham D. Reeve ( 2012 W. Reeve) Abbreviations in this article: ACE: Advanced Composition Explorer AGC: Automatic Gain Control CME: Coronal Mass
May 2012 Solar Activity ~ Radio and Geomagnetic Effects Whitham D. Reeve ( 2012 W. Reeve) Abbreviations in this article: ACE: Advanced Composition Explorer AGC: Automatic Gain Control CME: Coronal Mass
Energy distribution and lifetime of magnetospherically reflecting whistlers in the plasmasphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A5, 1199, doi:10.1029/2002ja009316, 2003 Energy distribution and lifetime of magnetospherically reflecting whistlers in the plasmasphere J. Bortnik, U. S.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A5, 1199, doi:10.1029/2002ja009316, 2003 Energy distribution and lifetime of magnetospherically reflecting whistlers in the plasmasphere J. Bortnik, U. S.
Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys
 Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys Lachlan Hennessy* RMIT University hennessylachlan@gmail.com James Macnae RMIT University *presenting author SUMMARY Lightning strikes generate
Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys Lachlan Hennessy* RMIT University hennessylachlan@gmail.com James Macnae RMIT University *presenting author SUMMARY Lightning strikes generate
SEMEP. Search for ElectroMagnetic Earthquake Precursors
 Page: 1 of 11 SEMEP Search for ElectroMagnetic Earthquake Precursors Identification of ionospheric perturbations connected to seismicity from the analysis VLF/LF signals on the DEMETER satellite Deliverable
Page: 1 of 11 SEMEP Search for ElectroMagnetic Earthquake Precursors Identification of ionospheric perturbations connected to seismicity from the analysis VLF/LF signals on the DEMETER satellite Deliverable
ionospheric satellite cluster scientific premises and proposed configuration
 ionospheric satellite cluster scientific premises and proposed configuration O. Fedorov, Institute of Space Research, Kyiv, Ukraine V. Korepanov, Lviv Centre of Institute of Space Research, Lviv, Ukraine
ionospheric satellite cluster scientific premises and proposed configuration O. Fedorov, Institute of Space Research, Kyiv, Ukraine V. Korepanov, Lviv Centre of Institute of Space Research, Lviv, Ukraine
Antennas and Propagation Chapters T4, G7, G8 Antenna Fundamentals, More Antenna Types, Feed lines and Measurements, Propagation
 Antennas and Propagation Chapters T4, G7, G8 Antenna Fundamentals, More Antenna Types, Feed lines and Measurements, Propagation =============================================================== Antenna Fundamentals
Antennas and Propagation Chapters T4, G7, G8 Antenna Fundamentals, More Antenna Types, Feed lines and Measurements, Propagation =============================================================== Antenna Fundamentals
ATS 351 Lecture 9 Radar
 ATS 351 Lecture 9 Radar Radio Waves Electromagnetic Waves Consist of an electric field and a magnetic field Polarization: describes the orientation of the electric field. 1 Remote Sensing Passive vs Active
ATS 351 Lecture 9 Radar Radio Waves Electromagnetic Waves Consist of an electric field and a magnetic field Polarization: describes the orientation of the electric field. 1 Remote Sensing Passive vs Active
SA11A Emission of ELF/VLF Waves by a Modulated Electrojet upwards into the Ionosphere and into the Earth- Ionosphere Waveguide
 SA11A-0297 Emission of ELF/VLF Waves by a Modulated Electrojet upwards into the Ionosphere and into the Earth- Ionosphere Waveguide Nikolai G. Lehtinen (nleht@stanford.edu) Umran S. Inan Stanford University
SA11A-0297 Emission of ELF/VLF Waves by a Modulated Electrojet upwards into the Ionosphere and into the Earth- Ionosphere Waveguide Nikolai G. Lehtinen (nleht@stanford.edu) Umran S. Inan Stanford University
Effects of magnetic storms on GPS signals
 Effects of magnetic storms on GPS signals Andreja Sušnik Supervisor: doc.dr. Biagio Forte Outline 1. Background - GPS system - Ionosphere 2. Ionospheric Scintillations 3. Experimental data 4. Conclusions
Effects of magnetic storms on GPS signals Andreja Sušnik Supervisor: doc.dr. Biagio Forte Outline 1. Background - GPS system - Ionosphere 2. Ionospheric Scintillations 3. Experimental data 4. Conclusions
Terry G. Glagowski W1TR / AFA1DI
 The Ionogram and Radio Propagation By Terry G. Glagowski / W1TR / AFA1DI - 9/29/2017 9:46 AM Excerpts from a presentation by Tom Carrigan / NE1R / AFA1ID by Terry G. Glagowski W1TR / AFA1DI Knowledge of
The Ionogram and Radio Propagation By Terry G. Glagowski / W1TR / AFA1DI - 9/29/2017 9:46 AM Excerpts from a presentation by Tom Carrigan / NE1R / AFA1ID by Terry G. Glagowski W1TR / AFA1DI Knowledge of
NVIS PROPAGATION THEORY AND PRACTICE
 NVIS PROPAGATION THEORY AND PRACTICE Introduction Near-Vertical Incident Skywave (NVIS) propagation is a mode of HF operation that utilizes a high angle reflection off the ionosphere to fill in the gap
NVIS PROPAGATION THEORY AND PRACTICE Introduction Near-Vertical Incident Skywave (NVIS) propagation is a mode of HF operation that utilizes a high angle reflection off the ionosphere to fill in the gap
MWA Ionospheric Science Opportunities Space Weather Storms & Irregularities (location location location) John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory
 MWA Ionospheric Science Opportunities Space Weather Storms & Irregularities (location location location) John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory Storm Enhanced Density: Longitude-specific Ionospheric Redistribution
MWA Ionospheric Science Opportunities Space Weather Storms & Irregularities (location location location) John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory Storm Enhanced Density: Longitude-specific Ionospheric Redistribution
Chapter 2 Analysis of Polar Ionospheric Scintillation Characteristics Based on GPS Data
 Chapter 2 Analysis of Polar Ionospheric Scintillation Characteristics Based on GPS Data Lijing Pan and Ping Yin Abstract Ionospheric scintillation is one of the important factors that affect the performance
Chapter 2 Analysis of Polar Ionospheric Scintillation Characteristics Based on GPS Data Lijing Pan and Ping Yin Abstract Ionospheric scintillation is one of the important factors that affect the performance
Propagation Tool.
 Propagation Propagation Tool http://www.hamqsl.com/solar.html The Ionosphere is made up of several layers at varying heights above the ground: The lowest level is the D Layer (37 to 56 miles), which
Propagation Propagation Tool http://www.hamqsl.com/solar.html The Ionosphere is made up of several layers at varying heights above the ground: The lowest level is the D Layer (37 to 56 miles), which
VLF Monitoring System for Characterizing the Lower Region Ionospheric Layer
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 68, 31 39, 2018 VLF Monitoring System for Characterizing the Lower Region Ionospheric Layer Nur A. Zakaria 1, *, Afifah Taat 1, Siti A. E. A. Rahim 1, Wan
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 68, 31 39, 2018 VLF Monitoring System for Characterizing the Lower Region Ionospheric Layer Nur A. Zakaria 1, *, Afifah Taat 1, Siti A. E. A. Rahim 1, Wan
OBJECTIVES: PROPAGATION INTRO RADIO WAVES POLARIZATION LINE OF SIGHT, GROUND WAVE, SKY WAVE IONOSPHERE REGIONS PROPAGATION, HOPS, SKIPS ZONES THE
 WAVE PROPAGATION OBJECTIVES: PROPAGATION INTRO RADIO WAVES POLARIZATION LINE OF SIGHT, GROUND WAVE, SKY WAVE IONOSPHERE REGIONS PROPAGATION, HOPS, SKIPS ZONES THE IONOSPHERIC LAYERS ABSORPTION AND FADING
WAVE PROPAGATION OBJECTIVES: PROPAGATION INTRO RADIO WAVES POLARIZATION LINE OF SIGHT, GROUND WAVE, SKY WAVE IONOSPHERE REGIONS PROPAGATION, HOPS, SKIPS ZONES THE IONOSPHERIC LAYERS ABSORPTION AND FADING
Lightning-associated VLF perturbations observed at low latitude: Occurrence and scattering characteristics
 Earth Planets Space, 65, 25 37, 2013 Lightning-associated VLF perturbations observed at low latitude: Occurrence and scattering characteristics Sushil Kumar and Abhikesh Kumar School of Engineering and
Earth Planets Space, 65, 25 37, 2013 Lightning-associated VLF perturbations observed at low latitude: Occurrence and scattering characteristics Sushil Kumar and Abhikesh Kumar School of Engineering and
POLAR AERONOMY AND RADIO SCIENCE (PARS) ULF/ELF/VLF PROJECT
 Page 1 of 28 POLAR AERONOMY AND RADIO SCIENCE (PARS) ULF/ELF/VLF PROJECT U. S. Inan and T. F. Bell STAR Laboratory, Stanford University Page 2 of 28 Outline 1. INTRODUCTION 2. SCIENTIFIC BACKGROUND 2.1.
Page 1 of 28 POLAR AERONOMY AND RADIO SCIENCE (PARS) ULF/ELF/VLF PROJECT U. S. Inan and T. F. Bell STAR Laboratory, Stanford University Page 2 of 28 Outline 1. INTRODUCTION 2. SCIENTIFIC BACKGROUND 2.1.
