MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) Summer 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: 1/22
|
|
|
- Eunice Douglas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may vary but the examiner may try to assess the understanding level of the candidate. 3) The language errors such as grammatical, spelling errors should not be given more importance. (Not applicable for subject English and Communication Skills). 4) While assessing figures, examiner may give credit for principal components indicated in the figure. The figures drawn by candidate and model answer may vary. The examiner may give credit for any equivalent figure drawn. 5) Credits may be given step wise for numerical problems. In some cases, the assumed constant values may vary and there may be some difference in the candidate s answers and model answer. 6) In case of some questions credit may be given by judgment on part of examiner of relevant answer based on candidate s understanding. 7) For programming language papers, credit may be given to any other program based on equivalent concept.. Marks I. A) Attempt any 3 of the following : i) Define the following terms and give their unit also: 4 ) Emf ) Current 3) Resistance 4) Potential difference Answer: Definition: (Note: Each definition with its unit carries mark) ) Emf: It is the force which creates potential difference across the terminals, by a source of electrical energy, to produce an electric current in a circuit. Unit- Volt (V) ) Current: It is defined as the rate of transfer of electric charge per unit time or current is flow electrons. Unit-Ampere (A) 3) Resistance: It is a property of substance by virtue of which it opposes the flow current through it. Unit- Ohm ( ) 4) Potential difference: The potential difference between two points, say A and B, is a measure of the energy used by one coulomb in moving from A and B. Unit- Volt (V) ii) Draw a neat schematic diagram of DC shunt and DC series motor. 4 Answer: Schematic diagram of DC shunt and DC series motor ( Each diagram Marks) 4
2 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / iii) State the importance of colour code in automobile electric wiring. 4 Answer: Importance of colour code in automobile electric wiring: It is worth mentioning that the wiring of present days automobiles has become quite complex because of the use of the number of additional electrical equipments and accessories as compared with the earlier automobiles. However with the use of coloured cables, wiring installation has been simplified as much as possible. In order to quickly identify and also to simplify the wiring system, the cables are coloured. In addition colour lines or threads are also used around the cables which provide a very wide choice of colour combinations. There are seven main colours namely brown, green, white, blue, red & black etc.. Brown: For battery circuit, Radio set, Socket & battery auxiliaries. Yellow: Dynamo circuit, Form dynamo circuit to corresponding circuit box 3. White: Used for all ignition circuits & all electrical components, Electrical petrol lamp starter solenoid switch. 4. Green: Employees for all the auxiliary circuits fed through the ignition switches and protected by the ignition auxiliary fuse. 5. Blue: Used for the head lamp circuits and fed form the terminals on the lighting switch. 6. Red: Used for all sides of tail lamp circuits fed from the terminal on the lighting switch, Fog lamp panel light & other lamps which are required only when the side lamps are in use. 7. Black: Used for earth circuit return however the component is not earthed a cable must be taken to a good earthing point on the chassis. iv) Define the term depletion Region with suitable diagram. 4 Answer: Definition of depletion Region: The area around the junction which is depleted of charge carriers (free electrons and holes) due to diffusion, across the junction is called as depletion region. 4 Fig : Depletion region
3 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 3/ B) Attempt any one of the following : 6 i) Explain in details the concepts of self inductance and mutual inductance. 6 Answer: ( concept Marks each and diagram Mark each ) Self inductance: The property of the coil due to which it opposes any increase or decrease of flux through it, is known as self inductance. Consider a coil of wire similar to the one shown in fig connected to a battery through a rheostat, it is found that whenever an effort is made to increase current through it, it is always opposed by the instantaneous production of counter e. m. f. of self induction. If now an effort is made to decrease the current, then again it is delayed due to the production of self induced e. m. f., this time in opposite direction. Fig :Self inductance: Mutual inductance: If any change of current in coil A is always accompanied by the production of mutually induced e.m.f.in coil B. Mutual inductance may, therefore, be defined as the ability of one coil to produce an e.m.f.in a nearby coil by induction when the current in the first coil changes. This action being reciprocal, the second coil can also induce an e. m. f. in the first when current in the second coil changes. This ability of reciprocal induction is measured in terms of the coefficient of mutual induction M. Fig :Mutual inductance ii) Draw the graphic symbols for the following : ) Earth ) Two way switch 3) Variable resistance 4) Fixed capacitor 5) Transformer 6) Energy meter 6
4 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 4/ Answer: Graphic symbols for ( One symbol carries one mark ). Earth. Two way switch 3. Variable resistance 4. Fixed capacitor 5. Transformer 6. Energy meter
5 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 5/ II. Attempt any four of the following : 6 i) Give the definition of the following:. Magnetic lines of force. Magnetic flux 4 3. Magnetic flux density 4. Reluctance Answer: Definitions: ( One definition carries one mark ) ) Magnetic lines of force: It is defined as a line along which an isolated N- pole would travel if it is allowed to move freely in a magnetic field. ) Magnetic flux: The total number of lines of force in any particular magnetic field is called magnetic flux. 3) Magnetic flux density: The flux per unit area in a plane at right angles to the flux is known as flux density. 4) Reluctance- It is defined as the opposition to the flow of flux in material. ii) Describe with necessary diagram the wiring system for ground return system. 4 Answer : ( Description Marks and diagram Marks) The use of fully insulated cables was made for electrical units in the wiring system of earlier automobile just like the domestic and industrial wiring system. Figure show a simple circuit of a car engine cranking motor having insulated connecting cables. The insulated return system or ground return system is much more dependable under road shops and conditions of vibration. It is for this reason that insulated return system is used in many commercial vehicles. In the case of insulated return system a single failure to the metal earth of the vehicle does not put the complete electrical system out of action except the concerned unit. Fig : Wiring system for ground return system
6 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 6/ iii) With neat sketch, explain the construction of any one type of stepper motor. 4 Answer: Construction of any one type of stepper motor: (any one type - Explanation Marks and Diagram Marks). Variable Reluctance Motors 0 Construction: It is constructed from ferromagnetic material with salient poles. The stator is made from A stack of steel lamination and six equally spaced projecting poles each wound with an exciting coil. The rotor which may be solid or laminated as four projecting teeth of the same width as the stator teeth. There are three independent phases A, B and C and each one can be energized by direct current pulse from the drive circuit. Fig shows that if all the rotors are perfectly aligned with respect to themselves then the stator teeth of various stacks have progressive angular displacement 0. Permanent Magnet motor:-
7 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 7/ Construction: It s stator construction is similar to that of the single stack VR motor. But the rotor is made of a permanent magnet material like hard ferrite. The stator has projecting poles but rotor is cylindrical and magnetized permanent magnet. iv) With the aid of neat diagram, explain the working of PNP transistor. 04 Answer: Working of PNP Transistor: (Working Marks and Diagram Marks) 0 Fig : PNP transistor In this transistor the majority charge carriers are holes instead of electrons. The holes are emitted from the p-type emitter across the forward biased EB junction, into the base. It constitutes the emitter current I E. In the lightly doped base there are very few number of electrons available for recombination. It constitutes the base current I B. Therefore % of total emitted holes will flow out via the base terminal and the remaining near about 98% are drawn across the collector by the electric field at the reversed biased collector junction.it constitutes the collector current I C. So the forward bias at the EB junction controls the collector and emitter current. In this way almost the entire current flows in the collector circuit. The emitter current is equal to the sum of collector and base current. I E = I B +I C 0 v) Draw the block diagram of instrumentation system and state the function of each component. 04 Answer: (Function 3 Marks and Diagram Marks) Block diagram of instrumentation system Function of instrumentation system: ) Primary sensing element- The quantity under measurement makes its first contact with the primary sensing element of measurement system. In other words measurand is first detected by primary sensor. The first stage of measurement system is known as a detector transducer stage. 3
8 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 8/ ) Variable conversion unit- The output of the primary sensing element may be electrical signal of any form. It may be a voltage, frequency or some other electrical parameter. Sometimes this output is not suited to the system. For the instrument to perform the desired function, it may be necessary to convert this output to some other suited form while preserving the information content of the original signal. 3) Variable Manipulation element- The function of this element is to manipulate the signal presented to it preserving the original nature of the signal. Manipulation means only a change in numerical value of the signal. 4) Data transmission element- The signal conditioning and transmission stage is commonly known as intermediate stage. This stage is used to transmit the data from one place to another. The transmission of data may be in wired or wireless form. 5) Data presentation element-the information about the quantity under measurement has to be conveyed to the personnel handling the instrument or the system for monitoring, control, or analysis purposes. The information conveyed must be in a form intelligible to the personnel or to the intelligent instrumentation system. This function is done by data presentation element. vi) Differentiate between L filter and C filter on the following parameters: ) Place of filter ) Size of filter 3) Expression for ripple factor 4) Application Answer: Differentiate between L filter and C filter : Sr. no Parameter L-filter C-filter Place of filter In series with load Across the load Size of filter Bulky Small and compact 3 Expression for ripple R L factor RF RF 3 L 4 3 f C R L 4 Application Heavy load Light load III. Attempt any four of the following: 6 i) Discuss the working of piezoelectric transducer. 04 Answer: Working of piezoelectric transducer: (Working Marks and Diagram Marks) Piezoelectric effect: Certain materials when mechanically strained generate within themselves an electric charge. This effect is called as piezoelectric effect. This effect is also reversible. This means that if a charge is applied, the material deforms mechanically. Such materials when subjected to alternating electric field will expand and contract alternatively. Working: consider the above figure where a piezo crystal is sandwiched between two metal electrodes, if pressure or force is applied on the crystal then, the material deforms mechanically and generates electrical output which is proportional to applied force or pressure. 0
9 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 9/ 0 Fig : Piezoelectric transducer ii) a) State the principle of working of a DC motor. b) Draw the VI characteristics of SCR. Answer: (DC motor principle marks, VI characteristics of SCR Marks) a) Principle of working of a DC motor: When a electric current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, mechanical force experienced on the conductor, the direction is given by fleming left hand rule and hence conductor moves in the direction of force. F= B.I.l Where, B= field strength I= current flowing in conductor L= length of the conductor b) VI characteristics of SCR 4 Fig : VI characteristics of SCR
10 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 0/ iii) Draw the symbols of NAND gates. Give their truth tables. 4 Answer:(Symbol Marks, Truth table Marks) A inputs B Output Y= A. B iv) Draw and describe power triangle of AC circuit. 4 Answer: ( Power Triangle Marks, description Marks) The power triangle for RLC system is shown in fig. The power triangle is a right angle triangle of which the base is power consumed in resistive element, vertical side is power consumed in reactive element & diagonal is total power. Apparent Power, S P Q, Unit VA or KVA Active Power, P or K = V x I x cosø, Unit Watt or Kw Reactive Power, Q = V x I x sin ø, Unit VAR or KVAR v) Define the following dynamic characteristics : ) Speed of response ) Lag 3) Fidelity 4) Dynamic error Answer: Definition: ( Marks each). Speed of response: Speed of response is defined as the value of the rapidity with which an instrument responds to a change in the value of the quantity being measured.. Lag: It refers to retardation or delay in the response of an instrument to change in the input signal. 4
11 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / 3. Fidelity: It is defined as the degree to which a measurement system indicates changes in the measured quantity without any dynamic error. 4. Dynamic error: The difference between the indicated quantity and the true value of the time varying quantity if no static error is assumed is known as the dynamic error. IV. A)Attempt any three of the following : i) Define the following terms related to alternating quantity: ) Waveform ) Phase difference 4 3) Time period 4) Form factor Answer: Definition: ( Marks each). Waveform: The shape of the curve obtained by plotting the instantaneous value against time.. Phase difference: It is the difference of phase between two alternating quantities. 3. Time period: The time taken in seconds to complete one cycle of an alternating quantity is called time period. 4. Form factor: It is defined as the ratio of rms value and average value for alternating currents and voltage. ii) Draw the wiring diagram for turn indicator and describe its function. 4 Answer: Wiring diagram for turn indicator: Fig : Turn indicator
12 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / Turn indicator The direction indicators permit the driver to signal his intention to make a right or a left turn. Figure shows the circuit diagram of this type of direction indicator. When the signal lever is moved one or the other way, the circuit is completed between the battery and the proper indicating lights on the front and the rear of the vehicle as well as on the dash board. The circuit is completed through a flasher unit which is a device that closes and opens the circuit about 70 to 80 times per minute. This sends a flashing signal which is more noticeable than a steady light. The flashing action takes place because of the heating of a thermostatic blade in the flasher unit. When the blade is heated due to current flowing through the winding of the flasher, it wraps thereby opening a pair of contacts. It in turn opens the circuit. After this the blade cools and straightens to close the circuit. iii) Describe the working of LVDT. 4 Answer: (Any one diagram marks,working marks) LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transducer): OR Fig : LVDT LVDT is electromechanical transducer that can convert the rectilinear motion of an object to which it is coupled mechanically into a corresponding electrical signal. In LVDT motion of magnetic core changes the mutual inductance of two secondary coils relative to primary coil. It is based on a variable inductance principle for displacement measurements. It provides an ac voltage output proportional to the displacement of a core passing through its windings as shown in fig. Function of LVDT for displacement measurement: The operation of LVDT is based on position of core. The different cases of LVDT operation are: Case: core is at null position The primary winding is connected to the ac source. Assume that the core is exactly at the centre of the coil. Due to equal flux linkage the secondary induced voltage are equal but they have opposite polarities. The output voltage e0 is therefore zero corresponding to the central position of the core. This position is called null position.
13 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 3/ Case : Core is at left side If the core is displaced from its null position towards secondary i.e e0 then flux linked to secondary e0 is increase and flux linked to secondary e0 is decrease. e0=e0- e0 Therefore the induced voltage e0 is greater than e0 and the output voltage of LVDT i.e e0 will be positive as shown in fig. Case 3: Core is at right side Similarly if the core is displaced from its null position towards secondary i.e e0 then flux linked to secondary e0 is increase and flux linked to secondary e0 is decrease. Then e0 will be greater than e0 and the output voltage e0 will be negative as shown in fig. e0= e0-e0 iv) What are the different types of transformer (constructional types)? Describe them with suitable diagrams. Answer :( Types marks, Description marks, Diagram marks) There are two different types of transformers. Core type. Shell type. Core type: The construction of core type transformer is shown in fig. The core of this transformer is in form of rectangular frame made from laminations. It provides a single magnetic circuit as shown in fig. The primary and secondary windings are uniformly distributed on two limbs of the core. Both the windings are of cylindrical shape and they are arranged in a concentric manner with the low voltage winding placed near the core. 4 ½ Fig : Core type. Shell type: The primary and secondary windings are placed on the central limb of the core. The high voltage and low voltage windings are of sandwich type which is in the form of interleaved pancakes. This type of core provides double magnetic circuit. This type of core provides a better mechanical support and protection for the windings.
14 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 4/ ½ Fig. Shell type 4. B)Attempt any one of the following : 6 i) Draw the symbols of photodiode. Describe its working and give any two applications of the 6 same. Answer: ( Symbol-Marks,operational diagram marksworking-marks, Application-Marks) Symbol of Photo diode: Symbol- Photodiode figure: operation of photodiode Working:. The light is always focused through a glass lens on the junction of photodiode.. As the photodiode is reverse biased, the depletion region is quite wide, penetrated on both sides of the junction. 3. The photons incident on the depletion region will impart their energy to the ions present there and generate electron hole pairs. 4. The number of electron hole pairs will be dependent on the intensity of light. These electrons and holes will be attracted towards the positive and negative terminals of external supply, to constitute the photo current. 5. With increase in the light intensity, more number of electron hole pairs are generated and the photocurrent increases. Thus the photocurrent is proportional to the light intensity. Applications of Photodiode: ) It is used in Alarm circuits. ) It is used in Counter circuit. ii) a) List the necessity of multiplexers (any points) b) With the help of suitable block diagram, describe the operation of a multiplexer. Answer ( Necessity- marks) a) Necessity of multiplexers. In most of electronics systems, the digital data is available on more than one line. It is necessary to route this data over a single line. Under such circumstances we require a circuit which select one of the many inputs at a time. This circuit is nothing else but a multiplexer, which has many inputs, one output and some select inputs. 4
15 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 5/. Multiplexer improves the reliability of the digital system because it reduces the number of external wired connections. b) Operation of a multiplexer: ( Operation- 3 marks,diagram-marks) It is special combinational circuit that gets one out of several inputs to a single output and it is one of most widely used standard logic circuit in digital design. In a multiplexer the input selected is controlled by a set of select inputs. Fig shows the block diagram of a multiplexer with n input lines and one output line. For selecting one out of inputs for connections to the output a set of m select input is required where m n. Depending upon the digital code applied at the select inputs one out of n data source is selected and transmitted to a single output channel. Normally a strobe ( or enable) input (G) is incorporated which helps in cascading and it is generally active low which means it performs its intended operation when it is LOW 3 Enable input Select input Output G S S I I 0 0 I 0 I 3 X X 0 Y
16 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 6/ V. Attempt any four of following : 6 i) Describe in brief the working of Pirani vacuum gauge. 4 Answer: Working of Pirani vacuum gauge: Figure. Pirani vacuum gauge Working: As shown in the figure the thermal conductivity of the gas is measured by detecting the amount of heat lost from an electrically heated wire placed in a gas chamber. Heat is conducted from wire by conduction through the gas and greater the thermal conductivity of the gas, the lower will be the temperature of heater wire. As electrical resistance of heater element varies with temperature, that resistance of heater wire is a measure of pressure ii) Draw a neat schematic diagram of shaded pole motor and give any two applications of the same. 4 Answer: (diagram marks, application marks) Fig : Shaded pole motor Applications: (any TWO) i) Used for small fan ii) Toys iii) Instruments iv) Ventilators
17 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 7/ iii) Describe the principle of working of SCR with necessary sketches. 4 Answer: Principle of working of SCR: ( working marks, sketch marks) An SCR has two states that is either it does not conduct or it conducts heavily. Therefore SCR behaves like a switch. There are two methods to turn on SCR. First to keep the Gate open and make the supply voltage equal to the break over voltage. The second is to operate SCR with supply voltage less than break over voltage and then turn it on by means of small voltage, applied to the Gate. Applying small positive voltage to the gate is the normal way to close an SCR because the break over voltage is usually much greater than the supply voltage. To open SCR, reduce the supply voltage to zero. Figure. Without gate voltage Figure: With gate voltage iv) Draw and explain the wiring diagram of wind shield wiper. 4 Answer: Wiring diagram of wind shield wiper: (Wiring diagram - marks & description marks) Figure: Wiring diagram of Wind shield wiper The motor operated wind shield wiper uses a motor of self-switching, two pole design, having a permanent magnet field system, together with gear box. Figure shows wiring of wiper with, DC compound wound motor used for circuit of wiper, showing normal & fast speed operation positions. When switch position is on Normal Speed
18 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 8/ Position, series circuit of Resistance & shunt winding is in parallel with armature of motor. For this position motor gives normal speed. When switch position is on Fast Speed Position, only shunt winding is in parallel with armature of motor. For this position motor gives fast speed. The motor shaft is connected to blade through mechanical linkage with reduction gear box. v) A step down transformer operates on a 50 Hz ac supply with a primary voltage of 30 V. The cross sectional area of the core is 50 cm. Calculate : ) The maximum flux m. ) The maximum flux density Bm. 3) Voltage induced in the secondary side. Assume primary and secondary turns to be 500 and 50 respectively. Answer: Given: V =30 V, f=50 Hz,A=50 x 0-4 m,n =500, N=50. Solution: ) The maximum flux m. E V f m N m.07 0 Wb m 3 ) The maximum flux density Bm: B m m A B m T 3) Voltage induced in the secondary side. E E f m N E 5 V vi) Describe the working of seven segment LED display. 4 Answer: Working of Seven segment LED display: Seven segment displays consists of Eight LEDs. Depending on the various digits and letters to be displayed the combination of LEDs are forward biased. e.g. suppose we want to display the digit 3 then LED a,b,c,d should only be forward biased the two type of seven segment display are available.
19 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 9/ There are two types (consider any one ). Common anode type. Common cathode type In common anode type all anodes of LEDs are connected together and common point is connected to +Vcc In Common cathode type all cathodes of LEDs are connected together and the common point is connected to the ground. Fig : Common anode type OR Fig :Common cathode type 6. Attempt any four of the following : 6 i) Define the terms gate and filp flop. Draw symbols of RS (Using NAND Gate) and D filp flop. 4 Answer: (Definitions Marks, symbols Marks) GATE : A digital circuit with one or more input signals but only one output signal is called as a Logic Gate. FLIP FLOP: The basic digital memory circuit, which is a bistable multi-vibrator circuit having two stable states, is known as a FLIP FLOP.
20 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: 0/ Symbol: D Flip-flop S-R Flip-flop ii) Compare series and parallel circuit on any four points. 4 Answer: Comparison of series and parallel circuit: (Any 4- each point carry Mark) Sr No. 3 Series Circuit All the resistors in series circuit carry the same current. The total voltage V applied across the series resistive circuit is sum of voltage drops across the individual resistors. V = V + V + V3 + Equivalent Resistance RT = R + R +R3+.. Rn Parallel Circuit Voltage across each resistors connected in Parallel circuit is same. The total current I is sum of currents through the individual resistors. I = I + I + I3 +.. Equivalent Resistance /RT =/R +/R + /R3 +.. /Rn 4 4 Equivalent Resistance, RT is higher than each individual resistance. Equivalent Resistance, RT is smaller than the smallest resistor connected in parallel circuit. iii) Describe how amplification takes place in a transistor amplifier. 4 Answer: Transistor as an amplifier: (Diagram Marks, Description Marks ) Fig Transistor as an amplifier
21 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / A transistor raises the strength of a weak signal and thus acts as an amplifier figure shows the basic circuit of a transistor amplifier. The weak single is applied between emitter base junction and output is taken across the load R C connected in the collector circuit. V EE is applied in the input circuit in addition to the signal as shown. As the input circuit has low resistance, therefore a small change in signal voltage causes an appreciable change in emitter current. This causes almost the same change in collector current due voltage across it. Thus a weak signal applied in the input circuit appears in the amplified form in the collector circuit. It is this way that a transistor acts as an amplifier iv) Draw a neat labeled diagram of RTD and state its operating principle. 4 Answer: (Diagram marks,principle marks) Figure: RTD Resistance thermometer: The resistance of a conductor changes when its temperature is changed. The resistance thermometer or RTD is an instrument used to measure electrical resistance in terms of temperature. The relationship between resistance and temperature is given by : R t = R o (+α Δt) Where, R t - resistance at t temperature R o- resistance at zero temperature α - temperature co-efficient Δt - temperature difference
22 (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / v) Draw a neat diagram of electromagnetic flow meter and describe its working. 4 Answer: Electromagnetic flow meter: (Diagram marks, working marks) Fig : Electromagnetic flow meter Working: It consist basically of a pair of insulated electrodes buried flush in the opposite sides of a nonconducting, nonmagnetic pipe carrying the liquid whose flow is to be measured. The pipe is surrounded by an electromagnet which produces a magnetic field. The arrangement is analogous to a conductor moving across a magnetic field. Therefore, voltage is included across the electrode. This voltage is given by:- E= Blv volt Where, B= flux density; Wb/m, l = length of conductor = diameter of pipe; m, And v = Velocity of conductor (flow); m/s Thus, assuming a constant magnetic field, the magnitude of the voltage appearing across the electrode will be directly proportional to velocity, i.e flow of fluid.
Contents. Acknowledgments. About the Author
 Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
 VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY
 CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS 1 Electric Circuit Principles 2 Electronic Circuit Principles 3 Generation 4 Distribution 5 Utilisation The expected learning outcome is
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS 1 Electric Circuit Principles 2 Electronic Circuit Principles 3 Generation 4 Distribution 5 Utilisation The expected learning outcome is
SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY
 BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY
 BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
1. Explain in detail the constructional details and working of DC motor.
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
3. What is hysteresis loss? Also mention a method to minimize the loss. (N-11, N-12)
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE 6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I UNIT I : MAGNETIC CIRCUITS AND MAGNETIC MATERIALS Part A (2 Marks) 1. List
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE 6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I UNIT I : MAGNETIC CIRCUITS AND MAGNETIC MATERIALS Part A (2 Marks) 1. List
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS
 Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARAD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATIOD (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 Subject Code: 12169 Model Answer Page 1 of 28 Important suggestions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 12169 Model Answer Page 1 of 28 Important suggestions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
GRADE 11 NOVEMBER 2015 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 11 NOVEMBER 2015 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY MARKS: 200 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 10 pages including a formula sheet. 2 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (EC/NOVEMBER
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 11 NOVEMBER 2015 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY MARKS: 200 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 10 pages including a formula sheet. 2 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (EC/NOVEMBER
Construction Electrician Level 2
 Level 2 Rev. September 2008 Unit: B1 Electrical Code II Level: Two Duration: 120 hours Theory: Practical: 99 hours 21 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is designed to provide the Electrician apprentice
Level 2 Rev. September 2008 Unit: B1 Electrical Code II Level: Two Duration: 120 hours Theory: Practical: 99 hours 21 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is designed to provide the Electrician apprentice
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1. The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2. The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1. The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2. The model answer and the answer written by candidate
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
3.1.Introduction. Synchronous Machines
 3.1.Introduction Synchronous Machines A synchronous machine is an ac rotating machine whose speed under steady state condition is proportional to the frequency of the current in its armature. The magnetic
3.1.Introduction Synchronous Machines A synchronous machine is an ac rotating machine whose speed under steady state condition is proportional to the frequency of the current in its armature. The magnetic
Synchronous Machines Study Material
 Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING 1. Just as a voltage amplifier signal voltage a power amplifier. 1.amplifier power 2.amplifier signal 3.converts the signal ac power into DC power 4.converts a dc power into useful
ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING 1. Just as a voltage amplifier signal voltage a power amplifier. 1.amplifier power 2.amplifier signal 3.converts the signal ac power into DC power 4.converts a dc power into useful
BJT. Bipolar Junction Transistor BJT BJT 11/6/2018. Dr. Satish Chandra, Assistant Professor, P P N College, Kanpur 1
 BJT Bipolar Junction Transistor Satish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics P P N College, Kanpur www.satish0402.weebly.com The Bipolar Junction Transistor is a semiconductor device which
BJT Bipolar Junction Transistor Satish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics P P N College, Kanpur www.satish0402.weebly.com The Bipolar Junction Transistor is a semiconductor device which
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM. Unit Objectives. Unit Objectives 2/29/2012
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Introduction. Inductors in AC Circuits.
 Module 3 AC Theory What you ll learn in Module 3. Section 3.1 Electromagnetic Induction. Magnetic Fields around Conductors. The Solenoid. Section 3.2 Inductance & Back e.m.f. The Unit of Inductance. Factors
Module 3 AC Theory What you ll learn in Module 3. Section 3.1 Electromagnetic Induction. Magnetic Fields around Conductors. The Solenoid. Section 3.2 Inductance & Back e.m.f. The Unit of Inductance. Factors
EE401,EC401,DEE19,DETE19
 EE401,EC401,DEE19,DETE19 IV SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY 2013 LINEAR & DIGITAL ICs Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What is
EE401,EC401,DEE19,DETE19 IV SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY 2013 LINEAR & DIGITAL ICs Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What is
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment)
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
Power Electrician Level 3
 s Power Electrician Level 3 Rev. September 2008 Power Electrician Unit: C1 Electrical Code III Level: Three Duration: 60 hours Theory: Practical: 60 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is
s Power Electrician Level 3 Rev. September 2008 Power Electrician Unit: C1 Electrical Code III Level: Three Duration: 60 hours Theory: Practical: 60 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit of instruction is
PART A. 1. List the types of DC Motors. Give any difference between them. BTL 1 Remembering
 UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
1. (a) Determine the value of Resistance R and current in each branch when the total current taken by the curcuit in figure 1a is 6 Amps.
 Code No: 07A3EC01 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production
Code No: 07A3EC01 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 I INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad-500043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Course Code : AEE018
I INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad-500043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Course Code : AEE018
DE52/DC52 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICAL & ELECT ENGG DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. Derive an expression for the current flowing at any instant during the discharge of a capacitor C across a resistor R. b. The coil of a moving coil instrument is wound with 50 turns of wire. The
Q.2 a. Derive an expression for the current flowing at any instant during the discharge of a capacitor C across a resistor R. b. The coil of a moving coil instrument is wound with 50 turns of wire. The
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2014 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2014 Caribbean Examinations Council
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2014 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2014 Caribbean Examinations Council
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICITY
 INTRODUCTION ELECTRONICS ND ELECTRICITY The science of Electronics and Electricity makes a very important contribution to our everyday existence. Electricity is concerned with the generation, transmission
INTRODUCTION ELECTRONICS ND ELECTRICITY The science of Electronics and Electricity makes a very important contribution to our everyday existence. Electricity is concerned with the generation, transmission
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS
 Part 66 Cat. B1 Module 4 ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 67 Figure 1-4. Standard diode color code system Color Digit Diode suffix
Part 66 Cat. B1 Module 4 ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 67 Figure 1-4. Standard diode color code system Color Digit Diode suffix
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electro techniques
 9210-137 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electro techniques Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler, drawing
9210-137 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electro techniques Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler, drawing
Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals
 1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
Walchand Institute of Technology. Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering. Transformer
 Walchand Institute of Technology Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Transformer 1. What is transformer? explain working principle of transformer. Electrical power transformer is a static device
Walchand Institute of Technology Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Transformer 1. What is transformer? explain working principle of transformer. Electrical power transformer is a static device
Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP Task Grid
 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS)
 Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A30203 : II B.
Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A30203 : II B.
UNIT IX ELECTRONIC DEVICES
 UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
CHAPTER 5 CONCEPTS OF ALTERNATING CURRENT
 CHAPTER 5 CONCEPTS OF ALTERNATING CURRENT INTRODUCTION Thus far this text has dealt with direct current (DC); that is, current that does not change direction. However, a coil rotating in a magnetic field
CHAPTER 5 CONCEPTS OF ALTERNATING CURRENT INTRODUCTION Thus far this text has dealt with direct current (DC); that is, current that does not change direction. However, a coil rotating in a magnetic field
Placement Paper For Electrical
 Placement Paper For Electrical Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is (A) conductively linked. (B) inductively linked. (C) not linked at all. (D) electrically linked. Ans : B Q.2 A salient pole synchronous
Placement Paper For Electrical Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is (A) conductively linked. (B) inductively linked. (C) not linked at all. (D) electrically linked. Ans : B Q.2 A salient pole synchronous
I p = V s = N s I s V p N p
 UNIT G485 Module 1 5.1.3 Electromagnetism 11 For an IDEAL transformer : electrical power input = electrical power output to the primary coil from the secondary coil Primary current x primary voltage =
UNIT G485 Module 1 5.1.3 Electromagnetism 11 For an IDEAL transformer : electrical power input = electrical power output to the primary coil from the secondary coil Primary current x primary voltage =
Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology (College Code: 109) Affiliated to UPTU, Approved by AICTE Electrical Engg.
 Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology (College Code: 19) Electrical Engg. (EE-11/21) Unit-I DC Network Theory 1. Distinguish the following terms: (a) Active and passive elements (b) Linearity and
Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology (College Code: 19) Electrical Engg. (EE-11/21) Unit-I DC Network Theory 1. Distinguish the following terms: (a) Active and passive elements (b) Linearity and
Electrical Machines (EE-343) For TE (ELECTRICAL)
 PRACTICALWORKBOOK Electrical Machines (EE-343) For TE (ELECTRICAL) Name: Roll Number: Year: Batch: Section: Semester: Department: N.E.D University of Engineering &Technology, Karachi Electrical Machines
PRACTICALWORKBOOK Electrical Machines (EE-343) For TE (ELECTRICAL) Name: Roll Number: Year: Batch: Section: Semester: Department: N.E.D University of Engineering &Technology, Karachi Electrical Machines
Revised April Unit/Standard Number. Proficiency Level Achieved: (X) Indicates Competency Achieved to Industry Proficiency Level
 Unit/Standard Number Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of state,
Unit/Standard Number Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of state,
Power. Power is the rate of using energy in joules per second 1 joule per second Is 1 Watt
 3 phase Power All we need electricity for is as a source of transport for energy. We can connect to a battery, which is a source of stored energy. Or we can plug into and electric socket at home or in
3 phase Power All we need electricity for is as a source of transport for energy. We can connect to a battery, which is a source of stored energy. Or we can plug into and electric socket at home or in
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Lesson 1 Introducing the Course on Basic Electrical Contents 1 Introducing the course (Lesson-1) 4 Introduction... 4 Module-1 Introduction... 4 Module-2 D.C. circuits.. 4 Module-3
Module 1 Introduction Lesson 1 Introducing the Course on Basic Electrical Contents 1 Introducing the course (Lesson-1) 4 Introduction... 4 Module-1 Introduction... 4 Module-2 D.C. circuits.. 4 Module-3
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. Subject Code: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Downloaded From JNTU World. B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER
 Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. The four areas in Figure 20.34 are in a magnetic field.
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. The four areas in Figure 20.34 are in a magnetic field.
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY By: Fadhil A. Hasan ELECTRICAL MACHINES
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Year: Second 2016-2017 By: Fadhil A. Hasan ELECTRICAL MACHINES І Module-II: AC Transformers o Single phase transformers o Three-phase transformers
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Year: Second 2016-2017 By: Fadhil A. Hasan ELECTRICAL MACHINES І Module-II: AC Transformers o Single phase transformers o Three-phase transformers
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
Ultrasonic. Advantages
 Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
Revised April Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018
 Unit/Standard Number High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018 Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100
Unit/Standard Number High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018 Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100
Analog Electronic Circuits
 Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
Chapter Moving Charges and Magnetism
 100 Chapter Moving Charges and Magnetism 1. The power factor of an AC circuit having resistance (R) and inductance (L) connected in series and an angular velocity ω is [2013] 2. [2002] zero RvB vbl/r vbl
100 Chapter Moving Charges and Magnetism 1. The power factor of an AC circuit having resistance (R) and inductance (L) connected in series and an angular velocity ω is [2013] 2. [2002] zero RvB vbl/r vbl
Construction Electrician/Industrial Electrician/Power Electrician Common Core Level 2
 Common Core Level 2 Unit: B1 Commercial Electrical Code Level: Two Duration: 60 hours Theory: Practical: 60 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge about
Common Core Level 2 Unit: B1 Commercial Electrical Code Level: Two Duration: 60 hours Theory: Practical: 60 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge about
TRANSFORMERS INTRODUCTION
 Tyco Electronics Corporation Crompton Instruments 1610 Cobb International Parkway, Unit #4 Kennesaw, GA 30152 Tel. 770-425-8903 Fax. 770-423-7194 TRANSFORMERS INTRODUCTION A transformer is a device that
Tyco Electronics Corporation Crompton Instruments 1610 Cobb International Parkway, Unit #4 Kennesaw, GA 30152 Tel. 770-425-8903 Fax. 770-423-7194 TRANSFORMERS INTRODUCTION A transformer is a device that
An Instrumentation System
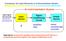 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Questions on Electromagnetism
 Questions on Electromagnetism 1. The dynamo torch, Figure 1, is operated by successive squeezes of the handle. These cause a permanent magnet to rotate within a fixed coil of wires, see Figure 2. Harder
Questions on Electromagnetism 1. The dynamo torch, Figure 1, is operated by successive squeezes of the handle. These cause a permanent magnet to rotate within a fixed coil of wires, see Figure 2. Harder
Generator Advanced Concepts
 Generator Advanced Concepts Common Topics, The Practical Side Machine Output Voltage Equation Pitch Harmonics Circulating Currents when Paralleling Reactances and Time Constants Three Generator Curves
Generator Advanced Concepts Common Topics, The Practical Side Machine Output Voltage Equation Pitch Harmonics Circulating Currents when Paralleling Reactances and Time Constants Three Generator Curves
UNIT II MEASUREMENT OF POWER & ENERGY
 UNIT II MEASUREMENT OF POWER & ENERGY Dynamometer type wattmeter works on a very simple principle which is stated as "when any current carrying conductor is placed inside a magnetic field, it experiences
UNIT II MEASUREMENT OF POWER & ENERGY Dynamometer type wattmeter works on a very simple principle which is stated as "when any current carrying conductor is placed inside a magnetic field, it experiences
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-1 Transistor
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-1 Transistor
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) PART - A
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
Page ENSC387 - Introduction to Electro-Mechanical Sensors and Actuators: Simon Fraser University Engineering Science
 Motor Driver and Feedback Control: The feedback control system of a dc motor typically consists of a microcontroller, which provides drive commands (rotation and direction) to the driver. The driver is
Motor Driver and Feedback Control: The feedback control system of a dc motor typically consists of a microcontroller, which provides drive commands (rotation and direction) to the driver. The driver is
Inductance, capacitance and resistance
 Inductance, capacitance and resistance As previously discussed inductors and capacitors create loads on a circuit. This is called reactance. It varies depending on current and frequency. At no frequency,
Inductance, capacitance and resistance As previously discussed inductors and capacitors create loads on a circuit. This is called reactance. It varies depending on current and frequency. At no frequency,
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 Some useful data:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS.
 Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17321 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17321 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Unit 3 Magnetism...21 Introduction The Natural Magnet Magnetic Polarities Magnetic Compass...21
 Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...4 Negative Atomic Charge...4 Positive
Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...4 Negative Atomic Charge...4 Positive
Basic Electronics Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Basic Electronics Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 39 Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) (Construction, characteristics (Dc & Ac), Applications,
Basic Electronics Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 39 Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) (Construction, characteristics (Dc & Ac), Applications,
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A
 Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
B.Tech II SEM Question Bank. Electronics & Electrical Engg UNIT-1
 UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
Basic Electrical Training
 Basic Electrical Training Electricians Tools Explain how various hand tools are used by an electrician Discuss the safe use of hand tools and power tools Perform basic calculations and measurement conversions
Basic Electrical Training Electricians Tools Explain how various hand tools are used by an electrician Discuss the safe use of hand tools and power tools Perform basic calculations and measurement conversions
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Unit 15: Electrical Circuits and their Applications
 Unit 15: Electrical Circuits and their Applications Level: 3 Unit type: Internal Guided learning hours: 60 Unit in brief This unit covers the principles of electricity, including measurements of electrical
Unit 15: Electrical Circuits and their Applications Level: 3 Unit type: Internal Guided learning hours: 60 Unit in brief This unit covers the principles of electricity, including measurements of electrical
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 03 ELECTRCIAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch : DC MACHINES AND TRANSFORMERS
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 03 ELECTRCIAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch : DC MACHINES AND TRANSFORMERS
Summer 2015 Examination. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17215 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17215 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Section:A Very short answer question
 Section:A Very short answer question 1.What is the order of energy gap in a conductor, semi conductor, and insulator?. Conductor - no energy gap Semi Conductor - It is of the order of 1 ev. Insulator -
Section:A Very short answer question 1.What is the order of energy gap in a conductor, semi conductor, and insulator?. Conductor - no energy gap Semi Conductor - It is of the order of 1 ev. Insulator -
PART-A UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
PART 2 - ACTUATORS. 6.0 Stepper Motors. 6.1 Principle of Operation
 6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER EI6402 ELECTRICAL MACHINES Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER EI6402 ELECTRICAL MACHINES Regulation 2013 Academic
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL
 ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
Q.1 a) Attempt any SIX of the following: 12M. (i) Give comparison between active transducer and passive transducer. Ans:- (Any Two) 1M each
 Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
Chapter 5 Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators
 Chapter 5: Electric logic sensors and actuators -IE337 Chapter 5 Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators 1 5.1 Introduction to Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators Electric sensors and actuators can be classified
Chapter 5: Electric logic sensors and actuators -IE337 Chapter 5 Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators 1 5.1 Introduction to Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators Electric sensors and actuators can be classified
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
UNIT VIII-SPECIAL PURPOSE ELECTRONIC DEVICES. 1. Explain tunnel Diode operation with the help of energy band diagrams.
 UNIT III-SPECIAL PURPOSE ELECTRONIC DEICES 1. Explain tunnel Diode operation with the help of energy band diagrams. TUNNEL DIODE: A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode which is
UNIT III-SPECIAL PURPOSE ELECTRONIC DEICES 1. Explain tunnel Diode operation with the help of energy band diagrams. TUNNEL DIODE: A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode which is
Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals
 Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...5 Negative Atomic Charge...5
Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...5 Negative Atomic Charge...5
L T P EE 441: Analog Electronics (EE/IE) (3 1 3) Theory Marks =100 Sessional Marks = 50 Laboratory Marks = 50 Time = 3 hours
 EE 441: Analog Electronics (EE/IE) (3 1 3) 1. Bond Model of silicon crystal: Intrinsic carrier concentration, Effect of doping on carrier concentration. Holes and electrons, Majority and Minority carriers,
EE 441: Analog Electronics (EE/IE) (3 1 3) 1. Bond Model of silicon crystal: Intrinsic carrier concentration, Effect of doping on carrier concentration. Holes and electrons, Majority and Minority carriers,
