What frequencies does the larynx produce?
|
|
|
- Stuart Jeffry Morton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HPP Activity 48v3 What frequencies does the larynx produce? Exploration Open up the DataStudio file with the microphone setup: SoundBasic.ds. Make the oscilloscope view active. Press Start and hum an ahhh sound into the microphone. Change the time/div setting until you can get several cycles of the signal to display. GE Do you think the sound wave you produce with your humming has a definite frequency associated with it? What evidence do you have for your opinion? 2. Now display the signal generator output on the oscilloscope. You may have to change the time/div setting to get several cycles to display. The signal generator should be producing a pure sine wave. How does the sine wave shape compare with the humming sound wave shape? A mathematical procedure called the Fourier transform can give information about the frequencies present in a signal. You can get the computer to perform a Fourier transform on your data by setting up a Fast Fourier Transform, or FFT, display. Close the oscilloscope display. Create an FFT display of the microphone voltage. Set the sample rate to 10,000 samples/s on the FFT display. Click the Start button. Start humming. When you have a stable signal click the Stop button. GE What frequencies are strong in your "ahhh" sound? 2. Obtain a Fast Fourier Transform of the sine wave signal. What frequencies are present in this signal? Supported in part by NSF-CCLI Program under grants DUE # and DUE #
2 HPP Activity 48v Start humming the "ahhh" sound again and form the FFT of this signal. Without changing the pitch of your voice, change the sound from "ahhh" to "eee". What happens to the frequencies shown in the FFT? 4. Perform an FFT analysis of the sound produced by the larynx model. Does it produce one or multiple frequencies? 5. What might you do to the larynx model to change the intensities of the frequencies it produces without changing the actual frequencies? Would changing the tension of the latex strips work? Can you think of anything else? 6. Using available materials, try your ideas. Describe the results here. We have two problems to study related to the experiments you just did. The first problem is to understand why the vocal folds produced a series of almost equally spaced frequencies. The second problem is to understand why many of the produced frrequencies disappear or have reduced intensities once the sound wave interacts with the oral/nasal cavity. The two problems are related and can be at least partially understood in terms of a concept called standing waves. We will develop this idea now. Obtain a slinky and "fix" one of the ends so it cannot move. You can do this by either placing it in a clamp or having someone hold it. Stretch your whole Slinky to its full length so it hangs freely in the air, fixed at one end and in your hand at the other end. Shake the non-fixed end of the slinky to create a standing wave. Practice until you are able to produce standing waves with two nodes (at the two ends), three nodes (two at the ends and one in the middle), and four nodes (two at the ends and two between the ends). There are some sample pictures below to guide your work. Nodes at the ends Nodes in the middle & at the ends GE Determine the frequency of the side to side (or up and down) oscillations necessary to create each of the following three standing waves:
3 HPP Activity 48v3 3 a. 2 nodes (one at each end); find frequency = f 0 b. 3 nodes (at the ends and one in the middle); find frequency = f 1 c. 4 nodes (at the ends and two between the ends); find frequency = f 2 Sketch the relevant standing wave patterns and record your frequency values. 2. Write the mathematical relationship between the frequencies you found above. What would you expect for the frequency of f n? 3. Stretch half of your Slinky about the same length as the whole Slinky above. What is now different from the activity you did above? How would you expect that to change the behavior of the system? Explain. 4. After having stretched your half Slinky to the appropriate length and keeping one end fixed, determine and record the frequency of the oscillations necessary to create a standing wave with: a. 2 nodes (one at each end); find frequency = f 0 b. 3 nodes (at the ends and one in the middle); find frequency = f 1 5. Write the mathematical relationship between the frequencies you found in question #4. What would you expect for the frequency of f n? 6. Compare your answers to questions 2 and 5. Invention
4 HPP Activity 48v3 4 Let's try to find a relationship between the length of Slinky L and the allowed wavelengths. GE Given that the endpoints of the Slinky must remain still (nodes), why is it not possible to place a wave with any arbitrary wavelength on the string? 2. What is the simplest standing wave pattern that could be fit on the Slinky? 3. What is the relationship between the Slinky length L and the wavelength λ for this case? 4. What is the next simplest standing wave pattern that can be fit on the Slinky? 5. What is the relationship between the Slinky length L and the wavelength λ in this case? 6. Try to develop a general formula for the allowed wavelengths for standing waves on the Slinky with both ends fixed. Check your result with the instructor. 7. Use your result from question 6 to write down a formula relating the allowed frequences for a standing wave and the length for a Slinky with both ends fixed. Application GE 5. Let s try to relate standing waves on the Slinky and string to the sound frequencies produced by the vocal folds. 1. Do you think the vocal folds can vibrate with any frequency? Explain your reasoning or evidence.
5 HPP Activity 48v In what ways might the vocal folds be like the Slinky used in the previous experiment? 3. Develop a hypothesis to explain the frequency pattern observed when you made the ahhh sound. Application GE 7. Standing Sound Waves and The Speed of Sound. Obtain a long glass tube with water reservoir tuning fork rubber mallet Get the instructor to show you how to set up a standing wave in an air column. 1. Do you think that the open end of the tube is a node or an antinode? 2. Do you think that the water surface is a nod or an antinode? 3. The standing sound wave can be represented as a pressure versus position graph. Draw the simplest possible standing wave pattern that could fit in the air column. 4. What is the relationship between wavelength and tube length L for this case. 5. What is the next simplest standing wave pattern that can fit it the tube? 6. What is the relationship between wavelength and tube length L for this case?
6 HPP Activity 48v Develop a general formula for the the relationship between wavelength and tube length for standing waves with one end fixed and one end free. Check you result with the instructor. 8. Use the result from question 7 to find a formula relating allowed frequencies and the length of the tube. 9. Devise an experiment for measuring the speed of sound in air using standing wave observations. Describe your plan here. 10. Record your data. 11. Analyse your data. What is your estimate of the speed of sound in air?
Introduction. Physics 1CL WAVES AND SOUND FALL 2009
 Introduction This lab and the next are based on the physics of waves and sound. In this lab, transverse waves on a string and both transverse and longitudinal waves on a slinky are studied. To describe
Introduction This lab and the next are based on the physics of waves and sound. In this lab, transverse waves on a string and both transverse and longitudinal waves on a slinky are studied. To describe
Properties of Sound. Goals and Introduction
 Properties of Sound Goals and Introduction Traveling waves can be split into two broad categories based on the direction the oscillations occur compared to the direction of the wave s velocity. Waves where
Properties of Sound Goals and Introduction Traveling waves can be split into two broad categories based on the direction the oscillations occur compared to the direction of the wave s velocity. Waves where
(i) node [1] (ii) antinode...
![(i) node [1] (ii) antinode... (i) node [1] (ii) antinode...](/thumbs/96/126586647.jpg) 1 (a) When used to describe stationary (standing) waves explain the terms node...... [1] (ii) antinode....... [1] (b) Fig. 5.1 shows a string fixed at one end under tension. The frequency of the mechanical
1 (a) When used to describe stationary (standing) waves explain the terms node...... [1] (ii) antinode....... [1] (b) Fig. 5.1 shows a string fixed at one end under tension. The frequency of the mechanical
Resonant Tubes A N A N
 1 Resonant Tubes Introduction: Resonance is a phenomenon which is peculiar to oscillating systems. One example of resonance is the famous crystal champagne glass and opera singer. If you tap a champagne
1 Resonant Tubes Introduction: Resonance is a phenomenon which is peculiar to oscillating systems. One example of resonance is the famous crystal champagne glass and opera singer. If you tap a champagne
(a) What is the tension in the rope? (b) With what frequency must the rope vibrate to create a traveling wave with a wavelength of 2m?
 1. A rope is stretched between two vertical supports. The points where it s attached (P and Q) are fixed. The linear density of the rope, μ, is 0.4kg/m, and the speed of a transverse wave on the rope is
1. A rope is stretched between two vertical supports. The points where it s attached (P and Q) are fixed. The linear density of the rope, μ, is 0.4kg/m, and the speed of a transverse wave on the rope is
Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound
 Name ID number Date Lab CRN Lab partner Lab instructor Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound Objective Because sound is something that we can only hear, it is difficult to analyze. You have probably seen
Name ID number Date Lab CRN Lab partner Lab instructor Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound Objective Because sound is something that we can only hear, it is difficult to analyze. You have probably seen
Lab 5: Cylindrical Air Columns
 Lab 5: Cylindrical Air Columns Objectives By the end of this lab you should be able to: Calculate the normal mode frequencies of an air column. correspond to a pressure antinode - the middle of a hump.
Lab 5: Cylindrical Air Columns Objectives By the end of this lab you should be able to: Calculate the normal mode frequencies of an air column. correspond to a pressure antinode - the middle of a hump.
Standing waves in a string
 Standing waves in a string Introduction When you shake a string, a pulse travels down its length. When it reaches the end, the pulse can be reflected. A series of regularly occurring pulses will generate
Standing waves in a string Introduction When you shake a string, a pulse travels down its length. When it reaches the end, the pulse can be reflected. A series of regularly occurring pulses will generate
PC1141 Physics I. Speed of Sound. Traveling waves of speed v, frequency f and wavelength λ are described by
 PC1141 Physics I Speed of Sound 1 Objectives Determination of several frequencies of the signal generator at which resonance occur in the closed and open resonance tube respectively. Determination of the
PC1141 Physics I Speed of Sound 1 Objectives Determination of several frequencies of the signal generator at which resonance occur in the closed and open resonance tube respectively. Determination of the
Waves & Interference
 Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing waves The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define, apply,
Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing waves The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define, apply,
Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points]
![Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points]](/thumbs/87/96934113.jpg) Name Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] 1. To demonstrate standing waves, one end of a string is attached to a tuning fork with frequency 120 Hz. The other end
Name Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] 1. To demonstrate standing waves, one end of a string is attached to a tuning fork with frequency 120 Hz. The other end
Sound. Use a Microphone to analyze the frequency components of a tuning fork. Record overtones produced with a tuning fork.
 Sound PART ONE - TONES In this experiment, you will analyze various common sounds. You will use a Microphone connected to a computer. Logger Pro will display the waveform of each sound, and will perform
Sound PART ONE - TONES In this experiment, you will analyze various common sounds. You will use a Microphone connected to a computer. Logger Pro will display the waveform of each sound, and will perform
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
A Level. A Level Physics. WAVES: Combining Waves (Answers) OCR. Name: Total Marks: /30
 Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. OCR A Level A Level Physics WAVES: Combining Waves (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. To produce
Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. OCR A Level A Level Physics WAVES: Combining Waves (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. To produce
A Level. A Level Physics. WAVES: Combining Waves (Answers) AQA. Name: Total Marks: /30
 Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. AQA A Level A Level Physics WAVES: Combining Waves (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. To produce
Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. AQA A Level A Level Physics WAVES: Combining Waves (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. To produce
Physics Standing Waves. Tues. 4/18, and Thurs. 4/20
 Physics 116 2017 Standing Waves Tues. 4/18, and Thurs. 4/20 A long string is firmly connected to a stationary metal rod at one end. A student holding the other end moves her hand rapidly up and down to
Physics 116 2017 Standing Waves Tues. 4/18, and Thurs. 4/20 A long string is firmly connected to a stationary metal rod at one end. A student holding the other end moves her hand rapidly up and down to
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
Speed of Sound in Air
 Speed of Sound in Air OBJECTIVE To explain the condition(s) necessary to achieve resonance in an open tube. To understand how the velocity of sound is affected by air temperature. To determine the speed
Speed of Sound in Air OBJECTIVE To explain the condition(s) necessary to achieve resonance in an open tube. To understand how the velocity of sound is affected by air temperature. To determine the speed
PHYSICS LAB. Sound. Date: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY
 PHYSICS LAB Sound Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Sound Investigations Sound Investigations 78 Part I -
PHYSICS LAB Sound Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Sound Investigations Sound Investigations 78 Part I -
MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 11 Velocity of Waves 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.) What is the longest wavelength at which a sound wave will
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 11 Velocity of Waves 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.) What is the longest wavelength at which a sound wave will
Sound of Music. This lab is due at the end of the laboratory period
 Name: Partner(s): 1114 section: Desk # Date: Purpose Sound of Music This lab is due at the end of the laboratory period To create and play musical notes using standing waves in a pipe closed at one end.
Name: Partner(s): 1114 section: Desk # Date: Purpose Sound of Music This lab is due at the end of the laboratory period To create and play musical notes using standing waves in a pipe closed at one end.
PhyzLab: Fork it Over
 PhyzLab: Fork it Over a determination of the speed of sound Pre-Lab. STANDING WAVES IN GENERAL a. Consider the standing waves illustrated below. i. Label each end either fixed or free. ii. Label the nodes
PhyzLab: Fork it Over a determination of the speed of sound Pre-Lab. STANDING WAVES IN GENERAL a. Consider the standing waves illustrated below. i. Label each end either fixed or free. ii. Label the nodes
Worksheet 15.2 Musical Instruments
 Worksheet 15.2 Musical Instruments 1. You and your group stretch a spring 12 feet across the floor and you produce a standing wave that has a node at each end and one antinode in the center. Sketch this
Worksheet 15.2 Musical Instruments 1. You and your group stretch a spring 12 feet across the floor and you produce a standing wave that has a node at each end and one antinode in the center. Sketch this
3A: PROPERTIES OF WAVES
 3A: PROPERTIES OF WAVES Int roduct ion Your ear is complicated device that is designed to detect variations in the pressure of the air at your eardrum. The reason this is so useful is that disturbances
3A: PROPERTIES OF WAVES Int roduct ion Your ear is complicated device that is designed to detect variations in the pressure of the air at your eardrum. The reason this is so useful is that disturbances
Review of Standing Waves on a String
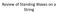 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
a. Determine the wavelength of the sound. b. Determine the speed of sound in the air inside the tube.
 1995B6. (10 points) A hollow tube of length Q. open at both ends as shown above, is held in midair. A tuning fork with a frequency f o vibrates at one end of the tube and causes the air in the tube to
1995B6. (10 points) A hollow tube of length Q. open at both ends as shown above, is held in midair. A tuning fork with a frequency f o vibrates at one end of the tube and causes the air in the tube to
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String
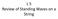 L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P36-1 Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File waves 45
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P36-1 Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File waves 45
Waves and Modes. Part I. Standing Waves. A. Modes
 Part I. Standing Waves Waves and Modes Whenever a wave (sound, heat, light,...) is confined to a finite region of space (string, pipe, cavity,... ), something remarkable happens the space fills up with
Part I. Standing Waves Waves and Modes Whenever a wave (sound, heat, light,...) is confined to a finite region of space (string, pipe, cavity,... ), something remarkable happens the space fills up with
5: SOUND WAVES IN TUBES AND RESONANCES INTRODUCTION
 5: SOUND WAVES IN TUBES AND RESONANCES INTRODUCTION So far we have studied oscillations and waves on springs and strings. We have done this because it is comparatively easy to observe wave behavior directly
5: SOUND WAVES IN TUBES AND RESONANCES INTRODUCTION So far we have studied oscillations and waves on springs and strings. We have done this because it is comparatively easy to observe wave behavior directly
Chapter 18. Superposition and Standing Waves
 Chapter 18 Superposition and Standing Waves Particles & Waves Spread Out in Space: NONLOCAL Superposition: Waves add in space and show interference. Do not have mass or Momentum Waves transmit energy.
Chapter 18 Superposition and Standing Waves Particles & Waves Spread Out in Space: NONLOCAL Superposition: Waves add in space and show interference. Do not have mass or Momentum Waves transmit energy.
AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR
 AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR NAME: HB: ACTIVITY I. BOUNDARY BEHAVIOR As a wave travels through a medium, it will often reach the end of the medium and encounter an obstacle or perhaps another medium through
AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR NAME: HB: ACTIVITY I. BOUNDARY BEHAVIOR As a wave travels through a medium, it will often reach the end of the medium and encounter an obstacle or perhaps another medium through
Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase. Out of Phase
 Superposition Interference Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere,
Superposition Interference Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere,
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts
 Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VIII Control of Sound The sound characteristics (acoustics) of a room depend upon a great many complex factors room size/shape wall/floor/ceiling materials
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VIII Control of Sound The sound characteristics (acoustics) of a room depend upon a great many complex factors room size/shape wall/floor/ceiling materials
Experiment: P34 Resonance Modes 1 Resonance Modes of a Stretched String (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P34-1 Experiment: P34 Resonance Modes 1 Resonance Modes of a Stretched String (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P34-1 Experiment: P34 Resonance Modes 1 Resonance Modes of a Stretched String (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows
Diddley Bow. (Sound Project) OBJECTIVES
 Diddley Bow (Sound Project) OBJECTIVES How are standing waves created on a vibrating string? How are harmonics related to physics and music? What factors determine the frequency and pitch of a standing
Diddley Bow (Sound Project) OBJECTIVES How are standing waves created on a vibrating string? How are harmonics related to physics and music? What factors determine the frequency and pitch of a standing
Physics 1021 Experiment 3. Sound and Resonance
 1 Physics 1021 Sound and Resonance 2 Sound and Resonance Introduction In today's experiment, you will examine beat frequency using tuning forks, a microphone and LoggerPro. You will also produce resonance
1 Physics 1021 Sound and Resonance 2 Sound and Resonance Introduction In today's experiment, you will examine beat frequency using tuning forks, a microphone and LoggerPro. You will also produce resonance
Resonance in Air Columns
 Resonance in Air Columns When discussing waves in one dimension, we observed that a standing wave forms on a spring when reflected waves interfere with incident waves. We learned that the frequencies at
Resonance in Air Columns When discussing waves in one dimension, we observed that a standing wave forms on a spring when reflected waves interfere with incident waves. We learned that the frequencies at
Name: Lab Partner: Section:
 Chapter 11 Wave Phenomena Name: Lab Partner: Section: 11.1 Purpose Wave phenomena using sound waves will be explored in this experiment. Standing waves and beats will be examined. The speed of sound will
Chapter 11 Wave Phenomena Name: Lab Partner: Section: 11.1 Purpose Wave phenomena using sound waves will be explored in this experiment. Standing waves and beats will be examined. The speed of sound will
SOUND & MUSIC. Sound & Music 1
 SOUND & MUSIC Sound is produced by a rapid variation in the average density or pressure of air molecules. We perceive sound as these pressure changes cause our eardrums to vibrate. Sound waves are produced
SOUND & MUSIC Sound is produced by a rapid variation in the average density or pressure of air molecules. We perceive sound as these pressure changes cause our eardrums to vibrate. Sound waves are produced
Resonance Tube Lab 9
 HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
H. Pipes. Open Pipes. Fig. H-1. Simplest Standing Wave on a Slinky. Copyright 2012 Prof. Ruiz, UNCA H-1
 H. Pipes We proceed now to the study of standing waves in pipes. The standing waves in the pipe are actually sound waves. We cannot see sound waves in air. However, we can readily hear the tones. The advantage
H. Pipes We proceed now to the study of standing waves in pipes. The standing waves in the pipe are actually sound waves. We cannot see sound waves in air. However, we can readily hear the tones. The advantage
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 WAVES: STANDING WAVES QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS PAN FLUTES (2016;1) Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m s -1. A pan flute is a musical instrument made of a set of pipes that are closed
WAVES: STANDING WAVES QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS PAN FLUTES (2016;1) Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m s -1. A pan flute is a musical instrument made of a set of pipes that are closed
TAP 324-4: What factors affect the note produced by a string?
 TAP 324-4: What factors affect the note produced by a string? Explore one factor that affects the pitch of the note from a plucked string. Introduction If you are even vaguely familiar with a guitar, you
TAP 324-4: What factors affect the note produced by a string? Explore one factor that affects the pitch of the note from a plucked string. Introduction If you are even vaguely familiar with a guitar, you
Waves and Sound. AP Physics 1
 Waves and Sound AP Physics 1 What is a wave A WAVE is a vibration or disturbance in space. A MEDIUM is the substance that all SOUND WAVES travel through and need to have in order to move. Classes of waves
Waves and Sound AP Physics 1 What is a wave A WAVE is a vibration or disturbance in space. A MEDIUM is the substance that all SOUND WAVES travel through and need to have in order to move. Classes of waves
EXPERIMENT 8: SPEED OF SOUND IN AIR
 LAB SECTION: NAME: EXPERIMENT 8: SPEED OF SOUND IN AIR Introduction: In this lab, you will create standing sound waves in a column of air confined to a tube. You will be able to change the frequency of
LAB SECTION: NAME: EXPERIMENT 8: SPEED OF SOUND IN AIR Introduction: In this lab, you will create standing sound waves in a column of air confined to a tube. You will be able to change the frequency of
Demonstrate understanding of wave systems. Demonstrate understanding of wave systems. Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
 Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Subject Reference Physics 3.3 Title Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Level 3 Credits 4 Assessment External This achievement standard involves demonstrating
Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Subject Reference Physics 3.3 Title Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Level 3 Credits 4 Assessment External This achievement standard involves demonstrating
Lecture 19. Superposition, interference, standing waves
 ecture 19 Superposition, interference, standing waves Today s Topics: Principle of Superposition Constructive and Destructive Interference Beats Standing Waves The principle of linear superposition When
ecture 19 Superposition, interference, standing waves Today s Topics: Principle of Superposition Constructive and Destructive Interference Beats Standing Waves The principle of linear superposition When
Sound. Production of Sound
 Sound Production o Sound Sound is produced by a vibrating object. A loudspeaker has a membrane or diaphragm that is made to vibrate by electrical currents. Musical instruments such as gongs or cymbals
Sound Production o Sound Sound is produced by a vibrating object. A loudspeaker has a membrane or diaphragm that is made to vibrate by electrical currents. Musical instruments such as gongs or cymbals
Name: Date: Period: IB Physics SL Y2 Option A (Sight and Wave Phenomena Part 1) Midterm Exam Study Guide Exam Date: Thursday, March 12, 2015
 Name: Date: Period: Objectives: IB Physics SL Y2 Option A (Sight and Wave Phenomena Part 1) Midterm Exam Study Guide Exam Date: Thursday, March 12, 2015 A.1.1 Describe the basic structure of the human
Name: Date: Period: Objectives: IB Physics SL Y2 Option A (Sight and Wave Phenomena Part 1) Midterm Exam Study Guide Exam Date: Thursday, March 12, 2015 A.1.1 Describe the basic structure of the human
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Experiment P31: Waves on a String (Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P31-1 Experiment P31: (Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Waves 45 m 700 P31 P31_WAVE.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Interface Pulley
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P31-1 Experiment P31: (Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Waves 45 m 700 P31 P31_WAVE.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Interface Pulley
Stay Tuned: Sound Waveform Models
 Stay Tuned: Sound Waveform Models Activity 24 If you throw a rock into a calm pond, the water around the point of entry begins to move up and down, causing ripples to travel outward. If these ripples come
Stay Tuned: Sound Waveform Models Activity 24 If you throw a rock into a calm pond, the water around the point of entry begins to move up and down, causing ripples to travel outward. If these ripples come
Music. Sound Part II
 Music Sound Part II What is the study of sound called? Acoustics What is the difference between music and noise? Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear
Music Sound Part II What is the study of sound called? Acoustics What is the difference between music and noise? Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear
SUMMARY. ) f s Shock wave Sonic boom UNIT. Waves transmit energy. Sound is a longitudinal mechanical wave. KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY
 UNIT D SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 9 Waves transmit energy. Crest, trough, amplitude, wavelength Longitudinal and transverse waves Cycle Period, frequency f 1_ T Universal wave equation v fλ Wave
UNIT D SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 9 Waves transmit energy. Crest, trough, amplitude, wavelength Longitudinal and transverse waves Cycle Period, frequency f 1_ T Universal wave equation v fλ Wave
Part I. Open Open Pipes. A 35 cm long string is played at its fundamental frequency.
 Part I Open Open Pipes A 35 cm long pipe is played at its fundamental frequency. 1. What does the waveform look like inside the pipe? 2. What is this frequency s wavelength? 3. What is this frequency being
Part I Open Open Pipes A 35 cm long pipe is played at its fundamental frequency. 1. What does the waveform look like inside the pipe? 2. What is this frequency s wavelength? 3. What is this frequency being
26 Sep. 10 PHYS102 2
 RESONANCE IN STRINGS INTRODUCTION A sine wave generator drives a string vibrator to create a standing wave pattern in a stretched string. The driving frequency and the length, density, and tension of the
RESONANCE IN STRINGS INTRODUCTION A sine wave generator drives a string vibrator to create a standing wave pattern in a stretched string. The driving frequency and the length, density, and tension of the
Sound & Music. how musical notes are produced and perceived. calculate the frequency of the pitch produced by a string or pipe
 Add Important Sound & Music Page: 53 NGSS Standards: N/A Sound & Music MA Curriculum Frameworks (2006): N/A AP Physics Learning Objectives: 6.D.3., 6.D.3.2, 6.D.3.3, 6.D.3.4, 6.D.4., 6.D.4.2, 6.D.5. Knowledge/Understanding
Add Important Sound & Music Page: 53 NGSS Standards: N/A Sound & Music MA Curriculum Frameworks (2006): N/A AP Physics Learning Objectives: 6.D.3., 6.D.3.2, 6.D.3.3, 6.D.3.4, 6.D.4., 6.D.4.2, 6.D.5. Knowledge/Understanding
Chapter 17. Linear Superposition and Interference
 Chapter 17 Linear Superposition and Interference Linear Superposition If two waves are traveling through the same medium, the resultant wave is found by adding the displacement of the individual waves
Chapter 17 Linear Superposition and Interference Linear Superposition If two waves are traveling through the same medium, the resultant wave is found by adding the displacement of the individual waves
(3) A traveling wave transfers, but it does not transfer.
 AP PHYSICS TEST 9 Waves and Sound (1) Give a good physics definition of a wave. (2) Any wave has as its source. (3) A traveling wave transfers, but it does not transfer. (4) What is a mechanical wave?
AP PHYSICS TEST 9 Waves and Sound (1) Give a good physics definition of a wave. (2) Any wave has as its source. (3) A traveling wave transfers, but it does not transfer. (4) What is a mechanical wave?
Musical instruments: strings and pipes
 Musical instruments: strings and pipes Physics 211 Syracuse University, Physics 211 Spring 2017 Walter Freeman April 24, 2017 W. Freeman Musical instruments: strings and pipes April 24, 2017 1 / 11 Announcements
Musical instruments: strings and pipes Physics 211 Syracuse University, Physics 211 Spring 2017 Walter Freeman April 24, 2017 W. Freeman Musical instruments: strings and pipes April 24, 2017 1 / 11 Announcements
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
What Do You Think? For You To Do GOALS
 Let Us Entertain You Activity 2 Sounds in Strings GOALS In this activity you will: Observe the effect of string length and tension upon pitch produced. Control the variables of tension and length. Summarize
Let Us Entertain You Activity 2 Sounds in Strings GOALS In this activity you will: Observe the effect of string length and tension upon pitch produced. Control the variables of tension and length. Summarize
Date Period Name. Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
Sound Waves and Beats
 Physics Topics Sound Waves and Beats If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Traveling Waves (Serway
Physics Topics Sound Waves and Beats If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Traveling Waves (Serway
Welcome to PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price. Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized
 Welcome to PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized Guitar Tuning bar pair Big string Gong rod Beats: Two Sources with Slightly Different
Welcome to PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized Guitar Tuning bar pair Big string Gong rod Beats: Two Sources with Slightly Different
1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves [2] lamp eye
![1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves [2] lamp eye 1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves [2] lamp eye](/thumbs/88/115297818.jpg) 1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves............. [2] (b) (i) Describe what is meant by a plane polarised wave.... [2] (ii) Light from a filament
1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves............. [2] (b) (i) Describe what is meant by a plane polarised wave.... [2] (ii) Light from a filament
Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase. Out of Phase
 Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
Chapter PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES
 2 4 Chapter 13-14 PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A load of 45 N attached to a spring that is hanging vertically
2 4 Chapter 13-14 PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A load of 45 N attached to a spring that is hanging vertically
Regents Physics Lab #28R. Sound Waves
 Name Date Regents Physics Lab #28R Period Mrs. Nadworny Partners: Due Date Research Problem Sound Waves The sound produced by a tuning fork in air exists as variations in air pressure that spread out longitudinally
Name Date Regents Physics Lab #28R Period Mrs. Nadworny Partners: Due Date Research Problem Sound Waves The sound produced by a tuning fork in air exists as variations in air pressure that spread out longitudinally
ABC Math Student Copy
 Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
Study of Standing Waves to Find Speed of Sound in Air
 Study of Standing Waves to Find Speed of Sound in Air Purpose Using mobile devices as sound analyzer and sound generator to study standing waves and determine the speed of sound in air. Theory The velocity
Study of Standing Waves to Find Speed of Sound in Air Purpose Using mobile devices as sound analyzer and sound generator to study standing waves and determine the speed of sound in air. Theory The velocity
Preview. Sound Section 1. Section 1 Sound Waves. Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance. Section 3 Harmonics
 Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
Resonance and resonators
 Resonance and resonators Dr. Christian DiCanio cdicanio@buffalo.edu University at Buffalo 10/13/15 DiCanio (UB) Resonance 10/13/15 1 / 27 Harmonics Harmonics and Resonance An example... Suppose you are
Resonance and resonators Dr. Christian DiCanio cdicanio@buffalo.edu University at Buffalo 10/13/15 DiCanio (UB) Resonance 10/13/15 1 / 27 Harmonics Harmonics and Resonance An example... Suppose you are
Standing Waves. Equipment
 rev 12/2016 Standing Waves Equipment Qty Items Parts Number 1 String Vibrator WA-9857 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8967 1 Pulley ME-9448B 1 Universal Table Clamp ME-9376B 1 Small Rod ME-8988 2 Patch Cords
rev 12/2016 Standing Waves Equipment Qty Items Parts Number 1 String Vibrator WA-9857 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8967 1 Pulley ME-9448B 1 Universal Table Clamp ME-9376B 1 Small Rod ME-8988 2 Patch Cords
Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound. Period T time taken for one complete vibrational cycle
 Unit 1: Waves Lesson: Sound Sound is a mechanical wave, a longitudinal wave, a pressure wave Periodic sound waves have: Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound Period
Unit 1: Waves Lesson: Sound Sound is a mechanical wave, a longitudinal wave, a pressure wave Periodic sound waves have: Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound Period
KUNDT S APPARATUS (with speaker & mic)
 ISTRUCTIO SHEET KUDT S PPRTUS (with speaker & mic) Cat: SW1996-001 Kundt s apparatus DESCRIPTIO: This apparatus is used to reproduce Kundt s experiments to study wave motion inside a tube by using sound
ISTRUCTIO SHEET KUDT S PPRTUS (with speaker & mic) Cat: SW1996-001 Kundt s apparatus DESCRIPTIO: This apparatus is used to reproduce Kundt s experiments to study wave motion inside a tube by using sound
PHYSICS 107 LAB #3: WAVES ON STRINGS
 Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /40 PHYSICS 107 LAB #3: WAVES ON STRINGS Equipment: Function generator, amplifier, driver, elastic string, pulley and clamp, rod and table
Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /40 PHYSICS 107 LAB #3: WAVES ON STRINGS Equipment: Function generator, amplifier, driver, elastic string, pulley and clamp, rod and table
Speed of Sound. Introduction. Ryerson University - PCS 130
 Introduction Speed of Sound In many experiments, the speed of an object such as a ball dropping or a toy car down a track can be measured (albeit with some help from devices). In these instances, these
Introduction Speed of Sound In many experiments, the speed of an object such as a ball dropping or a toy car down a track can be measured (albeit with some help from devices). In these instances, these
AP Physics B (Princeton 15 & Giancoli 11 & 12) Waves and Sound
 AP Physics B (Princeton 15 & Giancoli 11 & 12) Waves and Sound Preview What are the two categories of waves with regard to mode of travel? Mechanical Electromagnetic Which type of wave requires a medium?
AP Physics B (Princeton 15 & Giancoli 11 & 12) Waves and Sound Preview What are the two categories of waves with regard to mode of travel? Mechanical Electromagnetic Which type of wave requires a medium?
Waves & Sound. In this chapter you will be working with waves that are periodic or that repeat in a regular pattern.
 Name: Waves & Sound Hr: Vocabulary Wave: A disturbance in a medium. In this chapter you will be working with waves that are periodic or that repeat in a regular pattern. Wave speed = (wavelength)(frequency)
Name: Waves & Sound Hr: Vocabulary Wave: A disturbance in a medium. In this chapter you will be working with waves that are periodic or that repeat in a regular pattern. Wave speed = (wavelength)(frequency)
Chapter 12. Preview. Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect. Section 1 Sound Waves
 Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
Interference & Superposition. Creating Complex Wave Forms
 Interference & Superposition Creating Complex Wave Forms Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing
Interference & Superposition Creating Complex Wave Forms Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 14-7 Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same medium combine, or superpose, by simple addition. 14-7 Superposition and Interference If two pulses combine to give
14-7 Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same medium combine, or superpose, by simple addition. 14-7 Superposition and Interference If two pulses combine to give
Waves transfer energy NOT matter Two categories of waves Mechanical Waves require a medium (matter) to transfer wave energy Electromagnetic waves no
 1 Waves transfer energy NOT matter Two categories of waves Mechanical Waves require a medium (matter) to transfer wave energy Electromagnetic waves no medium required to transfer wave energy 2 Mechanical
1 Waves transfer energy NOT matter Two categories of waves Mechanical Waves require a medium (matter) to transfer wave energy Electromagnetic waves no medium required to transfer wave energy 2 Mechanical
Warm-Up. Think of three examples of waves. What do waves have in common? What, if anything, do waves carry from one place to another?
 Warm-Up Think of three examples of waves. What do waves have in common? What, if anything, do waves carry from one place to another? WAVES Physics Waves If you can only remember one thing Waves transmit
Warm-Up Think of three examples of waves. What do waves have in common? What, if anything, do waves carry from one place to another? WAVES Physics Waves If you can only remember one thing Waves transmit
Psychology of Language
 PSYCH 150 / LIN 155 UCI COGNITIVE SCIENCES syn lab Psychology of Language Prof. Jon Sprouse 01.10.13: The Mental Representation of Speech Sounds 1 A logical organization For clarity s sake, we ll organize
PSYCH 150 / LIN 155 UCI COGNITIVE SCIENCES syn lab Psychology of Language Prof. Jon Sprouse 01.10.13: The Mental Representation of Speech Sounds 1 A logical organization For clarity s sake, we ll organize
16.3 Standing Waves on a String.notebook February 16, 2018
 Section 16.3 Standing Waves on a String A wave pulse traveling along a string attached to a wall will be reflected when it reaches the wall, or the boundary. All of the wave s energy is reflected; hence
Section 16.3 Standing Waves on a String A wave pulse traveling along a string attached to a wall will be reflected when it reaches the wall, or the boundary. All of the wave s energy is reflected; hence
A2 WAVES. Waves. 1 The diagram represents a segment of a string along which a transverse wave is travelling.
 A2 WAVES Waves 1 The diagram represents a segment of a string along which a transverse wave is travelling. (i) What is the amplitude of the wave? [1] (ii) What is the wavelength of the wave? [1] (iii)
A2 WAVES Waves 1 The diagram represents a segment of a string along which a transverse wave is travelling. (i) What is the amplitude of the wave? [1] (ii) What is the wavelength of the wave? [1] (iii)
Chapter 9: Wave Interactions
 Chapter 9: Wave Interactions Mini Investigation: Media Changes, page 15 A. In each situation, the transmitted wave keeps the orientation of the original wave while the reflected wave has the opposite orientation.
Chapter 9: Wave Interactions Mini Investigation: Media Changes, page 15 A. In each situation, the transmitted wave keeps the orientation of the original wave while the reflected wave has the opposite orientation.
Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns
 Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Some types of headphones use the phenomena of constructive and destructive interference to cancel out outside noises.
Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Some types of headphones use the phenomena of constructive and destructive interference to cancel out outside noises.
Lecture 2: Acoustics
 ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 2: Acoustics 1. Acoustics, Sound & the Wave Equation 2. Musical Oscillations 3. The Digital Waveguide Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 2: Acoustics 1. Acoustics, Sound & the Wave Equation 2. Musical Oscillations 3. The Digital Waveguide Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
28 The diagram shows an experiment which has been set up to demonstrate two-source interference, using microwaves of wavelength λ.
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 28 The diagram shows an experiment which has been set up to demonstrate two-source interference, using microwaves of wavelength λ. 9702/1/M/J/02 X microwave transmitter S 1 S 2
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 28 The diagram shows an experiment which has been set up to demonstrate two-source interference, using microwaves of wavelength λ. 9702/1/M/J/02 X microwave transmitter S 1 S 2
Key Vocabulary: Wave Interference Standing Wave Node Antinode Harmonic Destructive Interference Constructive Interference
 Key Vocabulary: Wave Interference Standing Wave Node Antinode Harmonic Destructive Interference Constructive Interference 1. Work with two partners. Two will operate the Slinky and one will record the
Key Vocabulary: Wave Interference Standing Wave Node Antinode Harmonic Destructive Interference Constructive Interference 1. Work with two partners. Two will operate the Slinky and one will record the
KUNDT S APPARATUS (with speaker & mic)
 ISTRUCTIO SHEET KUDT S PPRTUS (with speaker & mic) Cat: SW1996-001 This apparatus is used to reproduce Kundt s experiments to study wave motion inside a tube by using sound and by creating standing waves.
ISTRUCTIO SHEET KUDT S PPRTUS (with speaker & mic) Cat: SW1996-001 This apparatus is used to reproduce Kundt s experiments to study wave motion inside a tube by using sound and by creating standing waves.
Standing waves. Consider a string with 2 waves of equal amplitude moving in opposite directions. or, if you prefer cos T
 Waves 2 1. Standing waves 2. Transverse waves in nature: electromagnetic radiation 3. Polarisation 4. Dispersion 5. Information transfer and wave packets 6. Group velocity 1 Standing waves Consider a string
Waves 2 1. Standing waves 2. Transverse waves in nature: electromagnetic radiation 3. Polarisation 4. Dispersion 5. Information transfer and wave packets 6. Group velocity 1 Standing waves Consider a string
While you are hearing a sound, dip the ends of the tuning fork into the beaker of water. What is the result?
 SOUND STATIONS LAB Name PROPERTIES OF SOUND Visit each station. Follow the directions for that station and write your observations and the answers to any questions on this handout. You don't have to visit
SOUND STATIONS LAB Name PROPERTIES OF SOUND Visit each station. Follow the directions for that station and write your observations and the answers to any questions on this handout. You don't have to visit
Lab 9 Fourier Synthesis and Analysis
 Lab 9 Fourier Synthesis and Analysis In this lab you will use a number of electronic instruments to explore Fourier synthesis and analysis. As you know, any periodic waveform can be represented by a sum
Lab 9 Fourier Synthesis and Analysis In this lab you will use a number of electronic instruments to explore Fourier synthesis and analysis. As you know, any periodic waveform can be represented by a sum
L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3]
![L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3] L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3]](/thumbs/94/121079208.jpg) L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3] resonance clocks pendulum springs harmonic motion mechanical waves sound waves golden rule for waves musical instruments The Doppler effect Doppler radar radar guns Review
L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3] resonance clocks pendulum springs harmonic motion mechanical waves sound waves golden rule for waves musical instruments The Doppler effect Doppler radar radar guns Review
Chapter 3. Experiment 1: Sound. 3.1 Introduction
 Chapter 3 Experiment 1: Sound 3.1 Introduction Sound is classified under the topic of mechanical waves. A mechanical wave is a term which refers to a displacement of elements in a medium from their equilibrium
Chapter 3 Experiment 1: Sound 3.1 Introduction Sound is classified under the topic of mechanical waves. A mechanical wave is a term which refers to a displacement of elements in a medium from their equilibrium
