Multiuser Detection in Large-Dimension Multicode MIMO-CDMA Systems with Higher-Order Modulation
|
|
|
- Crystal Allen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The 2011 Militay Communications Confeence - Tack 1 - Wavefoms and Signal Pocessing Multiuse Detection in Lage-Dimension Multicode MIMO-CDMA Systems with Highe-Ode Modulation Pitam Som and A. Chockalingam Depatment of ECE, Indian Institute of Science, Bangaloe , India Abstact In this pape, we ae inteested in high spectal efficiency multicode CDMA systems with lage numbe of uses employing single/multiple tansmit antennas and highe-ode modulation. In paticula, we conside a local neighbohood seach based multiuse detection algoithm which offes vey good pefomance and complexity, suited fo systems with lage numbe of uses employing M-QAM/M-PSK. We apply the algoithm on the chip matched filte output vecto. We demonstate nea-single use (SU) pefomance of the algoithm in CDMA systems with lage numbe of uses using 4- QAM/16-QAM/64-QAM/8-PSK on AWGN, fequency-flat, and fequency-selective fading channels. We futhe show that the algoithm pefoms vey well in multicode multiple-input multiple-output(mimo) CDMA systems as well, outpefoming othe linea detectos and intefeence canceles epoted in the liteatue fo such systems. The pe-symbol complexity of the seach algoithm is O(K 2 n 2 tn 2 cm), K: numbe of uses, n t: numbe of tansmit antennas at each use, n c: numbe of speading codes multiplexed on each tansmit antenna, M: modulation alphabet size, making the algoithm attactive fo multiuse detection in lage-dimension multicode MIMO- CDMA systems with M-QAM. Keywods Multicode MIMO, DS-CDMA, highe-ode modulation, nea-optimal pefomance, local neighbohood seach. I. INTRODUCTION MIMO techniques ae attactive to achieve high-spectal efficiency wieless tansmissions, and they have been widely adopted in cuent wieless standads including LTE-A and WiFi. Diect-sequence code division multiple access (CDMA) has been attactive in both militay as well as non-militay (2G/3G cellula) communication scenaios. It is of inteest to incease the spectal efficiencies achieved in CDMA systems. This can be achieved though the use of i) highe-ode modulation, ii) multicode opeation, and iii) MIMO techniques. Multicode scheme divides a high ate data steam into multiple low ate substeams, and tansmits these substeams in paallel using multiple speading codes. Fo example, in CDMA based wieless communication standads, e.g., HSDPA and HSUPA [1-[3, M-QAM modulated multicode opeation has been intoduced in the physical laye in ode to povide enhanced data ates. In fequencyselective channels, multipath induced code-domain intefeence in such systems can seiously degade pefomance. In addition to code-domain intefeence, spatial intefeence will esult if MIMO tansmission is adopted. Conventional matched filte (MF) detection esults in poo pefomance in such cases. It has been shown that in ode to achieve high spectal efficiencies using highe-ode modulation in CDMA, multiuse detection [4 is essential [5. Achieving optimal/nea-optimal multiuse detection pefomance, when the dimensionality of the detection poblem is lage, is challenging. Paticulaly, the size of maximumlikelihood (ML) solution space in multicode MIMO-CDMA is M Kntnc (M: modulation alphabet size, K: numbe of uses, n t : numbe of tansmit antennas at each use, n c : numbe of codes multiplexed on each tansmit antenna), which makes ML detection impactical fo lage Kn t n c log 2 M. In this pape, ou focus is on achieving nea-ml pefomance in lage-dimension multicode MIMO-CDMA with highe-ode modulation at low complexities. Seveal papes on multiuse detection in CDMA with higheode modulation (without o with multicode MIMO) mainly conside linea detectos including MF, decoelating/zeofocing (ZF), and minimum mean squae eo (MMSE) detectos. Fo example, in [5, the spectal efficiency analysis in lage CDMA systems with highe-ode modulation is fo MF and MMSE detectos. Ealy pefomance analysis woks on MMSE detection in CDMA with highe ode modulation is due to Milstein et al [6-[9. In [10, van Houtum analyzed the BER pefomance of quasi-synchonous CDMA with M- QAM/M-PSK and Walsh-Hadamad codes in the pesence of synchonization eos smalle than the chip time fo MF detection. In [11, Rhee et al poposed a multicaie 16- QAM CDMA tansceive system, which used a combination of decoelato and RAKE eceive. In [12,[13, Yu et al developed appoximations fo the symbol/bit eo ate of LMMSE eceives fo M-QAM in Rayleigh faded CDMA channels. In [14, it has been shown that chip-level LMMSE equalize with eceive divesity povides a significant pefomance enhancement in HSDPA system. Chip-level LMMSE has been extended to MIMO multicode CDMA in [15. Intefeence canceling detectos with highe ode modulation have also been widely studied [16,[17. In [18, Huang et al poposed a goup detection scheme fo multicode MIMO. In [19, Meue and Webe studied an iteative multiuse detection scheme, which is closely elated to paallel intefeence cancellation (PIC), fo TD-CDMA with higheode modulation. Pefomance of multicode CDMA with successive intefeence cancellation (SIC) in Nakagami-m channel channels is pesented in [20. In [21, Xia and Wang deived analytical BER expessions fo multicode CDMA with M-QAM using a PIC eceive. Recently, this wok has been extended fo bit-inteleaved coded M-QAM (BIC-MQAM) [22. A fequency-domain PIC scheme fo multicode MIMO-CDMA is studied in [23. In [24, Change and Lee pesented a two stage intefeence cancelling scheme fo detection in multicode MIMO. This pape also poposed powe allocation stategies at the tansmitte based on the feedback fom eceive in ode to balance signal-to-noise /11/$ IEEE 364
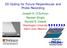
2 atio in all substeams of data, and theeby impoving the pefomance futhe. In [25, eceives that cancel codedomain and space-domain intefeences in multicode MIMO in adhoc netwok settings ae pesented. In [26, Yang et al showed that with usage of LCZ and ZCZ sequences as speading codes the BER pefomance of SIC schemes in multicode schemes can be impoved significantly. Highe-ode QAM detection in CDMA using othe techniques including semi-definite pogamming (SDP) have been studied [27. Howeve, most of the above mentioned detectos eithe scale well in complexity but pefom pooly (e.g., MF, ZF, MMSE), o pefom well but do not scale well in complexity (e.g., intefeence canceles), making them inadequate fo use in communication systems with lage dimensions. Achieving high spectal efficiencies needs signaling to be done in lage dimensions (e.g., in hundeds), i.e., lage K, n t, n c, M in multicode MIMO-CDMA. Recently, algoithms ooted in atificial intelligence/machine leaning have been shown to be attactive to achieve nea-optimal pefomance in communication poblems in lage dimensions [28-[32. In this pape, we conside a low complexity algoithm based on local neighbohood seach fo multiuse detection in multicode MIMO-CDMA systems using M-QAM/M- PSK, and demonstate its nea-optimal pefomance in lage (hundeds of) dimensions. The algoithm stats fom an initial solution vecto, which can be the output fom any known lowcomplexity detecto such as ZF, MMSE detectos. This initial solution is efined (in tems of ML cost) though an iteative low-complexity seach in the neighbohood to get the final solution vecto. We apply the algoithm on the chip-matched filte output vecto in multicode MIMO-CDMA. Simulation esults fo 16-QAM/64-QAM/8-PSK show that the algoithm achieves nea-single use BER pefomance in multiuse multicode MIMO CDMA. The pe-symbol complexity of the algoithm is O(K 2 n 2 tn 2 cm). A key advantage is that the algoithm offes both scalability to lage dimensions as well as nea-optimal pefomance in lage dimensions. II. SYSTEM MODEL We conside K-use DS-CDMA on the uplink. Without loss of geneality, we conside synchonous CDMA whee each use employs n t tansmit antennas and multiplexes n c substeams of data in the code domain using n c speading codes on each tansmit antenna with N chips pe symbol. The base station (BS) eceives the signal using n eceive antennas. Figue 1 shows the system model consideed. Let x k denote the kth use s tansmit data symbol vecto of size n t n c 1, which is given by x k = [ x T k,1,x T k,2,,x T k,n t T, (1) whee x k,j is the sub-vecto of size n c 1 on jth antenna of kth use, given by x k,j = [ x k,j,1,x k,j,2,,x k,j,nc T, (2) whee x k,j,i A is the complex data symbol mounted on ith code on jth antenna of kth use, and A is the modulation alphabet (e.g., M-QAM/M-PSK). Stacking the tansmit vectos fom all the K uses, the oveall Kn t n c 1 sized tansmit vecto is given by x = [ x T 1,x T 2,,x T K T. (3) The speading wavefom on kth use s ith code, denoted by c k,i (t), is given by c k,i (t) = N 1 n=0 c n k,iφ(t nt c ), k = 1,,K, (4) whee T c is one chip duation, c n k,i {±1} is the nth chip of kth use s ith code, φ(t) is the chip wavefom, which is assumed to be ectangula, i.e., unity fo 0 t T c and zeo othewise, N = T s /T c is the pocessing gain, and T s is one data symbol duation. Thee ae n c diffeent speading codes assigned to each use. So thee ae a total of Kn c diffeent speading codes. Each use euses its assigned codes on all its n t tansmit antennas. The ith code sequence of kth use, denoted by c k,i, is given by c k,i = [ c 0 k,i,c 1 k,i,,c N 1 T. k,i (5) Putting all n c codes on jth antenna of use k in a N n c matix fom, we wite C k,j = [ c k,1,c k,2,,c k,nc. (6) Because of code euse, same codes ae used in all tansmit antennas in a given use. We theefoe wite kth use s full code matix of size N n t n c as C k = [ C k,j,c k,j, n t times. (7) Putting the code matices of all uses togethe, the oveall system code matix C of size N Kn t n c is witten as C = [ C 1,C 2,,C K. (8) So, the oveall input to the channel in N chip intevals is given by Cx, whee nth ow denotes the tansmit vecto at the nth chip inteval. Conside fequency-selective fading channel model, whee multiple esolvable paths exist between each use and the BS. Without loss of geneality, let L denote the numbe of esolvable paths between any pai of tansmit and eceive antennas. Let h l k,p,j CN(0,Ω l) denote the complex channel gain on the lth path between jth tansmit antenna of kth use and the pth eceive antenna at the BS. We assume that the channel coefficients emain constant ove one symbol duation. Exponential powe-delay pofile with Ω l = E[ h l k,p,j 2 = Ω 0 e βl, l = 0,,L 1, (9) is assumed, whee β is the ate of exponential decay of aveage path powe. It is also assumed that the delay spead is small compaed to the symbol duation (i.e., L << N), so that thee is inte-chip intefeence but no inte-symbol intefeence. The eceived sample at nth chip of pth eceive antenna is y p (n) = K L 1 n t n c k=1 l=0 j=1 i=1 h l k,p,jc n,l k,i x k,j,i + w p (n) (10) 365
3 x k,j,i k j i : data symbol : use index : Tx antenna index : code index x 1,1,1 Reuse of codes acoss antennas c 1,1 c k,i k i Use 1 Tx : speading code : use index : code index x 1,1,nc c 1,nc Tx Antenna 1 Receive at BS Input data 1 : n cn t seial to paallel convesion x 1,2,1 x 1,2,nc c 1,1 c 1,nc c 1,1 Tx Antenna 2 Channel Rx Antenna 1 Rx Antenna 2 Chip matched filteing y Detection Detected data x 1,nt,1 x 1,nt,nc c 1,nc Tx Antenna n t Rx Antenna n Use 2 Tx Use K Tx Fig. 1. Multicode MIMO-CDMA System Model. whee c n,l k,i is the nth enty of the l chip delayed code sequence vecto c l k,i = [0,0, l times,c 0 k,i,c1 k,i,,cn l 1 k,i T, and w p (n) is the complex Gaussian noise sample with zeo mean and vaiance σ 2. Note that c 0 k,i in the above is the same as c k,i defined in (5). We want to develop a linea vecto channel model compising the eceived samples fo eceive pocessing at the BS. Let us take the N 1 eceived vecto at pth x antenna y p as y p = [y p (0),y p (1),,y p (N 1) T, (11) and the oveall n N 1 eceived vecto ove all eceive antennas as y = [ y T 1,y T 2,,y T n T. (12) We poceed to detemine the equivalent code matix (S) and channel matix (H) at the eceive side, such that the linea vecto channel equation with tansmit vecto x can be witten in the fom y = SHx + w, (13) whee w is n N 1 noise vecto, given by w = [ w T 1,w T 2,,w T n T, (14) whee w p is the noise vecto at the pth x antenna, given by w p = [w p (0),w p (1),,w p (N 1) T. (15) Let h k,p,j denote the L 1 multipath channel coefficient vecto coesponding to kth use s jth tansmit and BS s pth eceive antennas, which is given by h k,p,j = [ h 0 k,p,j,h 1 k,p,j,,h L 1 k,p,j. (16) Since the fades emain same fo all the n c codes fo a given tx-x antenna pai, we define a n c L n c channel matix H k,p,j = diag { h k,p,j,h k,p,j, n c times }. (17) Putting togethe the above matices fo all n t tansmit antennas fom use k to eceive antenna p, define the n t n c L n t nc channel matix H k,p = diag { H k,p,1,h k,p,2,,h k,p,nt }. (18) Likewise, the channel matix of size Kn t n c L Kn t n c at the pth x antenna fom all the K uses can be witten as H p = diag { H 1,p,H 2,p,,H K,p }. (19) The oveall channel matix between all the uses and the BS eceive is of size n Kn t n c L Kn t n c, and is given by H = [ H T 1,H T 2,,H T n T. (20) The eceive side code matix S becomes diffeent fom tansmit side code matix C because of the fact that at the eceive side additional effect of multipath channel gains on the tansmit symbols have to be consideed. The data steam coesponding to ith code on jth tansmit antenna of use k (c k,i ) is eceived at the pth eceive antenna though L esolvable paths. Combining the delayed code sequences coesponding to L paths, we wite the N L matix S p,k,j,i = [ c 0 k,i,c 1 k,i,,c L 1 k,i. (21) Putting togethe the code matices coesponding to all n c codes on jth tx antenna of use k, we wite N n c L matix S p,k,j = [ S p,k,j,1,s p,k,j,2,,s p,k,j,nc. (22) 366
4 The N n t n c L code matix coesponding all tansmit antennas of use k can be obtained by concatenating S p,k,j n t times as codes ae eused acoss all tx antennas, i.e., S p,k = [ S p,k,j,s p,k,j, n t times. (23) The oveall code matix of size N Kn t n c L coesponding to pth x antenna can be obtained by combining all S p,k s as S p = [ S p,1,s p,2,,s p,k. (24) The code matices acoss the eceive antennas emain same. Theefoe, the oveall eceive side code matix S of size n N n Kn t n c L is given by S = diag { S p,s p, n times }. (25) With the above definitions of channel and code matices H and S, we will cay out eceive pocessing on the linea vecto channel model in (13). III. DETECTION ALGORITHM Conside the complex system model (13) y = }{{} SH x + w, (26) =A whee y C d, d = n N, A C d dt, d t = Kn t n c x A Kntnc and w C d. We convet the complex system model in (26) to a eal system model, given by y = A x + w, (27) whee, defining y = y I + jy Q, A = A I + ja Q, x = x I + jx Q, w = w I + jw Q, ( ) y = [yi T yq T T AI A, A = Q, A Q A I x = [x T I x T Q T, w = [w T I w T Q T, (28) so that A R 2d 2dt, y R 2d 1, x S 2dt 1, and w R 2d 1. With this eal system model, when x takes values fom squae M-QAM alphabet, each enty of x can be thought of as an element fom M-PAM signal set S such that, S {(2m 1 M) : m = 1,2,, M}. Assuming channel state infomation to be available at the eceive, the optimal maximal likelihood (ML) solution vecto, x,ml, is x,ml = = ag min x S 2d t ag min x S 2d t y A x 2 x T A T A x 2y T A x. (29) }{{} ψ(x ) The detection poblem in (29) is exponentially complex in d t. We conside a low-complexity algoithm, temed as likelihood ascent seach (LAS) algoithm [28,[29,[30. Details of the algoithm ae developed below. The algoithm attempts to each the global minima of the objective function in (29) an iteative fashion, stating fom an initial solution vecto. This initial solution vecto, x (0), can be the output of a low-complexity linea detecto, e.g., MF, ZF, MMSE detectos. Let x (t) denote the solution vecto afte tth iteation of the algoithm. In each iteation, the solution vecto updates one of its enty such that the cost function undegoes maximum eduction. The iteative pocedue teminates when none of the possible updates educes the cost function any futhe. The update ule at tth iteation, assuming the symbol update happens at the qth enty of the solution vecto, can be witten as x (t) = x (t 1) + θ (t) q e q, (30) whee e q is unit vecto with its qth enty as one, and all othe enties as zeo, and θ q (t) is change in the value of qth enty of x (t 1). The task at each iteation is to find out q and θ q (t) that minimizes the ML cost in that iteation. The change in cost function in the tth iteation is given by (t) q = ψ ( x (t) ) ( ψ x (t 1) ) = θ (t) 2 q G (q,q) 2θ q (t) z q (t), (31) whee G (q,q) is the (q,q)th enty of G = A T A, z q (t) is the qth enty of the z (t) = A T (y A x (t 1) ). If (t) q is negative fo some q, then eduction of the cost function at tth iteation is possible. Let us assume that qth enty of x (t 1) has taken the value s q (t 1) S. Then, θ q (t) can take values only fom the set S q (t) {(2m 1 M s q (t 1) ) : m = 1,, M}, so that the qth enty of x (t) can also be an element of S. We find out the cost function diffeence coesponding to each possible value of θ q (t) S q (t) using (31) and detemine the minimum among the negative cost diffeence values thus obtained. Let (t) q,min be the minimum cost diffeence value fo symbol update at the qth enty of x (t 1). We compae the minimum cost diffeence value (t) q,min s fo q = 1,2,,2d t, and detemine the least among them. Let us call the least cost diffeence value thus obtained as (t) min, which is given by (t) min = min{ (t) q,min : q = 1,,2d t}. (32) Let the values of q and θ q (t) coesponding to (t) min be q(t) min and θ (t) min, espectively. The symbol update at ith iteation then becomes x (t) = x (t 1) + θ (t) min e. (33) q (t) min We also obseve that z (t+1) can be obtained fom z (t) as z (t+1) = A T (y A x (t) ) = A T ( y A x (t 1) ) (t) θ min Ge q (t) min = z (t) θ (t) min Ge. (34) q (t) min The algoithm teminates when (t) q 0, q {1,,2d t } and fo all possible values of θ q (t), i.e., thee is no negative cost diffeence, and hence futhe eduction of cost of the objective function is not possible. Since the seach is only based on local neighbohood (i.e., 1-symbol neighbohood) athe than exhaustive seach, the final solution vecto fom the algoithm can be a local minima. Howeve, the pefomance of this simple algoithm is found to get inceasingly close to optimal pefomance fo inceasing values of d t. 367
5 A. Computational Complexity The algoithm is compised of the following main components: i) computation of G, ii) computation of initial solution vecto x (0), iii) computation of z (1), and iv) seach opeations. The complexity of calculating G is O(d 2 td ). Computation of initial vecto using ZF/MMSE involves taking invese of a matix of size d t d t, whose complexity is O(d 3 t). The computation of z (1) compises of two components: multiplication of G and x (0), and subtaction of A T y fom Gx (0). The complexity involved in this is O(d 2 t). Fom simulations, the aveage complexity involved in one seach iteation and aveage numbe of iteations equied ae found to be clealy sub-cubic in d t and linea in M. So the oveall complexity ode is dominated by the cubic tem in the MMSE matix invesion. Combining all the above complexities, the total complexity is O(d 3 tm). Since d t symbols ae detected, the aveage pe-symbol complexity of the algoithm is O(d 2 tm), i.e., O(K 2 n 2 tn 2 cm). IV. SIMULATION RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS We evaluated the BER pefomance of LAS detection algoithm though simulations in uplink DS-CDMA with 4- QAM, 16-QAM, 64-QAM and 8 PSK, as a function of aveage SNR unde diffeent channel conditions (AWGN, fequency-flat fading, and fequency-selective fading) fo diffeent values of n c, n t, and n. Simulations ae caied out fo systems with lage dimensions, i.e., lage Kn t n c, to illustate the scalability of the algoithm to lage dimensions as well as achievability of nea-single use pefomance in lage dimensions. We also pesent the compaison of BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS algoithm with those of few othe algoithms available in the liteatue fo both single use as well as multiuse multicode MIMO. The aveage SNR fo kth use is P k /σ 2, whee P k = n t E s n c N is the total tansmit powe of kth use in one symbol duation, and E s is aveage symbol enegy. The output of MMSE detecto is used as the initial solution vecto fo LAS algoithm in all simulations; consequently, the algoithm is efeed to as MMSE-LAS in all the BER pefomance figues. Pefomance on AWGN channel: In Fig. 2, we plot the BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto fo DS-CDMA with 4-QAM, 16-QAM and 64-QAM on AWGN channels with n c = n t = n = 1 (i.e., system with single tansmit antenna pe use, single code pe tansmit antenna, and single eceive antenna at the BS). The numbe of uses and pocessing gain ae kept at K = 128 and N = 256, espectively. The pefomance of MMSE detecto as well as the single use (SU) pefomance ae also plotted fo compaison. Note that obtaining the tue ML pefomance fo such a lage dimension system with K = 128 though exhaustive seach o sphee decoding is pohibitively complex. Hence, we have used SU pefomance (i.e., pefomance with no multiuse intefeence) as a lowe bound on the ML pefomance in ode to assess the neaness of MMSE-LAS pefomance to ML pefomance. Fom Fig. 2, we see that the pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto is close to SU pefomance, wheeas K=128, N=256 AWGN Channel 4 QAM 16 QAM Single Use, 4 QAM Single Use, 16 QAM Single Use, 64 QAM MMSE, 4 QAM MMSE, 16 QAM MMSE, 64 QAM MMSE LAS, 4 QAM MMSE LAS, 16 QAM MMSE LAS, 64 QAM 64 QAM Fig. 2. BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto as a function of aveage SNR in AWGN channel fo 4-QAM/16-QAM/64-QAM with K = 128, N = 256, n t = n = n c = 1. K=192,N=256, Flat Fading Channel 16 QAM 4 QAM 64 QAM Single Use, 4 QAM Single Use, 16 QAM Single Use, 64 QAM MMSE, 4 QAM MMSE, 16 QAM MMSE, 64 QAM MMSE LAS, 4 QAM MMSE LAS, 16 QAM MMSE LAS, 64 QAM Fig. 3. BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto as a function of aveage SNR in flat Rayleigh fading fo 4-QAM/16-QAM/64-QAM with K = 192, N = 256, n t = n = n c = 1. MMSE pefomance is fa fom SU pefomance. This shows the effectiveness of the seach opeation caied out in MMSE-LAS to impove the MMSE pefomance towads SU pefomance. Pefomance on flat Rayleigh fading: Figue 3 shows a simila set of BER pefomance plots fo flat Rayleigh fading with 4-QAM, 16-QAM, 64-QAM and n c = n t = n = 1. The numbe of uses and pocessing gain used ae K = 192 and N = 256. Hee again, MMSE-LAS achieves nea-su pefomance fo all the modulations consideed, maintaining significant SNR advantage ove the MMSE detecto (about 5 db at BER). Multicode CDMA in fequency-selective fading: In Fig. 4, we pesent the MMSE-LAS detecto s BER pefomance fo multicode CDMA with 4-QAM, 16-QAM, 64-QAM in fequency-selective fading with n c = 4, n t = 1, K = 32, N = 128, L = 3, β = 0, and n = 2. The vaiance of the channel coefficients ae nomalized, i.e. L 1 l=0 Ω l is set to 1. Multicode MIMO-CDMA in fequency-selective fading: In Fig. 5, multicode MIMO-CDMA is consideed in fequency- 368
6 K=32, N=128, n t =1,n c =4,=n =2, L=3, β=0 MMSE, 4 QAM MMSE, 16 QAM MMSE, 64 QAM MMSE LAS, 4 QAM MMSE LAS, 16 QAM MMSE LAS, 64 QAM Single Use, 4 QAM Single Use, 16 QAM Single Use, 64 QAM 1 Stage SIC [27 2 Stage SIC [27 Goup Detecto [21 MMSE LAS 4 QAM, n t =n =4, n c =8, L=3, β =0.5, N= Fig. 4. BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto as a function of aveage SNR fo multicode CDMA in fequency-selective fading with n c = 4, n t = 1, n = 2, K = 32, N = 128, L = 3. Unifom powe delay pofile. 4 QAM K=64, n t =n c =n =2, L=3, N=256, β=0 16 QAM 4 QAM, MMSE 16 QAM, MMSE 64 QAM, MMSE 4 QAM, MMSE LAS 16 QAM, MMSE LAS 64 QAM, MMSE LAS 4 QAM, Single Use 16 QAM, Single Use 64 QAM, Single Use 64 QAM Fig. 6. Compaison of MMSE-LAS detecto pefomance with the pefomance of intefeence cancele in [27 and goup detecto in [21 fo 4-QAM in single use multicode MIMO with n c = 8, n t = 4, n = 4, K = 1, N = 32, L = 3, β = 0.5. Intefeence Cancelle [28 MMSE LAS 4 QAM, n t =2, n =4, n c =8, K=2, L=3, β =0.5, N= Fig. 5. BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto as a function of aveage SNR fo multicode MIMO-CDMA in fequency-selective fading with n c = 2, n t = n = 2, K = 64, N = 256, L = 3. Unifom powe delay pofile. selective fading with n c = 2, n t = 2, K = 64, N = 256, L = 3, β = 0, n = 2. BER plots ae shown fo 4-QAM, 16-QAM and 64-QAM. In multicode CDMA (Fig. 4) and multicode MIMO-CDMA (Fig. 5), MMSE-LAS outpefoms MMSE detecto, and pefoms close to SU pefomance. Compaison with othe IC detectos: Figue 6 compaes the BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto fo single use multicode MIMO with those of the multi-stage SIC eceive poposed in [24, and the goup detecto poposed in [18. The numbe of antennas both at tansmitte and eceive side is kept at n t = n = 4. The othe simulation paametes ae taken as in [24, i.e., N = 32, L = 3, n c = 8, β = 0.5 and 4-QAM. It can be seen that at BER, MMSE-LAS BER cuve is bette than the goup detecto [18 by about 3 db. The SIC in [24 exhibits eo floos. [24 also poposed a tansmit powe allocation scheme to bette the pefomance of the SIC. But powe allocation equies feedback fom eceive and also esults in additional pocessing ovehead at the tansmitte. The pefomance achieved by 2-stage SIC with powe allocation scheme in [24 could not bette the Fig. 7. Compaison of MMSE-LAS detecto pefomance with the pefomance of the IC in [28 fo 4-QAM in multicode MIMO-CDMA with n c = 8, n t = 2, n = 4, K = 2, N = 32, L = 3, β = 0.5. pefomance of the goup detecto in [18, wheeas MMSE- LAS outpefoms even the goup detecto. Figue 7 pesents the compaison of MMSE-LAS BER pefomance as a function of aveage SNR fo multiuse multicode MIMO with that of the IC detecto poposed in [25. The simulation paametes, consideed as in [25, ae N = 32, n c = 2, K = 2, n t = 2, n = 4, n c = 8, L = 3, β = 0.5. At BER MMSE-LAS is nealy 10 db bette than the IC algoithm pesented in [25. The IC eceive in [25 suffes fom eo floo while MMSE-LAS does not. It is to be noted that [18, [24 and [25 divide the data steams into multiple segments and fomulates detection poblem individually fo each goup teating othe segments contibution to eceived signal powe as noise. Wheeas we have fomulated the poblem at the chip matched filte output as joint detection poblem ove all the data steams. This esults in the impoved pefomance obseved in Figs. 6, 7. BER Pefomance fo M-PSK: Finally, in Fig. 8, we pesent the MMSE-LAS detecto s BER pefomance fo 8-PSK with 369
7 8 PSK, K=128, N=256, n c =n t =n =1, L=3, β=0(fo Multipath Fading) MMSE, AWGN MMSE, Flat fading MMSE, Multipath fading MMSE LAS, AWGN MMSE LAS, Flat fading MMSE LAS, Multipath fading Single Use, AWGN Single Use, Flat fading Single Use, Multipath fading Fig. 8. BER pefomance of MMSE-LAS detecto as a function of aveage SNR fo DS-CDMA with 8-PSK in AWGN, flat fading, and fequencyselective fading channels. K = 128, N = 256, n t = n = n c = 1. K = 128, N = 256, n t = n c = n = 1, in AWGN, flat fading and fequency-selective fading channels. Fo fequencyselective fading, L is taken to be 3 with unifom powe delay pofile. Fo convenience in handling M-PSK symbols, we did not decompose the vecto channel model into in-phase and quadatue pats, and applied the detection algoithm diectly on the complex system model. The esults in Fig. 8 establishes the suitability of LAS algoithm fo M-PSK and its ability to achieve nea SU pefomance. V. CONCLUSIONS We pesented a low complexity detection scheme based on local neighbohood seach fo multicode multi-antenna uplink DS-CDMA systems with highe-ode modulation. The detecto was shown to scale well fo lage dimensions and give nea SU BER pefomance. Simulation esults showed that the consideed MMSE-LAS detecto exhibits significant pefomance advantage ove the othe detection algoithms epoted in the liteatue fo multicode MIMO-CDMA. With its attactive featues like low complexity/scalability and nea optimal pefomance, the LAS detecto pesented in this pape can addess the challenge of achieving highe data ates in the next geneation MIMO-CDMA wieless systems. REFERENCES [1 H. Holma and A. Toskala, HSDPA/HSUPA fo UMTS, John Wiley & Sons, [2 3GPP TS v7.8.0, Multiplexing and channel coding (FDD), Release 7, May [3 3GPP TS v7.5.0, Speading and modulation (FDD), Release 7, May [4 S. Vedu, Multiuse Detection, Cambidge Univesity Pess, [5 O. Pato and G. P. Fettweis, On the spectal efficiency of DS- CDMA with highe ode modulation in pesence of fading, Poc. IEEE WCNC 2005, pp , Mach [6 L. B. Milstein and M. S. Lim, On the pefomance of a highe ode alphabet size in CDMA, IEEE Commun. Lett., pp. 9-11, Jan [7 P. K. Shamain and L. B. Milstein, Using highe ode constellations with minimum mean squae eo (MMSE) eceive fo sevee multipath CDMA channel, Poc. IEEE PIMRC 1998., Septembe [8 P. K. Shamain and L. B. Milstein, Minimum mean squae eo (MMSE) eceive employing 16-QAM in CDMA channel with naowband Gaussian intefeence, Poc. IEEE MILCOM 99, Nov [9 J.-H. Pein, S. Buljoe, J. Zeidle, and L. B. Milstein, Pefomance evaluation of space-path divesity and highe alphabet size fo CDMA, 31st Asiloma Conf. on Signals, Systems and Computes, vol. 1, pp , Novembe [10 W. J. van Houtum, Quasi-synchonous code-division multiple access with high-ode modulation, IEEE Tans. Commun., vol. 49, no. 7, pp , July [11 J-H. Rhee, M-Y. Woo, and D-K. Kim, Multichannel joint detection of multicaie 16-QAM DS/CDMA system fo high-speed data tansmission, IEEE Tans. Veh. Tech., vol. 52, no. 1, pp , Jan [12 K. Yu, J. S. Evans, and I. B. Collings, Pefomance analysis of LMMSE eceives fo M-ay QAM in Rayleigh faded CDMA channels, IEEE Tans. Veh. Tech., pp , Septembe [13 K. Yu and I. Oppemann, Symbol/bit-eo ate of LMMSE eceive fo M-ay QAM in multipath faded CDMA Channels, IEEE Tans. Wieless Commun., vol. 4, no. 4, pp , July [14 J.-B. Lande and A. Saadani, Receive Divesity and LMMSE Equalization Benefits fo HSDPA: Realistic Netwok Thoughputs, Poc. IEEE PIMRC 2007, pp. 1-5, Septembe [15 B.-H. Kim, X. Zhang, and M. Fluy, Linea MMSE space-time equalize fo MIMO multicode CDMA systems, IEEE Tans. Commun., vol. 57, no. 10, pp , Octobe [16 Y. Ba-Ness and N. J. M. van Waes, Multistage detecto fo adaptive sepaation of QAM-modulated multiuse CDMA signals, Poc. IEEE ISSSTA 98, vol. 3, pp , [17 K. Yen, On the pefomance of M-QAM signalling with multiuse detection and intefeence cancellation, Poc. IEEE PIMRC 2002, vol. 2, pp , Septembe [18 H. Huang, H. Viswanathan, G. J. Foschini, Multiple antennas in cellula CDMA systems: tansmission, detection, and spectal efficiency, IEEE Tans. Wieless Commun., vol. 1, no. 3, pp , July [19 M. Meue and T. Webe, Genealized data estimate efinement techniques fo iteative multiuse detection in TD-CDMA including highe ode modulation, Poc. ICT 2003, pp , [20 T-M. Wu and L-J. Chen, Successive intefeence canceles fo multicode DS-CDMA systems ove Nakagami-m fading channels, Poc. IEEE VTC 2005 (Fall), pp , Septembe [21 B. Xia and J. Wang, Analytical study of QAM with intefeence cancellation fo high-speed multicode CDMA, IEEE Tans. on Veh. Tech., vol. 54, no. 3, pp , May [22 B. Xia and H. Zhu, Coded QAM in multicode CDMA systems, Poc. IEEE VTC 2010 (Sping), pp. 1-5, May [23 A. Nakajima, G. Deepshikha, and F. Adachi, Fequency-domain iteative paallel intefeence cancellation fo multicode DS-CDMA-MIMO multiplexing, Poc. IEEE VTC 2005 (Fall), pp , Septembe [24 C. S. Pak and K. B. Lee, Tansmit powe allocation fo successive intefeence cancellation in multicode MIMO systems, IEEE Tans. on Commun., vol. 56, no. 12, pp. 1-14, Decembe [25 T. Sikanth, S. Manoha, A. Chockalingam, and L. B. Milstein, Multicode MIMO fo high data ate mobile ad-hoc netwoks, Poc. IEEE GLOBECOM 2006, Novembe [26 J-D. Yang, X. Jin, K-Y. Song, J-S. No, and D-J. Shin, Multicode MIMO systems with quatenay LCZ and ZCZ sequences, IEEE Tans. Veh. Tech., vol. 57, no. 4, pp , July [27 Z. Mao, X. Wang, and X. Wang, Semidefinite pogamming elaxation appoach fo multiuse detection of QAM Signals, IEEE Tans. on Wieless Commun., vol. 6, no. 12, pp , Decembe [28 K. V. Vadhan, S. K. Mohammed, A. Chockalingam, and B. S. Rajan, A low-complexity detecto fo lage-mimo systems and multicaie CDMA systems, IEEE J. Sel. Aeas Commun., vol. 26, no. 3, pp , Apil [29 Y. Sun, A family of likelihood ascent seach multiuse detectos: An uppe bound of bit eo ate and a lowe bound of asymptotic multiuse efficiency, IEEE Tans. Commun., pp , June [30 S. K. Mohammed, A. Chockalingam, and B. S. Rajan, A lowcomplexity nea-ml pefomance achieving algoithm fo lage MIMO detection, Poc. IEEE ISIT 2008, Toonto, July [31 T. Datta, N. Sinidhi, A. Chockalingam, and B. S. Rajan, Randomestat eactive tabu seach algoithm fo detection in lage-mimo systems, IEEE Commun. Lett., vol. 14, no. 12, pp , Decembe [32 P. Som, T. Datta, A. Chockalingam, and B. S. Rajan, Impoved lage- MIMO detection based on damped belief popagation, Poc. IEEE ITW 2010, Januay
Low-Complexity Time-Domain SNR Estimation for OFDM Systems
 Low-Complexity Time-Domain SR Estimation fo OFDM Systems A. jaz, A.B. Awoseyila and B.G. Evans A low-complexity SR estimation algoithm fo OFDM systems in fequency-selective fading channels is poposed.
Low-Complexity Time-Domain SR Estimation fo OFDM Systems A. jaz, A.B. Awoseyila and B.G. Evans A low-complexity SR estimation algoithm fo OFDM systems in fequency-selective fading channels is poposed.
OPTIMUM MEDIUM ACCESS TECHNIQUE FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 9 th Febuay. Vol. 3 No. 5 - JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 99-5 www.jatit.og E-ISSN: 7-395 OPTIMUM MEDIUM ACCESS TECHNIQUE FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS SYSTEMS N.AMUTHA PRABHA, V.MANIANDAN VIT UNIVERSITY,
9 th Febuay. Vol. 3 No. 5 - JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 99-5 www.jatit.og E-ISSN: 7-395 OPTIMUM MEDIUM ACCESS TECHNIQUE FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS SYSTEMS N.AMUTHA PRABHA, V.MANIANDAN VIT UNIVERSITY,
VLSI Implementation of Low Complexity MIMO Detection Algorithms
 , Impact Facto :.643 eissn : 349-000 & pissn : 394-4544 Intenational Jounal of Reseach and Applications (Ap-Jun 015 Tansactions) (6): 309-313 Intenational Confeence on Emeging Tends in Electonics & Telecommunications
, Impact Facto :.643 eissn : 349-000 & pissn : 394-4544 Intenational Jounal of Reseach and Applications (Ap-Jun 015 Tansactions) (6): 309-313 Intenational Confeence on Emeging Tends in Electonics & Telecommunications
Cyclic Constellation Mapping Method for PAPR Reduction in OFDM system
 2013 8th Intenational Confeence on Communications and Netwoking in China (CHINACOM) Cyclic Constellation Mapping Method fo PAPR Reduction in OFDM system Yong Cheng, Jianhua Ge, Jun Hou, and Fengkui Gong
2013 8th Intenational Confeence on Communications and Netwoking in China (CHINACOM) Cyclic Constellation Mapping Method fo PAPR Reduction in OFDM system Yong Cheng, Jianhua Ge, Jun Hou, and Fengkui Gong
On Performance of SCH OFDMA CDM in Frequency Selective Indoor Environment
 Inteleave On Pefomance of SCH OFDMA CDM in Fequency Selective Indoo Envionment Suva Sekha Das,2, Muhammad Imadu Rahman, Fank H.P. Fitzek, Ramjee Pasad Cente fo TeleInFastuktu (CTiF), Aalbog Univesity,
Inteleave On Pefomance of SCH OFDMA CDM in Fequency Selective Indoo Envionment Suva Sekha Das,2, Muhammad Imadu Rahman, Fank H.P. Fitzek, Ramjee Pasad Cente fo TeleInFastuktu (CTiF), Aalbog Univesity,
Efficient Power Control for Broadcast in Wireless Communication Systems
 Efficient Powe Contol fo Boadcast in Wieless Communication Systems A. T. Chonopoulos Compute Science Depatment Univesity of Texas at San Antonio San Antonio, TX Email:atc@cs.utsa.edu P. Cotae Depatment
Efficient Powe Contol fo Boadcast in Wieless Communication Systems A. T. Chonopoulos Compute Science Depatment Univesity of Texas at San Antonio San Antonio, TX Email:atc@cs.utsa.edu P. Cotae Depatment
Design of A Circularly Polarized E-shaped Patch Antenna with Enhanced Bandwidth for 2.4 GHz WLAN Applications
 VNU Jounal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 31, No. 2 (2015) 1-7 Design of A Ciculaly Polaized E-shaped Patch Antenna with Enhanced Bandwidth fo 2.4 GHz WLAN Applications Hong Van Tam 1, Luong
VNU Jounal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 31, No. 2 (2015) 1-7 Design of A Ciculaly Polaized E-shaped Patch Antenna with Enhanced Bandwidth fo 2.4 GHz WLAN Applications Hong Van Tam 1, Luong
Spread Spectrum Codes Identification by Neural Networks
 in "Systems and Contol: heoy and Applications", published by WSES, 2, pp. 257-262, ISBN 96-852-4 Spead Spectum Codes Identification by Neual Netwoks Céline BOUDER, Gilles BUREL Laboatoie d Electonique
in "Systems and Contol: heoy and Applications", published by WSES, 2, pp. 257-262, ISBN 96-852-4 Spead Spectum Codes Identification by Neual Netwoks Céline BOUDER, Gilles BUREL Laboatoie d Electonique
Spectrum Sharing between Public Safety and Commercial Users in 4G-LTE
 1 Spectum Shaing between Public Safety and Commecial Uses in 4G-LTE Haya Shajaiah, Ahmed Abdel-Hadi and Chales Clancy Badley Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Viginia Tech, Alington, VA, 22203,
1 Spectum Shaing between Public Safety and Commecial Uses in 4G-LTE Haya Shajaiah, Ahmed Abdel-Hadi and Chales Clancy Badley Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Viginia Tech, Alington, VA, 22203,
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 1 Due on Nov. 8, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii)
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 1 Due on Nov. 8, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii)
where and are polynomials with real coefficients and of degrees m and n, respectively. Assume that and have no zero on axis.
 function whee is an unknown constant epesents fo the un-modeled dynamics The pape investigates the position contol of electical moto dives that can be configued as stuctue of Fig 1 This poblem is fomulated
function whee is an unknown constant epesents fo the un-modeled dynamics The pape investigates the position contol of electical moto dives that can be configued as stuctue of Fig 1 This poblem is fomulated
Analysis of a Fractal Microstrip Patch Antenna
 124 Analysis of a Factal Micostip Patch Antenna Vibha Rani Gupta and Nisha Gupta* Bila Institute of Technology, Mesa, Ranchi-835215, Jhakhand, India. vgupta@bitmesa.ac.in, ngupta@bitmesa.ac.in Abstact-
124 Analysis of a Factal Micostip Patch Antenna Vibha Rani Gupta and Nisha Gupta* Bila Institute of Technology, Mesa, Ranchi-835215, Jhakhand, India. vgupta@bitmesa.ac.in, ngupta@bitmesa.ac.in Abstact-
Design and Implementation of 4 - QAM VLSI Architecture for OFDM Communication
 Design and Implementation of 4 - QAM VLSI Achitectue fo OFDM Communication R. Achitha 1, S. Bhagyalakshmi 2, V. Jaya Suthi 3, D. T. Menakadevi 4 U.G. Students, Depatment of ECE, Adhiyamaan College of Engineeing,
Design and Implementation of 4 - QAM VLSI Achitectue fo OFDM Communication R. Achitha 1, S. Bhagyalakshmi 2, V. Jaya Suthi 3, D. T. Menakadevi 4 U.G. Students, Depatment of ECE, Adhiyamaan College of Engineeing,
Optimal Design of Smart Mobile Terminal Antennas for Wireless Communication and Computing Systems
 Optimal Design of Smat Mobile Teminal Antennas fo Wieless Communication and Computing Systems Autho Lu, Junwei, Yang, Shiyou Published 2007 Confeence Title 2007 4th Intenational Symposium on Electomagnetic
Optimal Design of Smat Mobile Teminal Antennas fo Wieless Communication and Computing Systems Autho Lu, Junwei, Yang, Shiyou Published 2007 Confeence Title 2007 4th Intenational Symposium on Electomagnetic
INCREMENTAL REDUNDANCY (IR) SCHEMES FOR W-CDMA HS-DSCH
 ICREMETAL REDUDACY (IR) SCHEMES FOR W-CDMA HS-DSCH Amitava Ghosh 1, Kenneth Stewat, Rapeepat Ratasuk 1, Eoin Buckley, and Raa Bachu 1 Advanced Radio Technology, GTSS, Motoola, Alington Heights, IL, USA
ICREMETAL REDUDACY (IR) SCHEMES FOR W-CDMA HS-DSCH Amitava Ghosh 1, Kenneth Stewat, Rapeepat Ratasuk 1, Eoin Buckley, and Raa Bachu 1 Advanced Radio Technology, GTSS, Motoola, Alington Heights, IL, USA
Power Minimization in Uni-directional Relay Networks with Cognitive Radio Capabilities
 00 5th Intenational Symposium on elecommunications (IS'00) Poe Minimization in Uni-diectional Relay Netoks ith Cognitive Radio Capabilities Adalan Alizadeh Seyed Mohammad-Sajad Sadough Cognitive elecommunication
00 5th Intenational Symposium on elecommunications (IS'00) Poe Minimization in Uni-diectional Relay Netoks ith Cognitive Radio Capabilities Adalan Alizadeh Seyed Mohammad-Sajad Sadough Cognitive elecommunication
Figure Geometry for Computing the Antenna Parameters.
 Spheical Coodinate Systems Definitions Figue 1.2.1 Geomety fo Computing the Antenna Paametes. Antenna Radiation Patten: The distibution of adiated enegy fom an antenna ove a suface of constant adius centeed
Spheical Coodinate Systems Definitions Figue 1.2.1 Geomety fo Computing the Antenna Paametes. Antenna Radiation Patten: The distibution of adiated enegy fom an antenna ove a suface of constant adius centeed
PERFORMANCE OF TOA ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES IN INDOOR MULTIPATH CHANNELS
 PERFORMANCE OF TOA ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES IN INDOOR MULTIPATH CHANNELS Xinong Li, Kaveh Pahlavan, and Jacques Beneat Cente fo Wiele Infomation Netwo Studies Electical and Compute Engineeing Depatment, Woceste
PERFORMANCE OF TOA ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES IN INDOOR MULTIPATH CHANNELS Xinong Li, Kaveh Pahlavan, and Jacques Beneat Cente fo Wiele Infomation Netwo Studies Electical and Compute Engineeing Depatment, Woceste
LLR Reliability Improvement for Multilayer Signals
 LLR Reliability mpovement fo Multilaye Signals C. Regueio, J. Baueco, J. Montalban, P. Angueia, J.L. Odiales, M. Velez Abstact The limitations and igidness of cuent use of spectum esouces have fosteed
LLR Reliability mpovement fo Multilaye Signals C. Regueio, J. Baueco, J. Montalban, P. Angueia, J.L. Odiales, M. Velez Abstact The limitations and igidness of cuent use of spectum esouces have fosteed
A Simple Improvement to the Viterbi and Viterbi Monomial-Based Phase Estimators
 Univesity of New Oleans ScholaWoks@UNO Electical Engineeing Faculty Publications Depatment of Electical Engineeing 006 A Simple Impovement to the Vitebi and Vitebi Monomial-Based Phase Estimatos Kenneth
Univesity of New Oleans ScholaWoks@UNO Electical Engineeing Faculty Publications Depatment of Electical Engineeing 006 A Simple Impovement to the Vitebi and Vitebi Monomial-Based Phase Estimatos Kenneth
Wireless Communication (Subject Code: 7EC3)
 COMPUCOM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT, JAIPUR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION) Notes Wieless Communication (Subject Code: 7EC3) Pepaed By: LOKESH KUMAR ARYA Class: B. Tech. IV Yea, VII
COMPUCOM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT, JAIPUR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION) Notes Wieless Communication (Subject Code: 7EC3) Pepaed By: LOKESH KUMAR ARYA Class: B. Tech. IV Yea, VII
Channel Modelling ETIM10. Fading Statistical description of the wireless channel
 Channel Modelling ETIM10 Lectue no: 3 Fading Statistical desciption of the wieless channel Ghassan Dahman \ Fedik Tufvesson Depatment of Electical and Infomation Technology Lund Univesity, Sweden 013-01-8
Channel Modelling ETIM10 Lectue no: 3 Fading Statistical desciption of the wieless channel Ghassan Dahman \ Fedik Tufvesson Depatment of Electical and Infomation Technology Lund Univesity, Sweden 013-01-8
MACRO-DIVERSITY VERSUS MICRO-DIVERSITY SYSTEM CAPACITY WITH REALISTIC RECEIVER RFFE MODEL
 MACRO-DIVERSITY VERSUS MICRO-DIVERSITY SYSTEM CAACITY WITH REALISTIC RECEIVER RFFE MODEL I Ouachani, Duhamel, K Gosse, S Rouquette-Léveil and D Bateman *Laboatoie des Signaux et Systèmes 3 ue Joliot-Cuie
MACRO-DIVERSITY VERSUS MICRO-DIVERSITY SYSTEM CAACITY WITH REALISTIC RECEIVER RFFE MODEL I Ouachani, Duhamel, K Gosse, S Rouquette-Léveil and D Bateman *Laboatoie des Signaux et Systèmes 3 ue Joliot-Cuie
A Transmission Scheme for Continuous ARQ Protocols over Underwater Acoustic Channels
 A Tansmission Scheme fo Continuous ARQ Potocols ove Undewate Acoustic Channels Mingsheng Gao 1, Wee-Seng Soh 1 and Meixia Tao 2 1 Dept. of Electical & Compute Engineeing, National Univesity of Singapoe,
A Tansmission Scheme fo Continuous ARQ Potocols ove Undewate Acoustic Channels Mingsheng Gao 1, Wee-Seng Soh 1 and Meixia Tao 2 1 Dept. of Electical & Compute Engineeing, National Univesity of Singapoe,
On Reducing Blocking Probability in Cooperative Ad-hoc Networks
 On educing Blocking Pobability in Coopeative Ad-hoc Netwoks Ayda Basyouni, Walaa Hamouda ept of Electical and Compute Engineeing Concodia Univesity, Monteal, Canada Email: {a basy,hamouda}@ececoncodiaca
On educing Blocking Pobability in Coopeative Ad-hoc Netwoks Ayda Basyouni, Walaa Hamouda ept of Electical and Compute Engineeing Concodia Univesity, Monteal, Canada Email: {a basy,hamouda}@ececoncodiaca
ISSN: [Reddy & Rao* et al., 5(12): December, 2016] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Reddy & Rao* et al., 5(12): December, 2016] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Reddy & Rao* et al., 5(12): December, 2016] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/95/122747775.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY SIMULATION COMPARISONS OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE WITH ESTIMATOR AND PLL V. Nasi Reddy *, S. Kishnajuna Rao*, S.Nagenda Kuma * Assistant
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY SIMULATION COMPARISONS OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE WITH ESTIMATOR AND PLL V. Nasi Reddy *, S. Kishnajuna Rao*, S.Nagenda Kuma * Assistant
Performance Evaluation of Maximum Ratio combining Scheme in WCDMA System for Different Modulations
 Intenational Jounal of Emeging Technologies in Engineeing Reseach (IJETER) Volume 4, Issue 5, ay (6) www.ijete.evescience.og efomance Evaluation of aimum Ratio combining Scheme in WCDA System fo Diffeent
Intenational Jounal of Emeging Technologies in Engineeing Reseach (IJETER) Volume 4, Issue 5, ay (6) www.ijete.evescience.og efomance Evaluation of aimum Ratio combining Scheme in WCDA System fo Diffeent
The Periodic Ambiguity Function Its Validity and Value
 The Peiodic Ambiguity Function Its Validity and Value Nadav Levanon Dept. of Electical Engineeing Systems Tel Aviv Univesity Tel Aviv, Isael nadav@eng.tau.ac.il Abstact The peiodic ambiguity function (PAF)
The Peiodic Ambiguity Function Its Validity and Value Nadav Levanon Dept. of Electical Engineeing Systems Tel Aviv Univesity Tel Aviv, Isael nadav@eng.tau.ac.il Abstact The peiodic ambiguity function (PAF)
Parameters of spinning AM reticles
 Paametes of spinning AM eticles onald G. Digges, Cal E. Halfod, and Glenn D. Boeman A new method of obtaining amplitude modulation (AM) fo detemining taget location with spinning eticles is pesented. The
Paametes of spinning AM eticles onald G. Digges, Cal E. Halfod, and Glenn D. Boeman A new method of obtaining amplitude modulation (AM) fo detemining taget location with spinning eticles is pesented. The
IEEE Broadband Wireless Access Working Group < Modifications to the Feedback Methodologies in UL Sounding
 Poject Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.16 Boadband Wieless Access Woking Goup Modifications to the Feedback Methodologies in UL Sounding 2008-01-14 Souce(s) Fed Vook, Jeff Zhuang,
Poject Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.16 Boadband Wieless Access Woking Goup Modifications to the Feedback Methodologies in UL Sounding 2008-01-14 Souce(s) Fed Vook, Jeff Zhuang,
Analytical Performance Evaluation of Mixed Services with Variable Data Rates for the Uplink of UMTS
 Analytical Pefomance Evaluation of Mixed Sevices with Vaiable Data Rates fo the Uplink of UMTS Laissa Popova and Wolfgang Koch Lehstuhl fü Mobilkommunikation, Univesität Elangen-Nünbeg, Gemany Email: {popova,
Analytical Pefomance Evaluation of Mixed Sevices with Vaiable Data Rates fo the Uplink of UMTS Laissa Popova and Wolfgang Koch Lehstuhl fü Mobilkommunikation, Univesität Elangen-Nünbeg, Gemany Email: {popova,
ABSTRACTT FFT FFT-' Proc. of SPIE Vol U-1
 Phase econstuction stategies in phase-locking system based on multi-apetue wave font sensos P.A. Semenov, S.D. Pol skikh Shvabe-Reseach, Moscow, Russian Fedeation; e-mail: pite@bk.u ABSTRACTT System of
Phase econstuction stategies in phase-locking system based on multi-apetue wave font sensos P.A. Semenov, S.D. Pol skikh Shvabe-Reseach, Moscow, Russian Fedeation; e-mail: pite@bk.u ABSTRACTT System of
INVESTIGATION OF CLOSE-TO-WALL WIRELESS SENSOR DEPLOYMENT USING 2D FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN MODELLING. Y. Wu and I. J.
 2 nd Intenational Confeence on Wieless Communications in Undegound and Confined Aeas August 25-27, 2008 Val-d O - Québec - Canada INVESTIGATION OF CLOSE-TO-WALL WIRELESS SENSOR DEPLOYMENT USING 2D FINITE-DIFFERENCE
2 nd Intenational Confeence on Wieless Communications in Undegound and Confined Aeas August 25-27, 2008 Val-d O - Québec - Canada INVESTIGATION OF CLOSE-TO-WALL WIRELESS SENSOR DEPLOYMENT USING 2D FINITE-DIFFERENCE
Performance Analysis of Z-Source Inverter Considering Inductor Resistance
 Pefomance Analysis of Z-Souce Invete Consideing Inducto Resistance Fatma A. Khea * and Essam Eddin M. Rashad ** Electic Powe and Machines Engineeing Depatment, Faculty of Engineeing, anta Univesity, anta,
Pefomance Analysis of Z-Souce Invete Consideing Inducto Resistance Fatma A. Khea * and Essam Eddin M. Rashad ** Electic Powe and Machines Engineeing Depatment, Faculty of Engineeing, anta Univesity, anta,
Spatial Coding Techniques for Molecular MIMO
 Spatial Coding Techniques fo Molecula MIMO Matin Damath, H. Bikan Yilmaz, Chan-Byoung Chae, and Pete Adam Hoehe Faculty of Engineeing, Kiel Univesity, Gemany, Email: {md, ph}@tf.uni-kiel.de School of Integated
Spatial Coding Techniques fo Molecula MIMO Matin Damath, H. Bikan Yilmaz, Chan-Byoung Chae, and Pete Adam Hoehe Faculty of Engineeing, Kiel Univesity, Gemany, Email: {md, ph}@tf.uni-kiel.de School of Integated
CCSDS Coding&Synchronization Working Group March Washington DC, USA SLS-C&S_08-CNES02
 CCSDS Coding&Synchonization Woking Goup Mach 2008 1 Washington DC, USA DVB-S2 like fame constuction and LDPC codes ate o/and size extension fo use of Vaiable Coding & Modulation suitable fo X and Ka bands
CCSDS Coding&Synchonization Woking Goup Mach 2008 1 Washington DC, USA DVB-S2 like fame constuction and LDPC codes ate o/and size extension fo use of Vaiable Coding & Modulation suitable fo X and Ka bands
A New Method of VHF Antenna Gain Measurement Based on the Two-ray Interference Loss
 7 nd Intenational Confeence on Atificial Intelligence and Engineeing Applications (AIEA 7) ISBN: 978--6595-485- A New Method of VH Antenna Gain Measuement Based on the Two-ay Intefeence Loss ZHIEI YANG,
7 nd Intenational Confeence on Atificial Intelligence and Engineeing Applications (AIEA 7) ISBN: 978--6595-485- A New Method of VH Antenna Gain Measuement Based on the Two-ay Intefeence Loss ZHIEI YANG,
Performance Analysis of the Parallel Optical All-pass Filter Equalizer for Chromatic Dispersion Compensation at 10 Gb/s
 Pefomance Analysis of the Paallel Optical All-pass Filte Equalize fo Chomatic Dispesion Compensation at Gb/s Wai Pang Ng, Membe, IEEE, W. Loedhammacaka, Student Membe, IEEE, R.A. Cyan, and Z. Ghassemlooy,
Pefomance Analysis of the Paallel Optical All-pass Filte Equalize fo Chomatic Dispesion Compensation at Gb/s Wai Pang Ng, Membe, IEEE, W. Loedhammacaka, Student Membe, IEEE, R.A. Cyan, and Z. Ghassemlooy,
Design of FIR Filter using Filter Response Masking Technique
 Design of FIR Filte using Filte Response Masking Technique Sandeep Shivastava, Alok Jain, Ram Kuma Soni Abstact- In this pape autho is tying to implement Fequency esponse masking (FRM) technique. In this
Design of FIR Filte using Filte Response Masking Technique Sandeep Shivastava, Alok Jain, Ram Kuma Soni Abstact- In this pape autho is tying to implement Fequency esponse masking (FRM) technique. In this
Distributed Spectrum Allocation via Local Bargaining
 Distibuted Spectum Allocation via Local Bagaining Lili Cao Shanghai Jiaotong Univesity, Shanghai, P.R. China Email: cao li li@yahoo.com Haitao Zheng Micosoft Reseach Asia, Beijing, P.R. China Email: htzheng@ieee.og
Distibuted Spectum Allocation via Local Bagaining Lili Cao Shanghai Jiaotong Univesity, Shanghai, P.R. China Email: cao li li@yahoo.com Haitao Zheng Micosoft Reseach Asia, Beijing, P.R. China Email: htzheng@ieee.og
ONE-WAY RADAR EQUATION / RF PROPAGATION
 ONE-WAY RADAR EQUATION / RF PROPAGATION The one-way (tansmitte to eceive) ada equation is deived in this section. This equation is most commonly used in RWR o ESM type of applications. The following is
ONE-WAY RADAR EQUATION / RF PROPAGATION The one-way (tansmitte to eceive) ada equation is deived in this section. This equation is most commonly used in RWR o ESM type of applications. The following is
Demosaicking using Adaptive Bilateral Filters
 Demosaicking using Adaptive Bilateal Filtes Ekine Akuiyibo Timothy Atobatele EE 362, Winte 2006 0. Abstact Digital cameas sample the continuous spectum using an aay of colo filtes such that each pixel
Demosaicking using Adaptive Bilateal Filtes Ekine Akuiyibo Timothy Atobatele EE 362, Winte 2006 0. Abstact Digital cameas sample the continuous spectum using an aay of colo filtes such that each pixel
Design of an LLC Resonant Converter Using Genetic Algorithm
 Design of an LLC Resonant Convete Using Genetic Algoithm H. H. Nien, C. K. Huang, S. K. Changchien, C. H Chan Dept. of Electical Engineeing, Chienkuo Technology Univesity E-mail: nien@ctu.edu.tw Dept,
Design of an LLC Resonant Convete Using Genetic Algoithm H. H. Nien, C. K. Huang, S. K. Changchien, C. H Chan Dept. of Electical Engineeing, Chienkuo Technology Univesity E-mail: nien@ctu.edu.tw Dept,
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS VTU RESULTS FORUM BOOKSPAR ANDROID APP UNIT-4
 NTENN & PROPGTION 6EC6 1EC6 UNIT- Unit : Loop and Hon ntenna: Intoduction, small loop, compaison of fa field of small loop and shot dipole, loop antenna geneal case, fa field pattens of cicula loop, adiation
NTENN & PROPGTION 6EC6 1EC6 UNIT- Unit : Loop and Hon ntenna: Intoduction, small loop, compaison of fa field of small loop and shot dipole, loop antenna geneal case, fa field pattens of cicula loop, adiation
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Poceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 4, 2 http://acousticalsociety.og/ 62nd Meeting Acoustical Society of Ameica San Diego, Califonia 3 Octobe - 4 Novembe 2 Session 4pEA: Engineeing Acoustics 4pEA8.
Poceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 4, 2 http://acousticalsociety.og/ 62nd Meeting Acoustical Society of Ameica San Diego, Califonia 3 Octobe - 4 Novembe 2 Session 4pEA: Engineeing Acoustics 4pEA8.
ECE 6640 Digital Communications
 ECE 6640 Digital Communications D. Badley J. Bazuin Assistant ofesso Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing College of Engineeing and Applied Sciences Chapte 5 5. Communications Link Analysis. 1.
ECE 6640 Digital Communications D. Badley J. Bazuin Assistant ofesso Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing College of Engineeing and Applied Sciences Chapte 5 5. Communications Link Analysis. 1.
Hexagonal Shaped Microstrip Patch Antenna for Satellite and Military Applications
 Intenational Jounal of Engineeing and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 49 8958, Volume-7 Issue-5, June 08 Hexagonal Shaped Micostip Patch Antenna fo Satellite and Militay Applications Jayaenjini N, Unni
Intenational Jounal of Engineeing and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 49 8958, Volume-7 Issue-5, June 08 Hexagonal Shaped Micostip Patch Antenna fo Satellite and Militay Applications Jayaenjini N, Unni
A New Buck-Boost DC/DC Converter of High Efficiency by Soft Switching Technique
 A New Buck-Boost D/D onvete of High Efficiency by Soft Switching Technique Dong-Kul Kwak, Seung-Ho Lee, and Do-Young Jung Pofessional Gaduate School of Disaste Pevention, Kangwon National Univesity, 45-711,
A New Buck-Boost D/D onvete of High Efficiency by Soft Switching Technique Dong-Kul Kwak, Seung-Ho Lee, and Do-Young Jung Pofessional Gaduate School of Disaste Pevention, Kangwon National Univesity, 45-711,
Single-User MIMO ML Successive Interference Canceling Receiver with HARQ-IR Protocol
 Single-Use MIMO ML Successive Intefeence Canceling Receive with HARQ-IR Potocol Elena Lukashova, Floian Kaltenbege, Raymond Knopp EURECOM Campus SophiaTech, 40 Route des Chappes, 0640 Biot, Fance Email:
Single-Use MIMO ML Successive Intefeence Canceling Receive with HARQ-IR Potocol Elena Lukashova, Floian Kaltenbege, Raymond Knopp EURECOM Campus SophiaTech, 40 Route des Chappes, 0640 Biot, Fance Email:
Realistic Simulation of a Wireless Signal Propagation in an Urban Environment
 Realistic Simulation of a Wieless Signal Popagation in an Uban Envionment Keyukuma J. Patel Univesity of Southen Queensland Toowoomba, Austalia e-mail: keyupatel@ieee.og Andew Y. J. Lee Nanyang Technological
Realistic Simulation of a Wieless Signal Popagation in an Uban Envionment Keyukuma J. Patel Univesity of Southen Queensland Toowoomba, Austalia e-mail: keyupatel@ieee.og Andew Y. J. Lee Nanyang Technological
PSO driven RBFNN for design of equilateral triangular microstrip patch antenna
 Indian Jounal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 38, August 009, pp 33-37 PSO diven RBF fo design of equilateal tiangula micostip patch antenna Vidya Saga Chintakindi,$, Shyam Sunda Pattnaik,#,*, O P Bajpai
Indian Jounal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 38, August 009, pp 33-37 PSO diven RBF fo design of equilateal tiangula micostip patch antenna Vidya Saga Chintakindi,$, Shyam Sunda Pattnaik,#,*, O P Bajpai
N2-1. The Voltage Source. V = ε ri. The Current Source
 DC Cicuit nalysis The simplest cicuits to undestand and analyze ae those that cay diect cuent (DC). n this note we continue ou study of DC cicuits with the topics of DC voltage and cuent souces, the idea
DC Cicuit nalysis The simplest cicuits to undestand and analyze ae those that cay diect cuent (DC). n this note we continue ou study of DC cicuits with the topics of DC voltage and cuent souces, the idea
Near-field Computation and. Uncertainty Estimation using Basic. Cylindrical-Spherical Formulae
 Nea-field Computation and Uncetainty Estimation using Basic Cylindical-Spheical Fomulae Poject... IEC 63 Subject... Basic Nea-Field Computation Document numbe... N/A Revision... 3 Autho... F.D. du Plessis
Nea-field Computation and Uncetainty Estimation using Basic Cylindical-Spheical Fomulae Poject... IEC 63 Subject... Basic Nea-Field Computation Document numbe... N/A Revision... 3 Autho... F.D. du Plessis
ECE 6640 Digital Communications
 ECE 6640 Digital Communications D. Badley J. Bazuin Assistant ofesso Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing College of Engineeing and Applied Sciences Chapte 5 5. Communications Link Analysis. 1.
ECE 6640 Digital Communications D. Badley J. Bazuin Assistant ofesso Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing College of Engineeing and Applied Sciences Chapte 5 5. Communications Link Analysis. 1.
Throughput Maximization of Ad-hoc Wireless Networks Using Adaptive Cooperative Diversity and Truncated ARQ
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 56, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 008 1907 Thoughput Maimization of Ad-hoc Wieless Netwoks Using Adaptive Coopeative Divesity and Tuncated ARQ Lin Dai, Membe, IEEE, and Khaled
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 56, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 008 1907 Thoughput Maimization of Ad-hoc Wieless Netwoks Using Adaptive Coopeative Divesity and Tuncated ARQ Lin Dai, Membe, IEEE, and Khaled
Optic Cable Tracking and Positioning Method Based on Distributed Optical Fiber Vibration Sensing
 08 5th Intenational Confeence on Electical & Electonics Engineeing and Compute Science (ICEEECS 08) Optic Cable Tacking and Positioning Method Based on Distibuted Optical Fibe Vibation Sensing Zhang Chao,
08 5th Intenational Confeence on Electical & Electonics Engineeing and Compute Science (ICEEECS 08) Optic Cable Tacking and Positioning Method Based on Distibuted Optical Fibe Vibation Sensing Zhang Chao,
Residual Self-Interference Mitigation in Full-Duplex Two-Way MIMO Relaying Network
 Residual Self-Intefeence Mitigation in Full-Duplex Two-Way MIMO Relaying Netwok Thesis submitted in patial fulfillment of the equiements fo the degee of Maste of Science in Electonics and Communications
Residual Self-Intefeence Mitigation in Full-Duplex Two-Way MIMO Relaying Netwok Thesis submitted in patial fulfillment of the equiements fo the degee of Maste of Science in Electonics and Communications
Analysis of the optimized low-nonlinearity lateral effect sensing detector
 Jounal of hysics: Confeence Seies Analysis of the optimized low-nonlineaity lateal effect sensing detecto To cite this aticle: Saeed Olyaee et al J. hys.: Conf. Se. 76 4 Related content - Neual netwok
Jounal of hysics: Confeence Seies Analysis of the optimized low-nonlineaity lateal effect sensing detecto To cite this aticle: Saeed Olyaee et al J. hys.: Conf. Se. 76 4 Related content - Neual netwok
An Approach to Cooperative Satellite Communications in 4G Mobile Systems
 JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATION, VOL. 4, NO., NOVEMBER 9 85 An Appoach to Coopeative atellite Communications in 4G Mobile ystems Yui Labado, Masoumeh Kaimi, Deng an, and Jey Mille Floida Intenational Univesity,
JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATION, VOL. 4, NO., NOVEMBER 9 85 An Appoach to Coopeative atellite Communications in 4G Mobile ystems Yui Labado, Masoumeh Kaimi, Deng an, and Jey Mille Floida Intenational Univesity,
Low Profile MIMO Diversity Antenna with Multiple Feed
 2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-424X Jounal of Basic and Applied Scientific Reseach www.textoad.com Low Pofile MIMO Divesity Antenna with Multiple Feed Waqas Ahmad, Muhammad Wasif Nisa, Ehsan Ullan
2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-424X Jounal of Basic and Applied Scientific Reseach www.textoad.com Low Pofile MIMO Divesity Antenna with Multiple Feed Waqas Ahmad, Muhammad Wasif Nisa, Ehsan Ullan
mobile FSO communication has not been realized, particularly for ad hoc networking and communication environments.
 Optimal Communication Coveage fo Fee-Space-Optical MANET Building Blocks Muat Yuksel, Jayasi Akella, Shivkuma Kalyanaaman, Patha Dutta ensselae Polytechnic Institute, ECSE Depatment, JEC 6049 1 8 th Steet,
Optimal Communication Coveage fo Fee-Space-Optical MANET Building Blocks Muat Yuksel, Jayasi Akella, Shivkuma Kalyanaaman, Patha Dutta ensselae Polytechnic Institute, ECSE Depatment, JEC 6049 1 8 th Steet,
Chamber Influence Estimation for Radiated Emission Testing in the Frequency Range of 1 GHz to 18 GHz
 Chambe Influence Estimation fo Radiated Emission Testing in the Fequency Range of 1 GHz to 18 GHz Alexande Kiz Electomagnetic Compatibility and RF-Engineeing ARC eibesdof eseach GmbH eibesdof, Austia alexande.kiz@acs.ac.at
Chambe Influence Estimation fo Radiated Emission Testing in the Fequency Range of 1 GHz to 18 GHz Alexande Kiz Electomagnetic Compatibility and RF-Engineeing ARC eibesdof eseach GmbH eibesdof, Austia alexande.kiz@acs.ac.at
Chapter 9 Cascode Stages and Current Mirrors
 Chapte 9 Cascode Stages and Cuent Mios 9. Cascode Stage 9. Cuent Mios CH 9 Cascode Stages and Cuent Mios Boosted Output Impedances S O S m out E O E m out g g Bipola Cascode Stage [ g ( )] out m O O O
Chapte 9 Cascode Stages and Cuent Mios 9. Cascode Stage 9. Cuent Mios CH 9 Cascode Stages and Cuent Mios Boosted Output Impedances S O S m out E O E m out g g Bipola Cascode Stage [ g ( )] out m O O O
Near-field emission prediction of CESAME
 Nea-field emission pediction of CESAME E. Sicad, S. Ben Dhia, E. Lamoueux INSA-GEI, 135 Av de Rangueil 31077 Toulouse Fance B. Vignon, L. Couau ST Micoelectonics, Cental R&D Colles, Fance Contact : etienne.sicad@insa-toulouse.f
Nea-field emission pediction of CESAME E. Sicad, S. Ben Dhia, E. Lamoueux INSA-GEI, 135 Av de Rangueil 31077 Toulouse Fance B. Vignon, L. Couau ST Micoelectonics, Cental R&D Colles, Fance Contact : etienne.sicad@insa-toulouse.f
UNCERTAINTY ESTIMATION OF SIZE-OF-SOURCE EFFECT MEASUREMENT FOR 650 NM RADIATION THERMOMETERS
 XIX IMEKO Wold Congess Fundamental and Applied Metology Septembe 6 11, 29, Lisbon, Potugal UNCERTAINTY ESTIMATION OF SIZE-OF-SOURCE EFFECT MEASUREMENT FOR 65 NM RADIATION THERMOMETERS Fumihio Sakuma, Laina
XIX IMEKO Wold Congess Fundamental and Applied Metology Septembe 6 11, 29, Lisbon, Potugal UNCERTAINTY ESTIMATION OF SIZE-OF-SOURCE EFFECT MEASUREMENT FOR 65 NM RADIATION THERMOMETERS Fumihio Sakuma, Laina
Probabilistic Spectrum Assignment for QoS-constrained Cognitive Radios with Parallel Transmission Capability
 Pobabilistic Spectum Assignment fo QoS-constained Cognitive Radios with Paallel Tansmission Capability Haythem Ahmad any Salameh epatment of Telecommunication Engineeing Yamouk Univesity haythem@yuedujo
Pobabilistic Spectum Assignment fo QoS-constained Cognitive Radios with Paallel Tansmission Capability Haythem Ahmad any Salameh epatment of Telecommunication Engineeing Yamouk Univesity haythem@yuedujo
2D Coding for Future Perpendicular and Probe Recording
 2D Coding fo Futue Pependicula and Pobe Recoding Joseph A. O Sullivan Naveen Singla Ronald S. Indec Washington Univesity Saint Louis, Missoui s Outline: 2D Coding fo 2D ISI Motivation: 2D Intesymbol Intefeence
2D Coding fo Futue Pependicula and Pobe Recoding Joseph A. O Sullivan Naveen Singla Ronald S. Indec Washington Univesity Saint Louis, Missoui s Outline: 2D Coding fo 2D ISI Motivation: 2D Intesymbol Intefeence
Signal Extraction Technology
 Extaction Technology Intoduction Masimo SET pulse oximety is a new and fundamentally distinct method of acquiing, pocessing and epoting ateial oxygen satuation and pulse ate. As illustated below, Masimo
Extaction Technology Intoduction Masimo SET pulse oximety is a new and fundamentally distinct method of acquiing, pocessing and epoting ateial oxygen satuation and pulse ate. As illustated below, Masimo
Experimental Investigation of Influence on Non-destructive Testing by Form of Eddy Current Sensor Probe
 Expeimental Investigation of Influence on Non-destuctive Testing by Fom of Eddy Cuent Senso Pobe Fengyun Xie * and Jihui Zhou School of Mechanical and Electonical Engineeing, East China Jiaotong Univesity,
Expeimental Investigation of Influence on Non-destuctive Testing by Fom of Eddy Cuent Senso Pobe Fengyun Xie * and Jihui Zhou School of Mechanical and Electonical Engineeing, East China Jiaotong Univesity,
Multiagent Reinforcement Learning Dynamic Spectrum Access in Cognitive Radios
 Sensos & Tansduces 204 by IFSA Publishing, S L http://wwwsensospotalcom Multiagent Reinfocement Leaning Dynamic Spectum Access in Cognitive Radios Wu Chun, 2 Yin Mingyong, 2 Ma Shaoliang, Jiang Hong School
Sensos & Tansduces 204 by IFSA Publishing, S L http://wwwsensospotalcom Multiagent Reinfocement Leaning Dynamic Spectum Access in Cognitive Radios Wu Chun, 2 Yin Mingyong, 2 Ma Shaoliang, Jiang Hong School
Impact of bilateral filter parameters on medical image noise reduction and edge preservation
 The Univesity of Toledo The Univesity of Toledo Digital Repositoy Theses and Dissetations 2009 Impact of bilateal filte paametes on medical image noise eduction and edge pesevation Michael D. Lekan Medical
The Univesity of Toledo The Univesity of Toledo Digital Repositoy Theses and Dissetations 2009 Impact of bilateal filte paametes on medical image noise eduction and edge pesevation Michael D. Lekan Medical
Optimal Strategies in Jamming Resistant Uncoordinated Frequency Hopping Systems. Bingwen Zhang
 Optimal Stategies in Jamming Resistant Uncoodinated Fequency Hopping Systems by Bingwen Zhang A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE in patial fulfillment of the equiements
Optimal Stategies in Jamming Resistant Uncoodinated Fequency Hopping Systems by Bingwen Zhang A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE in patial fulfillment of the equiements
Quality-Driven Joint Rate and Power Adaptation for Scalable Video Transmissions over MIMO Systems
 Quality-Diven Joint Rate and Powe Adaptation fo Scalable Video Tansmissions ove MIMO Systems Xiang Chen, Student Membe, IEEE, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Fellow, IEEE, James A. Ritcey, Fellow, IEEE, Chung-Nan Lee,
Quality-Diven Joint Rate and Powe Adaptation fo Scalable Video Tansmissions ove MIMO Systems Xiang Chen, Student Membe, IEEE, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Fellow, IEEE, James A. Ritcey, Fellow, IEEE, Chung-Nan Lee,
Regionalized Interference Alignment in Two-Tiered Cognitive Heterogeneous Networks
 Jounal of Communications Vol 9, No, Novembe egionalized Intefeence Alignment in Two-Tieed Cognitive eteogeneous Netwoks Jingwen Yang, Li Li*, and Xiaoping Zhou College of Infomation, echanical and Electical
Jounal of Communications Vol 9, No, Novembe egionalized Intefeence Alignment in Two-Tieed Cognitive eteogeneous Netwoks Jingwen Yang, Li Li*, and Xiaoping Zhou College of Infomation, echanical and Electical
Instant Active Positioning with One LEO Satellite
 Instant Active Positioning with One LEO Satellite NADAV LEVANON el Aviv Univesity, el Aviv, Isael Received Decembe 997; Revised June 999 ABSRAC: Autonomous position detemination in the Globalsta satellite
Instant Active Positioning with One LEO Satellite NADAV LEVANON el Aviv Univesity, el Aviv, Isael Received Decembe 997; Revised June 999 ABSRAC: Autonomous position detemination in the Globalsta satellite
Design of Microstrip Antenna for Wireless Local Area Network
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com Intenational Jounal of Compute Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Jounal of Compute Science and Infomation Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 4, Apil 205, pg.36 365
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com Intenational Jounal of Compute Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Jounal of Compute Science and Infomation Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 4, Apil 205, pg.36 365
Performance analysis of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in fading mobile radio channels
 MILCOM 95, SAN IEGO, CA, NOV. 995 Pefomance analysis of ARQ Go-Back-N potocol in fading mobile adio channels Michele Zozi y, Ramesh R. Rao z, Lauence B. Milstein z y ipatimento di Elettonica e Infomazione,
MILCOM 95, SAN IEGO, CA, NOV. 995 Pefomance analysis of ARQ Go-Back-N potocol in fading mobile adio channels Michele Zozi y, Ramesh R. Rao z, Lauence B. Milstein z y ipatimento di Elettonica e Infomazione,
Antenna fundamentals: With answers to questions and problems (See also Chapter 9 in the textbook.)
 adio Technology Metopolia/A. Koivumäki Antenna fundamentals: With answes to questions and poblems (See also Chapte 9 in the textbook.) 1. a) Make up a definition fo the tem "antenna". Answe: One definition:
adio Technology Metopolia/A. Koivumäki Antenna fundamentals: With answes to questions and poblems (See also Chapte 9 in the textbook.) 1. a) Make up a definition fo the tem "antenna". Answe: One definition:
Mitigation of GPS Multipath Using Polarization and Spatial Diversities
 Mitigation of GPS Multipath Using Polaization and Spatial ivesities Matthew Benneman, Jade Moton Chun Yang Fank van Gaas Miami Univesity Sigtem Technology, Inc. Ohio Univesity BIOGRAPIES Matthew Benneman
Mitigation of GPS Multipath Using Polaization and Spatial ivesities Matthew Benneman, Jade Moton Chun Yang Fank van Gaas Miami Univesity Sigtem Technology, Inc. Ohio Univesity BIOGRAPIES Matthew Benneman
S11 PHY114 Problem Set 8
 S11 PHY114 Poblem Set 8 S. G. Rajeev Apil 4, 2011 Due Monday 4 Ap 2011 1. Find the wavelength of the adio waves emitted by the Univesity of Rocheste adio station (88.5 Mhz)? The numbe of bits pe second
S11 PHY114 Poblem Set 8 S. G. Rajeev Apil 4, 2011 Due Monday 4 Ap 2011 1. Find the wavelength of the adio waves emitted by the Univesity of Rocheste adio station (88.5 Mhz)? The numbe of bits pe second
DESIGN AND PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF RECTANGULAR MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA FOR GSM APPLICATION
 DESIGN AND PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF RECTANGULAR MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA FOR GSM APPLICATION RAHUL T. DAHATONDE, SHANKAR B. DEOSARKAR Dept. of E & TC, D. Babasaheb Ambedka Technological Univesity, Lonee,
DESIGN AND PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF RECTANGULAR MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA FOR GSM APPLICATION RAHUL T. DAHATONDE, SHANKAR B. DEOSARKAR Dept. of E & TC, D. Babasaheb Ambedka Technological Univesity, Lonee,
An Efficient Control Approach for DC-DC Buck-Boost Converter
 2016 Published in 4th Intenational Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineeing and Science 3-5 Novembe 2016 (ISITES2016 Alanya/Antalya - Tukey) An Efficient Contol Appoach fo DC-DC Buck-Boost Convete
2016 Published in 4th Intenational Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineeing and Science 3-5 Novembe 2016 (ISITES2016 Alanya/Antalya - Tukey) An Efficient Contol Appoach fo DC-DC Buck-Boost Convete
GAMMA SHAPED MONOPOLE PATCH ANTENNA FOR TABLET PC
 GAMMA SHAPED MONOPOLE PATCH ANTENNA FOR TABLET PC Islam Md. Rafiqul, Mohammad Shawkat Habib and Khaizuan Abdullah Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Intenational Islamic Univesity Malaysia,
GAMMA SHAPED MONOPOLE PATCH ANTENNA FOR TABLET PC Islam Md. Rafiqul, Mohammad Shawkat Habib and Khaizuan Abdullah Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Intenational Islamic Univesity Malaysia,
Taking Advantage of Overhearing in Low Power Listening WSNs: A Performance Analysis of the LWT-MAC Protocol
 DOI.7/s36--28-4 Taking Advantage of Oveheaing in Low Powe Listening WSNs: A Pefomance Analysis of the LWT-MAC Potocol Cistina Cano Bois Bellalta Anna Sfaiopoulou Miquel Olive Jaume Baceló Spinge Science+Business
DOI.7/s36--28-4 Taking Advantage of Oveheaing in Low Powe Listening WSNs: A Pefomance Analysis of the LWT-MAC Potocol Cistina Cano Bois Bellalta Anna Sfaiopoulou Miquel Olive Jaume Baceló Spinge Science+Business
Feasibility of a triple mode, low SAR material coated antenna for mobile handsets
 Loughboough Univesity Institutional Repositoy Feasibility of a tiple mode, low SAR mateial coated antenna fo mobile handsets This item was submitted to Loughboough Univesity's Institutional Repositoy by
Loughboough Univesity Institutional Repositoy Feasibility of a tiple mode, low SAR mateial coated antenna fo mobile handsets This item was submitted to Loughboough Univesity's Institutional Repositoy by
Analysis and Implementation of LLC Burst Mode for Light Load Efficiency Improvement
 Analysis and Implementation of LLC Bust Mode fo Light Load Efficiency Impovement Bin Wang, Xiaoni Xin, Stone Wu, Hongyang Wu, Jianping Ying Delta Powe Electonics Cente 238 Minxia Road, Caolu Industy Zone,
Analysis and Implementation of LLC Bust Mode fo Light Load Efficiency Impovement Bin Wang, Xiaoni Xin, Stone Wu, Hongyang Wu, Jianping Ying Delta Powe Electonics Cente 238 Minxia Road, Caolu Industy Zone,
Binary Systematic Network Coding for Progressive Packet Decoding
 Binay Systematic etwok Coding fo Pogessive Packet Decoding Andew L. Jones, Ioannis Chatzigeogiou and Andea Tassi School of Computing and Communications, Lancaste Univesity, United Kingdom Email: {a.jones2,
Binay Systematic etwok Coding fo Pogessive Packet Decoding Andew L. Jones, Ioannis Chatzigeogiou and Andea Tassi School of Computing and Communications, Lancaste Univesity, United Kingdom Email: {a.jones2,
Audio Engineering Society. Convention Paper. Presented at the 120th Convention 2006 May Paris, France
 Audio Engineeing Society Convention Pape Pesented at the 120th Convention 2006 May 20 23 Pais, Fance This convention pape has been epoduced fom the autho's advance manuscipt, without editing, coections,
Audio Engineeing Society Convention Pape Pesented at the 120th Convention 2006 May 20 23 Pais, Fance This convention pape has been epoduced fom the autho's advance manuscipt, without editing, coections,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 100 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Pocedia Engineeing 1 (215 ) 1 14 25th DAAAM Intenational Symposium on Intelligent Manufactuing and Automation DAAAM 214 Measuement of Complex Pemittivity
Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Pocedia Engineeing 1 (215 ) 1 14 25th DAAAM Intenational Symposium on Intelligent Manufactuing and Automation DAAAM 214 Measuement of Complex Pemittivity
AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Inteface Pactices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 48-1 2015 Test Method fo Measuing Shielding Effectiveness of Passive and Active Devices Using a GTEM Cell NOTICE
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Inteface Pactices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 48-1 2015 Test Method fo Measuing Shielding Effectiveness of Passive and Active Devices Using a GTEM Cell NOTICE
Current Compensation Techniques for Lowvoltage High-performance Current Mirror Circuits
 Southen Illinois Univesity Cabondale OpenSIUC Aticles Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing 7-06 Cuent Compensation Techniques fo Lowvoltage High-pefomance Cuent Mio Cicuits Stefan Leitne Haibo
Southen Illinois Univesity Cabondale OpenSIUC Aticles Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing 7-06 Cuent Compensation Techniques fo Lowvoltage High-pefomance Cuent Mio Cicuits Stefan Leitne Haibo
Sliding Mode Control for Half-Wave Zero Current Switching Quasi-Resonant Buck Converter
 Sliding Mode Contol fo Half-Wave Zeo Cuent Switching Quasi-Resonant Buck Convete M. Ahmed, Student membe, IEEE, M. Kuisma, P. Silventoinen Abstact This pape focuses on the pactical implementation of sliding
Sliding Mode Contol fo Half-Wave Zeo Cuent Switching Quasi-Resonant Buck Convete M. Ahmed, Student membe, IEEE, M. Kuisma, P. Silventoinen Abstact This pape focuses on the pactical implementation of sliding
Optimised Wireless Network Using Smart Mobile Terminal Antenna (SMTA) System
 Optimised Wieless Netwok Using Smat Mobile Teminal Antenna (SMTA) System Autho Lu, Junwei, Sciven, Ian, Wate, Wayne Published 2010 Confeence Title Poceedings of IEEE APEMC2010 DOI https://doi.og/10.1109/apemc.2010.5475858
Optimised Wieless Netwok Using Smat Mobile Teminal Antenna (SMTA) System Autho Lu, Junwei, Sciven, Ian, Wate, Wayne Published 2010 Confeence Title Poceedings of IEEE APEMC2010 DOI https://doi.og/10.1109/apemc.2010.5475858
Volume 1, Number 1, 2015 Pages 1-12 Jordan Journal of Electrical Engineering ISSN (Print): , ISSN (Online):
 JJEE Volume, Numbe, 5 Pages - Jodan Jounal of Electical Engineeing ISSN (Pint): 49-96, ISSN (Online): 49-969 Discimination between Tansfome Inush Cuent and Intenal Fault using Combined DFT-ANN Appoach
JJEE Volume, Numbe, 5 Pages - Jodan Jounal of Electical Engineeing ISSN (Pint): 49-96, ISSN (Online): 49-969 Discimination between Tansfome Inush Cuent and Intenal Fault using Combined DFT-ANN Appoach
Exploring Convolutional Neural Network Structures and Optimization Techniques for Speech Recognition
 INTERSPEECH 2013 Exploing Convolutional Neual Netwok Stuctues and Optimization Techniques fo Speech Recognition Ossama Abdel-Hamid 1, Li Deng 2, Dong Yu 2 1 Depatment of Compute Science and Engineeing,
INTERSPEECH 2013 Exploing Convolutional Neual Netwok Stuctues and Optimization Techniques fo Speech Recognition Ossama Abdel-Hamid 1, Li Deng 2, Dong Yu 2 1 Depatment of Compute Science and Engineeing,
The Experimental Study of Possibility for Radar Target Detection in FSR Using L1-Based Non-Cooperative Transmitter
 The Expeimental Study of Possibility fo Rada Taget Detection in FSR Using L1-Based on-coopeative Tansmitte Ch. Kabakchiev 1, I. Gavanov, V. Beha 3, H. Rohling 4 1 Faculty of Mathematics & Infomatics,Sofia
The Expeimental Study of Possibility fo Rada Taget Detection in FSR Using L1-Based on-coopeative Tansmitte Ch. Kabakchiev 1, I. Gavanov, V. Beha 3, H. Rohling 4 1 Faculty of Mathematics & Infomatics,Sofia
Equalization Techniques for MIMO Systems in Wireless Communication: A Review
 Equalization Techniques fo MIMO Systems in Wieless Communication: A Review Rashmi Kashyap, Jaspal Bagga Abstact-The main objective of this pape is to povide a eview of equalization techniques in multiple
Equalization Techniques fo MIMO Systems in Wieless Communication: A Review Rashmi Kashyap, Jaspal Bagga Abstact-The main objective of this pape is to povide a eview of equalization techniques in multiple
Electrical characterization of thin film ferroelectric capacitors
 1 Electical chaacteization of thin film feoelectic capacitos M. P. J. Tiggelman, K. Reimann, M. Klee, D. Beelen, W. Keu, J. Schmitz, and R. J. E. Hueting Abstact Tunable capacitos can be used to facilitate
1 Electical chaacteization of thin film feoelectic capacitos M. P. J. Tiggelman, K. Reimann, M. Klee, D. Beelen, W. Keu, J. Schmitz, and R. J. E. Hueting Abstact Tunable capacitos can be used to facilitate
1 Performance and Cost
 Pefomance and Cost Analysis and Reseach of Ai-Cooled Using Small Diamete Coppe Tubes Wu Yang, Li Changsheng and Deng Bin Abstact Replacing coppe tubes with aluminum tubes and using coppe tubes with smalle
Pefomance and Cost Analysis and Reseach of Ai-Cooled Using Small Diamete Coppe Tubes Wu Yang, Li Changsheng and Deng Bin Abstact Replacing coppe tubes with aluminum tubes and using coppe tubes with smalle
Comparison Between Known Propagation Models Using Least Squares Tuning Algorithm on 5.8 GHz in Amazon Region Cities
 106 Compaison Between Known Popagation Models Using Least Squaes Tuning Algoithm on 5.8 GHz in Amazon Region Cities Buno S. L. Casto, Mácio R. Pinheio, Gevásio P. S. Cavalcante Fedeal Univesity of Paá
106 Compaison Between Known Popagation Models Using Least Squaes Tuning Algoithm on 5.8 GHz in Amazon Region Cities Buno S. L. Casto, Mácio R. Pinheio, Gevásio P. S. Cavalcante Fedeal Univesity of Paá
