TRANSFER IMPEDANCE MODEL OF MEASUREMENT PATH FOR ESD SIMULATOR CALIBRATION
|
|
|
- Gertrude Terry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EMC 6 8 th INERNAIONAL WROCLAW SMPOSIUM AND EXHIBIION ON ELECROMAGNEIC COMPAIBILI, WROCLAW, 8 3 JUNE, 6 RANSFER IMPEDANCE MODEL OF MEASUREMEN PAH FOR ESD SIMULAOR CALIBRAION Janusz Baran, omasz Dróżdż, Jan Sroka 3, echnical University of Częstochowa, Institute of Electronics and Control Systems, Częstochowa, Poland baranj@el.pcz.czest.pl, drozdz@el.pcz.czest.pl 3 Schaffner EMC AG, est Systems, Luterbach, Switzerland, jan.sroka@schaffner.com Abstract: he paper deals with deriving a frequency dependent transfer impedance of a measurement path for calibration of an electrostatic discharge (ESD) simulator. he transfer impedance is derived from the scattering parameters of the calibration system components, i.e. the Pellegrini target, the cable with attenuator and the broadband oscilloscope, measured in the range from MHz to 6GHz. he frequency analysis of the whole path reveals high frequency effects neglected by the simple resistance models and makes possible reduction of the calibration uncertainty. Keywords: ESD simulator, calibration, scattering parameters, transfer impedance, two-port network. INRODUCION Electrostatic discharge (ESD) simulators (or generators) are used for testing immunity of electric and electronic equipment to electrostatic discharges and disturbances. o ensure reliability of the testing, the generators have to be calibrated, especially in terms of standardized shape of the discharge current impulse. It is ruled by the IEC standard []. he parameters that have to be preserved to ensure repeatability of the calibration are: the rise time, the peak current and the tail current after 3 and 6 nanoseconds. i [A] recorded impulse theoretical specification 3 6 t [ns] Fig.. ypical waveform of kv ESD impulse and its theoretical specification calculated with formula proposed in [] A typical waveform of the ESD impulse recorded experimentally is presented in Fig. along with "theoretical" impulse calculated on the basis of the formula proposed in []. his analytic approximation is employed in literature [,3,] and will be further used in this work. ESD Gen. Fig.. Measurement system for the ESD simulator calibration ESD Gen. target (current converter) I R cable with attenuator R U Fig. 3. Simplified DC model of the target. I discharge current, U oscilloscope input voltage (cable and attenuator neglected). Parameters measured for the target analyzed in the paper: R =.6, R =7.88R R = U /I =. he ESD simulator is tested in a system whose principal elements are shown in Fig.. he discharge hits a special current converter the Pellegrini target (see Fig.), connected to a high frequency oscilloscope by a coaxial cable with an attenuator. Earlier works, e.g. [], assumed a simple DC model of the target shown in Fig.3. However, due to the time scale of the waveforms and the target design, the high frequency features of the measurement path up to gigahertz should be also taken into consideration. Such approach makes possible better evaluation of distortions introduced in the path from the discharge current I to the oscilloscope input voltage U, and I OSC
2 Z IN Z INC Z INO I I I arget (current Cable with converter) U attenuator U Osc ESD Gen. Z R =U /I Z R C=U /I Fig.. wo-port network diagram of the ESD simulator measurement path consequently improves accuracy of the calibration which is currently based on simple resistance models. In this work we use the scattering parameters S to construct linear two-port networks with frequency dependent parameters as models of the target and cable with attenuator and calculate the transfer impedance from I to U. It is an extension of works [,3], where the transfer impedance of the target only was derived in the same way.. MODEL OF HE MEASUREMEN PAH.. Scattering and admittance parameters of the target he two-port network diagram used for analysis of the ESD simulator measurement system is shown in Fig.. he input quantities are the scattering parameters measured with a network analyzer separately for the target and the cable with 9dB attenuator. Because of the target construction it is impossible to connect to it directly the two ports of the analyzer. herefore a special adapter was used (Fig.) and the scattering matrix of the target was calculated from the measurements for adapter-target (A) and adapteradapter (AA) configurations. Fig.. Adapters (left) and the target (right) [] We assume that two identical adapters connected face to face have symmetric scattering matrices and there are no reflections. In this case the scattering matrix of a single adapter AA S A S, () AA S and the parameters of the target can be calculated as [3]: S S A A A A A S S S S. () A S A S A S he scattering parameters of the cable with the attenuator were measured directly. Because in the subsequent calculations we use the admittance parameters, the scattering parameters S have to be recalculated into using standard formulas: S S SS S S SS r, (3a) S, (3b) S S SS r r S, (3c) S S SS r r S S SS S S SS r, (3d) where the normalizing constants are assumed equal to reference impedances, in this case the impedances of the network analyzer ports, i.e. r =Z p =r =Z p =.. ransfer impedance of the measurement path he transfer impedance Z R_C =U /I (see Fig.) can be expressed as a function of the admittance parameters C of the substitute two-port network of the target and cable with attenuator connected in series: C U ZIN ZR _ C, () C I where Z IN is the target input impedance. (Index denotes the target, C the cable with attenuator, C the cascade connection of the two). he impedance Z IN can be expressed as a function of the target admittance parameters and the target load impedance Z O, which is constituted by the remaining part of the path, i.e. the cable with attenuator and the oscilloscope: U ZO Z IN, () I Z O
3 where. he admittance parameters C are calculated from the transmission matrix (ABCD parameters) A C of the substitute two-port network with equations: A A,,,. (6) A A A A Recalculation into the transmission parameters is convenient because the substitute matrix A C is a product of the transmission matrices of the cascaded components: C C C C A A A A A A A C C. (7) A A A A he transmission parameters of a two-port network are related back to its admittance parameters as follows: A, A, A, A. (8) Calculations using equations (8) have to be carried out both for the target and the cable with attenuator. he target load impedance Z O occurring in () is the input impedance of the cable: U ZO Z. (9) INC I o determine Z INC we use equation () with quantities corresponding to the cable: C ZO ZINC, () C C Z C C C C C where O and Z O is the cable load impedance which is in turn the input impedance of the oscilloscope. he impedance Z O can be calculated directly from the measured reflection parameter S of the oscilloscope: O U S ZO ZINO Z, () O p I S where Z p = is the source impedance (impedance of port of the network analyzer). 3. RESULS OF MEASUREMENS AND CALCULAIONS In the analysis we use data of the S-parameters of the Pellegrini target, cable with 9dB attenuator and oscilloscope (ektronix SCD) measured using the vector network analyzer in Schaffner EMC AG laboratory in wide frequency range from MHz to 6GHz. he measurements are given in the realimaginary part form. he S-parameters of the target, the adapters and the oscilloscope were measured for 37 frequency values and the parameters of the cable with attenuator for 69 frequencies. he greater number of measurement points in this case is dictated by necessity of more precise modeling the cable as a delay line. All the measured S-parameters data have to be interpolated to the same grid of linearly equidistant frequencies, for which the discrete Fourier transform of the discharge impulse will be further calculated. We used either simple linear interpolation or cubic splines, but in both cases the results are very similar. he DC values were obtained by extrapolation of the data towards zero frequency. Fig. 6 shows the graph of the target input impedance Z IN calculated with equation (). Looking at the real part of the impedance we can read out the low frequency resistance R IN.97, which is smaller than for the DC model from Fig.3. At about 3GHz Z IN has a high resonance peak resulting from the target construction. In Fig. 7 there are shown the frequency characteristics of the cable input impedance Z INC and the oscilloscope input impedance Z INO, obtained with equations () and () respectively. In low frequencies they are approximately standard resistances. Re(Z IN ) [] Im(Z IN ) [] Re(Z IN ) [] Im(Z IN ) [] Fig. 6. Input impedance Z IN (f) of the target Z INC Z INO Fig. 7. Input impedances: Z INC (f) of the cable and Z INO (f) of the oscilloscope Fig. 8 and 9 present the transfer impedance Z R_C of the whole considered path, calculated with equation (), versus frequency as well as the transfer impedance Z R_ =U /I of the target only. When we compare them, it is clear that large phase shift visible in Fig. 9 is introduced by the cable which works like a delay line in high frequencies. Both impedances have distinct resonant
4 peaks around 3GHz due to the target. In Fig. 8 we see that in low frequencies the reactance parts of the impedances tend towards zero so the whole path is approximately resistive with R R_C.38 (or.8 without the 9dB attenuator) and the target itself has resistance R R_.he tiny difference (.3) reveals small attenuation of the signal in the cable. hese two resistances are slightly greater than the transfer resistance of simplified DC model from Fig. 3. Re(Z R ) [] Im(Z R ) [] Z R- Z R-C Fig. 8. ransfer impedances: Z R_ (f) of the target and Z R_C (f) of the cascaded connection of the target and cable with 9dB attenuator (linear frequency scale) Z R- calculate the transform of the voltage by multiplication in the frequency domain: U ( f) ZR _ C ( f) I( f), (3) and return to the time domain using the inverse transform: u() t Re( IDF[ U( f)]). () Fig. shows the results for the considered transfer impedance model compared with the DC model. he clearly visible 8ns delay of the voltage u (t) represents the propagation time of the signal across the measurement path. he quality of the waveform at the output of the transfer impedance model depends on: ) time window o =N/f s (N number of samples, f s sampling frequency in time) of the impulse that must be wide enough to let the impulse fade and therefore avoid discontinuity artifacts in DF. Otherwise the calculated response is "non-causal" and looks like curve 3 in Fig. b for o =ns, ) spectrum range and sampling frequency. he wide spectrum range reveals high frequency features of the system (e.g. resonant peak of the target) while the greater number of frequency data shows the details of the spectrum and reduces the DF errors DC model - Z R- (f) and attenuator 3 - Z R-C (f), o =ns Z R [] Z R-C u [V] arg(z R ) [rad] Fig. 9. ransfer impedances Z R_ (f) and Z R_C (f) in magnitude-phase angle representation. DISORION OF HE ESD IMPULSE IN HE MEASUREMEN PAH Having known the frequency dependence of the transfer impedance Z R_C (f) it is possible to determine the distortion introduced by the measurement path from the specified or theoretical impulse current i (t) to the oscilloscope input voltage u (t). We transform the impulse, sampled with frequency twice as high as the upper frequency of the S- parameters data (according to the sampling theorem), into the frequency domain using the discrete Fourier transform: DF[ i ( t)] I ( f ), () a) b) u [V] 3 6 t [ns] DC model 3 - Z R-C (f), o =ns 3 6 t [ns] Fig.. he discharge impulse as voltage at the output of: - the DC target model, the target represented by Z R_ (f) loaded by the cable and oscilloscope, 3 - the path represented by Z R_C (f) loaded by oscilloscope, for time window a) o =ns and b) o =ns. Waveforms and are sketched with 9dB attenuation for better comparison
5 It is important to determine differences between the characteristic parameters of waveforms and 3 in Fig. which can be a measure of the impulse distortion neglected by the DC model in comparison with the transfer impedance model. We calculated relative differences with respect to the DC model, i.e. xdc xzr ex () xdc for the rise time, the peak value and the 3ns value for several combinations of time window and spectrum range and stated that the rise time and the peak value are most sensitive to correct choice of the time window and spectrum range which is shown in Fig.. a) b) epeak etr,, -, -, spectrum range [GHz],3,,, -, -, -,3 spectrum range [GHz] 3 6 time window [ns] 6 3 time window [ns] 3 3 he difference of the rise time (Fig. a) is small regardless of the time window when the spectrum range do not include the resonance of the target at 3GHz. In these conditions the compared models are similar. When the spectrum range includes the resonance (bars for and 6GHz) the models produce large differences, but only for short time windows. It results from discontinuity of the windowed impulse and coarse calculations of DF so these results are not reliable (see Fig. b). he difference decreases to about.% while extending the time window to ns or more which also increases the number of DF points (for ns and 6GHz N=8). he differences of the peak value (Fig. b) for longer time windows, which can be considered reliable, slightly decrease and stabilize with extending the spectrum range. he differences of the impulse magnitude at 3ns (Fig. c) and 6ns are about % and are less sensitive to the choice of frequency range and time window. It is interesting to observe how the transfer impedance model of the path affects the impulse in the frequency domain. In Fig. the power spectrum density (PSD) of the voltage u (t) obtained using Z R_C (f) is compared with that of the DC model. hey clearly differ above GHz, but this divergence is not significant because the signal power density emphasized by the resonance around 3GHz is still very low. he ratio of the difference of the impulses energy for f>ghz to the difference over the whole range is very small [ PSDu ( _ DC ) PSDu ( _ ZR )] from to 6GHz.% [ PSD( u ) PSD( u )] from to 6GHz _ DC _ ZR which means that the main reason of the divergence are different real and non-zero imaginary parts of Z R_C (f) at frequencies below GHz. hat explains why the differences of the impulse parameters shown in Fig. depend little on the frequency range if the time window is long enough., c) -e3,,, spectrum range [GHz] 3 6 time window [ns] 3 Fig.. Relative differences: a) e tr of the rise time (calculated from. to.9 of the peak value), b) e peak of the peak value, c) e 3 of the magnitude 3ns after. of the peak value, between the characteristic parameters of the DC model impulse and the transfer impedance model impulse versus frequency range f s / and time window o PSD(u ) DC model Z R-C (f) model Fig.. Comparison of the power spectrum density of voltage impulse u for the DC model and the frequency dependent transfer impedance model
6 . CONCLUSION he approach presented in the paper enables better evaluation of how the individual parts of the measurement system can affect calibration results and whether the calibration procedures currently applied are accurate enough. he investigation shows that the divergence between the transfer impedance and the DC model of the path that affects the discharge impulse specifications lies rather in slightly different gains at frequencies below GHz than in resonances at 3GHz and above, where the power density of the impulse is very low. At this stage we neglect the possible distortion of the signal inside the oscilloscope which can be modeled by an appropriate voltage transfer function. his problem was considered in [] but the analysis can be further developed. he other potential way to make the analysis more accurate is parametric modeling of the transfer impedance using an AR or ARMA model obtained from the data, because they are well suited to model line spectra. +Janusz Baran was born in Częstochowa, Poland, in 96. He received M.Sc. in electrical engineering from Częstochowa echnical University in 98 and Ph.D. from Lublin echnical University in 99. Since 986 he has been with Institute of Electronics and Control Systems at Częstochowa echnical University. His research interests include signal processing, nonlinear control and adaptive systems. omasz Dróżdż was born in Częstochowa, Poland, in 966. In 99 he received M.Sc. in electrical engineering from Częstochowa echnical University and since then he has been with Institute of Electronics and Control Systems at Częstochowa echnical University. His research interests include measurement systems and electromagnetic compatibility. Jan Sroka was born in Szczerców in Poland on January 9. He received M.Sc, Ph.D. and D.Sc. degrees in electrical engineering from Warsaw University of echnology in 97, 98 and 99 respectively. Since 99 he has been by SCHAFFNER EMC AG in Switzerland in different departments: Research and echnology, Component Development and est Systems. His current research interests is investigation and experiments in establishing uncertainty budget in EMC calibration and testing. ACKNOWLEDGMEN he authors would like to thank to SCHAFFNER EMC Ltd. for enabling investigation of the presented problem. REFERENCES [] IEC 6--. esting and Measuring echniques. Electrostatic Discharge Immunity est. May, 999. [] J. Sroka (), arget influence on the calibration uncertainty of ESD simulators, th Int. Symposium and Exhibition on EMC Zurich, pp [3] J. Sroka (), Calibration uncertainty of ESD simulator estimated with frequency dependent transfer impedance of the target, 6 th Int. Wrocław Symposium and Exhibition on EMC, Wrocław, pp. 9 3,. [] J. Sroka (3), Oscilloscope influence on the calibration uncertainty of the peak current of ESD simulators. th International Symposium and Exhibition on EMC, Zurich 3 Zürich, February 3, pp [] Dróżdż, Ocena zniekształceń prądu w kalibracji symulatorów wyładowań elektrostatycznych, doctor's thesis, echnical University of Częstochowa, Electrical Engineering Faculty. (in Polish, in printing)
Frequency Approach to Analysis of ESD Pulse
 本文は pp.339-344 Frequency Approach to Analysis of ESD Pulse Janusz Baran Non-member (Czestochowa University of Technology, Poland) Jan Sroka Non-member (EMC-Testcenter Zurich, Switzerland) Keywords : electrostatic
本文は pp.339-344 Frequency Approach to Analysis of ESD Pulse Janusz Baran Non-member (Czestochowa University of Technology, Poland) Jan Sroka Non-member (EMC-Testcenter Zurich, Switzerland) Keywords : electrostatic
A Combined Impedance Measurement Method for ESD Generator Modeling
 A Combined Impedance Measurement Method for ESD Generator Modeling Friedrich zur Nieden, Stephan Frei Technische Universität Dortmund AG Bordsysteme Dortmund, Germany David Pommerenke Missouri University
A Combined Impedance Measurement Method for ESD Generator Modeling Friedrich zur Nieden, Stephan Frei Technische Universität Dortmund AG Bordsysteme Dortmund, Germany David Pommerenke Missouri University
Measuring the Invasiveness of High-Impedance Probes
 Measuring the Invasiveness of High-Impedance Probes Uwe Arz 1 Pavel Kabos 2 Dylan F. Williams 2 1 Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Braunschweig, Germany 2 National Institute of Standards and Technology,
Measuring the Invasiveness of High-Impedance Probes Uwe Arz 1 Pavel Kabos 2 Dylan F. Williams 2 1 Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Braunschweig, Germany 2 National Institute of Standards and Technology,
Validation & Analysis of Complex Serial Bus Link Models
 Validation & Analysis of Complex Serial Bus Link Models Version 1.0 John Pickerd, Tektronix, Inc John.J.Pickerd@Tek.com 503-627-5122 Kan Tan, Tektronix, Inc Kan.Tan@Tektronix.com 503-627-2049 Abstract
Validation & Analysis of Complex Serial Bus Link Models Version 1.0 John Pickerd, Tektronix, Inc John.J.Pickerd@Tek.com 503-627-5122 Kan Tan, Tektronix, Inc Kan.Tan@Tektronix.com 503-627-2049 Abstract
Transient calibration of electric field sensors
 Transient calibration of electric field sensors M D Judd University of Strathclyde Glasgow, UK Abstract An electric field sensor calibration system that operates in the time-domain is described and its
Transient calibration of electric field sensors M D Judd University of Strathclyde Glasgow, UK Abstract An electric field sensor calibration system that operates in the time-domain is described and its
EMC Overview. What is EMC? Why is it Important? Case Studies. Examples of calculations used in EMC. EMC Overview 1
 EMC Overview What is EMC? Why is it Important? Case Studies. Examples of calculations used in EMC. EMC Overview 1 What Is EMC? Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): The process of determining the interaction
EMC Overview What is EMC? Why is it Important? Case Studies. Examples of calculations used in EMC. EMC Overview 1 What Is EMC? Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): The process of determining the interaction
RF and Microwave Network Characterization - A Concept-Map Based Tutorial -
 RF and Microwave Network Characterization - A Concept-Map Based Tutorial - K.C. Gupta, R. Ramadoss and H. Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder Boulder
RF and Microwave Network Characterization - A Concept-Map Based Tutorial - K.C. Gupta, R. Ramadoss and H. Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder Boulder
Modeling and Practical Suggestions to Improve ESD Immunity Test Repeatability
 17 th Symposium IMEKO TC, 3 rd Symposium IMEKO TC 19 and 15 th IWDC Workshop Sept. -1, 1, Kosice, Slovakia Modeling and Practical Suggestions to Improve ESD Immunity Test Repeatability. Morando 1, M. Borsero,.
17 th Symposium IMEKO TC, 3 rd Symposium IMEKO TC 19 and 15 th IWDC Workshop Sept. -1, 1, Kosice, Slovakia Modeling and Practical Suggestions to Improve ESD Immunity Test Repeatability. Morando 1, M. Borsero,.
Wideband highly linear gain
 Wideband Gain Block Amplifier Design echniques Here is a thorough review of the device design requirements for a general-purpose amplifier FIC By Chris Arnott F Micro Devices Wideband highly linear gain
Wideband Gain Block Amplifier Design echniques Here is a thorough review of the device design requirements for a general-purpose amplifier FIC By Chris Arnott F Micro Devices Wideband highly linear gain
THE PROPAGATION OF PARTIAL DISCHARGE PULSES IN A HIGH VOLTAGE CABLE
 THE PROPAGATION OF PARTIAL DISCHARGE PULSES IN A HIGH VOLTAGE CABLE Z.Liu, B.T.Phung, T.R.Blackburn and R.E.James School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommuniications University of New South Wales
THE PROPAGATION OF PARTIAL DISCHARGE PULSES IN A HIGH VOLTAGE CABLE Z.Liu, B.T.Phung, T.R.Blackburn and R.E.James School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommuniications University of New South Wales
A Simplified Extension of X-parameters to Describe Memory Effects for Wideband Modulated Signals
 Jan Verspecht bvba Mechelstraat 17 B-1745 Opwijk Belgium email: contact@janverspecht.com web: http://www.janverspecht.com A Simplified Extension of X-parameters to Describe Memory Effects for Wideband
Jan Verspecht bvba Mechelstraat 17 B-1745 Opwijk Belgium email: contact@janverspecht.com web: http://www.janverspecht.com A Simplified Extension of X-parameters to Describe Memory Effects for Wideband
Where DSP meets Measurement Science: A Sound Example. By Andrew Hurrell PhD
 Where DSP meets Measurement Science: A Sound Example By Andrew Hurrell PhD Measuring ultrasound why bother? 6 million ultrasound scans within NHS during 2004-2005 Ultrasound has potential for: Thermal
Where DSP meets Measurement Science: A Sound Example By Andrew Hurrell PhD Measuring ultrasound why bother? 6 million ultrasound scans within NHS during 2004-2005 Ultrasound has potential for: Thermal
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
Influence Of Lightning Strike Location On The Induced Voltage On a Nearby Overhead Line
 NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE NPSC22 563 Influence Of Lightning Strike Location On The Induced Voltage On a Nearby Overhead Line P. Durai Kannu and M. Joy Thomas Abstract This paper analyses the voltages
NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE NPSC22 563 Influence Of Lightning Strike Location On The Induced Voltage On a Nearby Overhead Line P. Durai Kannu and M. Joy Thomas Abstract This paper analyses the voltages
IEC Electrical fast transient / Burst immunity test
 CONDUCTED RF EQUIPMENT POWER AMPLIFIERS IEC 61000-4-4 Electrical fast transient / Burst immunity test IEC 61000-4-4 Electrical fast transient / Burst immunity test Markus Fuhrer Phenomenom open a contact
CONDUCTED RF EQUIPMENT POWER AMPLIFIERS IEC 61000-4-4 Electrical fast transient / Burst immunity test IEC 61000-4-4 Electrical fast transient / Burst immunity test Markus Fuhrer Phenomenom open a contact
Non-ideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems
 Nonideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE30 Lab Section 008 October 27, 2006 Abstract In the world of electronics,
Nonideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE30 Lab Section 008 October 27, 2006 Abstract In the world of electronics,
Department of Electronics &Electrical Engineering
 Department of Electronics &Electrical Engineering Question Bank- 3rd Semester, (Network Analysis & Synthesis) EE-201 Electronics & Communication Engineering TWO MARKS OUSTIONS: 1. Differentiate between
Department of Electronics &Electrical Engineering Question Bank- 3rd Semester, (Network Analysis & Synthesis) EE-201 Electronics & Communication Engineering TWO MARKS OUSTIONS: 1. Differentiate between
Multi-Resolution Wavelet Analysis for Chopped Impulse Voltage Measurements
 Multi-Resolution Wavelet Analysis for Chopped Impulse Voltage Measurements EMEL ONAL Electrical Engineering Department Istanbul Technical University 34469 Maslak-Istanbul TURKEY onal@elk.itu.edu.tr http://www.elk.itu.edu.tr/~onal
Multi-Resolution Wavelet Analysis for Chopped Impulse Voltage Measurements EMEL ONAL Electrical Engineering Department Istanbul Technical University 34469 Maslak-Istanbul TURKEY onal@elk.itu.edu.tr http://www.elk.itu.edu.tr/~onal
Γ L = Γ S =
 TOPIC: Microwave Circuits Q.1 Determine the S parameters of two port network consisting of a series resistance R terminated at its input and output ports by the characteristic impedance Zo. Q.2 Input matching
TOPIC: Microwave Circuits Q.1 Determine the S parameters of two port network consisting of a series resistance R terminated at its input and output ports by the characteristic impedance Zo. Q.2 Input matching
Aries Kapton CSP socket
 Aries Kapton CSP socket Measurement and Model Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 5/19/04 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 4 Setup... 4 MEASUREMENTS...
Aries Kapton CSP socket Measurement and Model Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 5/19/04 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 4 Setup... 4 MEASUREMENTS...
Lecture Fundamentals of Data and signals
 IT-5301-3 Data Communications and Computer Networks Lecture 05-07 Fundamentals of Data and signals Lecture 05 - Roadmap Analog and Digital Data Analog Signals, Digital Signals Periodic and Aperiodic Signals
IT-5301-3 Data Communications and Computer Networks Lecture 05-07 Fundamentals of Data and signals Lecture 05 - Roadmap Analog and Digital Data Analog Signals, Digital Signals Periodic and Aperiodic Signals
1000BASE-T1 EMC Test Specification for Common Mode Chokes
 IEEE 1000BASE-T1 EMC Test Specification for Common Mode Chokes Version 1.0 Author & Company Dr. Bernd Körber, FTZ Zwickau Title 1000BASE-T1 EMC Test Specification for Common Mode Chokes Version 1.0 Date
IEEE 1000BASE-T1 EMC Test Specification for Common Mode Chokes Version 1.0 Author & Company Dr. Bernd Körber, FTZ Zwickau Title 1000BASE-T1 EMC Test Specification for Common Mode Chokes Version 1.0 Date
Scattered thoughts on Scattering Parameters By Joseph L. Cahak Copyright 2013 Sunshine Design Engineering Services
 Scattered thoughts on Scattering Parameters By Joseph L. Cahak Copyright 2013 Sunshine Design Engineering Services Scattering parameters or S-parameters (aka Spars) are used by RF and microwave engineers
Scattered thoughts on Scattering Parameters By Joseph L. Cahak Copyright 2013 Sunshine Design Engineering Services Scattering parameters or S-parameters (aka Spars) are used by RF and microwave engineers
Theory of Telecommunications Networks
 Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 2277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 0 Fax ++49 30 / 753 0 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz Tutorial
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 2277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 0 Fax ++49 30 / 753 0 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz Tutorial
Scattering Parameters for the Keefe Clarinet Tonehole Model
 Presented at the 1997 International Symposium on Musical Acoustics, Edinourgh, Scotland. 1 Scattering Parameters for the Keefe Clarinet Tonehole Model Gary P. Scavone & Julius O. Smith III Center for Computer
Presented at the 1997 International Symposium on Musical Acoustics, Edinourgh, Scotland. 1 Scattering Parameters for the Keefe Clarinet Tonehole Model Gary P. Scavone & Julius O. Smith III Center for Computer
Agilent Time Domain Analysis Using a Network Analyzer
 Agilent Time Domain Analysis Using a Network Analyzer Application Note 1287-12 0.0 0.045 0.6 0.035 Cable S(1,1) 0.4 0.2 Cable S(1,1) 0.025 0.015 0.005 0.0 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Frequency (GHz) 0.005
Agilent Time Domain Analysis Using a Network Analyzer Application Note 1287-12 0.0 0.045 0.6 0.035 Cable S(1,1) 0.4 0.2 Cable S(1,1) 0.025 0.015 0.005 0.0 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Frequency (GHz) 0.005
Correlation Between Measured and Simulated Parameters of a Proposed Transfer Standard
 Correlation Between Measured and Simulated Parameters of a Proposed Transfer Standard Jim Nadolny AMP Incorporated ABSTRACT Total radiated power of a device can be measured using a mode stirred chamber
Correlation Between Measured and Simulated Parameters of a Proposed Transfer Standard Jim Nadolny AMP Incorporated ABSTRACT Total radiated power of a device can be measured using a mode stirred chamber
Development of the Transformer for Contactless Power Suppliers
 27 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 27 (2013) Published online (http://hdl.handle.net/10114/8198) Development of the ransformer for Contactless Power
27 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 27 (2013) Published online (http://hdl.handle.net/10114/8198) Development of the ransformer for Contactless Power
Aries Center probe CSP socket Cycling test
 Aries Center probe CSP socket Cycling test RF Measurement Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 10/27/04 1 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 5 Setup...
Aries Center probe CSP socket Cycling test RF Measurement Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 10/27/04 1 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 5 Setup...
2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal.
 1 2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS 2.1.1 Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal. 2 Time Scaling. Figure 2.4 Time scaling of a signal. 2.1.2 Classification of Signals
1 2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS 2.1.1 Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal. 2 Time Scaling. Figure 2.4 Time scaling of a signal. 2.1.2 Classification of Signals
GIS Instrument Transformers: EMC Conformity Tests for a Reliable Operation in an Upgraded Substation
 GIS Instrument Transformers: EMC Conformity Tests for a Reliable Operation in an Upgraded Substation W. Buesch 1) G. Palmieri M.Miesch J. Marmonier O. Chuniaud ALSTOM LTD 1) ALSTOM LTD High Voltage Equipment
GIS Instrument Transformers: EMC Conformity Tests for a Reliable Operation in an Upgraded Substation W. Buesch 1) G. Palmieri M.Miesch J. Marmonier O. Chuniaud ALSTOM LTD 1) ALSTOM LTD High Voltage Equipment
Microwave Devices and Circuit Design
 Microwave Devices and Circuit Design Ganesh Prasad Srivastava Vijay Laxmi Gupta MICROWAVE DEVICES and CIRCUIT DESIGN GANESH PRASAD SRIVASTAVA Professor (Retired) Department of Electronic Science University
Microwave Devices and Circuit Design Ganesh Prasad Srivastava Vijay Laxmi Gupta MICROWAVE DEVICES and CIRCUIT DESIGN GANESH PRASAD SRIVASTAVA Professor (Retired) Department of Electronic Science University
Specific Research Reports of the National Institute of Industrial Safety, NIIS-SRR-NO.26 (2002) UDC :
 Specific Research Reports of the National Institute of Industrial Safety, NIIS-SRR-NO.26 (2002) UDC 621.391.823:621.317.34 ** *** by Hajime TOMITA** and Toshiyuki UEKI*** Abstract: Electric and electronic
Specific Research Reports of the National Institute of Industrial Safety, NIIS-SRR-NO.26 (2002) UDC 621.391.823:621.317.34 ** *** by Hajime TOMITA** and Toshiyuki UEKI*** Abstract: Electric and electronic
MEASUREMENTS OF COUPLING THROUGH BRAIDED SHIELD VIA NEW CONDUCTED IMMUNITY TECH- NIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 11, 61 68, 2009 MEASUREMENTS OF COUPLING THROUGH BRAIDED SHIELD VIA NEW CONDUCTED IMMUNITY TECH- NIQUE M. Ghassempouri College of Electrical Engineering Iran
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 11, 61 68, 2009 MEASUREMENTS OF COUPLING THROUGH BRAIDED SHIELD VIA NEW CONDUCTED IMMUNITY TECH- NIQUE M. Ghassempouri College of Electrical Engineering Iran
Custom Interconnects Fuzz Button with Hardhat Test Socket/Interposer 1.00 mm pitch
 Custom Interconnects Fuzz Button with Hardhat Test Socket/Interposer 1.00 mm pitch Measurement and Model Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 12/14/2015 1 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS...2 OBJECTIVE...
Custom Interconnects Fuzz Button with Hardhat Test Socket/Interposer 1.00 mm pitch Measurement and Model Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 12/14/2015 1 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS...2 OBJECTIVE...
T + T /13/$ IEEE 236. the inverter s input impedances on the attenuation of a firstorder
 Emulation of Conducted Emissions of an Automotive Inverter for Filter Development in HV Networks M. Reuter *, T. Friedl, S. Tenbohlen, W. Köhler Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology
Emulation of Conducted Emissions of an Automotive Inverter for Filter Development in HV Networks M. Reuter *, T. Friedl, S. Tenbohlen, W. Köhler Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology
SENSITIVITY AND UNCERTAINTY ANALYSIS FOR CALCULABLE ANTENNA FACTOR OF THE DIRECT-FEED BICONICAL ANTENNA
 006-015 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. SENSITIVITY AND UNCERTAINTY ANALYSIS FOR CALCULABLE ANTENNA FACTOR OF THE DIRECT-FEED BICONICAL ANTENNA Syarfa Zahirah Sapuan 1,,
006-015 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. SENSITIVITY AND UNCERTAINTY ANALYSIS FOR CALCULABLE ANTENNA FACTOR OF THE DIRECT-FEED BICONICAL ANTENNA Syarfa Zahirah Sapuan 1,,
Ultra Wideband Indoor Radio Channel Measurements
 Ultra Wideband Indoor Radio Channel Measurements Matti Hämäläinen, Timo Pätsi, Veikko Hovinen Centre for Wireless Communications P.O.Box 4500 FIN-90014 University of Oulu, FINLAND email: matti.hamalainen@ee.oulu.fi
Ultra Wideband Indoor Radio Channel Measurements Matti Hämäläinen, Timo Pätsi, Veikko Hovinen Centre for Wireless Communications P.O.Box 4500 FIN-90014 University of Oulu, FINLAND email: matti.hamalainen@ee.oulu.fi
Accurate Modeling of Core-Type Distribution Transformers for Electromagnetic Transient Studies
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 17, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2002 969 Accurate Modeling of Core-Type Distribution Transformers for Electromagnetic Transient Studies Taku Noda, Member, IEEE, Hiroshi Nakamoto,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 17, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2002 969 Accurate Modeling of Core-Type Distribution Transformers for Electromagnetic Transient Studies Taku Noda, Member, IEEE, Hiroshi Nakamoto,
SIZE REDUCTION AND HARMONIC SUPPRESSION OF RAT-RACE HYBRID COUPLER USING DEFECTED MICROSTRIP STRUCTURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 26, 87 96, 211 SIZE REDUCTION AND HARMONIC SUPPRESSION OF RAT-RACE HYBRID COUPLER USING DEFECTED MICROSTRIP STRUCTURE M. Kazerooni * and M. Aghalari
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 26, 87 96, 211 SIZE REDUCTION AND HARMONIC SUPPRESSION OF RAT-RACE HYBRID COUPLER USING DEFECTED MICROSTRIP STRUCTURE M. Kazerooni * and M. Aghalari
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF A TRANSIENT INDUCED VOLTAGE TO AN OVERHEAD CONTROL CABLE FROM A GROUNDING CIRCUIT
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF A TRANSIENT INDUCED VOLTAGE TO AN OVERHEAD CONTROL CABLE FROM A GROUNDING CIRCUIT Akihiro AMETANI, Tomomi OKUMURA, Naoto NAGAOKA, Nobutaka, MORI Doshisha University - Japan
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF A TRANSIENT INDUCED VOLTAGE TO AN OVERHEAD CONTROL CABLE FROM A GROUNDING CIRCUIT Akihiro AMETANI, Tomomi OKUMURA, Naoto NAGAOKA, Nobutaka, MORI Doshisha University - Japan
Alternative Coupling Method for Immunity Testing of Power Grid Protection Equipment
 Alternative Coupling Method for Immunity Testing of Power Grid Protection Equipment Christian Suttner*, Stefan Tenbohlen Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology (IEH), University of
Alternative Coupling Method for Immunity Testing of Power Grid Protection Equipment Christian Suttner*, Stefan Tenbohlen Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology (IEH), University of
EE 340 Transmission Lines. Spring 2012
 EE 340 Transmission Lines Spring 2012 Physical Characteristics Overhead lines An overhead transmission line usually consists of three conductors or bundles of conductors containing the three phases of
EE 340 Transmission Lines Spring 2012 Physical Characteristics Overhead lines An overhead transmission line usually consists of three conductors or bundles of conductors containing the three phases of
Ileana-Diana Nicolae ICMET CRAIOVA UNIVERSITY OF CRAIOVA MAIN BUILDING FACULTY OF ELECTROTECHNICS
 The Designing, Realization and Testing of a Network Filter used to Reduce Electromagnetic Disturbances and to Improve the EMI for Static Switching Equipment Petre-Marian Nicolae Ileana-Diana Nicolae George
The Designing, Realization and Testing of a Network Filter used to Reduce Electromagnetic Disturbances and to Improve the EMI for Static Switching Equipment Petre-Marian Nicolae Ileana-Diana Nicolae George
Theoretical maximum data rate estimations for PLC in automotive power distribution systems
 Theoretical maximum data rate estimations for PLC in automotive power distribution systems Alexander Zeichner, Zongyi Chen, Stephan Frei TU Dortmund University Dortmund, Germany alexander.zeichner@tu-dortmund.de
Theoretical maximum data rate estimations for PLC in automotive power distribution systems Alexander Zeichner, Zongyi Chen, Stephan Frei TU Dortmund University Dortmund, Germany alexander.zeichner@tu-dortmund.de
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 AMETEK CO., LTD. NAGOYA OFFICE. (Main Laboratory) Onna, Atsugi-shi, Kanagawa-ken, Japan
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 AMETEK CO., LTD. NAGOYA OFFICE (Main Laboratory) 5-1-1 Onna, Atsugi-shi, Kanagawa-ken, 243-0032 Japan (Commercial Office) 1-329 Kifune, Meito-ku Nagoya-shi,
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 AMETEK CO., LTD. NAGOYA OFFICE (Main Laboratory) 5-1-1 Onna, Atsugi-shi, Kanagawa-ken, 243-0032 Japan (Commercial Office) 1-329 Kifune, Meito-ku Nagoya-shi,
Analysis and Design of Autonomous Microwave Circuits
 Analysis and Design of Autonomous Microwave Circuits ALMUDENA SUAREZ IEEE PRESS WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents Preface xiii 1 Oscillator Dynamics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Operational
Analysis and Design of Autonomous Microwave Circuits ALMUDENA SUAREZ IEEE PRESS WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents Preface xiii 1 Oscillator Dynamics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Operational
Amplitude and Phase Modulation Effects of Waveform Distortion in Power Systems
 Electrical Power Quality and Utilisation, Journal Vol. XIII, No., 007 Amplitude and Phase Modulation Effects of Waveform Distortion in Power Systems Roberto LANGELLA and Alfredo ESA Seconda Università
Electrical Power Quality and Utilisation, Journal Vol. XIII, No., 007 Amplitude and Phase Modulation Effects of Waveform Distortion in Power Systems Roberto LANGELLA and Alfredo ESA Seconda Università
ANALYSIS OF BROADBAND GAN SWITCH MODE CLASS-E POWER AMPLIFIER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 38, 151 16, 213 ANALYSIS OF BROADBAND GAN SWITCH MODE CLASS-E POWER AMPLIFIER Ahmed Tanany, Ahmed Sayed *, and Georg Boeck Berlin Institute of Technology,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 38, 151 16, 213 ANALYSIS OF BROADBAND GAN SWITCH MODE CLASS-E POWER AMPLIFIER Ahmed Tanany, Ahmed Sayed *, and Georg Boeck Berlin Institute of Technology,
Internal Model of X2Y Chip Technology
 Internal Model of X2Y Chip Technology Summary At high frequencies, traditional discrete components are significantly limited in performance by their parasitics, which are inherent in the design. For example,
Internal Model of X2Y Chip Technology Summary At high frequencies, traditional discrete components are significantly limited in performance by their parasitics, which are inherent in the design. For example,
Appendix. RF Transient Simulator. Page 1
 Appendix RF Transient Simulator Page 1 RF Transient/Convolution Simulation This simulator can be used to solve problems associated with circuit simulation, when the signal and waveforms involved are modulated
Appendix RF Transient Simulator Page 1 RF Transient/Convolution Simulation This simulator can be used to solve problems associated with circuit simulation, when the signal and waveforms involved are modulated
9 Specifications. Specifications NOMINAL CHARACTERISTICS
 9 Specifications Specifications NOMINAL CHARACTERISTICS WARRANTED CHARACTERISTICS Nominal characteristics describe parameters and attributes that are guaranteed by design, but do not have associated tolerances.
9 Specifications Specifications NOMINAL CHARACTERISTICS WARRANTED CHARACTERISTICS Nominal characteristics describe parameters and attributes that are guaranteed by design, but do not have associated tolerances.
S Parameter Extraction Approach to the Reduction of Dipole Antenna Measurements
 S Parameter Extraction Approach the Reduction of Dipole Antenna Measurements Aaron Kerkhoff, Applied Research Labs, University of Texas at Austin February 14, 2008 Modern test equipment used for antenna
S Parameter Extraction Approach the Reduction of Dipole Antenna Measurements Aaron Kerkhoff, Applied Research Labs, University of Texas at Austin February 14, 2008 Modern test equipment used for antenna
Fundamentals of RF Design RF Back to Basics 2015
 Fundamentals of RF Design 2015 Updated January 1, 2015 Keysight EEsof EDA Objectives Review Simulation Types Understand fundamentals on S-Parameter Simulation Additional Linear and Non-Linear Simulators
Fundamentals of RF Design 2015 Updated January 1, 2015 Keysight EEsof EDA Objectives Review Simulation Types Understand fundamentals on S-Parameter Simulation Additional Linear and Non-Linear Simulators
Circuital and Numerical Modeling of Electrostatic Discharge Generators
 Circuital and Numerical Modeling of Electrostatic Discharge Generators Spartaco Caniggia ITLTEL S.p.. Settimo Milanese 219, Milan, Italy Francescaromana Maradei Department of Electrical Engineering University
Circuital and Numerical Modeling of Electrostatic Discharge Generators Spartaco Caniggia ITLTEL S.p.. Settimo Milanese 219, Milan, Italy Francescaromana Maradei Department of Electrical Engineering University
Current clamps for AC current
 Current clamps for AC current "C100" series The "C100" series is a range of thirteen transformer clamps with all the advantages of our old "C30" series clamps whilst incorporating considerable improvements,
Current clamps for AC current "C100" series The "C100" series is a range of thirteen transformer clamps with all the advantages of our old "C30" series clamps whilst incorporating considerable improvements,
Saturation of Active Loop Antennas
 Saturation of Active Loop Antennas Alexander Kriz EMC and Optics Seibersdorf Laboratories 2444 Seibersdorf, Austria Abstract The EMC community is working towards shorter test distances for radiated emission
Saturation of Active Loop Antennas Alexander Kriz EMC and Optics Seibersdorf Laboratories 2444 Seibersdorf, Austria Abstract The EMC community is working towards shorter test distances for radiated emission
Lesson 1: Introduction and Backgrounds on Microwave Circuits. Giuseppe Macchiarella Polytechnic of Milan, Italy Electronic and Information Department
 Lesson 1: Introduction and Backgrounds on Microwave Circuits Giuseppe Macchiarella Polytechnic of Milan, Italy Electronic and Information Department A very general definition A microwave filter is a -port
Lesson 1: Introduction and Backgrounds on Microwave Circuits Giuseppe Macchiarella Polytechnic of Milan, Italy Electronic and Information Department A very general definition A microwave filter is a -port
EN :2007+A1:2011 Electromagnetic compatibility Emission standard for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments
 EMC Page 3 / 33 Test report No.: EN 61000-6-3:2007+A1:2011 Electromagnetic compatibility Emission standard for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments Date of measurement: 2013-10-16
EMC Page 3 / 33 Test report No.: EN 61000-6-3:2007+A1:2011 Electromagnetic compatibility Emission standard for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments Date of measurement: 2013-10-16
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE319
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE39 Laboratory Experiment Parasitic Capacitance and Oscilloscope Loading This lab is designed to familiarize you with some
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE39 Laboratory Experiment Parasitic Capacitance and Oscilloscope Loading This lab is designed to familiarize you with some
Techniques to reduce electromagnetic noise produced by wired electronic devices
 Rok / Year: Svazek / Volume: Číslo / Number: Jazyk / Language 2016 18 5 EN Techniques to reduce electromagnetic noise produced by wired electronic devices - Tomáš Chvátal xchvat02@stud.feec.vutbr.cz Faculty
Rok / Year: Svazek / Volume: Číslo / Number: Jazyk / Language 2016 18 5 EN Techniques to reduce electromagnetic noise produced by wired electronic devices - Tomáš Chvátal xchvat02@stud.feec.vutbr.cz Faculty
The Impact Of Signal Jumping Across Multiple Different Reference Planes On Electromagnetic Compatibility
 Copyright by Dr. Andrew David Norte, All Rights Reserved March 18 th, 2012 The Impact Of Signal Jumping Across Multiple Different Reference Planes On Electromagnetic Compatibility David Norte, PhD www.the-signal-and-power-integrity-institute.com
Copyright by Dr. Andrew David Norte, All Rights Reserved March 18 th, 2012 The Impact Of Signal Jumping Across Multiple Different Reference Planes On Electromagnetic Compatibility David Norte, PhD www.the-signal-and-power-integrity-institute.com
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
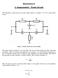 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
A MODEL FOR SHIELDING EFFECTIVENESS EVALUATION
 6 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ELECTROMECHANICAL AND POWER SYSTEMS October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova A MODEL FOR SHIELDING EFFECTIVENESS EVALUATION Petre OGRUTAN, Lia Elena ACIU, Dan BIDIAN Transilvania
6 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ELECTROMECHANICAL AND POWER SYSTEMS October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova A MODEL FOR SHIELDING EFFECTIVENESS EVALUATION Petre OGRUTAN, Lia Elena ACIU, Dan BIDIAN Transilvania
Vector Network Analyzer Application note
 Vector Network Analyzer Application note Version 1.0 Vector Network Analyzer Introduction A vector network analyzer is used to measure the performance of circuits or networks such as amplifiers, filters,
Vector Network Analyzer Application note Version 1.0 Vector Network Analyzer Introduction A vector network analyzer is used to measure the performance of circuits or networks such as amplifiers, filters,
Aries QFP microstrip socket
 Aries QFP microstrip socket Measurement and Model Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 2/18/05 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 4 Setup... 4
Aries QFP microstrip socket Measurement and Model Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 2/18/05 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 4 Setup... 4
SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS. MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation
 SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation 2 Response to Sinusoidal Inputs Frequency Domain Analysis Introduction 3 We ve looked at system impulse and step responses Also interested
SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation 2 Response to Sinusoidal Inputs Frequency Domain Analysis Introduction 3 We ve looked at system impulse and step responses Also interested
A GTEM BEST PRACTICE GUIDE APPLYING IEC TO THE USE OF GTEM CELLS
 - 27-39 H1 A BEST PRACTICE GUIDE APPLYING IEC 61-4-2 TO THE USE OF CELLS A. Nothofer, M.J. Alexander, National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, UK, D. Bozec, D. Welsh, L. Dawson, L. McCormack, A.C. Marvin,
- 27-39 H1 A BEST PRACTICE GUIDE APPLYING IEC 61-4-2 TO THE USE OF CELLS A. Nothofer, M.J. Alexander, National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, UK, D. Bozec, D. Welsh, L. Dawson, L. McCormack, A.C. Marvin,
EFFECT OF INTEGRATION ERROR ON PARTIAL DISCHARGE MEASUREMENTS ON CAST RESIN TRANSFORMERS. C. Ceretta, R. Gobbo, G. Pesavento
 Sept. 22-24, 28, Florence, Italy EFFECT OF INTEGRATION ERROR ON PARTIAL DISCHARGE MEASUREMENTS ON CAST RESIN TRANSFORMERS C. Ceretta, R. Gobbo, G. Pesavento Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of
Sept. 22-24, 28, Florence, Italy EFFECT OF INTEGRATION ERROR ON PARTIAL DISCHARGE MEASUREMENTS ON CAST RESIN TRANSFORMERS C. Ceretta, R. Gobbo, G. Pesavento Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of
A Simplified Extension of X-parameters to Describe Memory Effects for Wideband Modulated Signals
 A Simplified Extension of X-parameters to Describe Memory Effects for Wideband Modulated Signals Jan Verspecht*, Jason Horn** and David E. Root** * Jan Verspecht b.v.b.a., Opwijk, Vlaams-Brabant, B-745,
A Simplified Extension of X-parameters to Describe Memory Effects for Wideband Modulated Signals Jan Verspecht*, Jason Horn** and David E. Root** * Jan Verspecht b.v.b.a., Opwijk, Vlaams-Brabant, B-745,
Report for Excelsys EMC Measurements for 4Xgen Purchase Order: Project Number EMT07J026 Rev. B
 Report for Excelsys on EMC Measurements for 4Xgen Purchase Order: Project Number EMT07J026 Rev. B Rev Date Comment A April 2007 Change in DoC content B May 2007 Added Immunity Section EMT is a TÜV Appointed
Report for Excelsys on EMC Measurements for 4Xgen Purchase Order: Project Number EMT07J026 Rev. B Rev Date Comment A April 2007 Change in DoC content B May 2007 Added Immunity Section EMT is a TÜV Appointed
Name Date: Course number: MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START EXPERIMENT 10. Electronic Circuits
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Experimental Evaluation Scheme of UWB Antenna Performance
 Tokyo Tech. Experimental Evaluation Scheme of UWB Antenna Performance Sathaporn PROMWONG Wataru HACHITANI Jun-ichi TAKADA TAKADA-Laboratory Mobile Communication Research Group Graduate School of Science
Tokyo Tech. Experimental Evaluation Scheme of UWB Antenna Performance Sathaporn PROMWONG Wataru HACHITANI Jun-ichi TAKADA TAKADA-Laboratory Mobile Communication Research Group Graduate School of Science
Designing and Application of -type Miniaturized Lumped Equalizer
 016 International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Intellectualization (ICEITI 016) IBN: 978-1-60595-364-9 Designing and Application of -type Miniaturized Lumped Equalizer Yi Wang, Yuntao
016 International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Intellectualization (ICEITI 016) IBN: 978-1-60595-364-9 Designing and Application of -type Miniaturized Lumped Equalizer Yi Wang, Yuntao
Agilent 83440B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters
 Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Sources of transient electromagnetic disturbance in medium voltage switchgear
 Sources of transient electromagnetic disturbance in medium voltage switchgear Dennis Burger, Stefan Tenbohlen, Wolfgang Köhler University of Stuttgart Stuttgart, Germany dennis.burger@ieh.uni-stuttgart.de
Sources of transient electromagnetic disturbance in medium voltage switchgear Dennis Burger, Stefan Tenbohlen, Wolfgang Köhler University of Stuttgart Stuttgart, Germany dennis.burger@ieh.uni-stuttgart.de
MEASUREMENT AND STANDARDS
 MEASUREMENT AND STANDARDS I. MEASUREMENT PRINCIPLES 1. MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Measurement is a process of associating a number with a quantity by comparing the quantity to a standard Instrument refers to
MEASUREMENT AND STANDARDS I. MEASUREMENT PRINCIPLES 1. MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Measurement is a process of associating a number with a quantity by comparing the quantity to a standard Instrument refers to
Methods for Testing Impulse Noise Tolerance
 Methods for Testing Impulse Noise Tolerance May,6,2015 Larry Cohen Overview Purpose: Describe some potential test methods for impulse noise tolerance What we will cover in this presentation: Discuss need
Methods for Testing Impulse Noise Tolerance May,6,2015 Larry Cohen Overview Purpose: Describe some potential test methods for impulse noise tolerance What we will cover in this presentation: Discuss need
. /, , #,! 45 (6 554) &&7
 ! #!! % &! # ( )) + %,,. /, 01 2 3+++ 3, #,! 45 (6 554)15546 3&&7 ))5819:46 5) 55)9 3# )) 8)8)54 ; 1150 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 51, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2002 Effects of DUT
! #!! % &! # ( )) + %,,. /, 01 2 3+++ 3, #,! 45 (6 554)15546 3&&7 ))5819:46 5) 55)9 3# )) 8)8)54 ; 1150 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 51, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2002 Effects of DUT
TD-100. HAEFELY HIPOTRONICS Technical Document
 HAEFELY HIPOTRONICS Technical Document Breaking the limit of power capacitor resonance frequency with help of PD pulse spectrum to check and setup PD measurement P. Treyer, P. Mraz, U. Hammer, S. Gonzalez
HAEFELY HIPOTRONICS Technical Document Breaking the limit of power capacitor resonance frequency with help of PD pulse spectrum to check and setup PD measurement P. Treyer, P. Mraz, U. Hammer, S. Gonzalez
What are S-parameters, anyway? Scattering parameters offer an alternative to impedance parameters for characterizing high-frequency devices.
 What are S-parameters, anyway? Scattering parameters offer an alternative to impedance parameters for characterizing high-frequency devices. Rick Nelson, Senior Technical Editor -- Test & Measurement World,
What are S-parameters, anyway? Scattering parameters offer an alternative to impedance parameters for characterizing high-frequency devices. Rick Nelson, Senior Technical Editor -- Test & Measurement World,
CHAPTER 4. Practical Design
 CHAPTER 4 Practical Design The results in Chapter 3 indicate that the 2-D CCS TL can be used to synthesize a wider range of characteristic impedance, flatten propagation characteristics, and place passive
CHAPTER 4 Practical Design The results in Chapter 3 indicate that the 2-D CCS TL can be used to synthesize a wider range of characteristic impedance, flatten propagation characteristics, and place passive
Differential Signal and Common Mode Signal in Time Domain
 Differential Signal and Common Mode Signal in Time Domain Most of multi-gbps IO technologies use differential signaling, and their typical signal path impedance is ohm differential. Two 5ohm cables, however,
Differential Signal and Common Mode Signal in Time Domain Most of multi-gbps IO technologies use differential signaling, and their typical signal path impedance is ohm differential. Two 5ohm cables, however,
VARIABLE-FREQUENCY PRONY METHOD IN THE ANALYSIS OF ELECTRICAL POWER QUALITY
 Metrol. Meas. Syst., Vol. XIX (2012), No. 1, pp. 39-48. METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Index 330930, ISSN 0860-8229 www.metrology.pg.gda.pl VARIABLE-FREQUENCY PRONY METHOD IN THE ANALYSIS OF ELECTRICAL
Metrol. Meas. Syst., Vol. XIX (2012), No. 1, pp. 39-48. METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Index 330930, ISSN 0860-8229 www.metrology.pg.gda.pl VARIABLE-FREQUENCY PRONY METHOD IN THE ANALYSIS OF ELECTRICAL
Real-Time Digital Down-Conversion with Equalization
 Real-Time Digital Down-Conversion with Equalization February 20, 2019 By Alexander Taratorin, Anatoli Stein, Valeriy Serebryanskiy and Lauri Viitas DOWN CONVERSION PRINCIPLE Down conversion is basic operation
Real-Time Digital Down-Conversion with Equalization February 20, 2019 By Alexander Taratorin, Anatoli Stein, Valeriy Serebryanskiy and Lauri Viitas DOWN CONVERSION PRINCIPLE Down conversion is basic operation
OPSJ1900 J1900 Open Pluggable Specification Products
 J1900 Open Pluggable Specification Products Extensive range of computational power and letting you choose between diffrent operating systems, Finlux always offers you the most suitable choice that will
J1900 Open Pluggable Specification Products Extensive range of computational power and letting you choose between diffrent operating systems, Finlux always offers you the most suitable choice that will
Chapter 5 Electromagnetic interference in flash lamp pumped laser systems
 Chapter 5 Electromagnetic interference in flash lamp pumped laser systems This chapter presents the analysis and measurements of radiated near and far fields, and conducted emissions due to interconnects
Chapter 5 Electromagnetic interference in flash lamp pumped laser systems This chapter presents the analysis and measurements of radiated near and far fields, and conducted emissions due to interconnects
Network Analysis Basics
 Adolfo Del Solar Application Engineer adolfo_del-solar@agilent.com MD1010 Network B2B Agenda Overview What Measurements do we make? Network Analyzer Hardware Error Models and Calibration Example Measurements
Adolfo Del Solar Application Engineer adolfo_del-solar@agilent.com MD1010 Network B2B Agenda Overview What Measurements do we make? Network Analyzer Hardware Error Models and Calibration Example Measurements
Application of the Ansoft Serenade 7.0 PC Software in a Wireless Course
 Session 2520 Application of the Ansoft Serenade 7.0 PC Software in a Wireless Course Willie K. Ofosu Telecommunications Department Penn State Wilkes-Barre Abstract Wireless applications have experienced
Session 2520 Application of the Ansoft Serenade 7.0 PC Software in a Wireless Course Willie K. Ofosu Telecommunications Department Penn State Wilkes-Barre Abstract Wireless applications have experienced
EE 340 Transmission Lines
 EE 340 Transmission Lines Physical Characteristics Overhead lines An overhead transmission line usually consists of three conductors or bundles of conductors containing the three phases of the power system.
EE 340 Transmission Lines Physical Characteristics Overhead lines An overhead transmission line usually consists of three conductors or bundles of conductors containing the three phases of the power system.
An Analysis of the Fields on the Horizontal Coupling Plane in ESD testing
 An Analysis of the Fields on the Horizontal Coupling Plane in ESD testing Stephan Frei David Pommerenke Technical University Berlin, Einsteinufer 11, 10597 Berlin, Germany Hewlett Packard, 8000 Foothills
An Analysis of the Fields on the Horizontal Coupling Plane in ESD testing Stephan Frei David Pommerenke Technical University Berlin, Einsteinufer 11, 10597 Berlin, Germany Hewlett Packard, 8000 Foothills
Corona noise on the 400 kv overhead power line - measurements and computer modeling
 Corona noise on the 400 kv overhead power line - measurements and computer modeling A. MUJČIĆ, N.SULJANOVIĆ, M. ZAJC, J.F. TASIČ University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Digital Signal
Corona noise on the 400 kv overhead power line - measurements and computer modeling A. MUJČIĆ, N.SULJANOVIĆ, M. ZAJC, J.F. TASIČ University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Digital Signal
Aries Kapton CSP socket Cycling test
 Aries Kapton CSP socket Cycling test RF Measurement Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 10/21/04 1 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 5 Setup...
Aries Kapton CSP socket Cycling test RF Measurement Results prepared by Gert Hohenwarter 10/21/04 1 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 3 Test procedures... 5 Setup...
Computer Aided-Program for Validation of HV Impulse Measuring Systems from Unit Step Response
 Computer Aided-Program for Validation of HV Impulse Measuring Systems from Unit Step Response P. YUTTHAGOWITH and S. PHOOMVUTHISARN Center of Excellence in Electrical Power Technology, Faculty of Engineering
Computer Aided-Program for Validation of HV Impulse Measuring Systems from Unit Step Response P. YUTTHAGOWITH and S. PHOOMVUTHISARN Center of Excellence in Electrical Power Technology, Faculty of Engineering
The Measurement and Uncertainty Analysis of Antenna Factor of Microwave Antennas Based on Standard Site Method
 Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 2017, 10, 138-145 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns ISSN Online: 1913-3723 ISSN Print: 1913-3715 The Measurement and ncertainty nalysis of ntenna Factor
Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 2017, 10, 138-145 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns ISSN Online: 1913-3723 ISSN Print: 1913-3715 The Measurement and ncertainty nalysis of ntenna Factor
Dr. Ali Muqaibel. Associate Professor. Electrical Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Dhahran, Saudi Arabia
 By Associate Professor Electrical Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Wednesday, December 1, 14 1 st Saudi Symposium for RADAR Technology 9 1 December
By Associate Professor Electrical Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Wednesday, December 1, 14 1 st Saudi Symposium for RADAR Technology 9 1 December
Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses
 Chapter - 6 Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses 6.1 Introduction principle of peaking circuit In certain applications like high power microwaves (HPM), pulsed laser drivers, etc., very fast rise times
Chapter - 6 Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses 6.1 Introduction principle of peaking circuit In certain applications like high power microwaves (HPM), pulsed laser drivers, etc., very fast rise times
Dependence of Antenna Cross-polarization Performance on Waveguide-to-Coaxial Adapter Design
 Dependence of Antenna Cross-polarization Performance on Waveguide-to-Coaxial Adapter Design Vince Rodriguez, Edwin Barry, Steve Nichols NSI-MI Technologies Suwanee, GA, USA vrodriguez@nsi-mi.com Abstract
Dependence of Antenna Cross-polarization Performance on Waveguide-to-Coaxial Adapter Design Vince Rodriguez, Edwin Barry, Steve Nichols NSI-MI Technologies Suwanee, GA, USA vrodriguez@nsi-mi.com Abstract
About the High-Frequency Interferences produced in Systems including PWM and AC Motors
 About the High-Frequency Interferences produced in Systems including PWM and AC Motors ELEONORA DARIE Electrotechnical Department Technical University of Civil Engineering B-dul Pache Protopopescu 66,
About the High-Frequency Interferences produced in Systems including PWM and AC Motors ELEONORA DARIE Electrotechnical Department Technical University of Civil Engineering B-dul Pache Protopopescu 66,
