LAB INSTRUMENTATION. RC CIRCUITS.
|
|
|
- Hannah Haynes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAB INSTRUMENTATION. RC CIRCUITS. I. OBJECTIVE a) Becoming accustomed to using the lab instrumentation (voltage supply, digital multimeter, signal generator, oscilloscope) necessary to the experimental study of some electronic devices and circuits. II. COMPONENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION The instruments we will use are the ones available in the Electronic Devices and Circuits lab: regulated power supply, digital multimeter, signal generator and dual channel oscilloscope. For electrical connections we will use conductors equipped with jacks at both ends and screened probes. III. THEORETICAL ASPECTS 1. THE POWER SUPPLY A regulated power supply has the purpose of maintaining the output voltage constant at the variation in certain limits of some quantities (input voltage, load, temperature, etc.). The d.c. power supplies are used for feeding most of the electric circuits, supplying them d.c. electric power. In the lab we use triple power supply (HM8040) that contains three floating supplies: two independent supplies (0-20V/0.5A) and one dependent supply (5V/1A). Fig. 1. The front panel of the power supply HM8040 1
2 On the front panel the double power supply has (Fig.1): - OUTPUT - push button for activating/deactivating all the outputs ; - the optic working LED: is on when the supply is powered with the network voltage; - each independent supply has two output terminals: red for plus and black for minus ; - potentiometers for adjusting the output voltage (VOLTAGE) and the limiting current (CURRENT): - 3-digit switchable display for current and voltage. Display resolution is 0.1V / 1Ma ATTENTION If during an experiment the ampermeter of the source shows a high value (over 100mA) turn off the supply because there can be a fault on the experimental board. 2. THE DIGITAL MULTIMETER The digital multimeter is an electronic instrument use to measure resistances, voltages and currents (dc and ac). For ac sinusoidal signals the effective value is measured. The signal processing and results display is digital. For each quantity the apparatus is equipped with several measuring domains. The best reading precision is obtained using the domain that has the smallest end of scale, without outrunning the scale. Usually the multimeters have three measuring terminals: the measuring terminal (V, Ω, ma, hot wire, + ); usually the wire applied to this terminal has the red color for all measured quantities except the direct current with an intensity greater than 2A. Sometimes the ma and V,Ω terminals are separated; the measuring terminal (10A: hot wire, + ) only for measuring high values of direct current intensity (max 10A); the reference terminal (COM, cold wire, ground, - ) with respect to which all the measurements are made; usually the wire applied to this terminal is black. 3. THE SIGNAL GENERATOR The signal generator is an electronic instrument that provides variable signals of different shapes (sine, square, triangle, pulse, etc) allowing the modification of several parameters: amplitude, frequency, duty cycle, etc. The generator is used to apply variable signals to the electronic circuit that are experimentally studied. 2
3 4. THE CATHODIC OSCILLOSCOPE The oscilloscope is the most useful and versatile electronic test instrument. As usually used, it lets us see voltages in a circuit as a function of time, triggering on a particular point on the waveform so that a stationary display results. The images obtained on the screen are called oscillograms. The oscilloscope can be used for: visualizing the time variation of electric voltages, as for measuring their parameters: peak to peak value, amplitude, the value of the dc component, period (frequency); visualizing the relationship between two time varying voltages, being able to determine the ratio of the frequencies and their phase difference; tracing the characteristic curves of some devices or materials (static characteristics of some devices or electric circuits, the hysteresis cycle of ferromagnetic materials, etc.) The oscilloscope can work in two modes: Y-t mode: the y(t) curve appears on the screen Y-X mode: the y(x) curve appears on the screen, by eliminating the time between the y(t) and x(t) relations. 3
4 The oscilloscopes used in lab are: HAMEH HM303, HM304, HM507, HM1507 or Metrix OX6152. All the oscilloscopes are the same functions. CONTROL ELEMENTS, SIGNALING AND ACCESS ON THE FRONT PANEL OF THE OSCILLOSCOPE - POWER switch: by acting on the switch the oscilloscope will be supplied with the network voltage 230V a.c.; - Adjusting elements for the control of the spot s (trace s) intensity and clarity on the oscilloscope screen: Brightness (controls the intensity of the trace), Focus (controls the focus of the trace) Astigmatism (is used in correlation with the focus to obtain a well defined spot); ATTENTION An too big intensity can cause the destruction of the luminescent substance on the screen of the oscilloscope; - Adjusting elements for the spot (trace) movement on the vertical and horizontal: one for both channels on the x axis and one for each on the y axis; - The magnifying glass on the X and Y axis: allows the visualization of the magnified signal on the vertical and horizontal with a certain factor usually 5 or 10 for the accurate reading of the signal to be measured; - Calibrating knobs for the oscilloscope; - Selecting device of the channel we want to visualize on the screen: we can display the signal taken from one channel, both signals simultaneous or the sum of the signals on the two channels; - Knob, switch or potentiometer for: Adjusting the scale factor: time (one for both channels) voltage (one for each channel) - Switch for the coupling manner of the input signal (AC, DC, GND); The oscilloscope is dc-coupled (DC): what we see on the screen is the signal voltage, dc value and all. If we want to see a small signal riding on o large dc voltage we can switch the input to ac coupling (AC) which capacitively couples the input with a time constant of about 0.1 second. The 4
5 oscilloscope also has a grounded input position (GND), which lets us see where zero volts is on the screen. - Switch for the selection of the working mode Y-t or Y-X; - Switch for synchronizing: internal or external; - Switch for selecting the channels (one channel, the other one or both); - Input BNC jacks: one for each channel; - BNC jacks for applying an external synchronization signal (when the time base works in external synchronization regime). III. EXPLORATIONS AND RESULTS 1. OBTAINING DC VOLTAGES 1.1. ONE SIGN VOLTAGE (UNIPOLAR) Adjust the voltage of one supply at desired voltage; Activate the output of the voltage source (OUTPUT pushbutton) Measure the voltage with the digital multimeter on the 0-20V DC domain, the COM terminal connected to the - terminal of the supply; Are the voltages read on the buit-in voltmeter and with the multimeter identical or different? Why? Having to power a circuit with +12V with respect to the ground, which terminal of the supply will we connect to the ground wire and which to the power wire of the circuit? What if the circuit has to be powered with 12V with respect to the ground? Is it possible to obtain a dc voltage of 40V with the double supply? If yes, how? Remarks For supplying an electronic circuit, we first adjust the voltage of the power supply at the desired value, connect the supply wires of the circuit and finally activate the output of the source. Any time we make some modifications in the experimental board (changing the connections, introducing a measuring instrument, etc.) we will do it with the board not supplied. 2. VOLTAGE VISUALIZATION WITH THE OSCILLOSCOPE 2.1. SETING THE OSCILLOSCOPE Power on the oscilloscope using the POWER switch. Place the spot in the center of the screen using the vertical and horizontal displacement potentiometers. Select the one channel visualization in Y-t mode. 5
6 ATTENTION Working with an extremely bright spot leads to the destruction of the luminescent substance on the cathode tube screen. You may adjust the focus and astigmatism potentiometer to obtain a more clearly delimited spot. If the spot doesn t appear you can act on the horizontal and vertical deflection knobs or/and the brightness potentiometer. 2.2 VISUALIZING IN Y-T MODE a) One signal visualization: do following After starting the oscilloscope make the operations: Select the DC position if we want to visualize the signal with its dc component, or the AC position if we want to visualize just the alternating component of the signal. Generate a sinusoidal signal from the signal generator. Using a coaxial probe connect the output terminal of the signal generator with an input terminal of the oscilloscope (channel 1 or channel 2) From the time base change the time measure to be able to visualize the signal. b) Visualizing two signals simultaneously Apply to one channel a variable signal from the signal generator and to the other channel a dc voltage from the power supply. Adjust the oscilloscope settings to be able to visualize both signals simultaneously. To obtain the optimum image on the oscilloscope screen you adjust the X and Y position knobs. a) One signal visualization Draw the waveform obtained on the oscilloscope screen. b) Visualizing two signals simultaneously Draw the two waveforms obtained on the oscilloscope screen MEASUREMENTS IN Y-T MODE To help the measurements, the oscilloscope screen is squared. Each division contains 5 subdivisions. The measurement of voltages and time (period) is done by direct reading of the spot deviation on vertical (Volt/div) respectively on the horizontal (Time /div). 6
7 a) Voltages measurements You can measure amplitude, peak-to-peak value and dc component of a signal. To do this, you multiply the vertical deviation read on the screen with the indication corresponding to the position of the knob. For example: if the total vertical deviation is 4.2 div and the knob is in the position 0.1V/div the total value of the voltage is: 4,2 div x 0,1 V/div = 0,42 V b) Period measurement The measurement is made using the time base knob indications. To do this you multiply the number of horizontal divisions, corresponding to a period, with the indications corresponding to the position of the knob. For example, if the horizontal deviation is 4.6 divisions and the indication is 5ms/div, the Ty period will be: Ty = 4,6 div x 5ms/div = 23ms Draw the waveforms obtained on the oscilloscope screen. Read and write the amplitude of the signals. Compute and write the frequency of the signals MEASUREMENTS IN Y-X MODE Apply two signals on both channels of the oscilloscope. Set the oscilloscope in Y-X working mode by pushing the XY button. Draw the graphic obtained on the oscilloscope screen. 3. RC Circuits Build the circuits in Fig. 5. Apply the following input voltages: - sine wave, 10 V amplitude, 0.5 khz frequency - sine wave, 10 V amplitude, 10 khz frequency - sine wave, 10 V amplitude, 100 khz frequency On the oscilloscope, in Y-t mode, visualise the input and output signals, simultaneously, for all three cases. 7
8 Fig. 5. RC Circuits Draw the waveforms from the oscilloscope. Determine the cut-off frequency of the circuits. 8
Oscilloscope Measurements
 PC1143 Physics III Oscilloscope Measurements 1 Purpose Investigate the fundamental principles and practical operation of the oscilloscope using signals from a signal generator. Measure sine and other waveform
PC1143 Physics III Oscilloscope Measurements 1 Purpose Investigate the fundamental principles and practical operation of the oscilloscope using signals from a signal generator. Measure sine and other waveform
Experiment 9 The Oscilloscope and Function Generator
 Experiment 9 The Oscilloscope and Function Generator Introduction The oscilloscope is one of the most important electronic instruments available for making circuit measurements. It displays a curve plot
Experiment 9 The Oscilloscope and Function Generator Introduction The oscilloscope is one of the most important electronic instruments available for making circuit measurements. It displays a curve plot
Oscilloscope and Function Generators
 MEHRAN UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, JAMSHORO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP # 02 Oscilloscope and Function Generators Roll. No: Checked by: Date: Grade: Object: To
MEHRAN UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, JAMSHORO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP # 02 Oscilloscope and Function Generators Roll. No: Checked by: Date: Grade: Object: To
University of TN Chattanooga Physics1040L 8/29/2012 PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 6: USE OF THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 6: USE OF THE OSCILLOSCOPE Object: To become familiar with the operation of the oscilloscope and be able to use an oscilloscope for: 1. Measuring the frequency of an oscillator, 2.
PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 6: USE OF THE OSCILLOSCOPE Object: To become familiar with the operation of the oscilloscope and be able to use an oscilloscope for: 1. Measuring the frequency of an oscillator, 2.
EECE208 INTRO To ELECTRICAL ENG LAB. LAB 2. Instrumentation
 EECE208 INTRO To ELECTRICAL ENG LAB Dr. Charles Kim LAB 2. Instrumentation Objectives A brief description of the equipment (Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Power Supply, and Digital Multimeter) and its
EECE208 INTRO To ELECTRICAL ENG LAB Dr. Charles Kim LAB 2. Instrumentation Objectives A brief description of the equipment (Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Power Supply, and Digital Multimeter) and its
Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL
 Phase-Locked Loop Analog Communications Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain how the phase detector s input frequencies
Phase-Locked Loop Analog Communications Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain how the phase detector s input frequencies
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
EECE208 INTRO To ELECTRICAL ENG LAB. LAB 2. Instrumentation
 EECE208 INTRO To ELECTRICAL ENG LAB Dr. Charles Kim LAB 2. Instrumentation Objectives A brief description of the equipment (Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Power Supply, and Digital Multimeter) and its
EECE208 INTRO To ELECTRICAL ENG LAB Dr. Charles Kim LAB 2. Instrumentation Objectives A brief description of the equipment (Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Power Supply, and Digital Multimeter) and its
Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope
 PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
2 AC and RMS. To pass this lab you must solve tasks 1-2. Tasks 3 and 4 are included in the grading of the course.
 2 AC and RMS Purpose of the lab: to familiarize yourself with the oscilloscope to familiarize yourself with AC voltages and different waveforms to study RMS and average values In this lab, you have the
2 AC and RMS Purpose of the lab: to familiarize yourself with the oscilloscope to familiarize yourself with AC voltages and different waveforms to study RMS and average values In this lab, you have the
The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.( ) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization
 The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.(0908322) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization Objectives To be familiar with the main blocks of the oscilloscope and
The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.(0908322) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization Objectives To be familiar with the main blocks of the oscilloscope and
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 210 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 210 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Laboratory Experiment 1. Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Laboratory Experiment 1 Function Generator and Oscilloscope The purpose of this first laboratory assignment is to acquaint you with the function generator
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Laboratory Experiment 1 Function Generator and Oscilloscope The purpose of this first laboratory assignment is to acquaint you with the function generator
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics Week 21 Electricity & Electronics Section 10.5, Oscilloscope
 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics Week 21 Electricity & Electronics Section 10.5, Oscilloscope Field trip to Deerhaven Generation Plant: Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Electricity
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics Week 21 Electricity & Electronics Section 10.5, Oscilloscope Field trip to Deerhaven Generation Plant: Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Electricity
Introduction to Basic Laboratory Instruments
 Introduction to Contents: 1. Objectives... 2 2. Laboratory Safety... 2 3.... 2 4. Using a DC Power Supply... 2 5. Using a Function Generator... 3 5.1 Turn on the Instrument... 3 5.2 Setting Signal Type...
Introduction to Contents: 1. Objectives... 2 2. Laboratory Safety... 2 3.... 2 4. Using a DC Power Supply... 2 5. Using a Function Generator... 3 5.1 Turn on the Instrument... 3 5.2 Setting Signal Type...
Notes on Experiment #1
 Notes on Experiment #1 Bring graph paper (cm cm is best) From this week on, be sure to print a copy of each experiment and bring it with you to lab. There will not be any experiment copies available in
Notes on Experiment #1 Bring graph paper (cm cm is best) From this week on, be sure to print a copy of each experiment and bring it with you to lab. There will not be any experiment copies available in
EE 201 Function / Arbitrary Waveform Generator and Oscilloscope Tutorial
 EE 201 Function / Arbitrary Waveform Generator and Oscilloscope Tutorial 1 This is a programmed learning instruction manual. It is written for the Agilent DSO3202A Digital Storage Oscilloscope. The prerequisite
EE 201 Function / Arbitrary Waveform Generator and Oscilloscope Tutorial 1 This is a programmed learning instruction manual. It is written for the Agilent DSO3202A Digital Storage Oscilloscope. The prerequisite
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL. FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS REV1
 UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
Chapter 5: DC voltage.
 Chapter 5: DC voltage. 1. Introduction to electric circuits A. Electric generator (dry cell) - An electric generator transforms any form of energy into electrical energy e.g. Battery or dry cell converts
Chapter 5: DC voltage. 1. Introduction to electric circuits A. Electric generator (dry cell) - An electric generator transforms any form of energy into electrical energy e.g. Battery or dry cell converts
Test No. 1. Introduction to Scope Measurements. Report History. University of Applied Sciences Hamburg. Last chance!! EEL2 No 1
 University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
EECS 318 Electronics Lab Laboratory #2 Electronic Test Equipment
 EECS 318 Electronics Lab Laboratory #2 Electronic Test Equipment Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to acquaint you with the electronic sources and measuring equipment you will be using throughout
EECS 318 Electronics Lab Laboratory #2 Electronic Test Equipment Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to acquaint you with the electronic sources and measuring equipment you will be using throughout
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING. Test No. 1. Introduction to Scope Measurements. 1. Correction. Term Correction. Term...
 2. Correction. Correction Report University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No.
2. Correction. Correction Report University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No.
Laboratory equipments. Parameters of digital signals.
 Laboratory 1 Laboratory equipments. Parameters of digital signals. 1.1 Objectives This laboratory presents detailed description of the equipments used during the lab and measurement techniques specifically
Laboratory 1 Laboratory equipments. Parameters of digital signals. 1.1 Objectives This laboratory presents detailed description of the equipments used during the lab and measurement techniques specifically
electrical noise and interference, environmental changes, instrument resolution, or uncertainties in the measurement process itself.
 MUST 382 / EELE 491 Spring 2014 Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements Electrical laboratory work depends upon various devices to supply power to a circuit, to generate controlled input signals, and for
MUST 382 / EELE 491 Spring 2014 Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements Electrical laboratory work depends upon various devices to supply power to a circuit, to generate controlled input signals, and for
Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University
 Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University Experiment 6: Oscilloscope (For room 506) Objectives: 1. To familiarize you with the Oscilloscope and Function Generator User Manual: Oscilloscope 1 5 9 4 7
Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University Experiment 6: Oscilloscope (For room 506) Objectives: 1. To familiarize you with the Oscilloscope and Function Generator User Manual: Oscilloscope 1 5 9 4 7
FYSP1110/K1 (FYSP110/K1) USE OF AN OSCILLOSCOPE
 FYSP1110/K1 (FYSP110/K1) USE OF AN OSCILLOSCOPE 1 Introduction In this exercise you will get basic knowledge about how to use an oscilloscope. You ll also measure properties of components, which you are
FYSP1110/K1 (FYSP110/K1) USE OF AN OSCILLOSCOPE 1 Introduction In this exercise you will get basic knowledge about how to use an oscilloscope. You ll also measure properties of components, which you are
Oscilloscope. 1 Introduction
 Oscilloscope Equipment: Capstone, BK Precision model 2120B oscilloscope, Wavetek FG3C function generator, 2-3 foot coax cable with male BNC connectors, 2 voltage sensors, 2 BNC banana female adapters,
Oscilloscope Equipment: Capstone, BK Precision model 2120B oscilloscope, Wavetek FG3C function generator, 2-3 foot coax cable with male BNC connectors, 2 voltage sensors, 2 BNC banana female adapters,
UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL. UCORE ELECTRONICS
 UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 4 3.1. Display Description...
UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 4 3.1. Display Description...
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1
 EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA BARBARA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE 2A & 2B Laboratory Equipment Information
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA BARBARA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 2A & 2B Laboratory Equipment Information Table of Contents Digital Multi-Meter (DMM)... 1 Features... 1 Using
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA BARBARA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 2A & 2B Laboratory Equipment Information Table of Contents Digital Multi-Meter (DMM)... 1 Features... 1 Using
Lab 0: Orientation. 1 Introduction: Oscilloscope. Refer to Appendix E for photos of the apparatus
 Lab 0: Orientation Major Divison 1 Introduction: Oscilloscope Refer to Appendix E for photos of the apparatus Oscilloscopes are used extensively in the laboratory courses Physics 2211 and Physics 2212.
Lab 0: Orientation Major Divison 1 Introduction: Oscilloscope Refer to Appendix E for photos of the apparatus Oscilloscopes are used extensively in the laboratory courses Physics 2211 and Physics 2212.
EEE1016 Electronics I
 EEE1016 Electronics I: Appendices EEE1016 Electronics I Experiment BE1: Diode Circuits 1.0 Objectives To observe the operations of a half-wave rectifier and a full-wave bridge rectifier To observe the
EEE1016 Electronics I: Appendices EEE1016 Electronics I Experiment BE1: Diode Circuits 1.0 Objectives To observe the operations of a half-wave rectifier and a full-wave bridge rectifier To observe the
Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm
 Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm EGR 220: Engineering Circuit Theory Lab 1: Introduction to Laboratory Equipment Pre-lab Read through the entire lab handout
Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm EGR 220: Engineering Circuit Theory Lab 1: Introduction to Laboratory Equipment Pre-lab Read through the entire lab handout
PHY152 Experiment 4: Oscillations in the RC-Circuits (Measurements with an oscilloscope)
 PHY152 Experiment 4: Oscillations in the RC-Circuits (Measurements with an oscilloscope) If you have not used an oscilloscope before, the web site http://www.upscale.utoronto.ca/generalinterest/harrison/oscilloscope/oscilloscope.html
PHY152 Experiment 4: Oscillations in the RC-Circuits (Measurements with an oscilloscope) If you have not used an oscilloscope before, the web site http://www.upscale.utoronto.ca/generalinterest/harrison/oscilloscope/oscilloscope.html
B. Equipment. Advanced Lab
 Advanced Lab Measuring Periodic Signals Using a Digital Oscilloscope A. Introduction and Background We will use a digital oscilloscope to characterize several different periodic voltage signals. We will
Advanced Lab Measuring Periodic Signals Using a Digital Oscilloscope A. Introduction and Background We will use a digital oscilloscope to characterize several different periodic voltage signals. We will
Exercise 1: Circuit Block Familiarization
 Exercise 1: Circuit Block Familiarization EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to locate and identify the circuit blocks and components on the DIGITAL LOGIC FUNDAMENTALS
Exercise 1: Circuit Block Familiarization EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to locate and identify the circuit blocks and components on the DIGITAL LOGIC FUNDAMENTALS
Laboratory Equipment Instruction Manual 2011
 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Instrumentation Laboratory GB341 Laboratory Equipment Instruction Manual 2011 Page 1. Wires and Cables A-2 2. Protoboard A-3 3. DC
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Instrumentation Laboratory GB341 Laboratory Equipment Instruction Manual 2011 Page 1. Wires and Cables A-2 2. Protoboard A-3 3. DC
Experiment 5 The Oscilloscope
 Experiment 5 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a cathode ray oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is
Experiment 5 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a cathode ray oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is
PHYSICS 171 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS LAB II. Experiment 4. Alternating Current Measurement
 PHYSICS 171 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS LAB II Experiment 4 Alternating Current Measurement Equipment: Supplies: Oscilloscope, Function Generator. Filament Transformer. A sine wave A.C. signal has three basic properties:
PHYSICS 171 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS LAB II Experiment 4 Alternating Current Measurement Equipment: Supplies: Oscilloscope, Function Generator. Filament Transformer. A sine wave A.C. signal has three basic properties:
LAB 7: THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 LAB 7: THE OSCILLOSCOPE Equipment List: Dual Trace Oscilloscope HP function generator HP-DMM 2 BNC-to-BNC 1 cables (one long, one short) 1 BNC-to-banana 1 BNC-probe Hand-held DMM (freq mode) Purpose: To
LAB 7: THE OSCILLOSCOPE Equipment List: Dual Trace Oscilloscope HP function generator HP-DMM 2 BNC-to-BNC 1 cables (one long, one short) 1 BNC-to-banana 1 BNC-probe Hand-held DMM (freq mode) Purpose: To
Exercise 4 - THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 Exercise 4 - THE OSCILLOSCOPE INTRODUCTION You have been exposed to analogue oscilloscopes in the first year lab. As you are probably aware, the complexity of the instruments, along with their importance
Exercise 4 - THE OSCILLOSCOPE INTRODUCTION You have been exposed to analogue oscilloscopes in the first year lab. As you are probably aware, the complexity of the instruments, along with their importance
The Oscilloscope. Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift ( ) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope.
 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
EXAMPLE. Use this jack for the red test lead when measuring. current from 0 to 200mA. Figure P-1
 Digital Multimeters ON / OFF power switch Continuity / Diode Test Function Resistance Function Ranges from 200Ω to 200MΩ Transistor Test Function DC Current Function Ranges from 2mA to 20A. AC Current
Digital Multimeters ON / OFF power switch Continuity / Diode Test Function Resistance Function Ranges from 200Ω to 200MΩ Transistor Test Function DC Current Function Ranges from 2mA to 20A. AC Current
PHYSICS 326 LAB # 1: The Oscilloscope and Signal Generators 1/6
 PHYSICS 326 LAB # 1: The Oscilloscope and Signal Generators 1/6 PURPOSE: To be sure that each student begins the course with at least the minimum required knowledge of two instruments which we will be
PHYSICS 326 LAB # 1: The Oscilloscope and Signal Generators 1/6 PURPOSE: To be sure that each student begins the course with at least the minimum required knowledge of two instruments which we will be
Experiment # 1 Introduction to Lab Equipment
 Experiment # 1 Introduction to Lab Equipment 1. Synopsis: In this introductory lab, we will review the basic concepts of digital logic design and learn how to use the equipment available in the laboratory.
Experiment # 1 Introduction to Lab Equipment 1. Synopsis: In this introductory lab, we will review the basic concepts of digital logic design and learn how to use the equipment available in the laboratory.
2 : AC signals, the signal generator and the Oscilloscope
 2 : AC signals, the signal generator and the Oscilloscope Expected outcomes After conducting this practical, the student should be able to do the following Set up a signal generator to provide a specific
2 : AC signals, the signal generator and the Oscilloscope Expected outcomes After conducting this practical, the student should be able to do the following Set up a signal generator to provide a specific
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department. EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 3 The Oscilloscope
 POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 3 The Oscilloscope Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of the Experiment The main objective
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 3 The Oscilloscope Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of the Experiment The main objective
Electric Circuit II Lab Manual Session #1
 Department of Electrical Engineering Electric Circuit II Lab Manual Session #1 Subject Lecturer Dr. Yasser Hegazy Name:-------------------------------------------------- Group:--------------------------------------------------
Department of Electrical Engineering Electric Circuit II Lab Manual Session #1 Subject Lecturer Dr. Yasser Hegazy Name:-------------------------------------------------- Group:--------------------------------------------------
2 Oscilloscope Familiarization
 Lab 2 Oscilloscope Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout the course you will investigate
Lab 2 Oscilloscope Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout the course you will investigate
Introduction to basic laboratory instruments
 Introduction to basic laboratory instruments 1. OBJECTIVES... 2 2. LABORATORY SAFETY... 2 3. BASIC LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS... 2 4. USING A DC POWER SUPPLY... 2 5. USING A FUNCTION GENERATOR... 3 5.1 TURN
Introduction to basic laboratory instruments 1. OBJECTIVES... 2 2. LABORATORY SAFETY... 2 3. BASIC LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS... 2 4. USING A DC POWER SUPPLY... 2 5. USING A FUNCTION GENERATOR... 3 5.1 TURN
THE CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE
 The Department of Engineering SS1.2 THE CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE Objectives The objective of this laboratory is for you to familiarise yourself with the operation of a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO). Once
The Department of Engineering SS1.2 THE CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE Objectives The objective of this laboratory is for you to familiarise yourself with the operation of a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO). Once
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 7 LAMPS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to introduce the concept of resistance change
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 7 LAMPS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to introduce the concept of resistance change
APPENDIX D DISCUSSION OF ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS
 APPENDIX D DISCUSSION OF ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS DC POWER SUPPLIES We will discuss these instruments one at a time, starting with the DC power supply. The simplest DC power supplies are batteries which
APPENDIX D DISCUSSION OF ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS DC POWER SUPPLIES We will discuss these instruments one at a time, starting with the DC power supply. The simplest DC power supplies are batteries which
CHAPTER 6. Motor Driver
 CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
Sonoma State University Department of Engineering Science Spring 2017
 EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 4 Introduction to AC Measurements (I) AC signals, Function Generators and Oscilloscopes Function Generator (AC) Battery
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 4 Introduction to AC Measurements (I) AC signals, Function Generators and Oscilloscopes Function Generator (AC) Battery
Exercise 2: Demodulation (Quadrature Detector)
 Analog Communications Angle Modulation and Demodulation Exercise 2: Demodulation (Quadrature Detector) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain demodulation
Analog Communications Angle Modulation and Demodulation Exercise 2: Demodulation (Quadrature Detector) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain demodulation
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology
 Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering AU ST /E EE LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SESSIONAL COURSE Student Name : Student ID
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering AU ST /E EE LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SESSIONAL COURSE Student Name : Student ID
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 2 BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS
 1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 2 BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS The oscilloscope is the most versatile and most important tool in this lab and is probably the best tool an electrical engineer uses. This outline guides
1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 2 BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS The oscilloscope is the most versatile and most important tool in this lab and is probably the best tool an electrical engineer uses. This outline guides
Lab #1 Lab Introduction
 Cir cuit s 212 Lab Lab #1 Lab Introduction Special Information for this Lab s Report Because this is a one-week lab, please hand in your lab report for this lab at the beginning of next week s lab. The
Cir cuit s 212 Lab Lab #1 Lab Introduction Special Information for this Lab s Report Because this is a one-week lab, please hand in your lab report for this lab at the beginning of next week s lab. The
CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO).
 1. 1 To study CRO. CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO). Apparatus: - C.R.O, Connecting probe (BNC cable). Theory:An CRO is easily the most useful instrument available for testing
1. 1 To study CRO. CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO). Apparatus: - C.R.O, Connecting probe (BNC cable). Theory:An CRO is easily the most useful instrument available for testing
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering -
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering - Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Safety Rules and Operating Procedures... 3 Troubleshooting Hints... 4 Experiment
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering - Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Safety Rules and Operating Procedures... 3 Troubleshooting Hints... 4 Experiment
Physics 1442 and 1444 Questions and problems Only
 Physics 1442 and 1444 Questions and problems Only U15Q1 To measure current using a digital multimeter the probes of the meter would be placed the component. ) in parallel with ) in series with C) adjacent
Physics 1442 and 1444 Questions and problems Only U15Q1 To measure current using a digital multimeter the probes of the meter would be placed the component. ) in parallel with ) in series with C) adjacent
EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL
 EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL BREADBOARD A solderless breadboard, like the basic model in Figure 1, consists of a series of square holes, and those columns of holes are connected to each other via
EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL BREADBOARD A solderless breadboard, like the basic model in Figure 1, consists of a series of square holes, and those columns of holes are connected to each other via
Physics 323. Experiment # 1 - Oscilloscope and Breadboard
 Physics 323 Experiment # 1 - Oscilloscope and Breadboard Introduction In order to familiarise yourself with the laboratory equipment, a few simple experiments are to be performed. References: XYZ s of
Physics 323 Experiment # 1 - Oscilloscope and Breadboard Introduction In order to familiarise yourself with the laboratory equipment, a few simple experiments are to be performed. References: XYZ s of
332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title: Function Generators and Oscilloscopes Suggested Equipment:
 RUTGERS UNIVERSITY The State University of New Jersey School of Engineering Department Of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title:
RUTGERS UNIVERSITY The State University of New Jersey School of Engineering Department Of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title:
ECE 53A: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering I
 ECE 53A: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Assignment #1: Instrument Operation, Basic Resistor Measurements and Kirchhoff s Laws Fall 2007 General Guidelines: - Record data and observations
ECE 53A: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Assignment #1: Instrument Operation, Basic Resistor Measurements and Kirchhoff s Laws Fall 2007 General Guidelines: - Record data and observations
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING. Electrical Engineering Science. Laboratory Manual
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Experiment #1 OHM S LAW... 3 Experiment # 2 SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS... 8
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Experiment #1 OHM S LAW... 3 Experiment # 2 SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS... 8
EE EXPERIMENT 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP INTRODUCTION
 EE 2101 - EXPERIMENT 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP INTRODUCTION A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose voltage and current are related by a differential equation. For a capacitor, the
EE 2101 - EXPERIMENT 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP INTRODUCTION A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose voltage and current are related by a differential equation. For a capacitor, the
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015
 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
Laboratory 1 Generating and viewing signals rev. 20e. Oscilloscope Settings
 1 2 Laboratory 1 Generating and viewing signals rev. 20e Purpose: Familiarization with the basic functions of an oscilloscope and of a signal generator. Adjusting and measuring specific parameters of signals.
1 2 Laboratory 1 Generating and viewing signals rev. 20e Purpose: Familiarization with the basic functions of an oscilloscope and of a signal generator. Adjusting and measuring specific parameters of signals.
ECE 480: SENIOR DESIGN LABORATORY
 ECE 480: SENIOR DESIGN LABORATORY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY I. TITLE: Lab I - Introduction to the Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter
ECE 480: SENIOR DESIGN LABORATORY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY I. TITLE: Lab I - Introduction to the Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter
Instrument Usage in Circuits Lab
 Instrument Usage in Circuits Lab This document contains descriptions of the various components and instruments that will be used in Circuit Analysis laboratory. Descriptions currently exist for the following
Instrument Usage in Circuits Lab This document contains descriptions of the various components and instruments that will be used in Circuit Analysis laboratory. Descriptions currently exist for the following
Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Exercise 1: AC Waveform Generator Familiarization
 Exercise 1: AC Waveform Generator Familiarization EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to operate an ac waveform generator by using equipment provided. You will verify
Exercise 1: AC Waveform Generator Familiarization EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to operate an ac waveform generator by using equipment provided. You will verify
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
Agilent 33522A Function Arbitrary Waveform Generator. Tektronix TDS 3012B Oscilloscope
 Agilent 33522A Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator and Tektronix TDS 3012B Oscilloscope Agilent 33522A Function Arbitrary Waveform Generator The signal source for this lab is the Agilent 33522A Function
Agilent 33522A Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator and Tektronix TDS 3012B Oscilloscope Agilent 33522A Function Arbitrary Waveform Generator The signal source for this lab is the Agilent 33522A Function
EEE1016 Electronics I
 EEE1016 Electronics I Experiment BE2: Transistor Circuits 1.0 Objectives To analyze the output characteristic of an npn transistor in the common-emitter circuit To evaluate values of DC current gain (hfe)
EEE1016 Electronics I Experiment BE2: Transistor Circuits 1.0 Objectives To analyze the output characteristic of an npn transistor in the common-emitter circuit To evaluate values of DC current gain (hfe)
ELECTRONICS LAB. OSCILLOSCOPE
 ELECTRONICS LAB. OSCILLOSCOPE Yrd. Doç. Dr. Taha İMECİ Arş. Gör. Ezgi YAMAÇ Arş. Gör. Ufuk ŞANVER İSTANBUL COMMERCE UNIVERSITY Contents OSCILLOSCOPE... 2 CRT PART... 3 2 VERTICAL CONTROL PART... 4 3 HORIZONTAL
ELECTRONICS LAB. OSCILLOSCOPE Yrd. Doç. Dr. Taha İMECİ Arş. Gör. Ezgi YAMAÇ Arş. Gör. Ufuk ŞANVER İSTANBUL COMMERCE UNIVERSITY Contents OSCILLOSCOPE... 2 CRT PART... 3 2 VERTICAL CONTROL PART... 4 3 HORIZONTAL
General Construction & Operation of Oscilloscopes
 Science 14 Lab 2: The Oscilloscope Introduction General Construction & Operation of Oscilloscopes An oscilloscope is a widely used device which uses a beam of high speed electrons (on the order of 10 7
Science 14 Lab 2: The Oscilloscope Introduction General Construction & Operation of Oscilloscopes An oscilloscope is a widely used device which uses a beam of high speed electrons (on the order of 10 7
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 Name: MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.091 Hands-On Introduction to EE Lab Skills Laboratory No. 1 Oscilloscopes, Multimeter, Function Generator IAP 2008 1 Objective In this laboratory, you will
Name: MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.091 Hands-On Introduction to EE Lab Skills Laboratory No. 1 Oscilloscopes, Multimeter, Function Generator IAP 2008 1 Objective In this laboratory, you will
Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) The Oscilloscope Required Components: 1 10 resistor 2 100 resistors 2 lk resistors 1 2k resistor 2 4.7M resistors 1 0.F capacitor 1 0.1 F capacitor 1 1.0uF
Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) The Oscilloscope Required Components: 1 10 resistor 2 100 resistors 2 lk resistors 1 2k resistor 2 4.7M resistors 1 0.F capacitor 1 0.1 F capacitor 1 1.0uF
Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits. Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors. Table of Contents:
 Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors Table of Contents: Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab Assignment 1 Background 2 National Instruments
Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors Table of Contents: Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab Assignment 1 Background 2 National Instruments
Exercise 2-1. PAM Signals EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Signal sampling DISCUSSION
 Exercise 2-1 PAM Signals EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the generation of both natural and flat-top sampled PAM signals. You will verify how the frequency
Exercise 2-1 PAM Signals EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the generation of both natural and flat-top sampled PAM signals. You will verify how the frequency
Combinational logic: Breadboard adders
 ! ENEE 245: Digital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 1 Combinational logic: Breadboard adders ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 1 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following:
! ENEE 245: Digital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 1 Combinational logic: Breadboard adders ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 1 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following:
Lab 3: RC Circuits. Construct circuit 2 in EveryCircuit. Set values for the capacitor and resistor to match those in figure 2 and set the frequency to
 Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
Exercise 1: Frequency and Phase Modulation
 Exercise 1: Frequency and Phase Modulation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe frequency modulation and an FM circuit. You will also be able to describe
Exercise 1: Frequency and Phase Modulation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe frequency modulation and an FM circuit. You will also be able to describe
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT : 1 TITLE : Half-Wave Rectifier & Filter OUTCOME : Upon completion of this unit, the student should be able to: i. Construct
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT : 1 TITLE : Half-Wave Rectifier & Filter OUTCOME : Upon completion of this unit, the student should be able to: i. Construct
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Experiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction In this experiment we shall learn how an analog signal can be sampled in the time domain and then how the same samples can be used to reconstruct the original
Experiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction In this experiment we shall learn how an analog signal can be sampled in the time domain and then how the same samples can be used to reconstruct the original
Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope, and Multisim
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2110: CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope,
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2110: CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope,
ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
 ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Supplies Needed Motor control board, Transmitter (with good batteries), Receiver Equipment Used Oscilloscope, Function Generator,
ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Supplies Needed Motor control board, Transmitter (with good batteries), Receiver Equipment Used Oscilloscope, Function Generator,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS. Faculty: 1.Shaik.Jakeer Hussain 2.P.Sandeep patil 3.P.Ramesh Babu
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Faculty: 1.Shaik.Jakeer Hussain 2.P.Sandeep patil 3.P.Ramesh Babu UNIT-I ELECTRON DYNAMICS AND CRO: Motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields. Simple problems
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Faculty: 1.Shaik.Jakeer Hussain 2.P.Sandeep patil 3.P.Ramesh Babu UNIT-I ELECTRON DYNAMICS AND CRO: Motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields. Simple problems
EE EXPERIMENT 1 (2 DAYS) BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS INTRODUCTION DAY 1
 EE 2101 - EXPERIMENT 1 (2 DAYS) BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS INTRODUCTION The oscilloscope is the most versatile and most important tool in this lab and is probably the best tool an electrical engineer
EE 2101 - EXPERIMENT 1 (2 DAYS) BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS INTRODUCTION The oscilloscope is the most versatile and most important tool in this lab and is probably the best tool an electrical engineer
30 MHz Oscilloscope Scientech 801C
 30 MHz Oscilloscope Scientech 801C Learning Material Ver. 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100, :
30 MHz Oscilloscope Scientech 801C Learning Material Ver. 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100, :
Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide
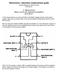 Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide Andras Meszaros, Mark Horvath 2015.02.01. 5. Measurement Basic circuits with operational amplifiers 2015.02.01. In this measurement you will need both controllable
Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide Andras Meszaros, Mark Horvath 2015.02.01. 5. Measurement Basic circuits with operational amplifiers 2015.02.01. In this measurement you will need both controllable
PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. Diodes and Transistors 1
 Part I Diodes Purpose PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. In this experiment, you will investigate the current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode and examine the applications of
Part I Diodes Purpose PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. In this experiment, you will investigate the current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode and examine the applications of
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES
 EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
ECE65 Introduction to the Function Generator and the Oscilloscope Created by: Eldridge Alcantara (Spring 2007)
 ECE65 Introduction to the Function Generator and the Oscilloscope Created by: Eldridge Alcantara (Spring 2007) I. Getting Started with the Function Generator OUTPUT Red Clip Small Black Clip 1) Turn on
ECE65 Introduction to the Function Generator and the Oscilloscope Created by: Eldridge Alcantara (Spring 2007) I. Getting Started with the Function Generator OUTPUT Red Clip Small Black Clip 1) Turn on
Name Date: Course number: MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START EXPERIMENT 10. Electronic Circuits
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
