Polarization effects in two-photon nonresonant ionization of argon with extremeultraviolet and infrared femtosecond pulses
|
|
|
- Norah Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Polarization effects in two-photon nonresonant ionization of argon with extremeultraviolet and infrared femtosecond pulses O'Keeffe, P; Lopez, Rodrigo; Mauritsson, Johan; Johansson, Ann; Lhuillier, A; Veniard, V; Taieb, R; Maquet, A; Meyer, M Published in: Physical Review A (Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics) DOI: /PhysRevA Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): O'Keeffe, P., Lopez, R., Mauritsson, J., Johansson, A., L'Huillier, A., Veniard, V.,... Meyer, M. (2004). Polarization effects in two-photon nonresonant ionization of argon with extreme-ultraviolet and infrared femtosecond pulses. Physical Review A (Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics), 69(5). DOI: /PhysRevA General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research. You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal Take down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. L UNDUNI VERS I TY PO Box L und
2 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 69, (R) (2004) Polarization effects in two-photon nonresonant ionization of argon with extreme-ultraviolet and infrared femtosecond pulses P. O Keeffe, 1 R. López-Martens, 2 J. Mauritsson, 2 A. Johansson, 2 A. L Huillier, 2 V. Véniard, 3 R. Taïeb, 3 A. Maquet, 3 and M. Meyer 1,4 1 LURE, Centre Universitaire Paris-Sud, Bâtiment 209D, F Orsay Cedex, France 2 Department of Physics, Lund Institute of Technology, P.O. Box 118, S Lund, Sweden 3 LCP-MR, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, 11 Rue Pierre et Marie Curie, F Paris Cedex 05, France 4 CEA/DRECAM/SPAM, CEN Saclay, F Gif-sur-Yvette, France (Received 18 June 2003; published 4 May 2004) We report the results of experimental and theoretical investigations of the two-color, two-photon ionization of Ar atoms, using femtosecond pulses of infrared laser radiation in combination with its extreme-ultraviolet harmonics. It is shown that the intensities of the photoelectron lines resulting from the absorption of photons from both fields strongly depend both on the respective phases of the fields and on atomic quantities such as the asymmetry parameter. These phases, which are notoriously difficult to measure, can be estimated by changing the polarization state of the laser radiation. DOI: /PhysRevA PACS number(s): Rm, Fb, Ky Photoionization measurements provide invaluable information on the structure of the electronic cloud of an atom or a molecule. The general features of photoionization, namely, the energy dependence, the angular distribution of the photoelectrons, and resonance effects, have been studied in great detail using mainly synchrotron radiation sources [1 3]. More specific investigations have been carried out by means of two-photon pump-probe experiments combining laser and synchrotron radiation [4,5]. Novel high-order harmonic generation (HHG) sources providing ultrashort extremeultraviolet (XUV) or x-ray pulses lasting a few femtoseconds [6] or less [7,8] will provide a deeper insight into the electronic relaxation processes and into the dynamics of photoionization [9]. Today, femtosecond XUV sources such as high-order harmonic radiation or the recent TESLA freeelectron laser [10] are in the process of being developed and characterized. The number of pump-probe studies with these sources is therefore still rather limited and experiments often serve as a characterization tool for the sources themselves [7,8,11]. Electron spectra obtained from irradiation of a gas sample with harmonic emission, reflecting the harmonic intensity distribution, contain a series of lines separated by 2. The combination of the harmonic pulse with part of the fundamental infrared (IR) beam in the interaction chamber will give rise to additional lines, when the intensity of the dressing IR beam is high enough W/cm 2 [12] and when both pulses overlap in time and space (see Fig. 1). Inthe intensity ranges considered here, these so-called sidebands are the result of a two-photon ionization process, as the presence of the IR beam leads to an additional absorption or emission of one IR photon simultaneously with the absorption of the XUV photon. The intensity and shape of the sidebands depend strongly on the characteristics of the two femtosecond pulses [13] and can therefore be utilized to characterize the XUV pulses [11,14]. Since a given sideband is made up of contributions from two consecutive harmonics, the sideband intensity will depend on the phase difference between the two harmonics as well as on the angular momenta and the relative phases of the outgoing electrons [15,16]. The former property has been recently used to show that harmonics generated in argon were phase locked, indicating that the light was emitted as a train of attosecond pulses [7]. In this paper, we investigate experimentally and theoretically the influence of the state of polarization of the IR probe pulse (linear polarization with an angle relative to that of the XUV field and the degree of ellipticity) on the formation of the sidebands resulting from interfering amplitudes involving two harmonics. In the case of photoionization with linearly polarized photons, the ionization signal is independent of the harmonic phases and the variation of the angle between the two polarization vectors of the XUV and IR field allows us to determine the asymmetry parameter for the one-photon ionization process. On the other hand, the sideband intensity is very sensitive to the relative phase of two consecutive harmonics, when the ellipticity of the IR photon is changed. It is demonstrated that the controlled variation of the polarization states of the light can provide detailed information on the photoionization process, especially on the asymmetry parameter describing the angular distribution of the electrons produced by absorbing the XUV photon, by measuring the angle integrated ionization signal. The experimental conditions used for the present study have been described in detail elsewhere [17]. Briefly, XUV photons are produced by HHG in an Ar gas cell from an intense 1 mj,50 fs IR laser 810 nm running at 1 khz repetition rate (see Fig. 2). The generated harmonics are focused into the acceptance volume of a magnetic bottle electron spectrometer (MBES) installed in an experimental chamber filled with a static pressure of about 10 4 mbar Ar gas. One-photon ionization of the Ar 3p shell (binding energy about 15.8 ev) by the harmonics leads to a series of equidistant lines in the photoelectron spectrum corresponding to the photoionization process by the 11th 17 ev up to the 25th harmonic 38 ev. The observation of higher harmonics is limited by the reflectivity of the focusing gold mirror used in the experimental vacuum chamber. In the in /2004/69(5)/051401(4)/$ The American Physical Society
3 O KEEFFE et al. PHYSICAL REVIEW A 69, (R) (2004) FIG. 3. Variation of the sideband intensity as a function of the relative angle between the polarization vectors of the XUV and the IR beams. Experimental data for different sidebands: * SB 14, SB 16, SB 18, SB 20, and SB 22. Theoretical calculations: -- SB 14, - SB 16, SB 18, SB 20, and SB 22. FIG. 1. (a) Scheme of the dominant photon absorption and emission processes involved in the generation of the sideband of order 2N (2N is the net amount of absorbed energy). (b) Photoelectron spectrum as a function of temporal delay between the XUV and the IR pulses. (c) Typical spectrum recorded at perfect temporal overlap between XUV and IR pulses =0 fs with an IR beam intensity of about W/cm 2. teraction region, the XUV beam intersects the IR probe beam 0.6 mj at an angle of about 8. The spatial overlap between both beams and especially the size of the IR beam can be controlled by mechanical adjustment of a convex lens f =50 cm. The temporal overlap is changed through an optical delay line introduced in the path of the beam used for HHG. In order to manipulate the polarization of the IR (probe) beam, a half-wave plate is installed just in front of the focusing lens, enabling us to change the relative angle between the polarization vector of the IR and the harmonic beam. Alternatively, a quarter-wave plate allows us to vary the degree of ellipticity of the IR beam from linear to circular. FIG. 2. (Color online) Schematic of the experimental setup. HHG, high harmonic generation; Al, Aluminum filter; MBES, Magnetic bottle electron spectrometer; WP, Retarding wave plate; L, Adjustable lens; FM, Gold focusing mirror. A typical photoelectron spectrum is shown in Fig. 1(b) giving the photoelectron intensity as a function of electron kinetic energy (horizontal axis) and time delay between the two pulses (vertical axis). Figure 1(c) shows the spectrum obtained when both pulses are best temporally overlapped. The dominant structures in Fig. 1(b) are the vertical lines, which are not much affected by the presence of the IR pulses and which correspond to direct photoionization of Ar 3p electrons by the XUV photons. The spin-orbit splitting of about 0.18 ev between the Ar + 3p 5 2 P 1/2 and 2 P 3/2 components [22] is not resolved in the present experiment. The sidebands show up for temporal delays between about 40 and +40 fs. The harmonic pulse durations, extracted from the combined knowledge of the energy-integrated sideband intensity profile and the independently measured 50 fs duration of the IR pulse, are found to be 30 fs, independent of the XUV photon energy. The shorter XUV pulse duration ensures that all atoms excited by XUV pulses are dressed by the same IR field at optimum spatial and temporal overlap. When two linearly polarized photon beams are used, the intensity of the sidebands shows a strong and characteristic variation as a function of the relative angle between both electrical field vectors (Fig. 3). Due to the 2 acceptance angle of the magnetic bottle analyzer, the intensity of the sidebands is independent of the precise shape of the angular distributions of the photoelectrons created in the two-photon process. The experimental results of Fig. 3 show a strong polarization dependence of the sideband intensity giving about 60% less intensity when the XUV and IR beams are crosspolarized =90 compared to the case when they have the same direction of polarization =0, as expected from simple classical arguments. In general, the observed variation is induced by a polarization dependent coupling between the intermediate (s or d) state and the final p and f continua. Furthermore, all sidebands seem to behave, within the experimental error, in the same way, indicating that the influence of the resonant 3s-np excitations [18], which lie in the same photon energy region as the 17th and
4 POLARIZATION EFFECTS IN TWO-PHOTON PHYSICAL REVIEW A 69, (R) (2004) 19th harmonics, can be neglected for the present experiment. The transition amplitude for the sideband denoted SB 2N is given by (atomic units are used, unless otherwise stated): T 2N n,l,m,k + = T 2N 1 n,l,m,k e i 2N 1 + L + T 2N+1 n,l,m,k e i 2N+1 L, 1 where n,l,m defines the initial state of the atom and k is the wave vector of the outgoing electron. L, 2N 1, and 2N+1 are the absolute phases of the fields of the IR laser and of the neighboring harmonics, respectively. T + T corresponds to the absorption emission of one laser photon. The fact that two quantum paths lead to the same final state gives rise to strong interferences. In the soft-photon approximation, where the photon energy of the dressing laser is small against the harmonic XUV photons L H and against the energy of the outgoing electrons L k 2 /2 and where only low harmonic intensities are considered [19,20], the amplitudes are expressed as ± T 2N 1 n,l,m,k I H = i J ±1 ± L. k T 1 n,l,m,k, 2 2N 1 where L + = IL / L 2 L for the absorption of one laser photon L = IL / L 2 L * for emission, and H and L are the polarization vectors for the harmonic and laser field respectively. T 1 n,l,m,k represents the one-photon transition amplitude between the state nlm and a continuum state with energy E k = 1 2 k2 =E nlm + 2N 1 + L. In the soft-photon approximation the energy of the intermediate state coincides with that of the final state. The effect of the laser field is entirely contained in the Bessel function J ±1 and the exchange of the laser photon appears through the factor L k. For moderate laser intensities, which is the case here, one can retain only the lowest-order term in the expansion of the Bessel function and the difference between the two amplitudes lies only in the term L.k which becomes complex conjugate for T. Finally, the angle-integrated sideband intensity, which is the relevant quantity for a comparison with the experimental data, is given as the average over the individual intensity I 2N n,l,m for each magnetic sublevel m of the initial state: I 2N n,l,m = d k T 2N n,l,m,k 2. Within the framework of the soft-photon approximation, the two-photon amplitudes are expressed in terms of known one-photon dipole matrix elements associated to the transition from the initial p state towards the s and d continua [21]. The atomic phases that enter the two-photon amplitudes [16] do not appear explicitly, although Eq. (2) involves a complex quantity due to the contributions of the s- and d-continuum phase shifts. We stress at this point that in contrast to one-photon ionization, the angle-integrated sideband intensities depend on these s and d phase shifts of the continuum wave functions. 3 FIG. 4. Variation of sideband intensity as a function of the angle of rotation of the major axis of the ellipse described by the tip of the electric-field vector relative to the polarization direction of the XUV field. [The degree of ellipticity is tan.] (a) Theoretical calculations for sideband 14 for different. (b) Experimental data for different sidebands: * SB 14, SB 16, SB 18 SB 20, and SB 22. Broken line: theoretical calculation averaged over all for SB 14. When both fields are linearly polarized, the harmonic phase and intensity dependence factorize and the normalized sideband intensity depends only on the angle between the two polarizations. One can show that when starting from a p state the sideband intensity is proportional to I 2N n,l =1,m =1 3 E k 5+2 E k sin2, where E k is the usual one-photon asymmetry parameter 21. The resulting theoretical curves, displayed in Fig. 3 as a function of, are in good agreement with the experimental data regarding the general shape and the relative intensity variation. Only for the lowest sidebands some differences are observed, but, as indicated above, for these lines the softphoton approximation is not applicable. A fit of the experimental data for the highest sideband with the above formula leads to asymmetry parameters equal to 1.7±0.1, in reasonable agreement with other experimentally determined data 22 for this range of photon energy. In the same way as for the case of two linearly polarized photons, we have also calculated the two-photon ionization probability as a function of ellipticity of the IR field (see Fig. 4). In this case, L is a complex vector and no factorization is possible. The amplitudes now depend on the state of polarization of the probe beam and can be expressed in a similar way as in Eq. (4), i.e.,
5 O KEEFFE et al. PHYSICAL REVIEW A 69, (R) (2004) I 2N n,l =1,m =1 cos cos 4 sin E k 5+2 E k sin2 cos 2 sin 1, where is defined as the angle of rotation of the major axis of the ellipse described by the tip of the electric-field vector relative to the polarization direction of the XUV field. The degree of ellipticity is equal to tan. As a consequence the results are sensitive to the phase difference =2 L + 2N 1 2N+1, 5 6 where L = depends on the time delay between the two pulses. The theoretical results plotted in Fig. 4 as a function of the time delay strongly vary with. Experimentally, however, the finite XUV and IR beams intersect at a nonzero angle implying that all possible phase differences between the two beams are sampled throughout the interaction region imaged by the MBES. The resulting variation of the sideband intensity is given as a function of the angle of rotation,, in Fig. 4(b). The intensities of the sidebands are only weakly influenced by the degree of ellipticity and, again, the result does not depend on the sideband energy. An average calculated over all possible for different sideband orders, shown by the broken line in Fig. 4(b), accounts for this experimental feature. This curve is in qualitative agreement with the experimental data, but does not allow us to deduce the phase differences between subsequent harmonics. On the basis of the present data, we conclude that the variation of the polarization state of the IR field with respect to the linearly polarized XUV field can provide information about the phase differences between consecutive harmonics as well as atomic quantities involving continuum states. Further experiments and calculations are certainly needed and the present experiments represent only a starting point for this type of measurement. Two-photon experiments combined with angular distribution measurements and the variation of polarization characteristics of the IR probe beam provide an ideal testing ground for exploring the internal dynamics of photoionization of field-dressed atoms. In this way, they are of fundamental interest for many experiments planned at the new femtosecond XUV and x-ray sources. The authors acknowledge the support of the European Community (TMR-grant Access to Large Scale Facilities, Contract No. HPRI-CT , RTD-project X-Ray FEL Pump-Probe, Contract HRPI-CT , the ATTO network Grant No. HPRN-CT ) and the Swedish Science Council. [1] V. Schmidt, Rep. Prog. Phys. 55, 1483 (1992). [2] V. Schmidt, Electron Spectrometry of Atoms using Synchrotron Radiation (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997). [3] G. B. Armen et al., J. Phys. B 33, R49 (2000). [4] K. Godehusen et al., Phys. Rev. A 58, R3371 (1998). [5] Ph. Wernet et al., Phys. Rev. A 64, (2001). [6] T. Brabec and F. Krausz, Rev. Mod. Phys. 72, 545 (2000). [7] P. M. Paul et al., Science 292, 1689 (2001). [8] M. Hentschel et al., Nature (London) 414, 509 (2001). [9] M. Drescher et al., Nature (London) 419, 803 (2002). [10] V. Ayvazyan et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3825 (2002). [11] J. Norin et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, (2002). [12] J. M. Schins et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 2180 (1994). [13] T. E. Glover et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 2468 (1996). [14] E. S. Toma et al., Phys. Rev. A 62, (2000). [15] R. Taïeb et al., Phys. Rev. A 62, (2000). [16] V. Véniard et al., Phys. Rev. A 54, 721 (1996). [17] R. Lopez-Martens et al., Eur. Phys. J. D 26, 105 (2003). [18] S. L. Sorensen et al., Phys. Rev. A 50, 1218 (1994). [19] N. M. Kroll and K. M. Watson, Phys. Rev. A 8, 804 (1973). [20] A. Cionga et al., Phys. Rev. A 47, 1830 (1993). [21] D. J. Kennedy and S. T. Manson, Phys. Rev. A 5, 227 (1972). [22] D. M. P. Holland et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 195, 331 (1982)
TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES
 TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES Luca Poletto CNR - Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies Laboratory for UV and X-Ray Optical Research Padova, Italy e-mail:
TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES Luca Poletto CNR - Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies Laboratory for UV and X-Ray Optical Research Padova, Italy e-mail:
Amplitude and phase control of attosecond light pulses
 Amplitude and phase control of attosecond light pulses Lopez, Rodrigo; Varju, Katalin; Johnsson, Per; Mauritsson, J; Mairesse, Y; Salieres, P; Gaarde, M B; Schafer, K J; Persson, Anders; Svanberg, Sune;
Amplitude and phase control of attosecond light pulses Lopez, Rodrigo; Varju, Katalin; Johnsson, Per; Mauritsson, J; Mairesse, Y; Salieres, P; Gaarde, M B; Schafer, K J; Persson, Anders; Svanberg, Sune;
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
High-Energy 6.2-fs Pulses for Attosecond Pulse Generation
 Laser Physics, Vol. 15, No. 6, 25, pp. 838 842. Original Text Copyright 25 by Astro, Ltd. Copyright 25 by MAIK Nauka /Interperiodica (Russia). ATTOSECOND SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY High-Energy 6.2-fs Pulses
Laser Physics, Vol. 15, No. 6, 25, pp. 838 842. Original Text Copyright 25 by Astro, Ltd. Copyright 25 by MAIK Nauka /Interperiodica (Russia). ATTOSECOND SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY High-Energy 6.2-fs Pulses
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10864 1. Supplementary Methods The three QW samples on which data are reported in the Letter (15 nm) 19 and supplementary materials (18 and 22 nm) 23 were grown
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10864 1. Supplementary Methods The three QW samples on which data are reported in the Letter (15 nm) 19 and supplementary materials (18 and 22 nm) 23 were grown
Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 13, 2018 Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization Pivnenko, Sergey Published in: Proceedings of the European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Link
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 13, 2018 Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization Pivnenko, Sergey Published in: Proceedings of the European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Link
A soft X-ray view on ultrafast demagnetization
 A soft X-ray view on ultrafast demagnetization Boris Vodungbo Laboratoire de Chimie Physique Matière et Rayonnement Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS Paris, France Laboratoire d Optique Appliquée ENSTA
A soft X-ray view on ultrafast demagnetization Boris Vodungbo Laboratoire de Chimie Physique Matière et Rayonnement Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS Paris, France Laboratoire d Optique Appliquée ENSTA
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M.
 DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
Photon Diagnostics. FLASH User Workshop 08.
 Photon Diagnostics FLASH User Workshop 08 Kai.Tiedtke@desy.de Outline What kind of diagnostic tools do user need to make efficient use of FLASH? intensity (New GMD) beam position intensity profile on the
Photon Diagnostics FLASH User Workshop 08 Kai.Tiedtke@desy.de Outline What kind of diagnostic tools do user need to make efficient use of FLASH? intensity (New GMD) beam position intensity profile on the
Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission
 Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission L. Wimmer, G. Herink, D. R. Solli, S. V. Yalunin, K. E. Echternkamp, and C. Ropers Near-infrared pulses of 800 nm wavelength, 50 fs duration and at 1 khz repetition
Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission L. Wimmer, G. Herink, D. R. Solli, S. V. Yalunin, K. E. Echternkamp, and C. Ropers Near-infrared pulses of 800 nm wavelength, 50 fs duration and at 1 khz repetition
Duffey, T. P.; Kammen, D; Schawlow, A. L.; Svanberg, Sune; Xia, H.-R; Xiao, G.-G; Yan, G.Y
 Laser spectroscopy using beam-overlap modulation Duffey, T. P.; Kammen, D; Schawlow, A. L.; Svanberg, Sune; Xia, H.-R; Xiao, G.-G; Yan, G.Y Published in: Optics Letters DOI: 10.1364/OL.10.000597 Published:
Laser spectroscopy using beam-overlap modulation Duffey, T. P.; Kammen, D; Schawlow, A. L.; Svanberg, Sune; Xia, H.-R; Xiao, G.-G; Yan, G.Y Published in: Optics Letters DOI: 10.1364/OL.10.000597 Published:
Light-in-flight recording. 6: Experiment with view-time expansion using a skew reference wave
 Light-in-flight recording. 6: Experiment with view-time expansion using a skew reference wave Pettersson, Sven-Göran; Bergstrom, Hakan; Abramson, Nils Published in: Applied Optics DOI: 10.1364/AO.28.000766
Light-in-flight recording. 6: Experiment with view-time expansion using a skew reference wave Pettersson, Sven-Göran; Bergstrom, Hakan; Abramson, Nils Published in: Applied Optics DOI: 10.1364/AO.28.000766
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.acc-ph] 18 Jul 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.acc-ph] 18 Jul 2003 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.acc-ph] 18 Jul 2003](/thumbs/95/125580206.jpg) DESY 03 091 ISSN 0418-9833 July 2003 arxiv:physics/0307092v1 [physics.acc-ph] 18 Jul 2003 Two-color FEL amplifier for femtosecond-resolution pump-probe experiments with GW-scale X-ray and optical pulses
DESY 03 091 ISSN 0418-9833 July 2003 arxiv:physics/0307092v1 [physics.acc-ph] 18 Jul 2003 Two-color FEL amplifier for femtosecond-resolution pump-probe experiments with GW-scale X-ray and optical pulses
A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl
 A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl BACKGROUND Multipass optical systems (MOS) are broadly used in absorption, Raman, fluorescence,
A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl BACKGROUND Multipass optical systems (MOS) are broadly used in absorption, Raman, fluorescence,
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers
 Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Attosecond technology - quantum control of high harmonic generation for phase matching
 Attosecond technology - quantum control of high harmonic generation for phase matching Xiaoshi Zhang, Amy Lytle, Oren Cohen, Ivan P. Christov, Margaret M. Murnane, Henry C. Kapteyn JILA, University of
Attosecond technology - quantum control of high harmonic generation for phase matching Xiaoshi Zhang, Amy Lytle, Oren Cohen, Ivan P. Christov, Margaret M. Murnane, Henry C. Kapteyn JILA, University of
Laser Locking with Doppler-free Saturated Absorption Spectroscopy
 Laser Locking with Doppler-free Saturated Absorption Spectroscopy Paul L. Stubbs, Advisor: Irina Novikova W&M Quantum Optics Group May 12, 2010 Abstract The goal of this project was to lock the frequency
Laser Locking with Doppler-free Saturated Absorption Spectroscopy Paul L. Stubbs, Advisor: Irina Novikova W&M Quantum Optics Group May 12, 2010 Abstract The goal of this project was to lock the frequency
Laser Induced Ignition with Resonant Multiphoton Absorption in Oxygen
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Physics Seminars Physics 11-22-2013 Laser Induced Ignition with Resonant Multiphoton Absorption in Oxygen Steven F. Adams steven.adams@wright.edu Follow this and additional
Wright State University CORE Scholar Physics Seminars Physics 11-22-2013 Laser Induced Ignition with Resonant Multiphoton Absorption in Oxygen Steven F. Adams steven.adams@wright.edu Follow this and additional
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2015.137 Controlled steering of Cherenkov surface plasmon wakes with a one-dimensional metamaterial Patrice Genevet *, Daniel Wintz *, Antonio Ambrosio *, Alan
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2015.137 Controlled steering of Cherenkov surface plasmon wakes with a one-dimensional metamaterial Patrice Genevet *, Daniel Wintz *, Antonio Ambrosio *, Alan
Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
Intense and Broadband THz Source using Laser-Induced Gas Plasma
 Contract #: FA9550-09-C-0059 Page: 1 of 21 Intense and Broadband THz Source using Laser-Induced Gas Plasma Phase I Final Report Report Period: 11/1/2008 7/31/2009 Contract: FA9550-09-C-0059 CLIN#: 0001CC
Contract #: FA9550-09-C-0059 Page: 1 of 21 Intense and Broadband THz Source using Laser-Induced Gas Plasma Phase I Final Report Report Period: 11/1/2008 7/31/2009 Contract: FA9550-09-C-0059 CLIN#: 0001CC
Electro-Optical Measurements at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) Linac at the PSI. First Results
 Electro-Optical Measurements at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) Linac at the PSI First Results Overview motivation electro-optical sampling general remarks experimental setup synchronisation between TiSa-laser
Electro-Optical Measurements at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) Linac at the PSI First Results Overview motivation electro-optical sampling general remarks experimental setup synchronisation between TiSa-laser
Experimental Physics. Experiment C & D: Pulsed Laser & Dye Laser. Course: FY12. Project: The Pulsed Laser. Done by: Wael Al-Assadi & Irvin Mangwiza
 Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses
 564 Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses Hidemi Tsuchida National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, 305-8568 JAPAN Tel: 81-29-861-5342;
564 Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses Hidemi Tsuchida National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, 305-8568 JAPAN Tel: 81-29-861-5342;
First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation
 SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
Characteristic mode based pattern reconfigurable antenna for mobile handset
 Characteristic mode based pattern reconfigurable antenna for mobile handset Li, Hui; Ma, Rui; Chountalas, John; Lau, Buon Kiong Published in: European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 2015
Characteristic mode based pattern reconfigurable antenna for mobile handset Li, Hui; Ma, Rui; Chountalas, John; Lau, Buon Kiong Published in: European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 2015
DOUBLE OPTICAL GATING STEVE GILBERTSON. B.S., Kansas State University, 2005 AN ABSTRACT OF A DISSERTATION
 DOUBLE OPTICAL GATING by STEVE GILBERTSON B.S., Kansas State University, 2005 AN ABSTRACT OF A DISSERTATION submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department
DOUBLE OPTICAL GATING by STEVE GILBERTSON B.S., Kansas State University, 2005 AN ABSTRACT OF A DISSERTATION submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department
LCLS-II-HE Instrumentation
 LCLS-II-HE Instrumentation Average Brightness (ph/s/mm 2 /mrad 2 /0.1%BW) LCLS-II-HE: Enabling New Experimental Capabilities Structural Dynamics at the Atomic Scale Expand the photon energy reach of LCLS-II
LCLS-II-HE Instrumentation Average Brightness (ph/s/mm 2 /mrad 2 /0.1%BW) LCLS-II-HE: Enabling New Experimental Capabilities Structural Dynamics at the Atomic Scale Expand the photon energy reach of LCLS-II
EQUATION CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 TOWARDS INTENSE SINGLE ATTOSECOND PULSE GENERATION FROM A 400 NM DRIVING LASER YAN CHENG
 EQUATION CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 TOWARDS INTENSE SINGLE ATTOSECOND PULSE GENERATION FROM A 400 NM DRIVING LASER by YAN CHENG B.A., University of Science and Technology of China, 2009 A THESIS submitted in
EQUATION CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 TOWARDS INTENSE SINGLE ATTOSECOND PULSE GENERATION FROM A 400 NM DRIVING LASER by YAN CHENG B.A., University of Science and Technology of China, 2009 A THESIS submitted in
On-line spectrometer for FEL radiation at
 On-line spectrometer for FEL radiation at FERMI@ELETTRA Fabio Frassetto 1, Luca Poletto 1, Daniele Cocco 2, Marco Zangrando 3 1 CNR/INFM Laboratory for Ultraviolet and X-Ray Optical Research & Department
On-line spectrometer for FEL radiation at FERMI@ELETTRA Fabio Frassetto 1, Luca Poletto 1, Daniele Cocco 2, Marco Zangrando 3 1 CNR/INFM Laboratory for Ultraviolet and X-Ray Optical Research & Department
X-ray generation by femtosecond laser pulses and its application to soft X-ray imaging microscope
 X-ray generation by femtosecond laser pulses and its application to soft X-ray imaging microscope Kenichi Ikeda 1, Hideyuki Kotaki 1 ' 2 and Kazuhisa Nakajima 1 ' 2 ' 3 1 Graduate University for Advanced
X-ray generation by femtosecond laser pulses and its application to soft X-ray imaging microscope Kenichi Ikeda 1, Hideyuki Kotaki 1 ' 2 and Kazuhisa Nakajima 1 ' 2 ' 3 1 Graduate University for Advanced
Laser Induced Damage Threshold of Optical Coatings
 White Paper Laser Induced Damage Threshold of Optical Coatings An IDEX Optics & Photonics White Paper Ronian Siew, PhD Craig Hanson Turan Erdogan, PhD INTRODUCTION Optical components are used in many applications
White Paper Laser Induced Damage Threshold of Optical Coatings An IDEX Optics & Photonics White Paper Ronian Siew, PhD Craig Hanson Turan Erdogan, PhD INTRODUCTION Optical components are used in many applications
High Rep-Rate KrF Laser Development and Intense Pulse Interaction Experiments for IFE*
 High Rep-Rate KrF Laser Development and Intense Pulse Interaction Experiments for IFE* Y. Owadano, E. Takahashi, I. Okuda, I. Matsushima, Y. Matsumoto, S. Kato, E. Miura and H.Yashiro 1), K. Kuwahara 2)
High Rep-Rate KrF Laser Development and Intense Pulse Interaction Experiments for IFE* Y. Owadano, E. Takahashi, I. Okuda, I. Matsushima, Y. Matsumoto, S. Kato, E. Miura and H.Yashiro 1), K. Kuwahara 2)
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses
 atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
SUSPENSION CRITERIA FOR IMAGE MONITORS AND VIEWING BOXES.
 SUSPENSION CRITERIA FOR IMAGE MONITORS AND VIEWING BOXES. Tingberg, Anders Published in: Radiation Protection Dosimetry DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncs302 Published: 2013-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published
SUSPENSION CRITERIA FOR IMAGE MONITORS AND VIEWING BOXES. Tingberg, Anders Published in: Radiation Protection Dosimetry DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncs302 Published: 2013-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published
Phase-sensitive high-speed THz imaging
 Phase-sensitive high-speed THz imaging Toshiaki Hattori, Keisuke Ohta, Rakchanok Rungsawang and Keiji Tukamoto Institute of Applied Physics, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8573
Phase-sensitive high-speed THz imaging Toshiaki Hattori, Keisuke Ohta, Rakchanok Rungsawang and Keiji Tukamoto Institute of Applied Physics, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8573
J-KAREN-P Session 1, 10:00 10:
 J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title: Methods of Attosecond X-Ray Pulse Generation Author: Zholents, Alexander Publication Date: 05-08-2005 Publication Info:
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title: Methods of Attosecond X-Ray Pulse Generation Author: Zholents, Alexander Publication Date: 05-08-2005 Publication Info:
Citation (APA): Markos, C. (2017). Photo Contest Optics & Photonics News, 28(12), DOI: /OPN
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 29, 2018 Photo Contest 2017 Markos, Christos Published in: Optics & Photonics News Link to article, DOI: 10.1364/OPN.28.12.000022 Publication date: 2017 Document Version
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 29, 2018 Photo Contest 2017 Markos, Christos Published in: Optics & Photonics News Link to article, DOI: 10.1364/OPN.28.12.000022 Publication date: 2017 Document Version
High Average Power, High Repetition Rate Side-Pumped Nd:YVO 4 Slab Laser
 High Average Power, High Repetition Rate Side-Pumped Nd:YVO Slab Laser Kevin J. Snell and Dicky Lee Q-Peak Incorporated 135 South Rd., Bedford, MA 173 (71) 75-9535 FAX (71) 75-97 e-mail: ksnell@qpeak.com,
High Average Power, High Repetition Rate Side-Pumped Nd:YVO Slab Laser Kevin J. Snell and Dicky Lee Q-Peak Incorporated 135 South Rd., Bedford, MA 173 (71) 75-9535 FAX (71) 75-97 e-mail: ksnell@qpeak.com,
Resonantly-enhanced harmonic generation in Argon
 Resonantly-enhanced harmonic generation in Argon P. Ackermann, * H. Münch, and T. Halfmann Institut für Angewandte Physik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Hochschulstraße 6, D-64289 Darmstadt, Germany
Resonantly-enhanced harmonic generation in Argon P. Ackermann, * H. Münch, and T. Halfmann Institut für Angewandte Physik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Hochschulstraße 6, D-64289 Darmstadt, Germany
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT
 ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
Instructions for the Experiment
 Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Non-reciprocal phase shift induced by an effective magnetic flux for light
 Non-reciprocal phase shift induced by an effective magnetic flux for light Lawrence D. Tzuang, 1 Kejie Fang, 2,3 Paulo Nussenzveig, 1,4 Shanhui Fan, 2 and Michal Lipson 1,5 1 School of Electrical and Computer
Non-reciprocal phase shift induced by an effective magnetic flux for light Lawrence D. Tzuang, 1 Kejie Fang, 2,3 Paulo Nussenzveig, 1,4 Shanhui Fan, 2 and Michal Lipson 1,5 1 School of Electrical and Computer
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus
 Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Theoretical Approach. Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION:
 Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic radiation covers a vast spectrum of frequencies and wavelengths. This includes the very energetic gamma-rays radiation with a wavelength range from 0.005 1.4
Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic radiation covers a vast spectrum of frequencies and wavelengths. This includes the very energetic gamma-rays radiation with a wavelength range from 0.005 1.4
Wisconsin FEL Initiative
 Wisconsin FEL Initiative Joseph Bisognano, Mark Bissen, Robert Bosch, Michael Green, Ken Jacobs, Hartmut Hoechst, Kevin J Kleman, Robert Legg, Ruben Reininger, Ralf Wehlitz, UW-Madison/SRC William Graves,
Wisconsin FEL Initiative Joseph Bisognano, Mark Bissen, Robert Bosch, Michael Green, Ken Jacobs, Hartmut Hoechst, Kevin J Kleman, Robert Legg, Ruben Reininger, Ralf Wehlitz, UW-Madison/SRC William Graves,
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Heterogeneity and homogeneity in library and information science research
 Heterogeneity and homogeneity in library and information science research Åström, Fredrik Published in: Information Research Published: 2007-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Heterogeneity and homogeneity in library and information science research Åström, Fredrik Published in: Information Research Published: 2007-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Non resonant slots for wide band 1D scanning arrays
 Non resonant slots for wide band 1D scanning arrays Bruni, S.; Neto, A.; Maci, S.; Gerini, G. Published in: Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, 3-8 July 2005,
Non resonant slots for wide band 1D scanning arrays Bruni, S.; Neto, A.; Maci, S.; Gerini, G. Published in: Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, 3-8 July 2005,
NanoSpective, Inc Progress Drive Suite 137 Orlando, Florida
 TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
Quantifying the energy of Terahertz fields using Electro-Optical Sampling. Tom George. LCLS, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship Program
 Quantifying the energy of Terahertz fields using Electro-Optical Sampling Tom George LCLS, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship Program San Jose State University SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Quantifying the energy of Terahertz fields using Electro-Optical Sampling Tom George LCLS, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship Program San Jose State University SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
Carrier envelope phase effects on polarization gated attosecond spectra
 Carrier envelope phase effects on polarization gated attosecond spectra Mahendra Man Shakya, S.Gilbertson, Hiroki Mashiko, C.Nakamura,C. Li, E.Moon, Z.Duan, Jason Tackett, and Zenghu Chang a J.R.Macdonald
Carrier envelope phase effects on polarization gated attosecond spectra Mahendra Man Shakya, S.Gilbertson, Hiroki Mashiko, C.Nakamura,C. Li, E.Moon, Z.Duan, Jason Tackett, and Zenghu Chang a J.R.Macdonald
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW INJECTION LOCKING RING LASER AMPLIFIER USING A COUNTER INJECTION: MULTIWAVELENGTH AMPLIFICATION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW INJECTION LOCKING RING LASER AMPLIFIER USING A COUNTER INJECTION: MULTAVELENGTH AMPLIFICATION Rosen Vanyuhov Peev 1, Margarita Anguelova Deneva 1, Marin Nenchev Nenchev 1,2 1 Dept.
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW INJECTION LOCKING RING LASER AMPLIFIER USING A COUNTER INJECTION: MULTAVELENGTH AMPLIFICATION Rosen Vanyuhov Peev 1, Margarita Anguelova Deneva 1, Marin Nenchev Nenchev 1,2 1 Dept.
Chad A. Husko 1,, Sylvain Combrié 2, Pierre Colman 2, Jiangjun Zheng 1, Alfredo De Rossi 2, Chee Wei Wong 1,
 SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
FA Noncollinear Optical Parametric Amplifier
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Polarization Sagnac interferometer with a common-path local oscillator for heterodyne detection
 1354 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 16, No. 9/September 1999 Beyersdorf et al. Polarization Sagnac interferometer with a common-path local oscillator for heterodyne detection Peter T. Beyersdorf, Martin M. Fejer,
1354 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 16, No. 9/September 1999 Beyersdorf et al. Polarization Sagnac interferometer with a common-path local oscillator for heterodyne detection Peter T. Beyersdorf, Martin M. Fejer,
Title: Laser marking with graded contrast micro crack inside transparent material using UV ns pulse
 Cover Page Title: Laser marking with graded contrast micro crack inside transparent material using UV ns pulse laser Authors: Futoshi MATSUI*(1,2), Masaaki ASHIHARA(1), Mitsuyasu MATSUO (1), Sakae KAWATO(2),
Cover Page Title: Laser marking with graded contrast micro crack inside transparent material using UV ns pulse laser Authors: Futoshi MATSUI*(1,2), Masaaki ASHIHARA(1), Mitsuyasu MATSUO (1), Sakae KAWATO(2),
A 100MHz CMOS wideband IF amplifier
 A 100MHz CMOS wideband IF amplifier Sjöland, Henrik; Mattisson, Sven Published in: IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits DOI: 10.1109/4.663569 1998 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
A 100MHz CMOS wideband IF amplifier Sjöland, Henrik; Mattisson, Sven Published in: IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits DOI: 10.1109/4.663569 1998 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in. Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca
 Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania
 Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Chapter 21. Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs
 Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
PGx11 series. Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA APPLICATIONS. Available models
 PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
1. INTRODUCTION 2. LASER ABSTRACT
 Compact solid-state laser to generate 5 mj at 532 nm Bhabana Pati*, James Burgess, Michael Rayno and Kenneth Stebbins Q-Peak, Inc., 135 South Road, Bedford, Massachusetts 01730 ABSTRACT A compact and simple
Compact solid-state laser to generate 5 mj at 532 nm Bhabana Pati*, James Burgess, Michael Rayno and Kenneth Stebbins Q-Peak, Inc., 135 South Road, Bedford, Massachusetts 01730 ABSTRACT A compact and simple
Optical phase-coherent link between an optical atomic clock. and 1550 nm mode-locked lasers
 Optical phase-coherent link between an optical atomic clock and 1550 nm mode-locked lasers Kevin W. Holman, David J. Jones, Steven T. Cundiff, and Jun Ye* JILA, National Institute of Standards and Technology
Optical phase-coherent link between an optical atomic clock and 1550 nm mode-locked lasers Kevin W. Holman, David J. Jones, Steven T. Cundiff, and Jun Ye* JILA, National Institute of Standards and Technology
Doppler-Free Spetroscopy of Rubidium
 Doppler-Free Spetroscopy of Rubidium Pranjal Vachaspati, Sabrina Pasterski MIT Department of Physics (Dated: April 17, 2013) We present a technique for spectroscopy of rubidium that eliminates doppler
Doppler-Free Spetroscopy of Rubidium Pranjal Vachaspati, Sabrina Pasterski MIT Department of Physics (Dated: April 17, 2013) We present a technique for spectroscopy of rubidium that eliminates doppler
Today s Outline - January 25, C. Segre (IIT) PHYS Spring 2018 January 25, / 26
 Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 HW #2 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today
Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 HW #2 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today
Pulse Shaping Application Note
 Application Note 8010 Pulse Shaping Application Note Revision 1.0 Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026-8878 USA Shaping ultrafast optical pulses with liquid crystal spatial
Application Note 8010 Pulse Shaping Application Note Revision 1.0 Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026-8878 USA Shaping ultrafast optical pulses with liquid crystal spatial
General Physics Laboratory Experiment Report 2nd Semester, Year 2018
 PAGE 1/13 Exp. #2-7 : Measurement of the Characteristics of the Light Interference by Using Double Slits and a Computer Interface Measurement of the Light Wavelength and the Index of Refraction of the
PAGE 1/13 Exp. #2-7 : Measurement of the Characteristics of the Light Interference by Using Double Slits and a Computer Interface Measurement of the Light Wavelength and the Index of Refraction of the
Nd:YSO resonator array Transmission spectrum (a. u.) Supplementary Figure 1. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO.
 a Nd:YSO resonator array µm Transmission spectrum (a. u.) b 4 F3/2-4I9/2 25 2 5 5 875 88 λ(nm) 885 Supplementary Figure. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO. (a) Scanning electron microscope
a Nd:YSO resonator array µm Transmission spectrum (a. u.) b 4 F3/2-4I9/2 25 2 5 5 875 88 λ(nm) 885 Supplementary Figure. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO. (a) Scanning electron microscope
Improvement of terahertz imaging with a dynamic subtraction technique
 Improvement of terahertz imaging with a dynamic subtraction technique Zhiping Jiang, X. G. Xu, and X.-C. Zhang By use of dynamic subtraction it is feasible to adopt phase-sensitive detection with a CCD
Improvement of terahertz imaging with a dynamic subtraction technique Zhiping Jiang, X. G. Xu, and X.-C. Zhang By use of dynamic subtraction it is feasible to adopt phase-sensitive detection with a CCD
Introduction to the Physics of Free-Electron Lasers
 Introduction to the Physics of Free-Electron Lasers 1 Outline Undulator Radiation Radiation from many particles The FEL Instability Advanced FEL concepts The X-Ray Free-Electron Laser For Angstrom level
Introduction to the Physics of Free-Electron Lasers 1 Outline Undulator Radiation Radiation from many particles The FEL Instability Advanced FEL concepts The X-Ray Free-Electron Laser For Angstrom level
Quantum frequency standard Priority: Filing: Grant: Publication: Description
 C Quantum frequency standard Inventors: A.K.Dmitriev, M.G.Gurov, S.M.Kobtsev, A.V.Ivanenko. Priority: 2010-01-11 Filing: 2010-01-11 Grant: 2011-08-10 Publication: 2011-08-10 Description The present invention
C Quantum frequency standard Inventors: A.K.Dmitriev, M.G.Gurov, S.M.Kobtsev, A.V.Ivanenko. Priority: 2010-01-11 Filing: 2010-01-11 Grant: 2011-08-10 Publication: 2011-08-10 Description The present invention
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report. Introduction and Background
 Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Ultra-stable flashlamp-pumped laser *
 SLAC-PUB-10290 September 2002 Ultra-stable flashlamp-pumped laser * A. Brachmann, J. Clendenin, T.Galetto, T. Maruyama, J.Sodja, J. Turner, M. Woods Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Rd.,
SLAC-PUB-10290 September 2002 Ultra-stable flashlamp-pumped laser * A. Brachmann, J. Clendenin, T.Galetto, T. Maruyama, J.Sodja, J. Turner, M. Woods Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Rd.,
Terahertz spectroscopy measurements
 0 Terahertz spectroscopy measurements For general medicine and pharmacy students author: József Orbán, PhD. teaching facility: Univerity of Pécs, Medical School Department of Biophysics research facility:
0 Terahertz spectroscopy measurements For general medicine and pharmacy students author: József Orbán, PhD. teaching facility: Univerity of Pécs, Medical School Department of Biophysics research facility:
Multi-Wavelength, µm Tunable, Tandem OPO
 Multi-Wavelength, 1.5-10-µm Tunable, Tandem OPO Yelena Isyanova, Alex Dergachev, David Welford, and Peter F. Moulton Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Introduction Abstract:
Multi-Wavelength, 1.5-10-µm Tunable, Tandem OPO Yelena Isyanova, Alex Dergachev, David Welford, and Peter F. Moulton Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Introduction Abstract:
Doppler-free Fourier transform spectroscopy
 Doppler-free Fourier transform spectroscopy Samuel A. Meek, 1 Arthur Hipke, 1,2 Guy Guelachvili, 3 Theodor W. Hänsch 1,2 and Nathalie Picqué 1,2,3* 1. Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, Hans-Kopfermann-Straße
Doppler-free Fourier transform spectroscopy Samuel A. Meek, 1 Arthur Hipke, 1,2 Guy Guelachvili, 3 Theodor W. Hänsch 1,2 and Nathalie Picqué 1,2,3* 1. Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, Hans-Kopfermann-Straße
Progress of the TEO experiment at FLASH
 Progress of the TEO experiment at VUV-FEL at DESY - Armin Azima S. Duesterer, J. Feldhaus, H. Schlarb, H. Redlin, B. Steffen, DESY Hamburg K. Sengstock, Uni Hamburg Adrian Cavalieri, David Fritz, David
Progress of the TEO experiment at VUV-FEL at DESY - Armin Azima S. Duesterer, J. Feldhaus, H. Schlarb, H. Redlin, B. Steffen, DESY Hamburg K. Sengstock, Uni Hamburg Adrian Cavalieri, David Fritz, David
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS. Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments
 COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments 1 Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments 1 Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS. Topics
 COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes. Lecture 24 : Kerr lens modelocking: An application of self focusing
 Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes Lecture 24 : Kerr lens modelocking: An application of self focusing Objectives This lecture deals with the application of self focusing phenomena to ultrafast
Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes Lecture 24 : Kerr lens modelocking: An application of self focusing Objectives This lecture deals with the application of self focusing phenomena to ultrafast
VELA PHOTOINJECTOR LASER. E.W. Snedden, Lasers and Diagnostics Group
 VELA PHOTOINJECTOR LASER E.W. Snedden, Lasers and Diagnostics Group Contents Introduction PI laser step-by-step: Ti:Sapphire oscillator Regenerative amplifier Single-pass amplifier Frequency mixing Emphasis
VELA PHOTOINJECTOR LASER E.W. Snedden, Lasers and Diagnostics Group Contents Introduction PI laser step-by-step: Ti:Sapphire oscillator Regenerative amplifier Single-pass amplifier Frequency mixing Emphasis
Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser
 28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
Intermediate Physics PHYS102
 Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
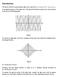 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
THz meets X-rays: Matthias C. Hoffmann, LCLS Laser Science & Technology Division SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA, 94025
 THz meets X-rays: Ultrafast X-ray Experiments Using Terahertz Excitation Matthias C. Hoffmann, LCLS Laser Science & Technology Division SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA, 94025 Overview
THz meets X-rays: Ultrafast X-ray Experiments Using Terahertz Excitation Matthias C. Hoffmann, LCLS Laser Science & Technology Division SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA, 94025 Overview
Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope
 Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope Eex Nex Luminescence Photon E 0 Disclaimer Safety the first!!! This presentation is not manual. It is just brief set of rule to remind procedure
Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope Eex Nex Luminescence Photon E 0 Disclaimer Safety the first!!! This presentation is not manual. It is just brief set of rule to remind procedure
TECHNIQUES FOR PUMP-PROBE SYNCHRONISATION OF FSEC RADIATION PULSES
 TECHNIQUES FOR PUMP-PROBE SYNCHRONISATION OF FSEC RADIATION PULSES Abstract The production of ultra-short photon pulses for UV, VUV or X-ray Free-Electron Lasers demands new techniques to measure and control
TECHNIQUES FOR PUMP-PROBE SYNCHRONISATION OF FSEC RADIATION PULSES Abstract The production of ultra-short photon pulses for UV, VUV or X-ray Free-Electron Lasers demands new techniques to measure and control
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005](/thumbs/91/105523130.jpg) Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
Teaching the Uncertainty Principle In Introductory Physics
 Teaching the Uncertainty Principle In Introductory Physics Elisha Huggins, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH Eliminating the artificial divide between classical and modern physics in introductory physics
Teaching the Uncertainty Principle In Introductory Physics Elisha Huggins, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH Eliminating the artificial divide between classical and modern physics in introductory physics
Quasi-Phase Matching of Soft X-ray Light from. High-Order Harmonic Generation using. Waveguide Structures
 Quasi-Phase Matching of Soft X-ray Light from High-Order Harmonic Generation using Waveguide Structures by Emily Abbott Gibson B.S. Engineering Physics, Colorado School of Mines, 1997 A thesis submitted
Quasi-Phase Matching of Soft X-ray Light from High-Order Harmonic Generation using Waveguide Structures by Emily Abbott Gibson B.S. Engineering Physics, Colorado School of Mines, 1997 A thesis submitted
INFRARED MEASUREMENTS OF THE SYNTHETIC DIAMOND WINDOW OF A 110 GHz HIGH POWER GYROTRON
 GA A23723 INFRARED MEASUREMENTS OF THE SYNTHETIC DIAMOND WINDOW by I.A. GORELOV, J. LOHR, R.W. CALLIS, W.P. CARY, D. PONCE, and M.B. CONDON JULY 2001 This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored
GA A23723 INFRARED MEASUREMENTS OF THE SYNTHETIC DIAMOND WINDOW by I.A. GORELOV, J. LOHR, R.W. CALLIS, W.P. CARY, D. PONCE, and M.B. CONDON JULY 2001 This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored
Medical Imaging. X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Medical Imaging X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging From: Physics for the IB Diploma Coursebook 6th Edition by Tsokos, Hoeben and Headlee And Higher Level Physics 2 nd Edition
Medical Imaging X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging From: Physics for the IB Diploma Coursebook 6th Edition by Tsokos, Hoeben and Headlee And Higher Level Physics 2 nd Edition
