Musical Acoustics, C. Bertulani. Musical Acoustics. Lecture 14 Timbre / Tone quality II
|
|
|
- Stella McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Musical Acoustics Lecture 14 Timbre / Tone quality II
2 Odd vs Even Harmonics and Symmetry Sines are Anti-symmetric about mid-point If you mirror around the middle you get the same shape but upside down f(t) = N A N Fourier series sin( 2πNf 1 t + φ ) N Sines are anti-symmetric Cosines are symmetric 2
3 3 n=1 Odd à even But symmetry depends on choice of origin n=3 Odd à even n=2 Evenà odd Additional symmetry of odd sines if you consider reflection at the red line. About this line, odd harmonics are symmetric but even ones are antisymmetric
4 Symmetry of the triangle wave 4 Obeys same symmetry as the odd harmonics so cannot contain even harmonic components Both triangle waves and square waves contain odd Fourier components. amplitude f 3f 5f 7f frequency
5 5 Sawtooth wave What overtones are present in this wave? Use its symmetry to guess the answer.
6 Spectrum of a sawtooth wave 6 All integer harmonics are present. The additional symmetry about the ¼ wave that both triangle and square wave have is not present in the sawtooth.
7 Summary: Synthesis of a square wave 7 Fourier Analysis is the decomposition of a wave into the sine wave components from which it can be built up. A Fourier Analysis is a representation of all the components that comprise a waveform, amplitude versus frequency and phase versus frequency.
8 Sound Spectrum of Musical Instruments 8 Each musical instrument has its own characteristic sounds - quite complex! Any note played on an instrument has fundamental + harmonics of fundamental. Higher harmonics - brighter sound Less harmonics - mellower sound Harmonic content of note can/does change with time: Takes time for harmonics to develop - attack (leading edge of sound) Harmonics don t decay away at same rate (trailing edge of sound) Higher harmonics tend to decay more quickly Sound output of musical instrument is not uniform with frequency Details of construction, choice of materials, finish, etc. determine resonant structure (formants) associated with instrument - mechanical vibrations!
9 9 Formants Musical instrument may have formant. The human voice has formant regions determined by the size and shape of the the vocal tract. Formant regions are not directly related the fundamental frequency and may remain more or less constant as the fundamental changes. If the fundamental is well below or low in the formant range, the quality of the sound is rich, but if the fundamental is above the formant regions the sound is thin and in the case of vowels may make them impossible to produce accurately - the reason singers often seem to have poor diction on the high notes. Spectrum of the vowel "ah" showing three formant regions. Vertical lines are harmonics produced by vibration of the vocal cords and based on a low fundamental. The vowel has a characteristic spectral shape.
10 Noise 10 Blowing gently across a microphone
11 Hypothetical instrument s timbre 11 Resonance curve Noise spectrum Fourier spectrum (Resonance minus noise)
12 12 Blowing into open tube tube
13 Frequency Modulation and Vibrato 13 Vibrato - Periodic variation of frequency A simple signal: sin[2πf(t)t] with vibrato f(time) = freq 1 + vib wid sin(2π.vib rate.time) vib wid = vibrato width amount of vibrato vib rate = vibrato rate frequency of vibrato Typical vibrato values: vib rate = 5 Hertz normal range: 1-6 Hertz, with slight acceleration during tone vib wid minimum: 0 (none) usual maximum for instruments:.01*freq 1 (1%) usual maximum for voices:.05*freq 1 (5%)
14 Example: Tenor Voice Vibrato 14 Tenor voice has 5 Hertz vibrato rate and vibrato width of 4.5% slow vibrato fast vibrato Vibrato rate vib rate = > 10 Hertz (over 10 seconds) vib wid =.01 * freq 1 (1%)
15 Vibrato Amount small vibrato large vibrato vib rate = 5 Hertz vib wid = >.05 * freq 1 (0-5% over 0:10 s) A sine wave with vibrato becomes a full spectrum when vib rate is in the audio range (above 20 Hz), especially as vib rate approaches freq 1. Since it is no longer vibrato, we use the term modulation frequency instead of vibrato rate. When vib rate is above 20 Hz: freq mod = vib rate Vibrato à FM With FM, we may not get the frequency out that we put in.we call the base frequency of the outer sine wave the carrier frequency f car : f(time) = f car + vib wid sin(2π.f mod.time) 15
16 16 Vibrato à FM FM uses a modulation index as well as the vibrato width to describe the amount of modulation. The relationship between them is vib wid = Index * freq mod or Index = vib wid / freq mod Typical values for modulation index: 0 <= Index <= 10 Example freq mod = 1 ---> 6 Hz ---> Hz (= vib rate ) (vib) (FM) Index =.02 (vib wid =.02 * freq mod ) When the frequency of the modulator reaches 6 Hertz (at 5 seconds), the effect changes from vibrato to FM. The frequency changes of all the harmonics get much faster during FM.
17 Guitar E4 string plucked near its midpoint. The nearly symmetric disturbance created results in a spectrum of mostly odd harmonics. 17
18 Guitar E4 string struck while lightly touched at its midpoint, producing a spectrum of even harmonics only. 18
19 Plucked at Midpoint Touched at Midpoint 19
20 Guitar E4 string struck and touched at the midpoint, but with the microphone placed over the soundhole, rather than behind the bridge. 20
21 High resolution spectrum of the second partial of E4, with additional peaks from the harmonics of the E2 and A2 strings, caused by energy transfer through the bridge. 21
22 Consonance, dissonance, and beats Harmony is the study of how sounds work together to create effects desired by the composer. When we hear more than one frequency of sound and the combination sounds good, we call it consonance. When the combination sounds bad or unsettling, we call it dissonance. Consonance and dissonance are related to beats. When frequencies are far enough apart that there are no beats, we get consonance. When frequencies are too close together, we hear beats that are the cause of dissonance. Beats occur when two frequencies are close, but not exactly the same. 22
23 How we hear pitch High frequency sounds selectively vibrate the basilar membrane of the inner ear near the entrance port (the oval window). Lower frequencies travel further along the membrane before causing appreciable excitation of the membrane. cross section of the cochlea 23
24 Consonance, dissonance, and roughness Ear can t distinguish too close frequencies. An average frequency is heard, as well as the beats. 2. Lower frequency fixed and the higher raised slowly à frequencies were still indistinguishable, but the beat frequency too high to make out à a roughness to the total sound. 3. Dissonance continues until the higher frequency becomes distinguishable from the lower and 2. are within the critical band. Critical band around some central frequency will be stimulated by frequencies within about 15% of that central frequency.
25 25 Subjective tones The response of a system is linear when the output is directly proportional to the input, that is, any change in the input produces a proportional change in the output. When plotted on a graph, a straight line results. A non-linear system is one where such a proportional relationship between input and output does not hold, as shown in the corresponding graph. The result of the non-linear characteristics of the ear is the addition of harmonics when the incoming sound is of sufficient intensity.
26 Subjective and Combination tones When two tones are perceived simultaneously, other tones often appear, because of distortion effects in the ear. Relatively high intensity levels are required for combination tones to be heard, and strong differences exist between individuals as to how many are heard. If two sine tones are played at a sufficient intensity level, one high (x) and the other low (y), the combination tones usually heard are the difference tones, at frequencies equal to (x - y), (2y - x) and (3y - 2x). The summation tones of frequencies (x + y) and (2x + y) are seldom if ever heard, even when in the audible range, possibly because of masking effects. The threshold of such tones varies greatly between individuals, since it depends on non-linear characteristics of the inner ear, but generally it lies between 50 and 60 db. Beats, on the other hand, can be heard at low intensities. When a single tone is played loudly enough, additional harmonics will be heard that are not present in the original tone. These added tones, being frequency multiples of the original tone, are called aural harmonics. 26
Musical Acoustics, C. Bertulani. Musical Acoustics. Lecture 13 Timbre / Tone quality I
 1 Musical Acoustics Lecture 13 Timbre / Tone quality I Waves: review 2 distance x (m) At a given time t: y = A sin(2πx/λ) A -A time t (s) At a given position x: y = A sin(2πt/t) Perfect Tuning Fork: Pure
1 Musical Acoustics Lecture 13 Timbre / Tone quality I Waves: review 2 distance x (m) At a given time t: y = A sin(2πx/λ) A -A time t (s) At a given position x: y = A sin(2πt/t) Perfect Tuning Fork: Pure
A-110 VCO. 1. Introduction. doepfer System A VCO A-110. Module A-110 (VCO) is a voltage-controlled oscillator.
 doepfer System A - 100 A-110 1. Introduction SYNC A-110 Module A-110 () is a voltage-controlled oscillator. This s frequency range is about ten octaves. It can produce four waveforms simultaneously: square,
doepfer System A - 100 A-110 1. Introduction SYNC A-110 Module A-110 () is a voltage-controlled oscillator. This s frequency range is about ten octaves. It can produce four waveforms simultaneously: square,
INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010
 Name: ID#: INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010 Midterm Exam #2 Thursday, 25 March 2010, 7:30 9:30 p.m. Closed book. You are allowed a calculator. There is a Formula
Name: ID#: INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010 Midterm Exam #2 Thursday, 25 March 2010, 7:30 9:30 p.m. Closed book. You are allowed a calculator. There is a Formula
UIUC Physics 406 Acoustical Physics of Music. Tone Quality Timbre
 Tone Quality Timbre A pure tone (aka simple tone) consists of a single frequency, e.g. f = 100 Hz. Pure tones are rare in nature natural sounds are often complex tones, consisting of/having more than one
Tone Quality Timbre A pure tone (aka simple tone) consists of a single frequency, e.g. f = 100 Hz. Pure tones are rare in nature natural sounds are often complex tones, consisting of/having more than one
2. When is an overtone harmonic? a. never c. when it is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency b. always d.
 PHYSICS LAPP RESONANCE, MUSIC, AND MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS REVIEW I will not be providing equations or any other information, but you can prepare a 3 x 5 card with equations and constants to be used on the
PHYSICS LAPP RESONANCE, MUSIC, AND MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS REVIEW I will not be providing equations or any other information, but you can prepare a 3 x 5 card with equations and constants to be used on the
Acoustics and Fourier Transform Physics Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 1/12/2018
 1 Acoustics and Fourier Transform Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 1/12/2018 I. INTRODUCTION Time is fundamental in our everyday life in the 4-dimensional
1 Acoustics and Fourier Transform Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 1/12/2018 I. INTRODUCTION Time is fundamental in our everyday life in the 4-dimensional
Physics 115 Lecture 13. Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018
 Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
Advanced Audiovisual Processing Expected Background
 Advanced Audiovisual Processing Expected Background As an advanced module, we will not cover introductory topics in lecture. You are expected to already be proficient with all of the following topics,
Advanced Audiovisual Processing Expected Background As an advanced module, we will not cover introductory topics in lecture. You are expected to already be proficient with all of the following topics,
COMP 546, Winter 2017 lecture 20 - sound 2
 Today we will examine two types of sounds that are of great interest: music and speech. We will see how a frequency domain analysis is fundamental to both. Musical sounds Let s begin by briefly considering
Today we will examine two types of sounds that are of great interest: music and speech. We will see how a frequency domain analysis is fundamental to both. Musical sounds Let s begin by briefly considering
Chapter 12. Preview. Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect. Section 1 Sound Waves
 Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
A mechanical wave is a disturbance which propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium.
 Waves and Sound Mechanical Wave A mechanical wave is a disturbance which propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium. Water Waves Wave Pulse People Wave
Waves and Sound Mechanical Wave A mechanical wave is a disturbance which propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium. Water Waves Wave Pulse People Wave
Review of Standing Waves on a String
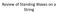 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String
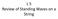 L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
Principles of Musical Acoustics
 William M. Hartmann Principles of Musical Acoustics ^Spr inger Contents 1 Sound, Music, and Science 1 1.1 The Source 2 1.2 Transmission 3 1.3 Receiver 3 2 Vibrations 1 9 2.1 Mass and Spring 9 2.1.1 Definitions
William M. Hartmann Principles of Musical Acoustics ^Spr inger Contents 1 Sound, Music, and Science 1 1.1 The Source 2 1.2 Transmission 3 1.3 Receiver 3 2 Vibrations 1 9 2.1 Mass and Spring 9 2.1.1 Definitions
Structure of Speech. Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping
 Structure of Speech Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping Speech acoustics Source-Filter Theory Speech Source characteristics Speech Filter characteristics
Structure of Speech Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping Speech acoustics Source-Filter Theory Speech Source characteristics Speech Filter characteristics
MUSC 316 Sound & Digital Audio Basics Worksheet
 MUSC 316 Sound & Digital Audio Basics Worksheet updated September 2, 2011 Name: An Aggie does not lie, cheat, or steal, or tolerate those who do. By submitting responses for this test you verify, on your
MUSC 316 Sound & Digital Audio Basics Worksheet updated September 2, 2011 Name: An Aggie does not lie, cheat, or steal, or tolerate those who do. By submitting responses for this test you verify, on your
Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990.
 Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990. Acoustics 1 1 Introduction Acoustics 2! The word acoustics refers to the science of sound and is a subcategory of physics! Room acoustics
Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990. Acoustics 1 1 Introduction Acoustics 2! The word acoustics refers to the science of sound and is a subcategory of physics! Room acoustics
Spectrum. Additive Synthesis. Additive Synthesis Caveat. Music 270a: Modulation
 Spectrum Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Spectrum Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Music 270a: Modulation
 Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 Spectrum When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 Spectrum When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Sound 16-1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can travel through h any kind of matter, but not through a vacuum. The speed of sound is different in different materials; in general, it is slowest
Chapter 16 Sound 16-1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can travel through h any kind of matter, but not through a vacuum. The speed of sound is different in different materials; in general, it is slowest
ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC)
 ALL ABOUT NOISE ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC) Any type of electrical transmission where the current repeatedly changes direction, and the voltage varies between maxima and minima. Therefore, any electrical
ALL ABOUT NOISE ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC) Any type of electrical transmission where the current repeatedly changes direction, and the voltage varies between maxima and minima. Therefore, any electrical
Complex Sounds. Reading: Yost Ch. 4
 Complex Sounds Reading: Yost Ch. 4 Natural Sounds Most sounds in our everyday lives are not simple sinusoidal sounds, but are complex sounds, consisting of a sum of many sinusoids. The amplitude and frequency
Complex Sounds Reading: Yost Ch. 4 Natural Sounds Most sounds in our everyday lives are not simple sinusoidal sounds, but are complex sounds, consisting of a sum of many sinusoids. The amplitude and frequency
What is Sound? Part II
 What is Sound? Part II Timbre & Noise 1 Prayouandi (2010) - OneOhtrix Point Never PSYCHOACOUSTICS ACOUSTICS LOUDNESS AMPLITUDE PITCH FREQUENCY QUALITY TIMBRE 2 Timbre / Quality everything that is not frequency
What is Sound? Part II Timbre & Noise 1 Prayouandi (2010) - OneOhtrix Point Never PSYCHOACOUSTICS ACOUSTICS LOUDNESS AMPLITUDE PITCH FREQUENCY QUALITY TIMBRE 2 Timbre / Quality everything that is not frequency
Physics 101. Lecture 21 Doppler Effect Loudness Human Hearing Interference of Sound Waves Reflection & Refraction of Sound
 Physics 101 Lecture 21 Doppler Effect Loudness Human Hearing Interference of Sound Waves Reflection & Refraction of Sound Quiz: Monday Oct. 18; Chaps. 16,17,18(as covered in class),19 CR/NC Deadline Oct.
Physics 101 Lecture 21 Doppler Effect Loudness Human Hearing Interference of Sound Waves Reflection & Refraction of Sound Quiz: Monday Oct. 18; Chaps. 16,17,18(as covered in class),19 CR/NC Deadline Oct.
Sound is the human ear s perceived effect of pressure changes in the ambient air. Sound can be modeled as a function of time.
 2. Physical sound 2.1 What is sound? Sound is the human ear s perceived effect of pressure changes in the ambient air. Sound can be modeled as a function of time. Figure 2.1: A 0.56-second audio clip of
2. Physical sound 2.1 What is sound? Sound is the human ear s perceived effect of pressure changes in the ambient air. Sound can be modeled as a function of time. Figure 2.1: A 0.56-second audio clip of
Physics I Notes: Chapter 13 Sound
 Physics I Notes: Chapter 13 Sound I. Properties of Sound A. Sound is the only thing that one can hear! Where do sounds come from?? Sounds are produced by VIBRATING or OSCILLATING OBJECTS! Sound is a longitudinal
Physics I Notes: Chapter 13 Sound I. Properties of Sound A. Sound is the only thing that one can hear! Where do sounds come from?? Sounds are produced by VIBRATING or OSCILLATING OBJECTS! Sound is a longitudinal
Math and Music: Understanding Pitch
 Math and Music: Understanding Pitch Gareth E. Roberts Department of Mathematics and Computer Science College of the Holy Cross Worcester, MA Topics in Mathematics: Math and Music MATH 110 Spring 2018 March
Math and Music: Understanding Pitch Gareth E. Roberts Department of Mathematics and Computer Science College of the Holy Cross Worcester, MA Topics in Mathematics: Math and Music MATH 110 Spring 2018 March
Lecture 7: Superposition and Fourier Theorem
 Lecture 7: Superposition and Fourier Theorem Sound is linear. What that means is, if several things are producing sounds at once, then the pressure of the air, due to the several things, will be and the
Lecture 7: Superposition and Fourier Theorem Sound is linear. What that means is, if several things are producing sounds at once, then the pressure of the air, due to the several things, will be and the
Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) Chirp Signal. Chirp Signal cont. CMPT 468: Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis
 Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) CMPT 468: Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 26, 29 Till now we
Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) CMPT 468: Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 26, 29 Till now we
Chapter 2. Meeting 2, Measures and Visualizations of Sounds and Signals
 Chapter 2. Meeting 2, Measures and Visualizations of Sounds and Signals 2.1. Announcements Be sure to completely read the syllabus Recording opportunities for small ensembles Due Wednesday, 15 February:
Chapter 2. Meeting 2, Measures and Visualizations of Sounds and Signals 2.1. Announcements Be sure to completely read the syllabus Recording opportunities for small ensembles Due Wednesday, 15 February:
Hearing and Deafness 2. Ear as a frequency analyzer. Chris Darwin
 Hearing and Deafness 2. Ear as a analyzer Chris Darwin Frequency: -Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude against -..5 Time (s) Waveform Amplitude against time amp Hz Frequency: 5-Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude
Hearing and Deafness 2. Ear as a analyzer Chris Darwin Frequency: -Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude against -..5 Time (s) Waveform Amplitude against time amp Hz Frequency: 5-Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude
Music. Sound Part II
 Music Sound Part II What is the study of sound called? Acoustics What is the difference between music and noise? Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear
Music Sound Part II What is the study of sound called? Acoustics What is the difference between music and noise? Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
CMPT 468: Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis
 CMPT 468: Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 6, 23 Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) Till now we ve seen signals
CMPT 468: Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 6, 23 Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) Till now we ve seen signals
Perception of pitch. Definitions. Why is pitch important? BSc Audiology/MSc SHS Psychoacoustics wk 5: 12 Feb A. Faulkner.
 Perception of pitch BSc Audiology/MSc SHS Psychoacoustics wk 5: 12 Feb 2009. A. Faulkner. See Moore, BCJ Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing, Chapter 5. Or Plack CJ The Sense of Hearing Lawrence
Perception of pitch BSc Audiology/MSc SHS Psychoacoustics wk 5: 12 Feb 2009. A. Faulkner. See Moore, BCJ Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing, Chapter 5. Or Plack CJ The Sense of Hearing Lawrence
Lab 9 Fourier Synthesis and Analysis
 Lab 9 Fourier Synthesis and Analysis In this lab you will use a number of electronic instruments to explore Fourier synthesis and analysis. As you know, any periodic waveform can be represented by a sum
Lab 9 Fourier Synthesis and Analysis In this lab you will use a number of electronic instruments to explore Fourier synthesis and analysis. As you know, any periodic waveform can be represented by a sum
CHAPTER 12 SOUND ass/sound/soundtoc. html. Characteristics of Sound
 CHAPTER 12 SOUND http://www.physicsclassroom.com/cl ass/sound/soundtoc. html Characteristics of Sound Intensity of Sound: Decibels The Ear and Its Response; Loudness Sources of Sound: Vibrating Strings
CHAPTER 12 SOUND http://www.physicsclassroom.com/cl ass/sound/soundtoc. html Characteristics of Sound Intensity of Sound: Decibels The Ear and Its Response; Loudness Sources of Sound: Vibrating Strings
ACOUSTICS. Sounds are vibrations in the air, extremely small and fast fluctuations of airpressure.
 ACOUSTICS 1. VIBRATIONS Sounds are vibrations in the air, extremely small and fast fluctuations of airpressure. These vibrations are generated from sounds sources and travel like waves in the water; sound
ACOUSTICS 1. VIBRATIONS Sounds are vibrations in the air, extremely small and fast fluctuations of airpressure. These vibrations are generated from sounds sources and travel like waves in the water; sound
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Resonance and resonators
 Resonance and resonators Dr. Christian DiCanio cdicanio@buffalo.edu University at Buffalo 10/13/15 DiCanio (UB) Resonance 10/13/15 1 / 27 Harmonics Harmonics and Resonance An example... Suppose you are
Resonance and resonators Dr. Christian DiCanio cdicanio@buffalo.edu University at Buffalo 10/13/15 DiCanio (UB) Resonance 10/13/15 1 / 27 Harmonics Harmonics and Resonance An example... Suppose you are
Fundamentals of Music Technology
 Fundamentals of Music Technology Juan P. Bello Office: 409, 4th floor, 383 LaFayette Street (ext. 85736) Office Hours: Wednesdays 2-5pm Email: jpbello@nyu.edu URL: http://homepages.nyu.edu/~jb2843/ Course-info:
Fundamentals of Music Technology Juan P. Bello Office: 409, 4th floor, 383 LaFayette Street (ext. 85736) Office Hours: Wednesdays 2-5pm Email: jpbello@nyu.edu URL: http://homepages.nyu.edu/~jb2843/ Course-info:
CS 591 S1 Midterm Exam
 Name: CS 591 S1 Midterm Exam Spring 2017 You must complete 3 of problems 1 4, and then problem 5 is mandatory. Each problem is worth 25 points. Please leave blank, or draw an X through, or write Do Not
Name: CS 591 S1 Midterm Exam Spring 2017 You must complete 3 of problems 1 4, and then problem 5 is mandatory. Each problem is worth 25 points. Please leave blank, or draw an X through, or write Do Not
Chapter 16. Waves and Sound
 Chapter 16 Waves and Sound 16.1 The Nature of Waves 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. 1 16.1 The Nature of Waves Transverse Wave 16.1 The Nature of Waves
Chapter 16 Waves and Sound 16.1 The Nature of Waves 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. 1 16.1 The Nature of Waves Transverse Wave 16.1 The Nature of Waves
PHYSICS LAB. Sound. Date: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY
 PHYSICS LAB Sound Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Sound Investigations Sound Investigations 78 Part I -
PHYSICS LAB Sound Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Sound Investigations Sound Investigations 78 Part I -
Perception of pitch. Importance of pitch: 2. mother hemp horse. scold. Definitions. Why is pitch important? AUDL4007: 11 Feb A. Faulkner.
 Perception of pitch AUDL4007: 11 Feb 2010. A. Faulkner. See Moore, BCJ Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing, Chapter 5. Or Plack CJ The Sense of Hearing Lawrence Erlbaum, 2005 Chapter 7 1 Definitions
Perception of pitch AUDL4007: 11 Feb 2010. A. Faulkner. See Moore, BCJ Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing, Chapter 5. Or Plack CJ The Sense of Hearing Lawrence Erlbaum, 2005 Chapter 7 1 Definitions
Unit 6: Waves and Sound
 Unit 6: Waves and Sound Brent Royuk Phys-109 Concordia University Waves What is a wave? Examples Water, sound, slinky, ER Transverse vs. Longitudinal 2 Wave Properties The magic of waves. Great distances
Unit 6: Waves and Sound Brent Royuk Phys-109 Concordia University Waves What is a wave? Examples Water, sound, slinky, ER Transverse vs. Longitudinal 2 Wave Properties The magic of waves. Great distances
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S. Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED Instructions: Please answer all questions in the examination booklet(s) provided. Completely
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED Instructions: Please answer all questions in the examination booklet(s) provided. Completely
VIBRATO DETECTING ALGORITHM IN REAL TIME. Minhao Zhang, Xinzhao Liu. University of Rochester Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 VIBRATO DETECTING ALGORITHM IN REAL TIME Minhao Zhang, Xinzhao Liu University of Rochester Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ABSTRACT Vibrato is a fundamental expressive attribute in music,
VIBRATO DETECTING ALGORITHM IN REAL TIME Minhao Zhang, Xinzhao Liu University of Rochester Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ABSTRACT Vibrato is a fundamental expressive attribute in music,
In Phase. Out of Phase
 Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
YAMAHA. Modifying Preset Voices. IlU FD/D SUPPLEMENTAL BOOKLET DIGITAL PROGRAMMABLE ALGORITHM SYNTHESIZER
 YAMAHA Modifying Preset Voices I IlU FD/D DIGITAL PROGRAMMABLE ALGORITHM SYNTHESIZER SUPPLEMENTAL BOOKLET Welcome --- This is the first in a series of Supplemental Booklets designed to provide a practical
YAMAHA Modifying Preset Voices I IlU FD/D DIGITAL PROGRAMMABLE ALGORITHM SYNTHESIZER SUPPLEMENTAL BOOKLET Welcome --- This is the first in a series of Supplemental Booklets designed to provide a practical
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts
 Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VIII Control of Sound The sound characteristics (acoustics) of a room depend upon a great many complex factors room size/shape wall/floor/ceiling materials
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VIII Control of Sound The sound characteristics (acoustics) of a room depend upon a great many complex factors room size/shape wall/floor/ceiling materials
Unit 6: Waves and Sound
 Unit 6: Waves and Sound Waves What is a wave? Examples Water, sound, slinky, ER Transverse vs. Longitudinal Brent Royuk Phys-109 Concordia University 2 Wave Properties The magic of waves. Great distances
Unit 6: Waves and Sound Waves What is a wave? Examples Water, sound, slinky, ER Transverse vs. Longitudinal Brent Royuk Phys-109 Concordia University 2 Wave Properties The magic of waves. Great distances
Preview. Sound Section 1. Section 1 Sound Waves. Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance. Section 3 Harmonics
 Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
Final Exam Study Guide: Introduction to Computer Music Course Staff April 24, 2015
 Final Exam Study Guide: 15-322 Introduction to Computer Music Course Staff April 24, 2015 This document is intended to help you identify and master the main concepts of 15-322, which is also what we intend
Final Exam Study Guide: 15-322 Introduction to Computer Music Course Staff April 24, 2015 This document is intended to help you identify and master the main concepts of 15-322, which is also what we intend
describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves;
 1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
Demonstrate understanding of wave systems. Demonstrate understanding of wave systems. Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
 Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Subject Reference Physics 3.3 Title Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Level 3 Credits 4 Assessment External This achievement standard involves demonstrating
Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Subject Reference Physics 3.3 Title Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Level 3 Credits 4 Assessment External This achievement standard involves demonstrating
Acoustic Phonetics. How speech sounds are physically represented. Chapters 12 and 13
 Acoustic Phonetics How speech sounds are physically represented Chapters 12 and 13 1 Sound Energy Travels through a medium to reach the ear Compression waves 2 Information from Phonetics for Dummies. William
Acoustic Phonetics How speech sounds are physically represented Chapters 12 and 13 1 Sound Energy Travels through a medium to reach the ear Compression waves 2 Information from Phonetics for Dummies. William
Spectrum Analysis: The FFT Display
 Spectrum Analysis: The FFT Display Equipment: Capstone, voltage sensor 1 Introduction It is often useful to represent a function by a series expansion, such as a Taylor series. There are other series representations
Spectrum Analysis: The FFT Display Equipment: Capstone, voltage sensor 1 Introduction It is often useful to represent a function by a series expansion, such as a Taylor series. There are other series representations
Modulation. Digital Data Transmission. COMP476 Networked Computer Systems. Sine Waves vs. Square Waves. Fourier Series. Modulation
 Digital Data Transmission Modulation Digital data is usually considered a series of binary digits. RS-232-C transmits data as square waves. COMP476 Networked Computer Systems Sine Waves vs. Square Waves
Digital Data Transmission Modulation Digital data is usually considered a series of binary digits. RS-232-C transmits data as square waves. COMP476 Networked Computer Systems Sine Waves vs. Square Waves
Perception of pitch. Definitions. Why is pitch important? BSc Audiology/MSc SHS Psychoacoustics wk 4: 7 Feb A. Faulkner.
 Perception of pitch BSc Audiology/MSc SHS Psychoacoustics wk 4: 7 Feb 2008. A. Faulkner. See Moore, BCJ Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing, Chapter 5. Or Plack CJ The Sense of Hearing Lawrence Erlbaum,
Perception of pitch BSc Audiology/MSc SHS Psychoacoustics wk 4: 7 Feb 2008. A. Faulkner. See Moore, BCJ Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing, Chapter 5. Or Plack CJ The Sense of Hearing Lawrence Erlbaum,
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology. Week 4. Signals through Systems
 Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Week 4 Signals through Systems Crucial ideas Any signal can be constructed as a sum of sine waves In a linear time-invariant (LTI) system, the response to a sinusoid
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Week 4 Signals through Systems Crucial ideas Any signal can be constructed as a sum of sine waves In a linear time-invariant (LTI) system, the response to a sinusoid
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
MUS 302 ENGINEERING SECTION
 MUS 302 ENGINEERING SECTION Wiley Ross: Recording Studio Coordinator Email =>ross@email.arizona.edu Twitter=> https://twitter.com/ssor Web page => http://www.arts.arizona.edu/studio Youtube Channel=>http://www.youtube.com/user/wileyross
MUS 302 ENGINEERING SECTION Wiley Ross: Recording Studio Coordinator Email =>ross@email.arizona.edu Twitter=> https://twitter.com/ssor Web page => http://www.arts.arizona.edu/studio Youtube Channel=>http://www.youtube.com/user/wileyross
PHYSICS. Sound & Music
 PHYSICS Sound & Music 20.1 The Origin of Sound The source of all sound waves is vibration. 20.1 The Origin of Sound The original vibration stimulates the vibration of something larger or more massive.
PHYSICS Sound & Music 20.1 The Origin of Sound The source of all sound waves is vibration. 20.1 The Origin of Sound The original vibration stimulates the vibration of something larger or more massive.
Whole geometry Finite-Difference modeling of the violin
 Whole geometry Finite-Difference modeling of the violin Institute of Musicology, Neue Rabenstr. 13, 20354 Hamburg, Germany e-mail: R_Bader@t-online.de, A Finite-Difference Modelling of the complete violin
Whole geometry Finite-Difference modeling of the violin Institute of Musicology, Neue Rabenstr. 13, 20354 Hamburg, Germany e-mail: R_Bader@t-online.de, A Finite-Difference Modelling of the complete violin
I have been playing banjo for some time now, so it was only natural to want to understand its
 Gangopadhyay 1 Bacon Banjo Analysis 13 May 2016 Suchisman Gangopadhyay I have been playing banjo for some time now, so it was only natural to want to understand its unique sound. There are two ways I analyzed
Gangopadhyay 1 Bacon Banjo Analysis 13 May 2016 Suchisman Gangopadhyay I have been playing banjo for some time now, so it was only natural to want to understand its unique sound. There are two ways I analyzed
Chapter 18. Superposition and Standing Waves
 Chapter 18 Superposition and Standing Waves Particles & Waves Spread Out in Space: NONLOCAL Superposition: Waves add in space and show interference. Do not have mass or Momentum Waves transmit energy.
Chapter 18 Superposition and Standing Waves Particles & Waves Spread Out in Space: NONLOCAL Superposition: Waves add in space and show interference. Do not have mass or Momentum Waves transmit energy.
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
ABC Math Student Copy
 Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns
 Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Some types of headphones use the phenomena of constructive and destructive interference to cancel out outside noises.
Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Some types of headphones use the phenomena of constructive and destructive interference to cancel out outside noises.
Computer Audio. An Overview. (Material freely adapted from sources far too numerous to mention )
 Computer Audio An Overview (Material freely adapted from sources far too numerous to mention ) Computer Audio An interdisciplinary field including Music Computer Science Electrical Engineering (signal
Computer Audio An Overview (Material freely adapted from sources far too numerous to mention ) Computer Audio An interdisciplinary field including Music Computer Science Electrical Engineering (signal
Sound Synthesis Methods
 Sound Synthesis Methods Matti Vihola, mvihola@cs.tut.fi 23rd August 2001 1 Objectives The objective of sound synthesis is to create sounds that are Musically interesting Preferably realistic (sounds like
Sound Synthesis Methods Matti Vihola, mvihola@cs.tut.fi 23rd August 2001 1 Objectives The objective of sound synthesis is to create sounds that are Musically interesting Preferably realistic (sounds like
Understanding the Relationship between Beat Rate and the Difference in Frequency between Two Notes.
 Understanding the Relationship between Beat Rate and the Difference in Frequency between Two Notes. Hrishi Giridhar 1 & Deepak Kumar Choudhary 2 1,2 Podar International School ARTICLE INFO Received 15
Understanding the Relationship between Beat Rate and the Difference in Frequency between Two Notes. Hrishi Giridhar 1 & Deepak Kumar Choudhary 2 1,2 Podar International School ARTICLE INFO Received 15
Introduction. Physics 1CL WAVES AND SOUND FALL 2009
 Introduction This lab and the next are based on the physics of waves and sound. In this lab, transverse waves on a string and both transverse and longitudinal waves on a slinky are studied. To describe
Introduction This lab and the next are based on the physics of waves and sound. In this lab, transverse waves on a string and both transverse and longitudinal waves on a slinky are studied. To describe
Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points]
![Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points]](/thumbs/87/96934113.jpg) Name Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] 1. To demonstrate standing waves, one end of a string is attached to a tuning fork with frequency 120 Hz. The other end
Name Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] 1. To demonstrate standing waves, one end of a string is attached to a tuning fork with frequency 120 Hz. The other end
Date Period Name. Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
Definition of Sound. Sound. Vibration. Period - Frequency. Waveform. Parameters. SPA Lundeen
 Definition of Sound Sound Psychologist's = that which is heard Physicist's = a propagated disturbance in the density of an elastic medium Vibrator serves as the sound source Medium = air 2 Vibration Periodic
Definition of Sound Sound Psychologist's = that which is heard Physicist's = a propagated disturbance in the density of an elastic medium Vibrator serves as the sound source Medium = air 2 Vibration Periodic
INTRODUCTION TO ACOUSTIC PHONETICS 2 Hilary Term, week 6 22 February 2006
 1. Resonators and Filters INTRODUCTION TO ACOUSTIC PHONETICS 2 Hilary Term, week 6 22 February 2006 Different vibrating objects are tuned to specific frequencies; these frequencies at which a particular
1. Resonators and Filters INTRODUCTION TO ACOUSTIC PHONETICS 2 Hilary Term, week 6 22 February 2006 Different vibrating objects are tuned to specific frequencies; these frequencies at which a particular
Laboratory Assignment 4. Fourier Sound Synthesis
 Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
An introduction to physics of Sound
 An introduction to physics of Sound Outlines Acoustics and psycho-acoustics Sound? Wave and waves types Cycle Basic parameters of sound wave period Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Outlines Phase Types of
An introduction to physics of Sound Outlines Acoustics and psycho-acoustics Sound? Wave and waves types Cycle Basic parameters of sound wave period Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Outlines Phase Types of
Linguistics 401 LECTURE #2. BASIC ACOUSTIC CONCEPTS (A review)
 Linguistics 401 LECTURE #2 BASIC ACOUSTIC CONCEPTS (A review) Unit of wave: CYCLE one complete wave (=one complete crest and trough) The number of cycles per second: FREQUENCY cycles per second (cps) =
Linguistics 401 LECTURE #2 BASIC ACOUSTIC CONCEPTS (A review) Unit of wave: CYCLE one complete wave (=one complete crest and trough) The number of cycles per second: FREQUENCY cycles per second (cps) =
Synthesis Techniques. Juan P Bello
 Synthesis Techniques Juan P Bello Synthesis It implies the artificial construction of a complex body by combining its elements. Complex body: acoustic signal (sound) Elements: parameters and/or basic signals
Synthesis Techniques Juan P Bello Synthesis It implies the artificial construction of a complex body by combining its elements. Complex body: acoustic signal (sound) Elements: parameters and/or basic signals
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE MUSICAL BEHAVIOR OF TRIANGLE INSTRUMENTS
 11th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
11th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
Section 1 Sound Waves. Chapter 12. Sound Waves. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Section 1 Sound Waves Sound Waves Section 1 Sound Waves The Production of Sound Waves, continued Sound waves are longitudinal. Section 1 Sound Waves Frequency and Pitch The frequency for sound is known
Section 1 Sound Waves Sound Waves Section 1 Sound Waves The Production of Sound Waves, continued Sound waves are longitudinal. Section 1 Sound Waves Frequency and Pitch The frequency for sound is known
BASIC SYNTHESIS/AUDIO TERMS
 BASIC SYNTHESIS/AUDIO TERMS Fourier Theory Any wave can be expressed/viewed/understood as a sum of a series of sine waves. As such, any wave can also be created by summing together a series of sine waves.
BASIC SYNTHESIS/AUDIO TERMS Fourier Theory Any wave can be expressed/viewed/understood as a sum of a series of sine waves. As such, any wave can also be created by summing together a series of sine waves.
SAMPLING THEORY. Representing continuous signals with discrete numbers
 SAMPLING THEORY Representing continuous signals with discrete numbers Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Art, and Music Carnegie Mellon University ICM Week 3 Copyright 2002-2013 by Roger
SAMPLING THEORY Representing continuous signals with discrete numbers Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Art, and Music Carnegie Mellon University ICM Week 3 Copyright 2002-2013 by Roger
RS380 MODULATION CONTROLLER
 RS380 MODULATION CONTROLLER The RS380 is a composite module comprising four separate sub-modules that you can patch together or with other RS Integrator modules to generate and control a wide range of
RS380 MODULATION CONTROLLER The RS380 is a composite module comprising four separate sub-modules that you can patch together or with other RS Integrator modules to generate and control a wide range of
Lab week 4: Harmonic Synthesis
 AUDL 1001: Signals and Systems for Hearing and Speech Lab week 4: Harmonic Synthesis Introduction Any waveform in the real world can be constructed by adding together sine waves of the appropriate amplitudes,
AUDL 1001: Signals and Systems for Hearing and Speech Lab week 4: Harmonic Synthesis Introduction Any waveform in the real world can be constructed by adding together sine waves of the appropriate amplitudes,
Name: SPH 3U Date: Unit 4: Waves and Sound Independent Study Unit. Instrument Chosen:
 Unit 4: Waves and Sound Independent Study Unit Name: Instrument Chosen: In this ISU, you will be investigating sound and waves, as well as analyzing a musical instrument of your choosing. It will be up
Unit 4: Waves and Sound Independent Study Unit Name: Instrument Chosen: In this ISU, you will be investigating sound and waves, as well as analyzing a musical instrument of your choosing. It will be up
Acoustic Resonance Lab
 Acoustic Resonance Lab 1 Introduction This activity introduces several concepts that are fundamental to understanding how sound is produced in musical instruments. We ll be measuring audio produced from
Acoustic Resonance Lab 1 Introduction This activity introduces several concepts that are fundamental to understanding how sound is produced in musical instruments. We ll be measuring audio produced from
A-126 VC Frequ. Shifter
 doepfer System A - 100 VC Frequency er A-126 1. Introduction A-126 VC Frequ. er Audio In Audio Out Module A-126 () is a voltage-controlled frequency shifter. The amount of frequency shift can be varied
doepfer System A - 100 VC Frequency er A-126 1. Introduction A-126 VC Frequ. er Audio In Audio Out Module A-126 () is a voltage-controlled frequency shifter. The amount of frequency shift can be varied
Extraction of Musical Pitches from Recorded Music. Mark Palenik
 Extraction of Musical Pitches from Recorded Music Mark Palenik ABSTRACT Methods of determining the musical pitches heard by the human ear hears when recorded music is played were investigated. The ultimate
Extraction of Musical Pitches from Recorded Music Mark Palenik ABSTRACT Methods of determining the musical pitches heard by the human ear hears when recorded music is played were investigated. The ultimate
The Multiplier-Type Ring Modulator
 The Multiplier-Type Ring Modulator Harald Bode Introduction- Robert A. Moog Vibrations of the air in the frequency range of 20-20,000 cycles per second are perceived as sound. The unit of frequency is
The Multiplier-Type Ring Modulator Harald Bode Introduction- Robert A. Moog Vibrations of the air in the frequency range of 20-20,000 cycles per second are perceived as sound. The unit of frequency is
SPEECH AND SPECTRAL ANALYSIS
 SPEECH AND SPECTRAL ANALYSIS 1 Sound waves: production in general: acoustic interference vibration (carried by some propagation medium) variations in air pressure speech: actions of the articulatory organs
SPEECH AND SPECTRAL ANALYSIS 1 Sound waves: production in general: acoustic interference vibration (carried by some propagation medium) variations in air pressure speech: actions of the articulatory organs
Fundamentals of Digital Audio *
 Digital Media The material in this handout is excerpted from Digital Media Curriculum Primer a work written by Dr. Yue-Ling Wong (ylwong@wfu.edu), Department of Computer Science and Department of Art,
Digital Media The material in this handout is excerpted from Digital Media Curriculum Primer a work written by Dr. Yue-Ling Wong (ylwong@wfu.edu), Department of Computer Science and Department of Art,
NAME STUDENT # ELEC 484 Audio Signal Processing. Midterm Exam July Listening test
 NAME STUDENT # ELEC 484 Audio Signal Processing Midterm Exam July 2008 CLOSED BOOK EXAM Time 1 hour Listening test Choose one of the digital audio effects for each sound example. Put only ONE mark in each
NAME STUDENT # ELEC 484 Audio Signal Processing Midterm Exam July 2008 CLOSED BOOK EXAM Time 1 hour Listening test Choose one of the digital audio effects for each sound example. Put only ONE mark in each
Lab 8. ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX SOUNDS AND SPEECH ANALYSIS Amplitude, loudness, and decibels
 Lab 8. ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX SOUNDS AND SPEECH ANALYSIS Amplitude, loudness, and decibels A complex sound with particular frequency can be analyzed and quantified by its Fourier spectrum: the relative amplitudes
Lab 8. ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX SOUNDS AND SPEECH ANALYSIS Amplitude, loudness, and decibels A complex sound with particular frequency can be analyzed and quantified by its Fourier spectrum: the relative amplitudes
Test Review # 7. Physics R: Form TR7.17A. v C M = mach number M = C v = speed relative to the medium v sound C v sound = speed of sound in the medium
 Physics R: Form TR7.17A TEST 7 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 7 Frequency and pitch. The higher the frequency of a sound wave is, the higher the pitch is. Humans can detect sounds with frequencies
Physics R: Form TR7.17A TEST 7 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 7 Frequency and pitch. The higher the frequency of a sound wave is, the higher the pitch is. Humans can detect sounds with frequencies
Lab 10 The Harmonic Series, Scales, Tuning, and Cents
 MUSC 208 Winter 2014 John Ellinger Carleton College Lab 10 The Harmonic Series, Scales, Tuning, and Cents Musical Intervals An interval in music is defined as the distance between two notes. In western
MUSC 208 Winter 2014 John Ellinger Carleton College Lab 10 The Harmonic Series, Scales, Tuning, and Cents Musical Intervals An interval in music is defined as the distance between two notes. In western
E40M Sound and Music. M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1
 E40M Sound and Music M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 LED Cube Project #3 In the next several lectures, we ll study Concepts Coding Light Sound Transforms/equalizers Devices LEDs Analog to digital converters
E40M Sound and Music M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 LED Cube Project #3 In the next several lectures, we ll study Concepts Coding Light Sound Transforms/equalizers Devices LEDs Analog to digital converters
