The Camera Versus the Human Eye
|
|
|
- Dwayne Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Camera Versus the Human Eye Nov 17, 2012 Roger Cicala This article was originally published as a blog. Permission was granted by Roger Cicala to republish the article on the CTI website. It is an excellent article for those police departments considering the use of cameras. This article started after I followed an online discussion about whether a 35mm or a 50mm lens on a full frame camera gives the equivalent field of view to normal human vision. This particular discussion immediately delved into the optical physics of the eye as a camera and lens an understandable comparison since the eye consists of a front element (the cornea), an aperture ring (the iris and pupil), a lens, and a sensor (the retina). Despite all the impressive mathematics thrown back and forth regarding the optical physics of the eyeball, the discussion didn t quite seem to make sense logically, so I did a lot of reading of my own on the topic. There won t be any direct benefit from this article that will let you run out and take better photographs, but you might find it interesting. You may also find it incredibly boring, so I ll give you my conclusion first, in the form of two quotes from Garry Winogrand:
2 A photograph is the illusion of a literal description of how the camera saw a piece of time and space. Photography is not about the thing photographed. It is about how that thing looks photographed. Basically in doing all this research about how the human eye is like a camera, what I really learned is how human vision is not like a photograph. In a way, it explained to me why I so often find a photograph much more beautiful and interesting than I found the actual scene itself. The Eye as a Camera System Superficially, it s pretty logical to compare the eye to a camera. We can measure the front toback length of the eye (about 25mm from the cornea to the retina), and the diameter of the pupil (2mm contracted, 7 to 8 mm dilated) and calculate lens like numbers from those measurements. You ll find some different numbers quoted for the focal length of the eye, though. Some are from physical measurements of the anatomic structures of the eye, others from optometric calculations, some take into account that the lens of the eye and eye size itself change with the contractions of various muscles. To summarize, though, one commonly quoted focal length of the eye is 17mm (this is calculated from the Optometric diopter value). The more commonly accepted value, however,
3 is 22mm to 24mm (calculated from physical refraction in the eye). In certain situations, the focal length may actually be longer. Since we know the approximate focal length and the diameter of the pupil, it s relatively easy to calculate the aperture (f stop) of the eye. Given a 17mm focal length and an 8mm pupil the eyeball should function as an f/2.1 lens. If we use the 24mm focal length and 8mm pupil, it should be f/3.5. There have actually been a number of studies done in astronomy to actually measure the f stop of the human eye, and the measured number comes out to be f/3.2 to f/3.5 (Middleton, 1958). At this point, both of you who read this far probably have wondered If the focal length of the eye is 17 or 24mm, why is everyone arguing about whether 35mm or 50mm lenses are the same field of view as the human eye? The reason is that the measured focal length of the eye isn t what determines the angle of view of human vision. I ll get into this in more detail below, but the main point is that only part of the retina processes the main image we see. (The area of main vision is called the cone of visual attention, the rest of what we see is peripheral vision ). Studies have measured the cone of visual attention and found it to be about 55 degrees wide. On a 35mm full frame camera, a 43mm lens provides an angle of view of 55 degrees, so that focal length provides exactly the same angle of view that we humans have. Damn if that isn t halfway between 35mm and 50mm. So the original argument is ended, the actual normal lens on a 35mm SLR is neither 35mm nor 50mm, it s halfway in between.
4 The Eye is Not a Camera System Having gotten the answer to the original discussion, I could have left things alone and walked away with yet another bit of fairly useless trivia filed away to amaze my online friends with. But NOOoooo. When I have a bunch of work that needs doing, I find I ll almost always choose to spend another couple of hours reading more articles about human vision. You may have noticed the above section left out some of the eye to camera analogies, because once you get past the simple measurements of aperture and lens, the rest of the comparisons don t fit so well. Consider the eye s sensor, the retina. The retina is almost the same size (32mm in diameter) as the sensor on a full frame camera (35mm in diameter). After that, though, almost everything is different. The retina of a human eye The first difference between the retina and your camera s sensor is rather obvious: the retina is curved along the back surface of the eyeball, not flat like the silicon sensor in the camera. The curvature has an obvious advantage: the edges of the retina are about the same distance from the lens as the center. On a flat sensor the edges are further away from the lens, and the center closer. Advantage retina it should have better corner sharpness.
5 The human eye also has a lot more pixels than your camera, about 130 million pixels (you 24 megapixel camera owners feeling humble now?). However, only about 6 million of the eye s pixels are cones (which see color), the remaining 124 million just see black and white. But advantage retina again. Big time. But if we look further the differences become even more pronounced On a camera sensor each pixel is set out in a regular grid pattern. Every square millimeter of the sensor has exactly the same number and pattern of pixels. On the retina there s a small central area, about 6mm across (the macula) that contains the densest concentration of photo receptors in the eye. The central portion of the macula (the fovea) is densely packed with only cone (color sensing) cells. The rest of the macula around this central color only area contains both rods and cones. The macula contains about 150,000 pixels in each 1mm square (compare that to 24,000,000 pixels spread over a 35mm x 24mm sensor in a 5DMkII or D3x) and provides our central vision (the 55 degree cone of visual attention mentioned above). Anyway, the central part of our visual field has far more resolving ability than even the best camera. The rest of the retina has far fewer pixels, most of which are black and white sensing only. It provides what we usually consider peripheral vision, the things we see in the corner of our
6 eye. This part senses moving objects very well, but doesn t provide enough resolution to read a book, for example. The total field of view (the area in which we can see movement) of the human eye is 160 degrees, but outside of the cone of visual attention we can t really recognize detail, only broad shapes and movement. The advantages of the human eye compared to the camera get reduced a bit as we leave the retina and travel back toward the brain. The camera sends every pixel s data from the sensor to a computer chip for processing into an image. The eye has 130 million sensors in the retina, but the optic nerve that carries those sensors signals to the brain has only 1.2 million fibers, so less than 10% of the retina s data is passed on to the brain at any given instant. (Partly this is because the chemical light sensors in the retina take a while to recharge after being stimulated. Partly because the brain couldn t process that much information anyway.) And of course the brain processes the signals a lot differently than a photography camera. Unlike the intermittent shutter clicks of a camera, the eye is sending the brain a constant feed video which is being processed into what we see. A subconscious part of the brain (the lateral geniculate nucleus if you must know) compares the signals from both eyes, assembles the most important parts into 3 D images, and sends them on to the conscious part of the brain for image recognition and further processing.
7 The subconscious brain also sends signals to the eye, moving the eyeball slightly in a scanning pattern so that the sharp vision of the macula moves across an object of interest. Over a few split seconds the eye actually sends multiple images, and the brain processes them into a more complete and detailed image. The subconscious brain also rejects a lot of the incoming bandwidth, sending only a small fraction of its data on to the conscious brain. You can control this to some extent: for example, right now your conscious brain is telling the lateral geniculate nucleus send me information from the central vision only, focus on those typed words in the center of the field of vision, move from left to right so I can read them. Stop reading for a second and without moving your eyes try to see what s in your peripheral field of view. A second ago you didn t see that object to the right or left of the computer monitor because the peripheral vision wasn t getting passed on to the conscious brain. If you concentrate, even without moving your eyes, you can at least tell the object is there. If you want to see it clearly, though, you ll have to send another brain signal to the eye, shifting the cone of visual attention over to that object. Notice also that you can t both read the text and see the peripheral objects the brain can t process that much data. The brain isn t done when the image has reached the conscious part (called the visual cortex). This area connects strongly with the memory portions of the brain, allowing you to recognize objects in the image. We ve all experienced that moment when we see something, but don t recognize what it is for a second or two. After we ve recognized it, we wonder why in the world it wasn t obvious immediately. It s because it took the brain a split second to access the memory files for image recognition. (If you haven t experienced this yet, just wait a few years. You will.) In reality (and this is very obvious) human vision is video, not photography. Even when staring at a photograph, the brain is taking multiple snapshots as it moves the center of focus over the
8 picture, stacking and assembling them into the final image we perceive. Look at a photograph for a few minutes and you ll realize that subconsciously your eye has drifted over the picture, getting an overview of the image, focusing in on details here and there and, after a few seconds, realizing some things about it that weren t obvious at first glance. So what s the Point? Well, I have some observations, although they re far away from which lens has the field of view most similar to human vision?. This information got me thinking about what makes me so fascinated by some photographs, and not so much by others. I don t know that any of these observations are true, but they re interesting thoughts (to me at least). All of them are based on one fact: when I really like a photograph, I spend a minute or two looking at it, letting my human vision scan it, grabbing the detail from it or perhaps wondering about the detail that s not visible. Photographs taken at a normal angle of view (35mm to 50mm) seem to retain their appeal whatever their size. Even web sized images shot at this focal length keep the essence of the shot. The shot below (taken at 35mm) has a lot more detail when seen in a large image, but the essence is obvious even when small. Perhaps the brain s processing is more comfortable recognizing an image it sees at its normal field of view. Perhaps it s because we photographers tend to subconsciously emphasize composition and subjects in a normal angle of view photograph. The photo above demonstrates something else I ve always wondered about: does our fascination and love for black and white photography occur because it s one of the few ways the dense cone (color only) receptors in our macula are forced to send a grayscale image to our brain? Perhaps our brain likes looking at just tone and texture, without color data clogging up that narrow bandwidth between eyeball and brain.
9 Like normal angle shots, telephoto and macro shots often look great in small prints or websized JPGs. I have an 8 10 of an elephant s eye and a similar sized macro print of a spider on my office wall that even from across the room look great. (At least they look great to me, but you ll notice that they re hanging in my office. I ve hung them in a couple of other places in the house and have been tactfully told that they really don t go with the living room furniture, so maybe they don t look so great to everyone.) There s no great composition or other factors to make those photos attractive to me, but I find them fascinating anyway. Perhaps because even at a small size, my human vision can see details in the photograph that I never could see looking at an elephant or spider with the naked eye.
10 On the other hand, when I get a good wide angle or scenic shot I hardly even bother to post a web sized graphic or make a small print (and I m not going to start for this article). I want it printed BIG. I think perhaps so that my human vision can scan through the image picking out the little details that are completely lost when its downsized. And every time I do make a big print, even of a scene I ve been to a dozen times, I notice things in the photograph I ve never seen when I was there in person. Perhaps the video my brain is making while scanning the print provides much more detail and I find it more pleasing than the composition of the photo would give when it s printed small (or which I saw when I was actually at the scene). And perhaps the subconscious scanning that my vision makes across a photograph accounts for why things like the rule of thirds and selective focus pulls my eye to certain parts of the photograph. Maybe we photographers simply figured out how the brain processes images and took advantage of it through practical experience, without knowing all the science involved. But I guess my only real conclusion is this: a photograph is NOT exactly what my eye and brain saw at the scene. When I get a good shot, it s something different and something better, like what Winogrand said in the two quotes above, and in this quote too: You see something happening and you bang away at it. Either you get what you saw or you get something else and whichever is better you print. About the author: Roger Cicala is the founder of LensRentals. This article was originally published here. Image credits: my eye up close by machinecodeblue, Nikh s eye through camera s eye from my eyes for your eyes : ) by slalit, Schematic of the Human Eye by entirelysubjective, My left eye retina by Richard Masoner / Cyclelicious, Chromatic aberration (sort of) by moppet65535
Physics 1230: Light and Color. Guest Lecture, Jack again. Lecture 23: More about cameras
 Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Guest Lecture, Jack again Lecture 23: More about
Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Guest Lecture, Jack again Lecture 23: More about
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Presented to you today by the Fort Collins Digital Camera Club
 Presented to you today by the Fort Collins Digital Camera Club www.fcdcc.com Photography: February 19, 2011 Fort Collins Digital Camera Club 2 Film Photography: Photography using light sensitive chemicals
Presented to you today by the Fort Collins Digital Camera Club www.fcdcc.com Photography: February 19, 2011 Fort Collins Digital Camera Club 2 Film Photography: Photography using light sensitive chemicals
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision, Color, and Illusions. Vision: How we see
 HDCC208N Fall 2018 One of many optical illusions - http://www.physics.uc.edu/~sitko/lightcolor/19-perception/19-perception.htm Vision, Color, and Illusions Vision: How we see The human eye allows us to
HDCC208N Fall 2018 One of many optical illusions - http://www.physics.uc.edu/~sitko/lightcolor/19-perception/19-perception.htm Vision, Color, and Illusions Vision: How we see The human eye allows us to
EC-433 Digital Image Processing
 EC-433 Digital Image Processing Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Dr. Arslan Shaukat 1 Fundamental Steps in DIP Image Acquisition An image is captured by a sensor (such as a monochrome or color TV camera)
EC-433 Digital Image Processing Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Dr. Arslan Shaukat 1 Fundamental Steps in DIP Image Acquisition An image is captured by a sensor (such as a monochrome or color TV camera)
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Chapter 25. Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
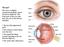 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
30 Lenses. Lenses change the paths of light.
 Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Chapter 25: Applied Optics. PHY2054: Chapter 25
 Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World
 Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Unit 3: Energy On the Move
 14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Chapter 29/30. Wave Fronts and Rays. Refraction of Sound. Dispersion in a Prism. Index of Refraction. Refraction and Lenses
 Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Topic 6 - Optics Depth of Field and Circle Of Confusion
 Topic 6 - Optics Depth of Field and Circle Of Confusion Learning Outcomes In this lesson, we will learn all about depth of field and a concept known as the Circle of Confusion. By the end of this lesson,
Topic 6 - Optics Depth of Field and Circle Of Confusion Learning Outcomes In this lesson, we will learn all about depth of field and a concept known as the Circle of Confusion. By the end of this lesson,
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
How to Optimize the Sharpness of Your Photographic Prints: Part I - Your Eye and its Ability to Resolve Fine Detail
 How to Optimize the Sharpness of Your Photographic Prints: Part I - Your Eye and its Ability to Resolve Fine Detail Robert B.Hallock hallock@physics.umass.edu Draft revised April 11, 2006 finalpaper1.doc
How to Optimize the Sharpness of Your Photographic Prints: Part I - Your Eye and its Ability to Resolve Fine Detail Robert B.Hallock hallock@physics.umass.edu Draft revised April 11, 2006 finalpaper1.doc
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Cameras have number of controls that allow the user to change the way the photograph looks.
 Anatomy of a camera - Camera Controls Cameras have number of controls that allow the user to change the way the photograph looks. Focus In the eye the cornea and the lens adjust the focus on the retina.
Anatomy of a camera - Camera Controls Cameras have number of controls that allow the user to change the way the photograph looks. Focus In the eye the cornea and the lens adjust the focus on the retina.
Determining MTF with a Slant Edge Target ABSTRACT AND INTRODUCTION
 Determining MTF with a Slant Edge Target Douglas A. Kerr Issue 2 October 13, 2010 ABSTRACT AND INTRODUCTION The modulation transfer function (MTF) of a photographic lens tells us how effectively the lens
Determining MTF with a Slant Edge Target Douglas A. Kerr Issue 2 October 13, 2010 ABSTRACT AND INTRODUCTION The modulation transfer function (MTF) of a photographic lens tells us how effectively the lens
E X P E R I M E N T 12
 E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
THE PHOTOGRAPHER S GUIDE TO DEPTH OF FIELD
 THE PHOTOGRAPHER S GUIDE TO DEPTH OF FIELD A Light Stalking Short Guide Cover Image Credit: Thomas Rey WHAT IS DEPTH OF FIELD? P hotography can be a simple form of art but at the core is a complex set
THE PHOTOGRAPHER S GUIDE TO DEPTH OF FIELD A Light Stalking Short Guide Cover Image Credit: Thomas Rey WHAT IS DEPTH OF FIELD? P hotography can be a simple form of art but at the core is a complex set
1. What are the components of your nervous system? 2. How do telescopes and human eyes work?
 Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
The Human Eye Looking at your own eye with an Eye Scope
 The Human Eye Looking at your own eye with an Eye Scope Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors
The Human Eye Looking at your own eye with an Eye Scope Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Getting light to imager. Capturing Images. Depth and Distance. Ideal Imaging. CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes
 CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes Last time: what is an image idea of image-based (raster representation) Today: image capture/acquisition, focus cameras and eyes displays and intensities Corrected
CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes Last time: what is an image idea of image-based (raster representation) Today: image capture/acquisition, focus cameras and eyes displays and intensities Corrected
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2)
 Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2) Brief review Optical instruments Camera Human eye Magnifying glass Telescope Microscope Optical Aberrations Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 31, Pg 1 The Lens Equation
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2) Brief review Optical instruments Camera Human eye Magnifying glass Telescope Microscope Optical Aberrations Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 31, Pg 1 The Lens Equation
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision. Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic
 Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Lens Aperture. South Pasadena High School Final Exam Study Guide- 1 st Semester Photo ½. Study Guide Topics that will be on the Final Exam
 South Pasadena High School Final Exam Study Guide- 1 st Semester Photo ½ Study Guide Topics that will be on the Final Exam The Rule of Thirds Depth of Field Lens and its properties Aperture and F-Stop
South Pasadena High School Final Exam Study Guide- 1 st Semester Photo ½ Study Guide Topics that will be on the Final Exam The Rule of Thirds Depth of Field Lens and its properties Aperture and F-Stop
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Blur Your Course into Focus (Jan 09)
 Blur Your Course into Focus (Jan 09) A good e-learning course always starts with good content. However, content alone isn t your only consideration when building e-learning courses. How your course LOOKS
Blur Your Course into Focus (Jan 09) A good e-learning course always starts with good content. However, content alone isn t your only consideration when building e-learning courses. How your course LOOKS
DSLR Cameras have a wide variety of lenses that can be used.
 Chapter 8-Lenses DSLR Cameras have a wide variety of lenses that can be used. The camera lens is very important in making great photographs. It controls what the sensor sees, how much of the scene is included,
Chapter 8-Lenses DSLR Cameras have a wide variety of lenses that can be used. The camera lens is very important in making great photographs. It controls what the sensor sees, how much of the scene is included,
PHYSICS. Chapter 35 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
Lecture Outline Chapter 27. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
Macro and Close-up Photography
 Photo by Daniel Schwen Macro and Close-up Photography Digital Photography DeCal 2010 Nathan Yan Kellen Freeman Some slides adapted from Zexi Eric Yan What Is Macro Photography? Macro commonly refers to
Photo by Daniel Schwen Macro and Close-up Photography Digital Photography DeCal 2010 Nathan Yan Kellen Freeman Some slides adapted from Zexi Eric Yan What Is Macro Photography? Macro commonly refers to
This document explains the reasons behind this phenomenon and describes how to overcome it.
 Internal: 734-00583B-EN Release date: 17 December 2008 Cast Effects in Wide Angle Photography Overview Shooting images with wide angle lenses and exploiting large format camera movements can result in
Internal: 734-00583B-EN Release date: 17 December 2008 Cast Effects in Wide Angle Photography Overview Shooting images with wide angle lenses and exploiting large format camera movements can result in
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Lecture 8. Lecture 8. r 1
 Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Visual Perception. Readings and References. Forming an image. Pinhole camera. Readings. Other References. CSE 457, Autumn 2004 Computer Graphics
 Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation
 VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
In order to manage and correct color photos, you need to understand a few
 In This Chapter 1 Understanding Color Getting the essentials of managing color Speaking the language of color Mixing three hues into millions of colors Choosing the right color mode for your image Switching
In This Chapter 1 Understanding Color Getting the essentials of managing color Speaking the language of color Mixing three hues into millions of colors Choosing the right color mode for your image Switching
EYE. The eye is an extension of the brain
 I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Light. Path of Light. Looking at things. Depth and Distance. Getting light to imager. CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes
 CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Sept. 2005 Adjusted after class stuff we didn t get to removed / mistakes fixed Light Electromagnetic
CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Sept. 2005 Adjusted after class stuff we didn t get to removed / mistakes fixed Light Electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
Physics of the Eye *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
Chapter 20 Human Vision
 Chapter 20 GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Characterize the physical parameters that are significant in human vision. Visual
Chapter 20 GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Characterize the physical parameters that are significant in human vision. Visual
Zone. ystem. Handbook. Part 2 The Zone System in Practice. by Jeff Curto
 A Zone S ystem Handbook Part 2 The Zone System in Practice by This handout was produced in support of s Camera Position Podcast. Reproduction and redistribution of this document is fine, so long as the
A Zone S ystem Handbook Part 2 The Zone System in Practice by This handout was produced in support of s Camera Position Podcast. Reproduction and redistribution of this document is fine, so long as the
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume
 Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Physics 2.2A for Achievement Standard 91169 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard 91169 Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Physics 2.2A for Achievement Standard 91169 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard 91169 Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Image Formation and Capture
 Figure credits: B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, A. Theuwissen, and J. Malik Image Formation and Capture COS 429: Computer Vision Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices
Figure credits: B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, A. Theuwissen, and J. Malik Image Formation and Capture COS 429: Computer Vision Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices
VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation
 VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
Visual Optics. Visual Optics - Introduction
 Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
One Week to Better Photography
 One Week to Better Photography Glossary Adobe Bridge Useful application packaged with Adobe Photoshop that previews, organizes and renames digital image files and creates digital contact sheets Adobe Photoshop
One Week to Better Photography Glossary Adobe Bridge Useful application packaged with Adobe Photoshop that previews, organizes and renames digital image files and creates digital contact sheets Adobe Photoshop
Autofocus Problems The Camera Lens
 NEWHorenstein.04.Lens.32-55 3/11/05 11:53 AM Page 36 36 4 The Camera Lens Autofocus Problems Autofocus can be a powerful aid when it works, but frustrating when it doesn t. And there are some situations
NEWHorenstein.04.Lens.32-55 3/11/05 11:53 AM Page 36 36 4 The Camera Lens Autofocus Problems Autofocus can be a powerful aid when it works, but frustrating when it doesn t. And there are some situations
25 Questions. All are multiple choice questions. 4 will require an additional written response explaining your answer.
 9 th Grade Digital Photography Final Review- Written Portion of Exam EXAM STRUCTURE: 25 Questions. All are multiple choice questions. 4 will require an additional written response explaining your answer.
9 th Grade Digital Photography Final Review- Written Portion of Exam EXAM STRUCTURE: 25 Questions. All are multiple choice questions. 4 will require an additional written response explaining your answer.
Photography (cont d)
 Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Getting Unlimited Digital Resolution
 Getting Unlimited Digital Resolution N. David King Wow, now here s a goal: how would you like to be able to create nearly any amount of resolution you want with a digital camera. Since the higher the resolution
Getting Unlimited Digital Resolution N. David King Wow, now here s a goal: how would you like to be able to create nearly any amount of resolution you want with a digital camera. Since the higher the resolution
Chapter 6 Human Vision
 Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Prof. Greg Francis and the eye PSY 310 Greg Francis The perceptual process Perception Recognition Processing Action Transduction Lecture 03 Why does my daughter look like a demon? Stimulus on receptors
Prof. Greg Francis and the eye PSY 310 Greg Francis The perceptual process Perception Recognition Processing Action Transduction Lecture 03 Why does my daughter look like a demon? Stimulus on receptors
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Aberrations, Camera, Eye
 Aberrations, Camera, Eye This is a question that we probably can't answer. If the Invisible Man is also blind because no light is being absorbed by his retinas, then when we die and become spirits that
Aberrations, Camera, Eye This is a question that we probably can't answer. If the Invisible Man is also blind because no light is being absorbed by his retinas, then when we die and become spirits that
Lenses and Focal Length
 Task 2 Lenses and Focal Length During this task we will be exploring how a change in lens focal length can alter the way that the image is recorded on the film. To gain a better understanding before you
Task 2 Lenses and Focal Length During this task we will be exploring how a change in lens focal length can alter the way that the image is recorded on the film. To gain a better understanding before you
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
STUDY NOTES UNIT I IMAGE PERCEPTION AND SAMPLING. Elements of Digital Image Processing Systems. Elements of Visual Perception structure of human eye
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING STUDY NOTES UNIT I IMAGE PERCEPTION AND SAMPLING Elements of Digital Image Processing Systems Elements of Visual Perception structure of human eye light, luminance, brightness
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING STUDY NOTES UNIT I IMAGE PERCEPTION AND SAMPLING Elements of Digital Image Processing Systems Elements of Visual Perception structure of human eye light, luminance, brightness
LOVED BY PROS. MADE FOR YOU. e - pl2
 LOVED BY PROS. MADE FOR YOU. > shooting great pictures has never been so easy. e - pl2 SOMe perfection is DeBAtABle. SOMe is not. In a way we didn t even design your E-PL2. You did. Because this is what
LOVED BY PROS. MADE FOR YOU. > shooting great pictures has never been so easy. e - pl2 SOMe perfection is DeBAtABle. SOMe is not. In a way we didn t even design your E-PL2. You did. Because this is what
Kent Messamore 3/12/2010
 Photo Composition Kent Messamore 3/12/2010 Composition Choosing a Subject Quality of Light Framing the Image Depth of Field Backgrounds and Foregrounds Viewpoint Leading Lines Contrasts Patterns Negative
Photo Composition Kent Messamore 3/12/2010 Composition Choosing a Subject Quality of Light Framing the Image Depth of Field Backgrounds and Foregrounds Viewpoint Leading Lines Contrasts Patterns Negative
Name Class Date. Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used.
 Assessment Chapter Test B Light and Our World USING KEY TERMS Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. concave
Assessment Chapter Test B Light and Our World USING KEY TERMS Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. concave
This has given you a good introduction to the world of photography, however there are other important and fundamental camera functions and skills
 THE DSLR CAMERA Before we Begin For those of you who have studied photography the chances are that in most cases you have been using a digital compact camera. This has probably involved you turning the
THE DSLR CAMERA Before we Begin For those of you who have studied photography the chances are that in most cases you have been using a digital compact camera. This has probably involved you turning the
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Depth Of Field or DOF
 Depth Of Field or DOF Why you need to use it. A comparison of the values. Image compression due to zoom lenses. Featuring: The Christmas decorations I forgot to pack away My sloping table, kitchen uplighter
Depth Of Field or DOF Why you need to use it. A comparison of the values. Image compression due to zoom lenses. Featuring: The Christmas decorations I forgot to pack away My sloping table, kitchen uplighter
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
Introduction. Strand F Unit 3: Optics. Learning Objectives. Introduction. At the end of this unit you should be able to;
 Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Introduction. Related Work
 Introduction Depth of field is a natural phenomenon when it comes to both sight and photography. The basic ray tracing camera model is insufficient at representing this essential visual element and will
Introduction Depth of field is a natural phenomenon when it comes to both sight and photography. The basic ray tracing camera model is insufficient at representing this essential visual element and will
COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR)
 COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR) PAPER TITLE: BASIC PHOTOGRAPHIC UNIT - 3 : SIMPLE LENS TOPIC: LENS PROPERTIES AND DEFECTS OBJECTIVES By
COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR) PAPER TITLE: BASIC PHOTOGRAPHIC UNIT - 3 : SIMPLE LENS TOPIC: LENS PROPERTIES AND DEFECTS OBJECTIVES By
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Introduction. The Human Eye. Physics 1CL OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS AND THE EYE SPRING 2010
 Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
So far, I have discussed setting up the camera for
 Chapter 3: The Shooting Modes So far, I have discussed setting up the camera for quick shots, relying on features such as Auto mode for taking pictures with settings controlled mostly by the camera s automation.
Chapter 3: The Shooting Modes So far, I have discussed setting up the camera for quick shots, relying on features such as Auto mode for taking pictures with settings controlled mostly by the camera s automation.
Buying the Right Photo Equipment
 Buying the Right Photo Equipment edition espresso Elin Rantakrans Buying the Right Photo Equipment 70 Tips from the Top WITH PHOTOS BY Ari Byström Simon Cederquist Kirti Casie Chetty David Elmfeldt Tobias
Buying the Right Photo Equipment edition espresso Elin Rantakrans Buying the Right Photo Equipment 70 Tips from the Top WITH PHOTOS BY Ari Byström Simon Cederquist Kirti Casie Chetty David Elmfeldt Tobias
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision
 The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors and neurons. Muscles
The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors and neurons. Muscles
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Physics 1230 Homework 8 Due Friday June 24, 2016
 At this point, you know lots about mirrors and lenses and can predict how they interact with light from objects to form images for observers. In the next part of the course, we consider applications of
At this point, you know lots about mirrors and lenses and can predict how they interact with light from objects to form images for observers. In the next part of the course, we consider applications of
