The Human Eye: Structures
|
|
|
- Jordan Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Human Eye: Structures
2
3 We will look at the following parts:
4 Take notes on this page
5 CORNEA (clear lens in front of eye) transparent covering of the front of the eye Allows for the passage of light into the eye and functions as a fixed lens.
6 allows for the passage of light into the eye and it also focuses the light
7 PUPIL (black hole) black hole in iris where light enters Pupil size is controlled by iris muscles
8 the hole where light enters into the eye
9 THE EYE: PUPIL When the eye needs more light to enter (when it is dark), the pupils get larger; allowing more light to enter the eye
10 THE EYE: PUPIL When the eye needs less light to enter (when it is very bright), the pupils get smaller; allowing less light to enter the eye
11 IRIS (colored part) colored part of eye controls light entering The iris is a colored, circular muscle
12 controls the amount of light entering the eye
13 SCLERA a tough white skin (made of tissue) that covers all of the eyeball except the cornea. SCLERA (white part) whites of the eye supports eyeball provides attachment for muscles
14 supports eyeball and provides attachment for muscles
15 LENS (lens behind pupil) converging lens allows us to see objects near and far
16 allows us to see objects near and far
17 RETINA internal membrane contains light-receptive cells (rods and cones) converts light to electrical signals
18 converts light waves to electrical signals
19 OPTIC NERVE Transmits electrical impulses from retina to the brain Creates blind spot Brain takes inverted image and flips it so we can see
20 Transmits electrical signals from retina to the brain
21 BLIND SPOT On retina where optic nerve leads back into the brain No rod or cone cells Other eye compensates for this area
22 Small spot on the back of the retina Other eye compensates for this area Try this test to prove you have a blind spot
23 THE EYE: Blind Spot (Fovea) On retina where optic nerve leads back into the brain No rod or cone cells Other eye compensates for this area Try this test to prove you have a blind spot
24 Blind Spot (Optic Disk) Close your right eye and look directly at the number 3. Can you see the yellow spot in your peripheral vision? Now slowly move towards or away from the screen. At some point, the yellow spot will disappear.
25
26 Your 2 Lenses: Cornea and Lens There are two lenses in your eye, the cornea and the lens. The cornea, the front surface of the eye, does most of the focusing in your eye The lens provides adjustable fine-tuning of the focus
27 How Your Lens Focuses Your lens has a small depth of field You can't see something close and far with both objects in focus at the same time Hold out your thumb about a foot away from your eye Then, alternately focus on thumb and me (right above your thumb) Note that you cannot see both me and your thumb sharply (in focus) at the same time You focus on one or the other by changing the bulge of your lens
28 thumb is out of focus less bulgy teacher is in focus thumb is in focus more bulgy Teacher is out of focus
29 Focusing Problems HYPEROPIA Far-sightedness Problem seeing close objects Distance between lens and retina too small Light focused behind retina Corrected with converging lenses
30 Far-Sighted (Hyperopia)
31 Focusing Problems PRESBYOPIA Form of far-sightedness Harder for people to read as they age Lens loses elasticity Corrected by glasses with converging lenses
32 Focusing Problems MYOPIA Near-sightedness Problem seeing objects far away Distance between lens and retina too large Light focused in front of retina Correct with diverging lenses
33 Near-Sighted (Myopia)
34 Diseases of the Eye ASTIGMATISM Eye cannot focus an object s image on a single point on retina Cornea is oval instead of spherical Causes blurred vision Some types can be corrected with lenses
35 Diseases of the Eye GLAUCOMA Group of diseases Affects optic nerve - pressure Loss of ganglion cells Gradual loss of sight and eventual blindness Check eyes regularly Can be treated
36 Diseases of the Eye CATARACTS Clouding forms in lens due to denaturing of lens protein Obstructs passage of light Caused by age, chronic exposure to UV, or due to trauma Removed by surgery
37 Vision Correction CONTACT LENSES Artificial lens placed over cornea Same as glasses Corrects for both near and far-sightedness Also used for cosmetic purposes (eye colour, Hollywood)
38 Videos How Eyes Work: An Introduction (10:48) Bill Nye The Science Guy on the Eyeball (2:12) How the Human Eye Works The Human Eye and How it Works (22:59)
39 Optical Illusions
40 Can your eyes/brain be tricked?
41 The Human Eye Your eyes are about to get a workout. Have you stretched your eye muscles yet? No? Then do that now!
42 Are you seeing spots?
43
44 Look at the cross for 10 seconds. What do you see?
45 Are these lines bent.?
46 or straight?
47 What shapes do you see?
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57 Do you see the rabbit or the duck?
58
59
60
61
62 What is wrong with Reading with this sentence? Aoccdrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a toatl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit a porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe.
63 Read This Out Loud.
64 Are You Sure? Read again.
65 Blind Spot On retina where optic nerve leads back into the brain No rod or cone cells Other eye compensates for this area Try this test to prove you have a blind spot
66 Blind Spot (Optic Disk) Close your right eye and look directly at the number 3. Can you see the yellow spot in your peripheral vision? Now slowly move towards or away from the screen. At some point, the yellow spot will disappear.
67 Now stare at the red dot with your right eye from 12 inches, covering your left eye with your left hand. Notice that the gap in the blue bar fills in (completes). Move your left hand to unblock your left eye and the gap re-appears.
68 Close left eye and approach screen while staring at the letters watch the dot!
69 Optical Illusion Video Clips 10 Best Optical Illusions of 2014 (10:18) 8 Moving Illusions (10:47) Q
LIGHT is To The Environmental Designer
 LIGHT is To The Environmental Designer The Architect and Interior Designer are interested in the environmental impact of light. creating an atmosphere creating a sense of space, both physically and experientially/
LIGHT is To The Environmental Designer The Architect and Interior Designer are interested in the environmental impact of light. creating an atmosphere creating a sense of space, both physically and experientially/
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
Input-output channels
 Input-output channels Human Computer Interaction (HCI) Human input Using senses Sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell Sight, hearing & touch have important role in HCI Input-Output Channels Human output
Input-output channels Human Computer Interaction (HCI) Human input Using senses Sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell Sight, hearing & touch have important role in HCI Input-Output Channels Human output
EYE. The eye is an extension of the brain
 I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception
 Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Perception. Selective Attention focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. Cocktail Party Effect
 Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Chapter 6 Human Vision
 Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision. Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic
 Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Sense Organs (Eye) The eye is the sense organ of sight. The eye is shaped like a ball and is located in bony
 Sense Organs (Eye) The eye is the sense organ of sight. The eye is shaped like a ball and is located in bony sockets in the skull. It is held in place by six muscles which are joined to the outside of
Sense Organs (Eye) The eye is the sense organ of sight. The eye is shaped like a ball and is located in bony sockets in the skull. It is held in place by six muscles which are joined to the outside of
Limitations of Data Mining in Healthcare.
 Limitations of Data Mining in Healthcare. Vitaly Herasevich, MD, PhD, FCCM Associate Professor of Anesthesiology and Medicine, Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Division of Critical
Limitations of Data Mining in Healthcare. Vitaly Herasevich, MD, PhD, FCCM Associate Professor of Anesthesiology and Medicine, Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Division of Critical
MTTTS17 Dimensionality reduction and visualization
 MTTTS17 Dimensionality reduction and visualization Spring 2018 Lecture 5: Human perception Jaakko Peltonen jaakko dot peltonen at uta dot fi 1 Human perception (part 1) Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at Cmabrigde
MTTTS17 Dimensionality reduction and visualization Spring 2018 Lecture 5: Human perception Jaakko Peltonen jaakko dot peltonen at uta dot fi 1 Human perception (part 1) Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at Cmabrigde
Animated Vision Associates. Allan N Hytowitz (N = 1).
 Animated Vision Associates Allan N Hytowitz (N = 1). Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic. Arthur C. Clarke s Third Law Communication Circa 1800 Circa 1862 Circa 1888 Circa
Animated Vision Associates Allan N Hytowitz (N = 1). Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic. Arthur C. Clarke s Third Law Communication Circa 1800 Circa 1862 Circa 1888 Circa
November 14, 2017 Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes 2- lacrimal apparatus:
 Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes eyebrows: protection from debris & sun eyelids: continuation of skin, protection & lubrication eyelashes:
Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes eyebrows: protection from debris & sun eyelids: continuation of skin, protection & lubrication eyelashes:
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15
 Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE
 Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE Eye Openers Museum of Vision You need a couple blank sheets of paper. Label each side #1 How We See #2 Binocular Vision #3 Optical Illusions #4 Persistence of Vision On Packet
Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE Eye Openers Museum of Vision You need a couple blank sheets of paper. Label each side #1 How We See #2 Binocular Vision #3 Optical Illusions #4 Persistence of Vision On Packet
Chapter Human Vision
 Chapter 6 6.1 Human Vision How Light Enters the Eye Light enters the eye through the pupil. The pupil appears dark because light passes through it without reflecting back Pupil Iris = Coloured circle of
Chapter 6 6.1 Human Vision How Light Enters the Eye Light enters the eye through the pupil. The pupil appears dark because light passes through it without reflecting back Pupil Iris = Coloured circle of
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume
 Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
12.1. Human Perception of Light. Perceiving Light
 12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Introduction. The Human Eye. Physics 1CL OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS AND THE EYE SPRING 2010
 Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
Lenses. Images. Difference between Real and Virtual Images
 Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
LO - Lab #06 - The Amazing Human Eye
 LO - Lab #06 - In this lab you will examine and model one of the most amazing optical systems you will ever encounter: the human eye. You might find it helpful to review the anatomy and function of the
LO - Lab #06 - In this lab you will examine and model one of the most amazing optical systems you will ever encounter: the human eye. You might find it helpful to review the anatomy and function of the
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
Aspects of Vision. Senses
 Lab is modified from Meehan (1998) and a Science Kit lab 66688 50. Vision is the act of seeing; vision involves the transmission of the physical properties of an object from an object, through the eye,
Lab is modified from Meehan (1998) and a Science Kit lab 66688 50. Vision is the act of seeing; vision involves the transmission of the physical properties of an object from an object, through the eye,
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
sclera pupil What happens to light that enters the eye?
 Human Vision Textbook pages 202 215 Before You Read Some people can see things clearly from a great distance. Other people can see things clearly only when they are nearby. Why might this be? Write your
Human Vision Textbook pages 202 215 Before You Read Some people can see things clearly from a great distance. Other people can see things clearly only when they are nearby. Why might this be? Write your
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision
 The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors and neurons. Muscles
The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors and neurons. Muscles
Biology 70 Slides for Lecture 1 Fall 2007
 Biology 70 Part II Sensory Systems www.biology.ucsc.edu 1 2 intensity vs spatial position (image formation) color 3 4 motion depth (monocular) 5 6 1 depth (binocular) 1. In the lectures on perception we
Biology 70 Part II Sensory Systems www.biology.ucsc.edu 1 2 intensity vs spatial position (image formation) color 3 4 motion depth (monocular) 5 6 1 depth (binocular) 1. In the lectures on perception we
Lenses. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
LESSON 5 - THE OPTICS OF THE EYE
 LESSON 5 - THE OPTICS OF THE EYE Overview: By dissecting a mammalian eye, students will learn how the lens in the eye focuses light to form an image of an object. They will also learn the main parts of
LESSON 5 - THE OPTICS OF THE EYE Overview: By dissecting a mammalian eye, students will learn how the lens in the eye focuses light to form an image of an object. They will also learn the main parts of
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World
 Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Soft Computing. Prof. Dr.-Ing. Adolfo Bauchspiess Universidade de Brasília - Brazil
 Soft Computing Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems Prof. Dr.-Ing. Adolfo Bauchspiess Universidade de Brasília - Brazil Summary 1 - Introduction Connectionist Intelligent Systems 2 - Artificial Neural Networks
Soft Computing Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems Prof. Dr.-Ing. Adolfo Bauchspiess Universidade de Brasília - Brazil Summary 1 - Introduction Connectionist Intelligent Systems 2 - Artificial Neural Networks
Photography (cont d)
 Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Chapter 20 Human Vision
 Chapter 20 GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Characterize the physical parameters that are significant in human vision. Visual
Chapter 20 GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Characterize the physical parameters that are significant in human vision. Visual
THE EYE. People of Asian descent have an EPICANTHIC FOLD in the upper eyelid; no functional difference.
 THE EYE The eye is in the orbit of the skull for protection. Within the orbit are 6 extrinsic eye muscles, which move the eye. There are 4 cranial nerves: Optic (II), Occulomotor (III), Trochlear (IV),
THE EYE The eye is in the orbit of the skull for protection. Within the orbit are 6 extrinsic eye muscles, which move the eye. There are 4 cranial nerves: Optic (II), Occulomotor (III), Trochlear (IV),
Handout G: The Eye and How We See
 Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
Human Eye Model OS-8477A
 Instruction Manual 02-3032A Human Eye Model OS-8477A 800-772-8700 www.pasco.com Table of Contents Contents Quick Start............................................................ Introduction...........................................................
Instruction Manual 02-3032A Human Eye Model OS-8477A 800-772-8700 www.pasco.com Table of Contents Contents Quick Start............................................................ Introduction...........................................................
Cow Eye Dissection. Online dissection, for kids abstaining:
 Cow Eye Dissection Introductory Discussion: Tell the students that we will be learning about what eyes are made of and how they work by dissecting a cow eye. Talk about where the eye comes from, and how
Cow Eye Dissection Introductory Discussion: Tell the students that we will be learning about what eyes are made of and how they work by dissecting a cow eye. Talk about where the eye comes from, and how
ABO Certification Training. Part I: Anatomy and Physiology
 ABO Certification Training Part I: Anatomy and Physiology Major Ocular Structures Centralis Nerve Major Ocular Structures The Cornea Cornea Layers Epithelium Highly regenerative: Cells reproduce so rapidly
ABO Certification Training Part I: Anatomy and Physiology Major Ocular Structures Centralis Nerve Major Ocular Structures The Cornea Cornea Layers Epithelium Highly regenerative: Cells reproduce so rapidly
What determines data speed?
 PHY385-H1F Introductory Optics Class 12 Outline: Section 5.7, Sub-sections 5.7.1 5.7.6 Fibre-Optics The Human Eye Corrective Lenses Pinhole Camera Camera Depth of Field What determines data speed? Broadband
PHY385-H1F Introductory Optics Class 12 Outline: Section 5.7, Sub-sections 5.7.1 5.7.6 Fibre-Optics The Human Eye Corrective Lenses Pinhole Camera Camera Depth of Field What determines data speed? Broadband
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein
 Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Choices and Vision. Jeffrey Koziol M.D. Thursday, December 6, 12
 Choices and Vision Jeffrey Koziol M.D. How does the eye work? What is myopia? What is hyperopia? What is astigmatism? What is presbyopia? How the eye works How the Eye Works 3 How the eye works Light rays
Choices and Vision Jeffrey Koziol M.D. How does the eye work? What is myopia? What is hyperopia? What is astigmatism? What is presbyopia? How the eye works How the Eye Works 3 How the eye works Light rays
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sheep Eye Dissection
 Sheep Eye Dissection Question: How do the various parts of the eye function together to make an image appear on the retina? Materials and Equipment: Preserved sheep eye Scissors Dissection tray Tweezers
Sheep Eye Dissection Question: How do the various parts of the eye function together to make an image appear on the retina? Materials and Equipment: Preserved sheep eye Scissors Dissection tray Tweezers
Chapter 25: Applied Optics. PHY2054: Chapter 25
 Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Introduction. Strand F Unit 3: Optics. Learning Objectives. Introduction. At the end of this unit you should be able to;
 Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
Material after quiz and still on everyone s Unit 11 test.
 Material after quiz and still on everyone s Unit 11 test. When light travels from a fast material like air into a slow material like glass, Snell s Law always works. Material from here on out though is
Material after quiz and still on everyone s Unit 11 test. When light travels from a fast material like air into a slow material like glass, Snell s Law always works. Material from here on out though is
Chapter 6: Perception
 Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Choices and Vision. Jeffrey Koziol M.D. Friday, December 7, 12
 Choices and Vision Jeffrey Koziol M.D. How does the eye work? What is myopia? What is hyperopia? What is astigmatism? What is presbyopia? How the eye works Light rays enter the eye through the clear cornea,
Choices and Vision Jeffrey Koziol M.D. How does the eye work? What is myopia? What is hyperopia? What is astigmatism? What is presbyopia? How the eye works Light rays enter the eye through the clear cornea,
ensory System III Eye Reflexes
 ensory System III Eye Reflexes Quick Review from Last Week Eye Anatomy Inside of the Eye choroid Eye Reflexes Eye Reflexes A healthy person has a number of eye reflexes: Pupillary light reflex Vestibulo-ocular
ensory System III Eye Reflexes Quick Review from Last Week Eye Anatomy Inside of the Eye choroid Eye Reflexes Eye Reflexes A healthy person has a number of eye reflexes: Pupillary light reflex Vestibulo-ocular
Grade 8. Light and Optics. Unit exam
 Grade 8 Light and Optics Unit exam Unit C - Light and Optics 1. Over the years many scientists have contributed to our understanding of light. All the properties listed below about light are correct except:
Grade 8 Light and Optics Unit exam Unit C - Light and Optics 1. Over the years many scientists have contributed to our understanding of light. All the properties listed below about light are correct except:
11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, Wednesday, 8 January, 14
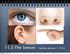 11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, 2014. TEST ON ALL OF HOMEOSTASIS (FOCUS ON REPRODUCTIVE AND NERVOUS SYSTEM) ON FRIDAY. Structure of the Eye Eye Anatomy and Function http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=0hzwmldldhi&feature=related
11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, 2014. TEST ON ALL OF HOMEOSTASIS (FOCUS ON REPRODUCTIVE AND NERVOUS SYSTEM) ON FRIDAY. Structure of the Eye Eye Anatomy and Function http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=0hzwmldldhi&feature=related
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Physics 2.2A for Achievement Standard 91169 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard 91169 Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Physics 2.2A for Achievement Standard 91169 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard 91169 Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2)
 Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2) Brief review Optical instruments Camera Human eye Magnifying glass Telescope Microscope Optical Aberrations Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 31, Pg 1 The Lens Equation
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2) Brief review Optical instruments Camera Human eye Magnifying glass Telescope Microscope Optical Aberrations Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 31, Pg 1 The Lens Equation
HUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Notes Physics - Grade 10
 HUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Notes Physics - Grade 10 Human Eye Eye is one of the most sensitive sense organs in the human body. Our eye enables us to see this beautiful world. It consists of a lens,
HUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Notes Physics - Grade 10 Human Eye Eye is one of the most sensitive sense organs in the human body. Our eye enables us to see this beautiful world. It consists of a lens,
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Optics: Lenses & Mirrors
 Warm-Up 1. A light ray is passing through water (n=1.33) towards the boundary with a transparent solid at an angle of 56.4. The light refracts into the solid at an angle of refraction of 42.1. Determine
Warm-Up 1. A light ray is passing through water (n=1.33) towards the boundary with a transparent solid at an angle of 56.4. The light refracts into the solid at an angle of refraction of 42.1. Determine
30 Lenses. Lenses change the paths of light.
 Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
The Eye and Vision. Activities: Linda Shore, Ed.D. Exploratorium Teacher Institute Exploratorium, all rights reserved
 The Eye and Vision By Linda S. Shore, Ed.D. Director,, San Francisco, California, United States lindas@exploratorium.edu Activities: Film Can Eyeglasses a pinhole can help you see better Vessels using
The Eye and Vision By Linda S. Shore, Ed.D. Director,, San Francisco, California, United States lindas@exploratorium.edu Activities: Film Can Eyeglasses a pinhole can help you see better Vessels using
Holy Cross High School. Medical Physics Homework
 Holy Cross High School Medical Physics Homework Homework 1: Refraction 1. A pupil shone light through a rectangular block as shown 75 222 15 40 50 a) The light changes direction as it passes from air to
Holy Cross High School Medical Physics Homework Homework 1: Refraction 1. A pupil shone light through a rectangular block as shown 75 222 15 40 50 a) The light changes direction as it passes from air to
Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms
 CHAPTER 16 14 SECTION Sound and Light Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens to light when it passes from one medium to another? How
CHAPTER 16 14 SECTION Sound and Light Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens to light when it passes from one medium to another? How
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Methods of Learning Learning The acquisition of new knowledge and skills. There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Methods of Learning Learning The acquisition of new knowledge and skills. There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different
Eye. Eye Major structural layer of the wall of the eye is a thick layer of dense C.T.; that layer has two parts:
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein
 By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Light is a form of radiant energy, consisting of electromagnetic waves a. Velocity of light: In air it is 300,000 km/second. b. Wave length: The wave-length of visible light to
By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Light is a form of radiant energy, consisting of electromagnetic waves a. Velocity of light: In air it is 300,000 km/second. b. Wave length: The wave-length of visible light to
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
In the following diagram the parts of the eye are visualized and labeled for you.
 Investigation 3.12B: The Eye In the preceding case study marker of the problem of greatest concern to you lay in finding the pupils fixed in a dilated position. But what is the pupil and what makes it
Investigation 3.12B: The Eye In the preceding case study marker of the problem of greatest concern to you lay in finding the pupils fixed in a dilated position. But what is the pupil and what makes it
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Vision. By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd
 Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
HSC Biology. Published Feb 9, 2017 HSC BIOLOGY OPTION: COMMUNICATION. By Sahar (99.1 ATAR)
 HSC Biology Year 2014 Mark 92.00 Pages 11 Published Feb 9, 2017 HSC BIOLOGY OPTION: COMMUNICATION By Sahar (99.1 ATAR) Your notes author, Sahar. Sahar achieved an ATAR of 99.1 in 2014 while attending Carlingford
HSC Biology Year 2014 Mark 92.00 Pages 11 Published Feb 9, 2017 HSC BIOLOGY OPTION: COMMUNICATION By Sahar (99.1 ATAR) Your notes author, Sahar. Sahar achieved an ATAR of 99.1 in 2014 while attending Carlingford
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
The Eye. Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division
 The Eye Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division Coats of the Eyeball 1- OUTER FIBROUS COAT is made up of : Posterior opaque part 2-THE SCLERA the dense white part 1- THE CORNEA the anterior
The Eye Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division Coats of the Eyeball 1- OUTER FIBROUS COAT is made up of : Posterior opaque part 2-THE SCLERA the dense white part 1- THE CORNEA the anterior
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
 CHAPTER 11 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical
CHAPTER 11 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical
High Touch High Tech
 Vision and Perception Games Supplies: Print out of Muller-Lyer Illusion handout Print out of Vision Perception handout Color print out of Afterimage handout Color print out of Movement Illusion handout
Vision and Perception Games Supplies: Print out of Muller-Lyer Illusion handout Print out of Vision Perception handout Color print out of Afterimage handout Color print out of Movement Illusion handout
The Human Eye Looking at your own eye with an Eye Scope
 The Human Eye Looking at your own eye with an Eye Scope Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors
The Human Eye Looking at your own eye with an Eye Scope Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Optics of the Human Eye
 Optics of the Human Eye References: Equipment: Ford, Kenneth W., Classical and Modern Physics Vol2 Xerox College Publishing 1972 pp. 900-922. Pasco Human Eye Model Instruction Manual (OS-8477) pp. 1-34.
Optics of the Human Eye References: Equipment: Ford, Kenneth W., Classical and Modern Physics Vol2 Xerox College Publishing 1972 pp. 900-922. Pasco Human Eye Model Instruction Manual (OS-8477) pp. 1-34.
The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World
 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena
The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
Eyeball Model Lab Date Block
 Science 8 Name Eyeball Model Lab Date Block Problem: Identify the twelve key parts of the eye and describe their function. Materials: dissecting scissors ping pong ball transparent plastic ordinary scissors
Science 8 Name Eyeball Model Lab Date Block Problem: Identify the twelve key parts of the eye and describe their function. Materials: dissecting scissors ping pong ball transparent plastic ordinary scissors
Multifocal and Accommodative
 What is an IOL? An intraocular lens (or IOL) is a tiny, artificial lens for the eye. It replaces the eye's natural lens. Retina Cornea Lens Macula The eye's normally clear lens bends (refracts) light rays
What is an IOL? An intraocular lens (or IOL) is a tiny, artificial lens for the eye. It replaces the eye's natural lens. Retina Cornea Lens Macula The eye's normally clear lens bends (refracts) light rays
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
The Future of the Web (Tuesday 30th October 2018) #ASSC2018
 The Future of the Web (Tuesday 30th October 2018) #ASSC2018 Stephen Whitelaw 30+ years experience with internet/web technologies. www.linkedin.com/in/stephenwhitelaw @toowist "I think there is a world
The Future of the Web (Tuesday 30th October 2018) #ASSC2018 Stephen Whitelaw 30+ years experience with internet/web technologies. www.linkedin.com/in/stephenwhitelaw @toowist "I think there is a world
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
