Peripheral Color Demo
|
|
|
- Erik Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short and Sweet Peripheral Color Demo Christopher W Tyler Division of Optometry and Vision Science, City University, London, UK Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute, San Francisco, Ca, USA i-perception 2015, 6(6) 1 5! The Author(s) 2015 DOI: / ipe.sagepub.com Abstract A set of structured demonstrations of the vividness of peripheral color vision is provided by arrays of multicolored disks scaled with eccentricity. These demonstrations are designed to correct the widespread misconception that peripheral color vision is weak or nonexistent. Keywords Periphery, color vision, eccentricity, cone distribution, fovea There is a widespread misconception even among vision scientists, and hence the population in general, that the high cone density in the fovea implies that color vision is restricted to the central vision, and conversely that the high density of rods in the periphery implies a lack of color vision in the periphery. For example, the Wikipedia article on peripheral vision says Peripheral vision is weak in humans, especially at distinguishing colour and shape...rod cells are unable to distinguish colour and are predominant at the periphery, while cone cells are concentrated mostly in the centre of the retina, the fovea. ( Peripheral_vision) In fact, however, both historical (Østerberg, 1935) and more recent (Curcio, Sloan, Packer, Hendrickson, Kalina, 1987; Song, Chui, Zhong, Elsner, & Burns, 2011) measurements of photoreceptor densities indicate otherwise. Despite the high concentration of cones in the fovea, even the central 5 of the retina contains only about 50,000 cones (1% of the total), while the remainder of the total population of about 5 million cones is distributed throughout the peripheral retina with an average density of about 5,000 cones/mm 2 (beyond about 10 eccentricity). Since the cone inner segments act as their light-catching apertures, and since their diameter is about 10 mm in peripheral retina (Jonas, Schneider & Naumann, 1992), this density implies that the light-catching area of the cones is about 0.3 mm 2 per mm 2 of peripheral retina, while the rod light-catching area accounts for most of the rest. Thus, about one third of the peripheral retina should be considered to support color vision (Williams, 1991). The mapping from retina to cortex can be approximated as a linear scaling from the fovea to the periphery, particularly for the cortical mappings of V2 and V3 (Schira, Tyler, Corresponding author: Christopher W Tyler, City University London, Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK. cwtyler2020@gmail.com Creative Commons CC-BY: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License ( which permits any use, reproduction and distribution of the work without further permission provided the original work is attributed as specified on the SAGE and Open Access pages ( sagepub.com/aboutus/openaccess.htm).
2 2 i-perception 6(6) Figure 1. Foveal color vividness demo designed to be viewed at two viewing distances. At a viewing distance of 12 the circular array width it spans the 5 fovea where the variegated color disks show the vividness of foveal color perception. At 60 the circular array width, it spans the 1 foveola, illustrating fineresolution color processing. Breakspear, & Spehar, 2009). To project from the retina to equal regions of early visual cortex, therefore, the stimuli should be scaled in proportion to eccentricity, and studies of peripheral color processing should use such scaling in order to assess the cortical capabilities of color processing. Indeed, with suitable areal scaling, color discrimination can be equated at all eccentricities This is not the place for an extensive review, but it should be noted that many studies of peripheral processing have used constant stimulus size and report progressive declines in hue discrimination (Nagy & Wolf, 1993; McKeefry, Murray & Parry, 2007; Mullen, 1991), chromatic saturation (Stabell & Stabell, 1982; Abramov, Gordon & Chan, 1992, McKeefry, Murray & Parry, 2007; Volbrecht & Nerger, 2012), and conspicuity (Gunther, 2014). Those studies using appropriate size scaling of the stimuli generally find approximate invariance of the processing properties as a function of eccentricity (Noorlander, Koenderink, den Ouden, & Edens, 1983; Rovamo & Iivanainen, 1991; Abramov, Gordon & Chan, 1991, 1992; Sakurai &
3 Tyler 3 Figure 2. Peripheral color vividness demo designed for two viewing distances when fixating steadily at the centre. At 12 the central gray disk width, it spans the periphery from 2.5 to 20. At the close-up distance of 3 the central gray disk width, it spans from about 10 to 50 eccentricity, illustrating the vividness of peripheral color processing. The central gray bar contains elements that are unscaled for eccentricity, to illustrate the perceptual fall off in peripheral color perception. Mullen, 2006). Where significant effects are reported, one may question the precise choice of scaling factor. Tyler (1987a), for example, proposed that the appropriate scaling factor should be based on stimulating the same number of cones at each eccentricity, whereas most scaling studies attempt to equate the number of ganglion cells stimulated or the cortical magnification factor per se (although some such studies do not apply this logic to the central foveal stimuli). These properties are indicated by the following demonstration images, which should be viewed at a distance so as to make the width of the central disk measure about one twelfth of the viewing distance (e.g., 1 inch diameter at a 12 inch viewing distance). This ratio corresponds to about the most liberal definition of the foveal region (5 diameter). Figure 1 shows an array of multicolored balloons within this foveal region scaled to stimulate about 1 cm 2 of visual cortex at each eccentricity. In Figure 2, the same form of array is scaled up to project to the periphery beyond the foveal limit (2.5 eccentricity) into the periphery. If periphery color vision had weaker color vision, the colors when viewing Figure 2 should appear desaturated relative to those in Figure 1, but inspection verifies that they do not. (To reach the farther periphery, the viewing distance should be reduced to 5 inches with the 1 inch central disk region, when the outer rim will reach out to 45 eccentricity with central fixation.) Figure 2 also includes an overlay of a horizontal line of
4 4 i-perception 6(6) Figure 3. Peripheral variegated color disks at 5 reduced scale show that peripheral color remains as vivid even close to the spatial summation limit. unscaled disks typical of unscaled studies of peripheral color vision, to allow comparison of its degradation with eccentricity under these conditions. Given that the natural units of cortical processing characterized by the concept of the hypercolumn are of the order of 2 mm wide in human visual cortex, the disks in Figures 1 and 2 should each stimulate about 25 such units. To check whether color processing is similarly uniform at a grain of about 1 hypercolumn, the sizes of each disk are reduced by a factor of five for the peripheral version in Figure 3. It can be seen that color is again visible out to the edge of the image without noticeable desaturation under these reduced stimulation conditions, so integration across multiple hypercolumnar units is not required to support peripheral color processing. If anything, inspection of the figures shows the color perception is more vivid in the periphery, as might be expected from the fact that the cone density decreases at a slower rate than linear reciprocity with eccentricity (Curcio et al., 1987). In fact, the cone density scales with approximately the 2/3 power of eccentricity out to 20 (Tyler, 1987b). Thus, the linear scaling of the disk sizes should result in the stimulation of about five times [(10 2/3 / 10 1 ) 2 ] more cones by 20 than 2 in areal terms, giving scope for cortical processing to account for the extra vividness that is perceptually observed.
5 Tyler 5 Declaration of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Funding The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Supported by CDRMP grant MR References Abramov, I., Gordon, J., & Chan, H. (1991). Color appearance in the peripheral retina: Effects of stimulus size. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 8, Abramov, I., Gordon, J., & Chan, H. (1992). Color appearance in the peripheral retina: Effects of a white surround. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 9, Curcio, C. A., Sloan, K. R. Jr., Packer, O., Hendrickson, A. E., & Kalina, R. E. (1987). Distribution of cones in human and monkey retina: Individual variability and radial asymmetry. Science, 236, Gunther, K. L. (2014). Non-cardinal color perception across the retina: Easy for orange, hard for burgundy and sky blue. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 31, Jonas, J. B., Schneider, U., & Naumann, G. O. (1992). Count and density of human retinal photoreceptors. Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 230, McKeefry, D. J., Murray, I. J., & Parry, N. R. (2007). Perceived shifts in saturation and hue of chromatic stimuli in the near peripheral retina. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 24, Mullen, K. T. (1991). Color vision as a post receptoral specialization of the central visual field. Vision Research, 31, Nagy, A. L., & Wolf, S. (1993). Red-green color discrimination in peripheral vision. Vision Research, 33, Noorlander, C., Koenderink, J. J., den Ouden, R. J., & Edens, B. W. (1983). Sensitivity to spatiotemporal colour contrast in the peripheral visual field. Vision Research, 23, Østerberg, G. A. (1935). Topography of the layer of rods and cones in the human retina. Acta Ophthalmolica, 13(Suppl. 6): Rovamo, J., & Iivanainen, A. (1991). Detection of chromatic deviations from white across the human visual field. Vision Research, 31, Schira, M. M., Tyler, C. W., Breakspear, M., & Spehar, B. (2009). The foveal confluence in human visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, Song, H., Chui, T. Y., Zhong, Z., Elsner, A. E., & Burns, S. A. (2011). Variation of cone photoreceptor packing density with retinal eccentricity and age. Investigative Ophthalmology and Vision Science, 52, Tyler, C. W. (1987a). Analysis of visual modulation sensitivity III. Meridional variations in peripheral flicker sensitivity. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 4, Tyler, C. W. (1987b). Analysis of human receptor density. In V. Lakshminarayanan (ed.), Basic and clinical applications of vision science (Vol. 60, pp ). Documenta Ophthalmologica Proceedings. Heidelberg: Springer. Volbrecht, V. J., & Nerger, J. L. (2012). Color appearance at 10 along the vertical and horizontal meridians. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 29, Williams, R. W. (1991). The human retina has a cone-enriched rim. Visual Neuroscience, 6, Author Biography Dr. Christopher W. Tyler has over 40 years of experience of research in visual and cognitive neuroscience.
Peripheral Color Vision and Motion Processing
 Peripheral Color Vision and Motion Processing Christopher W. Tyler Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute, San Francisco Abstract A demonstration of the vividness of peripheral color vision is provided
Peripheral Color Vision and Motion Processing Christopher W. Tyler Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute, San Francisco Abstract A demonstration of the vividness of peripheral color vision is provided
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones.
 Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Visual Perception. human perception display devices. CS Visual Perception
 Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception. Jeff Avery
 Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
CS 544 Human Abilities
 CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
Optical, receptoral, and retinal constraints on foveal and peripheral vision in the human neonate
 Vision Research 38 (1998) 3857 3870 Optical, receptoral, and retinal constraints on foveal and peripheral vision in the human neonate T. Rowan Candy a, *, James A. Crowell b, Martin S. Banks a a School
Vision Research 38 (1998) 3857 3870 Optical, receptoral, and retinal constraints on foveal and peripheral vision in the human neonate T. Rowan Candy a, *, James A. Crowell b, Martin S. Banks a a School
The human visual system
 The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling
 Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision.
 LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
Visibility, Performance and Perception. Cooper Lighting
 Visibility, Performance and Perception Kenneth Siderius BSc, MIES, LC, LG Cooper Lighting 1 Vision It has been found that the ability to recognize detail varies with respect to four physical factors: 1.Contrast
Visibility, Performance and Perception Kenneth Siderius BSc, MIES, LC, LG Cooper Lighting 1 Vision It has been found that the ability to recognize detail varies with respect to four physical factors: 1.Contrast
THE SPATIAL RESOLUTION CAPACITY OF HUMAN FOVEAL RETINA
 Vision Res. Vol. 29, No. 9, pp. 1095-I 101, 1989 Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved txw2-6989/89 $3.00 + 0.00 Copyright 0 1989 Maxwell Pergamon Macmillan plc THE SPATIAL RESOLUTION CAPACITY
Vision Res. Vol. 29, No. 9, pp. 1095-I 101, 1989 Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved txw2-6989/89 $3.00 + 0.00 Copyright 0 1989 Maxwell Pergamon Macmillan plc THE SPATIAL RESOLUTION CAPACITY
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Häkkinen, Jukka; Gröhn, Lauri Turning water into rock
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Häkkinen, Jukka; Gröhn, Lauri Turning
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Häkkinen, Jukka; Gröhn, Lauri Turning
The Photoreceptor Mosaic
 The Photoreceptor Mosaic Aristophanis Pallikaris IVO, University of Crete Institute of Vision and Optics 10th Aegean Summer School Overview Brief Anatomy Photoreceptors Categorization Visual Function Photoreceptor
The Photoreceptor Mosaic Aristophanis Pallikaris IVO, University of Crete Institute of Vision and Optics 10th Aegean Summer School Overview Brief Anatomy Photoreceptors Categorization Visual Function Photoreceptor
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Image and video processing (EBU723U) Colour Images. Dr. Yi-Zhe Song
 Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Multifocal Electroretinograms in Normal Subjects
 Multifocal Electroretinograms in Normal Subjects Akiko Nagatomo, Nobuhisa Nao-i, Futoshi Maruiwa, Mikki Arai and Atsushi Sawada Department of Ophthalmology, Miyazaki Medical College, Miyazaki, Japan Abstract:
Multifocal Electroretinograms in Normal Subjects Akiko Nagatomo, Nobuhisa Nao-i, Futoshi Maruiwa, Mikki Arai and Atsushi Sawada Department of Ophthalmology, Miyazaki Medical College, Miyazaki, Japan Abstract:
Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1
 Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1 Eye Dominance Often called eye dominance, eyedness, or seeing through the eye, is the tendency to prefer visual input a particular eye. It is similar to the laterality
Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1 Eye Dominance Often called eye dominance, eyedness, or seeing through the eye, is the tendency to prefer visual input a particular eye. It is similar to the laterality
Packing Geometry of Human Cone Photoreceptors: variations with eccentricity and evidence for local anisotropy. K.R. Sloan and C.A.
 Packing Geometry of Human Cone Photoreceptors: variations with eccentricity and evidence for local anisotropy K.R. loan and C.A. Curcio University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL, UA ABTRACT Disorder
Packing Geometry of Human Cone Photoreceptors: variations with eccentricity and evidence for local anisotropy K.R. loan and C.A. Curcio University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL, UA ABTRACT Disorder
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
USE OF COLOR IN REMOTE SENSING
 1 USE OF COLOR IN REMOTE SENSING (David Sandwell, Copyright, 2004) Display of large data sets - Most remote sensing systems create arrays of numbers representing an area on the surface of the Earth. The
1 USE OF COLOR IN REMOTE SENSING (David Sandwell, Copyright, 2004) Display of large data sets - Most remote sensing systems create arrays of numbers representing an area on the surface of the Earth. The
Effects of light and dark adaptation of rods on specific-hue threshold
 Vision Research 43 (2003) 2905 2914 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Effects of light and dark adaptation of rods on specific-hue threshold Ulf Stabell *, Bjørn Stabell Department of Psychology, University
Vision Research 43 (2003) 2905 2914 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Effects of light and dark adaptation of rods on specific-hue threshold Ulf Stabell *, Bjørn Stabell Department of Psychology, University
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016
 Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Bettina Selig. Centre for Image Analysis. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University
 2011-10-26 Bettina Selig Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Illumination - Reflection - Detection The Human Eye Digital
2011-10-26 Bettina Selig Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Illumination - Reflection - Detection The Human Eye Digital
Reflectance curves of some common foods. Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/4/11
 Colour Vision I: The re0nal basis of colour vision and the inherited colour vision deficiencies Prof. Kathy T. ullen What is colour? What physical aspect of the world does our sense of colour inform us
Colour Vision I: The re0nal basis of colour vision and the inherited colour vision deficiencies Prof. Kathy T. ullen What is colour? What physical aspect of the world does our sense of colour inform us
Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions
 Short Report Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions Perception 2016, Vol. 45(3) 328 336! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions:
Short Report Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions Perception 2016, Vol. 45(3) 328 336! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions:
Question From Last Class
 Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Human Visual System. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
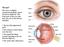 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
What is Color. Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception.
 Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington Visual sensory physiology.
 This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
TSBB15 Computer Vision
 TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Retina. last updated: 23 rd Jan, c Michael Langer
 Retina We didn t quite finish up the discussion of photoreceptors last lecture, so let s do that now. Let s consider why we see better in the direction in which we are looking than we do in the periphery.
Retina We didn t quite finish up the discussion of photoreceptors last lecture, so let s do that now. Let s consider why we see better in the direction in which we are looking than we do in the periphery.
The best retinal location"
 How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
Color Outline. Color appearance. Color opponency. Brightness or value. Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Color appearance
 Color Outline Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Three cone types with different spectral sensitivities. Each cone outputs only a single number that depends on how many photons were absorbed. If two physically
Color Outline Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Three cone types with different spectral sensitivities. Each cone outputs only a single number that depends on how many photons were absorbed. If two physically
Frequencies and Color
 Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
PERCEPTUAL INSIGHTS INTO FOVEATED VIRTUAL REALITY. Anjul Patney Senior Research Scientist
 PERCEPTUAL INSIGHTS INTO FOVEATED VIRTUAL REALITY Anjul Patney Senior Research Scientist INTRODUCTION Virtual reality is an exciting challenging workload for computer graphics Most VR pixels are peripheral
PERCEPTUAL INSIGHTS INTO FOVEATED VIRTUAL REALITY Anjul Patney Senior Research Scientist INTRODUCTION Virtual reality is an exciting challenging workload for computer graphics Most VR pixels are peripheral
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Mahdi Amiri. March Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September ) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this
 Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Image Processing. Michael Kazhdan ( /657) HB Ch FvDFH Ch. 13.1
 Image Processing Michael Kazhdan (600.457/657) HB Ch. 14.4 FvDFH Ch. 13.1 Outline Human Vision Image Representation Reducing Color Quantization Artifacts Basic Image Processing Human Vision Model of Human
Image Processing Michael Kazhdan (600.457/657) HB Ch. 14.4 FvDFH Ch. 13.1 Outline Human Vision Image Representation Reducing Color Quantization Artifacts Basic Image Processing Human Vision Model of Human
Decoding Natural Signals from the Peripheral Retina
 Decoding Natural Signals from the Peripheral Retina Brian C. McCann, Mary M. Hayhoe & Wilson S. Geisler Center for Perceptual Systems and Department of Psychology University of Texas at Austin, Austin
Decoding Natural Signals from the Peripheral Retina Brian C. McCann, Mary M. Hayhoe & Wilson S. Geisler Center for Perceptual Systems and Department of Psychology University of Texas at Austin, Austin
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ. Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. Topics
 Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital image processing is based on. Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis
 Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals Digital image processing is based on Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis 2.1 Visual Perception How images are formed in the eye? Eye
Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals Digital image processing is based on Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis 2.1 Visual Perception How images are formed in the eye? Eye
Optical Perspective of Polycarbonate Material
 Optical Perspective of Polycarbonate Material JP Wei, Ph. D. November 2011 Introduction Among the materials developed for eyeglasses, polycarbonate is one that has a number of very unique properties and
Optical Perspective of Polycarbonate Material JP Wei, Ph. D. November 2011 Introduction Among the materials developed for eyeglasses, polycarbonate is one that has a number of very unique properties and
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
CSE1710. Big Picture. Reminder
 CSE1710 Click to edit Master Week text 10, styles Lecture 19 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2013 Thursday, Nov 14, 2013 1 Big Picture For the next three class meetings, we will
CSE1710 Click to edit Master Week text 10, styles Lecture 19 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2013 Thursday, Nov 14, 2013 1 Big Picture For the next three class meetings, we will
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Does Colour Filling-In Account for Colour Perception in Natural Images?
 Special Issue: Seeing Colors Does Colour Filling-In Account for Colour Perception in Natural Images? i-perception 2018 Vol. 9(3), 1 10! The Author(s) 2018 DOI: 10.1177/2041669518768829 journals.sagepub.com/home/ipe
Special Issue: Seeing Colors Does Colour Filling-In Account for Colour Perception in Natural Images? i-perception 2018 Vol. 9(3), 1 10! The Author(s) 2018 DOI: 10.1177/2041669518768829 journals.sagepub.com/home/ipe
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
Human Vision, Color and Basic Image Processing
 Human Vision, Color and Basic Image Processing Connelly Barnes CS4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and
Human Vision, Color and Basic Image Processing Connelly Barnes CS4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and
CS 548: Computer Vision REVIEW: Digital Image Basics. Spring 2016 Dr. Michael J. Reale
 CS 548: Computer Vision REVIEW: Digital Image Basics Spring 2016 Dr. Michael J. Reale Human Vision System: Cones and Rods Two types of receptors in eye: Cones Brightness and color Photopic vision = bright-light
CS 548: Computer Vision REVIEW: Digital Image Basics Spring 2016 Dr. Michael J. Reale Human Vision System: Cones and Rods Two types of receptors in eye: Cones Brightness and color Photopic vision = bright-light
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
COLOR. and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
Eye. Eye Major structural layer of the wall of the eye is a thick layer of dense C.T.; that layer has two parts:
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION.
 TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION Vaughan W. Inman 1 & Brian H. Philips 2 1 SAIC, McLean, Virginia, USA 2 Federal Highway Administration, McLean, Virginia, USA Email: vaughan.inman.ctr@dot.gov
TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION Vaughan W. Inman 1 & Brian H. Philips 2 1 SAIC, McLean, Virginia, USA 2 Federal Highway Administration, McLean, Virginia, USA Email: vaughan.inman.ctr@dot.gov
Visual Requirements for High-Fidelity Display 1
 Michael J Flynn, PhD Visual Requirements for High-Fidelity Display 1 The digital radiographic process involves (a) the attenuation of x rays along rays forming an orthographic projection, (b) the detection
Michael J Flynn, PhD Visual Requirements for High-Fidelity Display 1 The digital radiographic process involves (a) the attenuation of x rays along rays forming an orthographic projection, (b) the detection
Large Scale Imaging of the Retina. 1. The Retina a Biological Pixel Detector 2. Probing the Retina
 Large Scale Imaging of the Retina 1. The Retina a Biological Pixel Detector 2. Probing the Retina understand the language used by the eye to send information about the visual world to the brain use techniques
Large Scale Imaging of the Retina 1. The Retina a Biological Pixel Detector 2. Probing the Retina understand the language used by the eye to send information about the visual world to the brain use techniques
Visual Perception. Overview. The Eye. Information Processing by Human Observer
 Visual Perception Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Class Introduction to DIP/DVP applications and examples Image as a function Concepts
Visual Perception Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Class Introduction to DIP/DVP applications and examples Image as a function Concepts
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
