(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
|
|
|
- Iris Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI. PANEL AND EMBEDDED CAPACTIVE CPC... G06F 3/0412 ( ); G06F 3/0414 TOUCH DISPLAY DEVICE ( ); G06F 3/044 ( ); G02F 1/ ( ); G02F I/ (71) Applicants: SHANGHAI TIANMA ( ); G02F 1/13439 ( ); G02F MICRO-ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD., I/13338 ( ); G06F 2203/04 III Shanghai (CN); TIANMA ( ); G06F 2203/ ( ); G02F MICRO-ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD., 220.1/52 ( ); G02F 220.1/121 ( ); Shenzhen (CN) G02F 1/1368 ( ) (72) Inventors: Xingyao Zhou, Shanghai (CN); Qijun (57) ABSTRACT Yao, Shanghai (CN); Hao Chen, The application disclose an embedded capacitive touch Shanghai (CN); Jun Ma, Shanghai display panel and an embedded capacitive touch display (CN); Liang Liu, Shanghai (CN) device, including: a first transparent Substrate and a second Substrate arranged opposite to each other, a grid-shaped (73) Assignee: SHANGHAI TIANMA metal conductive layer formed on the first transparent sub MICRO-ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD., strate, and a number of force touch detection electrodes Shanghai (CN) independent of each other formed on the second substrate, wherein the embedded capacitive touch display panel further (21) Appl. No.: 15/231,426 includes a color filter layer including at least red color resists, green color resists, and blue color resists, wherein the (22) Filed: Aug. 8, 2016 color resists in the same colors are arranged in respective color resist bars, and the color resist bars including green Related U.S. Application Data color resist resistance strips; and the grid-shaped metal (63) Continuation-in-part of application No. 14/ , conductive layer includes periodically arranged force touch filed on May 21, 2014, now Pat. No. 9,436,327. fixed potential electrodes and floating electrodes, wherein the force touch fixed potential electrodes are separate from (30) Foreign Application Priority Data the floating electrodes with gaps being formed between them, and the gaps include first gap sections which are Jul. 30, 2013 (CN) X parallel to the color resist bars, and which do not overlap with the green color resist resistance strips. Since the green Publication Classification color resists contribute to display brightness far more than the color resists of the other colors, the first gap sections can (51) Int. Cl. be arranged so that they do not overlap with the green color G06F 3/04 ( ) resist resistance strips to thereby alleviate the problem of a GO2F I/333 ( ) visible pattern of the grid-shaped metal conductive layer So GO2F I/335 ( ) as to improve the display performance of the embedded G06F 3/044 ( ) capacitive touch display panel without degrading a touch GO2F I/343 ( ) effect
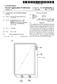
2 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 1 of 15 US 2016/ A1 sis, 8 s : s'ss sixes & x s as is & 8 s. ssists: S S 8 s is sš s's...38:8...s. sists. is sis saxxss: Wii-xx-xxx Fig.2 ---Prior Art
3 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 2 of 15 US 2016/ A1 ---Prior Art Fig.4 ---Prior Art
4 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 3 of 15 US 2016/ A1 Fig.5
5 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 4 of 15 US 2016/ A1 Fig.7
6 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 5 of 15 US 2016/ A1 S S & Š S Fig.8 8 S&
7 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 6 of 15 US 2016/ A1??????????, Fig Fig.10
8 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 7 of 15 US 2016/ A1 112 Fig.11
9 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 8 of 15 US 2016/ A1 C C C C C C C 3O C C C C C C Co X: Fig.15
10 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 9 of 15 US 2016/ A1 O N Nae}}(IN No. ± Fig.17
11 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 10 of 15 US 2016/ A1 Fig.18 v. 432 / a/
12
13 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 12 of 15 US 2016/ A1 Fig.20c 433a
14 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 13 of 15 US 2016/ A1
15 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 14 of 15 US 2016/ A Fig.23
16 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 15 of 15 US 2016/ A1 / 100 Fig.24
17 US 2016/ A1 Nov. 24, 2016 EMBEDDED CAPACTIVE TOUCH DISPLAY PANEL AND EMBEDDED CAPACTIVE TOUCH DISPLAY DEVICE CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application is a continuation-in-part applica tion of the U.S. application Ser. No. 14/ , filed on May 21, 2014, which claims priority to Chinese Application No X, filed Jul. 30, 2013, the contents of all of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety for all purposes. TECHNICAL FIELD 0002 The present application relates to the field of embedded capacitive touch display, and particularly relates to an embedded capacitive touch display panel and an embedded capacitive touch display device including the embedded capacitive touch display panel. BACKGROUND OF THE APPLICATION An embedded touch screen does not need a tradi tional externally-mounted touch screen, is formed by designing an integrated touch electrode structure at a color filter (CF) side, and can realize the need of lightening and thinning of a display panel. Generally, a touch electrode structure is designed to be provided with longitudinal driv ing electrodes and transversal sensing electrodes, wherein the sensing electrodes at both sides of each driving electrode are connected by a crossing bridge. Certainly, the positions and the connection modes of the driving electrodes and the sensing electrodes are not limited, the sensing electrodes can be longitudinal and the driving electrodes can be transversal in an electrode structure design, and the driving electrodes at both sides of each sensing electrode are connected by a metal crossing bridge. In addition, patterns of touch elec trodes can be various, wherein rhombus is the most basic pattern design in the prior art, but different electrode pattern designs can be selected for realizing different functions The specific structure of a liquid crystal display screen of an embedded touch screen in the prior art is as shown in FIG. 1, the liquid crystal display screen mainly includes an upper substrate 12 (namely, color filter (CF) side), a lower substrate 11 (TFT side), and a liquid crystal layer 10 located between the upper substrate 12 and the lower substrate 11, wherein the CF side is integrated with a black matrix 13 (BM), a touch electrode layer 14, a color filter layer 15 (which mainly includes a red color resist (R), a green color resist (G) and a blue color resist (B)), a metal crossing bridge layer 16 (which can also be a transparent oxide crossing bridge) and a over coat layer 17 (OC), respectively. The lower substrate 11 side is mainly integrated with a TFT array structure layer 19 and a transparent pixel electrode (ITO) layer 18 on the TFT array As shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, FIG. 3 is an enlarged view of a dotted line box (part A) in FIG. 2, the metal touch electrode layer 14 includes sensing electrodes 141 and driving electrodes 142 which are mutually insulated and located on the same layer, in order to insulate the sensing electrodes 141 from the driving electrodes 142, the sensing electrodes and the driving electrodes are separated to form gaps 1, so as to achieve the insulating purpose. In addition, the metal touch electrode layer 14 is grid-shaped and shielded by the black matrix 13. Generally, the formed gaps are located on the color filter layer, and randomly located on the red color resist (R), the green color resist (G) or the blue color resist (B). As shown in FIG. 1, when a liquid crystal display works, because a light L emitted by a backlight module is irradiated on the metal touch electrode layer 14, the light L is partly reflected on the channels of TFTs on the TFT array structure layer of the lower substrate 11 by the metal touch electrode layer 14 to cause an electricity leakage phenomenon of the TFTs. However, at the gaps 1, due to the absence of the metal touch electrode layer 14, when the light L of a backlight source is irradiated, a light-reflecting phenomenon is very weak, and the reason for this is that there is no any direct reflecting light in a vertical direction, the reflecting phenomenon of the light at an adjacent position in a slanting direction is only in a very Small angle range, and the Slanting reflected light has no obvious influence on the TFTs which are just opposite to the gaps 1, so that a corresponding TFT off-state current is low. All the TFTs corresponding to the color resists at the gaps 1 are not vertically irradiated by the reflected light, the display effect of the TFTs at the gaps are different from the display effect at non-gap parts, and when the intensity of the backlight source is increased or the TFT off-state current is increased, the patterns of the gaps between the sensing electrodes and the driving electrodes are highlighted on the liquid crystal display screen. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE APPLICATION In view of this, embodiments of the application provide an embedded capacitive touch display panel and an embedded capacitive touch display device. In an aspect, an embodiment of the application provides an embedded capacitive touch display panel including: a first transparent Substrate and a second Substrate arranged opposite to each other, a grid-shaped metal conductive layer formed on the first transparent Substrate, and a number of force touch detection electrodes independent of each other formed on the second substrate, wherein: 0007 the embedded capacitive touch display panel fur ther includes a color filter layer including at least red color resists, green color resists, and blue color resists, wherein the color resists in the same colors are arranged in respective color resist bars, and the color resist bars include green color resist resistance strips; and 0008 the grid-shaped metal conductive layer includes periodically arranged force touch fixed potential electrodes and floating electrodes, wherein the force touch fixed poten tial electrodes are separate from the floating electrodes with gaps being formed between them, and 0009 the gaps include first gap sections which are par allel to the color resist bars, and which do not overlap with the green color resist resistance strips In another aspect, an embodiment of the applica tion further provides an embedded capacitive touch display device including the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS In order to describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application more clearly, the drawings which are needed in the description of the embodi ments will be briefly introduced as follows, obviously, the
18 US 2016/ A1 Nov. 24, 2016 drawings in the following description are only some of the embodiments of the present application, and for those of ordinarily skilled in the art, other drawings can also be obtained in accordance with these drawings without any creative effort FIG. 1 is a structural schematic view of an embed ded touch liquid crystal display Screen in the prior art; 0013 FIG. 2 is a pattern of gaps between sensing elec trodes and driving electrodes of the embedded touch liquid crystal display Screen in the prior art; 0014 FIG. 3 is a partial enlarged view of part A in FIG. 2: 0015 FIG. 4 is a position relationship between the gaps between the sensing electrodes and the driving electrodes, and color resists in the embedded touch liquid crystal display Screen in the prior art; 0016 FIG. 5 is a structural schematic view of an embed ded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; 0017 FIG. 6 is a position relationship between sensing electrodes and driving electrodes in the embedded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; 0018 FIG. 7 is a position relationship between a color filter layer and a grid-shaped metal conductive layer in the embedded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; 0019 FIG. 8 is a pattern of gaps between the sensing electrodes and the driving electrodes in the embedded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; 0020 FIG. 9 is a partial enlarged view of part B in FIG. 8: 0021 FIG. 10 is a position relationship between the gaps and color resists in the embedded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; 0022 FIG. 11 is another position relationship between the gaps and the color resists in the embedded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; 0023 FIG. 12 is still another position relationship between the gaps and the color resists in the embedded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; 0024 FIG. 13 is still another position relationship between the gaps and the color resists in the embedded capacitive touch display panel in an embodiment; FIG. 14 is a structural schematic view of a first transparent Substrate in the embedded capacitive touch dis play panel in an embodiment; 0026 FIG. 15 is a structural schematic view of an embed ded touch screen liquid crystal display in another embodi ment, 0027 FIG. 16 illustrates a schematic structural diagram of an embedded capacitive touch display panel according to an embodiment of the application; 0028 FIG. 17 illustrates a schematic structural diagram of a color filter layer in the embedded capacitive touch display panel according to the embodiment of the applica tion; 0029 FIG. 18 illustrates a schematic diagram of floating electrodes and force touch fixed potential electrodes in the embedded capacitive touch display panel according to the embodiment of the application; 0030 FIG. 19 illustrates a partially enlarged diagram at B in FIG. 18; 0031 FIG. 20a to FIG. 20d illustrate positional relation ships between a first gap section and color resists in the embedded capacitive touch display panel according to the embodiment of the application respectively; 0032 FIG. 21 illustrates a schematic structural diagram of the embedded capacitive touch display panel according to the embodiment of the application, which is an embedded touch screen liquid crystal display; 0033 FIG. 22 illustrates a schematic structural diagram of force touch detection electrodes and fixed potential elec trodes in the embedded capacitive touch display panel according to the embodiment of the application; 0034 FIG. 23 is a schematic structural diagram of force touch detection electrodes and touch detection electrodes in the embedded capacitive touch display panel according to the embodiment of the application; and 0035 FIG. 24 is a schematic structural diagram of an embedded capacitive touch display device according to an embodiment of the application. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application are clearly and completely described in combination with the drawing in the embodiments of the present application, obviously, the described embodiments are only part of the embodiments of the present application, rather than all the embodiments. All the other embodiments, obtained by those of ordinarily skilled in the art in accor dance with the embodiments in the application without any creative effort, fall into the protection scope of the present application The present application discloses an embedded capacitive touch display panel and an embedded capacitive touch display device, wherein the positions of gaps between sensing electrodes and driving electrodes in the display panel are set to keep away from a green color resist bar. Thus the visible defects of patterns of metal touch electrodes are improved, and the display performance of the embedded touch screen is improved on the premise of causing no influence on touch effect In the embedded touch screen, in order to improve the visible defects of the patterns of the metal touch elec trodes and improve the display quality of a picture of an LCD, in the present application, from the point of optimally designing the positions where the sensing electrodes and the driving electrodes are separated to form gaps, the positions of the gaps are set to keep away from the green color resist bar, and the gaps can be formed on a red color resist bar and/or a blue color resist bar. Because the red color resistand the blue color resist are relatively low in penetration rate and cannot be easily identified by human eyes, the disadvanta geous phenomenon that the human-eye can see the patterns of the touch electrodes can be effectively avoided under common customer backlight intensity specifications. Wherein in a display brightness L, the contribution rate of each color resist is shown in the following formula: wherein R represents the red color resist, G presents the green color resist, and B represents the blue color resist. As shown in the formula aforementioned, for brightness, the contribution of the green color resist is far greater than the contribution of the red color resistand the contribution of the blue color resist, and the green color resist is brighter compared with the other adjacent color resists and easy to be sensed by human eyes during display.
19 US 2016/ A1 Nov. 24, For the green color resist G with a high penetration rate, if the positions of the gaps 1 correspond to the position of the green color resist bar G on the color filter layer, for example, the gaps 1 are in the position of the green color resist G as shown by the dotted line box in FIG.3 and FIG. 4, the phenomenon is more obvious. When the intensity of the backlight source is increased or the TFT off-state current is increased, the pattern of the gaps between the sensing electrodes and the driving electrodes is highlighted on the liquid crystal display Screen, in particular, when the posi tions of the gaps correspond to the positions of the green color resists, the phenomenon is especially obvious, and the display quality of the picture is seriously reduced. An Embodiment As shown in FIG. 5 to FIG. 14, the present appli cation discloses an embedded capacitive touch display panel, which includes: a first transparent Substrate 22, a grid-shaped metal conductive layer 24 formed on the first transparent substrate 22, a black matrix layer 23 formed between the first transparent substrate 22 and the grid shaped metal conductive layer 24 which is shielded by the black matrix layer 23, a second Substrate 21 arranged opposite to the first transparent Substrate 22, and a pixel element array (not shown in the figures) formed on the second substrate 21, wherein each pixel element is corre spondingly provided with a TFT (not shown in the figures); a light-shading structure is not provided at one side of each TFT away from the second substrate 21, because the work ing performance of the TFTs is influenced due to the existence of parasitic capacitance caused by arranging the light-shading structure, therefore, a light-shading structure will not provided at one side of each TFT away from the second substrate 21, and the multiple TFTs on the second substrate 21 form a TFT structure layer 29, as shown in FIG As shown in FIG. 6 to FIG. 9, FIG. 9 is a partial enlarged view of part B in FIG. 8, the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 24 includes multiple first metal electrodes 242 and multiple second metal electrodes 241 crossed with the multiple first metal electrodes 242, and each of the second metal electrodes 241 is divided into multiple sections by the multiple first metal electrodes 242; and the first metal electrodes 242 and the second metal electrodes 241 are separated from each other and form gaps 111, as shown in FIG. 6, wherein the first metal electrodes 242 are sensing electrodes, and the second metal electrodes 241 are driving electrodes As shown in FIG. 5 and FIG. 7, the embedded capacitive touch display panel further includes a color filter layer 25, wherein the color filter layer 25 includes red color resist units R, green color resist units G and blue color resist units B, and the color resist units with the same color are arrayed to form a color resist bar 251. Wherein the color resist bars 251 include a red color resist bar R, a green color resist bar G and a blue color resist bar B, the three color resist bars are mutually parallel or substantially parallel. In addition, each pixel element corresponds to one color resist unit, a part of the color resist units are surrounded by the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 24, and the TFTs in the pixel elements corresponding to the color resist units Sur rounded by the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 24 are shielded by the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 24. The other part of the color resist units are located at the gaps 111 formed by separation of the first metal electrodes 242 and the second metal electrodes 241, and are not surrounded by the grid-shaped metal conductive layer As shown in FIG. 9, the gaps 111 include a first gap part 112, the first gap part 112 is parallel to the color resist bars 251, and the first gap part 112 is not overlapped with the green color resist bar G, as shown in cross-sectional views of FIG. 10 and FIG. 11. In other words, the first gap part 112 parallel to the green color resist bar is kept away from the green color resist bar, or the green color resist bar parallel to the first gap part 112 is not located in the first gap part 112. As shown in FIG. 10, the first gap part 112 is arranged corresponding to the red color resist bar R; in another implementation of this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 11, the first gap part 112 is arranged corresponding to the blue color resist bar B. In still another implementation of this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 12 and FIG. 13, the first gap part 112 is arranged corresponding to the blue color resist bar B and the red color resist bar R. In addition, the gaps 111 further include a second gap part 113, and the second gap part 113 is perpendicular to the color resist bars 251, as shown in FIG As shown in FIG. 5, FIG. 6 and FIG. 14, the touch display panel further includes a conductive bridging layer 26, the multiple sections of the second metal electrode 241 are connected together by the conductive bridging layer 26, and the conductive bridging layer 26 is made of a metal material or a transparent conductive material. As shown in FIG. 14, the color filter layer 25 is arranged between the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 24 and the conductive bridging layer 26, the color filter layer includes multiple via holes K, and the multiple sections of the second metal electrode 241 are connected together by the conductive bridging layer 26 through the via holes K; and the color filter layer 25 is made of an insulating and non-conducting material. Another Embodiment This embodiment is based on the embodiment aforementioned, and the embedded capacitive touch display panel may be an embedded capacitive touch liquid crystal display. As shown in FIG. 15, the embedded capacitive touch liquid crystal display includes: a first transparent substrate 32, a grid-shaped metal conductive layer 34 formed on the first transparent substrate 32, a black matrix layer 33 formed between the first transparent substrate 32 and the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 34 which is shielded by the black matrix layer 33, a conductive bridging layer 36 located on the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 34, a color filter layer 35 located between the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 34 and the conductive bridging layer 36, a second substrate 31 arranged opposite to the first transparent Substrate 32, and a pixel element array (not shown in the figure) formed on the second substrate 31, wherein each pixel element is correspondingly provided with a TFT (not shown in the figure), a light-shading structure is not provided at one side of each TFT away from the second substrate 31, and the multiple TFTs on the second substrate 31 form a TFT structure layer 39; and the embed ded capacitive touch liquid crystal display further includes a liquid crystal layer 30 sandwiched between the first trans parent substrate 32 and the second substrate 31. The posi tions of the gaps between the sensing electrodes and the driving electrodes in the touch structure in the liquid crystal
20 US 2016/ A1 Nov. 24, 2016 display device are set to keep away from the green color resist bar. Thus the visible defects of the patterns of the metal touch electrodes are improved, and the display performance of the embedded capacitive touch liquid crystal display is improved on the premise of causing no influence on touch effect In addition, the embedded capacitive touch display panel in the embodiment may also be an embedded capaci tive touch organic light-emitting display panel or an embed ded capacitive touch color electronic paper. Another Embodiment An embodiment of the application provides an embedded capacitive touch display panel as illustrated in FIG. 16, which includes a first transparent substrate 41 and a second Substrate 42 arranged opposite to each other, a grid-shaped metal conductive layer 43 formed on the first transparent Substrate 41, and a number of force touch detection electrodes independent of each other formed on the second substrate 42: As illustrated in FIG. 16, the embedded capacitive touch display panel further includes a color filter layer 45 as illustrated in FIG. 17, which includes at least red color resists R. green color resists G, and blue color resists B, where the color resists in the same colors are arranged in respective color resist bars 451, and the color resist bars 451 include green color resist resistance strips As illustrated in FIG. 18, the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 43 includes force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and floating electrodes 432, where the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 are separate from the floating electrodes 432 with gaps 433 being formed between them; and as illustrated in FIG. 19 which is an enlarged diagram of the section in the dashed-line box B in FIG. 18. the gaps 433 include first gap sections 433a which are parallel to the color resist bars 451, and which do not overlap with the green color resist resistance Strips In the embedded capacitive touch display panel according to the embodiment of the application, the first gap sections 433a are arranged so that they do not overlap with the green color resist resistance strips, and since the green color resists contribute to display brightness far more than the color resists of the other colors, the first gap sections 433a can be arranged so that they do not overlap with the green color resist resistance strips to thereby alleviate the problem of a visible pattern of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating electrodes 432 so as to improve the display performance of the embedded capaci tive touch display panel without degrading a touch effect In a particular implementation, in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, as illustrated in FIG. 17, the color resist bars 451 generally include red color resist bars and blue color resist bars in addition to the green color resist bars, and the color resist bars of the three colors are generally parallel or substantially parallel to each other. Of course, if the color filter layer 45 further includes color resists of other colors, e.g., yellow color resists, then the color resist bars 451 will further include the yellow color resist bars, although a repeated description thereof will be omitted here Particularly in the embedded capacitive touch dis play panel above according to the embodiment of the application, the first gap sections 433a are arranged so that they do not overlap with the green color resist resistance strips, so the green color resist resistance strips parallel to the first gap sections 433a do not lie in the first gap sections 433a; and there are so lower transmitivities of the red color resists R and the blue color resists B that light transmitted through them will not be easily recognized by human eyes, thus avoiding in effect the pattern of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating electrodes 432 from being visible to human eyes with a normal custom backlight intensity specification, where contribution ratios of the color resists in the respective colors to the display brightness L are as shown in the equation of L=1.OOOOR G B, Where R represents the red color resists, G repre sents the green color resists, and B represents the blue color resists. As can be apparently seen from the above equation, the green color resists G contribute to the brightness far more than the red color resists R and the green color resists B so that they display more brightly than the adjacent other color resists, and thus are easier to be perceived by human eyes. For the green color resists G with a higher transmi tivity, this phenomenon will be more pronounced if the first gap sections 433a are positioned in correspondence to the green color resists G. If the intensity of backlight light sources is raised, or off-state current of TFTs is increased, then the pattern of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating electrodes 432 will become highlighted on a liquid crystal display screen, and particularly if the gaps 433 are positioned in correspondence to the green color resists G, then this phenomenon will become pronounced, thus seriously degrading the quality of display a picture Thus in order to alleviate the problem of the visible pattern of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating electrodes 432 so as to improve the performance of displaying on the embedded capacitive touch display panel without degrading the touch effect, in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, as illustrated in FIG.20a, the first gap sections 433a can be arranged in correspondence to the red color resist bars; or as illustrated in FIG. 20b, the first gap sections 433a can be arranged in correspondence to the blue color resist bars; or as illustrated in FIG. 20c and FIG. 20d, the first gap sections 433a can be arranged in corre spondence to the red color resist bars and the blue color resist bars Furthermore in order to alleviate the problem of the visible pattern of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating electrodes 432 so as to improve the performance of displaying on the embedded capacitive touch display panel without degrading the touch effect, in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above accord ing to the embodiment of the application, the widths of the respective first gap sections 433a can be set the same to thereby mitigate the differences between the first gap sec tions 433a Moreover in the embedded capacitive touch dis play panel above according to the embodiment of the application, as illustrated in FIG. 19, the gaps generally further include second gap sections 433b perpendicular to the color resist bars Alike furthermore in order to alleviate the problem of the visible pattern of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating electrodes 432 so as to
21 US 2016/ A1 Nov. 24, 2016 improve the performance of displaying on the embedded capacitive touch display panel without degrading the touch effect, in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, the widths of the respective second gap sections 433b can be set the same to thereby mitigate the differences between the second gap sections 433b In a particular implementation, in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, there may be various pat terns of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating electrodes 432 of the grid-shaped metal conductive layer As illustrated in FIG. 18, for example, in order to facilitate an application of a fixed potential, e.g., Ground, to the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431, the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 can be composed of a number of first metal electrode strips 431a, and a number of second metal electrode strips 431b intersecting the first metal electrode strips 431a, and the respective floating electrodes 432 are located in areas surrounded by every two adjacent first metal electrode strips 431a and every two adjacent second metal electrode strips 431b. That is, the first metal electrode strips 431a and the second metal electrode strips 431b are interconnected into a grid-like structure, and the floating electrode strips 432 are arranged in meshes of the grid-like structure. In another example, the pattern of the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 can alternatively be composed of a number of electrode blocks, and the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431 and the floating elec trodes 432 can be arranged alternately in both the row direction and the column direction, where the respective electrode blocks need to be electrically connected with wires for applying a fixed potential thereto. Moreover in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, the area of the smallest grid in the grid-shaped metal conductive layer 43 will not be defined, but particularly the Smallest grid can be arranged in corresponding to one or more color resist, and the embodi ment of the application will not be limited in this regard In a particular implementation, the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application can be particularly an embed ded capacitive touch liquid crystal display panel as illus trated in FIG. 21, which further includes a liquid crystal layer 47 arranged between the first transparent substrate 41 and the second substrate 42; or the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application can be particularly an embedded capacitive touch electroluminescence display panel, and the embodi ment of the application will not be limited in this regard. The embedded capacitive touch display panel will be described as an embedded capacitive touch liquid crystal display panel throughout the following description by way of an example In a particular implementation, in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, there may be a number of implementations of a pattern of a number of force touch detection electrodes 44 independent of each other formed on the second Substrate 42, several particular examples of which will be described below. Another Embodiment In the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, as illustrated in FIG. 16, the embedded capacitive touch display panel generally further includes pixel units 46 formed on the second Substrate 42 so that they are arranged in an array thereon, and a common electrode layer (not illustrated) including force touch detection electrodes 44 arranged in correspondence to the pixel units 46. That is, the common electrode layer can be segmented into the respective force touch detection electrodes 44, which are reused as the common electrode layer. In display phase, a common elec trode signal is applied to the respective force touch detection electrodes 44; and in force touch detection phase, the thickness of a liquid crystal box between the first transparent substrate 41 and the second substrate 42 at the section of the first transparent substrate 41 being pressed will be decreased so that the capacitance between the force touch fixed poten tial electrode 431 and the force touch detection electrode 44 at the section of the first transparent substrate 41 being pressed will be increased, so the pressure condition can be detected by detecting an electric signal of the force touch detection electrode 44. In the meanwhile, if the first trans parent substrate 41 is pressed by a human body, then the capacitance between the force touch fixed potential elec trode 431 and the force touch detection electrode 44 will be influenced by the capacitance of the human body through the floating electrode 432, and the touch condition can be further detected by detecting the electric signal of the force touch detection electrode 44, that is, the force touch detection electrode 44 can also function to detect a touch, that is, the force touch detection electrode 44 can function as a touch detection electrode. Another Embodiment In the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, as illustrated in FIG. 22, the respective force touch detection electrodes 44 can be reused as touch detection electrodes; and in the meanwhile, fixed potential electrodes 441 can be arranged between the respective force touch detection elec trodes 44 to thereby mitigate signal interference between the respective force touch detection electrodes 44. The thickness of a liquid crystal box between the first transparent substrate 41 and the second substrate 42 at the section of the first transparent Substrate 41 being pressed will be decreased so that the capacitance between the force touch fixed potential electrode 431 and the force touch detection electrode 44 at the section of the first transparent substrate 41 being pressed will be increased, and here if the first transparent substrate 41 is pressed by a human body, then the capacitance between the force touch fixed potential electrode 431 and the force touch detection electrode 44 will be also influenced by the capacitance of the human body through the floating elec trode 432, and both the pressure condition and the touch condition can be detected by detecting the electric signal of the force touch detection electrode Furthermore in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, in order to guarantee the sensitivity of touch detection to thereby enable the force touch detection elec trodes 44 to be more easily influenced by the capacitance of the human body, as illustrated in FIG. 22, the respective
22 US 2016/ A1 Nov. 24, 2016 force touch detection electrodes 44 can be arranged in correspondence to the floating electrodes 432, that is, the force touch detection electrodes 44 are arranged directly below the floating electrodes 432; and the respective fixed potential electrodes 441 can be arranged in correspondence to the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431, that is, the fixed potential electrodes 441 are arranged directly below the force touch fixed potential electrodes Furthermore in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, in order to mitigate signal interference between force touch detection and display, the embedded capacitive touch display panel can be driven in display phase and force touch detection phase in a time division mode. Moreover in order to mitigate RC loading, the common electrode layer can be segmented into the force touch detection electrodes 44 and the fixed potential electrodes 441, that is, the com mon electrode layer includes the fixed potential electrodes 441 and the force touch detection electrodes 44 arranged in correspondence to the pixel units 46. At this time, a common electrode signal needs to be applied to the respective force touch detection electrodes 44 and fixed potential electrodes 441 in display phase, and the common electrode signal may be further applied to the fixed potential electrodes 441 in force touch detection phase. Moreover as illustrated in FIG. 22, the respective force touch detection electrodes 44 can be connected with corresponding wires through via holes so that the signal is applied to the respective force touch detection electrodes 44, or signals fed back by the force touch detection electrodes 44 are received, through the W1S. Another Embodiment In the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, as illustrated in FIG. 23, a number of touch detection electrodes 442 independent of each other can be arranged between the respective force touch detection electrodes 44, that is, force touch detection and touch detection is performed respec tively by the different nodes. The thickness of a liquid crystal box between the first transparent substrate 41 and the second substrate 42 at the section of the first transparent substrate 41 being pressed will be decreased so that the capacitance between the force touch fixed potential electrode 431 and the force touch detection electrode 44 at the section of the first transparent Substrate 41 being pressed will be increased, so the pressure condition can be detected by detecting an electric signal of the force touch detection electrode 44. In the meanwhile, if the first transparent substrate 41 is pressed by a human body, then the capacitance of the touch detection electrode 442 will be influenced by the capacitance of the human body through the floating electrode 432, and the touch condition can be further detected by detecting an electric signal of the touch detection electrode Furthermore in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, in order to guarantee the sensitivity of touch detection to thereby enable the touch detection electrodes 442 to be more easily influenced by the capacitance of the human body, as illustrated in FIG. 23, the respective force touch detection electrodes 44 can be arranged in correspon dence to the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431, that is, the force touch detection electrodes 44 are arranged directly below the force touch fixed potential electrodes 431; and the respective touch detection electrodes 442 can be arranged in correspondence to the floating electrodes 432, that is, the touch detection electrodes 442 are arranged directly below the floating electrodes Furthermore in the embedded capacitive touch display panel above according to the embodiment of the application, in order to mitigate signal interference between pressure detection and display, the embedded capacitive touch display panel can be driven in display phase and force touch/touch detection phase in a time division mode. More over in order to mitigate RC loading, the common electrode layer can be segmented into the force touch detection electrodes 44 and the touch detection electrodes 442, that is, the common electrode layer includes the touch detection electrodes 442 and the force touch detection electrodes 44 arranged in correspondence to the pixel units 46. At this time, a common electrode signal needs to be applied to the respective force touch detection electrodes 44 and touch detection electrodes 442 in display phase, and the force touch detection electrodes 44 and the touch detection elec trodes 442 may detect in a time division mode or concur rently in force touch detection phase, although the embodi ment of the application will not be limited in this regard. Moreover as illustrated in FIG. 23, the respective force touch detection electrodes 44 and touch detection electrodes 442 can be connected with corresponding wires through via holes so that the signal is applied to the respective force touch detection electrodes 44 and touch detection electrodes 442, or signals fed back by the force touch detection electrodes 44 and touch detection electrodes 442 are received, through the wires. Another Embodiment 0069 Based upon the same inventive concept, an embodiment of the application further provides an embed ded capacitive touch display device as illustrated in FIG. 24 including the embedded capacitive touch display panel 100 above, where the display device can be a mobile phone, a tablet computer, a TV set, a display, a notebook computer, a digital photo frame, a navigator, or any other product or component capable of displaying. Reference can be made for the embodiments of the embedded capacitive touch display panel above for an implementation of the display device, so a repeated description thereof will be omitted here The embedded capacitive touch display panel and the embedded capacitive touch display device above accord ing to the embodiments of the application include: a first transparent Substrate and a second Substrate arranged oppo site to each other, a grid-shaped metal conductive layer formed on the first transparent substrate, and a number of force touch detection electrodes independent of each other formed on the second Substrate; and the embedded capaci tive touch display panel further includes a color filter layer including at least red color resists, green color resists, and blue color resists, where the color resists in the same colors are arranged in respective color resist bars, and the color resist bars include green color resist resistance strips; and the grid-shaped metal conductive layer includes periodically arranged force touch fixed potential electrodes and floating electrodes, where the force touch fixed potential electrodes are separate from the floating electrodes with gaps being formed between them, and the gaps include first gap sections which are parallel to the color resist bars, and which do not
23 US 2016/ A1 Nov. 24, 2016 overlap with the green color resist resistance strips. Since the green color resists contribute to display brightness far more than the color resists of the other colors, the first gap sections can be arranged so that they do not overlap with the green color resist resistance strips to thereby alleviate the problem of a visible pattern of the force touch fixed potential elec trodes and the floating electrodes so as to improve the display performance of the embedded capacitive touch dis play panel without degrading the touch effect Each part in the specification is described in a progressive mode, what is highlighted in each part is dif ferent from that in other parts, and for the same or similar parts between all the parts, reference could be made to each other For the above-mentioned illustration of the dis closed embodiments, those skilled in the art may realize or use the present application. Multiple modifications of these embodiments are obvious for those skilled in the art, and general principles defined herein may be realized in other embodiments without departing from the spirit or scope of the present application. Accordingly, the present application will not be limited to the embodiments shown herein, but accords with the widest scope consistent with the principles and novel characteristics disclosed herein. What is claimed is: 1. An embedded capacitive touch display panel, compris ing: a first transparent Substrate and a second substrate arranged opposite to each other, a grid-shaped metal con ductive layer formed on the first transparent Substrate, and a number of force touch detection electrodes independent of each other formed on the second substrate, wherein: the embedded capacitive touch display panel further com prises a color filter layer comprising at least red color resists, green color resists, and blue color resists, wherein the color resists in the same colors are arranged in respective color resist bars, and the color resist bars comprise green color resist resistance strips; and the grid-shaped metal conductive layer comprises peri odically arranged force touch fixed potential electrodes and floating electrodes, wherein the force touch fixed potential electrodes are separate from the floating elec trodes with gaps being formed between them, and the gaps comprise first gap sections which are parallel to the color resist bars, and which do not overlap with the green color resist resistance strips. 2. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 1, wherein the color resist bars further comprise red color resist bars and blue color resist bars, and the color resist bars of the three colors are parallel or substantially parallel to each other. 3. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 2, wherein the first gap sections are arranged in correspondence to the red color resist bars; and/or the first gap sections are arranged in correspondence to the blue color resist bars. 4. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 1, wherein the gaps further comprise second gap sections perpendicular to the color resist bars. 5. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 1, wherein the force touch fixed potential electrodes are composed of a number of first metal electrode strips, and a number of second metal electrode strips inter secting the first metal electrode strips, and the respective floating electrodes are located in areas Surrounded by every two adjacent first metal electrode strips and every two adjacent second metal electrode strips. 6. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 1, wherein the embedded capacitive touch display panel further comprises: pixel units formed on the second Substrate so that they are arranged in an array thereon, and a common electrode layer comprising force touch detec tion electrodes arranged in correspondence to the pixel units. 7. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 1, wherein the respective force touch detection electrodes are reused as touch detection electrodes; and fixed potential electrodes are arranged between the respective force touch detection electrodes. 8. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 7, wherein the respective force touch detection electrodes are arranged in correspondence to the floating electrodes; and the respective fixed potential electrodes are arranged in correspondence to the force touch fixed potential elec trodes. 9. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 7, wherein the embedded capacitive touch display panel further comprises: pixel units formed on the second Substrate so that they are arranged in an array thereon, and a common electrode layer comprising the fixed potential electrodes and the force touch detection electrodes arranged in correspondence to the pixel units. 10. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 1, wherein a number of touch detection elec trodes independent of each other are arranged between the respective force touch detection electrodes. 11. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 10, wherein the respective force touch detection electrodes are arranged in correspondence to the force touch fixed potential electrodes; and the respective touch detection electrodes are arranged in correspondence to the floating electrodes. 12. The embedded capacitive touch display panel accord ing to claim 10, wherein the embedded capacitive touch display panel further comprises: pixel units formed on the second Substrate so that they are arranged in an array thereon, and a common electrode layer comprising the force touch detection electrodes and the touch detection electrodes arranged in correspondence to the pixel units. 13. An embedded capacitive touch display device, com prising an embedded capacitive touch display panel, wherein the embedded capacitive touch display panel com prises: a first transparent Substrate and a second Substrate arranged opposite to each other, a grid-shaped metal con ductive layer formed on the first transparent Substrate, and a number of force touch detection electrodes independent of each other formed on the second substrate, wherein: the embedded capacitive touch display panel further com prises a color filter layer comprising at least red color resists, green color resists, and blue color resists, wherein the color resists in the same colors are arranged in respective color resist bars, and the color resist bars comprise green color resist resistance strips; and
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006
 (19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
120x124-st =l. (12) United States Patent. (10) Patent No.: US 9,046,952 B2. 220a 220b. 229b) s 29b) al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,449,544 B2
 USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
R GBWRG B w Bwr G B wird
 US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0362960 A1 Chang et al. US 20150362960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCHELECTRONIC DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0362960 A1 Chang et al. US 20150362960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCHELECTRONIC DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
40- It i? l? l (r. Nl
 (19) United States US 2014032O765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0320765 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND FABRICATION Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014032O765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0320765 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND FABRICATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0022695A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0022695 A1 Schmidt (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRICAL MULTILAYER COMPONENT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIC I/146 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 2014.0022695A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0022695 A1 Schmidt (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRICAL MULTILAYER COMPONENT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIC I/146 (2013.01);
M3 d. (12) United States Patent US 7,317,435 B2. Jan. 8, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Wei-Chieh Hsueh, Tainan (TW) T GND
 US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015
 (19) United States US 20150212614A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0212614 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) INTEGRATED POLARIZER AND (52) U.S. Cl. CONDUCTIVE
(19) United States US 20150212614A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0212614 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) INTEGRATED POLARIZER AND (52) U.S. Cl. CONDUCTIVE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0018076 A1 Chen et al. US 200700 18076A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ELECTROMAGNETIC DIGITIZER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0018076 A1 Chen et al. US 200700 18076A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ELECTROMAGNETIC DIGITIZER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0311941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311941 A1 Sorrentino (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) MOBILE DEVICE CASE WITH MOVABLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2015 0311941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311941 A1 Sorrentino (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) MOBILE DEVICE CASE WITH MOVABLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,757,375 B2
 US008757375B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,757,375 B2 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2014 (54) SUPPORT FOR A TABLET COMPUTER WITH! E:: 1938. Spur 3.32. u et al... A FUNCTION OF
US008757375B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,757,375 B2 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2014 (54) SUPPORT FOR A TABLET COMPUTER WITH! E:: 1938. Spur 3.32. u et al... A FUNCTION OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
VDD. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. I Data. (76) Inventors: Wen-Cheng Yen, Taichung (TW);
 (19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0325383A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0325383 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRON BEAM MELTING AND LASER B23K I5/00 (2006.01) MILLING COMPOSITE
(19) United States US 2016.0325383A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0325383 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRON BEAM MELTING AND LASER B23K I5/00 (2006.01) MILLING COMPOSITE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1. Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO6208561B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1 Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 9 (54) METHOD TO REDUCE CAPACITIVE 5,787,037 7/1998 Amanai... 365/185.23 LOADING IN
USOO6208561B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1 Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 9 (54) METHOD TO REDUCE CAPACITIVE 5,787,037 7/1998 Amanai... 365/185.23 LOADING IN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O151875A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151875 A1 Lehr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) LAMINATE INLAY PROCESS FOR SPORTS BOARDS (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O151875A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151875 A1 Lehr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) LAMINATE INLAY PROCESS FOR SPORTS BOARDS (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.250,058 B2
 US00925.0058B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.250,058 B2 Backes et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) CAPACITIVE ROTARY ENCODER USPC... 324/658, 686, 660, 661, 676, 207.13, 324/207.17,
US00925.0058B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.250,058 B2 Backes et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) CAPACITIVE ROTARY ENCODER USPC... 324/658, 686, 660, 661, 676, 207.13, 324/207.17,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O217945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0217945 A1 Miyamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TOUCH SENSOR, DISPLAY WITH TOUCH SENSOR, AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
(19) United States US 2004O217945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0217945 A1 Miyamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TOUCH SENSOR, DISPLAY WITH TOUCH SENSOR, AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
Y 6a W SES. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States. Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 (19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999
 USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
IIII. United States Patent 19 Delorme. 11 Patent Number: 5,894,701 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 20, Attorney, Agent, or Firn-Swabey Ogilvy Renault
 United States Patent 19 Delorme 54) WOODEN MODULARPANELING FOR INTERFOR DECORATION 76 Inventor: Claude Delorme, 9141 Pierre Elliott Trudeau, St-Léonard, Québec, Canada, HR 3WA. 21 Appl. No.: 08/910,667
United States Patent 19 Delorme 54) WOODEN MODULARPANELING FOR INTERFOR DECORATION 76 Inventor: Claude Delorme, 9141 Pierre Elliott Trudeau, St-Léonard, Québec, Canada, HR 3WA. 21 Appl. No.: 08/910,667
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
E3, ES 2.ÉAN 27 Asiaz
 (19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
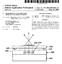 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
rectifying smoothing circuit
 USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
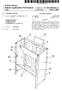 US 20030085640A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085640 A1 Chan (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) FOLDABLE CABINET Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
US 20030085640A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085640 A1 Chan (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) FOLDABLE CABINET Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
FDD Uplink 2 TDD 2 VFDD Downlink
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094409 A1 Li et al. US 2013 0094409A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094409 A1 Li et al. US 2013 0094409A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,314,819 B2. Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012
 USOO8314819B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) DISPLAYS WITH INTEGRATED 6,830,339 B2 * 12/2004 Maximus... 353/20 BACKLIGHTING 6,878.494 B2
USOO8314819B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) DISPLAYS WITH INTEGRATED 6,830,339 B2 * 12/2004 Maximus... 353/20 BACKLIGHTING 6,878.494 B2
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1
 US008769908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1 Santini (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2014 (54) MODULAR BUILDING PANEL 4,813,193 A 3, 1989 Altizer.............. (76) Inventor: Patrick
US008769908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1 Santini (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2014 (54) MODULAR BUILDING PANEL 4,813,193 A 3, 1989 Altizer.............. (76) Inventor: Patrick
24. United States Patent (19) Noé et al. 21 Appl. No. 261,066. least one correcting roller which has an adjustable depth of
 United States Patent (19) Noé et al. 11) 45) US005535610A Patent Number: 5,535,610 Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 1996 54 METHD AND APPARATUS FR ELMINATING CRSSBW IN METAL STRIP 75 Inventors: Rolf Noé; Andreas
United States Patent (19) Noé et al. 11) 45) US005535610A Patent Number: 5,535,610 Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 1996 54 METHD AND APPARATUS FR ELMINATING CRSSBW IN METAL STRIP 75 Inventors: Rolf Noé; Andreas
YAYA v.v. 20. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Miskin et al. US 20070273299A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 29, 2007 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) AC LIGHT EMITTING DODE AND AC LED DRIVE METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Miskin et al. US 20070273299A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 29, 2007 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) AC LIGHT EMITTING DODE AND AC LED DRIVE METHODS
& S S. SS S. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States. (75) Inventors: Miguel Angel Gomez Caudevilla,
 (19) United States US 2006.0125150A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0125150 A1 Gomez Caudevilla et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2006 (54) PLASTIC RECEPTACLE FOR DOMESTIC WASHING
(19) United States US 2006.0125150A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0125150 A1 Gomez Caudevilla et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2006 (54) PLASTIC RECEPTACLE FOR DOMESTIC WASHING
United States Patent (19) Morita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2O8236A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208236A1 Damink et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF AN OBJECT
(19) United States US 2010O2O8236A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208236A1 Damink et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF AN OBJECT
Computer. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Centralier. ining. sci: {xifoie. ataxis: 8.
 (19) United States US 201201696.60A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169660 A1 SEO (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING TOUCH SENSOR (76) Inventor: Seong-Mo
(19) United States US 201201696.60A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169660 A1 SEO (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING TOUCH SENSOR (76) Inventor: Seong-Mo
us Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ Al (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040150613Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150613
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040150613Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150613
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
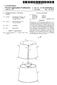 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0287650 A1 Anderson et al. US 20120287650A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) INTERCHANGEABLE LAMPSHADE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0287650 A1 Anderson et al. US 20120287650A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) INTERCHANGEABLE LAMPSHADE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
(19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
the sy (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2015 slope Zero-CIOSSing
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028830 A1 CHEN US 2015 0028830A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) CURRENTMODE BUCK CONVERTER AND ELECTRONIC
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028830 A1 CHEN US 2015 0028830A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) CURRENTMODE BUCK CONVERTER AND ELECTRONIC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0031036A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0031036A1 Reed et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2016 (54) LINEAR FRICTION WELDING (30) Foreign Application
US 2016.0031036A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0031036A1 Reed et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2016 (54) LINEAR FRICTION WELDING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
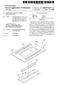 (19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0081252 A1 Markgraf et al. US 2013 0081252A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) ARRANGEMENT FOR FIXINGA COMPONENT INSIDE OF
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0081252 A1 Markgraf et al. US 2013 0081252A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) ARRANGEMENT FOR FIXINGA COMPONENT INSIDE OF
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Yilmaz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul.18, 2013
 US 2013 0181911A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0181911A1 Yilmaz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul.18, 2013 (54) ON-DISPLAY-SENSORSTACK (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 345/173
US 2013 0181911A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0181911A1 Yilmaz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul.18, 2013 (54) ON-DISPLAY-SENSORSTACK (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 345/173
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0103923 A1 Mansor et al. US 2012O103923A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (63) (60) RAIL CONNECTOR FORMODULAR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0103923 A1 Mansor et al. US 2012O103923A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (63) (60) RAIL CONNECTOR FORMODULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080285279A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0285279 A1 Ng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2008 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (LED) LIGHT BULB (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20080285279A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0285279 A1 Ng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2008 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (LED) LIGHT BULB (76) Inventors:
S/AN a. ', (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. El 1 -
 (19) United States US 20030011729A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0011729 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) VERTICALLY ALIGNED MODE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY WITH
(19) United States US 20030011729A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0011729 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) VERTICALLY ALIGNED MODE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY WITH
