(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006
|
|
|
- Charles Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
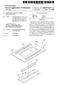
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM (52) U.S. Cl /38 TRANSISTOR LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Fang-Chen Luo, Hsinchu City (TW). (57) ABSTRACT Chang-Cheng Lo, Chia Yi Hsien (TW) Correspondence Address: WARE FRESSOLAVANDER SLUYS & A stacked storage capacitor structure for use in each pixel of ADOLPHSON, LLP a TFT-LCD, wherein a first storage capacitor is formed by BRADFORD GREEN BUILDINGS a first metal layer, a gate insulator layer and a second metal 755 MAIN STREET, PO BOX 224 layer. The second capacitor is formed by the second metal MONROE, CT (US) layer, a passivation insulator layer and an ITO layer. The first metal layer and the ITO layer are joined together through a (73) Assignee: AU Optronics Corporation via hole which is etched in one insulator etching step during (21) Appl. No.: 11/004,389 the overall fabrication process through both the gate insu lator and the passivation insulator layers. As such, the two (22) Filed: Dec. 3, 2004 capacitors are connected in parallel in a stacked configura Publication Classification tion. With the stacked storage capacitor structure, the charge storage capacity is increased without significantly affecting the aperture ratio of a pixel. The ITO and the pixel electrode (51) Int. Cl. can be different parts of an indium tine oxide layer deposited GO2F L/343 ( ) on the passivation insulator layer. pixel electrode segment 11 %2 line brary Via pixel 28 electrode segment
2
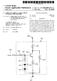
3 Patent Application Publication Jun. 8, 2006 Sheet 2 of 5 US 2006/ A1 a-si signal line Passivation insulator 24 Via 3 : \ A A warrrrrrrrrr vovrvivrwrvaravaravarravarvav % glass 30 Source-drain gate. metal M2 metal M1 gate insulator FIG Passivation TO 20 insulator 24 4, Via 2 pixel electrode 10 A?a. s YYY was SS gate metal glass 30 M1 FIG. 3 gate insulator 22 Source-drain metal M2
4 ..... w e o a s a : signal pixel line Via 3 his 21." -Si...::::::::::::::::::::::...: COO 2 Via Y N- TFT 50 FIG. 4
5 Patent Application Publication Jun. 8, 2006 Sheet 4 of 5 US 2006/ A1 a-si signal line passivation insulator Ssss XXX XX ITO 20 Via 2 % COO glass 30 insulator 22 pixel pixel electrode electrode passivation segment segment 11 Via 3 insulator 24 Via 4 11" & / gate insulator 22 FIG. 6 COmnOn line M1 glass 30
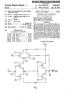
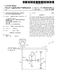
6 Patent Application Publication Jun. 8, 2006 Sheet 5 of 5 US 2006/ A1 Signal line gate line Via 1 SOUC6 drain Via 2 M2 dielectric 24 1O 4-1. dielectric 22 M1 Via 3 ITO 20 gate line 2 Signal line gate line 50 al Via 1 Source drain Via 4 M2 Via " O -> C1 C2 N dielectric 22 dielectric 24 M1 Via 2 TO 20 FIG. 8 Common line
7 US 2006/ A1 Jun. 8, 2006 STACKED STORAGE CAPACTOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM TRANSISTOR LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a storage capacitor structure for use in a thin film transistor liquid crystal display particularly an amorphous silicon thin film transistor liquid crystal display. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION It is known in the art that thin film transistor liquid crystal displays (commonly referred to as TFT-LCD) seek to minimize the area needed for the storage capacitor used in Such displays especially as the resolution of the display increases and therefore the pixel size decreases. The increase in display resolution is especially important for amorphous silicon TFT-LCD displays (a-si TFT-LCDs). In particular, it is well known that as the display resolution increases, the area available on each pixel of such displays for the fabri cation of the storage capacitor is diminished due to aperture ratio considerations. What this means is that for a given pixel it is desired that as the overall size of the pixel decreases, that the maximum amount of the pixel area be devoted to the pixel electrode rather than the storage capacitor associated with the pixel. As a result, as the resolution of a-si TFT LCD s has increased, the size of the storage capacitor is reduced to a point that the charge storage capacity signifi cantly affects the performance of the overall LCD display in terms of artifacts such as flicker, image retention and cross talk. It is therefore important that the storage capacitance and, particularly the area ratio of pixel electrode to the storage capacitance, be increased without adversely affect ing the aperture ratio of the pixel. 0003) In a conventional a-si TFT-LCD fabrication pro cess, the storage capacitor is either a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) structure or a metal-insulation-ito (MII) structure. In the MIM structure, the first capacitor plate is the gate metal and the second capacitor plate is the source drain metal separated by the gate insulator layer. In the MII structure, the first capacitor plate is the gate metal and the second capacitor plate is the ITO (indium-tin oxide) elec trode separated by both the gate insulator layer and the passivation insulator layer. However, when the resolution is increased, the area available for the storage capacitor is difficult to maintain without sacrificing the aperture ratio In order to increase charge storage capacity without sacrificing the aperture ratio of the pixel, or to maintain the charge storage capacity while increasing the aperture ratio of the pixel in an a-si TFT-LCD display, it would be desirable to better utilize all layers of conductors and insulators for purposes of increasing the capacitance of the storage capaci tor. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is a primary objective of the present invention to increase the charge storage capacity without significantly affecting the aperture ratio in a pixel. The present invention is directed to better utilization of all layers of conductors and insulators for the fabrication of a storage capacitor in an associated pixel of an a-si TFT-LCD array without changing the currently used fabrication processes for such a-si TFT LCD s. To accomplish this result, the source drain metal (M2) is used as a shared capacitor plate in a stacked capacitor structure comprising an MIM structure and a modified MII structure connected in parallel. In particular, the gate metal (M1) and the source-drain metal (M2) sand wich the gate insulator layer so as to form a first capacitor, and the second metal (M2) and the indium titanium oxide (ITO) electrode sandwich a passivation insulator layer so as to form a second capacitor. The two storage capacitors are stacked substantially on top of each other and are intercon nected so as to be electrically in parallel with each other, thereby raising the overall capacitance of the storage capaci tor while maintaining approximately the same area on the pixel as would be used in conventional storage capacitor fabrication More particularly, in an a-si TFT-LCD display a stacked storage capacitor structure is described herein wherein a first storage capacitor is formed by the first metal layer acting as a first plate and the second metal layer acting as a second plate, with the gate insulator layer sandwiched in between acting as the insulator for the first storage capacitor. The second capacitor is formed by use of the second metal electrode (M2) acting as the second plate and the ITO electrode acting as the first plate of the second capacitor, with the passivation insulator layer acting as the insulator for the second storage capacitor. The second metal electrode (M2) is shared by both capacitors and the second capacitor is stacked on top of the first capacitor. The first metal electrode (M1) and the ITO electrode are joined together through a via hole and this via hole is etched in one insulator etching step during the overall fabrication process through both the gate insulator and the passivation insulator layers. The middle electrode for the stacked structure is therefore the second metal which is connected to the pixel electrode through via holes in the passivation insulator layer. The ITO electrode is connected to the first metal electrode (M1) through a via hole which is etched through the gate insulator and the passivation insulator. The pixel electrode is connected to the drain of the TFT through another via hole in the passivation insulator Thus, the first aspect of the present invention provides a stacked storage capacitor structure for a thin film transistor liquid crystal display having a plurality of pixels, each pixel having a pixel area, wherein at least Some of the pixels have a storage capacitor formed Substantially within the pixel area and associated with a stacked storage capaci tor structure. The stacked storage capacitor structure com prises: 0008 a first storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a first electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by a second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a first insulator layer positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer, and 0009 a second storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a third electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by the second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a second insulator layer positioned between the first and second plates, wherein the first elec trically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer are electrically connected to each other so that the first and second storage capacitors are electrically connected in
8 US 2006/ A1 Jun. 8, 2006 parallel, and wherein the second electrically conductive layer is positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer According to the present invention, each of said at least some of the pixels has a gate line disposed at one edge section of the pixel area for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said one edge section According to the present invention, each of said at least Some of the pixels has a semiconductor Switching element and a pixel electrode electrically connected to the Switching element, and the pixel electrode is located within the pixel area adjacent to said one edge section in a non overlapping manner According to the present invention, the switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control terminal, the first Switching end operatively connected to a signal line, the second end operatively connected to the pixel electrode, and each of said at least some of the pixels further comprises a further gate line operatively connected to the Switching control terminal of the Switch element for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switching ends According to the present invention, the second electrically conductive layer (M2) is operatively connected to the second Switching end of the Switching element via the pixel electrode and the first electrically conductive layer (M1) is operatively connected to the gate line According to the present invention, the first switch ing end is a source terminal, the second Switching end is a drain terminal, and the Switching control terminal is a gate terminal of a transistor, wherein the first electrically con ductive layer is a gate metal layer, the first insulator layer is a gate insulator layer and second electrically conductive layer is a source-drain metal layer, and the third electrically conductive layer is made substantially of indium-tin oxide, and the second insulator layer is a passivation insulator layer According to the present invention, part of the passivation insulator layer is disposed adjacent to part of the gate insulator layer, and the pixel electrode is made Sub stantially of indium-tin oxide, and at least part of the pixel electrode and part of the third electrically conductor layer are disposed on different sections of the passivation insulator layer Alternatively, each of said at least some of the pixels comprises 0017 a semiconductor Switching element; 0018 a gate line disposed at one edge section of the pixel area for controlling the Switching element; and a common line disposed in a pixel section spaced from the gate line for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and wherein the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said pixel section According to the present invention, each of said at least some of the pixels has a first pixel electrode segment and a second pixel electrode segment located within the pixel area and separated by said pixel section in a non overlapping manner According to the present invention, the common line is Substantially parallel to the gate line According to the present invention, the switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control terminal, the first Switching end operatively connected to a signal line, the second end operatively connected to the first pixel electrode segment, wherein each of said at least some of the pixels further comprises a gate line operatively connected to the Switching control terminal of the switch element for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switching ends According to the present invention, the second electrically conductive layer (M2) is operatively connected to the second Switching end of the Switching element via the pixel electrode and the first electrically conductive layer (M1) is operatively connected to the common line According to the present invention, the first switch ing end is a source terminal, the second Switching end is a drain terminal, and the Switching control terminal is a gate terminal of a transistor, wherein the first electrically con ductive layer is a gate metal layer, the first insulator layer is a gate insulator layer and second electrically conductive layer is a source-drain metal layer, and the third electrically conductive layer is made substantially of indium-tin oxide, and the second insulator layer is a passivation insulator layer According to the present invention, part of the passivation insulator layer is disposed adjacent to part of the gate insulator layer, and the first and second pixel electrode segment are made Substantially of indium-tin oxide, wherein at least part of the first and second pixel electrode segments and part of the third electrically conductor layer are disposed on different sections of the passivation insulator layer The second aspect of the present invention pro vides a method of increasing charge storage capacity in a thin film transistor liquid crystal display having a plurality of pixels, each pixel having a pixel area and a pixel electrode located within the pixel area, wherein at least some of the pixels have a storage capacitor structure formed at a section of the pixel area substantially within the pixel area for storing electric charges associated with the pixel electrode, and wherein the section is adjacent to the pixel electrode in a non-overlapping manner. The method comprising the steps of: 0027 forming a first storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a first electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by a second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a first insulator layer positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer, and 0028 forming a second storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a third electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by the second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a second insulator layer positioned between the first and second plates; and 0029 electrically connecting the first electrically conduc tive layer to the third electrically conductive layer so that the first and second storage capacitors are electrically connected in parallel for forming the storage capacitor structure, and
9 US 2006/ A1 Jun. 8, 2006 wherein the second electrically conductive layer is posi tioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer The third aspect of the present invention provides a thin film transistor liquid crystal display, comprising: 0.031) a plurality of pixels arranged in rows and columns, each pixel having a pixel area, a plurality of signal lines disposed between the pixel columns; and 0032 a plurality of gate lines disposed between the pixel rows, wherein at least some of the pixels have a storage capacitor formed substantially within the pixel area, the storage capacitor comprising: 0033 a first storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a first electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by a second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a first insulator layer positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer; and 0034 a second storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a third electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by the second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a second insulator layer positioned between the first and second plates, wherein the first elec trically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer are electrically connected to each other so that the first and second storage capacitors are electrically connected in parallel, and wherein the second electrically conductive layer is positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer According to the present invention, each of said at least some of the pixels has a further gate line disposed at one edge section of the pixel area for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said one edge section. 0036). According to the present invention, each of said at least Some of the pixels has a semiconductor Switching element and a pixel electrode electrically connected to the Switching element, and the pixel electrode is located within the pixel area adjacent to said one edge section in a non overlapping manner According to the present invention, the switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control terminal, the first Switching end operatively connected to one of said plurality of signal lines, the second end operatively connected to the pixel electrode, and wherein the switching control terminal of the switch element is operatively connected to one of said plurality of gate lines for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switching ends Alternatively, each of said at least some of the pixels comprises a semiconductor switching element operatively connected to the gate line; and 0040 a common line disposed in a pixel section spaced from the gate line for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and wherein the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said pixel section According to the present invention, each of said at least Some of the pixels has a first pixel electrode segment and a second pixel electrode segment located within the pixel area and separated by said pixel section in a non overlapping manner, and the common line is disposed between two adjacent gate lines According to the present invention, the switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control terminal, wherein the first Switching end is operatively connected to one of said plurality of signal lines, the second end is operatively connected to the first pixel electrode segment, and the Switching control terminal of the switch element is operatively connected to one of the gate lines for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switching ends The present invention will become apparent upon reading the description taken in conjunction with FIGS BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0044) For a better understanding of the nature of the present invention, reference is made to the following figures in which: 0045 FIG. 1 is a plan view of a pixel where the storage capacitor is fabricated as a storage capacitor-on-gate (Cs on-gate) design; 0046 FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along line 2-2 of the pixel of FIG. 1; 0047 FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along line 3-3' of the pixel of FIG. 1; 0048 FIG. 4 is a plan view of a pixel where the storage capacitor is fabricated as a storage capacitor-on-common (Cs-on-com) design; 0049 FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view taken along line 5-5' of the pixel of FIG. 4; 0050 FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view taken along line 6-6' of the pixel of FIG. 4; 0051 FIG. 7 shows an equivalent circuit of the pixel of FIG. 1; and 0052 FIG. 8 shows an equivalent circuit of the pixel of FG, 2. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION 0053 As best seen in FIGS. 1, 2 and 3, a pixel according to the present invention which typically forms part of a pixel array comprises two general areas, one associated with the pixel electrode 10 and another associated with the control and storage capacitor area 12. The pixel fabrication tech nique shown in FIGS. 1, 2 and 3 is known in the art as a storage capacitor-on-gate design (Cs-on-gate). The fabrica tion technique in general is with regard to an amorphous silicon thin film transistor liquid crystal display (a-si TFT LCD) although the principles described could be used for other types of TFT-LCD displays, and as a p-si TFT-LCD display As seen in FIGS. 1, 2 and 3, a storage capacitor for use in maintaining the state of the pixel electrode and thus of the LCD pixel between scans, comprises two storage
10 US 2006/ A1 Jun. 8, 2006 capacitors shown diagrammatically as C1 and C2. The first capacitor C1 is formed between a first metal layer M1 (gate electrode) and a second metal layer M2. The second capaci tor C2 is also shown diagrammatically in FIGS. 2 and 3 and is formed between the second metal layer M2 and an indium tin oxide (ITO) layer 20. For capacitor C1, metal layer M1 forms the first plate of the capacitor and metal layer M2 forms the second plate of the capacitor and the dielectric material therebetween is the gate insulator 22. For capacitor C2, the second plate is fabricated by the same metal layer M2 and the first plate is formed by the ITO layer 20. The dielectric between these two plates is the passivation insu lator layer Capacitors C1 and C2 therefore share one plate, namely the metal layer M2, and the two capacitors are electrically connected in parallel to each other by the ITO layer 20 making contact with the metal layer M1 by means of Via 3 at region For fabricating such an a-si TFT-LCD a five-mask process is typically used. Such a process is well known in the art. First, the gate metal M1 is deposited on a glass Substrate 30. This gate metal is then patterned to the particular design needed for the pixels. A nitride layer is then deposited. Part of the nitride layer is the gate insulator layer 22. This is followed by the forming of an amorphous silicon (a-si) and n+ doped amorphous silicon layer (n+ a-si) by a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) process. In addition, n+ a-si and a-si islands are formed on the nitride layer. Then a metal layer is deposited and patterned so as to form the source-drain electrode and the shared capacitor plate M2. After the etching of n+a-si to form the conducting channel for the thin film transistor (TFT) 50, a passivation insulator layer 24 is deposited. Via holes Via 1. Via 2 and Via 3 are then created by selective etching. Via 1 is used for the drain contact, and Via 2 is used for providing a contact point on the shared capacitor plate M2. Via 3 is for providing a contact point on the gate metal layer M1 (gate electrode). Via 1 and Vail 2 are created by etching the passivation insulator layer 24, while Via 3 is created by etching both the passivation insulator layer 24 and the gate insulator layer 22. An ITO layer is then deposited on top of the etched layers and patterned. After etching, part of the ITO layer forms the pixel electrode 10, which contacts the source-drain metal or the shared capacitor plate M2 through Via 2. The pixel electrode 10 is also connected to the drain contact through Via 1. As such, the shared capacitor plate M2 is electrically connected to the drain of the TFT 50 through the pixel electrode 10. The part of the ITO layer that forms the ITO layer 20 and serves as the top capacitor plate for storage capacitor C2 is connected to the gate electrode (gate metal) M1 through Via 3 (see FIG. 7). In this manner, a stacked storage capacitor structure comprising capacitors C1 and C2 is formed As can be seen in FIGS. 2 and 3, this stacked storage capacitor structure effectively uses the same general area 12 (see FIG. 1) that would otherwise be used for a storage capacitor comprising only a single pair of plates; but by the design of the present invention, the stacked storage capacitor effectively obtains a second pair of plates to form capacitor C2, thereby nearly doubling the total capacitance of the storage capacitor while maintaining approximately the same area that would otherwise be used to form a storage capacitor with only a single pair of plates. The equivalent circuit of the pixel structure of FIG. 1 is shown in FIG FIGS. 4, 5 and 6 show another technique used to form an a-si TFT-LCD display known as storage capacitor on-common (Cs-on-com) design. As seen in FIG. 4, two pixel electrode segments 11 and 11' are separated by a region 13 having a common line M1. It is in this region that the stacked storage capacitor structure according to the present invention is formed FIGS. 5 and 6 show the cross-sectional views taken along lines 5-5 and 6-6' respectively. In this fabrica tion design, capacitor C1 has a first plate formed by the metal layer M1 (common line) and a second plate formed by the source-drain metal M2. The gate insulator layer 22 forms the dielectric for capacitor C1. The second capacitor C2 has a first plate formed by the ITO layer 20 and a second plate formed by the source-drain metal M2. The passivation insulator layer 24 is the dielectric for capacitor C2. Thus, C1 and C2 have a shared capacitor plate M2. The pixel electrode 11' is connected to the drain electrode 28 of the TFT 50 by Via 1 (see FIG. 4). The pixel electrode segment 11" is also connected to the shared capacitor plate M2 through Via 4. Similarly, the pixel electrode segment 11 is connected to the shared capacitor plate M2 through Via 3. The ITO layer 20 for capacitor C2 is connected to the common line M1 through Via 2 see FIG. 8). In this manner, a stacked storage capacitor structure is formed. The equivalent circuit for the pixel structure of FIG. 4 is shown in FIG. 8. As with the fabrication process as described in conjunction with FIGS. 2 and 3, a five-mask process can be used As can be seen in the equivalent circuits shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, the source-drain metal layer M2 is a shared capacitor plate for the storage capacitors C1 and C2 and these two capacitors are connected at Via 3 in parallel so as to increase the charge storage capacity associated with the pixel electrode 10 (FIG. 7) or with the pixel electrode segments 11, 11" (FIG. 8). In both embodiments, M1 and ITO 20 are separately used for two capacitor plates of the stacked capacitor structure, and insulator layers 22 and 24 are separately used as the dielectric for C1 and the dielectric for C2. The difference between the two embodiments is where M1 is connected to. All the electrically conductive layers M1, M2, ITO 20 and the insulator layers 22, 24 are generally required in the five-mask fabricating process for most TFT-LCD displays. It is therefore apparent from the present description that a stacked storage capacitor structure, according to the present invention, can be fabricated for a-si TFT-LCD display without additional material layers or masks. According to the present invention, the amount of pixel real estate associated with the storage capacitor is thereby minimized, which in turn maximizes the aperture ratio of the pixel, providing better performance as the resolution of the pixel increases It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations can be made in the structure and method of the present invention without departing from the scope of the present invention. As a result, it is intended that the present invention covers such modifications and variations provided that they fall within the scope of the following claims and their equivalents.
11 US 2006/ A1 Jun. 8, 2006 What is claimed is: 1. A stacked storage capacitor structure for a thin film transistor liquid crystal display having a plurality of pixels, each pixel having a pixel area, wherein at least some of the pixels have a storage capacitor formed Substantially within the pixel area and associated with a stacked storage capaci tor structure, the stacked storage capacitor structure com prising: a first storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a first electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by a second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a first insulator layer positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer, and a second storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a third electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by the second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a second insulator layer posi tioned between the first and second plates, wherein the first electrically conductive layer and the third electri cally conductive layer are electrically connected to each other so that the first and second storage capaci tors are electrically connected in parallel, and wherein the second electrically conductive layer is positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer. 2. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 1 wherein each of said at least some of the pixels has a gate line disposed at one edge section of the pixel area for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and wherein the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said one edge section. 3. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 2, wherein each of said at least Some of the pixels has a semiconductor Switching element and a pixel electrode electrically connected to the Switching element, and wherein the pixel electrode is located within the pixel area adjacent to said one edge section in a non-overlapping manner. 4. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 3, wherein the Switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control terminal, the first Switching end operatively connected to a signal line, the second end operatively connected to the pixel electrode, and wherein each of said at least some of the pixels further comprises a further gate line operatively connected to the Switching control terminal of the Switch element for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switch ing ends. 5. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 4, wherein the second electrically conductive layer (M2) is operatively connected to the second Switching end of the switching element via the pixel electrode and the first electrically conductive layer (M1) is operatively connected to the gate line. 6. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 5, wherein the first switching end is a source terminal, the second Switching end is a drain terminal, and the Switching control terminal is a gate terminal of a transistor, and wherein the first electrically conductive layer is a gate metal layer, the first insulator layer is a gate insulator layer and second electrically conductive layer is a source-drain metal layer. 7. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 6, wherein the third electrically conductive layer is made Substantially of indium-tin oxide, and the second insulator layer is a passivation insulator layer. 8. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 7, wherein part of the passivation insulator layer is disposed adjacent to part of the gate insulator layer, and the pixel electrode is made Substantially of indium-tin oxide, and wherein at least part of the pixel electrode and part of the third electrically conductor layer are disposed on different sections of the passivation insulator layer. 9. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 1, wherein each of said at least Some of the pixels comprises a semiconductor Switching element; a gate line disposed at one edge section of the pixel area for controlling the Switching element; and a common line disposed in a pixel section spaced from the gate line for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and wherein the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said pixel section. 10. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 9, wherein each of said at least some of the pixels has a first pixel electrode segment and a second pixel electrode segment located within the pixel area and separated by said pixel section in a non-overlapping manner. 11. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 9, wherein the common line is substantially parallel to the gate line. 12. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 10, wherein the Switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control termi nal, the first Switching end operatively connected to a signal line, the second end operatively connected to the first pixel electrode segment, and wherein each of said at least some of the pixels further comprises a gate line operatively con nected to the switching control terminal of the switch element for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switching ends. 13. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 12, wherein the second electrically conductive layer (M2) is operatively connected to the second Switching end of the switching element via the pixel electrode and the first electrically conductive layer (M1) is operatively connected to the common line. 14. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 13, wherein the first Switching end is a Source termi nal, the second Switching end is a drain terminal, and the Switching control terminal is a gate terminal of a transistor, and wherein the first electrically conductive layer is a gate metal layer, the first insulator layer is a gate insulator layer and second electrically conductive layer is a source-drain metal layer. 15. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 14, wherein the third electrically conductive layer is made Substantially of indium-tin oxide, and the second insulator layer is a passivation insulator layer. 16. A stacked storage capacitor structure as defined in claim 15, wherein part of the passivation insulator layer is disposed adjacent to part of the gate insulator layer, and the first and second pixel electrode segment are made Substan tially of indium-tin oxide, and wherein at least part of the first and second pixel electrode segments and part of the
12 US 2006/ A1 Jun. 8, 2006 third electrically conductor layer are disposed on different sections of the passivation insulator layer. 17. A method of increasing charge storage capacity in a thin film transistor liquid crystal display having a plurality of pixels, each pixel having a pixel area and a pixel electrode located within the pixel area, wherein at least some of the pixels have a storage capacitor structure formed at a section of the pixel area substantially within the pixel area for storing electric charges associated with the pixel electrode, and wherein the section is adjacent to the pixel electrode in a non-overlapping manner, said method comprising the steps of: forming a first storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a first electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by a second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a first insulator layer posi tioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer, and forming a second storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a third electrically conductive layer, a sec ond plate formed by the second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a second insulator layer positioned between the first and second plates; and electrically connecting the first electrically conductive layer to the third electrically conductive layer so that the first and second storage capacitors are electrically connected in parallel for forming the storage capacitor structure, and wherein the second electrically conduc tive layer is positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer. 18. A thin film transistor liquid crystal display compris 1ng: a plurality of pixels arranged in rows and columns, each pixel having a pixel area, a plurality of signal lines disposed between the pixel columns; and a plurality of gate lines disposed between the pixel rows, wherein at least Some of the pixels have a storage capacitor formed substantially within the pixel area, the storage capacitor comprising: a first storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a first electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by a second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a first insulator layer positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer, and a second storage capacitor having a first plate formed by a third electrically conductive layer, a second plate formed by the second electrically conductive layer and a dielectric formed by a second insulator layer posi tioned between the first and second plates, wherein the first electrically conductive layer and the third electri cally conductive layer are electrically connected to each other so that the first and second storage capaci tors are electrically connected in parallel, and wherein the second electrically conductive layer is positioned between the first electrically conductive layer and the third electrically conductive layer. 19. A thin-film liquid crystal display as defined in claim 18, wherein each of said at least some of the pixels has a further gate line disposed at one edge section of the pixel area for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and wherein the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said one edge section. 20. A thin-film liquid crystal display as defined in claim 18, wherein each of said at least some of the pixels has a semiconductor Switching element and a pixel electrode electrically connected to the Switching element, and wherein the pixel electrode is located within the pixel area adjacent to said one edge section in a non-overlapping manner. 21. A thin-film liquid crystal display as defined in claim 20, wherein the Switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control terminal, the first Switching end operatively connected to one of said plurality of signal lines, the second end operatively con nected to the pixel electrode, and wherein the switching control terminal of the switch element is operatively con nected to one of said plurality of gate lines for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switching ends. 22. A thin-film liquid crystal display as defined in claim 18, wherein each of said at least some of the pixels com prises a semiconductor Switching element operatively connected to the gate line a common line disposed in a pixel section spaced from the gate line for controlling electric charges in the storage capacitor, and wherein the storage capacitor is formed Substantially in said pixel section. 23. A thin-film liquid crystal display as defined in claim 18, wherein each of said at least some of the pixels has a first pixel electrode segment and a second pixel electrode seg ment located within the pixel area and separated by said pixel section in a non-overlapping manner. 24. A thin-film liquid crystal display as defined in claim 23, wherein the common line is disposed between two adjacent gate lines. 25. A thin-film liquid crystal display as defined in claim 23, wherein the Switching element has a first Switching end, a second Switching end and a Switching control terminal, wherein the first switching end is operatively connected to one of said plurality of signal lines, the second end is operatively connected to the first pixel electrode segment, and the switching control terminal of the switch element is operatively connected to one of the gate lines for causing the opening and closing between the first and second Switching ends.
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015
 (19) United States US 20150212614A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0212614 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) INTEGRATED POLARIZER AND (52) U.S. Cl. CONDUCTIVE
(19) United States US 20150212614A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0212614 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) INTEGRATED POLARIZER AND (52) U.S. Cl. CONDUCTIVE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0018076 A1 Chen et al. US 200700 18076A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ELECTROMAGNETIC DIGITIZER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0018076 A1 Chen et al. US 200700 18076A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ELECTROMAGNETIC DIGITIZER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,449,544 B2
 USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
VDD. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. I Data. (76) Inventors: Wen-Cheng Yen, Taichung (TW);
 (19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
y y (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, C 410C 422b 4200
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
E3, ES 2.ÉAN 27 Asiaz
 (19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 US008269735B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,269,735 B2 Sep. 18, 2012 (54) TOUCH SCREEN DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Kang-Woo Kim, Seoul (KR); Dong-Gi Seong,
US008269735B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,269,735 B2 Sep. 18, 2012 (54) TOUCH SCREEN DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Kang-Woo Kim, Seoul (KR); Dong-Gi Seong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
Publication number: A2. Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/ Meadowridge Drive Garland, Texas 75044(US)
 Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
120x124-st =l. (12) United States Patent. (10) Patent No.: US 9,046,952 B2. 220a 220b. 229b) s 29b) al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070107206A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0107206A1 Harris et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A Publication Classification
US 20070107206A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0107206A1 Harris et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A Publication Classification
40- It i? l? l (r. Nl
 (19) United States US 2014032O765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0320765 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND FABRICATION Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014032O765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0320765 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND FABRICATION Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7656482B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) TRANSFLECTIVE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY AND PANEL THEREFOR (75) Inventors: Seong-Ho Kim, Yongin-si (KR); Sung-Hwan Cho, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Jae-Hyun Kim,
USOO7656482B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) TRANSFLECTIVE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY AND PANEL THEREFOR (75) Inventors: Seong-Ho Kim, Yongin-si (KR); Sung-Hwan Cho, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Jae-Hyun Kim,
R GBWRG B w Bwr G B wird
 US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2. Chokkalingam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 1, 2009
 USOO7626469B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.626.469 B2 Chokkalingam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 1, 2009 (54) ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search... 33 1/8, 331/16-18,
USOO7626469B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.626.469 B2 Chokkalingam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 1, 2009 (54) ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search... 33 1/8, 331/16-18,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O145694A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Jang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O145694A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Jang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,314,819 B2. Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012
 USOO8314819B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) DISPLAYS WITH INTEGRATED 6,830,339 B2 * 12/2004 Maximus... 353/20 BACKLIGHTING 6,878.494 B2
USOO8314819B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) DISPLAYS WITH INTEGRATED 6,830,339 B2 * 12/2004 Maximus... 353/20 BACKLIGHTING 6,878.494 B2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008
 (19) United States US 200800 12008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0012008 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) MAKING ORGANIC THIN FILM (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 200800 12008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0012008 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) MAKING ORGANIC THIN FILM (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
Si,"Sir, sculptor. Sinitialising:
 (19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
(19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Kalevo (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2008
 US 2008.0075354A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0075354 A1 Kalevo (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMOVING SINGLET AND COUPLET (22) Filed: Sep. 25, 2006 DEFECTS FROM
US 2008.0075354A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0075354 A1 Kalevo (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMOVING SINGLET AND COUPLET (22) Filed: Sep. 25, 2006 DEFECTS FROM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1
 USOO6211068B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DUAL DAMASCENE PROCESS FOR 5,981,377 * 11/1999 Koyama... 438/633 MANUFACTURING INTERCONNECTS
USOO6211068B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DUAL DAMASCENE PROCESS FOR 5,981,377 * 11/1999 Koyama... 438/633 MANUFACTURING INTERCONNECTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0362960 A1 Chang et al. US 20150362960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCHELECTRONIC DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0362960 A1 Chang et al. US 20150362960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCHELECTRONIC DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0175533A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0175533 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2013 (54) SUBSTRATE INCLUDING THIN FILM Publication Classification
US 2013 0175533A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0175533 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2013 (54) SUBSTRATE INCLUDING THIN FILM Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
M3 d. (12) United States Patent US 7,317,435 B2. Jan. 8, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Wei-Chieh Hsueh, Tainan (TW) T GND
 US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
HHHHHH. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,079,455. McCafferty et al. tor to provide a negative feedback path for charging the
 United States Patent (19) McCafferty et al. (54. SURGE CURRENT-LIMITING CIRCUIT FOR A LARGE-CAPACITANCE LOAD 75 Inventors: Lory N. McCafferty; Raymond K. Orr, both of Kanata, Canada 73) Assignee: Northern
United States Patent (19) McCafferty et al. (54. SURGE CURRENT-LIMITING CIRCUIT FOR A LARGE-CAPACITANCE LOAD 75 Inventors: Lory N. McCafferty; Raymond K. Orr, both of Kanata, Canada 73) Assignee: Northern
United States Patent (19) Morris
 United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120169707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169707 A1 EBSUNO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC EL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification CONTROL
US 20120169707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169707 A1 EBSUNO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC EL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification CONTROL
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al.
 United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2
 USOO6683667B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2 Jin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 2004 (54) TFT-LCD WITH SCATTERING LAYER, 4,904,060 A * 2/1990 Grupp... 349/162 REFLECTOR,
USOO6683667B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2 Jin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 2004 (54) TFT-LCD WITH SCATTERING LAYER, 4,904,060 A * 2/1990 Grupp... 349/162 REFLECTOR,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Su US 2005O127853A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) MULTI-LEVEL DC BUS INVERTER FOR PROVIDING SNUSODAL AND PWM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Su US 2005O127853A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) MULTI-LEVEL DC BUS INVERTER FOR PROVIDING SNUSODAL AND PWM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,770,955 B1
 USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
(12) United States Patent
 US008193047B2 (12) United States Patent Ryoo et al. (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE HAVING SUFFICIENT PROCESS MARGIN AND METHOD OF FORMING SAME (75) Inventors: Man-Hyoung Ryoo, Gyeonggi-do (KR): Gi-Sung Yeo,
US008193047B2 (12) United States Patent Ryoo et al. (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE HAVING SUFFICIENT PROCESS MARGIN AND METHOD OF FORMING SAME (75) Inventors: Man-Hyoung Ryoo, Gyeonggi-do (KR): Gi-Sung Yeo,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Eklund (54) HIGH VOLTAGE MOS TRANSISTORS 75) Inventor: Klas H. Eklund, Los Gatos, Calif. 73) Assignee: Power Integrations, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 41,994 22
United States Patent (19) Eklund (54) HIGH VOLTAGE MOS TRANSISTORS 75) Inventor: Klas H. Eklund, Los Gatos, Calif. 73) Assignee: Power Integrations, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 41,994 22
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1 Ochiai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 US 20130194531A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194531 A1 Ochiai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 1, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classi?cation
US 20130194531A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194531 A1 Ochiai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 1, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classi?cation
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1. Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO6208561B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1 Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 9 (54) METHOD TO REDUCE CAPACITIVE 5,787,037 7/1998 Amanai... 365/185.23 LOADING IN
USOO6208561B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1 Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 9 (54) METHOD TO REDUCE CAPACITIVE 5,787,037 7/1998 Amanai... 365/185.23 LOADING IN
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822
 34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
United States Patent (19) Archibald
 United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,355,741 B2
 US0095741B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeon et al. () Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING A GATE (56) References Cited DRIVE CIRCUIT (71) Applicant: Samsung Display
US0095741B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeon et al. () Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING A GATE (56) References Cited DRIVE CIRCUIT (71) Applicant: Samsung Display
S/AN a. ', (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. El 1 -
 (19) United States US 20030011729A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0011729 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) VERTICALLY ALIGNED MODE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY WITH
(19) United States US 20030011729A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0011729 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) VERTICALLY ALIGNED MODE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O1893.99A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0189399 A1 Hu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) BIAS CIRCUIT FOR A RADIO FREQUENCY (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2004O1893.99A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0189399 A1 Hu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) BIAS CIRCUIT FOR A RADIO FREQUENCY (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
Computer. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Centralier. ining. sci: {xifoie. ataxis: 8.
 (19) United States US 201201696.60A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169660 A1 SEO (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING TOUCH SENSOR (76) Inventor: Seong-Mo
(19) United States US 201201696.60A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169660 A1 SEO (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING TOUCH SENSOR (76) Inventor: Seong-Mo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007024.1999A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007 (54) SYSTEMS FOR DISPLAYING IMAGES (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/76 INVOLVING REDUCED MURA
US 2007024.1999A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007 (54) SYSTEMS FOR DISPLAYING IMAGES (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/76 INVOLVING REDUCED MURA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060055032A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0055032A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2006 (54) PACKAGING WITH METAL STUDS FORMED ON SOLDER PADS
(19) United States US 20060055032A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0055032A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2006 (54) PACKAGING WITH METAL STUDS FORMED ON SOLDER PADS
United States Patent (19) Davis
 United States Patent (19) Davis 54 ACTIVE TERMINATION FOR A TRANSMISSION LINE 75 Inventor: 73 Assignee: Thomas T. Davis, Bartlesville, Okla. Phillips Petroleum Company, Bartlesville, Okla. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Davis 54 ACTIVE TERMINATION FOR A TRANSMISSION LINE 75 Inventor: 73 Assignee: Thomas T. Davis, Bartlesville, Okla. Phillips Petroleum Company, Bartlesville, Okla. 21 Appl. No.:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007724243B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,724.243 B2 Geaghan (45) Date of Patent: May 25, 2010 (54) TOUCH SENSORS INCORPORATING 4,731,694. A * 3/1988 Grabner et al... 361,280 CAPACTIVELY
US007724243B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,724.243 B2 Geaghan (45) Date of Patent: May 25, 2010 (54) TOUCH SENSORS INCORPORATING 4,731,694. A * 3/1988 Grabner et al... 361,280 CAPACTIVELY
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867. Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998
 USOO5804867A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867 Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998 54) THERMALLY BALANCED RADIO 5,107,326 4/1992 Hargasser... 257/579 FREQUENCY POWER TRANSISTOR
USOO5804867A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867 Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998 54) THERMALLY BALANCED RADIO 5,107,326 4/1992 Hargasser... 257/579 FREQUENCY POWER TRANSISTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0193956A1 XIAO et al. US 2017.0193956A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) A GOA CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0193956A1 XIAO et al. US 2017.0193956A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) A GOA CIRCUIT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2017
 (19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
YY/ Y(X NYNYYYYYY / 2 / / / MA / 13b. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A a. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0175674 A1 Shimizu et al. US 2011 0175674A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 21, 2011 (54) METHOD OF DRIVING TRANSISTOR AND DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0175674 A1 Shimizu et al. US 2011 0175674A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 21, 2011 (54) METHOD OF DRIVING TRANSISTOR AND DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) Patent Application Publication
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Ryken et al. US 2003.0076261A1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0076261 A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIPURPOSE MICROSTRIPANTENNA FOR USE ON MISSILE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Ryken et al. US 2003.0076261A1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0076261 A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIPURPOSE MICROSTRIPANTENNA FOR USE ON MISSILE (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0022695A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0022695 A1 Schmidt (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRICAL MULTILAYER COMPONENT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIC I/146 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 2014.0022695A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0022695 A1 Schmidt (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRICAL MULTILAYER COMPONENT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIC I/146 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
(19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
United States Patent Patent Number: 5,683,539 Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997
 USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
United States Patent (19)
 US006002389A 11 Patent Number: 6,002,389 Kasser (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 1999 United States Patent (19) 54) TOUCH AND PRESSURE SENSING METHOD 5,398,046 3/1995 Szegedi et al.... 345/174 AND APPARATUS
US006002389A 11 Patent Number: 6,002,389 Kasser (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 1999 United States Patent (19) 54) TOUCH AND PRESSURE SENSING METHOD 5,398,046 3/1995 Szegedi et al.... 345/174 AND APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,387,795 B1
 USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
us/ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 (19) United States / 112 / 108 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 (19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140353625A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0353625 A1 Yet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODES Publication Classification
US 20140353625A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0353625 A1 Yet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODES Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010OOO1276A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0001276 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 7, 2010 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR ARRAY PANEL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010OOO1276A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0001276 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 7, 2010 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR ARRAY PANEL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9641 137B2 (12) United States Patent Duenser et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,641,137 B2 May 2, 2017 (54) ELECTRIC AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT FOR AMPLIFYING AN OUTPUT SIGNAL OF A MCROPHONE
USOO9641 137B2 (12) United States Patent Duenser et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,641,137 B2 May 2, 2017 (54) ELECTRIC AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT FOR AMPLIFYING AN OUTPUT SIGNAL OF A MCROPHONE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Nakayama et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,916,413 Apr. 10, 1990 54 PACKAGE FOR PIEZO-OSCILLATOR (75) Inventors: Iwao Nakayama; Kazushige Ichinose; Hiroyuki Ogiso,
United States Patent (19) Nakayama et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,916,413 Apr. 10, 1990 54 PACKAGE FOR PIEZO-OSCILLATOR (75) Inventors: Iwao Nakayama; Kazushige Ichinose; Hiroyuki Ogiso,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O217945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0217945 A1 Miyamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TOUCH SENSOR, DISPLAY WITH TOUCH SENSOR, AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
(19) United States US 2004O217945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0217945 A1 Miyamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TOUCH SENSOR, DISPLAY WITH TOUCH SENSOR, AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2. Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010
 US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
United States Patent (19) Nilssen
 United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
(12) United States Patent
 US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
