(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US 2010OOO1276A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 7, 2010 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR ARRAY PANEL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data AND MANUFACTURING METHOD OF THE SAME Jul. 7, 2008 (KR) O08OO65548 Publication Classification (75) Inventors: Jang-Soo KIM, Yongin-si (KR): (51) Int. Cl. Sang-Soo KIM, Seoul (KR): HOIL 27/088 ( ) Shi-Yul KIM, Yongin-si (KR): HOIL 2 1/77 ( ) Jang-Sub KIM, Suwon-si (KR) (52) U.S. C /59:438/29;257/E27.06: 257/E (57) ABSTRACT Correspondence Address: CANTOR COLBURN, LLP A thin film transistor array panel includes an insulating Sub 20 Church Street, 22nd Floor strate, a gate line and a data line disposed on the insulating Hartford, CT (US) Substrate and insulated from and intersecting each other, a thin film transistor connected to the gate line and the data line, a partition disposed corresponding to the gate line and the (73) Assignee: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS data line and defining a color filter filling region, a color filter CO.,LTD., Suwon-si (KR) disposed in the filling region, a passivation layer disposed on the color filter and the partition, and a pixel electrode dis posed on the passivation layer and connected to the thin film (21) Appl. No.: 12/335,928 transistor through a contact hole disposed through the passi vation layer and the color filter. A plane shape of the color (22) Filed: Dec. 16, 2008 filter filling region is Substantially a rectangle a - 191b. 191a 191b a a XIV XIV 361b 36b 185b a 175b a S121 N Y 154b 173b124b 124a 173a154a
2 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 1 of 16 US 2010/ A1 FIG.1 PXa
3 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 2 of 16 US 2010/ A1 FIG b 191a aaraasasasa are Nz Zazzazzazza 135 % b 185b 175b 91 A. 191a 2 III N 171a III 185a 175a b 173b124b 124a 173a154a 121
4 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 3 of 16 US 2010/ A1 7 / \\ V
5 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 4 of 16 US 2010/ A1 FIG.4
6 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 5 of 16 US 2010/ A1
7 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 FIG.6 Sheet 6 of 16 US 2010/ A1 %-191b () 185b 175b No a
8 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 7 of 16 US 2010/ A1 FIG.7 91S a N 185a 91b. 175a غ Ø ZZZINI X 175b 185b
9 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 8 of 16 US 2010/ A1 s an s 2
10 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 9 of 16 US 2010/ A1 6 OIH
11 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 10 of 16 US 2010/ A1
12
13 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 12 of 16 US 2010/ A1 FIG.12 s N % 3N W NN BY-361a % % N 191a 3 s E}191 2 N 2 2 N % % N. 131 away AAx. N is II His a % Os-171a XIV XIV 361b - 2: Y 361b. 185b 175b is Nail is 3S. 175a in E b 173b124b 124a 173a154a
14 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 13 of 16 US 2010/ A1 FIG b 361b
15 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 14 of 16 US 2010/ A b191b 91 afs." 11 ATA ATH b 165b. 175b p 154a165a175a b 165b. 175b p 154a165a175a 230
16 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 15 of 16 US 2010/ A1 FIG.16 23O 154b 165b. 175b p 154a 165a175a 230
17 Patent Application Publication Jan. 7, 2010 Sheet 16 of 16,)? US 2010/ A1
18 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 THIN FILMITRANSISTOR ARRAY PANEL AND MANUFACTURING METHOD OF THE SAME This application claims priority to Korean Patent Application No filed on Jul. 7, 2008, and all the benefits accruing therefrom under 35 U.S.C. S119, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0002 (a) Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a thin film transistor array panel and a manufacturing method thereof (b) Description of the Related Art A liquid crystal display ( LCD) is one of the most widely used flat panel displays ( FPD), and it is composed of two display panels on which field generating electrodes are formed, and a liquid crystal layer interposed between the two display panels. A Voltage is applied to the field generating electrodes to generate an electric field on the liquid crystal layer, and the orientation of liquid crystal molecules of the liquid crystal layer is determined and the polarization of incident light is controlled through the generated electric field to display an image. Among the different types of LCDs, an LCD having a struc ture in which field generating electrodes are respectively formed on two display panels is widely used. Among the two display panels, a plurality of pixel electrodes and thin film transistors are arranged in a matrix on one display panel (hereinafter referred to as a thin film transistor array panel) and color filters of red, green, and blue are formed thereon, and a common electrode covers the entire surface of the other display panel (hereinafter referred to as a common electrode panel ). BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION As a liquid crystal display may include the pixel electrodes and the color filters disposed on different display panels, there are technical difficulties in manufacturing the liquid crystal display. For example, it is difficult to align the pixel electrodes and the color filters with each other, thereby generating an alignment error. To address this problem, a color filter on array ( CoA) structure, in which the pixel electrode and the color filter are formed on the same display panel, may be employed In a manufacturing method of forming the pixel electrode and the color filter on the same display panel, when forming the color filter along with the thin film transistor, the color filter may beformed by an inkjet printing method. In the inkjet method, liquid ink is sprayed (e.g., jetted) to predeter mined divided portions to implement eachink-colored image, and a plurality of colors including red, green, and blue can be advantageously formed at one time such that the manufactur ing process, time, and cost can be considerably reduced The liquid ink may be used in the inkjet printing Such that partitions to enclose the ink are required. The par titions prevent light leakage and have a function to enclose each color filter such that the partitions may have various shapes according to the shape of the pixel electrode and a position of a contact hole. However, if the partitions have various shapes, various mask patterns to form the various partitions are additionally required, and may increase the manufacturing process, time, and cost. Also, when filling the color filters in the partitions, a portion where the color filters are not sufficiently filled according to a complicated shape of the partitions may be generated, and the color filters may overflow to a neighboring pixel An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides a thin film transistor array panel and a manufactur ing method thereof including a partition and a pixel electrode having various patterns An exemplary embodiment of a thin film transistor array panel according includes an insulating Substrate, a gate line and a data line disposed on the insulating Substrate and insulated from and intersecting each other, a thin film tran sistor connected to the gate line and the data line, a partition disposed corresponding to the gate line and the data line and defining a color filter filling region, a color filter disposed in the filling region, a passivation layer disposed on the color filter and the partition, and a pixel electrode disposed on the passivation layer and connected to the thin film transistor through a contact hole disposed in the passivation layer and the color filter. A plane shape of the color filter filling region is Substantially a rectangle The boundaries of the passivation layer and the color filter adjacent to the contact hole may be disposed substantially coplanarly with each other The contact hole may be disposed at a position in the filling region The thickness of the partition and the color filter may be more than 0.3 micrometer (Lm), where the thickness is taken Substantially perpendicular to the insulating Sub Strate The partition may include a black pigment, and the passivation layer may include a photosensitive organic mate rial The partition may include an expansion portion dis posed in the filling region, and the contact hole may be dis posed coinciding with the expansion portion The boundaries of the passivation layer and the expansion portion defining the contact hole may be disposed Substantially coplanarly An exemplary embodiment of a manufacturing method of a thin film transistor array panel includes forming a gate line including a gate electrode on a Substrate, forming a gate insulating layer on the gate line, forming a semicon ductor and an ohmic contact layer on the gate insulating layer, forming a data line including a source electrode and a drain electrode on the ohmic contact layer, forming a lower passi Vation layer on the data line and the drain electrode, forming apartition with a quadrangle shape in a plan view on the lower passivation layer and corresponding to the gate line and the data line, forming a color filter in a filling region defined by the partition, forming an upper passivation layer on the color filter, simultaneously etching the upper passivation layer and the color filter to form a contact hole exposing the drain electrode, and forming a pixel electrode connected to the drain electrode through the contact hole on the upper passi Vation layer An exemplary embodiment of a manufacturing method of a thin film transistor array panel according to the present invention includes forming agate line including a gate electrode on a Substrate, forming a gate insulating layer on the gate line, forming a semiconductor and an ohmic contact layer on the gate insulating layer, forming a data line includ ing a source electrode and a drain electrode on the ohmic
19 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 contact layer, forming a lower passivation layer on the data line and the drain electrode, forming a partition including a straight portion corresponding to the gate line and data line, and an expansion portion overlapping at least a portion of the drain electrode on the lower passivation layer, forming a color filter in the filling region defined by the partition, forming an upper passivation layer on the color filter, simultaneously etching the upper passivation layer and the color filter to form a contact hole exposing the drain electrode, and forming a pixel electrode connected to the drain electrode through the contact hole on the upper passivation layer In an exemplary embodiment, the partition does not include a curved portion or a protrusion, such that the shape of the partition is not changed even though a contact hole is disposed in varying positions of a pixel, and the same mask for the partition may be used for various patterns of the pixel electrode In an exemplary embodiment, a portion of the thin film transistor array panel where the contact hole will be located, is not opened prior to the forming the partition con tact hole, such that an overall area of the partition may be minimized, thereby increasing the aperture ratio. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0021 FIG. 1 is an equivalent circuit diagram of an exem plary embodiment of one pixel in a liquid crystal display, according to the present invention FIG. 2 is a layout view of an exemplary embodiment of a liquid crystal display according to the present invention FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view of the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 2 taken along line III-III FIG. 4 is a top plan view showing an exemplary embodiment of a partition of the liquid crystal display shown in FIG FIG. 5 is a top plan view of an exemplary embodi ment a basic electrode for a pixel electrode, according to the present invention FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 are layout views showing exem plary embodiments of a pixel electrode, a drain electrode and a contact hole, according to the present invention FIGS. 8 to 11 are cross-sectional views sequentially showing an exemplary embodiment of a manufacturing method of a thin film transistor array panel for the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 2 and FIG FIG. 12 is a layout view of another exemplary embodiment of a thin film transistor array panel of a liquid crystal display, according to the present invention FIG. 13 is a top plan view showing an exemplary embodiment of a partition of the thin film transistor array panel shown in FIG FIG. 14 is a cross-sectional view of the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 12 taken along line XIV-XIV FIG. 15 and FIG. 16 are cross-sectional views sequentially showing an exemplary embodiment of a manu facturing method of the thin film transistor array panel for the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 12 and FIG FIG. 17 is a cross-sectional view of the thin film transistor array panel for the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 taken along the line III-III. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION The present invention will be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which exemplary embodiments of the invention are shown. As those skilled in the art would realize, the described embodiments may be modified in various different ways, all without departing from the spirit or scope of the present invention In the drawings, the thickness of layers, films, pan els, regions, etc., are exaggerated for clarity. Like reference numerals designate like elements throughout the specifica tion. It will be understood that when an element such as a layer, film, region, or substrate is referred to as being on another element, it can be directly on the other element or intervening elements may also be present. In contrast, when an element is referred to as being directly on' another ele ment, there are no intervening elements present It will be understood that, although the terms first, second, third, etc., may be used herein to describe various elements, components, regions, layers and/or sections, these elements, components, regions, layers and/or sections should not be limited by these terms. These terms are only used to distinguish one element, component, region, layer or section from another region, layer or section. Thus, a first element, component, region, layer or section discussed below could be termed a second element, component, region, layer or section without departing from the teachings of the present invention Spatially relative terms, such as lower, under. upper and the like, may be used herein for ease of descrip tion to describe the relationship of one element or feature to another element(s) or feature(s) as illustrated in the figures. It will be understood that the spatially relative terms are intended to encompass different orientations of the device in use or operation, in addition to the orientation depicted in the figures. For example, if the device in the figures is turned over, elements described as lower or under' relative to other elements or features would then be oriented upper' or over relative to the other elements or features. Thus, the exemplary term under can encompass both an orientation of above and below. The device may be otherwise oriented (rotated 90 degrees or at other orientations) and the spatially relative descriptors used herein interpreted accordingly The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only and is not intended to be limiting of the invention. As used herein, the singular forms a, an and the are intended to include the plural forms as well, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. It will be further understood that the terms comprises' and/ or comprising, when used in this specification, specify the presence of stated features, integers, steps, operations, ele ments, and/or components, but do not preclude the presence or addition of one or more other features, integers, steps, operations, elements, components, and/or groups thereof Embodiments of the invention are described herein with reference to cross-section illustrations that are schematic illustrations of idealized embodiments (and intermediate structures) of the invention. As such, variations from the shapes of the illustrations as a result, for example, of manu facturing techniques and/or tolerances, are to be expected. Thus, embodiments of the invention should not be construed as limited to the particular shapes of regions illustrated herein but are to include deviations in shapes that result, for example, from manufacturing For example, an implanted region illustrated as a rectangle will, typically, have rounded or curved features and/or a gradient of implant concentration at its edges rather than a binary change from implanted to non-implanted
20 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 region. Likewise, a buried region formed by implantation may result in some implantation in the region between the buried region and the Surface through which the implantation takes place. Thus, the regions illustrated in the figures are schematic in nature and their shapes are not intended to illus trate the actual shape of a region of a device and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention Unless otherwise defined, all terms (including tech nical and Scientific terms) used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. It will be further understood that terms, such as those defined in commonly used dictio naries, should be interpreted as having a meaning that is consistent with their meaning in the context of the relevant art and will not be interpreted in an idealized or overly formal sense unless expressly so defined herein All methods described herein can be performed in a suitable order unless otherwise indicated herein or otherwise clearly contradicted by context. The use of any and all examples, or exemplary language (e.g., such as'), is intended merely to better illustrate the invention and does not pose a limitation on the scope of the invention unless other wise claimed. No language in the specification should be construed as indicating any non-claimed element as essential to the practice of the invention as used herein Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings FIG. 1 is an equivalent circuit diagram of an exem plary embodiment of one pixel in a liquid crystal display, according to the present invention. 0044) Referring to FIG. 1, a liquid crystal display includes signal lines including a plurality of a gate line GL, a plurality of a pairs of data lines DLa and DLb, a plurality of a storage electrode line SL, and a plurality of a pixel PX connected to the signal lines, respectively. The liquid crystal display includes a lower panel 100 and an upper panel 200 facing each other, and a liquid crystal layer 3 interposed between the lower and upper panels 100 and Each pixel PX includes a pair of subpixels PXa and PXb. Each subpixel PXa/PXb respectively includes a switch ing element Qa? Qb, a liquid crystal capacitor Clca/Clcb, and a storage capacitor Csta/Cstb Each switching element Qa/Qb may be a three-ter minal element, such as a thin film transistor, disposed on the lower panel 100. The thin film transistor may include a con trol terminal connected to the gate line GL, an input terminal connected to the data line DLa/DLb, and an output terminal connected to the liquid crystal capacitor Clca/Clcb and the storage capacitor Csta/Cstb In the illustrated embodiment, the liquid crystal capacitor Clca/Clcb uses a subpixel electrode 191a/191b and a common electrode 270 as two terminals. The liquid crystal layer 3 disposed between subpixel electrodes 191a/191b and the common electrode 270, functions as a dielectric material In an exemplary embodiment, the storage electrode line SL is disposed on the lower display panel 100, and a subpixel electrode 191a/191b overlaps with an insulator interposed between the storage electrode line SL and the subpixel electrode 191a/191b. A predetermined voltage, such as the common Voltage Vcom, is applied to the storage capacitor Csta/Cstb, which functions as an assistant to the liquid crystal capacitor Clca/Clcb A predetermined difference in voltage is generated between Voltages charged to two liquid crystal capacitors Clca and Clcb. In one exemplary embodiment, the data volt age applied to the liquid crystal capacitor Clca is less or more than the data Voltage applied to the liquid crystal capacitor Clcb. When the voltages of the first and second liquid crystal capacitors Clca and Clcb are appropriately adjusted, it is possible to make images viewed from a side of the liquid crystal display be as similar as possible to the images viewed from a front of the liquid crystal display. Advantageously, it is possible to improve a side visibility of images displayed by the liquid crystal display Next, an exemplary embodiment of a liquid crystal display according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIG. 2 to FIG FIG. 2 is a layout view of an exemplary embodiment of a liquid crystal display according to the present invention, FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view of the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 2 taken along line III-III, FIG. 4 is a top plan view showing an exemplary embodiment of a partition of the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 2, and FIG. 5 is a top plan view of an exemplary embodiment of a basic electrode for a pixel electrode, according to the present invention Referring to FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, a liquid crystal display includes a lower display panel 100 and an upper display panel 200 facing to each other, and the liquid crystal layer 3 interposed between the two display panels 100 and 2OO Referring to FIG. 2, it appears that line III-III crosses through subpixel 191b at the right side end of Line III-III, after crossing subpixel 191a. However, FIG. 3 as a cross section along line III-III, does not show the Subpixel 191b at tie right of the drawing. Please advise if subpixel 191b should be shown in FIG Firstly, the lower panel 100 will be described A plurality of a gate line 121 and a plurality of s storage electrode line 131 and 135 are disposed on an insu lating substrate The gate lines 121 transmit gate signals, and sub stantially extend in a transverse direction. Each gate line 121 includes a plurality of first and second gate electrodes 124a and 124b protruding upward in a longitudinal direction in the layout view of FIG. 2, from a main portion of the gate line 121. The longitudinal direction is substantially perpendicular to the transverse direction, in the layout view The storage electrode lines 131 include a stem extending Substantially parallel to the gate lines 121, and a plurality of storage electrodes 135 extended from the stem. The storage electrodes 135 extend downward from the stem of the storage electrode line 131 in a direction toward the first and second gate electrodes 124a and 124b In alternative embodiments, shapes and arrange ment of the storage electrode lines 131 and/or 135 may be modified in various forms A gate insulating layer 140 is disposed on the gate lines 121 and the storage electrode lines 131 and 135. A plurality of a first semiconductor 154a and a second semicon ductor 154b are disposed on the gate insulating layer 140. In exemplary embodiments, the semiconductors 154a and 154b preferably include amorphous or crystallized silicon A pair of a plurality of ohmic contacts 161a, 161b, 163a, 163b, 165a, and 165b are disposed on the first and second semiconductors 154a and 154b. In exemplary embodiments, the ohmic contacts 161a, 161b, 163a, 163b, 165a, and 165b may include a material, such as n+hydroge
21 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 nated amorphous silicon, in which an n-type impurity is doped with a high concentration, or of silicide A plurality of a pair of data lines 171a and 171b, and a plurality of a first drain electrode 175a and a second drain electrode 175b are disposed on the ohmic contacts 161a, 161b, 163a, 163b, 165a, and 165b, and on the gate insulating layer The first and second data lines 171a and 171b trans mit data signals, extend Substantially in the longitudinal direction, and cross (e.g., overlap) the gate lines 121 and the stem of the storage electrode lines 131. Each of the first/ second data line 171a/171b includes a plurality of first/sec ond source electrodes 173a/173b extending toward the first/ second gate electrodes 124a/124b and curved with a U shape in the layout view. The first/second source electrodes 173a/173b is disposed opposite to the first/second drain elec trodes 175a/175b, with respect to the first/second gate elec trodes 124a/124b Each of the first and second drain electrodes 175a and 175b includes a first (distal) end essentially enclosed by the U shape first and second source electrodes 173a and 173b, respectively, in a layout view. From the first distal end, the first and second drain electrodes 175a and 175b extends upward (e.g., in the longitudinal direction) to a second end opposite to the first end. The second end of the first and second drain electrodes 175a and 175b, may have a relatively wide area, taken in the transverse and/or longitudinal direc tion, for connection with another layer in the liquid crystal display In alternative embodiments, shapes and arrange ment of the first and second drain electrodes 175a and 175b, and of the first and second data lines 171a and 171b, may be modified in various forms A first/second gate electrode 124a/124b, a first/sec ond source electrode 173a/173b, a first/second drain elec trode 175a/175b, and a first/second semiconductor 154a/ 154b, respectively form a first/second thin film transistor ( TFT) Qa/Qb. A channel of the first/second thin film tran sistor Qa? Qb is disposed on the first/second semiconductor 154a/154b, and defined by an between the first/second source electrode 173a/173b and the first/second drain electrode 175a/175b, respectively The ohmic contacts 163b and 165b are interposed only between the underlying semiconductor islands 154a and 154b, and the overlying data lines 171a and 171b and drain electrodes 175a and 175b. The ohmic contacts 163b and 165b reduce contact resistance between the underlying semicon ductor islands 154a and 154b, and the overlying data lines 171a and 171b and drain electrodes 175a and 175b The semiconductors 154a and 154b include a por tion exposed, e.g., not overlapped by the data lines 171a and 171b and the drain electrodes 175a and 175b, and a portion between the source electrodes 173a and 173b and the drain electrodes 175a and 175b In the illustrated embodiment, the ohmic contacts 161a, 161b, 163a, 163b, 165a, and 165b, and the data lines 171a, 171b, 173a, and 173b and the drain electrodes 175a and 175b have substantially the same plane shape as each other. The ohmic contacts 161a, 161b, 163a, 163b, 165a, and 165b, and the data lines 171a, 171b, 173a, and 173b and the drain electrodes 175a and 175b also have substantially a same plane shape as the semiconductors 154a and 154b, except for an exposed portion between the drain electrodes 175a and 175b, and the source electrodes 173a and 173b Referring to FIG. 3, a lower passivation layer 180p is disposed on the data lines 171a and 171b, the drain elec trodes 175a and 175b, and the exposed portions of the semi conductors 154a and 154b. The lower passivation layer 180p directly contacts the exposed portions of the semiconductors 154a and 154b. The lower passivation layer 180p may also directly contact an exposed portion of the gate insulating layer 140 disposed between the first and second source elec trodes 173a and 173b. In an exemplary embodiment, the lower passivation layer 180p may preferably include silicon nitride or silicon oxide A partition 361 is disposed directly on the lower passivation layer 180p. In an exemplary embodiment, the partition 361 may include a light blocking insulating material absorbing light and being black. The partition 361 may func tion as and be referred to as a light blocking member. Alter natively, a separate member from the partition, may be dis posed on the lower and/or upper panels 100 and 200 as the light blocking member. The partition 361 defines boundaries of a pixel. Referring to FIG. 4, the partition 361 is disposed corresponding to the gate lines 121 and the data lines 171a and 171b. As used herein, "corresponding means being sub stantially similar in dimension, relative positional placement and/or shape. The partition 361 includes first portions having a first extension direction substantially parallel to the trans verse direction, and second portions having a second exten sion direction Substantially parallel to the longitudinal direc tion. A width of the first portions, taken perpendicular to the first extension direction, is larger than a width of the second portions, taken perpendicular to the second extension direc tion. In the layout and plan views of FIGS. 2 and 4, a region enclosed by the partition 361, e.g., where the partition 361 forms a continuous boundary of the region, is shaped Sub stantially as a rectangle. The enclosed region functions as a filling region where a color filter 230 is filled during manu facturing. In a manufacturing process, the color filter 230 may be formed in the pixel defined by the partition 361, and the partition 361 is considered as not overlapping with or dis posed on the pixel. (0071. Again referring to FIGS. 2 and 3, the color filter 230 is disposed in the filling region Surrounded on all sides (in the layout and plan views) by a continuous portions of the parti tion The lower passivation layer 180p reduced or effec tively prevents the pigment of the color filter 230 from flow ing to the exposed semiconductors 154a and 154b An upper passivation layer 180g is disposed on the partition 361 and the color filter 230. In an exemplary embodiment, the upper passivation layer 180g may include an organic material having photosensitivity. Also, the upper passivation layer 180g preferably has a thickness, taken in a direction Substantially perpendicular to the insulating Sub strate 110, of more than 1.0 micrometer (um) to reduce a coupling effect between the pixel electrode 191 and the data lines 171a and 171b, and to substantially planarize an upper surface of the lower panel The upper passivation layer 1804, the color filter 230, and the lower passivation layer 180p include a plurality of contact holes 185a and 185b extending completely through the upper passivation layer 1804, the color filter 230, and the lower passivation layer 180p, and exposing the first and sec ond drain electrodes 175a and 175b, respectively. In an exem plary embodiment of a method of manufacturing, the contact holes 185a and 185b may be simultaneously formed in the
22 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 upper passivation layer 1804, the color filter 230, and the lower passivation layer 180p, such that boundaries defining the contact holes 185a and 185b in the upper passivation layer 1804, the color filter 230, and the lower passivation layer 180p, have substantially the same plane shape In an exemplary embodiment of the present inven tion, as shown in FIG. 4, the partition 361 is only disposed corresponding to the gate lines 121 and the data lines 171a and 171b, such that the partition 361 substantially forms a quadrangle, and is not presented in the pixel. Advantageously, the area occupied by the partition 361 is minimized, and the aperture ratio of the liquid crystal display is increased. A plurality of the pixel electrode 191 are disposed on and directly contacting the upper passivation layer 180g Each pixel electrode 191 includes the first and sec ond subpixel electrodes 191a and 191b separated from each other by a gap 91 (FIGS. 2 and 6), having a quadrangular belt shape. In exemplary embodiments, the first and second Sub pixel electrodes 191a and 191b respectively include a basic electrode 199, such as shown in FIG. 5, or at least one modi fication thereof Next, the basic electrode 199 will be described in detail with reference to FIG As shown in FIG. 5, the overall shape of the basic electrode 199 is a quadrangle in a plan view. The basic elec trode 199 includes a cross-shaped stem, including a trans verse stem 193 and alongitudinal stem 192 disposed substan tially perpendicular to each other. The basic electrode 199 is divided into a first sub-region Da, a second sub-region Db, a third sub-region Dc, and a fourth sub-region Dd by the trans verse stem 193 and the longitudinal stem 192. Each of the sub-regions Da-Da include a plurality of first to fourth minute branches 194a, 194b, 194c, and 194d The first minute branch 194a obliquely extends from the transverse stem 193 or the longitudinal stem 192 toward an upper-left direction, and the second minute branch 194b obliquely extends from the transverse stem 193 or the longitudinal stem 192 in an upper-right direction. Also, the third minute branch 194c obliquely extends from the trans verse stem 193 or the longitudinal stem 192 in a lower-left direction, and the fourth minute branch 194d obliquely extends from the transverse stem 193 or the longitudinal stem 192 in a lower-right direction. The first to fourth minute branches 194a-194d are extended in first to fourth extension directions, respectively The first to fourth minute branches 194a-194d form an angle of about 45 degrees or 135 degrees with the gate lines 121 or the transverse stem 193. The minute branches 194a 194d of two neighboring sub-regions Da-Da may disposed Substantially perpendicular to each other A width of the fourth minute branches 194a-194d taken in a direction perpendicular to the respective extension direction, may be substantially the same from a first end adjacent to the transverse stem 193 or the longitudinal stem 192, to a second (distal) end at a periphery of the basic electrode 199. Alternatively, the width of the minute branches 194a-194d may become wider at the first end and closer to the transverse stem 193 or the longitudinal stem 192. I0082) Again referring to FIG. 2 to FIG. 5, each of the first and second subpixel electrodes 191a and 191b may include one basic electrode 199. Each pixel electrode 191 includes the first and second subpixel electrodes 191a and 191b. An area occupied by the second subpixel electrode 191b may be larger than an area occupied by the first subpixel electrode 191a in the pixel electrode 191. In one exemplary embodiment, the basic electrodes 199 of the first and second subpixel elec trodes 191a and 191b, may be formed differently from each other, such that the area of the second subpixel electrode 191b being approximately 1.0 to 2.2 times the area of the first subpixel electrode 191a. I0083. Each first/second subpixel electrode 191a/191b is physically and electrically connected to the first/second drain electrode 175a/175b through the contact hole 185a/185b, respectively, and receive data Voltages from the first/second drain electrode 175a? 175b. I0084. A plane pattern of the pixel electrode 191 may be formed with various patterns, as shown in FIGS. 6 and 7 by varying the basic (e.g., reference) electrode 199. I0085 FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 are layout views showing exem plary embodiments of a pixel electrode, a drain electrode, and a contact hole, according to the present invention. I0086) Referring to FIGS. 6 and 7, the shape of the drain electrodes 175a and 175b is changed according to the plane pattern of the reference electrode 199, such that the positions of the contact holes 185a and 185b for connecting the pixel electrodes 191a and 191b are also changed. I0087 However, when the partition 361 is formed with the quadrangle shape as in the illustrated exemplary embodiment of the present invention, and the partition 361 is not presented in the pixel, manufacturing processes or a structure of the liquid crystal display are not negatively effected, even though the positions of the contact holes 185a and 185b are changed. I0088 An alignment layer 11 is disposed on and directly contacting the pixel electrode 191. I0089. Next, the upper panel 200 will be described Referring again to FIG. 3, the common electrode 270 is disposed on an insulating Substrate 210, and an align ment layer 21 is disposed thereon. The alignment layer 21 may be disposed directly on the common electrode 270 and/ or overlapping an entire Surface of the common electrode. In exemplary embodiments, each of the alignment layers 11 and 21 may be a vertical alignment layer Polarizers (not shown) may be disposed on one or more of outer surface of the display panels 100 and The liquid crystal layer 3 interposed between the lower panel 100 and the upper panel 200 includes liquid crystal molecules (not shown) having negative dielectric anisotropy If the gate lines 121 are applied with the gate signals, the data Voltage is applied to the first and second Subpixel electrodes 191a and 191b through the data lines 171a and 171b, respectively. The first and second subpixel electrodes 191a and 191b applied with the data voltage, and the common electrode 270 applied with the common voltage, together generate an electric field to the liquid crystal layer3. Edges of the minute branches 194a-194d (FIG. 5) distort the electric field to make horizontal components perpendicular to the edges of the minute branches 194a-194d. An inclination direction of the liquid crystal molecules is aligned in the direction determined by the horizontal components. The liq uid crystal molecules firstly tend to tilt in the direction per pendicular to the edges of the minute branches 194a-194d. However, the directions of the horizontal components of the electric field by the neighboring minute branches 194a-194d are opposite to each other, and the intervals between the minute branches 194a-194d are relatively narrow such that the liquid crystal molecules, tending to arrange in the oppo
23 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 site directions, are tilted in the direction parallel to the exten sion (e.g., length) direction of the minute branches 194a 194d In an exemplary embodiment of the present inven tion, the length directions in which the minute branches 194a 194d are extended in one pixel PX includes four directions, such that the inclined directions of the liquid crystal mol ecules are all the four directions. Advantageously, a viewing angle of the liquid crystal display is widened by varying the inclined directions of the liquid crystal molecules In an exemplary embodiment, the first subpixel electrode 191a and the second subpixel electrode 191b are applied with different data voltages through the different data lines 171a and 171b. The voltage of the first subpixel elec trode 191a, having the relatively smaller area, is higher than the voltage of the second subpixel electrode 191b, having the relatively larger area In this way, if the voltages of the first sub-pixel electrode 191a and the second sub-pixel electrode 191b are different from each other, the voltage applied to the first liquid crystal capacitor Clca formed between the first sub-pixel electrode 191a and the common electrode 270, and the volt age applied to the second liquid crystal capacitor Clcb formed between the second sub-pixel electrode 191b and the com mon electrode 270 are different from each other, such that the declination angle of the liquid crystal molecules of the Sub pixels PXa and PXb are different from each other. As the Voltages of the first and second liquid crystal capacitors Clca and Clcb are appropriately controlled, the images visible at a side of the liquid crystal display may be approximately or Substantially the same to the images shown at a front of the liquid crystal display, thereby improving the side visibility An exemplary embodiment of a manufacturing method of a thin film transistor array panel for the above described liquid crystal display will now be described with reference to FIGS. 8 to FIGS. 8 to 11 are cross-sectional views sequentially showing an exemplary embodiment of a manufacturing method of a thin film transistor array panel for the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 2 and FIG As shown in FIG. 8, a gate line 121 including gate electrodes 124a and 124b, is formed on an insulation sub Strate As shown in FIG. 9, a gate insulating layer 140, an amorphous silicon layer that is doped with an impurity, an amorphous silicon layer doped with an impurity, and a data conductive layer are sequentially deposited on the Substrate 110 including the gate line A photosensitive film (not shown) is coated on the data conductive layer, and is exposed and developed, such as by using a slit mask, to form a photoresist pattern having different thickness depending on a position. The data conduc tive layer, the doped amorphous silicon layer, and the non doped amorphous silicon layer are firstly etched by using the photoresist pattern as a mask to form semiconductors 154a and 154b, and the data conductive layer is secondly etched to form data lines 171a and 171b including source electrodes 173a and 173b and drain electrodes 175a and 175b The exposed amorphous silicon layer is etched by using the source electrodes 173a and 173b and the drain electrode 175a and 175b as an etch mask, to form ohmic contact layers 161a, 161b, 163a, 163b, 165a, and 165b. (0103) As shown in FIG.9 and FIG. 10, a lower passivation layer 180p is formed on the data lines 171a and 171b and the drain electrodes 175a and 175b. A black organic material is formed on the lower passivation layer 180p, and is patterned to form a partition A color filter 230 is formed in a pixel, which is defined by the partition 361. The color filter 230 may be formed by an inkjet printing method, which may include an inkjet head dripping a color filter solvent while being moved, and the color filter solvent is then dried The partition 361 in the illustrated embodiments is formed according to the gate line 121 and the data lines 171a and 171b, such that the region where the color filter 230 is filled, substantially forms a quadrangle. The partition 361 is arranged having Substantially straight (e.g., linear) portions at a boundary of the partition 361 and the enclosed region defin ing the pixel. The partition 361 of the illustrated embodiments does not include any protrusions extending into the enclosed region, such that a phenomenon in which the color filter 230 is not sufficiently filled when forming the color filter 230 by the inkjet printing method, may be reduced or effectively prevented As shown in FIG. 11, an upper passivation layer 180g is formed on the color filter 230 and the partition 361, and is patterned along with the color filter 230 and the lower passivation layer 180p to form contact holes 185a and 185b. When forming the upper passivation layer 180g made of a photosensitive organic material, the upper passivation layer 180g is exposed and developed, and the color filter 230 and the lower passivation layer 180p are dry-etched. The upper passivation layer 1804, the color filter 230, and the lower passivation layer 180p may be etched together such that the inner boundaries of the contact holes 185a and 185b formed in the upper passivation layer 1809, the color filter 230, and the lower passivation layer 180p have substantially the same plane pattern and coincide with each other. The edges of the upper passivation layer 1804, the color filter 230, and the lower passivation layer 180p at the contact holes 185a and 185b, are formed coplanarly with each other, as illustrated in FIG The partition 361 is disposed on a portion of the thin film transistor array panel corresponding to the gate line 121 and the data lines 171a and 171b and substantially forms the quadrangle such that the contact holes 185a and 185b may be positioned in a predetermined region of the pixel electrode 191. As shown in FIG. 6 and FIG. 7, even though the position of the contact holes 185a and 185b is changed according to the shape of the pixel electrode 191, it is not necessary to change the shape of the mask for forming the partition 361. Advantageously, a manufacturing process, time, and cost can be reduced. (0.108 Returning to FIG. 3, the pixel electrode 191 is formed on the upper passivation layer 180g. An alignment layer 11 may be formed on the pixel electrode Another exemplary embodiment of a thin film tran sistor array panel according to the present invention will now be described with reference to FIG. 12 to FIG FIG. 12 is a layout view of another exemplary embodiment of a thin film transistor array panel according to the present invention, FIG. 13 is a top plan view showing an exemplary embodiment of a partition of the thin film transis tor array panel shown in FIG. 12, and FIG. 14 is a cross sectional view of the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 12 taken along line XIV-XIV A thin film transistor array panel is substantially the same as the thin film transistor array panel shown in FIG. 2 to
24 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 FIG. 5 such that descriptions of the same elements will be omitted, and the same constituent elements as in the above described exemplary embodiment are indicated by the same reference numerals Referring to FIG. 12 to FIG. 14, a partition 361 includes a straight portion 361a disposed in the longitudinal direction and corresponding to the gate line 121 and the data lines 171a and 171b, and an expansion portion 361b disposed in the region enclosed by the partition 361, defining a pixel. Contact holes 185a and 185b are disposed overlapping the expansion portion 361b. Also, the contact holes 185a and 185b are extended completely through the upper passivation layer 1809, the expansion portion 361b and the lower passi vation layer 180p. The boundaries of the upper passivation layer 1809, the expansion portion 361b, and the lower passi vation layer 180p at the contact holes 185a and 185b have a substantially planar profile, and coincide with each other. The degree to which the boundaries of the upper passivation layer 1804, the expansion portion 361b, and the lower passivation layer 180p are aligned, depends on a process error range An exemplary embodiment of a manufacturing method of the thin film transistor array panel of FIG. 12 to FIG. 14 will be described with reference to FIG. 15 and FIG FIG. 15 and FIG. 16 are cross-sectional views sequentially showing the exemplary embodiment of a manu facturing method of the thin film transistor array panel for the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 12 to FIG A gate line 121, a gate insulating layer 140, a semi conductor 154, ohmic contact layers 161a, 161b, 163a, 163b, 165a, and 165b, and data lines 171a, 171b, 173a, 173b, 175a, and 175b are formed on a substrate 110 through the above described methods of FIG. 8 and FIG As shown in FIG. 15, a lower passivation layer 180p is formed on the data lines 171a, 171b, 173a, 173b, 175a, and 175b. A partition 361 including a straight portion361a and an expansion portion 361b is formed directly on the lower pas sivation layer 180p A color filter 230 is formed, such as by an inkjet printing method, and an upper passivation layer 180g is formed on the color filter As shown in FIG.16, the passivation layer 1809, the color filter 230, the partition 361, and the lower passivation layer 180p are then etched to form contact holes 185a and 185b The boundaries of the upper passivation layer 180g, the expansion portion 361b, and the lower passivation layer 180p defining the contact holes 185a and 185b, are substan tially linearly disposed in a same plane In an exemplary embodiment of the present inven tion, the expansion portion 361b is maintained at the position where the contact holes 185a and 185b will beformed, and is removed when forming the contact holes 185a and 185b, thereby further minimizing the area of the expansion portion 361b. In the conventional art, the expansion portion361b may be formed with a donut shape (e.g., concentric circles), to pre-open the portion where the contact holes 185a and 185b are formed, when forming the expansion portion 361b. In this way, if the portion where the contact holes 185a and 185b will be formed is previously formed, the expansion portion is formed with a larger size than the required size of the contact hole 185a and 185b, since a process margin would need to be considered. As a result, the area of the expansion portion361b becomes undesirably greater. I0121. However, in an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the expansion portion 361b is not previ ously formed and the expansion portion 361b is removed along with (e.g., at Substantially the same time as) the upper passivation layer 180g, such that the expansion portion 361b is formed without a difference from the required size of the contact hole 185a and 185b. Advantageously, the area of the expansion portion 361b may be minimized, thereby increas ing the aperture ratio Also, the area occupied by the expansion portion 361b may be minimized such that the distance between the straight portion 361a and the expansion portion 361b becomes greater than accomplished in the conventional art when forming the pixel electrode with the conventional pat tern. Advantageously, the flow of the color filter 230 material between the straight portion 361a and the expansion portion 361b is improved. Accordingly, the color filter 230 may be completely filled, e.g., without an empty space in the filling region. I0123. Also, when forming the color filter 230 by the inkjet process, the color filter 230 may flow on the opened portion where contact holes are disposed. However, if the contact holes 185a and 185b are formed after forming the expansion portion as in an exemplary embodiment of the present inven tion, the contact holes 185a and 185b are not contaminated by the color filter 230 when the color filter 230 is applied As shown in FIG. 14, a pixel electrode 191 con nected to the drain electrode 175a and 175b through the contact holes 185a and 185b is formed, and an alignment layer 11 is formed on the pixel electrode Another exemplary embodiment of a thin film tran sistor array panel for a liquid crystal display according to the present invention will be described with reference to FIG FIG. 17 is a cross-sectional view of another exem plary embodiment of the thin film transistor array panel of the liquid crystal display shown in FIG. 2 and FIG.3 taken along line III-III. I0127. A thin film transistor array panel of the illustrated embodiment is substantially the as the thin film transistor array panel shown in FIG.2 to FIG.3 such that descriptions of the same elements will be omitted, and the same constituent elements as in the above-described exemplary embodiment are indicated by the same reference numerals. I0128 Referring to FIG. 17, the partition 361 is thickerina direction perpendicular to the insulating substrate 110, than the partition 361 of the thin film transistor array panel shown in FIG. 3 and FIG. 14. In an exemplary embodiment, it is preferable that the thickness of the partition 361 is more than 2 micrometers (um) When a thickness of the color filter 230 and the partition 361 are both about um, and the differences between the thicknesses of the color filter 230 and the parti tion 361 are relatively small, the partition 361 must beformed with more than a predetermined width to prevent the color filter 230 from being overflowed into the neighboring pixel when forming the color filter 230 by the inkjet printing method. However, if the partition 361 is formed with a thick ness of more than 2 um as in an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the thickness difference between the par tition 361 and the color filter 230 may be more than 0.3 um, and overflow of the color filter 230 into the neighboring pixel may be reduced or effectively prevented, even though the partition 361 does not have a relative wide width (e.g., taken
25 US 2010/ A1 Jan. 7, 2010 parallel to the insulating Substrate 110.). Advantageously, the width of the partition 361 may be reduced, thereby increasing the aperture ratio of the pixel While this invention has been described in connec tion with exemplary embodiments, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the illustrated embodiments, but, on the contrary, is intended to cover various modifica tions and equivalent arrangements included within the spirit and scope of the appended claims. What is claimed is: 1. A thin film transistor array panel comprising: an insulating Substrate; a gate line and a data line disposed on the insulating Sub strate, insulated from and intersecting each other, a thin film transistor connected to the gate line and the data line; a partition disposed corresponding to the gate line and the data line, and defining a color filter filling region; a color filter disposed in the filling region; a passivation layer disposed on the color filter and the partition; and a pixel electrode disposed on the passivation layer and connected to the thin film transistor through a contact hole disposed through the passivation layer and the color filter, wherein a plane shape of the color filter filling region is Substantially a rectangle. 2. The thin film transistor array panel of claim 1, wherein boundaries of the passivation layer and the color filter adjacent to the contact hole are disposed substantially coplanarly. 3. The thin film transistor array panel of claim 1, wherein the contact hole is disposed at a position in the filling region. 4. The thin film transistor array panel of claim 1, wherein a thickness of the partition and the color filter is more than approximately 0.3 micrometer (Lm), the thickness taken Substantially perpendicular to the insulating Substrate. 5. The thin film transistor array panel of claim 1, wherein the partition includes a black pigment. 6. The thin film transistor array panel of claim 1, wherein the passivation layer includes a photosensitive organic material. 7. The thin film transistor array panel of claim 1, wherein the partition includes an expansion portion disposed in the filling region, and the contact hole is disposed coinciding with the expansion portion. 8. The thin film transistor array panel of claim 7, wherein: boundaries of the passivation layer and the expansion por tion defining the contact hole are disposed substantially coplanarly. 9. A manufacturing method of a thin film transistor array panel, the method comprising: forming a gate line including a gate electrode, on a Sub Strate; forming a gate insulating layer on the gate line; forming a semiconductor and an ohmic contact layer on the gate insulating layer, forming a data line including a source electrode and a drain electrode, on the ohmic contact layer; forming a lower passivation layer on the data line and the drain electrode: forming a partition having a quadrangle shape in a plan view on the lower passivation layer, and corresponding to the gate line and the data line; forming a color filter in a filling region defined by the partition; forming an upper passivation layer on the color filter, simultaneously etching the upper passivation layer and the color filter to form a contact hole exposing the drain electrode; and forming a pixel electrode connected to the drain electrode through the contact hole on the upper passivation layer. 10. A manufacturing method of a thin film transistor array panel, the method comprising: forming a gate line including a gate electrode, on a Sub Strate; forming a gate insulating layer on the gate line: forming a semiconductor and an ohmic contact layer on the gate insulating layer, forming a data line including a source electrode and a drain electrode, on the ohmic contact layer; forming a lower passivation layer on the data line and the drain electrode: forming apartition including a straight portion correspond ing to the gate line and data line, and an expansion portion overlapping at least a portion of the drain elec trode, on the lower passivation layer; forming a color filter in the filling region defined by the partition; forming an upper passivation layer on the color filter, simultaneously etching the upper passivation layer and the color filter to form a contact hole exposing the drain electrode; and forming a pixel electrode connected to the drain electrode through the contact hole on the upper passivation layer. c c c c c
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. JUNG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012
 (19) United States US 2012O314174A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0314174 A1 JUNG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2012O314174A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0314174 A1 JUNG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY (30) Foreign Application
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006
 (19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
y y (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, C 410C 422b 4200
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
120x124-st =l. (12) United States Patent. (10) Patent No.: US 9,046,952 B2. 220a 220b. 229b) s 29b) al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
(12) United States Patent
 US008193047B2 (12) United States Patent Ryoo et al. (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE HAVING SUFFICIENT PROCESS MARGIN AND METHOD OF FORMING SAME (75) Inventors: Man-Hyoung Ryoo, Gyeonggi-do (KR): Gi-Sung Yeo,
US008193047B2 (12) United States Patent Ryoo et al. (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE HAVING SUFFICIENT PROCESS MARGIN AND METHOD OF FORMING SAME (75) Inventors: Man-Hyoung Ryoo, Gyeonggi-do (KR): Gi-Sung Yeo,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7656482B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) TRANSFLECTIVE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY AND PANEL THEREFOR (75) Inventors: Seong-Ho Kim, Yongin-si (KR); Sung-Hwan Cho, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Jae-Hyun Kim,
USOO7656482B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) TRANSFLECTIVE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY AND PANEL THEREFOR (75) Inventors: Seong-Ho Kim, Yongin-si (KR); Sung-Hwan Cho, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Jae-Hyun Kim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0363715 A1 HA et al. US 20160363715A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2016 (54) CURVED DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0363715 A1 HA et al. US 20160363715A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2016 (54) CURVED DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING
(12) United States Patent
 US008269735B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,269,735 B2 Sep. 18, 2012 (54) TOUCH SCREEN DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Kang-Woo Kim, Seoul (KR); Dong-Gi Seong,
US008269735B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,269,735 B2 Sep. 18, 2012 (54) TOUCH SCREEN DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Kang-Woo Kim, Seoul (KR); Dong-Gi Seong,
E3, ES 2.ÉAN 27 Asiaz
 (19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017
 (19) United States US 201700 90651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0090651 A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 3/0416
(19) United States US 201700 90651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0090651 A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 3/0416
S/AN a. ', (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. El 1 -
 (19) United States US 20030011729A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0011729 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) VERTICALLY ALIGNED MODE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY WITH
(19) United States US 20030011729A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0011729 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) VERTICALLY ALIGNED MODE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY WITH
79 Hists air sigtais is a sign 83 r A. 838 EEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE
 US 20060011813A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0011813 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A PASSIVATION (22) Filed: Jan.
US 20060011813A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0011813 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A PASSIVATION (22) Filed: Jan.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008
 (19) United States US 200800 12008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0012008 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) MAKING ORGANIC THIN FILM (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 200800 12008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0012008 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) MAKING ORGANIC THIN FILM (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140353625A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0353625 A1 Yet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODES Publication Classification
US 20140353625A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0353625 A1 Yet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODES Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O145694A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Jang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O145694A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Jang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2
 USOO6683667B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2 Jin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 2004 (54) TFT-LCD WITH SCATTERING LAYER, 4,904,060 A * 2/1990 Grupp... 349/162 REFLECTOR,
USOO6683667B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2 Jin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 2004 (54) TFT-LCD WITH SCATTERING LAYER, 4,904,060 A * 2/1990 Grupp... 349/162 REFLECTOR,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,355,741 B2
 US0095741B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeon et al. () Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING A GATE (56) References Cited DRIVE CIRCUIT (71) Applicant: Samsung Display
US0095741B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeon et al. () Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING A GATE (56) References Cited DRIVE CIRCUIT (71) Applicant: Samsung Display
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0022695A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0022695 A1 Schmidt (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRICAL MULTILAYER COMPONENT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIC I/146 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 2014.0022695A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0022695 A1 Schmidt (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRICAL MULTILAYER COMPONENT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIC I/146 (2013.01);
R GBWRG B w Bwr G B wird
 US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0175533A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0175533 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2013 (54) SUBSTRATE INCLUDING THIN FILM Publication Classification
US 2013 0175533A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0175533 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2013 (54) SUBSTRATE INCLUDING THIN FILM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
M3 d. (12) United States Patent US 7,317,435 B2. Jan. 8, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Wei-Chieh Hsueh, Tainan (TW) T GND
 US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 2014.0034923A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0034923 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification DISPLAY
US 2014.0034923A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0034923 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9, B2. Han et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2016
 USOO9354476B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,354.476 B2 Han et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) WINDOW PANEL FOR A DISPLAY USPC... 361/679, 679.55-679.58,679.21, APPARATUS 361/679.26,679.27,679.09:
USOO9354476B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,354.476 B2 Han et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) WINDOW PANEL FOR A DISPLAY USPC... 361/679, 679.55-679.58,679.21, APPARATUS 361/679.26,679.27,679.09:
United States Patent (19) Morris
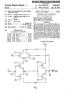 United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070107206A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0107206A1 Harris et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A Publication Classification
US 20070107206A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0107206A1 Harris et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0103414 A1 Baik US 2015O103414A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) LENS MODULE (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRO-MECHANCS CO.,LTD.,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0103414 A1 Baik US 2015O103414A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) LENS MODULE (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRO-MECHANCS CO.,LTD.,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
(12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
Publication number: A2. Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/ Meadowridge Drive Garland, Texas 75044(US)
 Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2. Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010
 US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. to (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140203306A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0203306 A1 to (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR LIGHT-EMITTING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICE CPC...
(19) United States US 20140203306A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0203306 A1 to (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR LIGHT-EMITTING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICE CPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 US 20070228931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0228931 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) WHITE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE Publication Classification
US 20070228931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0228931 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) WHITE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
Y 6a W SES. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States. Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 (19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015O113835A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0113835 A1 Rosenberger (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) SHOE PAD FOR ATTACHMENT TO THE Publication Classification
US 2015O113835A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0113835 A1 Rosenberger (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) SHOE PAD FOR ATTACHMENT TO THE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,850,085 B2. Claessen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2010
 United States Patent US007850085B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,850,085 B2 Claessen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2010 (54) BARCODE SCANNER WITH MIRROR 2002/010O805 A1 8, 2002 Detwiler ANTENNA 2007/0063045
United States Patent US007850085B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,850,085 B2 Claessen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2010 (54) BARCODE SCANNER WITH MIRROR 2002/010O805 A1 8, 2002 Detwiler ANTENNA 2007/0063045
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
VDD. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. I Data. (76) Inventors: Wen-Cheng Yen, Taichung (TW);
 (19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,770,955 B1
 USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Nakayama et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,916,413 Apr. 10, 1990 54 PACKAGE FOR PIEZO-OSCILLATOR (75) Inventors: Iwao Nakayama; Kazushige Ichinose; Hiroyuki Ogiso,
United States Patent (19) Nakayama et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,916,413 Apr. 10, 1990 54 PACKAGE FOR PIEZO-OSCILLATOR (75) Inventors: Iwao Nakayama; Kazushige Ichinose; Hiroyuki Ogiso,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,449,544 B2
 USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. Penn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003
 US 2003O147052A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0147052 A1 Penn et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH CONTRAST PROJECTION Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional
US 2003O147052A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0147052 A1 Penn et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH CONTRAST PROJECTION Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170070208A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0070208A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) PIEZOELECTRIC OSCILLATOR AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20170070208A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0070208A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) PIEZOELECTRIC OSCILLATOR AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
in-s-he Gua (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,388,499 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 Vddint : SFF LSOUT Tien et al.
 (12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
(12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O155237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0155237 A1 Kerber (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) SELF-ALIGNED JUNCTION PASSIVATION Publication Classification
US 2004O155237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0155237 A1 Kerber (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) SELF-ALIGNED JUNCTION PASSIVATION Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,475,870 B1 Huang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002
 US006475870B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,475,870 B1 Huang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) P-TYPE LDMOS DEVICE WITH BURIED 5,525,824 A * 6/1996 Himi et a1...... 257/370
US006475870B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,475,870 B1 Huang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) P-TYPE LDMOS DEVICE WITH BURIED 5,525,824 A * 6/1996 Himi et a1...... 257/370
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
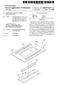 (19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
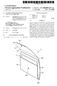 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822
 34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.436,043 B2
 USOO7436043B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.436,043 B2 Sung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 14, 2008 (54) N-WELL AND N* BURIED LAYER 5,786,617 A * 7/1998 Merrill et al.... 257/371 SOLATION
USOO7436043B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.436,043 B2 Sung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 14, 2008 (54) N-WELL AND N* BURIED LAYER 5,786,617 A * 7/1998 Merrill et al.... 257/371 SOLATION
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1 Ochiai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 US 20130194531A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194531 A1 Ochiai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 1, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classi?cation
US 20130194531A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194531 A1 Ochiai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 1, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classi?cation
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7325359B2 (12) United States Patent Vetter (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 5, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) PROJECTION WINDOW OPERATOR Inventor: Gregory J. Vetter,
USOO7325359B2 (12) United States Patent Vetter (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 5, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) PROJECTION WINDOW OPERATOR Inventor: Gregory J. Vetter,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
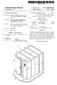 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
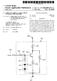 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,665 B2
 USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,068,465 B2
 USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
part data signal (12) United States Patent control 33 er m - sm is US 7,119,773 B2
 US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0286339 A1 Pyo et al. US 20150286339A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) DISPLAY DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0286339 A1 Pyo et al. US 20150286339A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) DISPLAY DEVICE
