(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
|
|
|
- Jason Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD OF CONTROLLING IT (75) Inventor: Sang Ui Choi, Chungcheongnam-do (KR) Correspondence Address: GREENBLUM & BERNSTEIN, P.L.C ROLAND CLARKE PLACE RESTON, VA (US) (73) Assignee: Ceragem Co., Ltd., Seoul (KR) (21) Appl. No.: 10/757,436 (22) Filed: Jan. 15, 2004 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 13, 2003 (KR) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl."... A61F 7700; A61F 7/12: A61B 17/00 (52) U.S. Cl /96; 607/108; 606/ (57) ABSTRACT The present invention provides a bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus using a means for controlling a loca tion of a hyperthermo-radiative device wherein a moving location of the hyperthermo-radiative device can be con trolled based on an actually moved distance of the hyper thermo-radiative device. In the present invention, the means for controlling the location of the hyperthermo-radiative device comprises (a) a reciprocating unit including a belt gear for converting a rotational force of an electric-powered motor into a forward and rearward reciprocating motion, a belt member that is engaged and in contact with an outer peripheral Surface of the belt gear and reciprocated forward or rearward, the hyperthermo-radiative device connected to the belt member to reciprocate forward and rearward, and a pulley; and (b) a signal Sensor unit including a rotational shaft for directly transmitting the rotational force, a signal rotating plate rotated together with the belt gear by the rotational shaft, and a Sensor member that is adjacent to both faces of the Signal rotating plate to Sense a signal from the Signal rotating plate and transmit the Sensed signal to a control unit. According to the present invention, Since a moving distance of the hyperthermo-radiative device can be controlled using the means for controlling the location of the hyperthermo-radiative device on the order of millimeters, the hyperthermo-radiative device can be accurately located on the position of a vertebra input by a user, thereby enhancing the effects of treatment. 126
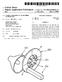
2 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2005 Sheet 1 of 5 US 2005/ A1 FIG 1 FIG 2
3 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2005 Sheet 2 of 5 US 2005/ A1 FIG 3
4 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2005 Sheet 3 of 5 US 2005/ A1 FIG 4
5 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2005 Sheet 4 of 5 US 2005/ A1 FIG 5 1OO n. Number of through-holes r : Radi US Of belt gear
6 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2005 Sheet 5 of 5 US 2005/ A1 FIG 6 Input Signal by user Positive direction - Negative direction - Compare current location with input position Nila Drive motor in positive direction Drive motor in negative direction Move hyperthermoradiative device Move hyperthermo radiative device Compare location EN yperthermo-radiative device with input position Compare location of yperthermo-radiative device with input position
7 US 2005/ A1 Mar. 24, 2005 BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD OF CONTROLLING T BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0001) 1. Field of Invention 0002 The present invention relates to a bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus. More particularly, the present invention relates to a bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus designed to accurately position a hyperthermo-radiative device at user's vertebral acupunc ture points, and a method of controlling the hot compress and acupressure apparatus Description of the Prior Art 0004 Generally, a conventional box type hot compress and acupressure apparatus was improved into a mat type hot compress and acupressure apparatus that in turn has been improved into a bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus. The bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus has a bed type frame as a basic structure on which a mat can be mounted. Further, in the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus, a hyperthermo-radiative device is mounted and reciprocated in a predetermined range within the mat. Typical bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatuses are disclosed in Korean Utility Model Patent Application No , Korean Patent Application No , Korean Utility Model Patent Application No and U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09/ The typical bed type hot compress and acupres Sure apparatus is also called as a mat for hot compress and acupressure in Korea Each of Such bed type hot compress and acupres Sure apparatuses has an advantage in that a vertebra region of a user who lies on the mat can be hyper thermally treated according to a program Stored in a control box of the apparatus. Thus, Such bed type hot compress and acupres Sure apparatuses have been used widely. In conventional bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatuses, rails nec essary for reciprocation of a hyperthermo-radiative device are made in the form of a gentle curve, a marginal Space is flexibly provided to a certain extent in a predetermined range when the hyperthermo-radiative device is recipro cated, or a predetermined resilient Spring is mounted in the hyperthermo-radiative device Meanwhile, in the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatuses used widely nowadays, the move ment of the hyperthermo-radiative device that has influence directly on hyperthermic treatment for users vertebrae is controlled by an automatic program. However, Such a con trol method is performed on the basis of a predetermined period of time. In other words, the conventional bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatuses which have been used heretofore are Set Such that their hyperthermo-radiative devices are moved in accordance with the passage of time based on conditions that have been input through remote controls by users However, since the conventional bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus is controlled with the passage of time regardless of an actually moved distance of the hyperthermo-radiative device, there is a difference in the moved distance of the hyperthermo-radiative device between a case where a great deal of overload per unit time is exerted on the hyperthermo-radiative device and a case where no overload is exerted thereon Therefore, the conventional bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus has a disadvantage in that when a user wants to be hyper thermally treated on his specific region, a final location of a hyperthermo-radiative device of the apparatus may vary according to the amount of overload exerted thereon, and thus, uniform and equal effects of hyperthermic treatment cannot be obtained Sufficiently under the same conditions. This is an inevitable disadvan tage in the conventional bed type hot compress and acu pressure apparatus that controls the movement of the hyper thermo-radiative device based on time. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, the present invention is conceived to Solve the problems in the prior art. An object of the present invention is to provide a bed type hot compress and acu pressure apparatus, wherein a moving location of a hyper thermo-radiative device is controlled based on a distance by which the hyperthermo-radiative device has been actually moved, regardless of the passage of time Another object of the present invention is to pro vide a method of controlling a hot compress and acupressure apparatus, wherein a hyperthermo-radiative device can be accurately located at a desired region of user's vertebrae to be hyper thermally treated by controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device The present invention provides a bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus, wherein a moving location of a hyperthermo-radiative device is controlled based on a distance by which the hyperthermo-radiative device has been actually moved, regardless of the passage of time The bed type hot compress and acupressure appa ratus according to the present invention comprises (a) a bed frame that defines an entire shape of the apparatus and has members to be assembled with one another; (b) a main mat and an auxiliary mat placed and mounted on the bed frame; (c) two curved rails mounted at a central portion within the main mat; (d) a means for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device Such that a moving distance of the hyperthermo-radiative device can be controlled based on an actually moved distance thereof regardless of the passage of time; and (e) a control unit for allowing the user to arbitrarily control the means for reciprocating the hyper thermo-radiative device In the present invention, the means for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device comprises (i ) a reciprocating unit including a belt gear coupled to a motor shaft of an electric-powered motor to convert a rotational force of the electric-powered motor into a forward and rearward reciprocating motion, a belt member that is engaged and in contact with an Outer peripheral Surface of the belt gear and reciprocated forward or rearward by means of the belt gear, the hyperthermo-radiative device connected to the belt member to reciprocate forward and rearward, and a pulley disposed on a side opposite to the belt gear to reciprocate the belt member; and (ii) a signal Sensor unit including a rotational shaft connected to the motor Shaft and
8 US 2005/ A1 Mar. 24, 2005 the belt gear to directly transmit the rotational force, a signal rotating plate rotated together with the belt gear by the rotational shaft, and a sensor member that is adjacent to both faces of the signal rotating plate to sense a signal from the Signal rotating plate and transmit the sensed signal to a control unit ) Further, the present invention provides a method of controlling a bed type hot compress and acupressure appa ratus, wherein a hyperthermo-radiative device of the appa ratus is reciprocated and the reciprocating motion is con trolled based on a moving distance of a belt member by using the means for controlling the location of the hyper thermo-radiative device. In the method of controlling a location of the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus according to the present invention, a control method performed by the means for controlling the location of the hyperthermo-radiative device comprises steps of (a) comparing a current location of the hyperthermo-radiative device with the position of the vertebra input by the user, and determining a direction in which the hyperthermo-radiative device should be moved; (b) moving the hyperthermo radiative device by means of the electric-powered motor; (c) measuring, by the signal sensor unit, a location to which the hyperthermo-radiative device is actually moved, during the movement of the hyperthermo-radiative device, and com paring the actually moved location of the hyperthermo radiative device with the position designated by the user; (d) performing continuously step (c) if the actually moved location of the hyperthermo-radiative device differs from the Set position designated by the user; and (e) stopping the movement of the hyperthermo-radiative device and per forming the hyperthermic treatment if the location and position are identical to each other. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above and other objects, features and advan tages of the present invention will become apparent from the following description of preferred embodiments given in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which: 0016 FIG. 1 is a plan view schematically showing a bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus according to the present invention; 0017 FIG. 2 is a side view schematically showing the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus according to the present invention; 0018 FIG.3 is a conceptual view schematically showing a means for controlling a location of a hyperthermo-radia tive device; 0019 FIG. 4 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a cooperative relationship among main components of the means for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radia tive device; 0020 FIG. 5 is a conceptual view theoretically illustrat ing a method of controlling a location of the hyperthermo radiative device by using the means for controlling a loca tion of the hyperthermo-radiative device; and 0021 FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a method of controlling the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus according to the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS 0022 Hereinafter, a bed type hot compress and acupres Sure apparatus using a means for controlling a location of a hyperthermo-radiative device and a method of controlling the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus according to the present invention will be described in detail With reference to the accompanying drawings. It will be apparent that the accompanying drawings are merely pro Vided for the purpose of easy understanding of the technical features of the invention by those skilled in the art FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 are a plan view and a side view Schematically showing the bed type hot compress and acu pressure apparatus 200 according to the present invention, respectively The bed type hot compress and acupressure appa ratus 200 according to present invention comprises a bed frame 210 that defines an entire shape of the apparatus and has members to be assembled with one another. The bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus 200 according to present invention comprises a main mat 212 and an auxiliary mat 214 which can be placed and mounted on the bed frame 210. The main mat 212 has an empty space at a center portion thereof, and two curved rails 216 are installed in the empty. Space. A hyperthermo-radiative device 126 is mounted on the curved rails 216 to reciprocate forward and rearward thereon The bed type hot compress and acupressure appa ratus 200 according to present invention comprises a remote control (not shown) which allows a user to arbitrarily control the hyperthermo-radiative device 126, and a control unit (not shown) for automatically operating the hyperthermo radiative device 126 according to a predetermined program. In the present invention, since the remote control and the control unit are identical to those of conventional elements, a detailed description thereof will be omitted The bed type hot compress and acupressure appa ratus 200 according to present invention comprises a means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device. The bed type hot compress and acupressure appa ratus 200 according to present invention is characterized in that the means 100 for controlling a location of the hyper thermo-radiative device described above is used. The means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device will be described in detail below FIG.3 is a conceptual view schematically showing a main portion of a hot compress and acupressure apparatus mounted with the means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device. 0028) The means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device comprises a reciprocating unit 120 in which the movement of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 thereof is determined by a control unit (not shown). In the present invention, the reciprocating unit 120 comprises a belt gear 122 for receiving a rotational force generated by an electric-powered motor 112 and then con Verting it into a forward and rearward reciprocating motion. At this time, the belt gear 122 is mechanically connected to the electric-powered motor 112 for generating the rotational force in response to a control signal from the control unit and a motor shaft 114 for transmitting the rotational force
9 US 2005/ A1 Mar. 24, 2005 generated by the electric-powered motor 112. The belt gear 122 is employed to accurately and precisely convert the rotational force generated by the electric-powered motor 112 into the forward and rearward reciprocating motion. A belt member 124 is engaged and in contact with an outer peripheral surface of the belt gear 122. One end of the belt member 124 is connected to one side of the hyperthermo radiative device 126 for performing hyperthermic treatment for user's vertebrae, and the other end thereof is connected to the other side of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126. The belt member 124 transmits the forward and rearward reciprocating motion converted by the belt gear 122 to the hyperthermo-radiative device 126. Although a conventional rubber belt, chain, or timing belt may be used as the belt gear 122, it is most desirable to use the timing belt. The hyper thermo-radiative device 126 is also called as a hot compress and acupressure treatment element in Korea, and may be replaced with a massage device or the like, if necessary. In the present invention, the reciprocating unit 120 comprises a pulley 128 disposed on a side opposite to the belt gear 122 to reciprocate the belt member Further, the means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device comprises a signal Sensor unit 130 capable of controlling a Substantial moving distance of the belt member 124 according to the amount of rotation of the electric-powered motor 112. The Signal Sensor unit 130 comprises a rotational shaft 132 connected to the motor shaft 114 and the belt gear 122 to transmit the rotational force as it is. The rotational shaft 132 receives the rotational force generated by the electric-power motor 112 to Simul taneously rotate both the belt gear 122 and a Signal rotating plate 134 while allowing the belt gear 122 and the signal rotating plate 134 to rotate about the same axis through the Same rotating angle on concentric circles. A plurality of through-holes 138 are formed along a circumferential por tion inside of an Outer periphery of the Signal rotating plate 134 therethrough (see FIG. 4). The through-holes 138 serve as passages through which a signal generated by a Sensor member 136 disposed outside thereof can pass. Such a function of the through-holes 138 causes the Signal rotating plate 134 to be continuously rotated or stopped, thereby controlling the rotation of the Signal rotating plate 134. Since the number of the through-holes 138 is a parameter that determines the amounts of the forward and rearward motions of the belt gear 122 and the belt member 124, it is desirable to form the through-holes as many as possible In the present invention, the signal sensor unit 130 comprises the sensor member 136 that is adjacent to both faces of the Signal rotating plate 134. The Sensor member 136 functions to Sense a signal passing through the through holes 138 of the signal rotating plate 134 and transmit the signal to the control unit. To this end, the sensor member 136 comprises a signal emitting part 137a formed at one side portion extending from a body thereof and a signal Sensing part 137b formed at the other side portion. Further, the signal sensor unit 130 comprises a support 139 for supporting the rotational shaft 132 at one end thereof FIG. 4 is an exploded perspective view conceptu ally showing a cooperative relationship among the belt gear 122, the signal rotating plate 134 and the sensor member 136 constituting a main part of the means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device In the present invention, when a user operates the electric-powered motor 112 using a remote control (not shown), a rotational force of the electric-powered motor 112 is transmitted to the belt gear 122 and the Signal rotating plate 134 that in turn are rotated integrally. At this time, when the user inputs the position of his/her vertebra to be hyper thermally treated into the control unit, a distance from an actual location of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 as a reference location to the position of the vertebra to be treated is calculated by a central process unit (CPU; not shown), and the calculated value is transmitted to the Sensor member 136. Then, the signal emitting part 137a formed on one of the side portions of the sensor member 136 emits a predetermined signal to the Signal rotating plate 134 that is continuously rotated during the operation of the electric powered motor 112. At this time, the signal emitted from the signal emitting part 137a of the sensor member 136 passes through the through-holes 138 formed along the circumfer ential portion inside of the outer periphery of the Signal rotating plate 134. The Signal that has passed through the through-holes 138 is sensed by the signal sensing part 137b formed on the other of the side portions of the sensor member 136. On the contrary, portions of the Signal rotating plate 134 between the respective though-holes 138 cut off the Signal emitted by the Signal emitting part 137a, So that the Signal Sensing part 137b cannot Sense the emitted Signal. Therefore, the number of revolutions of the Signal rotating plate 134 and the belt gear 122 due to the rotation of the electric-powered motor 112 can be measured by means of the sensor member 136 and the through-holes 138 of the signal rotating plate 134. The number of revolutions is fed back into the control unit to find a position where the Signal rotating plate 134 should be stopped With such a mechanism of the present invention, the belt gear 122 and the Signal rotating plate 134 are rotated by the same number of revolutions through the same rotating angle as the electric-power motor 112 operates, and the belt gear 122 is stopped as Soon as the Signal rotating plate 134 is stopped FIG. 5 is a conceptual view illustrating a coopera tive relationship between the belt gear 122 and the Signal rotating plate 134 in the means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device. 0035) In FIG. 5, the belt member 124 is engaged with the outer peripheral Surface of the belt gear 122, and the rotational shaft 132 serves as a central axis of both the belt gear 122 and the Signal rotating plate 134. Thus, the belt gear 122 and the Signal rotating plate 134 define concentric circles around the rotational Shaft 132. Accordingly, even though the belt gear 122 and the Signal rotating plate 134 have different radii, it is possible to assume that the plurality of the through-holes 138 formed along the circumferential portion inside of the outer periphery of the Signal rotating plate 134 are formed on an Outer periphery of the belt gear 122. In FIG. 5, imaginary through-holes 138' are indicated by imaginary lines outside of the outer periphery of the belt gear 122 in consideration of the cooperative relationship. 0036). In FIG. 5, n imaginary through-holes 138' are formed outside of the outer periphery of the belt gear 122 and the radius of the belt gear 122 is r. At this time, the circumference of the belt gear 122 is 2 tr. Therefore, when the belt gear 122 is fully rotated once through 360 degrees, the angular distance is 2 tr, so that the belt member 124 is moved by 2Jur. Accordingly, when the Signal rotating plate 134 is rotated by the electric-powered motor 112 through an angle between two adjacent through-holes 138, the belt gear 122 is rotated through an angle between two adjacent
10 US 2005/ A1 Mar. 24, 2005 imaginary through-holes 138 so that the belt member 124 can be moved by 2 tr/n forward or rearward This description can be summarized as follow: The moving distance of the belt member 124 per rotation of the belt gear 122=27tr; and The moving distance of the belt member 124 per rotation through an angle between two adjacent through holes 138=2JUr/n As a more specific embodiment, a case where the number of the through-holes 138 formed in the signal rotating plate 134 is 100 and the radius of the belt gear 122 is 25 mm will be discussed as follows: The number of revolutions of the signal rotating plate 134=The number of revolutions of the belt gear 122; The moving distance of the belt member 124 per rotation of the signal rotating plate 134 (belt gear 122)=2LX 25=157 mm; and The moving distance of the belt member 124 per rotation through an angle between two adjacent through holes 138=2 LX25/100 = 1.57 mm Accordingly, when the belt gear 122 and the signal rotating plate 134 under the aforementioned conditions are used, the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 coupled to the belt member 124 can be controlled by a unit of 1.57 mm to a minimum. Further, in this case, Since the actual moving distance of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 is con trolled based on only the moving distance of the belt member 124 even though time has passed considerably, the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 can be accurately oper ated regardless of the passage of time In the present invention, therefore, the hyper thermo-radiative device 126 can be exactly moved forward or rearward to the position where the user wants to be hyper thermally treated his/her vertebra. 0046) When the user inputs information on the position of a vertebra required to be hyper thermally treated into the remote control, the control unit transmits the information to the electric-powered motor 112 so that the electric-powered motor 112 is rotated based on the information. The amount of rotation of the electric-powered motor 112 is controlled by the belt gear 122 and the belt member 124 on the order of millimeters. In the present invention, Since other Struc tural elements are identical to those of conventional bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatuses, a detailed description thereof will be omitted Moreover, the present invention provides a method of controlling the hyperthermo-radiative device of the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus based on the moving distance of the belt member using the means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device FIG. 6 is a flowchart schematically showing the method of controlling the bed type hot compress and acu pressure apparatus 200 according to the present invention The bed type hot compress and acupressure appa ratus 200 according to the present invention begins to operate when the user beforehand inputs the position of a vertebra required to be hyper thermally treated into the remote control. At first, the control unit compares a current location of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 with the position of the vertebra that has been input by the user, and determines a direction in which the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 should be moved. At this time, if the position information that has been input by the user is not completely consistent with the current location of the hyperthermo radiative device 126, the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 must be moved to the designated location corresponding to the position of the vertebra, this location will be a location in front of or at the rear of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126. Meanwhile, for the sake of explanation, it is more desirable to Set a point of reference. In the present invention, a direction in which the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 should be moved toward the pulley 128 is defined as a positive (+) direction, whereas a direction in which the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 should be moved toward the electric-powered motor 112 is defined as a negative (-) direction, respectively When a direction in which the hyperthermo-radia tive device 126 should be moved is determined, the electric powered motor 112 is operated in the positive (+) or negative (-) direction. At this time, the motor shaft 114 causes the belt gear 122 and the belt member 124 to move the hyperthermo radiative device 126 in practice. Such movement is the same as conventional hot compress and acupressure apparatuses Meanwhile, during the movement of the hyper thermo-radiative device 126, the means 100 for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device measures continuously and in real time a location to which the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 is actually moved and a position designated by the user by using the Signal Sensor unit 130, and then compares the location with the position. The comparison method will be described in detail below While the electric-powered motor 112 operates, a rotational force of the electric-powered motor 112 is trans mitted to the rotational shaft 132 that is connected to the motor shaft 114 and the belt gear 122. The rotational shaft 132 transmits the rotating force to the Signal rotating plate 134 through the belt gear 122. Since the Signal rotating plate 134 and the belt gear 122 define concentric circles around the rotational shaft 132, the signal rotating plate 134 and the belt gear 122 are rotated by the same number of revolutions. AS Soon as the Signal rotating plate 134 is stopped, the belt gear 122 is also stopped Meanwhile, since the signal emitting part 137a formed on one side portion of the sensor member 136 emits a predetermined Signal, and the Signal Sensing part 137b formed on the other side portion of the sensor member 136 Senses the emitted Signal, the Signal rotating plate 134 and the belt gear 122 are rotated continuously So far as a stop Signal transmitted by the control unit has not been received or the Sensed Signal conforms to a signal transmitted by the control unit. Therefore, the amount of rotation and the number of revolutions of the Signal rotating plate 134 are measured If the current location of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 that has been actually moved differs from a set position designated by the user, the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 is moved continuously. However, if the current location of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 is identical to the position designated by the user, the movement of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 is stopped and hyperther mic treatment is then performed. A hyperthermic treatment time can be determined by a program or arbitrarily input by the user When a predetermined treatment time has passed, the position of a vertebra input by the user is compared again
11 US 2005/ A1 Mar. 24, 2005 with the current location of the hyperthermo-radiative device 126, and the aforementioned processes are repeated The present invention controls the amount of rota tion and the number of revolutions of the Signal rotating plate 134 by means of the aforementioned method, so that the hyperthermo-radiative device 126 can be accurately moved by a required distance As described above, the present invention can control the rotation of the belt gear using the Signal rotating plate and the Sensor member. Therefore, there is an advan tage in that the moving distance of the hyperthermo-radia tive device can be controlled by the belt gear and the belt member on the order of millimeters Further, through the series of processes described above, the present invention can more accurately locate the hyperthermo-radiative device at a vertebral region (e.g., the fifth vertebra or the eighth vertebra) that is designated in advance by the user. Thus, there is an advantage that the user can more efficiently obtain the effects of hot compress and acupressure on a region desired by the user Although the present invention has been described in connection with the preferred embodiments of the means for controlling a location of the hyperthermo-radiative device and the bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus using the Same, the embodiments are for illustra tive purposes only and the present invention is not limited thereto. The scope of the present invention is defined by the appended claims It will be apparent that those skilled in the art can make various changes and modifications thereto without departing from the Scope and Spirit of the present invention, and the changes and modifications also fall within the Scope of the present invention. 1. A bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus comprising: a bed frame that defines an entire shape of the apparatus and has members to be assembled with one another; a main mat and an auxiliary mat placed and mounted on the bed frame; two curved rails mounted at a central portion within the main mat; a controller that controls a location of a hyperthermo radiative device Such that a moving distance of the hyperthermo-radiative device can be controlled based on an actually moved distance thereof, regardless of the passage of time, and a control unit that allows a user to arbitrarily control a reciprocating device that reciprocates the hyperthermo radiative device. 2. The apparatus as claimed in claim 1, wherein the controller that controls the location of the hyperthermo radiative device comprises: a reciprocating unit including a belt gear coupled to a motor Shaft of an electric-powered motor to convert a rotational force of the electric-powered motor into a forward and rearward reciprocating motion, a belt member that is engaged and in contact with an outer peripheral Surface of the belt gear and reciprocated forward or rearward through the belt gear, the hyper thermo-radiative device connected to the belt member to reciprocate forward and rearward, and a pulley disposed on a Side opposite to the belt gear to recip rocate the belt member; and a signal Sensor unit including a rotational shaft connected to the motor Shaft and the belt gear to directly transmit the rotational force, a signal rotating plate rotated together with the belt gear by the rotational shaft, and a Sensor member that is adjacent to both faces of the Signal rotating plate to Sense a signal from the Signal rotating plate and transmit the Sensed signal to the control unit. 3. A method of controlling a bed type hot compress and acupressure apparatus, wherein a hyperthermo-radiative device of the apparatus is reciprocated and a reciprocating motion is controlled based on a moving distance of the hyperthermo-radiative device, comprising: comparing a current location of the hyperthermo-radiative device with a position of a vertebra input by a user, and determining a direction in which the hyperthermo radiative device should be moved; moving the hyperthermo-radiative device through an electric-powered motor; measuring, by a signal sensor unit, a location to which the hyperthermo-radiative device is actually moved, during the movement of the hyperthermo-radiative device, and comparing an actually moved location of the hyper thermo-radiative device with the a position designated by the user; continuously performing the measuring if the actually moved location of the hyperthermo-radiative device differs from the position designated by the user; and Stopping the movement of the hyperthermo-radiative device and performing a treatment if the location and the position are identical to each other. 4. The method as claimed in claim 3, wherein the com paring the actually moved location of the hyperthermo radiative device with the position designated by the user further comprises: transmitting the rotational force of the electric-powered motor to a Signal rotating plate through a rotational shaft connected to a motor Shaft and a belt gear, and measuring the number of revolutions and an amount of rotation of the Signal rotating plate a Sensor member which is adjacent to both faces of the Signal rotating plate while the Signal rotating plate is rotated together with the belt gear about the rotational shaft; and moving the hyperthermo-radiative device by a required distance by controlling again the number of revolutions and the amount of rotation of the Signal rotating plate measured in the measuring.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,665 B2
 USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2
 US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354
![United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354](/thumbs/92/110916574.jpg) US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1
 USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
(19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0325383A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0325383 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRON BEAM MELTING AND LASER B23K I5/00 (2006.01) MILLING COMPOSITE
(19) United States US 2016.0325383A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0325383 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRON BEAM MELTING AND LASER B23K I5/00 (2006.01) MILLING COMPOSITE
202 19' 19 19' (12) United States Patent 202' US 7,050,043 B2. Huang et al. May 23, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2O8236A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208236A1 Damink et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF AN OBJECT
(19) United States US 2010O2O8236A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208236A1 Damink et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF AN OBJECT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
United States Patent (19) Lee
 United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0064060 A1 Wagner et al. US 2005OO64060A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MOLDING APPARATUS FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0064060 A1 Wagner et al. US 2005OO64060A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MOLDING APPARATUS FOR
( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub. No. : US 2017 / A1 ( 52 ) U. S. CI. CPC... HO2P 9 / 48 ( 2013.
 THE MAIN TEA ETA AITOA MA EI TA HA US 20170317630A1 ( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub No : US 2017 / 0317630 A1 Said et al ( 43 ) Pub Date : Nov 2, 2017 ( 54 ) PMG BASED
THE MAIN TEA ETA AITOA MA EI TA HA US 20170317630A1 ( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub No : US 2017 / 0317630 A1 Said et al ( 43 ) Pub Date : Nov 2, 2017 ( 54 ) PMG BASED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,297,615 B2
 US008297615B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,297,615 B2 Nakamura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 30, 2012 (54) SHEET PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (56) References Cited CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
US008297615B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,297,615 B2 Nakamura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 30, 2012 (54) SHEET PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (56) References Cited CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US009682771B2 () Patent No.: Knag et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2017 (54) CONTROLLING ROTOR BLADES OF A 5,676,334 A * /1997 Cotton... B64C 27.54 SWASHPLATELESS ROTOR 244.12.2
(12) United States Patent US009682771B2 () Patent No.: Knag et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2017 (54) CONTROLLING ROTOR BLADES OF A 5,676,334 A * /1997 Cotton... B64C 27.54 SWASHPLATELESS ROTOR 244.12.2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,920,822 B2
 USOO6920822B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Finan (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2005 (54) DIGITAL CAN DECORATING APPARATUS 5,186,100 A 2/1993 Turturro et al. 5,677.719 A * 10/1997 Granzow...
USOO6920822B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Finan (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2005 (54) DIGITAL CAN DECORATING APPARATUS 5,186,100 A 2/1993 Turturro et al. 5,677.719 A * 10/1997 Granzow...
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Essig (54) KNITTED FABRIC AND METHOD OF PRODUCING THE SAME 75 Inventor: Karl Essig, Reutlingen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: H. Stoll GmbH & Co., Reutlingen, Fed. Rep. of
United States Patent (19) Essig (54) KNITTED FABRIC AND METHOD OF PRODUCING THE SAME 75 Inventor: Karl Essig, Reutlingen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: H. Stoll GmbH & Co., Reutlingen, Fed. Rep. of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2
 US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109. Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, a. Assistant Examiner-Alan B.
 H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O248594A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0248594 A1 Nish (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) SETUP TOOL FOR GRINDER SHARPENING Publication Classification
US 2010O248594A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0248594 A1 Nish (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) SETUP TOOL FOR GRINDER SHARPENING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(12) United States Patent
 US008133074B1 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET REPROGRAMMING INTERFACE ASSEMBLY
US008133074B1 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET REPROGRAMMING INTERFACE ASSEMBLY
part data signal (12) United States Patent control 33 er m - sm is US 7,119,773 B2
 US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al.
 United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2
 USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
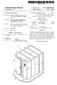 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 200900.00432A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0000432 A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2009 (54) TOOL HEAD STRUCTURE Publication Classification (51) Int.
US 200900.00432A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0000432 A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2009 (54) TOOL HEAD STRUCTURE Publication Classification (51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
(19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0031036A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0031036A1 Reed et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2016 (54) LINEAR FRICTION WELDING (30) Foreign Application
US 2016.0031036A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0031036A1 Reed et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2016 (54) LINEAR FRICTION WELDING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
IIH. United States Patent (19) Chen. (11) Patent Number: 5,318,090 (45. Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,068,465 B2
 USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
58 Field of Search /341,484, structed from polarization splitters in series with half-wave
 USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
25 N WSZ, SN2. United States Patent (19) (11) 3,837,162. Meitinger. (45) Sept. 24, 1974 % N. and carried on a projecting portion which is rigidly
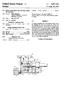 O United States Patent (19) Meitinger 54) DEVICE FOR ADJUSTING THE DIAL TRAIN OF WATCHES 76 Inventor: Heinz Meitinger, Theodor-Heuss-Str. 16 D-7075, Mutlangen, Germany 22 Filed: Mar. 26, 1973 (21) Appl.
O United States Patent (19) Meitinger 54) DEVICE FOR ADJUSTING THE DIAL TRAIN OF WATCHES 76 Inventor: Heinz Meitinger, Theodor-Heuss-Str. 16 D-7075, Mutlangen, Germany 22 Filed: Mar. 26, 1973 (21) Appl.
IIIHIIII. United States Patent (19) Tannenbaum
 United States Patent (19) Tannenbaum (54) ROTARY SHAKER WITH FLEXIBLE STRAP SUSPENSION 75) Inventor: Myron Tannenbaum, Cranbury, N.J. 73) Assignee: New Brunswick Scientific Co., Inc., Edison, N.J. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Tannenbaum (54) ROTARY SHAKER WITH FLEXIBLE STRAP SUSPENSION 75) Inventor: Myron Tannenbaum, Cranbury, N.J. 73) Assignee: New Brunswick Scientific Co., Inc., Edison, N.J. 21 Appl.
United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972
![United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972](/thumbs/91/105347464.jpg) United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 54. FOLDING FNS FOR MESSELES 3,273,500 9/1966 Kongelbeck... 244/3.28 (72) Inventor: Nils-Åke Birger Svensson, Karlskoga, Primary Examiner-Verlin
United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 54. FOLDING FNS FOR MESSELES 3,273,500 9/1966 Kongelbeck... 244/3.28 (72) Inventor: Nils-Åke Birger Svensson, Karlskoga, Primary Examiner-Verlin
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
United States Patent (19) Rannou et al.
 United States Patent (19) Rannou et al. (54) (75) 73 22) (21) 30) 52 (51) (58) (56) WIDE-BAND OMNIDIRECTIONAL ANTENNA Inventors: Jean Rannou; William Luther, both of Paris, France Assignee: Thomson-CSF,
United States Patent (19) Rannou et al. (54) (75) 73 22) (21) 30) 52 (51) (58) (56) WIDE-BAND OMNIDIRECTIONAL ANTENNA Inventors: Jean Rannou; William Luther, both of Paris, France Assignee: Thomson-CSF,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,564,782 B2. Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017
 USO09564782B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017 (54) WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND (56) References Cited AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE U.S.
USO09564782B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017 (54) WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND (56) References Cited AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
United States Patent 19 Perets
 United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
issi Field of search. 348/36, , 33) of the turret punch press machine; an image of the
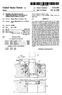 US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
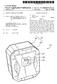 (19) United States US 2006O151349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0151349 A1 Andrews et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) TRADING CARD AND CONTAINER (76) Inventors: Robert
(19) United States US 2006O151349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0151349 A1 Andrews et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) TRADING CARD AND CONTAINER (76) Inventors: Robert
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
United States Patent (19)
 US006041720A 11 Patent Number: Hardy (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 United States Patent (19) 54 PRODUCT MANAGEMENT DISPLAY 5,738,019 4/1998 Parker... 108/61 X SYSTEM FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor:
US006041720A 11 Patent Number: Hardy (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 United States Patent (19) 54 PRODUCT MANAGEMENT DISPLAY 5,738,019 4/1998 Parker... 108/61 X SYSTEM FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor:
75 Inventors: Onofre Costilla-Vela, Nuevo Leon; : R. SS II.
 USOO5924.47OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,470 Costilla-Vela et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54 METHOD FOR PREHEATING MOLDS FOR 1-91960 4/1989 Japan... 164/457 ALUMINUM CASTINGS
USOO5924.47OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,470 Costilla-Vela et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54 METHOD FOR PREHEATING MOLDS FOR 1-91960 4/1989 Japan... 164/457 ALUMINUM CASTINGS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Swayney et al. USOO5743074A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 28, 1998 54) 76) 21) 22 51 (52) 58 LAWN MOWER DECK PROTECTING DEVICE Inventors: Ernest Edward Swayney; Norman
United States Patent 19 Swayney et al. USOO5743074A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 28, 1998 54) 76) 21) 22 51 (52) 58 LAWN MOWER DECK PROTECTING DEVICE Inventors: Ernest Edward Swayney; Norman
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
(19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
(12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, (73 Assignee: Molex Incorporated, Lisle, Ill. 57) ABSTRACT
 United States Patent (19) 11 US005577318A Patent Number: Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 1996 54 ELECTRICAL TERMINAL APPLICATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WEMPROVED TRACK ADJUSTMENT 2643514 8/1990
United States Patent (19) 11 US005577318A Patent Number: Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 1996 54 ELECTRICAL TERMINAL APPLICATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WEMPROVED TRACK ADJUSTMENT 2643514 8/1990
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0140775A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0140775 A1 HONG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2011 (54) COMBINED CELL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFICATION APPARATUS
(19) United States US 2011 0140775A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0140775 A1 HONG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2011 (54) COMBINED CELL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFICATION APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
Schaeff, LLP. 22 Filed: Nov. 2, 1998 (51) Int. Cl."... B21D 51/ U.S. Cl... 72/329; 72/ Field of Search... 72/327, 328, 329, 72/348
 United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001 0026740A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0026740 A1 YAMANISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) PROCESSING MACHINE WITH NUMERICAL CONTROLAPPARATUS (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2001 0026740A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0026740 A1 YAMANISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) PROCESSING MACHINE WITH NUMERICAL CONTROLAPPARATUS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,387,795 B1
 USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O254338A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0254338 A1 FISHER, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) MULTI-PAWL ROUND-RECLINER MECHANISM (76)
(19) United States US 2011 O254338A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0254338 A1 FISHER, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) MULTI-PAWL ROUND-RECLINER MECHANISM (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090090231A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0090231 A1 Kondo (43) Pub. Date: ADr. 9, 9 2009 (54) BAND SAW MACHINE Publication Classification O O (51)
(19) United States US 20090090231A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0090231 A1 Kondo (43) Pub. Date: ADr. 9, 9 2009 (54) BAND SAW MACHINE Publication Classification O O (51)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O227191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0227191A1 Feaser (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2005 (54) CANDLEWICK TRIMMER (76) Inventor: Wendy S. Feaser, Hershey,
(19) United States US 2005O227191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0227191A1 Feaser (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2005 (54) CANDLEWICK TRIMMER (76) Inventor: Wendy S. Feaser, Hershey,
United States Patent (19) Mori
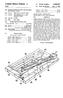 United States Patent (19) Mori 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1991 54 PAPER-CUTTING MACHINE AND METHOD OF CUTTNG PAPER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Chuzo Mori, Katsushika, Japan Carl Manufacturing
United States Patent (19) Mori 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1991 54 PAPER-CUTTING MACHINE AND METHOD OF CUTTNG PAPER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Chuzo Mori, Katsushika, Japan Carl Manufacturing
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999
 USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
US 20l30l45796Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1 Frank (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 US 20l30l45796Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0145796 A1 Frank (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) CUTTING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. PRODUCING FOAM
US 20l30l45796Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0145796 A1 Frank (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) CUTTING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. PRODUCING FOAM
