E3, ES 2.ÉAN 27 Asiaz
|
|
|
- Robert Franklin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
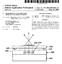
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification METHODS OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME (51) Int. Cl. HOIL 5/52 ( ) (71) Applicant: ELECTRONICS AND HOIL 5/56 ( ) TELECOMMUNICATIONS (52) U.S. Cl. RESEARCH INSTITUTE, Daejeon CPC... HOIL 51/5203 ( ); HOIL 51/56 (KR) ( ) USPC /40: 438/27 (72) Inventors: Jae Bon KOO, Daejeon (KR); Hojun RYU, Seoul (KR); Chi-Sun HWANG, Daejeon (KR); Jeong Ik LEE, Gunpo-si (57) ABSTRACT (KR); Hye Yong CHU, Daejeon (KR) (73) Assignee: Electronics and Telecommunications Disclosed are dual mode display devices and methods of Research Institute, Daejeon (KR) manufacturing the same. The dual mode display device may include a first substrate, a first electrode on the first substrate, (21) Appl. No.: 13/763,383 a second substrate opposite to the first electrode and the first substrate, a second electrode between the second substrate (22) Filed: Feb. 8, 2013 and the first electrode, a third electrode between the first electrode and the second electrode, an optic Switching layer (30) Foreign Application Priority Data between the first electrode and the third electrode, and an organic light-emitting layer between the second electrode and Jul. 12, 2012 (KR) OO76275 the third electrode I t --OO 90 E. EY 60 8O E3 E3, ES 2.ÉAN 27 Asiaz & & : 8 c ) ( (8 ) ( y & 8 O & & O 3 o o O p 40 Xxx-xx-XXX-XXXXX-XXX-XXX-XXXX-XXXXXXxxxxxx sa O O
2 Patent Application Publication Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 1 of 8 US 2014/ A1 Fig Fl IN
3 Patent Application Publication Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 2 of 8 US 2014/ A1 00}
4 Patent Application Publication Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 3 of 8 US 2014/ A1
5 Patent Application Publication Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 4 of 8 US 2014/ A1 og )
6 Patent Application Publication Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 5 of 8 US 2014/ A1
7 Patent Application Publication Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 6 of 8 US 2014/ A1 08???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????>]****** zºno.? [-
8 Patent Application Publication 00? 06 08// >6/ Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 7 of 8??????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????rzh!!!!!--Nºr?=#No.v-No.ÈNo.? 09 ==No.? E?!--(?)=?\!No.. US 2014/ A1
9 Patent Application Publication Jan. 16, 2014 Sheet 8 of 8 US 2014/ A1 S S 8 6) 8 8)8) (3. c) (3) 88) 8 8) 6
10 US 2014/OO A1 Jan. 16, 2014 DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND METHODS OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This U.S. non-provisional patent application claims priority under 35 U.S.C. S 119 to Korean Patent Application No , filed on Jul. 12, 2012, the entirety of which is incorporated by reference herein. BACKGROUND 0002 The inventive concept relates to display devices and methods of manufacturing the same and, more particularly, to dual mode display devices of a reflection type and a self-light emitting type and methods of manufacturing the same A flat panel display (FPD) industry may be impor tant with the development of information age. The FPD may display an image by controlling an intensity of transmitted light or self-emitting light according to image controlling signals. The FPDs may include a liquid crystal display (LCD) and an organic light-emitting display (OLED) The LCDs may be categorized as any one of a trans mission type LCD and a reflection type LCD. In the trans mission type LCD, white light generated from a back light unit may be transmitted through two polarizing plates and a liquid crystal layer, so as to be modulated. The white light may pass through a color filer to realize a color. Since the reflection type LCD may be driven in a low voltage, it may be widely applied to a mobile device, a notebook, a computer, a monitor, and a television. The transmission type LCD may use a portion of the white light transmitted through the polar izing plates and the color filer, so that light efficiency of the transmission type LCD may be low. Additionally, the back light unit may increase power consumption of the transmis sion type LCD. Thus, various researches have been conducted for the reflection type LCD from which the back light unit is removed. The reflection type LCD may show an image by reflecting an external light in bright Surroundings The OLED has been spotlighted because of low power consumption and self-emitting properties thereof. The OLED may include a plurality of substrates opposite to each other, a plurality of electrodes disposed between the sub strate, and an organic light-emitting material. The Substrates may include flexible substrates such as plastic. Thus the OLED may be realized as a stretchable display. The organic light-emitting material may form excitons being pairs of elec trons and holes Supplied through the electrodes. The excitons may emit light in the organic light-emitting material. Thus, the OLED may show the image by self-emitting light The OLED may be combined with the reflection type LCD to realize a dual mode display device. The dual mode display device may adapt to an external environment to actualize Super-saving electric power. SUMMARY 0007 Embodiments of the inventive concept may provide dual mode display devices having self-light-emitting mode and reflection mode and methods of manufacturing the same Embodiments of the inventive concept may also provide dual mode display devices capable of improving productivity and methods of manufacturing the same In one aspect, a dual mode display device may include: a first substrate; a first electrode on the first substrate; a second substrate opposite to the first electrode and the first substrate; a second electrode between the second substrate and the first electrode; a third electrode between the first electrode and the second electrode; an optic Switching layer between the first electrode and the third electrode; and an organic light-emitting layer between the second electrode and the third electrode In some embodiments, the dual mode display device may further include: a passivation layer disposed between the third electrode and the optic switching layer In other embodiments, the dual mode display device may further include: an adhesive layer disposed between the passivation layer and the optic Switching layer In even other embodiments, the adhesive layer may include a polymer film In yet other embodiments, the dual mode display device may further include: a thin film transistor part adjacent to the third electrode and disposed between the passivation layer and the organic light-emitting layer In yet still other embodiments, the optic switching layer may include photonic crystal capsules In further embodiments, the optic switching layer may include electronic-ink microcapsules In still further embodiments, the optic switching layer may include a liquid crystal layer In even further embodiments, the first electrode may be a transparent electrode; and the second electrode may be a reflecting electrode In yet further embodiments, the first electrode may be a reflecting electrode; and the second electrode may be a transparent electrode In another aspect, a method of manufacturing a dual mode display device may include: forming a passivation layer on a dummy Substrate; forming a thin film transistor part and a third electrode connected to the thin film transistor part on the passivation layer, forming an organic light-emitting layer on the third electrode and the thin film transistor parts; form ing a second electrode on the organic light-emitting layer; forming a second Substrate covering the second electrode: removing the dummy Substrate; forming a first electrode on a first Substrate opposite to the second Substrate; and bonding the first substrate to the second substrate with an optic switch ing layer inserted between the first electrode and the passiva tion layer In some embodiments, the dummy substrate may be removed by a dry etching process, a wet etching process, or a chemical mechanical polishing process In other embodiments, bonding the first substrate to the second Substrate may include: forming the optic Switch ing layer on the first electrode; forming an adhesive layer on the optic Switching layer, and bonding the adhesive layer to the passivation layer. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The inventive concept will become more apparent in view of the attached drawings and accompanying detailed description FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view illustrat ing a display device according to embodiments of the inven tive concept;
11 US 2014/OO A1 Jan. 16, FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a dual mode display device according to a first embodiment of the inventive concept; 0025 FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a dual mode display device according to a second embodiment of the inventive concept; and 0026 FIGS. 4 to 12 are cross-sectional views illustrating methods of manufacturing dual mode display devices accord ing to first and second embodiments of the inventive concept. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EMBODIMENTS The inventive concept will now be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying draw ings, in which exemplary embodiments of the inventive con cept are shown. The advantages and features of the inventive concept and methods of achieving them will be apparent from the following exemplary embodiments that will be described in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be noted, however, that the inventive concept is not limited to the following exemplary embodiments, and may be implemented in various forms. Accordingly, the exemplary embodiments are provided only to disclose the inventive con cept and let those skilled in the art know the category of the inventive concept. In the drawings, embodiments of the inventive concept are not limited to the specific examples provided herein and are exaggerated for clarity The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only and is not intended to limit the invention. As used herein, the singular terms a. an and the are intended to include the plural forms as well, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. As used herein, the term and/or includes any and all combinations of one or more of the associated listed items. It will be under stood that when an element is referred to as being con nected' or coupled to another element, it may be directly connected or coupled to the other element or intervening elements may be present Similarly, it will be understood that when an ele ment such as a layer, region or Substrate is referred to as being on another element, it can be directly on the other element or intervening elements may be present. In contrast, the term directly means that there are no intervening elements. It will be further understood that the terms comprises, com prising., includes and/or including', when used herein, specify the presence of stated features, integers, steps, opera tions, elements, and/or components, but do not preclude the presence or addition of one or more other features, integers, steps, operations, elements, components, and/or groups thereof FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view illustrat ing a display device according to embodiments of the inven tive concept Referring to FIG. 1, a display device according to embodiments of the inventive concept includes a first elec trode 20, a second electrode 90 on the first electrode 20, a third electrode 60 between the first electrode 20 and the second electrode 90, an optic switching layer 30 between the first electrode 20 and the third electrode 60, an organic light emitting layer 80 between the second electrode 90 and the third electrode 60, and a passivation layer 50 between the organic light-emitting layer 80 and the optic Switching layer 3O The first electrode 20 and the second electrode 90 may be cathodes applying negative Voltages to the optic switching layer 30 and the organic light-emitting layer 80, respectively. The third electrode 60 may be a common anode applying a positive Voltage to the he optic Switching layer 30 and the organic light-emitting layer A thin film transistor part 70 is disposed between the optic Switching layer 30 and the organic light-emitting layer 80. The thin film transistor part 70 is connected to the third electrode 60. The thin film transistor part 70 and the third electrode 60 are fixed on the passivation layer 50. The passi vation layer 50 may separate the optic switching layer 30 from the organic light-emitting layer The organic light-emitting layer 80 may emit self emitting light by a bias current between the second electrode 90 and the third electrode 60. The organic light-emitting layer 80 may perform a self-light-emitting mode of the display device. The display device may effectively show a self-light emitting mode image in a dark room. Even though not shown in the drawings, the organic light-emitting layer 80 may include a hole injecting layer, a hole transporting layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transporting layer, and an electron injecting layer which are disposed on the third elec trode The optic switching layer 30 may absorb or transmit external light. The absorption or transmission of the external light may be determined by an electric field in the optic switching layer 30. The electric field is induced between the first electrode 20 and the third electrode 60. The optic switch ing layer 30 is driven in a reflection mode of the display device. The display device may show a reflection mode image in a bright space Thus, the display device according to the inventive concept may realize a dual mode. The dual mode display device may minimize energy consumption. The dual mode display device may display the image in back or front of the dual mode display device according to reflexibility and/or transmissivity of the first electrode 20 or the second electrode 90. These will be described with reference to FIGS. 2 and 3 in more detail FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a dual mode display device according to a first embodiment of the inventive concept Referring to FIG. 2, a dual mode display device according to the first embodiment may display the image in back thereof. The dual mode display device may include a first substrate 10 and a second substrate 100. One surface of the first substrate 10 corresponds to a back side of the dual mode display device, and one surface of the second Substrate 100 corresponds to a front side of the dual mode display device. In other words, the dual mode display device accord ing to the first embodiment may display the image in a back ward direction from the second substrate 100 toward the first substrate 10. The first electrode 20 is a transparent electrode transmitting the self-emitting light and the external light, and the second electrode 90 a reflecting electrode reflecting the self-emitting light and the external light The first electrode 20 may include at least one of transparent metals (e.g., indium tin oxide (ITO) and indium Zinc oxide (IZO)) and transparent conductive materials (e.g., a silver nano-wire, a carbon nano-tube, graphene, PEDOT: PSS, polyaniline, and polythiophene) The second electrode 90 may include at least one of opaque metals such as tungsten (W), aluminum (Al), and
12 US 2014/OO A1 Jan. 16, 2014 silver (Ag). The first electrode 20 and the second electrode 90 may be fixed on the first substrate 10 and the second substrate 100, respectively. Each of the first substrate 10 and the second Substrate 100 may include a transparent glass or plastic The third electrode 60 is a pixel electrode defining a sub-pixel. The third electrode 60 may include a transparent metal such as ITO or IZO The thin film transistor part 70 may include a sam pling thin film transistor 71, a driving thin film transistor 72, and a programming thin film transistor 73. Each of the Sam pling thin film transistor 71, the driving thin film transistor 72, and the programming thin film transistor 73 may include an active layer 74, a gate insulating layer 75 on the active layer 74 and the passivation layer 50, a gate electrode 76 on the gate insulating layer 75 disposed on the active layer 74, a gate upper insulating layer 75 disposed on the gate electrode 76 and the gate insulating layer 75, and source/drain electrodes 78 and 79. The source/drain electrodes 78 and 79 may be disposed at both sides of the gate electrode 76, respectively. The source/drain electrodes 78 and 79 may penetrate the gate upper insulating layer 77 and the gate insulating layer 75, so as to be connected to the active layer 76. FIG. 2 shows the thin film transistor part 70 having a top gate structure. However, the inventive concept is not limited thereto. In other embodi ments, the thin film transistor part 70 may have a bottom gate Structure The thin film transistor part 70 may control a bias voltage and a bias current applied to the third electrode 60. The bias Voltage is a turned-on data signal in response to a gate signal. The sampling thin film transistor 71 may control the bias Voltage. The data signal and the gate signal may be applied through a data line (not shown) and a gate line (not shown), respectively. The bias current may be applied to the third electrode 60 from a current source (not shown). 0044) The driving thin film transistor 72 and the program ming thin film transistor 73 may control the bias current. In FIG. 2, the third electrode 60 is connected to a drain electrode 79 of the programming thin film transistor 73. However, the inventive concept is not limited thereto. In other embodi ments, the sampling thin film transistor 71 and the program ming thin film transistor 73 may be connected in common to the third electrode The first electrode 20 transmits the external light and a reflected light, and the second electrode 90 reflects the external light. The optic switching layer 30 may not transmit the external light and the reflected light when the electric field is not generated between the first electrode 20 and the third electrode 60. The bias voltage may induce the electric field between the first electrode 20 and the third electrode 60. The optic Switching layer 30 may transmit the external light and the reflected light when the electric field is generated between the first and third electrodes 20 and 60. However, the inven tive concept is not limited thereto At this time, the second electrode 90 is in a floating state. The driving thin film transistor 72 and the programming thin film transistor 73 may be turned-off. Additionally, the current source does not supply the bias current. When the organic light-emitting layer 80 is transparent, the reflection mode image may be shown in black, white, or color. If the organic light-emitting layer 80 has a color, the reflection mode image may be shown in color The optic switching layer 30 may include elec tronic-ink microcapsules 32 or photonic crystal capsules. Example, the electronic-ink microcapsules 32 may include electronic-ink particles 34 and a capsule 36. The electronic ink particles 34 may be densely disposed in the capsule 36. At this time, the optic switching layer 30 may transmit the exter nal light and the self-emitting light. On the other hand, if an electric field is induced between the first electrode 20 and the third electrode 60, the electronic-ink particles 34 may be widely dispersed in the capsule 36. Thus, the switching cap sules 32 may block the external light and the self-emitting light. The optic Switching layer 30 may include a liquid crys tal layer. The liquid crystal layer may include any one of nematic liquid crystal, Smectic liquid crystal, and cholesteric liquid crystal An adhesive layer 40 is disposed between the optic switching layer 30 and the passivation layer 50. The adhesive layer 40 fixes the capsules 36. Additionally, the adhesive layer 40 may increase electric characteristics between the first elec trode 20 and the third electrode 60. The adhesive layer 40 may include a polymer film having resistivity and a dielectric constant equal to or less than predetermined values. The passivation layer 50 may include a transparent dielectric layer Such as a silicon oxide layer or a silicon oxynitride layer. The adhesive layer 40 may be a laminated liquid crystal protecting film The organic light-emitting layer 80 may include a transparent material. The organic light-emitting layer 80 may transmit external light or reflected light of a white color. The organic light-emitting layer 80 may have one of three primary colors. The organic light-emitting layer 80 may give a color to the external light or the reflected light. The organic light emitting layer 80 may include an electron transporting layer, a hole transporting layer, and a light-emitting layer. The light emitting layer may emit the self-emitting light of a red color, agreen color, or a blue color. The intensity of the self-emitting light may increase in proportion to the bias current. At this time, the first electrode 20 is in a floating state. The first electrode 20 and the optic switching layer 30 may transmit the self-emitting light. An image of the self-light-emitting mode may be transmitted through the optic switching layer 30 and then be shown in back of the dual mode display device As a result, the dual mode display device according to the first embodiment may display the image of the reflec tion mode or the self-light-emitting mode in back thereof FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a dual mode display device according to a second embodiment of the inventive concept Referring to FIG. 3, a dual mode display device according to the second embodiment may display an image in front thereof. In other words, the dual mode display device according to the second embodiment may display the image in a direction from the first substrate 10 toward the second substrate 100. In the present embodiment, the first electrode 20 is a reflecting electrode, and the second electrode 90 is a transparent electrode. The first electrode 20 may include an opaque metal. The opaque metal may include at least one of tungsten (W), aluminum (Al), and silver (Ag). The second electrode 90 may include at least one of indium tin oxide (ITO), indium zinc oxide (IZO), a silver nano-wire, a carbon nano-tube, graphene, PEDOT:PSS, polyaniline, and poly thiophene The organic light-emitting layer 80 may display the image of the self-light-emitting mode in front of the dual mode display device according to the second embodiment. The organic light-emitting layer 80 may include a transparent material. The reflection mode may realize a black, white, or
13 US 2014/OO A1 Jan. 16, 2014 color image. If the organic light-emitting layer 80 has any one of three primary colors, the dual mode display device may display the color image of the reflection mode in front thereof The first electrode 20 is the transparent electrode and the second electrode 90 is the reflecting electrode in the first embodiment. On the other hand, the first electrode 20 is the reflecting electrode and the second electrode 90 is the transparent electrode in the second embodiment Hereinafter, methods of manufacturing the dual mode display devices according to the first and second embodiments will be described with reference to FIGS. 4 to FIGS. 4 to 12 are cross-sectional views illustrating methods of manufacturing dual mode display devices accord ing to first and second embodiments of the inventive concept Referring to FIG. 4, the passivation layer 50 is formed on a dummy substrate 110. The passivation layer 50 may be formed by a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) pro cess or a rapid thermal treatment process. The passivation layer 50 may include a silicon oxide layer, a silicon nitride layer, or a silicon oxynitride layer. The dummy substrate 110 may include a glass Substrate or a plastic Substrate Referring to FIG. 5, the thin film transistor part 70 and the third electrode 60 are formed on the passivation layer 50. The thin film transistor part 70 may be formed by a plurality of unit processes. The unit processes may include a deposition process, a photolithography process, and an etch ing process The thin film transistorpart 70 may includean active layer 74, source/drain electrodes 78 and 79, a gate insulating layer 75, a gate upper insulating layer 77, and a gate electrode of a metal 76. The active layer 74 may include poly-silicon. The gate insulating layer 75 may include a dielectric layer Such as a silicon oxide layer. Each of the poly-silicon and the dielectric layer may be formed by a CVD process. The poly silicon may be patterned by a photolithography process and an etching process. The source/drain electrodes 78 and 79 and the gate electrode 76 may include a transparent metal such as ITO. The metals for the source? drain electrodes 78 and 70 and the gate electrode 76 may be formed by a deposition process Such as a sputtering process. The metals for the source/drain electrodes 78 and 70 and the gate electrode 76 may be pat terned by a photolithography process and an etching process The third electrode 60 may include a transparent metal such as ITO or IZO. The transparent metal may be formed by a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process such as a sputtering process or a molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) process. The transparent metal may be patterned by a photo lithography process and an etching process. At this time, the transparent metal for the third electrode 60 may beformed by the same deposition process as one of the gate electrode 76 and the source/drain electrodes 78 and 79. Alternatively, the transparent metal for the third electrode 60 may beformed by an additional deposition process. In other embodiments, the third electrode 60 may include a transparent conductive mate rial Such as a silver nano-wire, a carbon nano-tube, graphene, PEDOT:PSS, polyaniline, and/or polythiophene. The trans parent conductive material may beformed by a CVD process, a spin coating process, or an implanting process Referring to FIG. 6, the organic light-emitting layer 80 is formed on the thin film transistor 70 and the third electrode 60. The organic light-emitting layer 80 may be formed by a spin coating process, a sol-gel process, a thermal deposition process, or a CVD process Referring to FIG. 7, the second electrode 90 is formed on the organic light-emitting layer 80. The second electrode 90 may be formed of a transparent metal, an opaque metal, or a transparent conductive material by a PVD process or a CVD process. According to a first embodiment of the inventive concept, the second electrode 90 may be formed of the opaque metal having high reflexibility. The opaque metal may include tungsten (W), aluminum (Al), or silver (Ag). According to a second embodiment of the inventive concept, the second electrode 90 may be formed of the transparent metal or the transparent conductive material. The transparent metal may include ITO, IZO, or a silver nano-wire. The transparent conductive material may include a carbon nano tube, graphene, PEDOT:PSS, polyaniline, and/or poly thiophene. The graphene may be formed by a tape laminating process Referring to FIG.8, the second substrate 100 may be provided on the second electrode 90. The second substrate 100 may include glass or plastic. The plastic has flexibility. Even though not shown in the drawings, the second electrode 90 may be formed on the second substrate 100 and then the second electrode 90 formed on the second substrate 100 may be bonded to the organic light-emitting layer Referring to FIG. 9, the dummy substrate 110 is removed. The dummy substrate 110 may be removed by a wet etching process, a dry etching process, or a chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process. The passivation layer 50 may function as an etch stop layer in the removal process of the dummy substrate Referring to FIG. 10, the first electrode 20 is formed on the first substrate 10 opposite to the second substrate 100. The first electrode 20 may be formed of a transparent metal, a transparent conductive material, or an opaque metal by a PVD process or a CVD process. According to the first embodiment of the inventive concept, the first electrode 20 may include the transparent metal or the transparent conduc tive material. According to the second embodiment of the inventive concept, the first electrode 20 may include the opaque metal Referring to FIG. 11, the optic switching layer 30 is formed on the first electrode 20. The optic switching layer 30 may beformed on the first electrode 20 by a dropping process Referring to FIG. 12, the adhesive layer 40 is formed on the optic switching layer 30. The adhesive layer 40 may be formed of polymer by a spin coating process, a PVD process, or a CVD process Referring to FIG. 2 again, the adhesive layer 40 is bonded to the passivation layer 50. Even though not shown in the drawings, a sealant may be formed on edges of the first and second substrates 10 and 100, so that the first and second substrates 10 and 100 may be fixed. The organic light-emit ting layer 80 and the optic switching layer 30 may be fixed by the bonding of the first and second substrates 10 and According to embodiments of the inventive concept, the dual mode display device includes the first substrate, the second electrode opposite to the first electrode, the third electrode between the first and second electrodes, the optic switching layer between the first and third electrodes, and the organic light-emitting layer between the second and third electrodes. The organic light-emitting layer may display the image of the self-light-emitting mode. The self-light-emitting mode display device may be effectively driven in the dark room. The organic light-emitting layer may include the trans parent organic material. One of the first and second electrodes
14 US 2014/OO A1 Jan. 16, 2014 is the transparent electrode, and the other is the reflecting electrode. The reflecting electrode and the optic switching layer may display the image of the reflection mode. The image of the reflection mode may be shown by the external light. The reflection mode display device may be driven in the bright space. The dual mode display device of the self-light emitting mode and the reflection mode may minimize the energy consumption. Thus, the dual mode display device according to embodiments of the inventive concept may improve productivity While the inventive concept has been described with reference to example embodiments, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various changes and modifications may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the inventive concept. Therefore, it should be understood that the above embodiments are not limiting, but illustrative. Thus, the scope of the inventive concept is to be determined by the broadest permissible interpretation of the following claims and their equivalents, and shall not be restricted or limited by the foregoing description. What is claimed is: 1. A dual mode display device comprising: a first substrate; a first electrode on the first substrate; a second substrate opposite to the first electrode and the first substrate; a second electrode between the second substrate and the first electrode: a third electrode between the first electrode and the second electrode: an optic switching layer between the first electrode and the third electrode; and an organic light-emitting layer between the second elec trode and the third electrode. 2. The dual mode display device of claim 1, further com prising: a passivation layer disposed between the third electrode and the optic Switching layer. 3. The dual mode display device of claim 2, further com prising: an adhesive layer disposed between the passivation layer and the optic Switching layer. 4. The dual mode display device of claim 3, wherein the adhesive layer includes a polymer film. 5. The dual mode display device of claim 2, further com prising: a thin film transistor part adjacent to the third electrode and disposed between the passivation layer and the organic light-emitting layer. 6. The dual mode display device of claim 1, wherein the optic Switching layer includes photonic crystal capsules. 7. The dual mode display device of claim 1, wherein the optic Switching layer includes electronic-ink microcapsules. 8. The dual mode display device of claim 1, wherein the optic Switching layer includes a liquid crystal layer. 9. The dual mode display device of claim 1, wherein the first electrode is a transparent electrode; and wherein the second electrode is a reflecting electrode. 10. The dual mode display device of claim 1, wherein the first electrode is a reflecting electrode; and wherein the second electrode is a transparent electrode. 11. A method of manufacturing a dual mode display device, comprising: forming a passivation layer on a dummy Substrate; forming a thin film transistor part and a third electrode connected to the thin film transistor part on the passiva tion layer, forming an organic light-emitting layer on the third elec trode and the thin film transistor parts; forming a second electrode on the organic light-emitting layer; forming a second Substrate covering the second electrode: removing the dummy Substrate; forming a first electrode on a first Substrate opposite to the second Substrate; and bonding the first substrate to the second substrate with an optic switching layer inserted between the first electrode and the passivation layer. 12. The method of claim 11, wherein the dummy substrate is removed by a dry etching process, a wet etching process, or a chemical mechanical polishing process. 13. The method of claim 11, wherein bonding the first Substrate to the second Substrate comprises: forming the optic Switching layer on the first electrode, forming an adhesive layer on the optic Switching layer, and bonding the adhesive layer to the passivation layer. k k k k k
120x124-st =l. (12) United States Patent. (10) Patent No.: US 9,046,952 B2. 220a 220b. 229b) s 29b) al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
USOO9046952B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) DISPLAY DEVICE INTEGRATED WITH TOUCH SCREEN PANEL (75) Inventors: Gun-Shik Kim, Yongin (KR); Dong-Ki Lee, Yongin (KR) (73) Assignee: Samsung Display
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006
 (19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
y y (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, C 410C 422b 4200
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
79 Hists air sigtais is a sign 83 r A. 838 EEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE
 US 20060011813A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0011813 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A PASSIVATION (22) Filed: Jan.
US 20060011813A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0011813 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A PASSIVATION (22) Filed: Jan.
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
us Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ Al (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040150613Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150613
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040150613Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150613
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0175533A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0175533 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2013 (54) SUBSTRATE INCLUDING THIN FILM Publication Classification
US 2013 0175533A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0175533 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2013 (54) SUBSTRATE INCLUDING THIN FILM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7656482B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) TRANSFLECTIVE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY AND PANEL THEREFOR (75) Inventors: Seong-Ho Kim, Yongin-si (KR); Sung-Hwan Cho, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Jae-Hyun Kim,
USOO7656482B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) TRANSFLECTIVE LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY AND PANEL THEREFOR (75) Inventors: Seong-Ho Kim, Yongin-si (KR); Sung-Hwan Cho, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Jae-Hyun Kim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140353625A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0353625 A1 Yet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODES Publication Classification
US 20140353625A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0353625 A1 Yet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODES Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1
 USOO6211068B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DUAL DAMASCENE PROCESS FOR 5,981,377 * 11/1999 Koyama... 438/633 MANUFACTURING INTERCONNECTS
USOO6211068B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DUAL DAMASCENE PROCESS FOR 5,981,377 * 11/1999 Koyama... 438/633 MANUFACTURING INTERCONNECTS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/014711.6 A1 LEE et al. US 201701 471.16A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) TOUCH PANEL,
VDD. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. I Data. (76) Inventors: Wen-Cheng Yen, Taichung (TW);
 (19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
US 7,015,893 B2 Mar. 21,2006
 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007015893B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,015,893 B2 Mar. 21,2006 (54) PHOTOLUMINESCENT
111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007015893B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,015,893 B2 Mar. 21,2006 (54) PHOTOLUMINESCENT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0362960 A1 Chang et al. US 20150362960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCHELECTRONIC DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0362960 A1 Chang et al. US 20150362960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCHELECTRONIC DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2
 USOO6683667B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2 Jin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 2004 (54) TFT-LCD WITH SCATTERING LAYER, 4,904,060 A * 2/1990 Grupp... 349/162 REFLECTOR,
USOO6683667B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,683,667 B2 Jin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 2004 (54) TFT-LCD WITH SCATTERING LAYER, 4,904,060 A * 2/1990 Grupp... 349/162 REFLECTOR,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US008238998B2 (10) Patent No.: Park (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 7, 2012 (54) TAB ELECTRODE 4,653,501 A * 3/1987 Cartmell et al.... 600,392 4,715,382 A * 12/1987 Strand...... 600,392
(12) United States Patent US008238998B2 (10) Patent No.: Park (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 7, 2012 (54) TAB ELECTRODE 4,653,501 A * 3/1987 Cartmell et al.... 600,392 4,715,382 A * 12/1987 Strand...... 600,392
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
US 2011 OO63266A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0063266 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT OF DISPLAY PANEL, Publication Classification METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015
 (19) United States US 20150212614A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0212614 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) INTEGRATED POLARIZER AND (52) U.S. Cl. CONDUCTIVE
(19) United States US 20150212614A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0212614 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) INTEGRATED POLARIZER AND (52) U.S. Cl. CONDUCTIVE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9632220B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,632,220 B2 Hwang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) DECAL FOR MANUFACTURING USPC... 359/483.01, 484.04, 485.01-485.07, MULT-COLORED RETROREFLECTIVE
(12) United States Patent USOO9632220B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,632,220 B2 Hwang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) DECAL FOR MANUFACTURING USPC... 359/483.01, 484.04, 485.01-485.07, MULT-COLORED RETROREFLECTIVE
40- It i? l? l (r. Nl
 (19) United States US 2014032O765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0320765 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND FABRICATION Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014032O765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0320765 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND FABRICATION Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9423425B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) SIDE-CHANNEL ANALYSSAPPARATUS AND METHOD BASED ON PROFILE Applicant: Electronics and Telecommunications
USOO9423425B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) SIDE-CHANNEL ANALYSSAPPARATUS AND METHOD BASED ON PROFILE Applicant: Electronics and Telecommunications
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017
 (19) United States US 201700 90651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0090651 A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 3/0416
(19) United States US 201700 90651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0090651 A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 3/0416
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(19) United States US 2011 0115997A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115997 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL Publication Classification (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 US 20070228931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0228931 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) WHITE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE Publication Classification
US 20070228931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0228931 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) WHITE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,449,544 B2
 USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
(12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201601 39401A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/01394.01 A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) GLASS PHOSPHOR COLOR WHEEL AND (52) U.S. Cl. METHODS
US 201601 39401A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/01394.01 A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) GLASS PHOSPHOR COLOR WHEEL AND (52) U.S. Cl. METHODS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,355,741 B2
 US0095741B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeon et al. () Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING A GATE (56) References Cited DRIVE CIRCUIT (71) Applicant: Samsung Display
US0095741B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeon et al. () Date of Patent: May 31, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING A GATE (56) References Cited DRIVE CIRCUIT (71) Applicant: Samsung Display
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007724243B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,724.243 B2 Geaghan (45) Date of Patent: May 25, 2010 (54) TOUCH SENSORS INCORPORATING 4,731,694. A * 3/1988 Grabner et al... 361,280 CAPACTIVELY
US007724243B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,724.243 B2 Geaghan (45) Date of Patent: May 25, 2010 (54) TOUCH SENSORS INCORPORATING 4,731,694. A * 3/1988 Grabner et al... 361,280 CAPACTIVELY
M3 d. (12) United States Patent US 7,317,435 B2. Jan. 8, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Wei-Chieh Hsueh, Tainan (TW) T GND
 US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B1
 US008284.487B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,284.487 B1 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 9, 2012 (54) LARGE FORMAT TILED PROJECTION (56) References Cited DISPLAY SCREEN WITH FLEXBLE SURFACE
US008284.487B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,284.487 B1 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 9, 2012 (54) LARGE FORMAT TILED PROJECTION (56) References Cited DISPLAY SCREEN WITH FLEXBLE SURFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070107206A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0107206A1 Harris et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A Publication Classification
US 20070107206A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0107206A1 Harris et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0056204 A1 Sakariya et al. US 2016.0056204A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0056204 A1 Sakariya et al. US 2016.0056204A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201601 11776A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0111776 A1 OKUMURA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 21, 2016 (54) RADIO WAVE TRANSMISSIVECOVER (30) Foreign Application
US 201601 11776A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0111776 A1 OKUMURA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 21, 2016 (54) RADIO WAVE TRANSMISSIVECOVER (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060055032A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0055032A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2006 (54) PACKAGING WITH METAL STUDS FORMED ON SOLDER PADS
(19) United States US 20060055032A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0055032A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2006 (54) PACKAGING WITH METAL STUDS FORMED ON SOLDER PADS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,770,955 B1
 USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
Publication number: A2. Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/ Meadowridge Drive Garland, Texas 75044(US)
 Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O145694A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Jang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O145694A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Jang (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,593,696 B2
 USOO65.93696B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2003 (54) LOW DARK CURRENT LINEAR 5,132,593 7/1992 Nishihara... 315/5.41 ACCELERATOR 5,929,567 A 7/1999
USOO65.93696B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2003 (54) LOW DARK CURRENT LINEAR 5,132,593 7/1992 Nishihara... 315/5.41 ACCELERATOR 5,929,567 A 7/1999
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008
 (19) United States US 200800 12008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0012008 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) MAKING ORGANIC THIN FILM (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 200800 12008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0012008 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) MAKING ORGANIC THIN FILM (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0363715 A1 HA et al. US 20160363715A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2016 (54) CURVED DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0363715 A1 HA et al. US 20160363715A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2016 (54) CURVED DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090075412A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0075412 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) VERTICAL GROUP III-NITRIDE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE
(19) United States US 20090075412A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0075412 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) VERTICAL GROUP III-NITRIDE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170070208A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0070208A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) PIEZOELECTRIC OSCILLATOR AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20170070208A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0070208A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) PIEZOELECTRIC OSCILLATOR AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent
 US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
part data signal (12) United States Patent control 33 er m - sm is US 7,119,773 B2
 US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,314,819 B2. Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012
 USOO8314819B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) DISPLAYS WITH INTEGRATED 6,830,339 B2 * 12/2004 Maximus... 353/20 BACKLIGHTING 6,878.494 B2
USOO8314819B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimmel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) DISPLAYS WITH INTEGRATED 6,830,339 B2 * 12/2004 Maximus... 353/20 BACKLIGHTING 6,878.494 B2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170O80447A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0080447 A1 Rouaud (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2017 (54) DYNAMIC SYNCHRONIZED MASKING AND (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 20170O80447A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0080447 A1 Rouaud (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2017 (54) DYNAMIC SYNCHRONIZED MASKING AND (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1
 USOO6346966B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1 TOh (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 12, 2002 (54) IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM FOR 4,900.934. A * 2/1990 Peeters et al.... 250/461.2 MACHINE
USOO6346966B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1 TOh (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 12, 2002 (54) IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM FOR 4,900.934. A * 2/1990 Peeters et al.... 250/461.2 MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
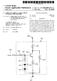 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2017
 (19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
