FDD Uplink 2 TDD 2 VFDD Downlink
|
|
|
- Regina Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1 Li et al. US A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER INFORMATION AND CARRIER INFORMATION INDICATION Inventors: Nan Li, Beijing (CN); Zhenping Hu, Beijing (CN); Dawei Zhang, Beijing (CN); Jin Xu, Beijing (CN) Assignee: CHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATION, Beijing (CN) Appl. No.: 13/704,119 PCT Fled: Jun. 27, 2011 PCT NO.: S371 (c)(1), (2), (4) Date: Jun. 28, 2010 PCT/CN11/76374 Dec. 13, 2012 Foreign Application Priority Data (CN) O4518 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. H047 72/04 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H04W 72/044 ( ) USPC /280 (57) ABSTRACT A method and device for obtaining carrier information and carrier information indication include: a user equipment obtains parameters of uplink carrier information according to the message sent by a network side in broadcast manner, or, the user equipment obtains parameters of uplink carrier infor mation according to the preset information. Time Division Duplex wireless communication system with asymmetry uplink frequency band and downlink frequency band can be Supported effectively, guard frequency band near the inter section occurred when the adjacent frequencies coexist is utilized fully, and frequency spectrum utilization rate is improved; further more, Time Division Duplex wireless com munication system with unequal uplink band width and downlink bandwidth can be supported, and the application of the Time Division Duplex system is expanded effectively. FDD Uplink 2 TDD 2 VFDD Downlink Zone A Zone B Zone C
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 4 US 2013/ A1 LTE FOD UE LTE FDDBS Fig. 1 FDDuplink & TDD & VFDD Downlink Zone A Zone B Zone C Fig. 2 Zone A A A 2% Zone B Zone C 2 W. W W Fig. 3
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 4 US 2013/ A1 network-side equipment issues a message to the 40 user equipment in broadcast manner and indicates a user equipment to obtain a parameter of uplink carrier information the user equipment obtains the parameter of the uplink carrier information according to the message issued by the network-side equipment in broadcast manner; or the user equipment obtains the parameter of the uplink carrier information according to preset information Fig FDD Uplink 3 TDD & FDD Downlink Zone A Zone C Fig. 5
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 4 US 2013/ A1 TDD Uplink Hf-offset 1-> TDD DOWnlink Hif-offset 2-> Hf-offset 3-D Hf-offset 4-> Fig. 6 the network-side equipment obtains a parameter for determining uplink carrier information the network-side equipment issues a message to the user equipment in broadcast manner and indicates the user equipment to obtain the parameter of the uplink carrier information the user equipment obtains the parameter which is sent by the network-side equipment in broadcast manner and used for determining the uplink carrier information the user equipment determines the position of the uplink carrier frequency according to a position parameter, and/or determines a size of the uplink carrier bandwidth according to a bandwidth parameter Fig. 7
5 Patent Application Publication Sheet 4 of 4 US 2013/ A O TEDD TDD o FDD Uplink Uplink TDD! Downlink FDDDownlink UL bandwidth DL bandwidth f-offset Fig O Uplink A. TEDD - TDD - FDD Uplink TD lost FDDDownlink UI bandwidth DL bandwidth foset Fig. 9
6 METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER INFORMATION AND CARRIER INFORMATION INDICATION This application claims the priority of Chinese Patent Application No , entitled METHOD AND EQUIPMENT FOR OBTAINING CAR RIER INFORMATION AND IDENTIFIER OF CARRIER INFORMATION IN TIME DIVISION DUPLEXING SYS TEM, filed with the Chinese Patent Office on Jun. 28, 2010, the entirety of which is incorporated by reference herein. FIELD OF THE INVENTION 0002 The present invention relates to the field of commu nication technology, and in particular to a method and equip ment for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier information. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The Time Division Duplex (TDD) technique is one of the duplex techniques used in a mobile communication system, which corresponds to the Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) technique In a communication system of TDD-mode, the uplink and downlink communications between a base station and a mobile station use different time slots in the same frequency band. The uplink and downlink communications use the same frequency band, and have the same bandwidths by separating the receiving channel from the sending channel by the time. The resources for the uplink or downlink com munication are not continuous in time domain, and the time resources are distributed to both the uplink and downlink communications For FDD, the uplink and downlink communications are respectively performed in two separate symmetrical fre quency channels, and a guard band is used to separate the uplink and downlink channels. Frequencies in pair must be used in FDD, the uplink and the downlink are distinguished by the frequency, and the resources for the uplink or downlink communication are continuous in time domain However, during the implementation of the present invention, the inventor discovered that there are at least the following problems in the prior art In a TDD system, the uplink and downlink transmis sions occupy all the bands. The interference between the uplink and the down link within the working band or at the edge of the working band can not be avoided when the TDD system is configured to work with the other mobile commu nication systems. If the band isolation is implemented by reserving the guide band, the spectrum resource is wasted greatly. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is provided a method and equipment for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier information according to the invention, so as to make operators effectively utilize a guard band near an intersection occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in a wireless system, thus improving spectrum utilization ratio To achieve the above object, it is provided a method for obtaining carrier information by user equipment accord ing to an embodiment of the invention, which is used to time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the method including the following steps: 0010) obtaining, by the user equipment, a parameter of uplink carrier information according to a message issued by a network side in broadcast manner; or obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of uplink carrier information according to preset information It is provided a method for indicating carrier infor mation according to an embodiment of the invention, which is used to a time division duplex wireless communication sys tem in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the method including the following steps: 0012 issuing, by a network-side equipment, a parameter of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner, or issuing, by a network-side equipment, an identi fier of uplink carrier information to the user equipment in broadcast manner It is provided a user equipment according to an embodiment of the invention, which is used to a time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the user equipment including: 0014 an obtaining module adapted to obtain a parameter of uplink carrier information according to a message issued by a network side in broadcast manner or obtain a parameter of uplink carrier information according to preset information It is provided a network-side equipment according to an embodiment of the invention, which is used to a time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the network-side equipment including: 0016 a sending module adapted to issue a parameter of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner or issue an identifier of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner As compared with the prior art, the embodiments of the invention have at least the following advantages The solution according to the present invention can effectively support Time division duplex wireless communi cation system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the guard band near the intersection occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless system is utilized fully, and thus the spectrum utilization ratio is improved. Further, the invention can Support the time division duplex wireless communication system is which the bandwidth of the uplink carrier is unequal to that of the downlink carrier, and the application of the time division duplex system is expanded effectively. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS In order to illustrate the technical solutions accord ing to the embodiments of the invention or in the prior art more clearly, drawings to be used in the description of the prior art or the embodiments will be described briefly here inafter. Apparently, the drawings described hereinafter are only some embodiments of the present invention, and other drawings may be obtained by those skilled in the art accord ing to those drawings without inventive efforts FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink: 0021 FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a structure of a TDD system time of Zone A:
7 0022 FIG.3 is a schematic diagram of performing a trans mission in guard bands of Zone A and Zone C FIG. 4 is a flowchart of a method for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier information according to a first embodiment of the invention; 0024 FIG.5 is a schematic diagram of a structure in which a TDD system coexists with a FDD system defined in an embodiment of the invention; 0025 FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of spacing informa tion between a position of an uplink carrier frequency and a position of a downlink carrier frequency defined in an embodiment of the invention; 0026 FIG. 7 is a flowchart of a method for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier information according to a second embodiment of the invention; 0027 FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of a time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink accord ing to a third embodiment of the invention; and 0028 FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram of a time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink accord ing to a fourth embodiment of the invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION In the existing time division duplex mobile commu nication system, the band occupied by the uplink slots is totally the same as that occupied by the down slots. To avoid the interference, in the prior art, it is necessary to perform band isolation by reserving a guard band. During the layout of the frequency, some band intervals are generally reserved between different wireless businesses, and the reserved band intervals can be used as the guard band which can not be used for the communication. As well known, since the frequency resources are limited and non-renewable, the frequency resource is wasted in the existing method in which the guard band is used To overcome the above problems and improve the utilization ratio of the spectrum resource, the asymmetric time division duplex wireless communication system based on the frequency offset can be adopted, so as to utilize the guard band occurred when FDD and TDD coexist. The term asymmetric' refers to the asymmetry between the uplink band and the downlink band. The so-called symmetric uplink and downlink bands refer that the bandwidth of the uplink is the same as that of the downlink and the center of the uplink is coincidence with that of the downlink. Except for the sym metry, the uplink and downlink bands are asymmetric. For example, the uplink and downlink bands have equal band widths, the center of the uplink band is not coincidence with the center of the downlink band; or the uplink and downlink bands have unequal bandwidths, and the center of the uplink band is not coincidence with the center of the downlink band; or the uplink and downlink bands have unequal bandwidths, the center of the uplink band is coincidence with the center of the downlink band; or carriers composing the uplink band are not continuous, and/or the carriers composing the downlink band are not continuous; or the uplink and downlink bands have no an overlap portion, or the like. In the time division duplex mode, the uplink and downlink bands are configured as asymmetric, so that the uplink and downlink transmission will not occupy all the bands, thus facilitating the decreased uplink and downlink interference within the working band or at the edge of the working band when the system is configured to work with other mobile communication system In FIG. 1, a schematic diagram of a time division duplex (TDD) wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink is shown. This system includes a Long Term Evolution (LTE) TDD based BS (Base Station), a TDD based UE (User Equip ment), a LTE FDD based BS, and an LTE FDD based UE In the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, assumed that the structure of the TDD system time (for example, a time slot distribution of the uplink and downlink, a sign distribution of the uplink and downlink) is as shown in FIG. 2. Zone A and Zone C are the guard bands, Zone B is the band occupied by TDD. The guard band of the Zone A is only permitted to perform the uplink transmission to avoid the interference of the adjacent FDD Uplink, and the guard band of the Zone C is only permitted to perform the downlink transmission to avoid the interference of the adjacent FDD downlink. The uplink and downlink transmissions of individual time slot resource in Zone A, Zone Band Zone Care shown in FIG.3. In this case, it can be seen that for Zone A and Zone C, the downlink will not be interfered by the uplink of the adjacent-frequency system In the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the bandwidths of the Zone A and Zone C can be the same or different. However, if it is necessary to use the spectrums in the Zone A and Zone C in pairs, the spectrums in the Zone A and Zone B in pairs, or the spectrums in the Zone Band Zone C in pairs, it can not be supported by the existing method for configuring system information In the existing method for configuring system infor mation, the d1-bandwidth (downlink bandwidth) parameter is defined in the Master Information Block (MIB), the ul-car rierfreq (a center frequency of the uplink carrier) parameter and the ul-bandwidth (uplink bandwidth) parameter are defined in the System Information Blocks (SIB2). For FDD, if there is no special indication, the duplex spacing defined in TS will be adopted; and for TDD, the ul-carrierfreq can not be configured and is defined as equal to the d1-carri erfreq, and the dil-bandwidth also can not be configured and is defined as equal to the ul-bandwidth For TDD, when the terminal detects a center fre quency of the downlink carrier d1-carrierfreq, it will be con sidered that the center frequency of the uplink carrier ul CarrierFreq is equal to the d1-carrierfreq, the default is to send the uplink data at the d1-carrierfreq. When the d1-band width is received, it will be considered that ul-bandwidth is equal to the d1-bandwidth, the configuration in which the center frequency of the uplink carrier is unequal to the center frequency of the downlink carrier or the bandwidth of uplink carrier is unequal to the bandwidth of downlink carrier can not be supported, i.e., the work of the special TDD system utilizing the guard band can not be Supported. Further, in the research for carrier aggregation, in the scene of the continu ous carrier aggregation in one band in the presently defined time division duplex (TDD) system, the maximum bandwidth of the downlink carrier is 50 MHz, the maximum bandwidth of the uplink carrier is 40 MHz, and the case in which the bandwidth of the uplink carrier is unequal to that of the downlink carrier will occur. In the case of TDD, the existing broadcast message does not support the case that the band
8 width of the uplink carrier is configured to be unequal to that of the downlink carrier, that is, can not support the above application Summarily, the broadcast message issued by the network side in the prior art does not support the configura tion in which the center frequency of the uplink carrier center frequencies is different from that of the downlink carrier and the configuration in which the bandwidth of the uplink carrier is different from that of the downlink carrier, that is, can not support the work of the special TDD system utilizing the guard band described above Because the existing method for obtaining position information and/or bandwidth information of the uplink car rier frequency by user equipment can not support the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the center frequency of the uplink carrier is different from that of the downlink carrier or the bandwidth of the uplink carrier is unequal to that of the downlink carrier, it is provided a method and device for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier information in a time division duplex system according to an embodiment of the invention, for Supporting the work of the above time division duplex wireless commu nication system. The time division duplex wireless commu nication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetri cal with that of the downlink is effectively supported. In addition, the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the bandwidth of the uplink carrier is unequal to that of the downlink carrier is also supported Hereinafter, the technical solutions in the embodi ments of the present invention are described clearly and com pletely in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Apparently, the described are only a part but not all of the embodiments of the present invention. Other embodiments obtained by those skilled in the art based on the embodiments in the present invention without creative effort will fall within the scope of protection of the present invention. First Embodiment As shown in FIG. 4, it is provided a method for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier infor mation according to a first embodiment of the invention, which is used to a time division duplex wireless communica tion system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink. The method includes the following steps Step 401, issuing, by a network-side equipment, a parameter of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner; or issuing, by a network-side equipment, an identifier of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner The uplink carrier information includes but not lim ited to an uplink carrier frequency and/or an uplink carrier bandwidth; the parameter of uplink carrier information include but not limited to: a position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency and/or a bandwidth parameter of an uplink carrier frequency which are configurable; and the positions of the uplink and downlink carrier frequency can be identical or not identical, the uplink and downlink carrier bandwidths can be equal or unequal In this step, the network-side equipment can issues the parameter of the uplink carrier information to the user equipment by a broadcast message, or issues the identifier of the uplink carrier information to the user equipment by a broadcast message The network-side equipment can also carry neither the parameter of the uplink carrier information nor the iden tifier of the uplink carrier information in the broadcast mes sage, the user equipment can obtain the parameter of uplink carrier information directly from the preset information when receiving the broadcast message without the parameter or the identifier Step 402, obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of the uplink carrier information according to a message issued by a network side in broadcast manner; or obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of the uplink carrier information according to preset information Specifically, when the message issued by the net work side in broadcast manner (i.e., the broadcast message) is received, (1)if the parameter of the uplink carrier information are carried in the message, the user equipment obtains the parameter of the uplink carrier information carried in the message issued by the network side in broadcast manner. (2) If the identifier of the uplink carrier information is carried in the message, the user equipment obtains the parameter of the uplink carrier information from preset information according to the identifier of uplink carrier information, in which the identifier of the uplink carrier information corresponds to the parameter of uplink carrier information. (3) If neither the parameter of the uplink carrier information nor the identifier of the uplink carrier information is carried in the message, the parameter of the uplink carrier information is directly obtained from the preset information, in which the preset information includes a position information for determining the uplink carrier frequency and/or a bandwidth information for determining the uplink carrier bandwidth. The preset information is directly set on the user equipment, or issued to the user equipment by the network side and stored on the user equipment If the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier frequency, the identifier of the uplink carrier frequency indicates whether the center fre quency of the uplink carrier is identical with that of the downlink carrier; and if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth, the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth indicates whether the uplink carrier bandwidth is identical with the downlink carrier bandwidth In the embodiment of the invention, the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency includes but not limited to: a center frequency of the uplink carrier frequency, starting position and ending position of the uplink carrier frequency, or spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink carrier frequency. The spacing information between the posi tion of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink carrier frequency includes but not limited to: a spacing between an edge of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an edge of the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spacing between the center frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the center frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spac ing between a start frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and a start frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, or a spacing between a end frequency of the uplink carrier band width and a end frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth.
9 0048. The bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency includes but not limited to: a size of the uplink band width It is to be noted that the technical solution according to the embodiment of the invention is applicable to the time division duplex wireless communication system with asym metric uplink and downlink bands. The band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, and the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system; the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, and the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the downlink bands of the wireless communication system; the band cor responding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, and the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system; the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent fre quency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system; one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coex ist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless commu nication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication sys tem and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communica tion system It can be seen that in the technical solution accord ing to the embodiment of the invention, the position param eter and/or bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency position parameters are obtained and the position and/or bandwidth of the uplink carrier frequency is deter mined according to the above parameters, so as to make the operator effectively utilize a guard band near an intersection occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in a wireless system and improve spectrum utilization ratio. The time division duplex wireless communication with asymmetric uplink and down bands can be Supported effec tively. Further, the time division duplex wireless communi cation system in which the uplink carrier bandwidth is unequal to the downlink carrier bandwidth can be supported. Second Embodiment 0051) To describe the technical solution according to the embodiment of the invention more clearly, the method for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier infor mation in this time division duplex system will be described in detail in connection with the second embodiment of the invention. The uplink carrier information includes but not limited to an uplink carrier frequency and/oran uplink carrier bandwidth. In the embodiment of the invention, a position parameter and/or bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency uplink carrier frequency can be defined in the broadcast information or specification. The position param eter of the uplink carrier frequency is used to indicate the position of the uplink carrier frequency, and the bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency is used to indicate the bandwidth of the uplink carrier. It is to be noted that the position parameter and/or bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency in the broadcast information are config urable In the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, taking FIGS. 2 and 5 as an example for description again, the uplink and downlink bands can respec tively correspond to Zone A and Zone C. Zone A and Zone B: Zone Band Zone C.; or Zone A, Zone Band Zone C, where the sizes and positions of Zone A, Zone B and Zone C can be configured according to the requirement of the coexistence Specifically, the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one (for example, Zone A) of the inter section bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adja cent frequency band in the wireless communication system, and the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is another one (for example, Zone C) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system. Alternatively, one (for example, Zone A) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, and the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one (for example, the band for downlink transmission in Zone B) of the downlink bands of the wireless communication system. Alternatively, one (for example, the band for uplink transmission in Zone B) of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, and the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is another one (for example, Zone C) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system. Alternatively, one (for example, Zone A) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one (for example, Zone C) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coex ist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one (for example, the band for uplink transmis sion in Zone B) of the uplink bands of the wireless commu nication system. Alternatively, the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one (for example, Zone A) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication sys tem and one (for example, the band for uplink transmission in Zone B) of the uplink bands of the wireless communication
10 system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier fre quency is one (for example, Zone C) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system. Alternatively, one (for example, Zone A) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one (for example, the band for uplink transmission in Zone B) of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one (for example, Zone C) of the intersection bands occurred when FDD and TDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system and one (for example, the band for uplink transmission in Zone B) of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system In this time division duplex wireless communica tion system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency includes but not limited to: a center fre quency of the uplink carrier frequency, starting position and ending position of the uplink carrier frequency, or spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier fre quency and the position of the downlink carrier frequency. The spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink carrier frequency includes: a spacing between a bandwidth edge of the uplink carrier and a bandwidth edge of the downlink carrier, a spacing between a center frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and a center frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spacing between a start frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and a start frequency of the down link carrier bandwidth, or a spacing between a end frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and a end frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth In the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency includes: a size of the uplink bandwidth In the embodiment of the invention, to determine the position of the uplink carrier frequency, the position param eter of the uplink carrier frequency is defined by the following manners which include but not limited to: (1) The Position Parameter Defined in the Specification Directly If the system, for example, the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, can be accepted in one region and the positions of the uplink and downlink frequencies can be fixed, the information, such as the position of the uplink carrier frequency (such as the posi tion of the carrier center frequency or the position of the carrier starting frequency) and the position of the downlink carrier frequency (such as the position of the carrier center frequency or the position of the carrier starting frequency), or the spacing between the uplink carrier frequency and the center frequencies of the downlink carrier can be directly defined into the specification, and the position of the uplink carrier frequency can be determined according to the above information. (2) Center Frequency of Uplink Carrier By defining the center frequency of the uplink car rier, the frequency position of the uplink carrier can be deter mined. For example, the centerfrequency of the uplink carrier can be indicated by E-UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number (EARFCN) For example, in the TDD system with an uplink carrier bandwidth of 20 MHz, the frequency ranging from 2570 MHz to 2590 MHz, and center frequency of 2580 MHz, the center frequency of the uplink carrier is directly defined as 2580 MHz, the bandwidthis directly defined as 20 MHZ, and the frequency position and bandwidth of the uplink carrier can be determined The position parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency can be UL CarrierFreq, which is configurable. UL CarrierFreq can be equal to or unequal to the center frequency of the downlink carrier DL-CarrierFreq. (3) Spacing Information (F-Offset) Between the Position of the Uplink Carrier Frequency and the Position of the Downlink Carrier Frequency As shown in FIG. 6, the spacing information is selectively defined by the following manners which includes but not limited to: the spacing f-offset 1 between the band width edge of the uplink carrier (TDD Uplink) and the band width edge of the downlink carrier (TDD Downlink); the spacingf-offset 2 between the center frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the center frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth; the spacing f-offset 3 between the start frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the start fre quency of the downlink carrier bandwidth; and the spacing f-offset 4 between the end frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the end frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth It is to be noted that in the embodiment of the inven tion, the quantification manner of the frequency spacing f offset can be the LTE based channel raster quantification. For example, LTE channel raster is 100 KHZ, and an available quantification of the frequency spacing is the integral times of the channel raster. For example, the spacing is 50 MHz, and the quantification can be described as Generally, the position of the uplink frequency is relatively low, and the position of the downlink frequency is relatively high, and f offset is negative. However in practice, there is possible that the position of the downlink frequency is relatively low and the position of the uplink frequency is relatively high, and f offset is positive. Thus, whether the frequency offset is positive or negative can be indicated by one bit, and the size of the frequency offset can be indicated by other bits. Other manner for indicating whether the fre quency offset is positive or negative is available Further, in the embodiment of the invention, the quantification can be performed in other units, for example, in 1 MHz, which can save bit cost. It can be seen that in practice, the frequency spacing of a pair of the uplink and downlink ranges from tens of MHZ to 100 MHz, which can generally be indicated by only 9 bits to 10 bits Based on this, as shown in FIG. 7, the method for obtaining carrier information and an identifier of carrier infor mation according to the embodiment of the invention includes the following steps Step 701, obtaining, by the network-side equip ment, a parameter for determining the uplink carrier informa tion. The uplink carrier information includes uplink carrier frequency and/or uplink carrier bandwidth; the parameter of uplink carrier information includes: a position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency and/or a bandwidth parameter of
11 the uplink carrier frequency. In the embodiment of the inven tion, the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency is taken as an example for the description For example, the network-side equipment can obtain the center frequency of the uplink carrier; or the net work-side equipment can obtain the spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink carrier frequency (for example, the spacing between an edge of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an edge of the downlink carrier bandwidth) and the like Step 702, issuing, by the network-side equipment, a parameter for determining the uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner, or issuing, by the net work-side equipment, an identifier of uplink carrier informa tion to the user equipment in broadcast manner Specifically, if the network-side equipment deter mines that it is necessary to notify the user equipment of the position parameter and/or bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency, the network-side equipment can send the position parameter and/or bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency to the user equipment in broadcast manner (such as broadcast message), i.e., the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency (the center frequency of the uplink carrier frequency, the starting and ending positions of the uplink carrier frequency, or the spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink carrier frequency) and/or the band width parameter of the uplink carrier frequency (the size of the uplink bandwidth) are carried in the broadcast message It is to be noted that if the uplink carrier information has been written into the specification and the related infor mation for determining the uplink carrier frequency (for example, determining the position of the uplink carrier fre quency) has been stored in the user equipment, the network side can send the identifier of the uplink carrier information to the user equipment in broadcast manner (for example, broad cast message). The identifier of uplink carrier information can be an identifier of the uplink carrier frequency oran identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth. In the case of the identifier of the uplink carrier frequency, the identifier of the uplink carrier frequency indicates whether the center frequency of the uplink carrier is equal to that of the downlink carrier; and in the case of the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth, the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth indicates whether the bandwidth of the uplink carrier is equal to that of the downlink carrier. Further, if the uplink carrier information has been written into the specification and the related information for determining uplink carrier frequency (for example, deter mining the position of the uplink carrier frequency) has been stored in the user equipment, the network side can send no information to the user equipment, and the user equipment sets the uplink carrier frequency and/or the uplink carrier bandwidth according to the stored related information for determining uplink carrier frequency Step 703, obtaining, by the user equipment, the information sent by the network side in broadcast manner so as to determine the parameter of the uplink carrier informa tion; or obtaining, by the user equipment, a preset parameter for determining the uplink carrier information In the embodiment of the invention, when the broad cast message is received from the network side, if the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency (the center fre quency of the uplink carrier frequency, the starting and ending positions of the uplink carrier frequency, or the spacing infor mation between the uplink carrier frequency position and the downlink carrier frequency position) and/or the bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency (the size of the uplink bandwidth) are carried in the broadcast message, the user equipment can obtain the parameter for determining the uplink carrier information directly according to the broadcast message Further, if the parameters of uplink carrier informa tion have been written into the specification and the related information for determining the uplink carrier frequency has been stored in the user equipment, because the user equip ment has stored the related information for determining the uplink carrier frequency, the user equipment can obtain the preset parameter for determining the uplink carrier informa tion according to the information stored by itself, even if the parameter of uplink carrier information is not carried in the broadcast message Specifically, when the network side issues the iden tifier of the uplink carrier information (for example, an iden tifier of the uplink carrier frequency or an identifier of the downlink carrier frequency) to the user equipment in broad cast manner, according to the identifier of the uplink carrier information, the user equipment determine that the preset parameter for determining the uplink carrier information is obtained according to the information stored by itself. In addition, in practical application, the user equipment can obtain the preset parameter for determining the uplink carrier information according to the information stored by itself. even if the parameter or identifier of the uplink carrier infor mation is not carried in the broadcast message received from the network side It is to be noted that in this step, before obtaining the preset parameter for determining the uplink carrier informa tion, the user equipment needs to store the parameter for determining the uplink carrier information. The method for storing the parameter includes but not limited to: Storing directly the related information defined in the specification (for example, the position of the uplink carrier frequency, the size of the uplink carrier frequency bandwidth, and the like): receiving the parameter for determining the uplink carrier information that is issued by the network side in broadcast manner, and storing the parameter Step 704, determining, by the user equipment, the position of the uplink carrier frequency according to the posi tion parameter of the uplink carrier frequency, and/or deter mining, by the user equipment, the size of the uplink carrier bandwidth according to the bandwidth parameter for the uplink carrier frequency In the embodiment of the invention, when the posi tion of the uplink carrier frequency is determined, the deter mined position can be a specific position point or a range, which will not be described any more in detail in the embodi ment of the invention. Third Embodiment As shown in FIG. 8, in the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the working frequency of FDD is / MHz, the work ing frequency of TDD is MHz, and the MHz can be used for the asymmetric time division duplex in pairs. (0079. In the MIB or SIB in the broadcast information (the broadcast information is only one carrying manner in the
12 invention, other message issued in broadcast manner is avail able), a new parameter f offset is defined for indicating that the spacing between the center frequencies of the uplink carrier and the downlink carrier is 40 MHz, which is repre sented as Once reading the downlink and uplink bandwidths in the broadcast information, the UE reads the spacing between the center frequencies of the uplink carrier and the downlink carrier in the broadcast information: f offset=- 400, and the center frequency UL CarrierFreq (37799) of the uplink carrier can be determined as 2575 MHz according to the EARFCN (numbered as ) corresponding to the center frequency 2615 MHz of the downlink carrier and the f offset parameter (-400). I0081 Further, EARFCN of the UL CarrierFreq can be directly added into the broadcast information. In the applica tion shown in FIG. 8, the value of the UL CarrierFreq is Fourth Embodiment As shown in FIG. 9, in the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the working frequency of FDD is / MHz, the work ing frequency of TDD is MHz, the / MHZ can be used for the asymmetric time division duplex in pairs A new parameter f offset is defined for indicating the spacing between the center frequencies of the uplink carrier and the downlink carrier in the MIB or SIB of the broadcast information. F offset is 42.5 MHz, which is repre sented as Once reading the downlink and uplink bandwidths in the broadcast information, the UE reads the spacing between the center frequencies of the uplink carrier and the downlink carrier in the broadcast information: f offset=- 425, and the working frequency UL CarrierFreq (37799) of the uplink can be determined as 2575 MHz according to the EARFCN (numbered as 38224) corresponding to the center frequency MHz of the downlink carrier and thef off set parameter (-425). I0085. Further, EARFCN of the UL CarrierFreq can be directly added into the broadcast information. In the applica tion shown in FIG. 9, the value of the UL CarrierFreq is Fifth Embodiment I0086 Based on the same inventive conception, it is further provided with a user equipment according to the embodiment of the present invention, which is used to a time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink. The user equipment includes: 0087 an obtaining module adapted to obtain a parameter of uplink carrier information according to a message issued by a network side in broadcast manner or obtaining a param eter of uplink carrier information according to preset infor mation The obtaining module can be divided into a first sub-module and a second sub-module. The first sub-module is adapted to receive the message from the network side, the second Sub-module is adapted to perform the operation of obtaining the parameter of the uplink carrier information. In the further description of the obtaining module, the second Sub-module is adapted to perform various operations of obtaining the parameter of the uplink carrier information. I0089. In the embodiment of the invention, the obtaining module is adapted to obtain the parameter of the uplink carrier information carried in a message, if the parameter of uplink carrier information is carried in the message Specifically, the obtaining module is adapted to obtain the parameter of the uplink carrier information from preset information according to an identifier of uplink carrier information, if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is carried in a message issued by the network side in broadcast manner, in which the identifier of the uplink carrier informa tion corresponds to the parameter of the uplink carrier infor mation The parameter of the uplink carrier information is directly obtained from preset information, if neither the parameter of the uplink carrier information nor the identifier of the uplink carrier information is carried in the message issued by the network side in broadcast manner, in which the preset information includes the position information for determining the uplink carrier frequency and/or the band width information for determining the uplink carrier band width The preset information is directly set on the user equipment, or issued to the user equipment by the network side and stored into the user equipment In the embodiment of the invention, the uplink car rier information includes an uplink carrier frequency and/or an uplink carrier bandwidth. In the case that the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier frequency, the identifier of the uplink carrier fre quency indicates whether the center frequency of the uplink carrier is identical to that of the downlink carrier. In the case that the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an iden tifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth, the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth indicates whether the uplink carrier bandwidth is identical to the downlink carrier bandwidth Further, the parameter of the uplink carrier informa tion include: a position parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency and/or a bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency; the position parameter and/or bandwidth param eter of the uplink carrier frequency are configurable The position parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency includes but not limited to: the center frequency of the uplink carrier frequency, the starting position and ending position of the uplink carrier frequency, or the spacing infor mation between the positions of the uplink carrier frequency and the downlink carrier frequency. The spacing information between the positions of the uplink carrier frequency and the downlink carrier frequency includes: spacing between the edges of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the downlink car rier bandwidth, spacing between the center frequencies of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the downlink carrier bandwidth, spacing between the starting frequencies of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the downlink carrier bandwidth, or spacing between the ending frequencies of the uplink carrier band width and the downlink carrier bandwidth; and the bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency include: a size of the uplink bandwidth The user equipment is applicable to the time divi sion duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink. The band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one
13 of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coex ist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier fre quency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, the band corre sponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the downlink bands of the wireless communication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is another com munication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band correspond ing to the downlink carrier frequency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication sys tem; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the downlink bands of the wireless com munication system and another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system Individual modules of the device according to the invention can be integrated as a whole, and can also be sepa rately deployed. The above modules can be integrated as one module, and can also be further divided into multiple sub modules. Sixth Embodiment 0098 Based on the same inventive conception, it is further provided with a network-side equipment according to the embodiment of the present invention, which is used to a time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink. The network-side equipment includes: 0099 a sending module adapted to issue a parameter of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner or issuing an identifier of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner. The uplink carrier information includes uplink carrier frequency and/or uplink carrier bandwidth The sending module is further adapted to send to the user equipment abroadcast message which does not carry the parameter of the uplink carrier information and the identifier of the uplink carrier information. When receiving the broad cast message, the user equipment can obtain the parameter of the uplink carrier information directly from the preset infor mation If the identifier of uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier frequency, the identifier of the uplink carrier frequency indicates whether the center fre quency of the uplink carrier is identical to that of the downlink carrier. 0102) If the identifier of uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth, the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth indicates whether the uplink carrier bandwidth is identical to the downlink carrier bandwidth. 0103) The parameter of uplink carrier information includes but not limited to: a position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency and/or a bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency which are configurable. The position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency includes: a center frequency of the uplink carrier frequency, starting position and ending position of the uplink carrier frequency, or spac ing information between the positions of the uplink carrier frequency and the downlink carrier frequency. The spacing information between the positions of the uplink carrier fre quency and the downlink carrier frequency includes: a spac ing between the edges of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spacing between the center frequencies of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spacing between the starting frequencies of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the downlink carrier bandwidth, or a spacing between the ending frequencies of the uplink carrier bandwidth and the downlink carrier band width. The bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency includes: a size of the uplink bandwidth The network-side equipment is applicable to the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink. The band corresponding to the uplink carrier fre quency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and communication system, the band corresponding to the down link carrier frequency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication sys tem, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier fre quency is one of the downlink bands of the wireless commu nication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the down link carrier frequency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication sys tem, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier fre quency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrierfrequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication sys tem; or the band corresponding to the uplink carrier frequency is FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless
14 communication system, the band corresponding to the down link carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system Individual modules of the device according to the invention can be integrated as a whole, and can also be sepa rately deployed. The above modules can be integrated as one module, and can also be further divided into multiple sub modules It can be seen that in the technical solutions accord ing to an individual embodiment of the invention, for the TDD system, the downlink bandwidth is 50 MHz, the uplink band width is 40 MHz. In the existing system, the bandwidths of the uplink and downlink in the TDD system are equal, which is unable to support the normal work of the above system. According to the technical solutions according to an indi vidual embodiment of the invention, the uplink carrier band width information is issued in the broadcast information, the information parameter is configurable, which is equal or unequal to the downlink bandwidth, the user equipment set the uplink carrier bandwidth according to the above informa tion, so as to effectively support the work of the system With the description of the above embodiments, it can be clearly learn by those skilled that the present invention can be implemented by hardware, and can also be imple mented by software tighter with necessary hardware plat form. Based on this understanding, the technical Solution according to the invention can be embodied in the form of software productions which software production can be stored in a non-volatile storage medium (such as CD-ROM, U disk, or mobile hard disk), including several instructions, for enabling a computing device (such as a personal computer, a server, or a network equipment) perform the methods accord ing to individual embodiments of the invention It can be understood by those skilled in the art that the figures are only schematic diagrams of the preferred embodiment, the module or flow in the figure are not neces sary for implementing the invention It can be understood by those skilled in the art that the modules in the device according to the embodiment can be distributed in the device according to the embodiment in accordance with the description in the embodiment, and can also be correspondingly varied to be located in one or more device different from that of the embodiment of the invention. The above modules of the embodiment can be combined into one module, and can also be further divided into multiple Sub-modules The above numbers in the invention are only for description, but not represent the advantage or disadvantage of the invention The disclosed above are only several specific embodiments of the present invention, however, the present invention is not limited to this, any variation that can be made by those skilled in the art falls within the scope of protection of the present invention. 1. A method for obtaining carrier information by user equipment, which is used to a time division duplex, TDD, wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the method comprising: obtaining, by the user equipment, a parameter of uplink carrier information according to a message issued by a network side in broadcast manner; or obtaining, by the user equipment, a parameter of uplink carrier informa tion according to preset information. 2. The method according to claim 1, wherein the obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of the uplink carrier information according to the message issued by the network side in broadcast manner, comprises: obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of the uplink carrier information carried in the message issued by the network side in broadcast manner, if the param eter of the uplink carrier information is carried in the message. 3. The method according to claim 1, wherein the obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of the uplink carrier information according to the preset information, comprises: obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of the uplink carrier information from the preset information according to an identifier of the uplink carrier informa tion, if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is carried in a message issued by the network side in broad cast manner, wherein the identifier of the uplink carrier information corresponds to the parameter of the uplink carrier information; and obtaining, by the user equipment, the parameter of the uplink carrier information directly from the preset infor mation, if neither the parameter of the uplink carrier information nor the identifier of the uplink carrier infor mation is carried in the message issued by the network side in broadcast manner, wherein the preset informa tion comprises position information for determining an uplink carrier frequency and/or bandwidth information for determining an uplink carrier bandwidth. 4. The method according to claim 3, wherein the preset information is directly set on the user equipment, or issued to the user equipment by the network side and stored into the user equipment. 5. The method according to claim 3, wherein the uplink carrier information comprises the uplink carrier frequency and/or the uplink carrier bandwidth: if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier frequency, the identifier of the uplink carrier frequency indicates whether a center frequency of the uplink carrier is identical to a center frequency of the downlink carrier, and if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth, the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth indicates whether the uplink carrier bandwidth is identical to the downlink carrier bandwidth. 6. The method according to claim 1, wherein the uplink carrier information comprises an uplink carrier frequency and/or an uplink carrier bandwidth: the parameter of the uplink carrier information comprises: a position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency and/or a bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency: wherein the position parameter and/or bandwidth param eter of the uplink carrier frequency are configurable. 7. The method according to claim 6, wherein the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency comprises: a center frequency of the uplink carrier frequency, a starting position and an ending position of the uplink carrier frequency, or spacing information between a position of the uplink carrier frequency and a position of the downlink carrier frequency; and
15 10 the spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink car rier frequency comprises: a spacing between an edge of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an edge of the down link carrier bandwidth, a spacing between a center fre quency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and a center frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spacing between a starting frequency of the uplink carrier band width and a starting frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, or a spacing between an ending frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an ending frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth. 8. The method according to claim 6, wherein the bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency comprises: a size of the uplink bandwidth. 9. The method according to claim 1, wherein in the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, Frequency Division Duplex, FDD, coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier fre quency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system; communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the downlink bands of the wireless communication system; one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent fre quency band in the wireless communication system; communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communica tion system; communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corre sponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coex ist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system; or communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corre sponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coex ist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system. 10. A method for indicating carrier information, which is used to a time division duplex, TDD, wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the method comprising: issuing, by a network-side equipment, a parameter of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broad cast manner; or issuing, by a network-side equipment, an identifier of uplink carrier information to a user equipment in broadcast manner. 11. The method according to claim 10, wherein the uplink carrier information comprises an uplink carrier frequency and/or an uplink carrier bandwidth: if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier frequency, the identifier of the uplink carrier frequency indicates whether a center frequency of the uplink carrier is identical to a center frequency of the downlink carrier, and if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth, the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth indicates whether the uplink carrier bandwidth is identical to the downlink carrier bandwidth. 12. The method according to claim 10, wherein the uplink carrier information comprises an uplink carrier frequency and/or an uplink carrier bandwidth: the parameter of the uplink carrier information comprises: a position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency and/or a bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier fre quency: wherein the position parameter and/or bandwidth param eter of the uplink carrier frequency are configurable. 13. The method according to claim 12, wherein the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency comprises: a center frequency of the uplink carrier frequency, a starting position and an ending position of the uplink carrier frequency, or a spacing information between a position of the uplink carrier frequency and a position of the downlink carrier frequency; and the spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink car rier frequency comprises: a spacing between an edge of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an edge of the down link carrier bandwidth, a spacing between a center fre quency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and a center frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spacing between a starting frequency of the uplink carrier band width and a starting frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, or a spacing between an ending frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an ending frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth. 14. The method according to claim 12, wherein the band width parameter of the uplink carrier frequency comprises: a size of the uplink bandwidth. 15. The method according to claim 10, wherein in the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, Frequency Division Duplex, FDD, coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier fre
16 11 quency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system; communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the downlink bands of the wireless communication system; one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is another one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent fre quency band in the wireless communication system; communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communica tion system, communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corre sponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coex ist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system, or communication system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system, the band corre sponding to the downlink carrier frequency is one of the intersection bands occurred when TDD and FDD coex ist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communi cation system and one of the uplink bands of the wireless communication system. 16. A user equipment, which is used to a time division duplex, TDD, wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, the user equipment comprising: an obtaining module adapted to obtain a parameter of uplink carrier information according to a message issued by a network side in broadcast manner or obtain a parameter of uplink carrier information according to preset information. 17. The user equipment according to claim 16, wherein the obtaining module is adapted to obtain the parameter of the uplink carrier information carried in the message issued by the network side in broadcast manner, if the parameter of the uplink carrier information is carried in the message. 18. The user equipment according to claim 16, wherein the obtaining module is adapted to obtain the parameter of the uplink carrier information from the preset informa tion according to an identifier of the uplink carrier infor mation, if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is carried in the message issued by the network side in broadcast manner, wherein the identifier of the uplink carrier information corresponds to the parameter of the uplink carrier information; and obtain the parameter of the uplink carrier information directly from the preset information, if neither the parameter of the uplink carrier information nor the iden tifier of the uplink carrier information is carried in the message issued by the network side in broadcast man ner, wherein the preset information comprises position information for determining an uplink carrier frequency and/or bandwidth information for determining an uplink carrier bandwidth. 19. The user equipment according to claim 18, wherein the preset information is directly set on the user equipment, or issued to the user equipment by the network side and stored into the user equipment. 20. The user equipment according to claim 18, wherein the uplink carrier information comprises the uplink carrier fre quency and/or the uplink carrier bandwidth: if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier frequency, the identifier of the uplink carrier frequency indicates whether a center frequency of the uplink carrier is identical to a center frequency of the downlink carrier, and if the identifier of the uplink carrier information is an identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth, the identifier of the uplink carrier bandwidth indicates whether the uplink carrier bandwidth is identical to the downlink carrier bandwidth. 21. The user equipment according to claim 20, wherein the parameter of uplink carrier information comprises: a position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency and/or a bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency; wherein the posi tion parameter and/or bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency are configurable; the position parameter of the uplink carrier frequency com prises: a center frequency of the uplink carrier fre quency, a starting position and an ending position of the uplink carrier frequency, or spacing information between a position of the uplink carrier frequency and a position of the downlink carrier frequency; the spacing information between the position of the uplink carrier frequency and the position of the downlink car rier frequency comprises: a spacing between an edge of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an edge of the down link carrier bandwidth, a spacing between a center fre quency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and a center frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, a spacing between a starting frequency of the uplink carrier band width and a starting frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth, or a spacing between an ending frequency of the uplink carrier bandwidth and an ending frequency of the downlink carrier bandwidth; and the bandwidth parameter of the uplink carrier frequency comprises: a size of the uplink bandwidth. 22. The user equipment according to claim 16, wherein in the time division duplex wireless communication system in which the band of the uplink is asymmetrical with that of the downlink, Frequency Division Duplex, FDD, coexist in adjacent frequency band in the wireless communication system, the band corresponding to the downlink carrier fre
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0110060 A1 YAN et al. US 2015O110060A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) METHOD FOR ADUSTING RESOURCE CONFIGURATION,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0110060 A1 YAN et al. US 2015O110060A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) METHOD FOR ADUSTING RESOURCE CONFIGURATION,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Li (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016031 6375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0316375 A1 Li (43) Pub. Date: (54) NETWORK CONTROLLER, STATION, AND H04B 7/06 (2006.01) METHOD FORESTABLISHING
(19) United States US 2016031 6375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0316375 A1 Li (43) Pub. Date: (54) NETWORK CONTROLLER, STATION, AND H04B 7/06 (2006.01) METHOD FORESTABLISHING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Let al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 0343359A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343359 A1 Let al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2013 0343359A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343359 A1 Let al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014005 1427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0051427 A1 Yamazaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2014 (54) BASE STATION AND CONTROL METHOD THEREOF (75)
(19) United States US 2014005 1427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0051427 A1 Yamazaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2014 (54) BASE STATION AND CONTROL METHOD THEREOF (75)
REPEATER I. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. REPEATER is. A v. (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20140370888A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0370888 A1 Kunimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, LOCATION REGISTRATION METHOD, REPEATER,
(19) United States US 20140370888A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0370888 A1 Kunimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, LOCATION REGISTRATION METHOD, REPEATER,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701.24860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/012.4860 A1 SHH et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMITTER AND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. THEREOF
(19) United States US 201701.24860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/012.4860 A1 SHH et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMITTER AND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. THEREOF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160255572A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0255572 A1 Kaba (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) ONBOARDAVIONIC SYSTEM FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN AN AIRCRAFT
(19) United States US 20160255572A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0255572 A1 Kaba (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) ONBOARDAVIONIC SYSTEM FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN AN AIRCRAFT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 201402862O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286202 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) BEAMFORMING WITH PHASE COMPENSATION (52) U.S. Cl.
US 201402862O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286202 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) BEAMFORMING WITH PHASE COMPENSATION (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070042773A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0042773 A1 Alcorn (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 22, 2007 (54) BROADBAND WIRELESS Publication Classification COMMUNICATION
US 20070042773A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0042773 A1 Alcorn (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 22, 2007 (54) BROADBAND WIRELESS Publication Classification COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO63341A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0063341 A1 Ishii et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, RADIO BASE STATION, SCHEDULING APPARATUS,
(19) United States US 2005OO63341A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0063341 A1 Ishii et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, RADIO BASE STATION, SCHEDULING APPARATUS,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080280631A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0280631 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR PROCESSING PAGING INFORMATION IN A WIRELESS MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 20080280631A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0280631 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR PROCESSING PAGING INFORMATION IN A WIRELESS MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
(19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
United States Patent (19) PeSola et al.
 United States Patent (19) PeSola et al. 54) ARRANGEMENT FORTRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING RADIO FREQUENCY SIGNAL AT TWO FREQUENCY BANDS 75 Inventors: Mikko Pesola, Marynummi; Kari T. Lehtinen, Salo, both of
United States Patent (19) PeSola et al. 54) ARRANGEMENT FORTRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING RADIO FREQUENCY SIGNAL AT TWO FREQUENCY BANDS 75 Inventors: Mikko Pesola, Marynummi; Kari T. Lehtinen, Salo, both of
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0026979 A1 Dimou et al. US 20170026979A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) METHODS AND APPARATUSES FOR LOWERING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0026979 A1 Dimou et al. US 20170026979A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) METHODS AND APPARATUSES FOR LOWERING
USOO A. United States Patent Patent Number: 5,327,575 Menich et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994
 b III USOO5327575A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,327,575 Menich et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 54 DIRECTIONAL HANDOVER CONTROLIN Assistant Examiner-Thanh C. Le E. NSE RADIOSYSTEMS
b III USOO5327575A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,327,575 Menich et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 54 DIRECTIONAL HANDOVER CONTROLIN Assistant Examiner-Thanh C. Le E. NSE RADIOSYSTEMS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054492 A1 Mende et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) ISOLATED PROBE WITH DIGITAL Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2015.0054492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054492 A1 Mende et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) ISOLATED PROBE WITH DIGITAL Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A : Offsetting a start of a frame for at least one device with
 US 200700.54680A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0054680 A1 MO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 8, 2007 (54) METHOD OF BAND MULTIPLEXING TO Publication Classification
US 200700.54680A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0054680 A1 MO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 8, 2007 (54) METHOD OF BAND MULTIPLEXING TO Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0028258 A1 Ma et al. US 20090028258A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR TRANSMISSION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0028258 A1 Ma et al. US 20090028258A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR TRANSMISSION
(12) United States Patent
 USOO813 1231B2 (12) United States Patent Yu et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.131,231 B2 Mar. 6, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CANCELING INTERFERENCE IN A HYBRD TERMINAL SUPPORTING BOTH
USOO813 1231B2 (12) United States Patent Yu et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.131,231 B2 Mar. 6, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CANCELING INTERFERENCE IN A HYBRD TERMINAL SUPPORTING BOTH
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,438,377 B1
 USOO6438377B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Savolainen (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 : (54) HANDOVER IN A MOBILE 5,276,906 A 1/1994 Felix... 455/438 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM 5,303.289 A 4/1994
USOO6438377B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Savolainen (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 : (54) HANDOVER IN A MOBILE 5,276,906 A 1/1994 Felix... 455/438 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM 5,303.289 A 4/1994
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO833 1271B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,331.271 B2 Dec. 11, 2012 (54) RELAY STATION AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMUSING THE SAME (75) Inventors:
USOO833 1271B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,331.271 B2 Dec. 11, 2012 (54) RELAY STATION AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMUSING THE SAME (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006.0143444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0143444 A1 Malkamaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data COMMUNICATING
US 2006.0143444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0143444 A1 Malkamaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data COMMUNICATING
lb / 1b / 2%: 512 /516 52o (54) (75) (DK) (73) Neubiberg (DE) (DK); Peter Bundgaard, Aalborg (21) Appl. No.: 12/206,567 In?neon Technologies AG,
 US 20100061279A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0061279 A1 Knudsen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 11, 2010 (54) (75) (73) TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING WIRELESS
US 20100061279A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0061279 A1 Knudsen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 11, 2010 (54) (75) (73) TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING WIRELESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115605 A1 Dimig et al. US 2011 0115605A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115605 A1 Dimig et al. US 2011 0115605A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0249222 A1 Li et al. US 20160249222A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) ACCESS NODE, A COMMUNICATION DEVICE, RESPECTIVE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0249222 A1 Li et al. US 20160249222A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) ACCESS NODE, A COMMUNICATION DEVICE, RESPECTIVE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0326360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0326360 A1 Malladi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 12, 2015 (54) NON-ORTHOGONAL MULTIPLE ACCESS (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0326360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0326360 A1 Malladi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 12, 2015 (54) NON-ORTHOGONAL MULTIPLE ACCESS (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011021 1485A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0211485 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR OPERATINGA MULT-USERMULTIPLE-INPUT
(19) United States US 2011021 1485A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0211485 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR OPERATINGA MULT-USERMULTIPLE-INPUT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160057718A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0057718A1 Sorrentino et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (60) METHODS AND WIRELESS DEVICES
(19) United States US 20160057718A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0057718A1 Sorrentino et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (60) METHODS AND WIRELESS DEVICES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,054,790 B2
 USO08054790B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Weaver (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2011 (54) FREQUENCY MAPPING FOR AWIRELESS 2005/0202784 A1* 9, 2005 Xu et al.... 455, 63.3 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
USO08054790B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Weaver (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2011 (54) FREQUENCY MAPPING FOR AWIRELESS 2005/0202784 A1* 9, 2005 Xu et al.... 455, 63.3 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent
 US007072416B1 (12) United States Patent Sudo et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,072,416 B1 Jul. 4, 2006 (54) TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING DEVICE AND TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING METHOD (75) Inventors:
US007072416B1 (12) United States Patent Sudo et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,072,416 B1 Jul. 4, 2006 (54) TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING DEVICE AND TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING METHOD (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,102,301 B2. Mosher (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2012
 USOO8102301 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,102,301 B2 Mosher (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2012 (54) SELF-CONFIGURING ADS-B SYSTEM 2008/010645.6 A1* 2008/O120032 A1* 5/2008 Ootomo et
USOO8102301 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,102,301 B2 Mosher (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2012 (54) SELF-CONFIGURING ADS-B SYSTEM 2008/010645.6 A1* 2008/O120032 A1* 5/2008 Ootomo et
PLLC. Jul. 2, 2008 (IL) all class II ZZ ,89 % %
 USOO792.9468B2 (12) United States Patent Goldhamer (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR IMPROVING COEXISTENCE BETWEEN ADJACENT TOD AND FDD WIRELESS NETWORKS Inventor: Mariana
USOO792.9468B2 (12) United States Patent Goldhamer (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR IMPROVING COEXISTENCE BETWEEN ADJACENT TOD AND FDD WIRELESS NETWORKS Inventor: Mariana
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0225175 A1 OBUCH et al. US 20130225175A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) RADIO COMMUNICATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0225175 A1 OBUCH et al. US 20130225175A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) RADIO COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,213,350 B2
 USOO8213OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,213,0 B2 Courseille () Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2012 (54) COMMUNICATION NETWORK WITH (56) References Cited RELAYING OF RADIO SIGNALS BY RELAY TERMINALS
USOO8213OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,213,0 B2 Courseille () Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2012 (54) COMMUNICATION NETWORK WITH (56) References Cited RELAYING OF RADIO SIGNALS BY RELAY TERMINALS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 201501 17275A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0117275 A1 PARK (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS OF Publication Classification TRANSMITTING
US 201501 17275A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0117275 A1 PARK (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS OF Publication Classification TRANSMITTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150319747A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0319747 A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) MULTIPLE USER ALLOCATION SIGNALING (52) U.S. CI. NAWIRELESS
US 20150319747A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0319747 A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) MULTIPLE USER ALLOCATION SIGNALING (52) U.S. CI. NAWIRELESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
GENERATING SCHEDULING BLOCK
 US 20100272003A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0272003 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 28, 2010 (54) SCHEDULINGAPPARATUS AND METHOD Sep. 29, 2009 (KR)... 10-2009-0092474
US 20100272003A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0272003 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 28, 2010 (54) SCHEDULINGAPPARATUS AND METHOD Sep. 29, 2009 (KR)... 10-2009-0092474
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7043221B2 (12) United States Patent Jovenin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 13, 2001
USOO7043221B2 (12) United States Patent Jovenin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 13, 2001
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O102948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0102948 A1 Stanwood et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 1, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2002O102948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0102948 A1 Stanwood et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 1, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0312599A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0312599 A1 Durst (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MEASURING Publication Classification PRODUCTIVITY
US 2010.0312599A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0312599 A1 Durst (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MEASURING Publication Classification PRODUCTIVITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090021447A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0021447 A1 Austin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 22, 2009 (54) ALIGNMENT TOOL FOR DIRECTIONAL ANTENNAS (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20090021447A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0021447 A1 Austin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 22, 2009 (54) ALIGNMENT TOOL FOR DIRECTIONAL ANTENNAS (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090034455A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0034455A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING CONTROL INFORMATION OF DATA CHANNEL
(19) United States US 20090034455A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0034455A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING CONTROL INFORMATION OF DATA CHANNEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
(19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O153472A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0153472 A1 Phan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) RELAYING MULTICAST DATA INA (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS
(19) United States US 2014O153472A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0153472 A1 Phan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) RELAYING MULTICAST DATA INA (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0205119 A1 Timofeev et al. US 2011 0205119A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2011 (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) DUAL-BEAM SECTORANTENNA
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0205119 A1 Timofeev et al. US 2011 0205119A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2011 (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) DUAL-BEAM SECTORANTENNA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8909273B2 (12) United States Patent Fukumoto et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 2014 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHOD, TERMINAL APPARATUS, AND COMMUNICATION
USOO8909273B2 (12) United States Patent Fukumoto et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 2014 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHOD, TERMINAL APPARATUS, AND COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,654,902 B2
 USOO94902B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Oh () Date of Patent: May 16, 2017 (54) METHODS FOR PERFORMING MACHINE (56) References Cited TYPE COMMUNICATION FOR THE PURPOSE OF COVERAGE ENHANCEMENT
USOO94902B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Oh () Date of Patent: May 16, 2017 (54) METHODS FOR PERFORMING MACHINE (56) References Cited TYPE COMMUNICATION FOR THE PURPOSE OF COVERAGE ENHANCEMENT
(O2 s. starriversion. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0217540 A1 Onggosanusi et al. US 20070217540A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 20, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) PRE-CODER SELECTION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0217540 A1 Onggosanusi et al. US 20070217540A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 20, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) PRE-CODER SELECTION
(12) United States Patent
 US008472368B2 (12) United States Patent Baldemair et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,472,368 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENTS
US008472368B2 (12) United States Patent Baldemair et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,472,368 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. Lu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015
 US 201500.94057A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0094057 A1 Lu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015 (54) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENT FOR D2D Publication Classification
US 201500.94057A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0094057 A1 Lu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015 (54) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENT FOR D2D Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,325,650 B2
 USOO8325650B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,325,650 B2 Hu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2012 (54) METHOD FOR REDUCING DELAY INA (56) References Cited COMMUNICATION SYSTEM EMPLOYING
USOO8325650B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,325,650 B2 Hu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2012 (54) METHOD FOR REDUCING DELAY INA (56) References Cited COMMUNICATION SYSTEM EMPLOYING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0248451 A1 Weissman et al. US 20160248451A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) TRANSCEIVER CONFIGURATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0248451 A1 Weissman et al. US 20160248451A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) TRANSCEIVER CONFIGURATION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Hunt USOO6868079B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM WITH REQUEST RE-TRANSMISSION UNTIL ACKNOWLEDGED (75) Inventor: Bernard Hunt,
(12) United States Patent Hunt USOO6868079B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM WITH REQUEST RE-TRANSMISSION UNTIL ACKNOWLEDGED (75) Inventor: Bernard Hunt,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 2014O169236A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0169236A1 CHOI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2014 (54) FEED FORWARD SIGNAL CANCELLATION Publication Classification
US 2014O169236A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0169236A1 CHOI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2014 (54) FEED FORWARD SIGNAL CANCELLATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 OO14910A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0014910 A1 YONGE, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2011 (54) CHANNEL REUSE IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (75)
(19) United States US 2011 OO14910A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0014910 A1 YONGE, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2011 (54) CHANNEL REUSE IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Chu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013
 US 2013 O155930A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0155930 A1 Chu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUB-1GHZ GROUP POWER SAVE Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 2013 O155930A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0155930 A1 Chu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUB-1GHZ GROUP POWER SAVE Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201403.35795A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0335795 A1 Wilbur (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2014 (54) SOFTWARE APPLICATIONS FOR DISPLAYING AND OR RECORDING
(19) United States US 201403.35795A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0335795 A1 Wilbur (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2014 (54) SOFTWARE APPLICATIONS FOR DISPLAYING AND OR RECORDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060013285A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION APPARATUS, BASE STATION AND SYSTEM (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060013285A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION APPARATUS, BASE STATION AND SYSTEM (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,449,544 B2
 USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
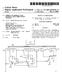 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090316659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0316659 A1 Lindoff et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) IDENTIFYING MULTI-COMPONENT CARRIER CELLS (75)
(19) United States US 20090316659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0316659 A1 Lindoff et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) IDENTIFYING MULTI-COMPONENT CARRIER CELLS (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070047712A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0047712 A1 Gross et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) SCALABLE, DISTRIBUTED ARCHITECTURE FOR FULLY CONNECTED
(19) United States US 20070047712A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0047712 A1 Gross et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) SCALABLE, DISTRIBUTED ARCHITECTURE FOR FULLY CONNECTED
(12) United States Patent
 USO08098.991 B2 (12) United States Patent DeSalvo et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) WIDEBAND RF PHOTONIC LINK FOR DYNAMIC CO-SITE
USO08098.991 B2 (12) United States Patent DeSalvo et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) WIDEBAND RF PHOTONIC LINK FOR DYNAMIC CO-SITE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0258938 A1 Sagfors et al. US 20130258938A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS AND NODES FOR SETTING (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) VALUES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0258938 A1 Sagfors et al. US 20130258938A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS AND NODES FOR SETTING (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) VALUES
TEPZZ 5Z 8 9B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 52/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
\ Y 4-7. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States. de La Chapelle et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 (19) United States US 2006027.0354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0270354 A1 de La Chapelle et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RF SIGNAL FEED THROUGH METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHIELDED
(19) United States US 2006027.0354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0270354 A1 de La Chapelle et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RF SIGNAL FEED THROUGH METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHIELDED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Kummetz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2012
 (19) United States US 20120309293A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0309293 A1 Kummetz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE REPEATER SYSTEMAND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 45.5/11.1
(19) United States US 20120309293A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0309293 A1 Kummetz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE REPEATER SYSTEMAND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 45.5/11.1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O2538.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0253843 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM OF MANAGEMENT FOR SWITCHINGVIRTUAL-REALITY
(19) United States US 2016O2538.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0253843 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM OF MANAGEMENT FOR SWITCHINGVIRTUAL-REALITY
2012 LitePoint Corp LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved.
 LTE TDD What to Test and Why 2012 LitePoint Corp. 2012 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Agenda LTE Overview LTE Measurements Testing LTE TDD Where to Begin? Building a LTE TDD Verification
LTE TDD What to Test and Why 2012 LitePoint Corp. 2012 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Agenda LTE Overview LTE Measurements Testing LTE TDD Where to Begin? Building a LTE TDD Verification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7400,595 B2. Callaway et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2008
 USOO7400595 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7400,595 B2 Callaway et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BATTERY 6,138,034 A * 10/2000 Willey... 455,522
USOO7400595 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7400,595 B2 Callaway et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BATTERY 6,138,034 A * 10/2000 Willey... 455,522
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9628236B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,628.236 B2 Takeda et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) BASE STATION APPARATUS, RADIO (58) Field of Classification Search COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent USOO9628236B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,628.236 B2 Takeda et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) BASE STATION APPARATUS, RADIO (58) Field of Classification Search COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100134353A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0134353 A1 Van Diggelen (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EXTENDING THE USABILITY PERIOD
(19) United States US 20100134353A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0134353 A1 Van Diggelen (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EXTENDING THE USABILITY PERIOD
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
title (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 Azadet et al.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0114762 A1 Azadet et al. US 2013 O114762A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) RECURSIVE DIGITAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0114762 A1 Azadet et al. US 2013 O114762A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) RECURSIVE DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0035840 A1 Fenton et al. US 2001 0035.840A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (63) PRECISE POSITONING SYSTEM FOR MOBILE GPS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0035840 A1 Fenton et al. US 2001 0035.840A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (63) PRECISE POSITONING SYSTEM FOR MOBILE GPS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201700.93036A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0093036A1 Elwell et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017 (54) TIME-BASED RADIO BEAMFORMING (52) U.S. Cl. WAVEFORMITRANSMISSION
(19) United States US 201700.93036A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0093036A1 Elwell et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2017 (54) TIME-BASED RADIO BEAMFORMING (52) U.S. Cl. WAVEFORMITRANSMISSION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1. Jin (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2002
 US 2002O13632OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0136320 A1 Jin (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2002 (54) FLEXIBLE BIT SELECTION USING TURBO Publication Classification
US 2002O13632OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0136320 A1 Jin (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2002 (54) FLEXIBLE BIT SELECTION USING TURBO Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0344873 A1 Sane et al. US 20130344873A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK RESELECTION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0344873 A1 Sane et al. US 20130344873A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK RESELECTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120309331A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0309331 A1 YEHEZKELY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MODULAR MILLIMETER-WAVE RADIO (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/101 FREQUENCY
US 20120309331A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0309331 A1 YEHEZKELY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MODULAR MILLIMETER-WAVE RADIO (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/101 FREQUENCY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 00954.81A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0095481 A1 Patelidas (43) Pub. Date: (54) POKER-TYPE CARD GAME (52) U.S. Cl.... 273/292; 463/12 (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2011 00954.81A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0095481 A1 Patelidas (43) Pub. Date: (54) POKER-TYPE CARD GAME (52) U.S. Cl.... 273/292; 463/12 (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 201203 06643A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0306643 A1 Dugan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2012 (54) BANDS FOR MEASURING BIOMETRIC INFORMATION (51) Int. Cl.
US 201203 06643A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0306643 A1 Dugan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2012 (54) BANDS FOR MEASURING BIOMETRIC INFORMATION (51) Int. Cl.
n+1 Int2n+3 in 4n+5 Inten+7 n+8 int-9 int. On 11 n+12n+13)
 US008599738B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 8,599,738 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2013 (54) TRASMISSIO METHOD FORWIRELESS 2009,0254790 A1* 10, 2009 Pietal.... T14,749 RELAY SYSTEMAD
US008599738B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 8,599,738 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2013 (54) TRASMISSIO METHOD FORWIRELESS 2009,0254790 A1* 10, 2009 Pietal.... T14,749 RELAY SYSTEMAD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
16-?t R.S. S. Y \
 US 20170 155182A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0155182 A1 Rijssemus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2017 (54) CABLE TAP Publication Classification - - -
US 20170 155182A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0155182 A1 Rijssemus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2017 (54) CABLE TAP Publication Classification - - -
