(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
|
|
|
- Alexis Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING CONTROL INFORMATION OF DATA CHANNEL FOR ENHANCEDUPLINK DATA TRANSMISSION (76) Inventors: Young Dae Lee, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Sung Duck Chun, Gyeonggi-do (KR) Correspondence Address: LEE, HONG, DEGERMAN, KANG & WAIMEY 660 S. FIGUEROASTREET, Suite 2300 LOS ANGELES, CA (US) (21) Appl. No.: 11/718,887 (22) PCT Filed: Nov. 9, 2005 (86). PCT No.: PCT/KROS/O3792 S371 (c)(1), (2), (4) Date: May 22, 2008 Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional application No. 60/627,098, filed on Nov. 9, (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Jun. 15, 2005 (KR) OO51299 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. H04L 12/24 ( ) H04L 29/08 ( ) H04W 28/00 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /329; 455/68 (57) ABSTRACT A method of transmitting/receiving control information of a data channel for enhanced uplink data transmission is dis closed, by which efficient radio resource allocation is enabled. The present invention includes the acquiring control information of data channel for enhanced uplink data trans mission; composing a Medium Access control (MAC) Proto col Data Unit (PDU) including the control information, and transmitting the MAC PDU via a first physical channel for user data transmission.
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 3 US 2009/ A1 FIG. 1
3
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 3 US 2009/ A1 r 2 a 5 E. C2 is s S a...) A I 2 26 R E - 2. E. X 2. A o S2 e ch ; t,, r O tly 2. S. A. d g s 5. s
5 METHOD OF TRANSMITTING/RECEIVING CONTROL INFORMATION OF DATA CHANNEL FOR ENHANCEDUPLINK DATA TRANSMISSION TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a method of trans mitting data in a mobile communication system, and more particularly, to a method of transmitting/receiving control information of a data channel for enhanced uplink data trans mission. Although the present invention is suitable for a wide Scope of applications, it is particularly Suitable for transmit ting/receiving the control information efficiently. BACKGROUND ART 0002 FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a network structure of a mobile communication system of UMTS (universal mobile telecommunications system) Referring to FIG. 1, a UMTS mainly consists of a user equipment (UE), a UMTS terrestrial radio access net work (hereinafter abbreviated UTRAN), and a core network (hereinafter abbreviated CN) The UTRAN consists of at least one radio network subsystems (hereinafter abbreviated RNS). And, each RRNS consists of one radio network controller (hereinafter abbre viated RNC) and at least one base station (hereinafter named Node B) managed by the RNC. And, at least one cell exists in one Node B FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of a radio interface protocol between UE and UTRAN (UMTS terrestrial radio access network) based on the 3GPP radio access network standard Referring to FIG. 2, a radio interface protocol hori Zontally consists of a physical layer, a data link layer, and a network layer and vertically consists of a user plane for data information transfer and a control plane for signaling transfer Protocol layers in FIG. 2 can be divided into a first layer (L1), a second layer (L2) and a third layer (L3) based on three lower layers of the OSI (open system interconnection) standard model widely known in communication systems The physical layer of the first layer provides an information transfer service to higher layers using a physical channel. The physical layer is connected to a medium access control layer above the physical layer via a transport channel. Data are transferred between the medium access control layer and the physical layer via the transport channel. And, data are transferred between different physical layers, i.e., the physi cal layer of a transmitting side and the other physical layer of a receiving side via the physical channel The medium access control (hereinafter abbreviated MAC) layer of the second layer provides a service to a radio link control layer above the MAC layer via a logical channel. And, the MAC layer is divided into various kinds of sublayers including a MAC-d sublayer, a MAC-e sublayer and the like according to a controlled transport channel type Structures of DCH (dedicated channel) and E-DCH (enhanced dedicated channel) are explained as follows DCH and E-DCH are transport channels dedicated to one user equipment. In particular, E-DCH is used for the user equipment to transfer uplink data to UTRAN and is capable of transferring the uplink data faster than DCH. To transfer data fast, E-DCH employs HARQ (hybrid ARQ). AMC (adaptive modulation and coding), Node B controlled scheduling and the like For E-DCH, Node B transfers downlink control information to UE to control E-DCH transfer of the US. The downlink control information includes response information (ACK/NACK), E-DCH resource allocation information for Node B controlled scheduling and the like. Meanwhile, UE transfers uplink control information to Node B. The uplink control information includes E-DCH resource allocation request information (rate request information) for Node B controlled scheduling, UE buffer status information, UE power status information and the like MAC-d flow is defined between MAC-cand MAC-e for E-DCH. In this case, a dedicated logical channel is mapped to MAC-d flow, MAC-d flow is mapped to the trans port channel E-DCH, the transport channel E-DCH is mapped to a physical channel E-DPDCH (enhanced dedicated physi cal data channel) again The MAC-d sublayer is in charge of managing DCH (dedicated channel) dedicated to a specific UE. And, MAC e/mac-es sublayer is in charge of a transport channel E-DCH (enhanced dedicated channel) used in transferring fast uplink data A transmitting side MAC-d sublayer configures MAC-d PDU (protocol data unit) from MAC-d SDU (service data unit) delivered from a higher layer, i.e., RLC layer. And, a receiving side MAC-d Sublayer plays a role in restoring MAC-d SDU from the MAC-d PDU received from a lower layer to deliver to a higher layer. In doing so, MAC-d sublayer mutually exchanges MAC-e Sublayer with MAC-d PDU or a physical layer with MAC-d PDU over DCH. The receiving side MAC-d sublayer restores MAC-d SDU to deliver to a higher layer using a MAC-d header attached to the MAC-d PDU A transmitting side MAC-e/MAC-es sublayer con figures MAC-e PDU from MAC-d PDUs delivered from a higher layer, i.e., MAC-d sublayer. A receiving side MAC-e sublayer plays a role in restoring MAC-es PDU from the MAC-e PDU received from a lower layer, i.e., physical layer. And, a receiving side MAC-es Sublayer plays a role in restor ing MAC-d PDUs from MAC-es PDU to deliver to the MAC e. In doing so, the MAC-e exchanges the physical layer with MAC-e PDUS via E-DCH. (0017 FIG. 3 is a diagram of a protocol for E-DCH Referring to FIG. 3, a MAC-e Sublayer supporting E-DCH exists below each MAC-d sublayer of UTRAN and UE. The MAC-e sublayer of the UTRAN is located at Node B and the MAC-e Sublayer exists in each UE, (0019. Meanwhile, a MAC-d sublayer of the UTRAN is located at SRNC in charge of managing the corresponding UE. And, the MAC-d sublayer exists in each UE Control information transmission over E-DCH is explained as follows In E-DCH, a scheduler exists in Node B. The sched uler plays a role in allocating optimal radio resources to UES existing within one cell to raise transmission efficiency of data arriving at the Node B from the entire UEs within each cell in uplink direction, respectively. Namely, in once cell, a UE in good radio channel status can transmit more data by giving more radio resource allocation to the corresponding UE, whereas another UE in poor radio channel status is made not to transmit interference signals over an uplink radio chan nel by giving less radio resource allocation to the correspond
6 ing UE. Hence, a quantity of uplink data transmissions in the entire cell can be optimized in the above-explained manner Yet, the scheduler considers other factors as well as the radio channel status of the UE in allocating radio resources to the UE. The scheduler needs control information from UEs. For example, the control information includes a power that can be used for EDCH by the UE, a quantity of data the UE attempts to transmit, and the like. In other words, although the UE is in excellent radio channel status, if there is no spare power the UE can use for the E-DCH or if there is no data the UE will transmit in uplink direction, it is not allowed to allocate the radio resources to the UE. Hence, the scheduler just allocates the radio resources to the UE having the spare power for the E-DCH and the data to transmit in uplink, thereby raising efficiency in using the radio resources within one cell So, the UE has to send control information to the scheduler at the Node B in various ways. For instance, the scheduler at the Node B can order the corresponding UE to report if the data to be transmitted in uplink exceeds a prede termined value or the Node B can order the UE to send the control information to the Node B itself periodically The UE, to which the radio resource was allocated, configures MAC-e PDU within the allocated radio resource and then transmits the MAC-e PDU to the Node B over E-DCH Namely, the UE having the data to be transmitted sends the control information to the Node B to notify that there is the data to be transmitted by the UE itself. The scheduler of the Node B then sends the information indicating the allocation of radio resource to the UE based on the control information having sent from the UE. In this case, the infor mation indicating the allocation of radio resource means a maximum powerfor uplink transmission from the UE, a ratio to a reference channel, etc. The UE configures MAC-e PDU within the allowed range based on the information indicating the allocation of the radio resource and then transmits the configured MAC-e PDU In brief, in the E-DCH, incase of having data to be transmitted, the UE informs the Node B that there is the data to be transmitted. Once the radio resource is allocated to the UE from the Node Br the corresponding UE transmits real user data in a direction of the Node B In this case, a size of the radio resource is named a radio resource allocation quantity, which means a maximum value of power allowed to the UE to use and the like in case that the UE transmits the data in uplink. IF there is no radio resource allocation quantity and if there exists the data to be sent in uplink, the UE sends radio resource allocation request information to the Node B. Once receiving a radio resource allocation message from the Node B, the UE transmits the data in uplink using the power within a radio resource allo cation quantity range indicated by the message If there is the radio resource allocated to the UE, i.e., if the radio resource allocation quantity is not Zero (there is data to be transmitted in uplink), the corresponding UE immediately transmits the data in the uplink As mentioned in the foregoing description, in order for the UE to transmit the user data in uplink, it is important for the UE to transmit the appropriate radio resource alloca tion request information to the Node B at the proper time to have a Suitable radio resource allocation quantity set by the Node B. The appropriate radio resource allocation quantity is important, which is because the allowable radio resource in the mobile communication system is limited However, the above-explained related art method has the following problem For instance, assuming that the power usable for uplink transmission of the UE is 10 dbm, if the quantity of the radio resource allocated to the UE is 20 dbm, this means a waste of the radio resource. If the power acceptable by the cell is 20 dbm, another UE loses its chance to transmit data in uplink Hence, the demand for a method of allocating a radio resource most efficiently within a radius of one Node B 1SS. DISCLOSURE OF INVENTION 0033 Accordingly, the present invention is directed to a method of transmitting/receiving control information of a data channel for enhanced uplink data transmission that Sub stantially obviates one or more problems due to limitations and disadvantages of the related art An object of the present invention is to provide a method of transmitting/receiving control information of a data channel for enhanced uplink data transmission, by which efficient radio resource allocation is enabled Additional advantages, objects, and features of the invention will be set forth in part in the description which follows and in part will become apparent to those having ordinary skill in the art upon examination of the following or may be learned from practice of the invention. The objectives and other advantages of the invention may be realized and attained by the structure particularly pointed out in the written description and claims hereofas well as the appended draw 1ngS To achieve these objects and other advantages and in accordance with the purpose of the invention, as embodied and broadly described herein, a method of transmitting con trol information of a data channel for enhanced uplink data transmission, in which the control information is transmitted from a mobile terminal, according to the present invention includes the step of transmitting the control information using MAC PDU (protocol data unit) including the control infor mation Preferably, the control information transmitting step includes the steps of including the control information in the MAC PDU and transmitting the MAC PDU over a first physi cal channel Preferably, the method further includes the step of transmitting information about whether the control informa tion is included in the MAC PDU only Preferably, the method further includes the step of if a plurality of control informations are included in the MAC PDU, including a first indicator identifying a plurality of the control informations in the MAC PDU Preferably, the MAC PDU includes the control information only. The MAC PDU includes the control infor mation and user data together. And, the data channel for the enhanced uplink data transmission includes an F.-DCH (en hanced dedicated channel) More preferably, the first physical channel includes an E-DPDCH (enhanced dedicated physical data channel Preferably, in the step of transmitting the informa tion about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only, the information about whether the control
7 information is included in the MAC PDU only is transmitted over a second physical channel More preferably, in the step of transmitting the information about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only, the information about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only is included in the MAC PDU. 0044) More preferably, in the step of transmitting the information about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only, the information about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only is included in a header of the MAC PDU More preferably, the method further includes the step of including a second indicator identifying a recipient receiving a plurality of the control informations in the MAC PDU In another aspect of the present invention, a method of receiving control information of a data channel for enhanced uplink data transmission, in which the control information is received by a base station, includes the step of receiving the control information using MAC PDU (protocol data unit) including the control information Preferably, the control information receiving step includes the steps of receiving a data block over a first physi cal channel and delivering the data block to a MAC layer to enable the MAC layer to acquire the control information Preferably, the method further includes the step of receiving information about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only Preferably, the method further includes the step of if a plurality of control informations are included in the MAC PDU, receiving a first indicator identifying a plurality of the control informations included in the MAC PDU Preferably, the MAC PDU includes the control information only. The MAC PDU includes the control infor mation and user data together. And, the data channel for the enhanced uplink data transmission includes an E-DCH (en hanced dedicated channel) More preferably, the first physical channel includes an E-DPDCH (enhanced dedicated physical data channel More preferably, in the step of receiving the infor mation about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only, the information about whether the con trol information is included in the MAC PDU only is received over a second physical channel More preferably, in the step of receiving the infor mation about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only, the MAC PDU including the information about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only is received More preferably, in the step of receiving the infor mation about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only, a header of the MAC PDU including the information about whether the control information is included in the MAC PDU only is received In another aspect of the present invention, a method of transmitting control information of a data channel for enhanced uplink data transmission, in which the control information is transmitted from a mobile terminal, includes the step of deciding whether the control information trans mitted by the mobile terminal is transmitted according to a channel Preferably, the method further includes the step of transmitting the control information according to a result of the deciding step Preferably, the control information is radio resource allocation request information More preferably, the radio resource allocation request information is information about a buffer status of the mobile terminal More preferably, the information about the buffer status is information relating to an absolute quantity of data stored in a buffer of the mobile terminal More preferably, the information about the buffer status is information about a variance of data stored in a buffer of the mobile terminal It is to be understood that both the foregoing general description and the following detailed description of the present invention are exemplary and explanatory and are intended to provide further explanation of the invention as claimed. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS 0062 FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a network structure of a mobile communication system of UMTS (universal mobile telecommunications system); 0063 FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of a radio interface protocol between UE and UTRAN (UMTS terrestrial radio access network) based on the 3GPP radio access network standard; and 0064 FIG. 3 is a diagram of a protocol for E-DCH. BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION 0065 Reference will now be made in detail to the pre ferred embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Wher ever possible, the same reference numbers will be used throughout the drawings to refer to the same or like parts First of all, the present invention proposes a method of sending radio resource allocation request information to a Node B from a UE. For this, the present invention proposes to use MAC PDU (protocol data unit) as the radio resource allocation request information transmitted from the UE. In particular, the present invention proposes to use not a signal transfer over such a physical channel as E-DPCCH (enhanced dedicated physical control channel) but a signal transfer of MAC Layer that is a higher Layer of the physical Layer for the radio resource allocation request information transmitted from the UE to the Node B. Namely, the radio resource allocation request information is sent using E-DPDCH (en hanced dedicated physical data channel) over which real user data is delivered So, a transmitting side includes control information Such as the radio resource allocation request information in MAC PDU and then delivers it to a physical layer of a lower layer. The physical layer transmits it over E-DPDCH. Mean while, a physical layer of a receiving side receives data block via E-DPDCH and then delivers it to a MAC layer of a higher layer. The MAC layer then decodes the received MAC PDU to extract the control information The control information corresponds to the informa tion for controlling E-DCH such as the radio resource allo
8 cation request information, information of physical layer data transfer status, high-quality base station information and the like The present invention proposes to transmit various kinds of information Such as data transfer status of physical layer, information of highest quality Node B and the like via the MAC layer as well as to deliver the radio resource allo cation request information via the MAC layer Namely, the present invention proposes to use one lower channel as a path for delivering both of the control information of the higher layer and the user data of the higher Layer And, the present invention proposes various types of MAC PDUs used in transmitting the control information in the above course. For this, to transmit the control information, the present invention proposes two types of the MAC PDUs, MAC PDU including the control information only(stand alone PDU) and MAC PDU including both of the control information and the user data (Piggybacked PDU). In this case, the MAC PDU including the control information only includes not the user data but the control information Such as the radio resource allocation request information the trans mitting side attempts to transmit only. Namely, to be provided with a service of an appropriate quality, the UE sends the control information to the Node B if necessary. In case of sending the control information to the Node B, the UE pref erably selects one of usable MAC PDU types to use according to its situation. In this case, the usable MAC PDU types can be classified into the MAC PDU including the control informa tion only and the MAC PDU including both of the control information and the user data In case of using the MAC PDU including the control information only, there are various gains. In most cases, a quantity of the control information is much smaller than that of the user data. Yet, in the radio channel, the larger a size of the data block to be transmitted gets, the higher the probabil ity of losing it in a radio space rises. In other words, the smaller the size of the data block becomes, the higher the probability of transmission Success in the radio space rises. And, the control information transmitted from the UE is essential for the UE to be provided with the service of the appropriate quality. Hence, it should be delivered to the Node B stably as fast as it can be. In the above-explained case, since the size of the MAC PDU including the control information only is small, the corresponding MAC PDU can be stably delivered to the Node B. Hence, the MAC PDU used in one preferred embodiment of the present invention is character ized in including the control information only Alternatively, the MAC PDU used in one preferred embodiment of the present invention may include both of the control information and the user data. For instance, assuming that the radio resource allocation quantity usable by the UE is greater than 0, if the UE transits the MAC PDU including the control information only, it is a waste of the radio resource. For example, assuming that the radio resource allocation quantity of the UE is 10 dbm, if power of 1 dbm is consumed in transmitting the MAC PDU including the control informa tion only, the UE wastes the resource of 9 dbm allocated to itself. If the 9 dbm of the radio resource allocation quantity is used intransmitting user data, the radio resource, which could have enhanced the quality of the radio service provided to the user, is wasted. To prevent the unnecessary waste of the radio resource, the MAC PDU can be set to include both of the control information and the user data, which is advantageous in raising efficiency in using the radio resource In the above-explained process according to one preferred embodiment of the present invention, it is able to use a physical layer in informing a receiving side that the control information is included in the MAC PDU only when the UE transmits the MAC PDU including the control infor mation only. (0075. In particular, in transmitting the MAC PDU includ ing the control information only, the UE transmits the MAC PDU itself to the receiving side over the E-DPDCH and sends the information indicating that the control information is included in the MAC-PDU to the transmitting side via E-DPCCH the transmitting uses in decoding the E-DPDCH. The transmitting side can be informed of the information indicating that the control information is included only in various ways. For instance, a specific 1-bit of the E-DPCCH is used or a specific pattern can be inserted in the E-DPCCH. In this case, the specific pattern is to use E-TFCI (enhanced transport format combination indicator) of the E-DPCCH is used, for example. The E-TFCI plays a role in indicating a size of MAC PDU that is being delivered over the E-DPDCH. A specific value of the E-TFCI can indicate that the MAC PDU includes the control information only. Hence, in case of transmitting the MAC PDU including the control information only, the transmitting side can set the specific value of the E-TFCI using the E-DPCCH. And, if a specific portion of the E-DPCCH, e.g., the E-TFCI indicates the specific value, the receiving side can operate on the assumption that the data which is being delivered via the Z-DPDCH includes the con trol information only According to another embodiment of the present inventions to indicate that control information is included in MAC PDU, a first bit of all MAC PDU is usable for indicating whether the control information is included. No limitation is put on a location of the bit. Yet, it is possible for the first bit to indicate whether the control information is included. For instance, if a first bit of MAC PDU is set, it means that control information exists in the MAC PDU. If a first bit of MAC PDU is not set, it means that control information does not exist in the MAC PDU. In this case, a transmitting side can set a first bit of MAC-e PDU intransmitting MAC PDU if control information is included in the MAC PDU. And, it is possible for a receiving side to decide that the control information does not exist in the MAC PDU if the first bit of the received MAC PDU is not set According to another embodiment of the present invention, it is able to indicate an existence or non-existence of control information using a specific portion of a header of MAC PDU. There is no limitation put on a type of the specific portion of the header. In the present embodiment, a DDI field is used for example. A field called DDI (data description indicator) exists in a header of MAC PDU. This plays a role in indicating that data blocks included in the MAC PDU corre spond to data of which logical channel and a role in indicating how large a size of the each of the blocks is. In the present embodiment, if the DDI designates a specific value, it means that control information exists in the MAC PDU. Hence, if the control information exists in the MAC PDU, a transmitting side preferably includes the DDI set to the specific value in the header part of the MAC PDU According to one preferred embodiment of the present invention, it is more preferable that each control infor mation configures one block if there are various kinds of
9 control information in MAC PDU. As mentioned in the fore going description, it is common that there are various kinds of control information a transmitting side transmits to a receiv ing side. And, a device facilitating new control information to be included in MAC PDU is frequently needed. Hence, it is preferable that control information included in MAC PDU is configured with extendability. Hence, according to a pre ferred embodiment of the present invention, control informa tions configure a control information block. For example, one control information block is allowed to include control infor mations about power only. In this case, it is preferable that one control information block includes an indicator indicating what kind of control information it is. In the above-explained example, the indicator indicating the control information about power is included in the control information block. If Such a control information block is used, a transmitting side includes control information blocks corresponding to an amount the transmitting side needs to transmit in MAC PDU. A receiving side is then able to handle each of the control information blocks in the received MAC PDU. Yet, a length of each information included in the control information block is variable or fixed. Hence, in case of a specific control infor mation block, if the length of the information of the control information block is variable, it is preferable that length infor mation is included right behind the indicator indicating the type of the control information Yet, in the above process, there can exist at least one or more receiving sides. For instance, in case of uplink, a receiving side includes Node B and RNC. Hence, either the Node B or the RNC may need the control information. Hence, according to one embodiment of the present invention, it is proposed that an indicator indicating a recipient of the control information is included in the control information block. Namely, if the indicator indicates that the recipient of the control information is the RNC, the Node B immediately delivers the received control information to the RNC. This is performed using recipient information included in the control information. The recipient information is very useful. If the Node B is an old model while the RNC is a new model, i.e., if the Node B is capable of recognizing a previous limited quantity of control information types only, the Node B can deliver the control information to the RNC using the recipient information of the control information without being updated despite being incapable of recognizing the control informa tion There is UE buffer status information within a mes sage a UE sends to Node B. The buffer status information can be used for the Node B to set a radio resource allocation quantity suitable for the UE. For instance, assuming that UE has to transmit 1,000-bit data and needs 10 dbm power required for transmitting the data for 10 ms, if Node B sets a radio resource allocation quantity allocated to the UE to 20 dbm, it is a serious waste of radio resource. Hence, UE preferably informs Node B of an accurate data volume to transmit For this, according to one embodiment of the present invention, a method that UE informs Node B of its buffer status information. In particular, the UE preferably uses two kinds of mechanisms. One is an absolute buffer status report and the other is a relative buffer status report In the absolute buffer status report, the UE reports a Volume of data accumulated in its buffer to the Node Bas it is. Namely, in case of having 100kbytes data, the UE reports the 100kbytes data to the Node B in direct. In doing so, limitation may be put on the expression of the buffer information sent to the Node B from the UE. Namely, the UE may be set to use 5-bits only in expressing its buffer for example. In Sucha case, the volume of data the UE can represent is not consecutive but can be reported by a predetermined unit only. For instance, it a unit of data volume the UE informs the Node B of is 10 kbytes, the UE informs the Node B of its buffer status by 10 kbyte unit under the circumstances. Despite the above-ex plained mechanism, the UE reports its data Volume repre sented intact to the Node B under the mechanism. I0083. The relative buffer status report is focused on report ing a status variation of buffer. For instance, the relative buffer status report is a method of informing Node B of a variance of UE's buffer between a current time point and a latest time point of sending buffer information from UE. For example, assuming that a UE's buffer quantity at the time point of sending buffer information to Node B lately is 50kbytes and ifa current UE's buffer quantity is 55 kbytes, a relative buffer status report message informs the Node B of a difference, 5 kbytes, between 55 kbytes and 50kbytes only. I0084 Compared to the absolute buffer status report, the relative buffer status report is advantageous in that the num ber of information, i.e., number of bits, required for delivering the same quantity of information is Small. Assuming that the information Substantially necessary for a user is user data, all control information between UE and Node B is not substan tially necessary for the user. Hence, a smaller quantity of the control information is preferred. In this aspect, the relative buffer status report is more advantageous than the absolute buffer status report in the cost required for representing the same control information. I0085. Yet, the relative buffer status report brings about problem in case that a message right before the report or a previous message is lost or damaged. For instance, it is assumed that a UE initially has 50kbyte data. And, it is also assumed that two relative buffer status report have been for warded, and each relative buffer status report includes 10 kbyte information. Namely, the UE has 70kbyte data at a time point of sending a second relative buffer status report. If a receiving side loses a first relative buffer status report mes sage, the receiving side will incorrectly decide that the UE has 60kbyte data after having receiving the second relative buffer status report. I0086 To correct this incorrect decision, the present inven tion proposes to mix the absolute and relative buffer status reports to use. It is apparent to those skilled in the art that there are various methods for using the absolute and relative buffer status reports simultaneously, For instance, if the absolute buffer status report is periodically transmitted or if the abso lute buffer status report is transmitted each time a prescribed reference is met, it is able to prevent a problem that a Node B may incorrectly estimate a buffer quantity of UE. For another instance, a UE can send an absolute buffer status report if a physical layer reports a failure of transmission of prescribed MAC PDU, if a transmission of a predetermined number of MAC PDUs is performed, or each time a central base station (serving cell) is changed. I0087. There is no limitation put on the method of trans mitting the relative buffer status information from the UE. And, the relative buffer status report can be transmitted in various ways First of all, a UE carried out a relative buffer status report each predetermined time. Namely, by making the rela
10 tive buffer status report regularly, the UE can inform the Node B of the accurate status of the UE Secondly, a UE can send a relative buffer status report each time a predetermined reference is met. Namely, for instance, each time a predetermined quantity of data, e.g., new 10kbyte data arrives at a UE's buffer, the UE informs a Node B of such a fact In the above-explained process, the buffer informa tion sent by the UE can be set by taking a total of all channels assigned to the UE as a reference or can be per logical channel assigned to the UE In case of using such a service as a voice service, if a UE informs a Node B of a buffer status, if a radio resource allocation quantity suitable for the buffer status is set, and if the UE transmits Voice data later, an unnecessarily long delay is brought about to degrade a quality sensed by a user. In this case, it is preferable that specific channels are set so that data can be immediately transmitted as soon as arrives. In case of the voice service, for example, if the voice service data arrives at a buffer, the UE preferably transmits the arriving data in uplink via a physical layer. Namely, the UTRAN can set a specific logical channel so that the UE can transmit data at any time Over the channel via which the UE can transmit data at any time, the method of transmitting the radio resource allocation request information, and more particularly, the UE's buffer information to the Node B from the UE has a problem. After the UE has transmitted the information, at the time point that the transmitted information arrives at the Node a, the user's voice information data corresponding to the control information has already arrived at Node B or is being transmitted from the UE. Or, the Node B has allocated the radio resource to the UE according to the information trans ferred from the RNC before receiving the buffer status infor mation from the UE, Hence, for the channel set to enable the UE to make a transmission at anytime, it is unnecessary for the UE to send the control information such as buffer infor mation Hence, according to one preferred embodiment of the present invention, it is proposed that the UE does not transmit the control information such as the buffer informa tion of channel over the channel set to enable the UE to make a transmission at any time. Over other channels, it is proposed that the UTRAN sends the control information such as buffer information to the system according to a setup. In the channel set to enable the UE to make a transmission at any time, there are a Voice service, a service Such as streaming, an SRB (signaling ratio bearer) Such as an RRC message in charge of signaling of an upper end of UE, etc. These services can be called guaranteed bit rate services, respectively. The channel set as GBR from the system, and more particularly, the chan nel set to enable uplink transmission at any time can make the uplink transmission at any time within a range of the quantity allocated from the system Accordingly. The present invention provides the fol lowing effects or advantages First of all, the present invention proposes the method of allocating radio resources in the mobile commu nication system, thereby enabling efficient and optimal data transmission It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations can be made in the present invention without departing from the spirit or scope of the inventions. Thus, it is intended that the present invention covers the modifications and variations of this invention pro vided they come within the scope of the appended claims and their equivalents. INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention is suitable for a wide scope of applications, it is particularly suitable fortransmitting/receiv ing the control information efficiently. 1. A method of transmitting control information for an uplink, the method comprising: composing a Medium Access Control (MAC) Protocol Data Unit (PDU) including the control information, the control information indicating an amount of resources required by a User Equipment (UE); and transmitting the MAC PDU to a network via an Enhanced Dedicated Channel (E-DCH), wherein a first format of the MAC PDU is used when the control information is transmitted with other informa tion in the MAC-PDU and a second format of the MAC PDU is used when the control information is transmitted alone in the MAC-PDU. 2. The method of claim 1, wherein the control information comprises scheduling information used by the network. 3. The method of claim 1, wherein the control information comprises buffer status information of the UE. 4. The method of claim 1, wherein the control information comprises transmission power information of the UE. 5. The method of claim 1, wherein a specific value of Enhanced-Transport Format Combination Indicator (E-TFCI) is set when the second format of the MAC PDU is used. 6. The method of claim 1, wherein the MAC PDU includes an indicator having a specific value to indicate that the MAC PDU includes the control information when the first format of the MAC PDU is used. 7. The method of claim 6, wherein the indicator comprises a Data Description Indicator (DDI). 8. The method of claim 1, wherein the other information transmitted with the control information in the MAC PDU is user data. 9. The method of claim 1, wherein the second format of the MAC PDU is a stand alone MAC PDU. 10. The method of claim 1, wherein the first format of the MAC PDU is a piggybacked MAC PDU. 11. The method of claim 5, wherein the specific value of E-TFCI is included in a E-DPCCH (Enhanced Dedicated Physical Control Channel). 12. The method of claim 10, wherein the control informa tion is piggybacked in the MAC PDU (canceled) 15. A method of receiving control information for an uplink, the method comprising: receiving a MAC (Medium Access Control) Protocol Data Unit (PDU) via an Enhanced Dedicated Channel (E-DCH) from a User equipment (UE); and acquiring the control information included in the MAC PDU, wherein the control information indicates an amount of resources requested by the User Equipment (UE) and wherein a first format of the MAC PDU is used by the UE when the control information is transmitted with other information in the MAC-PDU and a second format of
11 the MAC PDU is used by the UE when the control information is transmitted alone in the MAC-PDU. 16. The method of claim 15, further comprising allocating a resource to the UE using the control information. 17. The method of claim 15, wherein the control informa tion comprises scheduling information used by a network. 18. The method of claim 15, wherein the control informa tion comprises buffer status information of the UE. 19. The method of claim 15, wherein the control informa tion comprises transmission power information of the UE. 20. The method of claim 15, wherein a specific value of Enhanced-Transport Format Combination Indicator (E-TFCI) is set when the second format of the MAC PDU is used. 21. The method of claim 15, wherein the MAC PDU includes an indicator having a specific value indicating that the MAC-PDU includes the control information when the first format of the MAC-PDU is used. 22. The method of claim 21, wherein the indicator com prises a Data Description Indicator (DDI). 23. The method of claim 15, wherein the other information received with the control information in the MAC-PDU is user data. 24. The method of claim 21, wherein the indicator is included in a header of the MAC PDU. 25. The method of claim 15, wherein the second format of the MAC PDU is a stand alone MAC PDU. 26. The method of claim 15, wherein the first format of the MAC PDU is a piggybacked MAC PDU. 27. The method of claim 20, wherein the specific value of E-TFCI is included in a E-DPCCH (Enhanced Dedicated Physical Control Channel). 28. The method of claim 26, wherein the control informa tion is piggybacked in the MAC-PDU (canceled)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006.0143444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0143444 A1 Malkamaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data COMMUNICATING
US 2006.0143444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0143444 A1 Malkamaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data COMMUNICATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0110060 A1 YAN et al. US 2015O110060A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) METHOD FOR ADUSTING RESOURCE CONFIGURATION,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0110060 A1 YAN et al. US 2015O110060A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) METHOD FOR ADUSTING RESOURCE CONFIGURATION,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO63341A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0063341 A1 Ishii et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, RADIO BASE STATION, SCHEDULING APPARATUS,
(19) United States US 2005OO63341A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0063341 A1 Ishii et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, RADIO BASE STATION, SCHEDULING APPARATUS,
United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354
![United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354](/thumbs/92/110916574.jpg) US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0036381A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0036381A1 Nagashima (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM WITH DATA CHANGING/UPDATING FUNCTION
(19) United States US 2003.0036381A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0036381A1 Nagashima (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM WITH DATA CHANGING/UPDATING FUNCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
FDD Uplink 2 TDD 2 VFDD Downlink
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094409 A1 Li et al. US 2013 0094409A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094409 A1 Li et al. US 2013 0094409A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080280631A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0280631 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR PROCESSING PAGING INFORMATION IN A WIRELESS MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 20080280631A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0280631 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR PROCESSING PAGING INFORMATION IN A WIRELESS MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Hunt USOO6868079B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM WITH REQUEST RE-TRANSMISSION UNTIL ACKNOWLEDGED (75) Inventor: Bernard Hunt,
(12) United States Patent Hunt USOO6868079B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM WITH REQUEST RE-TRANSMISSION UNTIL ACKNOWLEDGED (75) Inventor: Bernard Hunt,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070042773A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0042773 A1 Alcorn (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 22, 2007 (54) BROADBAND WIRELESS Publication Classification COMMUNICATION
US 20070042773A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0042773 A1 Alcorn (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 22, 2007 (54) BROADBAND WIRELESS Publication Classification COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
(19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
REPEATER I. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. REPEATER is. A v. (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20140370888A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0370888 A1 Kunimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, LOCATION REGISTRATION METHOD, REPEATER,
(19) United States US 20140370888A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0370888 A1 Kunimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, LOCATION REGISTRATION METHOD, REPEATER,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,325,650 B2
 USOO8325650B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,325,650 B2 Hu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2012 (54) METHOD FOR REDUCING DELAY INA (56) References Cited COMMUNICATION SYSTEM EMPLOYING
USOO8325650B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,325,650 B2 Hu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2012 (54) METHOD FOR REDUCING DELAY INA (56) References Cited COMMUNICATION SYSTEM EMPLOYING
part data signal (12) United States Patent control 33 er m - sm is US 7,119,773 B2
 US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701.24860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/012.4860 A1 SHH et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMITTER AND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. THEREOF
(19) United States US 201701.24860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/012.4860 A1 SHH et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMITTER AND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. THEREOF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
(19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0203608 A1 Kang US 20070203608A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 30, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR 3 DIMENSIONAL TEXTILE DESIGN AND A COMPUTER-READABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0203608 A1 Kang US 20070203608A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 30, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR 3 DIMENSIONAL TEXTILE DESIGN AND A COMPUTER-READABLE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
(12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
PRACH --> Access Slot. (12) United States Patent. Message US 8,219,097 B2. AICH Preamble. Preamble. *Jul. 10, (45) Date of Patent:
 US008219097B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 10, 2012 (54) METHOD OF TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING RADIO ACCESS INFORMATION NAWIRELESS MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
US008219097B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 10, 2012 (54) METHOD OF TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING RADIO ACCESS INFORMATION NAWIRELESS MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
TEPZZ _668Z B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 56/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _668Z B_T (11) EP 2 166 802 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 18.03. Bulletin /12 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 6/00 (09.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ _668Z B_T (11) EP 2 166 802 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 18.03. Bulletin /12 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 6/00 (09.01) (21) Application
Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA)
 Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Resource Management: Scheduling, Handover Performance Results Background
Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Resource Management: Scheduling, Handover Performance Results Background
lb / 1b / 2%: 512 /516 52o (54) (75) (DK) (73) Neubiberg (DE) (DK); Peter Bundgaard, Aalborg (21) Appl. No.: 12/206,567 In?neon Technologies AG,
 US 20100061279A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0061279 A1 Knudsen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 11, 2010 (54) (75) (73) TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING WIRELESS
US 20100061279A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0061279 A1 Knudsen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 11, 2010 (54) (75) (73) TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING WIRELESS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,438,377 B1
 USOO6438377B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Savolainen (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 : (54) HANDOVER IN A MOBILE 5,276,906 A 1/1994 Felix... 455/438 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM 5,303.289 A 4/1994
USOO6438377B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Savolainen (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 : (54) HANDOVER IN A MOBILE 5,276,906 A 1/1994 Felix... 455/438 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM 5,303.289 A 4/1994
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Chu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013
 US 2013 O155930A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0155930 A1 Chu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUB-1GHZ GROUP POWER SAVE Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 2013 O155930A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0155930 A1 Chu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUB-1GHZ GROUP POWER SAVE Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941,174 B2
 US007941 174B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Breuer et al. () Date of Patent: May, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR MULTICODE TRANSMISSION (56) References Cited BY A SUBSCRIBER STATION (75) Inventors: Volker
US007941 174B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Breuer et al. () Date of Patent: May, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR MULTICODE TRANSMISSION (56) References Cited BY A SUBSCRIBER STATION (75) Inventors: Volker
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100134353A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0134353 A1 Van Diggelen (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EXTENDING THE USABILITY PERIOD
(19) United States US 20100134353A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0134353 A1 Van Diggelen (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EXTENDING THE USABILITY PERIOD
EDCH Background & Basics. Principles: scheduling, handover Performance Results
 Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Principles: scheduling, handover Performance Results Background E-DCH
Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Principles: scheduling, handover Performance Results Background E-DCH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160255572A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0255572 A1 Kaba (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) ONBOARDAVIONIC SYSTEM FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN AN AIRCRAFT
(19) United States US 20160255572A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0255572 A1 Kaba (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) ONBOARDAVIONIC SYSTEM FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN AN AIRCRAFT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Let al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 0343359A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343359 A1 Let al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2013 0343359A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343359 A1 Let al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,665 B2
 USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201403.35795A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0335795 A1 Wilbur (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2014 (54) SOFTWARE APPLICATIONS FOR DISPLAYING AND OR RECORDING
(19) United States US 201403.35795A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0335795 A1 Wilbur (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2014 (54) SOFTWARE APPLICATIONS FOR DISPLAYING AND OR RECORDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mustajairvi USOO6430163B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ALLOCATION OF CONTROL CHANNEL IN PACKET RADIO NETWORK (75) Inventor: Jari Mustajärvi, Espoo (FI)
(12) United States Patent Mustajairvi USOO6430163B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ALLOCATION OF CONTROL CHANNEL IN PACKET RADIO NETWORK (75) Inventor: Jari Mustajärvi, Espoo (FI)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268193 A1 Petersson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) ANTENNA DEVICE FOR A RADIO BASE STATION IN
(19) United States US 20070268193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268193 A1 Petersson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) ANTENNA DEVICE FOR A RADIO BASE STATION IN
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1. Jin (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2002
 US 2002O13632OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0136320 A1 Jin (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2002 (54) FLEXIBLE BIT SELECTION USING TURBO Publication Classification
US 2002O13632OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0136320 A1 Jin (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2002 (54) FLEXIBLE BIT SELECTION USING TURBO Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0029.108A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0029.108A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2011 (54) MUSIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION METHOD Publication Classification
US 2011 0029.108A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0029.108A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2011 (54) MUSIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION METHOD Publication Classification
ETSI TS V6.6.0 ( )
 TS 125 309 V6.6.0 (2006-03) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); FDD enhanced uplink; Overall description; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 25.309 version 6.6.0 Release 6) 1 TS 125
TS 125 309 V6.6.0 (2006-03) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); FDD enhanced uplink; Overall description; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 25.309 version 6.6.0 Release 6) 1 TS 125
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9423425B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) SIDE-CHANNEL ANALYSSAPPARATUS AND METHOD BASED ON PROFILE Applicant: Electronics and Telecommunications
USOO9423425B2 (12) United States Patent Kim et al. (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) SIDE-CHANNEL ANALYSSAPPARATUS AND METHOD BASED ON PROFILE Applicant: Electronics and Telecommunications
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1. (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 2, 2000 (JP)...
 (19) United States US 200200152O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0015202 A1 Michishita et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2002 (54) WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXING OPTICAL TRANSMISSION
(19) United States US 200200152O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0015202 A1 Michishita et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2002 (54) WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXING OPTICAL TRANSMISSION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,102,301 B2. Mosher (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2012
 USOO8102301 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,102,301 B2 Mosher (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2012 (54) SELF-CONFIGURING ADS-B SYSTEM 2008/010645.6 A1* 2008/O120032 A1* 5/2008 Ootomo et
USOO8102301 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,102,301 B2 Mosher (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2012 (54) SELF-CONFIGURING ADS-B SYSTEM 2008/010645.6 A1* 2008/O120032 A1* 5/2008 Ootomo et
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7400,595 B2. Callaway et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2008
 USOO7400595 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7400,595 B2 Callaway et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BATTERY 6,138,034 A * 10/2000 Willey... 455,522
USOO7400595 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7400,595 B2 Callaway et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BATTERY 6,138,034 A * 10/2000 Willey... 455,522
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O108129A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0108129 A1 Voglewede et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL FOR (21) Appl. No.: 10/012,530 DIGITAL
US 2003O108129A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0108129 A1 Voglewede et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL FOR (21) Appl. No.: 10/012,530 DIGITAL
58 Field of Search /341,484, structed from polarization splitters in series with half-wave
 USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
(2) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (2) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0088148A1 Chung et al. US 20090088148A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(19) United States (2) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0088148A1 Chung et al. US 20090088148A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0140775A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0140775 A1 HONG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2011 (54) COMBINED CELL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFICATION APPARATUS
(19) United States US 2011 0140775A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0140775 A1 HONG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2011 (54) COMBINED CELL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFICATION APPARATUS
75 Inventors: Onofre Costilla-Vela, Nuevo Leon; : R. SS II.
 USOO5924.47OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,470 Costilla-Vela et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54 METHOD FOR PREHEATING MOLDS FOR 1-91960 4/1989 Japan... 164/457 ALUMINUM CASTINGS
USOO5924.47OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,470 Costilla-Vela et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54 METHOD FOR PREHEATING MOLDS FOR 1-91960 4/1989 Japan... 164/457 ALUMINUM CASTINGS
III. I. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,121,014. Huang
 United States Patent (19) Huang (54) CMOS DELAY CIRCUIT WITH LABLE DELAY 75 Inventor: Eddy C. Huang, San Jose, Calif. 73) Assignee: VLSI Technology, Inc., San Jose, Calif. (21) Appl. o.: 6,377 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Huang (54) CMOS DELAY CIRCUIT WITH LABLE DELAY 75 Inventor: Eddy C. Huang, San Jose, Calif. 73) Assignee: VLSI Technology, Inc., San Jose, Calif. (21) Appl. o.: 6,377 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1
 US008187032B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2012 (54) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/76.1.
US008187032B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2012 (54) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/76.1.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011021 1485A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0211485 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR OPERATINGA MULT-USERMULTIPLE-INPUT
(19) United States US 2011021 1485A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0211485 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR OPERATINGA MULT-USERMULTIPLE-INPUT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(19) United States US 2002O191820A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191820 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR USING A PIEZOELECTRIC MEMBRANE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0225175 A1 OBUCH et al. US 20130225175A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) RADIO COMMUNICATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0225175 A1 OBUCH et al. US 20130225175A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) RADIO COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090303703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303703 A1 Kao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) SOLAR-POWERED LED STREET LIGHT Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20090303703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303703 A1 Kao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) SOLAR-POWERED LED STREET LIGHT Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090291 692A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0291692 A1 Kazmi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MEASUREMENTASSISTED DYNAMIC FREQUENCY-REUSE IN CELLULAR TELECOMMUNICATIONS
(19) United States US 20090291 692A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0291692 A1 Kazmi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MEASUREMENTASSISTED DYNAMIC FREQUENCY-REUSE IN CELLULAR TELECOMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner. Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green
 III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO6906581B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) FAST START-UP LOW-VOLTAGE BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: Tzung-Hung Kang,
(12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO6906581B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) FAST START-UP LOW-VOLTAGE BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: Tzung-Hung Kang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
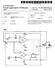 US 2011 O187416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0187416A1 Bakker (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) SMART DRIVER FOR FLYBACK Publication Classification CONVERTERS
US 2011 O187416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0187416A1 Bakker (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) SMART DRIVER FOR FLYBACK Publication Classification CONVERTERS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7356068B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,356,068 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) FREQUENC HOPPING SEQUENCE (56) References Cited GENERATOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO7356068B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,356,068 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) FREQUENC HOPPING SEQUENCE (56) References Cited GENERATOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
USOO A. United States Patent Patent Number: 5,327,575 Menich et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994
 b III USOO5327575A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,327,575 Menich et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 54 DIRECTIONAL HANDOVER CONTROLIN Assistant Examiner-Thanh C. Le E. NSE RADIOSYSTEMS
b III USOO5327575A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,327,575 Menich et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 54 DIRECTIONAL HANDOVER CONTROLIN Assistant Examiner-Thanh C. Le E. NSE RADIOSYSTEMS
us/ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 (19) United States / 112 / 108 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 (19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 OO14910A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0014910 A1 YONGE, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2011 (54) CHANNEL REUSE IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (75)
(19) United States US 2011 OO14910A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0014910 A1 YONGE, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2011 (54) CHANNEL REUSE IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (75)
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,226,021 B1. Anderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007
 United States Patent USOO7226021B1 (12) () Patent No.: Anderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DETECTING 4,728,063 A 3/1988 Petit et al.... 246,34 R RAIL BREAK OR VEHICLE
United States Patent USOO7226021B1 (12) () Patent No.: Anderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DETECTING 4,728,063 A 3/1988 Petit et al.... 246,34 R RAIL BREAK OR VEHICLE
& S S. SS S. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States. (75) Inventors: Miguel Angel Gomez Caudevilla,
 (19) United States US 2006.0125150A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0125150 A1 Gomez Caudevilla et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2006 (54) PLASTIC RECEPTACLE FOR DOMESTIC WASHING
(19) United States US 2006.0125150A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0125150 A1 Gomez Caudevilla et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2006 (54) PLASTIC RECEPTACLE FOR DOMESTIC WASHING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0026979 A1 Dimou et al. US 20170026979A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) METHODS AND APPARATUSES FOR LOWERING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0026979 A1 Dimou et al. US 20170026979A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) METHODS AND APPARATUSES FOR LOWERING
ETSI TS V6.1.0 ( )
 TS 125 309 V6.1.0 (2004-12) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); FDD enhanced uplink; Overall description; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 25.309 version 6.1.0 Release 6) 1 TS 125
TS 125 309 V6.1.0 (2004-12) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); FDD enhanced uplink; Overall description; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 25.309 version 6.1.0 Release 6) 1 TS 125
PCT. GN, GQ, GW, ML, MR, NE, SN, TD, TG). Gyeonggi-do (KR). CHUN, Sung Duck [KR/KR]; , Saetbyeol Hanyang Apt.
![PCT. GN, GQ, GW, ML, MR, NE, SN, TD, TG). Gyeonggi-do (KR). CHUN, Sung Duck [KR/KR]; , Saetbyeol Hanyang Apt. PCT. GN, GQ, GW, ML, MR, NE, SN, TD, TG). Gyeonggi-do (KR). CHUN, Sung Duck [KR/KR]; , Saetbyeol Hanyang Apt.](/thumbs/86/94092032.jpg) (12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (43) International Publication Date (10) International
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (43) International Publication Date (10) International
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O2538.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0253843 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM OF MANAGEMENT FOR SWITCHINGVIRTUAL-REALITY
(19) United States US 2016O2538.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0253843 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM OF MANAGEMENT FOR SWITCHINGVIRTUAL-REALITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070047712A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0047712 A1 Gross et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) SCALABLE, DISTRIBUTED ARCHITECTURE FOR FULLY CONNECTED
(19) United States US 20070047712A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0047712 A1 Gross et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) SCALABLE, DISTRIBUTED ARCHITECTURE FOR FULLY CONNECTED
CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT
 CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT 7.1 INTRODUCTION Originally developed to be used in GSM by the Europe Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), the AMR speech codec
CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT 7.1 INTRODUCTION Originally developed to be used in GSM by the Europe Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), the AMR speech codec
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O190276A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0190276A1 Taguchi (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CCD SENSOR CONTROL, (30) Foreign Application
US 2005O190276A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0190276A1 Taguchi (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CCD SENSOR CONTROL, (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,104 B1
 USOO6208104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Onoue et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) ROBOT CONTROL UNIT (58) Field of Search... 318/567, 568.1, 318/568.2, 568. 11; 395/571, 580;
USOO6208104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Onoue et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) ROBOT CONTROL UNIT (58) Field of Search... 318/567, 568.1, 318/568.2, 568. 11; 395/571, 580;
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007124695B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,124.695 B2 Buechler (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) MODULAR SHELVING SYSTEM 4,635,564 A 1/1987 Baxter 4,685,576 A 8, 1987 Hobson (76)
(12) United States Patent US007124695B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,124.695 B2 Buechler (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) MODULAR SHELVING SYSTEM 4,635,564 A 1/1987 Baxter 4,685,576 A 8, 1987 Hobson (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
