DETC SURFACE ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC CONTROL OF A HUMANOID ROBOT
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
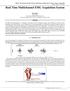
1 Proceedings of the ASME 2013 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 2013 August 4-7, 2013, Portland, Oregon, USA DETC SURFACE ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC CONTROL OF A HUMANOID ROBOT Alex W. Grammar M.S., ag153810@ohio.edu Electrical Engineering, Ohio University Athens, Ohio, USA Robert L. Williams II, Ph.D., williar4@ohio.edu Mechanical Engineering, Ohio University Athens, Ohio, USA ABSTRACT This paper details the development of an open-source surface electromyographic interface for controlling 1-DOF for the DARwIn-OP humanoid robot. This work also details the analysis of the relationship between surface electromyographic activity of the Biceps Brachii muscle and the angle of the elbow joint for the pseudo-static unloaded arm case. The human arm was mechanically modeled for a two link system actuated by a single muscle. The SEMG activity was found to be directly proportional to joint angle using a combination of custom joint angle measuring hardware and a surface electromyographic measuring circuit. This relationship allowed for straightforward control of the robot elbow joint directly. The interface was designed around the Arduino Microcontroller; another opensource platform. Software for the Arduino and DARwIn-OP were drawn from open source resources, allowing the entire system to be comprised of open-source components. A final surface electromyographic measuring and signal conditioning circuit was constructed. Data recording and processing software was also coded for the Arduino, thus achieving control of the robotic platform via surface electromyography. 1. INTRODUCTION This paper details the development of part of a telepresence system from first principles to a completed modular single degree of freedom teleoperation system for a humanoid robot using surface electromyographic (semg) signals to affect 1:1 motion between the user and the robot. For the initial system development a single degree of freedom was chosen; the right elbow due to the joint s simplicity and large controlling muscle. The design of the system was also made to be modular so that additional degrees of freedom would be simple to incorporate. To create this system the relationship between elbow joint angle and semg signals was determined and verified experimentally. After this the sensors, robot interface, and control software were designed and implemented. The purpose of this system is to facilitate the development of biologically-interfaced telepresence systems for humanoid robots. Being able to combine the adaptability of the human mind with the physical capabilities and robustness of a robot solves many issues in humanoid robotics (locomotion, stability), as well as allows humans to directly operate in any environment as if they were actually there. This project also seeks to open up this research to the open-source knowledge base by using open-source materials and components. The work begins with biomechanical modeling, continues with experimental verification of results, and then a final system design of the modular 1 DoF interface ensues. 2. BACKGROUND The DARwIn-OP robotic platform is an open-source humanoid robot with 20 degrees of freedom, integrated accelerometers, gyroscopes, cameras, Dynamixel MX-28 servos, and an onboard Intel Atom FitPC. It stands 455 mm tall and weighs 3 kg. Each leg has 6 DoF. The arm has 3. This system nears the human body s DoF with only those of the manipulators missing. The platform was developed by a joint venture between Robotis and Virginia Tech with a grant from the NSF.T he open source platform is intended for research and teaching purposes. The platform is shown below in Figure 1. [1] 1 Copyright 2013 by ASME
2 model. The upright position allows for the Triceps Brachii s contribution to be ignored as it is only stabilizing the muscle. Slowly moving affords a pseudostatic model where motion effects need not be considered. The human anatomical model can be seen below in figure where the Biceps acts as a tension cable for a simple, hinged, fixed-free, two segment armature. Starting from first principles, equations describing the forces at the elbow and muscle tension can be generated. The method is adapted from [5] (1) (2) (3) From the mechanical system depicted below in Error! Reference source not found., we can populate equations 1-3 with the force vector components and moments. Figure 1: DARwIn-OP humaniod robotic platform Surface electromyographic signals used in the system originate from the activity of human muscle tissue. Impulses from the brain travel down through major nerves that branch into motor units that split again in order to innervate individual muscle cells. This branching behavior amplifies the original neural pulse. The stronger the signal the harder the muscle is working. The exact relationship between force and joint angle is complex and varying for each joint. The signal is measured via invasive needle probes or conductive surface pads. Surface signals, while less invasive, are orders of magnitude smaller than those of needle probes and are much noisier. This can be overcome with additional processing. [2,3] It is common to use differential measurements tied into a high Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMMR) amplifier. Simple notch filtering of ambient noise is not appropriate as the majority of signal information is found within the 30 to 300 Hz band, centered at Hz. Typical post amplification filtering is the application of a band pass to remove low frequency motion and cardiac signals as well as high frequency ambient noise.[4] Figure 2: Human arm mechanical model below. (4) (5) (6) These equations can be arraigned into matrix form 2. BIOMECHANICAL MODELING To create the interface a model is needed to understand the relation between semg activity and joint angle. For our system we focus on contractions of the Biceps Brachii muscle in relation to the elbow joint angle. The position of the user, sitting upright and relaxed and slowly moving, allows for simplifications of the mechanical model versus the anatomical (7) 2 Copyright 2013 by ASME
3 From (7), it is seen that the Biceps tension is decoupled from the reaction forces. This allows for an expression of the Biceps tensions in terms of muscle and joint angle only We cannot measure the internal angle the Bicep makes in attaching to the forearm but the angle can be expressed in terms of the joint angle via vector loop closure. The loop consists of the vectors forming the upper arm, radius of the Bicep attachment, and the length of the Bicep. The loop is seen graphically below in Figure 3. (8) 2. MODELING RESULTS A Matlab simulation was developed to evaluate the model. The range of tested angles covered full extension to full flexion. The Human elbow joint range was taken from [6] to be a total of 150 degrees starting from full extension to full flexion; -90 degrees to 50 degrees. The results are seen below in Figure 4 and Muscle Tension vs. Joint Angle Muscle Tension (N) Joint Angle (deg) Figure 4: Muscle Tension (N) versus Joint angle (deg) Figure 3: Human arm vector loop closure 0 (10) (11) We can break this equation into both vertical and horizontal components. (12) Muscle Length (m) Muscle Length vs. Joint Angle We can use the classical Cartesian to Polar coordinate transformation function to determine an expression for muscle angle in terms of joint angle and can also write and expression for muscle length. (13) (14) Joint Angle (deg) Figure 5: Muscle Length (m) versus Joint Angle (deg) From biology we know that semg is involved with both the force of muscle contraction and the length of the muscle. With that in mind, two opposing theories were drawn from the above simulation. The first conclusion is that semg is directly related to muscle tension, the other being that semg is related to muscle length. As joint angle increases the behavior 3 Copyright 2013 by ASME
4 of semg will indicate the correct theory for this specific case of motion. With these two possible theories it was necessary to begin collecting data to verify the correct theory. The system can be seen being worn in Figure 8 and the VI in Figure EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS To determine which theory was correct an experimental setup was designed and constructed for simultaneous joint angle and semg readings. Having timelocked semg readings with a golden standard joint angle were vital to the final system design. The semg circuit consisted of an instrumentation amplifier with a high CMRR, single pole, Butterworth passband filter set to Hz, and a single stage noninverting amplifier. Typical semg readings are around 1mV and are very noisy. This circuit conditions the semg signal and amplifies desired signals in the passband by 385, bringing the final signal to DAQ appropriate levels. The recording circuit design for SEMG measurement is seen in Error! Reference source not found.. Figure 7: Joint angle reference armature Figure 6: semg capture circuit Figure 8: Experimental Setup To measure the joint angle a rotary encoder was constructed from a simple 3-tap potentiometer and mounted to a wearable armature. The wearable armature, shown in Figure 7, is a sports elbow brace designed for maximum mobility and joint stability. The joint angle is converted to a variable voltage signal. This signal is not calibrated to a set angle and must be zeroed in software. The joint angle device and semg circuit signals were integrated and recorded using LABVIEW software. The user was instructed to first place their arm in the neutral position so the software could zero the joint reference. After this they made slow, full sweeps of the arm covering the full range of motion. Figure 9: Labview VI for data capture 4 Copyright 2013 by ASME
5 After the data was collected it was imported into MATLAB for further processing. It was found that semg had a linear relationship with joint angle with a correlation coefficient of The repeated trials can be seen below. It was necessary to normalize the readings to their maximum and minimum values after applying a low pass filter (2 pole butterworth at 30 Hz). The repeated and processed trials are shown in Figure 10. A more detailed view of the raw and processed signals can be seen in Figure 11 and Figure Normalized Joint Angle and Processed SEMG Normalized Value Normalized and Filtered EMG and Joint Reference angles SEMG Joint Angle Normalized Value Sample # x 10 4 Figure 10: semg and joint angle reference signals for multiple contractions. Repeatability of measurements is sufficiently demonstrated Normalized Value Normalized SEMG and Joint Angle Reference for Three Flexion-Extention Motions Time(s) Figure 11: Raw semg and joint angle reference for three contractions Time (s) Figure 12: Filtered semg and joint angle reference for three contractions. The trend in the data suggests that SEMG is directly related more to muscle length rather than muscle tension in the pseudo-static, unloaded case. However, the data does not indicate a clear reason for this. To reconcile this finding a more complex model of muscle behavior is needed, but for the construction of the system a linear relationship is best suited for implementation. 5. FINAL SYSTEM The final system needs to communicate with both analog sensors and the robotic platform. The challenge presented by the DARwIn-OP is that it has only two USB ports that connect to the onboard computer. To work around this limitation an Arduino microcontroller was used as an intermediary. The Arduino collected semg data via the built in ADC. Meanwhile, the DARwIn-OP ran the open-source command line interpreter Tell DARwIn-OP [7] to process any plain text commands. The Arduino then processed its ADC values by normalizing them to operational min/max values and averaging readings over 20 samples. The determined joint angle was then written into plain text. Next, using another open source code segment, the Arduino was able to spoof a plug-and-play USB keyboard [8] (with associated USB-UART circuit interface) and manually typed each character into the command line to allow the robot to affect the commanded joint angle. Finally, the semg circuit had to be upgraded to include a full-wave rectifier to make the sensor output compatible for 0-5V ADCs. The final circuit is shown in Figure 13 and the overall system layout in Figure Copyright 2013 by ASME
6 conversion and communication elements of the system currently operate at a less than optimal rate. ADC times and board-robot communication needs to be increased dramatically to remove the delay between user movement and robot motion. Lastly, the system needs to be incorporated into a smaller, wearable package. When more DOF are added then the number of sensor leads will quickly become unmanageable. REFERENCES [1] R.L. Williams II, 2012, DARwIn-OP Humanoid Robot Kinematics, Proceedings of the ASME IDETC/CIE, Chicago IL, August 12-15, 2012, DETC [2] W. Herzog, J. Sokolosky, Y. T. Zhang, A. C. S. Guimaraes, EMG-force relationship in dynamically contracting cat plantaris muscle, Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology, vol. 8, pp , Figure 13: Final semg capture circuit [3] B. Sellers, Lecture, Topic: Introduction to EMG, ICT 224, Faculty of Engineering,Loughborough University, Leicestershire, UK. [4] N.A. Human EMG Kenyon College, Oct [5] R.Williams II, Engineering Biomechanics of Human Motion-NotesBook, Ohio University [6] M.Lee, A.Moroz, Physical Therapy, Merek Sharp & DohmeCrop, osteoarthritis&cdn=health&tm=8&f=10&tt=2&bt=1&bts=1&z u=http%3a// Figure 14: Final system layout. 6. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK The final system is a functional 1-DOF teleoperative system for controlling a humanoid robot via semg signals. For the elbow joint it was also found that for slow movements of the forearm in the upright sitting position the joint angle was directly related to the semg voltage level. The specific biology of this relationship is still unclear. It may be due to the level of muscle contraction, or simply a factor of increasing muscle density between the differential probes given a set neural impulse. Lastly, the entire system was designed to fully incorporate open source elements. This keeps with the theme of developing materials for the DARwIn-OP. [7] M. Krzyzan, Tell Darwin Reference, University of Georgia, Oct, [8] M. Heilemann, Practical Arduino- Projects: Virtual USB Keyboard, Oct Future work remains in three key areas. The relationship between joint angle and semg needs further investigation to give a biological foundation to the theory. The system responsiveness also needs some improvement, as the 6 Copyright 2013 by ASME
3-lead Muscle / Electromyography Sensor for Microcontroller Applications
 3-lead Muscle / Electromyography Sensor for Microcontroller Applications MyoWare Muscle Sensor (AT-04-001) DATASHEET FEATURES NEW - Wearable Design NEW - Single Supply +3.1V to +5.9V Polarity reversal
3-lead Muscle / Electromyography Sensor for Microcontroller Applications MyoWare Muscle Sensor (AT-04-001) DATASHEET FEATURES NEW - Wearable Design NEW - Single Supply +3.1V to +5.9V Polarity reversal
Real Time Multichannel EMG Acquisition System
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Real Time Multichannel EMG Acquisition System Jinal Rajput M.E Student Department of
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Real Time Multichannel EMG Acquisition System Jinal Rajput M.E Student Department of
EMG Electrodes. Fig. 1. System for measuring an electromyogram.
 1270 LABORATORY PROJECT NO. 1 DESIGN OF A MYOGRAM CIRCUIT 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Electromyograms The gross muscle groups (e.g., biceps) in the human body are actually composed of a large number of parallel
1270 LABORATORY PROJECT NO. 1 DESIGN OF A MYOGRAM CIRCUIT 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Electromyograms The gross muscle groups (e.g., biceps) in the human body are actually composed of a large number of parallel
University of Florida Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Intelligent Machine Design Laboratory EEL 4665 Spring 2013 LOSAT
 University of Florida Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Intelligent Machine Design Laboratory EEL 4665 Spring 2013 LOSAT Brandon J. Patton Instructors: Drs. Antonio Arroyo and Eric Schwartz
University of Florida Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Intelligent Machine Design Laboratory EEL 4665 Spring 2013 LOSAT Brandon J. Patton Instructors: Drs. Antonio Arroyo and Eric Schwartz
Emoto-bot Demonstration Control System
 Emoto-bot Demonstration Control System I am building a demonstration control system for VEX robotics that creates a human-machine interface for an assistive or companion robotic device. My control system
Emoto-bot Demonstration Control System I am building a demonstration control system for VEX robotics that creates a human-machine interface for an assistive or companion robotic device. My control system
NON INVASIVE TECHNIQUE BASED EVALUATION OF ELECTROMYOGRAM SIGNALS USING STATISTICAL ALGORITHM
 NON INVASIVE TECHNIQUE BASED EVALUATION OF ELECTROMYOGRAM SIGNALS USING STATISTICAL ALGORITHM Tanu Sharma 1, Karan Veer 2, Ravinder Agarwal 2 1 CSED Department, Global college of Engineering, Khanpur Kuhi
NON INVASIVE TECHNIQUE BASED EVALUATION OF ELECTROMYOGRAM SIGNALS USING STATISTICAL ALGORITHM Tanu Sharma 1, Karan Veer 2, Ravinder Agarwal 2 1 CSED Department, Global college of Engineering, Khanpur Kuhi
ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System
 ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System Elements of a Data Acquisition System 2 Analog Signal Data Acquisition Hardware Your Signal Data Acquisition DAQ Device System Computer Cable Terminal Block Data Acquisition
ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System Elements of a Data Acquisition System 2 Analog Signal Data Acquisition Hardware Your Signal Data Acquisition DAQ Device System Computer Cable Terminal Block Data Acquisition
Laboratory Project 1B: Electromyogram Circuit
 2240 Laboratory Project 1B: Electromyogram Circuit N. E. Cotter, D. Christensen, and K. Furse Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Abstract-You will
2240 Laboratory Project 1B: Electromyogram Circuit N. E. Cotter, D. Christensen, and K. Furse Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Abstract-You will
Baset Adult-Size 2016 Team Description Paper
 Baset Adult-Size 2016 Team Description Paper Mojtaba Hosseini, Vahid Mohammadi, Farhad Jafari 2, Dr. Esfandiar Bamdad 1 1 Humanoid Robotic Laboratory, Robotic Center, Baset Pazhuh Tehran company. No383,
Baset Adult-Size 2016 Team Description Paper Mojtaba Hosseini, Vahid Mohammadi, Farhad Jafari 2, Dr. Esfandiar Bamdad 1 1 Humanoid Robotic Laboratory, Robotic Center, Baset Pazhuh Tehran company. No383,
EDL Group #3 Final Report - Surface Electromyograph System
 EDL Group #3 Final Report - Surface Electromyograph System Group Members: Aakash Patil (07D07021), Jay Parikh (07D07019) INTRODUCTION The EMG signal measures electrical currents generated in muscles during
EDL Group #3 Final Report - Surface Electromyograph System Group Members: Aakash Patil (07D07021), Jay Parikh (07D07019) INTRODUCTION The EMG signal measures electrical currents generated in muscles during
Research Article. ISSN (Print) *Corresponding author Jaydip Desai
 Scholars Journal of Engineering and Technology (SJET) Sch. J. Eng. Tech., 2015; 3(3A):252-257 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Engineering and Technology (SJET) Sch. J. Eng. Tech., 2015; 3(3A):252-257 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
12/31/11 Analog to Digital Converter Noise Testing Final Report Page 1 of 10
 12/31/11 Analog to Digital Converter Noise Testing Final Report Page 1 of 10 Introduction: My work this semester has involved testing the analog-to-digital converters on the existing Ko Brain board, used
12/31/11 Analog to Digital Converter Noise Testing Final Report Page 1 of 10 Introduction: My work this semester has involved testing the analog-to-digital converters on the existing Ko Brain board, used
A New Low-Cost Bionic Hand
 Paper ID #15623 A New Low-Cost Bionic Hand Mr. TJ Brown, Middle Tennessee State University TJ Brown earned his Bachelor of Science in 2015 at Middle Tennessee State University where he studied Electro-Mechanical
Paper ID #15623 A New Low-Cost Bionic Hand Mr. TJ Brown, Middle Tennessee State University TJ Brown earned his Bachelor of Science in 2015 at Middle Tennessee State University where he studied Electro-Mechanical
Team RoBIU. Team Description for Humanoid KidSize League of RoboCup 2014
 Team RoBIU Team Description for Humanoid KidSize League of RoboCup 2014 Bartal Moshe, Chaimovich Yogev, Dar Nati, Druker Itai, Farbstein Yair, Levi Roi, Kabariti Shani, Kalily Elran, Mayaan Tal, Negrin
Team RoBIU Team Description for Humanoid KidSize League of RoboCup 2014 Bartal Moshe, Chaimovich Yogev, Dar Nati, Druker Itai, Farbstein Yair, Levi Roi, Kabariti Shani, Kalily Elran, Mayaan Tal, Negrin
Design and Control of the BUAA Four-Fingered Hand
 Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation Seoul, Korea May 21-26, 2001 Design and Control of the BUAA Four-Fingered Hand Y. Zhang, Z. Han, H. Zhang, X. Shang, T. Wang,
Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation Seoul, Korea May 21-26, 2001 Design and Control of the BUAA Four-Fingered Hand Y. Zhang, Z. Han, H. Zhang, X. Shang, T. Wang,
Laboratory Project 1: Design of a Myogram Circuit
 1270 Laboratory Project 1: Design of a Myogram Circuit Abstract-You will design and build a circuit to measure the small voltages generated by your biceps muscle. Using your circuit and an oscilloscope,
1270 Laboratory Project 1: Design of a Myogram Circuit Abstract-You will design and build a circuit to measure the small voltages generated by your biceps muscle. Using your circuit and an oscilloscope,
Parallel Robot Projects at Ohio University
 Parallel Robot Projects at Ohio University Robert L. Williams II with graduate students: John Hall, Brian Hopkins, Atul Joshi, Josh Collins, Jigar Vadia, Dana Poling, and Ron Nyzen And Special Thanks to:
Parallel Robot Projects at Ohio University Robert L. Williams II with graduate students: John Hall, Brian Hopkins, Atul Joshi, Josh Collins, Jigar Vadia, Dana Poling, and Ron Nyzen And Special Thanks to:
Physics applied to post-stroke rehabilitation: June 15, 2011 interim report
 Physics applied to post-stroke rehabilitation: June 15, 2011 interim report Adam Blumenau, David O. Girardo, Ephedyn L. Lin, Sahit Mandala*, and Marko B Popovic Worcester Polytechnic Institute, 100 Institute
Physics applied to post-stroke rehabilitation: June 15, 2011 interim report Adam Blumenau, David O. Girardo, Ephedyn L. Lin, Sahit Mandala*, and Marko B Popovic Worcester Polytechnic Institute, 100 Institute
FATIGUE INDEPENDENT AMPLITUDE-FREQUENCY CORRELATIONS IN EMG SIGNALS
 Fatigue independent amplitude-frequency correlations in emg signals. Adam SIEMIEŃSKI 1, Alicja KEBEL 1, Piotr KLAJNER 2 1 Department of Biomechanics, University School of Physical Education in Wrocław
Fatigue independent amplitude-frequency correlations in emg signals. Adam SIEMIEŃSKI 1, Alicja KEBEL 1, Piotr KLAJNER 2 1 Department of Biomechanics, University School of Physical Education in Wrocław
CS545 Contents XIV. Components of a Robotic System. Signal Processing. Reading Assignment for Next Class
 CS545 Contents XIV Components of a Robotic System Power Supplies and Power Amplifiers Actuators Transmission Sensors Signal Processing Linear filtering Simple filtering Optimal filtering Reading Assignment
CS545 Contents XIV Components of a Robotic System Power Supplies and Power Amplifiers Actuators Transmission Sensors Signal Processing Linear filtering Simple filtering Optimal filtering Reading Assignment
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY UNIT-4
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY UNIT-4 INTRODUCTION EMG is the study of muscle electrical signals. EMG is sometimes referred to as myoelectric activity. Muscle tissue conducts electrical potentials similar to the way
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY UNIT-4 INTRODUCTION EMG is the study of muscle electrical signals. EMG is sometimes referred to as myoelectric activity. Muscle tissue conducts electrical potentials similar to the way
Team Description for Humanoid KidSize League of RoboCup Stephen McGill, Seung Joon Yi, Yida Zhang, Aditya Sreekumar, and Professor Dan Lee
 Team DARwIn Team Description for Humanoid KidSize League of RoboCup 2013 Stephen McGill, Seung Joon Yi, Yida Zhang, Aditya Sreekumar, and Professor Dan Lee GRASP Lab School of Engineering and Applied Science,
Team DARwIn Team Description for Humanoid KidSize League of RoboCup 2013 Stephen McGill, Seung Joon Yi, Yida Zhang, Aditya Sreekumar, and Professor Dan Lee GRASP Lab School of Engineering and Applied Science,
ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Humanoid Kid-Size League of Robocup 2015
 ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Humanoid Kid-Size League of Robocup 2015 Yu DongDong, Liu Yun, Zhou Chunlin, and Xiong Rong State Key Lab. of Industrial Control Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou,
ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Humanoid Kid-Size League of Robocup 2015 Yu DongDong, Liu Yun, Zhou Chunlin, and Xiong Rong State Key Lab. of Industrial Control Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou,
Biomechanical Instrumentation Considerations in Data Acquisition ÉCOLE DES SCIENCES DE L ACTIVITÉ PHYSIQUE SCHOOL OF HUMAN KINETICS
 Biomechanical Instrumentation Considerations in Data Acquisition Data Acquisition in Biomechanics Why??? Describe and Understand a Phenomena Test a Theory Evaluate a condition/situation Data Acquisition
Biomechanical Instrumentation Considerations in Data Acquisition Data Acquisition in Biomechanics Why??? Describe and Understand a Phenomena Test a Theory Evaluate a condition/situation Data Acquisition
SRV02-Series. Rotary Servo Plant. User Manual
 SRV02-Series Rotary Servo Plant User Manual SRV02-(E;EHR)(T) Rotary Servo Plant User Manual 1. Description The plant consists of a DC motor in a solid aluminum frame. The motor is equipped with a gearbox.
SRV02-Series Rotary Servo Plant User Manual SRV02-(E;EHR)(T) Rotary Servo Plant User Manual 1. Description The plant consists of a DC motor in a solid aluminum frame. The motor is equipped with a gearbox.
Laboratory Mini-Projects Summary
 ME 4290/5290 Mechanics & Control of Robotic Manipulators Dr. Bob, Fall 2017 Robotics Laboratory Mini-Projects (LMP 1 8) Laboratory Exercises: The laboratory exercises are to be done in teams of two (or
ME 4290/5290 Mechanics & Control of Robotic Manipulators Dr. Bob, Fall 2017 Robotics Laboratory Mini-Projects (LMP 1 8) Laboratory Exercises: The laboratory exercises are to be done in teams of two (or
Design and Implementation of an Exoskeleton Arm Joint
 Design and Implementation of an Exoskeleton Arm Joint Prepared for: ECE 4600 Prepared by: Alex Reimer Colin Peterson Logan Froese Patrick Pagé Advisor: Robert McLeod, Ph.D, P. Eng Department of Electrical
Design and Implementation of an Exoskeleton Arm Joint Prepared for: ECE 4600 Prepared by: Alex Reimer Colin Peterson Logan Froese Patrick Pagé Advisor: Robert McLeod, Ph.D, P. Eng Department of Electrical
EMG. The study of muscle function through the investigation of the electrical signal the muscles produce
 EMG The study of muscle function through the investigation of the electrical signal the muscles produce Niek van Ulzen, 23-11-2010 niekroland.vanulzen@univr.it Program A. Theory (today) 1. Background Electricity
EMG The study of muscle function through the investigation of the electrical signal the muscles produce Niek van Ulzen, 23-11-2010 niekroland.vanulzen@univr.it Program A. Theory (today) 1. Background Electricity
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: , p-issn: , Volume 2, Issue 11 (November 2012), PP 37-43
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719, Volume 2, Issue 11 (November 2012), PP 37-43 Operative Precept of robotic arm expending Haptic Virtual System Arnab Das 1, Swagat
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719, Volume 2, Issue 11 (November 2012), PP 37-43 Operative Precept of robotic arm expending Haptic Virtual System Arnab Das 1, Swagat
WF Wolves & Taura Bots Humanoid Kid Size Team Description for RoboCup 2016
 WF Wolves & Taura Bots Humanoid Kid Size Team Description for RoboCup 2016 Björn Anders 1, Frank Stiddien 1, Oliver Krebs 1, Reinhard Gerndt 1, Tobias Bolze 1, Tom Lorenz 1, Xiang Chen 1, Fabricio Tonetto
WF Wolves & Taura Bots Humanoid Kid Size Team Description for RoboCup 2016 Björn Anders 1, Frank Stiddien 1, Oliver Krebs 1, Reinhard Gerndt 1, Tobias Bolze 1, Tom Lorenz 1, Xiang Chen 1, Fabricio Tonetto
EMG Signal Analysis and Application for Arm Exoskeleton Control.
 EMG Signal Analysis and Application for Arm Exoskeleton Control. 1 Anubhav Gupta, 2 Ritika Inamke, 1,2 Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Maharashtra Institute of Technology College of Engineering,Pune,
EMG Signal Analysis and Application for Arm Exoskeleton Control. 1 Anubhav Gupta, 2 Ritika Inamke, 1,2 Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Maharashtra Institute of Technology College of Engineering,Pune,
Rejuvenate An Old Tinius Olsen Machine with Computer Data Acquisition Using Its Existing Hardware and LabVIEW
 Rejuvenate An Old Tinius Olsen Machine with Computer Data Acquisition Using Its Existing Hardware and LabVIEW Jiaxin Zhao Indiana University Purdue University Fort Wayne Abstract Computer data acquisition
Rejuvenate An Old Tinius Olsen Machine with Computer Data Acquisition Using Its Existing Hardware and LabVIEW Jiaxin Zhao Indiana University Purdue University Fort Wayne Abstract Computer data acquisition
CHAPTER 7 INTERFERENCE CANCELLATION IN EMG SIGNAL
 131 CHAPTER 7 INTERFERENCE CANCELLATION IN EMG SIGNAL 7.1 INTRODUCTION Electromyogram (EMG) is the electrical activity of the activated motor units in muscle. The EMG signal resembles a zero mean random
131 CHAPTER 7 INTERFERENCE CANCELLATION IN EMG SIGNAL 7.1 INTRODUCTION Electromyogram (EMG) is the electrical activity of the activated motor units in muscle. The EMG signal resembles a zero mean random
Group #17 Arian Garcia Javier Morales Tatsiana Smahliuk Christopher Vendette
 Group #17 Arian Garcia Javier Morales Tatsiana Smahliuk Christopher Vendette Electrical Engineering Electrical Engineering Electrical Engineering Electrical Engineering Contents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Motivation
Group #17 Arian Garcia Javier Morales Tatsiana Smahliuk Christopher Vendette Electrical Engineering Electrical Engineering Electrical Engineering Electrical Engineering Contents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Motivation
Figure 1: Unity Feedback System. The transfer function of the PID controller looks like the following:
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Control Systems Design Lab Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Ola M. Skeik Experiment 3 PID Controller Overview This experiment
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Control Systems Design Lab Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Ola M. Skeik Experiment 3 PID Controller Overview This experiment
ZJUDancer Team Description Paper
 ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Tang Qing, Xiong Rong, Li Shen, Zhan Jianbo, and Feng Hao State Key Lab. of Industrial Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China Abstract. This document describes
ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Tang Qing, Xiong Rong, Li Shen, Zhan Jianbo, and Feng Hao State Key Lab. of Industrial Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China Abstract. This document describes
WIRELESS CONTROL OF A ROBOTIC ARM USING 3D MOTION TRACKING SENSORS AND ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS 13
 WIRELESS CONTROL OF A ROBOTIC ARM USING 3D MOTION TRACKING SENSORS AND ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS Fernando Ríos, Georgia Southern University; Rocío Alba-Flores, Georgia Southern University; Imani Augusma,
WIRELESS CONTROL OF A ROBOTIC ARM USING 3D MOTION TRACKING SENSORS AND ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS Fernando Ríos, Georgia Southern University; Rocío Alba-Flores, Georgia Southern University; Imani Augusma,
CONTROL IMPROVEMENT OF UNDER-DAMPED SYSTEMS AND STRUCTURES BY INPUT SHAPING
 CONTROL IMPROVEMENT OF UNDER-DAMPED SYSTEMS AND STRUCTURES BY INPUT SHAPING Igor Arolovich a, Grigory Agranovich b Ariel University of Samaria a igor.arolovich@outlook.com, b agr@ariel.ac.il Abstract -
CONTROL IMPROVEMENT OF UNDER-DAMPED SYSTEMS AND STRUCTURES BY INPUT SHAPING Igor Arolovich a, Grigory Agranovich b Ariel University of Samaria a igor.arolovich@outlook.com, b agr@ariel.ac.il Abstract -
SELF-BALANCING MOBILE ROBOT TILTER
 Tomislav Tomašić Andrea Demetlika Prof. dr. sc. Mladen Crneković ISSN xxx-xxxx SELF-BALANCING MOBILE ROBOT TILTER Summary UDC 007.52, 62-523.8 In this project a remote controlled self-balancing mobile
Tomislav Tomašić Andrea Demetlika Prof. dr. sc. Mladen Crneković ISSN xxx-xxxx SELF-BALANCING MOBILE ROBOT TILTER Summary UDC 007.52, 62-523.8 In this project a remote controlled self-balancing mobile
Using Rank Order Filters to Decompose the Electromyogram
 Using Rank Order Filters to Decompose the Electromyogram D.J. Roberson C.B. Schrader droberson@utsa.edu schrader@utsa.edu Postdoctoral Fellow Professor The University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio,
Using Rank Order Filters to Decompose the Electromyogram D.J. Roberson C.B. Schrader droberson@utsa.edu schrader@utsa.edu Postdoctoral Fellow Professor The University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio,
FalconBots RoboCup Humanoid Kid -Size 2014 Team Description Paper. Minero, V., Juárez, J.C., Arenas, D. U., Quiroz, J., Flores, J.A.
 FalconBots RoboCup Humanoid Kid -Size 2014 Team Description Paper Minero, V., Juárez, J.C., Arenas, D. U., Quiroz, J., Flores, J.A. Robotics Application Workshop, Instituto Tecnológico Superior de San
FalconBots RoboCup Humanoid Kid -Size 2014 Team Description Paper Minero, V., Juárez, J.C., Arenas, D. U., Quiroz, J., Flores, J.A. Robotics Application Workshop, Instituto Tecnológico Superior de San
An Integrated Package of Neuromusculoskeletal Modeling Tools in Simulink
 An Integrated Package of Neuromusculoskeletal Modeling Tools in Simulink R. Davoodi, I.E. Brown, N. Lan, M. Mileusnic and G.E. Loeb A.E. Mann Institute for Biomedical Engineering, University of Southern
An Integrated Package of Neuromusculoskeletal Modeling Tools in Simulink R. Davoodi, I.E. Brown, N. Lan, M. Mileusnic and G.E. Loeb A.E. Mann Institute for Biomedical Engineering, University of Southern
Vibration Fundamentals Training System
 Vibration Fundamentals Training System Hands-On Turnkey System for Teaching Vibration Fundamentals An Ideal Tool for Optimizing Your Vibration Class Curriculum The Vibration Fundamentals Training System
Vibration Fundamentals Training System Hands-On Turnkey System for Teaching Vibration Fundamentals An Ideal Tool for Optimizing Your Vibration Class Curriculum The Vibration Fundamentals Training System
sin(wt) y(t) Exciter Vibrating armature ENME599 1
 ENME599 1 LAB #3: Kinematic Excitation (Forced Vibration) of a SDOF system Students must read the laboratory instruction manual prior to the lab session. The lab report must be submitted in the beginning
ENME599 1 LAB #3: Kinematic Excitation (Forced Vibration) of a SDOF system Students must read the laboratory instruction manual prior to the lab session. The lab report must be submitted in the beginning
MEASURING AND ANALYZING FINE MOTOR SKILLS
 MEASURING AND ANALYZING FINE MOTOR SKILLS PART 1: MOTION TRACKING AND EMG OF FINE MOVEMENTS PART 2: HIGH-FIDELITY CAPTURE OF HAND AND FINGER BIOMECHANICS Abstract This white paper discusses an example
MEASURING AND ANALYZING FINE MOTOR SKILLS PART 1: MOTION TRACKING AND EMG OF FINE MOVEMENTS PART 2: HIGH-FIDELITY CAPTURE OF HAND AND FINGER BIOMECHANICS Abstract This white paper discusses an example
DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMANOID ROBOT FOR EDUCATION AND OUTREACH. K. Kelly, D. B. MacManus, C. McGinn
 DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMANOID ROBOT FOR EDUCATION AND OUTREACH K. Kelly, D. B. MacManus, C. McGinn Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland. ABSTRACT Robots
DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMANOID ROBOT FOR EDUCATION AND OUTREACH K. Kelly, D. B. MacManus, C. McGinn Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland. ABSTRACT Robots
FLCS V2.1. AHRS, Autopilot, Gyro Stabilized Gimbals Control, Ground Control Station
 AHRS, Autopilot, Gyro Stabilized Gimbals Control, Ground Control Station The platform provides a high performance basis for electromechanical system control. Originally designed for autonomous aerial vehicle
AHRS, Autopilot, Gyro Stabilized Gimbals Control, Ground Control Station The platform provides a high performance basis for electromechanical system control. Originally designed for autonomous aerial vehicle
Developer Techniques Sessions
 1 Developer Techniques Sessions Physical Measurements and Signal Processing Control Systems Logging and Networking 2 Abstract This session covers the technologies and configuration of a physical measurement
1 Developer Techniques Sessions Physical Measurements and Signal Processing Control Systems Logging and Networking 2 Abstract This session covers the technologies and configuration of a physical measurement
AUTOPILOT CONTROL SYSTEM - IV
 AUTOPILOT CONTROL SYSTEM - IV CONTROLLER The data from the inertial measurement unit is taken into the controller for processing. The input being analog requires to be passed through an ADC before being
AUTOPILOT CONTROL SYSTEM - IV CONTROLLER The data from the inertial measurement unit is taken into the controller for processing. The input being analog requires to be passed through an ADC before being
Project: Muscle Fighter
 체근전도신호처리에기반한새로운무선 HCI 개발에관한연구 Project: Muscle Fighter EMG application in GAME 서울대학교의용전자연구실박덕근, 권성훈, 김희찬 Contents Introduction Hardware Software Evaluation Demonstration Introduction About EMG About Fighting
체근전도신호처리에기반한새로운무선 HCI 개발에관한연구 Project: Muscle Fighter EMG application in GAME 서울대학교의용전자연구실박덕근, 권성훈, 김희찬 Contents Introduction Hardware Software Evaluation Demonstration Introduction About EMG About Fighting
Lecture 14 Interface Electronics (Part 2) ECE 5900/6900 Fundamentals of Sensor Design
 EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design 1 Lecture 14 Interface Electronics (Part 2) Interface Electronics (Part 2) 2 Linearizing Bridge Circuits (Sensor Tech Hand book) Precision Op amps, Auto Zero Op amps,
EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design 1 Lecture 14 Interface Electronics (Part 2) Interface Electronics (Part 2) 2 Linearizing Bridge Circuits (Sensor Tech Hand book) Precision Op amps, Auto Zero Op amps,
Total Hours Registration through Website or for further details please visit (Refer Upcoming Events Section)
 Total Hours 110-150 Registration Q R Code Registration through Website or for further details please visit http://www.rknec.edu/ (Refer Upcoming Events Section) Module 1: Basics of Microprocessor & Microcontroller
Total Hours 110-150 Registration Q R Code Registration through Website or for further details please visit http://www.rknec.edu/ (Refer Upcoming Events Section) Module 1: Basics of Microprocessor & Microcontroller
IMU Platform for Workshops
 IMU Platform for Workshops Lukáš Palkovič *, Jozef Rodina *, Peter Hubinský *3 * Institute of Control and Industrial Informatics Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Slovak University of Technology Ilkovičova
IMU Platform for Workshops Lukáš Palkovič *, Jozef Rodina *, Peter Hubinský *3 * Institute of Control and Industrial Informatics Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Slovak University of Technology Ilkovičova
National Instruments Our Mission
 NI ELVIS National Instruments Our Mission We equip engineers and scientists with tools that accelerate productivity, innovation, and discovery. 2 The NI Teaching Philosophy To inspire and prepare tomorrow
NI ELVIS National Instruments Our Mission We equip engineers and scientists with tools that accelerate productivity, innovation, and discovery. 2 The NI Teaching Philosophy To inspire and prepare tomorrow
Teaching Mechanical Students to Build and Analyze Motor Controllers
 Teaching Mechanical Students to Build and Analyze Motor Controllers Hugh Jack, Associate Professor Padnos School of Engineering Grand Valley State University Grand Rapids, MI email: jackh@gvsu.edu Session
Teaching Mechanical Students to Build and Analyze Motor Controllers Hugh Jack, Associate Professor Padnos School of Engineering Grand Valley State University Grand Rapids, MI email: jackh@gvsu.edu Session
MTE 360 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
 MTE 36 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering Laboratory #1: Introduction to Control Engineering In this laboratory, you will become familiar
MTE 36 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering Laboratory #1: Introduction to Control Engineering In this laboratory, you will become familiar
+ power. V out. - power +12 V -12 V +12 V -12 V
 Question 1 Questions An operational amplifier is a particular type of differential amplifier. Most op-amps receive two input voltage signals and output one voltage signal: power 1 2 - power Here is a single
Question 1 Questions An operational amplifier is a particular type of differential amplifier. Most op-amps receive two input voltage signals and output one voltage signal: power 1 2 - power Here is a single
EMG Sensor Shirt. Senior Project Written Hardware Description April 28, 2015 ETEC 474. By: Dylan Kleist Joshua Goertz
 EMG Sensor Shirt Senior Project Written Hardware Description April 28, 2015 ETEC 474 By: Dylan Kleist Joshua Goertz Table of Contents Introduction... 3 User Interface Board... 3 Bluetooth... 3 Keypad...
EMG Sensor Shirt Senior Project Written Hardware Description April 28, 2015 ETEC 474 By: Dylan Kleist Joshua Goertz Table of Contents Introduction... 3 User Interface Board... 3 Bluetooth... 3 Keypad...
A Machine Tool Controller using Cascaded Servo Loops and Multiple Feedback Sensors per Axis
 A Machine Tool Controller using Cascaded Servo Loops and Multiple Sensors per Axis David J. Hopkins, Timm A. Wulff, George F. Weinert Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, L-792, Livermore,
A Machine Tool Controller using Cascaded Servo Loops and Multiple Sensors per Axis David J. Hopkins, Timm A. Wulff, George F. Weinert Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, L-792, Livermore,
Modeling and Experimental Studies of a Novel 6DOF Haptic Device
 Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering Forum 2010 CSME FORUM 2010 June 7-9, 2010, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada Modeling and Experimental Studies of a Novel DOF Haptic Device
Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering Forum 2010 CSME FORUM 2010 June 7-9, 2010, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada Modeling and Experimental Studies of a Novel DOF Haptic Device
ECE-492 DESIGN DOCUMENT. Exoskeleton Arm Support System
 ECE-492 DESIGN DOCUMENT Exoskeleton Arm Support System The purpose of this project is to facilitate the movement of an arm by the use of an exoskeleton controlled by surface electromyography (EMG) signals.
ECE-492 DESIGN DOCUMENT Exoskeleton Arm Support System The purpose of this project is to facilitate the movement of an arm by the use of an exoskeleton controlled by surface electromyography (EMG) signals.
Design of a Bionic Hand Using Non Invasive Interface
 Design of a Bionic Hand Using Non Invasive Interface By Evan McNabb Electrical and Biomedical Engineering Design Project (4BI6) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering McMaster University Hamilton,
Design of a Bionic Hand Using Non Invasive Interface By Evan McNabb Electrical and Biomedical Engineering Design Project (4BI6) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering McMaster University Hamilton,
SERVO MOTOR CONTROL TRAINER
 SERVO MOTOR CONTROL TRAINER UC-1780A FEATURES Open & closed loop speed and position control. Analog and digital control techniques. PC based instrumentation include oscilloscope, multimeter and etc. PC
SERVO MOTOR CONTROL TRAINER UC-1780A FEATURES Open & closed loop speed and position control. Analog and digital control techniques. PC based instrumentation include oscilloscope, multimeter and etc. PC
Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's
 2240 Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's Abstract-You will construct and test two LED power-indicator circuits for your breadboard in preparation for building the Electromyogram circuit in Lab
2240 Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's Abstract-You will construct and test two LED power-indicator circuits for your breadboard in preparation for building the Electromyogram circuit in Lab
DC SERVO MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM
 DC SERVO MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM MODEL NO:(PEC - 00CE) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
DC SERVO MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM MODEL NO:(PEC - 00CE) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
ME 461 Laboratory #5 Characterization and Control of PMDC Motors
 ME 461 Laboratory #5 Characterization and Control of PMDC Motors Goals: 1. Build an op-amp circuit and use it to scale and shift an analog voltage. 2. Calibrate a tachometer and use it to determine motor
ME 461 Laboratory #5 Characterization and Control of PMDC Motors Goals: 1. Build an op-amp circuit and use it to scale and shift an analog voltage. 2. Calibrate a tachometer and use it to determine motor
The Design of Battle Field Robot
 The Design of Battle Field Robot D.Bubesh Kumar Mechanical Engineering Department Aarupadaiveedu Institute of Technology Vinayaka Mission University Kanchipuram,Tamilnadu,India Abstract -The battle field
The Design of Battle Field Robot D.Bubesh Kumar Mechanical Engineering Department Aarupadaiveedu Institute of Technology Vinayaka Mission University Kanchipuram,Tamilnadu,India Abstract -The battle field
CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
 168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
Training Schedule. Robotic System Design using Arduino Platform
 Training Schedule Robotic System Design using Arduino Platform Session - 1 Embedded System Design Basics : Scope : To introduce Embedded Systems hardware design fundamentals to students. Processor Selection
Training Schedule Robotic System Design using Arduino Platform Session - 1 Embedded System Design Basics : Scope : To introduce Embedded Systems hardware design fundamentals to students. Processor Selection
Enhanced performance of delayed teleoperator systems operating within nondeterministic environments
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2010 Enhanced performance of delayed teleoperator systems operating
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2010 Enhanced performance of delayed teleoperator systems operating
Position Control of AC Servomotor Using Internal Model Control Strategy
 Position Control of AC Servomotor Using Internal Model Control Strategy Ahmed S. Abd El-hamid and Ahmed H. Eissa Corresponding Author email: Ahmednrc64@gmail.com Abstract: This paper focuses on the design
Position Control of AC Servomotor Using Internal Model Control Strategy Ahmed S. Abd El-hamid and Ahmed H. Eissa Corresponding Author email: Ahmednrc64@gmail.com Abstract: This paper focuses on the design
EROS TEAM. Team Description for Humanoid Kidsize League of Robocup2013
 EROS TEAM Team Description for Humanoid Kidsize League of Robocup2013 Azhar Aulia S., Ardiansyah Al-Faruq, Amirul Huda A., Edwin Aditya H., Dimas Pristofani, Hans Bastian, A. Subhan Khalilullah, Dadet
EROS TEAM Team Description for Humanoid Kidsize League of Robocup2013 Azhar Aulia S., Ardiansyah Al-Faruq, Amirul Huda A., Edwin Aditya H., Dimas Pristofani, Hans Bastian, A. Subhan Khalilullah, Dadet
Elements of Haptic Interfaces
 Elements of Haptic Interfaces Katherine J. Kuchenbecker Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania kuchenbe@seas.upenn.edu Course Notes for MEAM 625, University
Elements of Haptic Interfaces Katherine J. Kuchenbecker Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania kuchenbe@seas.upenn.edu Course Notes for MEAM 625, University
ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Humanoid Kid-Size League of Robocup 2014
 ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Humanoid Kid-Size League of Robocup 2014 Yu DongDong, Xiang Chuan, Zhou Chunlin, and Xiong Rong State Key Lab. of Industrial Control Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou,
ZJUDancer Team Description Paper Humanoid Kid-Size League of Robocup 2014 Yu DongDong, Xiang Chuan, Zhou Chunlin, and Xiong Rong State Key Lab. of Industrial Control Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou,
RISE WINTER 2015 UNDERSTANDING AND TESTING SELF SENSING MCKIBBEN ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES
 RISE WINTER 2015 UNDERSTANDING AND TESTING SELF SENSING MCKIBBEN ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES Khai Yi Chin Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Michigan Abstract Due to their compliant properties,
RISE WINTER 2015 UNDERSTANDING AND TESTING SELF SENSING MCKIBBEN ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES Khai Yi Chin Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Michigan Abstract Due to their compliant properties,
Wireless Master-Slave Embedded Controller for a Teleoperated Anthropomorphic Robotic Arm with Gripping Force Sensing
 Wireless Master-Slave Embedded Controller for a Teleoperated Anthropomorphic Robotic Arm with Gripping Force Sensing Presented by: Benjamin B. Rhoades ECGR 6185 Adv. Embedded Systems January 16 th 2013
Wireless Master-Slave Embedded Controller for a Teleoperated Anthropomorphic Robotic Arm with Gripping Force Sensing Presented by: Benjamin B. Rhoades ECGR 6185 Adv. Embedded Systems January 16 th 2013
A3 Pro INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Oct 25, 2017 Revision IMPORTANT NOTES
 A3 Pro INSTRUCTION MANUAL Oct 25, 2017 Revision IMPORTANT NOTES 1. Radio controlled (R/C) models are not toys! The propellers rotate at high speed and pose potential risk. They may cause severe injury
A3 Pro INSTRUCTION MANUAL Oct 25, 2017 Revision IMPORTANT NOTES 1. Radio controlled (R/C) models are not toys! The propellers rotate at high speed and pose potential risk. They may cause severe injury
Name Kyla Jackson, Todd Germeroth, Jake Spooler Date May 5, 2010 Lab 3E Group 3 Experiment Title Project Deliverable 3
 Name Kyla Jackson, Todd Germeroth, Jake Spooler Date May 5, 2010 Lab 3E Group 3 Experiment Title Project Deliverable 3 Objective The objective of this project was to design and construct an ECG measurement
Name Kyla Jackson, Todd Germeroth, Jake Spooler Date May 5, 2010 Lab 3E Group 3 Experiment Title Project Deliverable 3 Objective The objective of this project was to design and construct an ECG measurement
Keywords Electromyographic (EMG) signals, Robotic arm, Root Mean Square (RMS) value, variance, LabVIEW
 Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Real Time Control
Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Real Time Control
Analog front-end electronics
 FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers Analog front-end electronics Spring 2017 Lecture #6 Bekkeng, 30.1.2017 Considerations for analog signals Signal source - grounded or floating Source
FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers Analog front-end electronics Spring 2017 Lecture #6 Bekkeng, 30.1.2017 Considerations for analog signals Signal source - grounded or floating Source
IT.MLD900 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER. Signal Conditioning
 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
USER MANUAL. SRV02 Rotary Servo Base Unit. Set Up and Configuration
 Ten modules to teach controls from the basic to advanced level SRV02 Base Unit Flexible Link Inverted Pendulum Ball and Beam USER MANUAL SRV02 Rotary Servo Base Unit Set Up and Configuration 2 DOF Robot
Ten modules to teach controls from the basic to advanced level SRV02 Base Unit Flexible Link Inverted Pendulum Ball and Beam USER MANUAL SRV02 Rotary Servo Base Unit Set Up and Configuration 2 DOF Robot
Robots Learning from Robots: A proof of Concept Study for Co-Manipulation Tasks. Luka Peternel and Arash Ajoudani Presented by Halishia Chugani
 Robots Learning from Robots: A proof of Concept Study for Co-Manipulation Tasks Luka Peternel and Arash Ajoudani Presented by Halishia Chugani Robots learning from humans 1. Robots learn from humans 2.
Robots Learning from Robots: A proof of Concept Study for Co-Manipulation Tasks Luka Peternel and Arash Ajoudani Presented by Halishia Chugani Robots learning from humans 1. Robots learn from humans 2.
Robot Task-Level Programming Language and Simulation
 Robot Task-Level Programming Language and Simulation M. Samaka Abstract This paper presents the development of a software application for Off-line robot task programming and simulation. Such application
Robot Task-Level Programming Language and Simulation M. Samaka Abstract This paper presents the development of a software application for Off-line robot task programming and simulation. Such application
Advances in Antenna Measurement Instrumentation and Systems
 Advances in Antenna Measurement Instrumentation and Systems Steven R. Nichols, Roger Dygert, David Wayne MI Technologies Suwanee, Georgia, USA Abstract Since the early days of antenna pattern recorders,
Advances in Antenna Measurement Instrumentation and Systems Steven R. Nichols, Roger Dygert, David Wayne MI Technologies Suwanee, Georgia, USA Abstract Since the early days of antenna pattern recorders,
Wireless Neural Loggers
 Deuteron Technologies Ltd. Electronics for Neuroscience Wireless Neural Loggers On-animal neural recording Deuteron Technologies provides a family of animal-borne neural data loggers for recording 8, 16,
Deuteron Technologies Ltd. Electronics for Neuroscience Wireless Neural Loggers On-animal neural recording Deuteron Technologies provides a family of animal-borne neural data loggers for recording 8, 16,
SELF STABILIZING PLATFORM
 SELF STABILIZING PLATFORM Shalaka Turalkar 1, Omkar Padvekar 2, Nikhil Chavan 3, Pritam Sawant 4 and Project Guide: Mr Prathamesh Indulkar 5. 1,2,3,4,5 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication,
SELF STABILIZING PLATFORM Shalaka Turalkar 1, Omkar Padvekar 2, Nikhil Chavan 3, Pritam Sawant 4 and Project Guide: Mr Prathamesh Indulkar 5. 1,2,3,4,5 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication,
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle
 Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle David. J. Hopkins, Paul Geraghty Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, MS/L-792, Livermore, CA. 94550 Abstract Proper configurations
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle David. J. Hopkins, Paul Geraghty Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, MS/L-792, Livermore, CA. 94550 Abstract Proper configurations
Introduction to MS150
 Introduction to MS150 Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A Operation
Introduction to MS150 Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A Operation
Accessible Power Tool Flexible Application Scalable Solution
 Accessible Power Tool Flexible Application Scalable Solution Franka Emika GmbH Our vision of a robot for everyone sensitive, interconnected, adaptive and cost-efficient. Even today, robotics remains a
Accessible Power Tool Flexible Application Scalable Solution Franka Emika GmbH Our vision of a robot for everyone sensitive, interconnected, adaptive and cost-efficient. Even today, robotics remains a
Korea Humanoid Robot Projects
 Korea Humanoid Robot Projects Jun Ho Oh HUBO Lab., KAIST KOREA Humanoid Projects(~2001) A few humanoid robot projects were existed. Most researches were on dynamic and kinematic simulations for walking
Korea Humanoid Robot Projects Jun Ho Oh HUBO Lab., KAIST KOREA Humanoid Projects(~2001) A few humanoid robot projects were existed. Most researches were on dynamic and kinematic simulations for walking
THE HUMAN POWER AMPLIFIER TECHNOLOGY APPLIED TO MATERIAL HANDLING
 THE HUMAN POWER AMPLIFIER TECHNOLOGY APPLIED TO MATERIAL HANDLING H. Kazerooni Mechanical Engineering Department Human Engineering Laboratory (HEL) University ofcajifomia, Berkeley, CA 94720-1740 USA E-Mail:
THE HUMAN POWER AMPLIFIER TECHNOLOGY APPLIED TO MATERIAL HANDLING H. Kazerooni Mechanical Engineering Department Human Engineering Laboratory (HEL) University ofcajifomia, Berkeley, CA 94720-1740 USA E-Mail:
Team Description Paper: Darmstadt Dribblers & Hajime Team (KidSize) and Darmstadt Dribblers (TeenSize)
 Team Description Paper: Darmstadt Dribblers & Hajime Team (KidSize) and Darmstadt Dribblers (TeenSize) Martin Friedmann 1, Jutta Kiener 1, Robert Kratz 1, Sebastian Petters 1, Hajime Sakamoto 2, Maximilian
Team Description Paper: Darmstadt Dribblers & Hajime Team (KidSize) and Darmstadt Dribblers (TeenSize) Martin Friedmann 1, Jutta Kiener 1, Robert Kratz 1, Sebastian Petters 1, Hajime Sakamoto 2, Maximilian
Team Description Paper: HuroEvolution Humanoid Robot for Robocup 2014 Humanoid League
 Team Description Paper: HuroEvolution Humanoid Robot for Robocup 2014 Humanoid League Chung-Hsien Kuo, Yu-Cheng Kuo, Yu-Ping Shen, Chen-Yun Kuo, Yi-Tseng Lin 1 Department of Electrical Egineering, National
Team Description Paper: HuroEvolution Humanoid Robot for Robocup 2014 Humanoid League Chung-Hsien Kuo, Yu-Cheng Kuo, Yu-Ping Shen, Chen-Yun Kuo, Yi-Tseng Lin 1 Department of Electrical Egineering, National
Dr. Ashish Dutta. Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, INDIA
 Introduction: History of Robotics - past, present and future Dr. Ashish Dutta Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, INDIA Origin of Automation: replacing human
Introduction: History of Robotics - past, present and future Dr. Ashish Dutta Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, INDIA Origin of Automation: replacing human
TigreSAT 2010 &2011 June Monthly Report
 2010-2011 TigreSAT Monthly Progress Report EQUIS ADS 2010 PAYLOAD No changes have been done to the payload since it had passed all the tests, requirements and integration that are necessary for LSU HASP
2010-2011 TigreSAT Monthly Progress Report EQUIS ADS 2010 PAYLOAD No changes have been done to the payload since it had passed all the tests, requirements and integration that are necessary for LSU HASP
Magnetic Levitation System
 Magnetic Levitation System Electromagnet Infrared LED Phototransistor Levitated Ball Magnetic Levitation System K. Craig 1 Magnetic Levitation System Electromagnet Emitter Infrared LED i Detector Phototransistor
Magnetic Levitation System Electromagnet Infrared LED Phototransistor Levitated Ball Magnetic Levitation System K. Craig 1 Magnetic Levitation System Electromagnet Emitter Infrared LED i Detector Phototransistor
Arduino Setup & Flexing the ExBow
 Arduino Setup & Flexing the ExBow What is Arduino? Before we begin, We must first download the Arduino and Ardublock software. For our Set-up we will be using Arduino. Arduino is an electronics platform.
Arduino Setup & Flexing the ExBow What is Arduino? Before we begin, We must first download the Arduino and Ardublock software. For our Set-up we will be using Arduino. Arduino is an electronics platform.
KMUTT Kickers: Team Description Paper
 KMUTT Kickers: Team Description Paper Thavida Maneewarn, Xye, Korawit Kawinkhrue, Amnart Butsongka, Nattapong Kaewlek King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi, Institute of Field Robotics (FIBO)
KMUTT Kickers: Team Description Paper Thavida Maneewarn, Xye, Korawit Kawinkhrue, Amnart Butsongka, Nattapong Kaewlek King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi, Institute of Field Robotics (FIBO)
