Surface Mount Removal Techniques Using MX-5200 Soldering & Rework System
|
|
|
- Trevor Adams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surface Mount Removal Techniques Using MX-5200 Soldering & Rework System Our thanks to Metcal for allowing us to reprint the following. Skills and techniques are designed to provide even the least experienced operator the power to perform some of the most difficult rework tasks in electronics today. By using lower temperatures, SmartHeat Technology offers a means of rework that is safer for today's smaller, densely populated, heat sensitive circuit boards and components. REMOVING DISCRETE AND PASSIVE COMPONENTS ABSTRACT This Technical Note outlines, step by step, the easiest ways to remove and replace surface mount devices, using the lowest possible temperatures with an MX-5200 Soldering and Rework System. Specifically, this document discusses: Removal and replacement of discrete and passive components (capacitors, resistors, SOTs) Removal of two-sided components (SOICs, SOJs, TSOPs) Removal of quad components (PLCCs, QFPs) Replacement of quad components including finepitched devices These tasks can all be accomplished using a Metcal Advanced Handpiece (MX-H1-AV) or standard MX- 500 MX-RM3E Hand-piece in conjunction with the MX Removal of some components may also be achieved using Metcal's MX-PTZ Hand-piece, or the MX-H2-UF Metcal UltraFine Hand-piece which uses UltraFine soldering cartridges (UFTC). Removing a CHIP CAP With a Metcal MX-H1-AV Advanced Hand-piece The Metcal systems offer a wide range of surface mount cartridges to remove small, discrete components such as 0805, 1206, 1210, 1808, 1812 or SOT-23. Metcal calls these cartridges their slot cartridges" and in most cases the slot is sized to match the lead width of the component. You must match the correct cartridge with the component you are removing. In a few cases, the slot of a larger cartridge can be tinned with wire solder to fill the void allowing it to be used to remove a component whose footprint is slightly smaller. 1. Choose the correct cartridge from the list below:
2 2. Choose the correct cartridge temperature for the removal task. When choosing the temperature, it is always best to choose the lowest temperature possible to accomplish the job. Metcal offers cartridges in 500, 600, 700 and certain 800 Series heaters. In most lead free cases, a 600 Series cartridge is sufficient to do the job. An exception would be when the printed circuit board (PCB) has a heavy ground plane and the component circuitry, or traces, are attached to that plane. In this case, use a 700 Series. If you think you need a 800 Series cartridge, call your local Metcal Representative or Distributor to be sure that your application warrants it. With the correct geometry 700 series should work even with lead free applications. 3. Metcal's slot cartridges may take seconds to heat to their designed temperature using the MX power supply. After allowing the cartridge to heat, tin the inside edges of the cartridge. Tinning the inside performs two functions. First, it assists heat delivery for quicker removal. Second, the solder on the inside edges will help pick the component off the board once it is reflowed. 4. Bring the cartridge down directly over the fluxed component so the inside edges make direct contact with the leads of the part. 5. Allow the cartridge to reflow the solder completely on both sides of the component. This requires a minimal degree of skill and judgment. 6. When you are certain it is completely reflowed, slightly twist the cartridge slightly in a circular motion and lift simultaneously. This action is necessary to break the surface tension bond of the solder or glue that has been holding the component to the lands. By being patient and allowing sufficient time for the solder joints to reflow completely, you reduce your risk of lifted pads. On the smaller discrete components, this generally means just two to three seconds. However, many printed circuit boards now have components mounted on both the top and bottom. When discrete components are mounted on the bottom of a PCB, they are usually secured with a chip-bonder epoxy. This will cause reflow to take a few seconds longer. Now you not only have to reflow the solder joints, but you must also melt or soften the epoxy by transferring the heat through the body of the component. Don't worry. The additional reflow time is never more than a couple of seconds. 7. After you have removed the component off the board, wipe it on the wet sponge or brass tip cleaning pad to dislodge it from the cartridge. Do not tap the cartridge on the workstand, as that may cause damage to the heater in the cartridge. Removing CHIP CAP s with a MX-PTZ Precision Tweezers Hand-piece The MX-PTZ Precision Tweezers offer a versatile option for removal of components with the PTTC Series of cartridges from 0.4mm tip to 7mm tips. Select the correct tweezers cartridges from the chart below (note these are fine tips, 0.4mm 1.27mm): Please see the Cartridges Part Number Code System chart for temperature designation and geometry.
3 These cartridges are designed for the removal, and sometimes placement, of 0402 chips. The larger PTTCx07 (7mm) tweezer cartridges are suitable for the removal of larger, two sided components such as SO IC s. First, we will look at chip removal. 1. Select the most suitable PTTC tweezer cartridges to suit the application. Ensure that the point or blades of the tweezer cartridge are truly aligned using the X and Y axis adjustments on the PTZ Hand-piece. 2. Flux the component to be removed. 3. Apply the PTTC tweezers tips to the component ensuring that all pads are in direct contact with the tweezers. Allow a few seconds for the heat to transfer to the entire component and, once the solder is melted gently squeeze the tweezers and lift the component away from the pads. Again, this requires a minimal degree of skill and judgment. Note: Patience is the key to ensuring that ALL leads of the device are in reflow, trying to raise the device prematurely could result in damaged pads. Replacing Discrete Components Metcal suggests using a fine-point cartridge such as the SMTC-1171 for soldering small discrete components. Choose the correct tip from the cartridge list from the charts below. Note: to ensure a good thermal transfer, the cartridge surface should have a close a match as possible to the working area. Power Tips These have been specifically designed to assist with thermally demanding lead free applications. For example, the STTCx45P has the same face dimensions as an STTC-x45, but with a shorter profile. And, the Power Tips will perform considerably better than a long thin version of the same tip and heater configuration.
4 Chisel Cartridges * Indicates a power version of this tip exists in above chart. Bevel Cartridges * Indicates a power version of this tip exists in above chart. Please see the Cartridges Part Number Code System chart for temperature designation and geometry. Working with Ceramic Capacitors and Sensitive Components You should select the lowest temperature cartridge possible to achieve the required solder joint when working with ceramic parts. Ceramics are more susceptible to thermal shock and by following a few simple steps you can virtually eliminate this risk to your components. In addition, by using a lower temperature cartridge, you will significantly increase your cartridge life. If any thermal challenges are found, and the temperature of the tip needs to be kept low, use a convection preheater such as the PCT-1000 Programmable Preheater or PCT-100 Focused Convection Preheater to provide supplemental heat energy from the bottom of the PCB as shown later in this document. The use of bottom side preheating will aid reflow considerably with 500 and 600 series heater cartridges. For those that need to active a low solder joint temperature for sensitive chip components under 265 C- 270 C (509 F-518 F) this can be evaluated with 500 series tips and preheater. 1. Clean the old solder from the pads of the component you just removed. Use a standard chisel or hoof tip soldering cartridge which best suits the pad size and a suitable solder braid. The ideal size tip. The closer the match in size increases thermal transfer and reduces the potential of abrasion to the PCB Solder resist. 2. Apply flux to the pads to ensure that the pads are free from oxidization and other contaminates.
5 3. Place the new component, holding it in place with a pair of tweezers or wooden stick (tooth picks / orangewood sticks are used by some operators). 4. Use a fine point cartridge to solder the leads to the pads. The cartridge should be placed at the junction where the lead meets the pad. This is the correct IPC method for making the solder joint and it allows the cartridge to ramp up the temperature of the component. Avoid placing the cartridge directly on the lead; placing the cartridge on the lead may thermally shock the component, or take longer than necessary to transfer the heat to the pad. Place the tip between the part and the pad and apply solder to the two points. Solder must not flow over the top of the chip components. REMOVAL OF SOIC s, SOJ s, AND TSOP s using the Metcal Advanced Handpiece (MX-H1-AV) or MX-RM3E (standard MX-500 hand-piece) Removing multi-leaded two sided components is very similar to removing discrete components when using SMTC tips. The choice of cartridge, however, is more crucial. Each SMTC removal cartridge that Metcal makes is component specific. If you remove many different two-sided components every day, you may want to consider using the MX-PTZ Precision Tweezers, which will work with both the MX-500P and MX-PS5200 Power Supplies. 5. After you have made the first solder joint, check component alignment and solder the other leads in the same manner. Select the correct cartridge from the list below Item Description Dim A mm (") Dim A2 mm (") Dim B mm (") Dim D mm (") SMTC-x42 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOIC (0.520) (0.520) (0.805) 3.18 (0.125) SMTC-x06 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOIC -14, (0.200) 5.08 (0.200) (0.400) 2.30 (0.90) SMTC-x04 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOIC (0.200) 5.08 (0.200) 4.32 (0.170) 2.30 (0.90) SMTC-x142 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOIC (0.204) 5.18 (0.204) 8.90 (0.350) 2.50 (0.100) SMTC-x20 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOMC (0.270) 6.86 (0.270) (0.440) 2.30 (0.090) SMTC-x138 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOP (0.270) 6.86 (0.270) 7.24 (0.285) 2.50 (0.100) SMTC-x124 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOJ (0.320) 8.13 (0.320) (0.470) 6.86 (0.270) SMTC-x47 Cartridge, Tunnel, DPAK 8.50 (0.335) 8.50 (0.335) 6.35 (0.250) 5.00 (0.200) SMTC-x26 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOJ-28, SOM (0.340) 8.00 (0.315) ( 0.740) 1.88 (0.074) SMTC-x10 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOIC (0.375) 9.53 (0.375) (0.520) 3.20 (0.125) SMTC-x09 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOIC (0.375) 9.53 (0.375) (0.620) 3.20 (0.125) SMTC-x07 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOIC (0.375) 9.53 (0.375) (0.720) 3.20 (0.125) SMTC-x107 Cartridge, Tunnel, SO (0.380) 8.10 (0.320) (0.750) 6.10 (0.240) SMTC-x40 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOJ-40. SOM (0.450) (0.410) (1.02) 1.90 (0.075) SMTC-x83 Cartridge, Tunnel, SOP (0.565) (0.510) (1.07) 2.70 (0.105) Please see the Cartridges Part Number Code System chart for temperature designation and geometry. 1. Choose the correct cartridge temperature. Again, Metcal makes different temperature Series for these removal cartridges, but we suggest using a 600 or 700 Series heaters for most applications. Exceptions would be heavy ground plane boards or components that are much larger and more dense. If 800 series cartridges are selected, tip life will be shorter and good tip care is essential, See Metcal tip care guide (the use of a convection preheater PCT 100 or PCT 1000 should also be considered as opposed to 800 series heaters.) Preheating a FR-4 PCB to 60-80ºc, will increase productivity and lower the required tip temperature which is safer for the application and increases tip life. Preheating ceramic or military substrates to 100ºC and polyimide PCBs to 120ºC will increase productivity and allow lower soldering
6 cartridge temperatures to be selected, protecting the PCB as well as increasing tip life. 2. After inserting the cartridge and allowing it to heat, fully tin the inside edges of the cartridge with wire solder. Apply flux to the component leads. 3. Bring the cartridge straight down on top of the leads of the component. Make sure that you have contact with all the leads. 4. Leave the cartridge on the leads without rocking or twisting the cartridge on the component. An approximate time would be two second to 8 seconds for removal. Patience is the key to not lifting a pad. 5. Once you are certain all leads are reflowed, use a slight twisting and wiping motion to remove the component off the board. The surface tension of the cartridge's tinned edges will hold the component in the cartridge. 6. Wipe the component on the Damp sponge or brass pad to dislodge it from the cartridge. 7. Re apply solder to tin the tip before replacing it in the stand to reduce oxidization of the soldering surfaces. REMOVING SOIC s, SOJ s, AND TSOP s WITH THE MX-PTZ PRECISION TWEEZERS 1. Select the most suitable PTTC Tweezer Cartridges to suit the component to be removed from the chart below. These are large tip tweezers 2mm 28mm Please see the Cartridges Part Number Code System chart for temperature designation and geometry. Ensure that the blades are truly aligned using the X and Y axis adjustments on the MX-PTZ Hand-piece as shown previously on page Flux the component to be removed. Gel flux is also a good option to consider in fine rework applications as it aids in the transfer of heat to the component faster than liquid flux, this is because of better surface coverage on leads than liquid flux. Gel flux is available from most solder paste suppliers 3. Do not mix lead-free and leaded fluxes (lead-free PCB reworked with leaded flux, will contaminate the PCB, you must use lead-free flux used with lead-free solder wick). If flux types are mixed, contamination can occur and undesirable residues left on the PCB, which can be difficult to remove and may become
7 conductive or aggressive with age. Sometimes this is shown as a white powder like material left on surface of PCB. 4. Apply the PTTC Tweezers to the component ensuring that all leads are in direct contact with the tweezers. Allow a few seconds for the heat to transfer to the entire component and, once in reflow, gently squeeze the tweezers and lift the component away from the PCB. Again, this requires a minimal degree of skill and judgment. prematurely could result in damaged pads. An arm rest is also a useful tool. This is available as a separate tool for use with irons or tweezers. Using a preheater to aid removal when using tweezers or tunnel tips will decrease time on the component and lower temperature tips can be used. Note: Patience is the key to ensuring that all leads of the device are in reflow, trying to raise the device PCT 100 Convection Preheater PCT-AR Arm rest is a useful tool, available separately. PAD CLEAN UP AND PREPARATION The following steps may be used for both two and foursided components regardless of the lead configuration or pitch. You may use a blade cartridge in conjunction with solder braid to clean off the pads. Never use a solder cartridge or a blade with wick by dragging it down the row of pads with heavy pressure. The heat combined with the abrasive action of the wick may cause the epoxy holding the pads on the board to soften resulting in a lifted pad or trace. Once again the use of a preheater will allow lower temperature tips to be used, reducing potential damage, especially on large PCBs or large BGA matrices. 1. Metcal makes a range of SMTC blade cartridges for cleaning the old solder off the pads. Choose the size of blade cartridge that best fits the row of pads. Hoof tips are also used frequently and work well for small area clean up. Use as low a temperature cartridge as the PCB will allow. Selecting a higher temperature series cartridge will not necessarily remove the old solder more quickly, and the excess heat may burn the board or lift a pad. The power of the MX-5200 System will allow you to use lower temperatures than other soldering systems, and it is recommended to use the MX-5200 with 600 or 700 series cartridges and a preheater. 2. Flux the PCB and when BGA pad cleaning, first wipe the blade over the pads lightly to dome the pads to form a round dome (removing any spikes) before using solder wick. If the wick is pushed against a solder spike before solder melts this can cause pad crater or a lifted pad. For more information contact OkI for the PowerPoint on BGA Cleaning process improvements. 3. Additional flux may be required after the initial doming of the pads to ensure proper and efficient solder removal with the wick. 4. Also, adding gel flux to solder wick will increase performance considerable as this increase capillary action of solder being sucked into the wick.
8 5. Lay the wick along the row of pads. 6. Bring the blade down on the wick and give it two or three seconds to melt the solder. Using the beveled edge of the blade cartridge gives better surface contact and will make the job quicker. 7. Gently wipe the solder across the array of pads working the wick towards the inside of the component pattern. No pressure is required as the SmartHeat cartridge will maintain its temperature. Conventional soldering systems lose temperature which cools the tip, in turn operators tend to add additional pressure to clean pads, this is what damages solder resist and causes pad crater and pad lift. 8. If the row of pads is longer than the blade, repeat this process for the remaining pads. 9. Repeat all of the above steps for each side of the pad array. Process Tip - Cut off excess wick each time cleaning is done, or the solder that will remain on the wick can attach to adjacent components causing damage or additional rework. This can also cause burns to the operator. Remember, cut the excess wick off when it is fully absorbed with solder. REPLACING TWO AND FOUR-SIDED COMPONENTS Metcal makes a number of hoof cartridges for replacing multi-leaded components. The particular hoof should be selected depending on the number of leads or the lead pitch. The hoof cartridge is designed to solder a number of leads simultaneously by depositing solder directly on the face of the cartridge. Once you ve practiced a bit, you will find it is the easiest and fastest way to solder multi-leaded components. 2. Making sure the number one lead is lined up with the number one pad, align the leads with the pads. Directly centre the leads onto the pads. 3. Holding the component steady with one hand, flux the opposing corner leads of the PCB. 4. Place enough solder onto the face of the cartridge so that it covers about one third of the cartridge. Keep the solder down towards the "toe" of the cartridge. 5. Bring the cartridge down and "paint" the leads where you applied the flux. The object here is to tack the part down, not make good solder joints. 6. Wipe the excess solder from the cartridge. 7. Make sure that the face of the hoof is shiny and wettable. You will not get good results if the cartridge is oxidized. If solder balls up on the face you need to tin the cartridge. Once the cartridge is tinned and shiny the solder should flow on the cartridge. 8. Apply enough solder to cover approximately one-half of the cartridge. The amount of solder will vary with the number of leads you have. For fewer leads apply less solder. 9. Flux an entire row of leads at a time. Work with the row of leads going from left to right in front of you. Work from left to right if you are right handed and vice-versa. 10. Hold the cartridge so the toe of the hoof runs parallel along the row of leads. 11. Bring the cartridge in on a flat landing onto the first lead. Immediately begin running the cartridge down the row of leads drawing a straight line. 12. When you reach the end, wipe the cartridge down the lead towards you. It is common for the last two pins to bridge. To remove a bridge, place tip on last two pins and wipe at 90º to leads outwards, the bridge will be removed. If not, apply flux and try again. 13. Repeat these steps for each row of leads. One third tinned hoof One Half tinned hoof Replacing Standard Pitch SOIC and Gull Wing Components 1. Align the component to the pads on the board. Note: The angle of the cartridge should be parallel, but can be up to 30º for good results. If the toe of the hoof is the front, then the right side should make contact right at the bend of the leg of the lead. It should be held in that position for the entire process. If you are left-handed, it will be just the opposite.
9 The speed is more crucial than the angle. The speed should be steady and slow enough to deposit the solder from the cartridge onto each of the leads as you draw it across. An approximate time is one second per lead. As you get more comfortable with the procedure, the speed gets less crucial. 5. Immediately start drawing the cartridge down the row of leads until you reach the end. Do not stop and restart or you will get bridging. 6. Remember to hold the cartridge parallel to the leads or up to 30 and to keep it at the end of the leads. 7. As the pitch gets finer, you can work faster. But don't work too fast or you will get good toe solder joints but poor heel joints as the solder will not have time to flow under lead. Lead Free Good Joints Pb Lead Replacing Fine Pitch Gull Wing Components Drag solder method with blade tip 1. Alignment of fine pitch components can be tricky. Take your time to ensure proper alignment. It will make all the difference in your successful application of this technique. After alignment, tack the component as you would for a standard pitch part. Use a little less solder on the end of the cartridge for "painting" the leads. 2. Working with one row of leads at a time, apply flux to an entire row of leads. 3. Wipe all excess solder from the face and top of the cartridge and start with fresh solder. 4. Apply enough solder on the tip to use for one wipe of one complete side of that component. Not only will the number of leads vary the amount of solder, but the pitch of the leads will also. The finer the leads, the less solder you will need, if more solder is needed this should be repeated or added to tip during first wipe, some operators prefer to add more solder while wiping back and forth with a generous amounts of flux on the leads. Heel Toe Heel Toe 8. Repeat the steps for all sides of the component. Point to point method soldering Select the appropriately sized conical or bent conical tip to suit the pitch of the component being reworked. This can be a straight or conical cartridge depending on your preference. 1. Align the component into place, apply flux to 2 corners and tack into position. 2. Apply flux to an entire row of leads. 3. Working on one point at a time, apply the cartridge onto the toe of the lead and wipe the cartridge outwards. Repeat for each point. 4. Use a small conical or bent conical tip. 5. Cover the lead with half the width with solder wire. Wipe tip inwards from edge of pad with tip touching pad. 6. As tip touches solder it will flow solder to the leads.
10 Removing Shorts between Gull Wing Leads Your chances of getting shorts or bridges between leads are greatly increased as the distance between the leads gets smaller. Working with fine pitch leads requires more skill and experience whether you are reworking with one of Metcal's hoof cartridges or any other type of equipment. Removal of these shorts is very simple following these steps. 1. Use Metcal's SMTC-x167 or a suitable sized hoof cartridge from the chart above. Note: Having more heat at the cartridge makes removing shorts more difficult. 2. Apply flux to the bridged leads. 8. If you did not get all of the bridge on the first try, wipe the excess solder from the cartridge and repeat the procedure and add additional flux. 9. If the bridge is extreme you can use your blade cartridge. First, wipe the blade free of solder on both edges. Then, using the beveled edged down, wipe the blade in the same manner down the fluxed leads. 10. For bridges on fine pitch components, the use of solder wick dipped into liquid flux can be an effective method of removal. Simply place the wick on the bridge, apply the soldering tip onto the wick, allow the solder to melt and flow into the wick and remove both together. 11. For very fine pitched applications, form the wick into a fine point and apply heat via soldering tip to the wick not the component lead. The solder will travel by capillary action away from the bridge. When performing these steps, if you leave the heat on the leads too long, the shorts will want to stay. This occurs when you have heated the leads and pads too much, causing them to act as the heat source instead of the cartridge. If this happens, allow the leads to cool down a little. Then try the procedure again. 3. Wipe all excess solder from the face and the top of the Hoof cartridge. 4. Make sure the cartridge is shiny and wettable. 5. Bring the cartridge in with the flat surface, making contact with the bridge; again holding the cartridge parallel to the leads at a 30º angle to the PCB. 6. Wipe the bridge outwards and away from the component. 7. The excess solder on the joints will go naturally to the heat source - the cartridge. Look at the face of the hoof and you should see the excess solder. REMOVING FOUR-SIDED COMPONENTS Removing larger component packages will generally require more heat and the use of flux for the best and fastest results. In the two steps below; the application of flux and the wrapping of wire solder are optional. You should check your written procedures to see if these steps are permitted. Select the correct SMTC cartridge from the chart below B B2 A A2 D Item Description Dim A2 mm (") Dim A mm (") Dim B2 mm (") Dim B mm (") Dim D mm (") SMTC-x118 Cartridge, Quad, VQFP (0.570) (0.610) (0.570) (0.610) 2.79 (0.110) SMTC-x12 Cartridge, Quad, PLCC (0.360) (0.400) 9.14 (0.360) (0.400) 3.80 (0.150) SMTC-x120 Cartridge, Quad, SQFP (0.440) (0.440) (0.440) (0.440) 2.54 (0.100) SMTC-x121 Cartridge, Quad, SQFP (0.330) 8.38 (0.330) 8.38 (0.330) 8.38 (0.330) 2.54 (0.100) SMTC-x13 Cartridge, Quad, PLCC (0.455) (0.500) (0.455) (0.500) 3.80 (0.150) SMTC-x14 Cartridge, Quad, PLCC (0.660) (0.700) (0.660) (0.700) 3.80 (0.150) SMTC-x159 Cartridge, Quad, TQFP (0.440) (0.480) (0.480) (0.520) 2.79 (0.110) SMTC-x16 Cartridge, Quad, PLCC (0.450) (0.500) (0.550) (0.600) 3.81 (0.150) SMTC-x17 Cartridge, Quad, PLCC (0.760) (0.800) (0.760) (0.800) 3.81 (0.150) SMTC-x21 Cartridge, Quad, QFP (0.635) (0.635) (0.635) (0.635) 3.30 (0.130) Please see the Cartridges Part Number Code System chart for temperature designation and geometry.
11 1. This is the one time Metcal suggests using higher temperature 700 or 800 series cartridges; it will make a tremendous difference in removal time. Remember: it is not only the temperature you put on the board that counts. It is the temperature plus the amount of time it is left on there that makes the difference. By removing the component faster, you reduce the chances of thermal damage. 2. If the component cannot be removed easily in seconds then this may cause excessive heating of the component leads and might result in a pad being lifted or damaged more easily. The use of a convection preheater can reduce the temperature and the process time if parts and substrate are thermally demanding; preheat the FR- 4 PCB to C and polyimide, ceramic and military substrates C. Example below 3. Allow the cartridge to heat fully. This is important, because if it is not up to full temperature your removal time will be increased. 4. Tin all inside edges of the cartridge. Just like your blade or hoof cartridge, the removal cartridges must remain shiny and wettable. If you try removing a component with a cartridge that is partially oxidized the reflow will take longer. This increases the chances of lifting pads because you will see some leads being reflowed appropriately. Those leads will be the areas of the cartridge that were tinned. The sections of the cartridge that were oxidized will take longer to reflow and you may lift pads trying to remove the component before it is ready. NOTE: If your cartridge is oxidized, or if there are flux residues prohibiting you from tinning the cartridge, use a brass brush (AC-BRUSH) to clean the inside edges. Heat the cartridge and wipe edges with the brush. 5. Flux all sides of the component. 6. Take some wire solder (.025 or.031 works best) and wrap it around the leads of the component. On J- leaded components this step is easy. The wire will wrap easily around the leads and stay in place. On gull-winged parts it is a little more difficult. Here's a hint. Try sticking the end of the solder behind the legs on one corner of the component and anchor the wire there. Then wrap the wire around the outside of the legs. This will help hold it in place.
12 7. Bring the cartridge straight down on top of the part, making full contact on all four sides of the leads. 8. Hold the cartridge in place without moving back and forth or rocking for about seconds. Once you practice this step a little, you will get a feel for the reflow and you will actually find it to be a little faster. 9. When you are certain you have full reflow, twist the handle between your thumb and forefinger just slightly. If you do have complete reflow you will feel the component move. If you do not, the cartridge will twist in the handle. This is a built in mechanism to prevent you from removing a component that is not ready, thereby decreasing the chances for lifting pads. 10. If you feel the component move, wipe it to one side just slightly and lift simultaneously. The component should be held in the tinned cartridge with surface tension. Some operators also use manual tweezers as a lifting aid. 11. Remove the component immediately by wiping it on the sponge or the brass tip cleaning pad. REPLACING J-LEADED COMPONENTS WITH A KNIFE TIP If components are too tightly packed for access with the hoof tip, you may need to use one of Metcal s knife cartridges: SMTC-x172 Cartridge, Hook, Long, 0.5mm (0.02") SMTC-x171 Cartridge, Conical, Bent, 0.76mm (0.03") SMTC-x161 Cartridge, Knife, Thin Tin Length, 4.8mm (0.18") SMTC-x173 Cartridge, Knife, Wide Tin Length, 4.8mm (0.18") Please see the Cartridges Part Number Code System chart for temperature designation and geometry. Doing multi-lead soldering of J-leaded components is best achieved with the knife cartridge. First, you ll need to tack the component in place. Follow these steps: 1. Flux the pads on opposing corners. 2. Make sure your cartridge is clean and wettable and apply solder to the bottom edge of the knife tip only on the side that will contact the leads. 3. Align the component to the board number one lead to number one pad. 4. Bring the cartridge in with the toe flat, meeting the lead and the fluxed pad at the same time. 5. Continue to hold the part with the finger and repeat this for the opposite corner pads. 6. Now the component should be fixed firmly on at least two corners. The solder joints won t look good, but their function is merely to hold the component while soldering. Now you are ready to solder. Work with one side at a time. 7. Wipe the tip free of excess solder. You need to make sure that the tip is shiny and wettable. 8. Apply solder to the bottom edge of the knife cartridge only on the side that will contact the leads. 9. Apply flux to the rest of the pads to be soldered on that side. 10. Work with the component leads in front of you going from left to right. If you are right handed start soldering from the far left lead. If you are left handed, work in reverse. 11. Bring the cartridge with the bottom edge in light contact with the pads, tilting in under the leads a little bit if possible. Err to the side of tilting the heel of the knife up a little bit to avoid catching the edge of a pad with it. The flatter the knife is to the board, the better the solder joint will be. 12. You will see the solder wick right down the leads, depositing an even amount to each lead. It will appear to short until you draw the tip down the row further. If the right amount of solder is used at the right speed then there should be no shorts. 13. If you added too little solder to the cartridge, you may run out before you reach the end of the row. If this happens, flux from where you ran to the end of the row, apply some further solder to the bottom of the knife and continue the process from where you left off. Removing Shorts from J-Leaded Components 1. Apply flux to the bridged leads.
13 2. Wipe all solder from the knife face. 3. Bring the knife cartridge in with the face flat on the pad and lift vertically. Repeat until all bridges are removed. Reworking Ultra Fine Devices on Densely Populated Boards With the size of components becoming smaller, the requirement for precision soldering is increasingly important. As a solution, Metcal developed the UltraFine Hand-piece and UFTC cartridges (Ultra fine Tip Cartridge). The hand-piece and cartridges are around 1/3 the size of the standard MX-RM3E handpiece and STTC cartridges, allowing for access to the most intricate PCB s without compromising performance. Please see the Cartridges Part Number Code System chart for temperature designation and geometry.
14 The UFTC fine tip cartridges are very useful for reworking ultra fine devices found on pacemakers, and hearing aids. The example shown is a 0.4mm pitch connector on cell phone. The shaft diameter of an UFTC is only 3mm, compared to shaft of an STTC cartridge which is 4.8mm. In addition, the length of the UFTC Cartridge is shorter, for even more accessibility and control. The size of the UFTC cartridge makes it easy to use in very restricted areas and under microscopes.
Surface Mount Rework Techniques
 Technical Note Surface Mount Rework Techniques Table of Contents Abstract:...1 Removing Discrete and Passive Components...1 Replacing Discrete Components...2 Removal of SOICS, SOJS, and SOPS...3 Pad Clean
Technical Note Surface Mount Rework Techniques Table of Contents Abstract:...1 Removing Discrete and Passive Components...1 Replacing Discrete Components...2 Removal of SOICS, SOJS, and SOPS...3 Pad Clean
ADVANCED HAND SOLDERING TECHNIQUES TRAINING CERTIFICATION TEST (DVD-111C) v.1
 This test consists of twenty multiple-choice questions. All questions are from the video: Advanced Hand Soldering Techniques DVD-111C. Use the supplied Answer Sheet and circle the letter corresponding
This test consists of twenty multiple-choice questions. All questions are from the video: Advanced Hand Soldering Techniques DVD-111C. Use the supplied Answer Sheet and circle the letter corresponding
Assembly Instructions for SCA6x0 and SCA10x0 series
 Technical Note 71 Assembly Instructions for SCA6x0 and SCA10x0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI'S DIL-8 and DIL-12 packages...2 3 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
Technical Note 71 Assembly Instructions for SCA6x0 and SCA10x0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI'S DIL-8 and DIL-12 packages...2 3 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
Assembly Instructions for SCC1XX0 series
 Technical Note 82 Assembly Instructions for SCC1XX0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI's 32-lead Dual In-line Package (DIL-32)...2 3 DIL-32 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
Technical Note 82 Assembly Instructions for SCC1XX0 series TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents...1 1 Objective...2 2 VTI's 32-lead Dual In-line Package (DIL-32)...2 3 DIL-32 Package Outline and Dimensions...2
HOTBAR REFLOW SOLDERING
 HOTBAR REFLOW SOLDERING Content 1. Hotbar Reflow Soldering Introduction 2. Application Types 3. Process Descriptions > Flex to PCB > Wire to PCB 4. Design Guidelines 5. Equipment 6. Troubleshooting Guide
HOTBAR REFLOW SOLDERING Content 1. Hotbar Reflow Soldering Introduction 2. Application Types 3. Process Descriptions > Flex to PCB > Wire to PCB 4. Design Guidelines 5. Equipment 6. Troubleshooting Guide
RAY S REWORK SECRETS TRAINING CERTIFICATION TEST (DVD-13C) v.3
 This test consists of twenty multiple-choice questions. All questions are from the video: Ray s Rework Secrets (DVD-13C). Each question has only one most correct answer. Circle the letter corresponding
This test consists of twenty multiple-choice questions. All questions are from the video: Ray s Rework Secrets (DVD-13C). Each question has only one most correct answer. Circle the letter corresponding
IPC J-STD-001E TRAINING AND CERTIFICATION PROGRAM LESSON PLAN FOR TRAINING CERTIFIED IPC SPECIALIST (CIS)
 Review Questions 1. Minimum end joint width for castellated terminations on a Class 2 product is. A. 100% (W). B. 25% (W). C. 50% (W). D. 75% (W). C, Clause. 7.5.6 Table 7-6, Page 29 2. For Class 3, a
Review Questions 1. Minimum end joint width for castellated terminations on a Class 2 product is. A. 100% (W). B. 25% (W). C. 50% (W). D. 75% (W). C, Clause. 7.5.6 Table 7-6, Page 29 2. For Class 3, a
Tip Heater Cartridge Handpiece
 Tip Heater Cartridge Handpiece Optional Items and Replacement Parts TD-100/Replacement Parts For additional information on the PACE products, contact: GSA Service Co, PACE US Government/Military Manufacturer's
Tip Heater Cartridge Handpiece Optional Items and Replacement Parts TD-100/Replacement Parts For additional information on the PACE products, contact: GSA Service Co, PACE US Government/Military Manufacturer's
ECE 477 Digital Systems Senior Design Project. Module 11 Board Assembly and Soldering Techniques
 2011 by D. G. Meyer ECE 477 Digital Systems Senior Design Project Module 11 Board Assembly and Soldering Techniques Outline I ve got my board, now what? Which end of this thing gets hot? Flux is your friend.
2011 by D. G. Meyer ECE 477 Digital Systems Senior Design Project Module 11 Board Assembly and Soldering Techniques Outline I ve got my board, now what? Which end of this thing gets hot? Flux is your friend.
An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging. Prof. G. V. Mahesh. Department of Electronic Systems Engineering
 An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 33 Reflow and Wave
An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 33 Reflow and Wave
Prepared by Qian Ouyang. March 2, 2013
 AN075 Rework Process for TQFN Packages Rework Process for TQFN Packages Prepared by Qian Ouyang March 2, 2013 AN075 Rev. 1.1 www.monolithicpower.com 1 ABSTRACT MPS proprietary Thin Quad Flat package No
AN075 Rework Process for TQFN Packages Rework Process for TQFN Packages Prepared by Qian Ouyang March 2, 2013 AN075 Rev. 1.1 www.monolithicpower.com 1 ABSTRACT MPS proprietary Thin Quad Flat package No
Soldering Techniques NIAGARA COLLEGE TECHNOLOGY DEPT.
 Soldering Techniques NIAGARA COLLEGE TECHNOLOGY DEPT. Soldering 101 Soldering is the process of joining two metals together to form an electrically ll and mechanically secure bond using heat and a third
Soldering Techniques NIAGARA COLLEGE TECHNOLOGY DEPT. Soldering 101 Soldering is the process of joining two metals together to form an electrically ll and mechanically secure bond using heat and a third
upad Proto Base Assembly Guide v2.0
 upad Proto Base Assembly Guide v2.0 Last Updated September 1, 2015 Table of Contents Preface... 3 Introduction... 3 Required Tools... 3 Flux Pen... 3 Soldering Iron... 3 Solder... 3 Diagonal Cutters...
upad Proto Base Assembly Guide v2.0 Last Updated September 1, 2015 Table of Contents Preface... 3 Introduction... 3 Required Tools... 3 Flux Pen... 3 Soldering Iron... 3 Solder... 3 Diagonal Cutters...
Soldering and Desoldering Instruction
 Soldering and Desoldering Instruction Soldering is defined as "the joining of metals by a fusion of alloys which have relatively low melting points". In other words, you use a metal that has a low melting
Soldering and Desoldering Instruction Soldering is defined as "the joining of metals by a fusion of alloys which have relatively low melting points". In other words, you use a metal that has a low melting
Application Note AN-1011
 AN-1011 Board Mounting Application Note for 0.800mm Pitch Devices For part numbers IRF6100, IRF6100PBF, IR130CSP, IR130CSPPBF, IR140CSP, IR140CSPPBF, IR1H40CSP, IR1H40CSPPBF By Hazel Schofield and Philip
AN-1011 Board Mounting Application Note for 0.800mm Pitch Devices For part numbers IRF6100, IRF6100PBF, IR130CSP, IR130CSPPBF, IR140CSP, IR140CSPPBF, IR1H40CSP, IR1H40CSPPBF By Hazel Schofield and Philip
SSRP LTC1746 Assembly Manual V0.1 Check the most recent version
 SSRP LTC1746 Assembly Manual V0.1 Check the most recent version http://oscar.dcarr.org/ssrp/hardware/ltc1746/ltc1746.php Introduction This manual details the general assembly process for the SSRP LTC1746
SSRP LTC1746 Assembly Manual V0.1 Check the most recent version http://oscar.dcarr.org/ssrp/hardware/ltc1746/ltc1746.php Introduction This manual details the general assembly process for the SSRP LTC1746
Custom Front Panel Upgrade Instructions
 Custom Front Panel Upgrade Instructions Here are the directions for upgrading your SP-II to an SP-IIB, with a custom blackanodized front panel and engraved lettering. There are only forty SP-IIB s in existence
Custom Front Panel Upgrade Instructions Here are the directions for upgrading your SP-II to an SP-IIB, with a custom blackanodized front panel and engraved lettering. There are only forty SP-IIB s in existence
Operation and Maintenance Manual for the TD-100 and MT-100 Handpieces P/N
 Operation and Maintenance Manual for the TD-100 and MT-100 Handpieces P/N 5050-0532 TITLE PAGE Safety Guidelines...3 Handpiece Connection...3 Tip Cartridge Installation...3 Accessory and Replacement Parts...4
Operation and Maintenance Manual for the TD-100 and MT-100 Handpieces P/N 5050-0532 TITLE PAGE Safety Guidelines...3 Handpiece Connection...3 Tip Cartridge Installation...3 Accessory and Replacement Parts...4
Chapter 11 Testing, Assembly, and Packaging
 Chapter 11 Testing, Assembly, and Packaging Professor Paul K. Chu Testing The finished wafer is put on a holder and aligned for testing under a microscope Each chip on the wafer is inspected by a multiple-point
Chapter 11 Testing, Assembly, and Packaging Professor Paul K. Chu Testing The finished wafer is put on a holder and aligned for testing under a microscope Each chip on the wafer is inspected by a multiple-point
SOLDERING TO TRANSDUCERS
 APPLICATION NOTE AN-13 SOLDERING TO TRANSDUCERS The purpose of this Application Note is to aid the user of Knowles transducers to: Provide good electrical connections to the transducer Avoid undesired
APPLICATION NOTE AN-13 SOLDERING TO TRANSDUCERS The purpose of this Application Note is to aid the user of Knowles transducers to: Provide good electrical connections to the transducer Avoid undesired
Application Note 5026
 Surface Laminar Circuit (SLC) Ball Grid Array (BGA) Eutectic Surface Mount Assembly Application Note 5026 Introduction This document outlines the design and assembly guidelines for surface laminar circuitry
Surface Laminar Circuit (SLC) Ball Grid Array (BGA) Eutectic Surface Mount Assembly Application Note 5026 Introduction This document outlines the design and assembly guidelines for surface laminar circuitry
The ADS200. AccuDrive. Production Soldering Station FPO. Solutions and systems for soldering, rework and repair of electronics
 The ADS200 AccuDrive Production Soldering Station FPO FPO FPO Solutions and systems for soldering, rework and repair of electronics Introducing the ADS200 Production Soldering Station Standard or Optional
The ADS200 AccuDrive Production Soldering Station FPO FPO FPO Solutions and systems for soldering, rework and repair of electronics Introducing the ADS200 Production Soldering Station Standard or Optional
Electronics Merit Badge Class 4. 12/30/2010 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 1
 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 12/30/2010 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 1 Soldering Safety Note: A Soldering Iron gets hotter than 374 F. Do not touch the soldering iron s metal parts or you will receive
Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 12/30/2010 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 1 Soldering Safety Note: A Soldering Iron gets hotter than 374 F. Do not touch the soldering iron s metal parts or you will receive
Any Questions? Contact us or Alligator Blinkie
 Alligator Blinkie The heart of this blinkie is a 12F1822 PIC produced by a company called Microchip. A PIC is a tiny, yet surprisingly powerful little computer. By itself, it can t do much it needs someway
Alligator Blinkie The heart of this blinkie is a 12F1822 PIC produced by a company called Microchip. A PIC is a tiny, yet surprisingly powerful little computer. By itself, it can t do much it needs someway
Effects of an Appropriate PCB Layout and Soldering Nozzle Design on Quality and Cost Structure in Selective Soldering Processes
 Effects of an Appropriate PCB Layout and Soldering Nozzle Design on Quality and Cost Structure in Selective Soldering Processes Reiner Zoch, Product Manager Christian Ott, Sales and Project Manager SEHO
Effects of an Appropriate PCB Layout and Soldering Nozzle Design on Quality and Cost Structure in Selective Soldering Processes Reiner Zoch, Product Manager Christian Ott, Sales and Project Manager SEHO
Soldering iron. Analog type of HAKKO FX-951 Lock key enables temperature control even on this analog type unit Supports the N 2 system.
 Soldering iron Analog type of HAKKO FX-951 Lock key enables temperature control even on this analog type unit Supports the N 2 system. Model No. FX950 Power consumption 75W Temperature range 200-450ºC
Soldering iron Analog type of HAKKO FX-951 Lock key enables temperature control even on this analog type unit Supports the N 2 system. Model No. FX950 Power consumption 75W Temperature range 200-450ºC
accessories The perfect complement for soldering and desoldering jobs
 accessories The perfect complement for soldering and desoldering jobs 44 KN- Nitrogen kit This is the ideal solution for improving the quality of any solder joint by using nitrogen because it provides
accessories The perfect complement for soldering and desoldering jobs 44 KN- Nitrogen kit This is the ideal solution for improving the quality of any solder joint by using nitrogen because it provides
Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 35 Vapour phase soldering BGA soldering and De-soldering Repair SMT failures
 An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 35 Vapour phase soldering
An Introduction to Electronics Systems Packaging Prof. G. V. Mahesh Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 35 Vapour phase soldering
SOLDERING MANUAL A simple, yet easy to follow manual for your basic soldering needs. Copyright 2017 TortugaPro. All Rights Reserved
 A simple, yet easy to follow manual for your basic soldering needs Copyright 2017 TortugaPro. All Rights Reserved Purpose Soldering is not limited to electrical and electronics work. It is a skill that
A simple, yet easy to follow manual for your basic soldering needs Copyright 2017 TortugaPro. All Rights Reserved Purpose Soldering is not limited to electrical and electronics work. It is a skill that
SMT in Practice. Special Seminar III. Dr. Peter W. Pachowicz Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Volgenau School of Engineering
 Special Seminar III SMT in Practice Dr. Peter W. Pachowicz Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Volgenau School of Engineering This seminar is dedicated to students taking senior design project
Special Seminar III SMT in Practice Dr. Peter W. Pachowicz Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Volgenau School of Engineering This seminar is dedicated to students taking senior design project
SMTA Great Lakes Chapter Meeting
 SMTA Great Lakes Chapter Meeting IPC-7711B/7721B Rework, Repair and Modification Presented By: Frank Honyotski Master IPC Trainer (MIT) STI Electronics, Inc. 1.1 Scope Procedure for rework/repair Aggregate
SMTA Great Lakes Chapter Meeting IPC-7711B/7721B Rework, Repair and Modification Presented By: Frank Honyotski Master IPC Trainer (MIT) STI Electronics, Inc. 1.1 Scope Procedure for rework/repair Aggregate
Ceramic Monoblock Surface Mount Considerations
 Introduction Technical Brief AN1016 Ceramic Monoblock Surface Mount Considerations CTS ceramic block filters, like many others in the industry, use a fired-on thick film silver (Ag) metallization. The
Introduction Technical Brief AN1016 Ceramic Monoblock Surface Mount Considerations CTS ceramic block filters, like many others in the industry, use a fired-on thick film silver (Ag) metallization. The
Better Soldering (A COOPER Tools Reprint) Overview Solder and Flux Base Material
 Better Soldering (A COOPER Tools Reprint) Purpose We hope this short manual will help explain the basics of Soldering. The emphasis will be on the care and use of equipment. Overview Soldering is accomplished
Better Soldering (A COOPER Tools Reprint) Purpose We hope this short manual will help explain the basics of Soldering. The emphasis will be on the care and use of equipment. Overview Soldering is accomplished
What the Designer needs to know
 White Paper on soldering QFN packages to electronic assemblies. Brian J. Leach VP of Sales and Marketing AccuSpec Electronics, LLC Defect free QFN Assembly What the Designer needs to know QFN Description:
White Paper on soldering QFN packages to electronic assemblies. Brian J. Leach VP of Sales and Marketing AccuSpec Electronics, LLC Defect free QFN Assembly What the Designer needs to know QFN Description:
Learn to Solder: Simon Says Stencil Kit Information & Instructions
 Learn to Solder: Simon Says Stencil Kit Information & Instructions This is considered an intermediate kit for people who have soldered through-hole components before and wish to learn how to reflow surface
Learn to Solder: Simon Says Stencil Kit Information & Instructions This is considered an intermediate kit for people who have soldered through-hole components before and wish to learn how to reflow surface
Operation and Maintenance Manual for the TD-100 and MT-100 Handpieces (Intelliheat and Heatwise/Tempwise Systems) P/N Rev A
 Operation and Maintenance Manual for the TD-100 and MT-100 Handpieces (Intelliheat and Heatwise/Tempwise Systems) P/N 5050-0532 Rev A TITLE PAGE Safety Guidelines...3 Handpiece Connection...3 Tip Cartridge
Operation and Maintenance Manual for the TD-100 and MT-100 Handpieces (Intelliheat and Heatwise/Tempwise Systems) P/N 5050-0532 Rev A TITLE PAGE Safety Guidelines...3 Handpiece Connection...3 Tip Cartridge
Introduction to Soldering Electronic Circuits
 Introduction to Soldering Electronic Circuits Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Kettering University Soldering Tools and Supplies Good quality pencil-type soldering iron Small gauge resign
Introduction to Soldering Electronic Circuits Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Kettering University Soldering Tools and Supplies Good quality pencil-type soldering iron Small gauge resign
Gertboard Assembly Manual Rev 1.1
 Gertboard Assembly Manual Rev 1.1 The Gertboard is an add-on GPIO expansion board for the Raspberry Pi computer. It comes with a large variety of components, including buttons, LEDs, A/D converters, DACs,
Gertboard Assembly Manual Rev 1.1 The Gertboard is an add-on GPIO expansion board for the Raspberry Pi computer. It comes with a large variety of components, including buttons, LEDs, A/D converters, DACs,
APPLICATION NOTE 6381 ORGANIC LAND GRID ARRAY (OLGA) AND ITS APPLICATIONS
 Keywords: OLGA, SMT, PCB design APPLICATION NOTE 6381 ORGANIC LAND GRID ARRAY (OLGA) AND ITS APPLICATIONS Abstract: This application note discusses Maxim Integrated s OLGA and provides the PCB design and
Keywords: OLGA, SMT, PCB design APPLICATION NOTE 6381 ORGANIC LAND GRID ARRAY (OLGA) AND ITS APPLICATIONS Abstract: This application note discusses Maxim Integrated s OLGA and provides the PCB design and
Zenterra TM Installation Guide
 Zenterra TM Installation Guide Installing the foam padding Please review this installation guide before you begin installing the floor. If you have any questions, please call us at 800-428-5306 any time
Zenterra TM Installation Guide Installing the foam padding Please review this installation guide before you begin installing the floor. If you have any questions, please call us at 800-428-5306 any time
Soldering Station. Power consumption 140W Temperature range ºC Temperature stability ±5ºC at idle temperature. Station
 Soldering Station Soldering station with two irons (Two-iron type of HAKKO FX-951) Two different soldering iron tips selected according to component sizes can be simultaneously used. Temperature on each
Soldering Station Soldering station with two irons (Two-iron type of HAKKO FX-951) Two different soldering iron tips selected according to component sizes can be simultaneously used. Temperature on each
Unit 12 Soldering. INTC 1307 Instrumentation Test Equipment Teaching Unit 12 Soldering
 RICHLAND COLLEGE School of Engineering Business & Technology Rev. 0 W. Slonecker Rev. 1 (8/26/2012) J. Bradbury INTC 1307 Instrumentation Test Equipment Teaching Unit 12 Soldering Unit 12 Soldering 2002
RICHLAND COLLEGE School of Engineering Business & Technology Rev. 0 W. Slonecker Rev. 1 (8/26/2012) J. Bradbury INTC 1307 Instrumentation Test Equipment Teaching Unit 12 Soldering Unit 12 Soldering 2002
Assembly Instructions for the 1.5 Watt Amplifier Kit
 Assembly Instructions for the 1.5 Watt Amplifier Kit 1.) All of the small parts are attached to a sheet of paper indicating both their value and id. 2.) Leave the parts affixed to the paper until you are
Assembly Instructions for the 1.5 Watt Amplifier Kit 1.) All of the small parts are attached to a sheet of paper indicating both their value and id. 2.) Leave the parts affixed to the paper until you are
Soldering Basics. Purpose We hope this short manual will help explain the basics of Soldering. The emphasis will be on the care and use of equipment.
 Soldering Basics Purpose We hope this short manual will help explain the basics of Soldering. The emphasis will be on the care and use of equipment. Overview Soldering is accomplished by quickly heating
Soldering Basics Purpose We hope this short manual will help explain the basics of Soldering. The emphasis will be on the care and use of equipment. Overview Soldering is accomplished by quickly heating
Our Top 10 Commonly Asked Soldering Questions This Year
 Our Top 10 Commonly Asked Soldering Questions This Year 1 Chip Component Shifting Can be related to components floating on the molten solder plus the equipment may have vibrations, which may not be felt
Our Top 10 Commonly Asked Soldering Questions This Year 1 Chip Component Shifting Can be related to components floating on the molten solder plus the equipment may have vibrations, which may not be felt
Exterra Installation Guide
 Exterra Installation Guide Installing the foam padding Please review this installation guide before you begin installing the floor. If you have any questions, please call us at 800-428-5306 any time Monday
Exterra Installation Guide Installing the foam padding Please review this installation guide before you begin installing the floor. If you have any questions, please call us at 800-428-5306 any time Monday
Pace Catalog. SX-70 Handpiece. SX-70 Replacement Parts Diagram. SX-70 parts Diagram See page 12 for the description of parts.
 SX-70 Handpiece SX-70 Replacement Parts Diagram SX-70 parts Diagram See page 12 for the description of parts page 11 SX-70 Handpiece SX-70 Replacement Parts ITEM 1 3 10 11 12 14 14 16 19 23 24 26 27 28
SX-70 Handpiece SX-70 Replacement Parts Diagram SX-70 parts Diagram See page 12 for the description of parts page 11 SX-70 Handpiece SX-70 Replacement Parts ITEM 1 3 10 11 12 14 14 16 19 23 24 26 27 28
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Force Transducer Output Tube Repair Kit
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Model 400-TR Force Transducer Output Tube Repair Kit June 4, 2004, Revision 5 Copyright 2004 Aurora Scientific Inc. Aurora Scientific Inc. 360 Industrial Pkwy. S., Unit 4 Aurora, Ontario,
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Model 400-TR Force Transducer Output Tube Repair Kit June 4, 2004, Revision 5 Copyright 2004 Aurora Scientific Inc. Aurora Scientific Inc. 360 Industrial Pkwy. S., Unit 4 Aurora, Ontario,
Soldering iron. Multi-station that enables soldering, desoldering, and SMD rework all with a single unit Supports the N 2 system.
 Soldering iron Multi-station that enables soldering, desoldering, and SMD rework all with a single unit Supports the N 2 system. Model No. FM203 Power consumption 140W Temperature range 200-450ºC Temperature
Soldering iron Multi-station that enables soldering, desoldering, and SMD rework all with a single unit Supports the N 2 system. Model No. FM203 Power consumption 140W Temperature range 200-450ºC Temperature
Sherlock Solder Models
 Introduction: Sherlock Solder Models Solder fatigue calculations in Sherlock are accomplished using one of the many solder models available. The different solder models address the type of package that
Introduction: Sherlock Solder Models Solder fatigue calculations in Sherlock are accomplished using one of the many solder models available. The different solder models address the type of package that
HAND SOLDERING FOR THROUGH-HOLE COMPONENTS (DVD-42C) TRAINING CERTIFICATION EXAM v.2
 This test consists of thirty multiple-choice questions. All questions are from the video: Hand Soldering for Through-Hole Components (DVD-42C). Each question has only one most correct answer. Circle the
This test consists of thirty multiple-choice questions. All questions are from the video: Hand Soldering for Through-Hole Components (DVD-42C). Each question has only one most correct answer. Circle the
Heartboard PCB Assembly Instructions
 Heartboard PCB Assembly Instructions Thanks for purchasing a Heartboard! These instructions will guide you through assembling and testing the Heartboard. Let s get started! Stuff you need Soldering iron
Heartboard PCB Assembly Instructions Thanks for purchasing a Heartboard! These instructions will guide you through assembling and testing the Heartboard. Let s get started! Stuff you need Soldering iron
Circuit Board Assembly Instructions for Babuinobot 1.0
 Circuit Board Assembly Instructions for Babuinobot 1.0 Brett Nelson January 2010 1 Features Sensor4 input Sensor3 input Sensor2 input 5v power bus Sensor1 input Do not exceed 5v Ground power bus Programming
Circuit Board Assembly Instructions for Babuinobot 1.0 Brett Nelson January 2010 1 Features Sensor4 input Sensor3 input Sensor2 input 5v power bus Sensor1 input Do not exceed 5v Ground power bus Programming
Repairing your Porsche 928 Central Warning System (CWS) controller
 Repairing your Porsche 928 Central Warning System (CWS) controller Disclaimer: This procedure is for a 1984 Porsche 928 S controller. Overview: Under the left foot pedal (dead pedal) of the Porsche 928
Repairing your Porsche 928 Central Warning System (CWS) controller Disclaimer: This procedure is for a 1984 Porsche 928 S controller. Overview: Under the left foot pedal (dead pedal) of the Porsche 928
Recommended Attachment Techniques for ATC Multilayer Chip Capacitors
 Recommended Attachment Techniques for ATC Multilayer Chip Capacitors Bulletin No. 201 ATC# 001-119 Rev. M; 8/07 1.0. SCOPE. This document describes the attachment techniques recommended by ATC for ceramic
Recommended Attachment Techniques for ATC Multilayer Chip Capacitors Bulletin No. 201 ATC# 001-119 Rev. M; 8/07 1.0. SCOPE. This document describes the attachment techniques recommended by ATC for ceramic
Solder Practice Kit MODEL AK-100. Elenco Electronics, Inc. Lesson Manual. Elenco Electronics, Inc.
 Solder Practice Kit MODEL AK-100 Elenco Electronics, Inc. 150 W. Carpenter Avenue Wheeling, IL 60090 (847) 541-3800 http://www.elenco.com e-mail: elenco@elenco.com Lesson Manual Elenco Electronics, Inc.
Solder Practice Kit MODEL AK-100 Elenco Electronics, Inc. 150 W. Carpenter Avenue Wheeling, IL 60090 (847) 541-3800 http://www.elenco.com e-mail: elenco@elenco.com Lesson Manual Elenco Electronics, Inc.
Introduction to Soldering
 Introduction to Soldering The Soldering Iron American Standard Wire Gage (AWG) Solder The Soldering Process Stripping & Tinning Wire Connecting/Soldering Wire Component Soldering De-Soldering Lab Exercise
Introduction to Soldering The Soldering Iron American Standard Wire Gage (AWG) Solder The Soldering Process Stripping & Tinning Wire Connecting/Soldering Wire Component Soldering De-Soldering Lab Exercise
Assembly Instructions: Kit #5
 Assembly Instructions: Kit #5 1. Insert the T-pin into one of the caps. 2. Insert the rotor core into the same cap as shown below. Apply some pressure to push the rotor core approximately 1/2" (10-12 mm)
Assembly Instructions: Kit #5 1. Insert the T-pin into one of the caps. 2. Insert the rotor core into the same cap as shown below. Apply some pressure to push the rotor core approximately 1/2" (10-12 mm)
Application Note. Soldering Guidelines for Module PCB Mounting Rev 13
 Application Note Soldering Guidelines for Module PCB Mounting Rev 13 OBJECTIVE The objective of this application note is to provide ANADIGICS customers general guidelines for PCB second level interconnect
Application Note Soldering Guidelines for Module PCB Mounting Rev 13 OBJECTIVE The objective of this application note is to provide ANADIGICS customers general guidelines for PCB second level interconnect
B. Flip-Chip Technology
 B. Flip-Chip Technology B1. Level 1. Introduction to Flip-Chip techniques B1.1 Why flip-chip? In the development of packaging of electronics the aim is to lower cost, increase the packaging density, improve
B. Flip-Chip Technology B1. Level 1. Introduction to Flip-Chip techniques B1.1 Why flip-chip? In the development of packaging of electronics the aim is to lower cost, increase the packaging density, improve
Throughout the course best practice will be observed as described in International Standard IPC 610.
 SOLDERING COURSE 560: 3 DAYS: Max 8 Candidates This provides all the skills necessary to work on modern electronic printed circuit boards. It is intended for candidates who have an understanding of electronics
SOLDERING COURSE 560: 3 DAYS: Max 8 Candidates This provides all the skills necessary to work on modern electronic printed circuit boards. It is intended for candidates who have an understanding of electronics
SMT Troubleshooting. Typical SMT Problems For additional process solutions, please refer to the AIM website troubleshooting guide
 SMT Troubleshooting Typical SMT Problems For additional process solutions, please refer to the AIM website troubleshooting guide Solder Balling Solder Beading Bridging Opens Voiding Tombstoning Unmelted
SMT Troubleshooting Typical SMT Problems For additional process solutions, please refer to the AIM website troubleshooting guide Solder Balling Solder Beading Bridging Opens Voiding Tombstoning Unmelted
Induction Heater Coil Kit Compact low voltage, high current induction coil
 Induction Heater Coil Kit Compact low voltage, high current induction coil Model: CT-400-KIT Features and Specifications High power water cool-able copper coil PCB Layout designed to reduce eddy losses
Induction Heater Coil Kit Compact low voltage, high current induction coil Model: CT-400-KIT Features and Specifications High power water cool-able copper coil PCB Layout designed to reduce eddy losses
Music Thing Modular SimpleEQ Construction Guide (1206 version)
 Music Thing Modular SimpleEQ Construction Guide (1206 version) Page 1 Useful Links The latest version of this doc and BOM can always be found at http://thonk.co.uk/documents/eq/ A build thread on the Muffwiggler
Music Thing Modular SimpleEQ Construction Guide (1206 version) Page 1 Useful Links The latest version of this doc and BOM can always be found at http://thonk.co.uk/documents/eq/ A build thread on the Muffwiggler
Application Note. Soldering Guidelines for Surface Mount Filters. 1. Introduction. 2. General
 Soldering Guidelines for Surface Mount Filters 1. Introduction This Application Guideline is intended to provide general recommendations for handling, mounting and soldering of Surface Mount Filters. These
Soldering Guidelines for Surface Mount Filters 1. Introduction This Application Guideline is intended to provide general recommendations for handling, mounting and soldering of Surface Mount Filters. These
WFE2P Solder Fume Extractor, Up to 2 Operators, Internal Pump 52F ACCESSORIES
 SOLDERING EQUIPMENT & SUPPLIES Find Datasheets Online FUME EXTRACTION BVX-100 SERIES BENCHTOP FUME EXTRACTION SYSTEM Single-User System with Multi-User Power For Thorough, Effective Fume Extraction No
SOLDERING EQUIPMENT & SUPPLIES Find Datasheets Online FUME EXTRACTION BVX-100 SERIES BENCHTOP FUME EXTRACTION SYSTEM Single-User System with Multi-User Power For Thorough, Effective Fume Extraction No
AN114. Scope. Safety. Materials H AND SOLDERING TUTORIAL FOR FINE PITCH QFP DEVICES. Optional. Required. 5. Solder flux - liquid type in dispenser
 H AND SOLDERING TUTORIAL FOR FINE PITCH QFP DEVICES Scope This document is intended to help designers create their initial prototype systems using Silicon Lab's TQFP and LQFP devices where surface mount
H AND SOLDERING TUTORIAL FOR FINE PITCH QFP DEVICES Scope This document is intended to help designers create their initial prototype systems using Silicon Lab's TQFP and LQFP devices where surface mount
Any Questions? Contact us or BSA Atomic Blinkie
 BSA Atomic Blinkie The heart of this blinkie is a tiny electronic chip embedded in each of the three LEDs. When power is applied, the chip tells the LED to turn on and off, or fade different colors By
BSA Atomic Blinkie The heart of this blinkie is a tiny electronic chip embedded in each of the three LEDs. When power is applied, the chip tells the LED to turn on and off, or fade different colors By
The Useless Machine. DIY Soldering Edition. Instruction Guide v0004
 The Useless Machine DIY Soldering Edition Instruction Guide v0004 TM For the best outcome, follow each step in order. We recommend reading this guide entirely before you get started. Tools required: Soldering
The Useless Machine DIY Soldering Edition Instruction Guide v0004 TM For the best outcome, follow each step in order. We recommend reading this guide entirely before you get started. Tools required: Soldering
Installation tutorial for Console Customs Xbox Mode Dual Button (RFX-5B) Rapid fire Microchip for all Wired and Wireless controllers
 Installation tutorial for Console Customs Xbox 360 5-Mode Dual Button (RFX-5B) Rapid fire Microchip for all Wired and Wireless controllers This tutorial is designed to aid you in installation of a console
Installation tutorial for Console Customs Xbox 360 5-Mode Dual Button (RFX-5B) Rapid fire Microchip for all Wired and Wireless controllers This tutorial is designed to aid you in installation of a console
Assembly instructions for the CS-1 ChemShield
 Page 1 Of 6 Assembly instructions for the CS-1 ChemShield What is S.M.D SMD=Surface mount devices, like all the components does not have leads, but gets soldered onto flat solder pads. The CS-1 assembly
Page 1 Of 6 Assembly instructions for the CS-1 ChemShield What is S.M.D SMD=Surface mount devices, like all the components does not have leads, but gets soldered onto flat solder pads. The CS-1 assembly
DEM ABPM KIT All Band Power Meter Assembly Notes and Pictures
 DEM ABPM KIT All Band Power Meter Assembly Notes and Pictures Paul Wade W1GHZ w1ghz@arrl.net Down East Microwave has kindly agreed to make kits available for my All Band Power Meter (Note: I receive no
DEM ABPM KIT All Band Power Meter Assembly Notes and Pictures Paul Wade W1GHZ w1ghz@arrl.net Down East Microwave has kindly agreed to make kits available for my All Band Power Meter (Note: I receive no
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 19 Soldering Tutorial
 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 19 Soldering Tutorial Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz o Using fixed resistors design and build a voltage divider divides 5 volts in half.
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 19 Soldering Tutorial Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz o Using fixed resistors design and build a voltage divider divides 5 volts in half.
Soldering Methods and Procedures for Vicor Power Modules
 APPLICATION NOTE AN:208 Soldering Methods and Procedures for Vicor Power Modules Lead-Free Pins (RoHS); TIN / LEAD PINS (see page 7) Contents Page Overview 1 Analysis of a Good Solder Joint 1 Soldering
APPLICATION NOTE AN:208 Soldering Methods and Procedures for Vicor Power Modules Lead-Free Pins (RoHS); TIN / LEAD PINS (see page 7) Contents Page Overview 1 Analysis of a Good Solder Joint 1 Soldering
Challenges of Evolving Technology in the Workplace. Tips. Bubba Powers. Board Density. Best Rework Soldering Practices. Power. Substrates.
 Real Estate Finishes Power Component Technology Board Density Tips Challenges of Evolving Technology in the Workplace Substrates Component Size Bubba Powers Manager of Technical Services Weller North America
Real Estate Finishes Power Component Technology Board Density Tips Challenges of Evolving Technology in the Workplace Substrates Component Size Bubba Powers Manager of Technical Services Weller North America
Solder is a metallic glue that holds the parts together and forms a connection that allows electrical current to flow.
 Proper Soldering & Desoldering High Performance Ultrasonic Range Finders Techniques of a MaxBotix Sensor Materials Needed for Soldering Goggles Hands-free clamp Wire stripper Soldering iron with stand
Proper Soldering & Desoldering High Performance Ultrasonic Range Finders Techniques of a MaxBotix Sensor Materials Needed for Soldering Goggles Hands-free clamp Wire stripper Soldering iron with stand
ArduTouch Music Synthesizer
 ArduTouch Music Synthesizer Assembly Instructions rev C Learn To Solder download for free at: http://mightyohm.com/soldercomic The following photos will show you how to solder. But feel free to download
ArduTouch Music Synthesizer Assembly Instructions rev C Learn To Solder download for free at: http://mightyohm.com/soldercomic The following photos will show you how to solder. But feel free to download
Please contact us at BLMAmodels.com for any spare part requests.
 BLMA Models 16623 Pear Blossom Ct. Whittier, California 90603 Phone: 562-712-7085 Ssales@blmamodels.com Cantilever Signal Bridge Instructions Thank you for purchasing this fine-scale model! This bridge
BLMA Models 16623 Pear Blossom Ct. Whittier, California 90603 Phone: 562-712-7085 Ssales@blmamodels.com Cantilever Signal Bridge Instructions Thank you for purchasing this fine-scale model! This bridge
EET 150 Introduction to EET Lab Activity 6 Introduction to Wire Splicing and Soldering
 Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts None for this activity EET 150 Equipment Required Hookup wire (22 AWG) Wire cutter/stripper Soldering Iron* Soldering Iron Stand* Solder (Use standard lead/tin
Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts None for this activity EET 150 Equipment Required Hookup wire (22 AWG) Wire cutter/stripper Soldering Iron* Soldering Iron Stand* Solder (Use standard lead/tin
Application Note. Soldering Guidelines for SMPS Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor Assemblies
 Application Note AN37-0012 Soldering Guidelines for SMPS Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor Assemblies 1. Introduction With a very low ESR and ESL and the ability to withstand very high levels of di/dt and dv/dt,
Application Note AN37-0012 Soldering Guidelines for SMPS Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor Assemblies 1. Introduction With a very low ESR and ESL and the ability to withstand very high levels of di/dt and dv/dt,
Flip Chip Installation using AT-GDP Rework Station
 Flip Chip Installation using AT-GDP Rework Station Introduction An increase in implementation of Flip Chips, Dies, and other micro SMD devices with hidden joints within PCB and IC assembly sectors requires
Flip Chip Installation using AT-GDP Rework Station Introduction An increase in implementation of Flip Chips, Dies, and other micro SMD devices with hidden joints within PCB and IC assembly sectors requires
QUALITY SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
 Q QUALITY SEMICONDUCTOR, INC. AN-20 Board Assembly Techniques for 0.4mm Pin Pitch Surface Mount Packages Application Note AN-20 The need for higher performance systems continues to push both silicon and
Q QUALITY SEMICONDUCTOR, INC. AN-20 Board Assembly Techniques for 0.4mm Pin Pitch Surface Mount Packages Application Note AN-20 The need for higher performance systems continues to push both silicon and
BAT DETECTOR A project of the Service Kring JOTA-JOTI.
 Manual Bat Detector kit Page 1 of 12 A project of the. Do you like the Bat Detector, do you have great ideas? Tell us, please see how on the last page. Manual Bat Detector kit... 1 Remarks... 2 Introduction...
Manual Bat Detector kit Page 1 of 12 A project of the. Do you like the Bat Detector, do you have great ideas? Tell us, please see how on the last page. Manual Bat Detector kit... 1 Remarks... 2 Introduction...
4ms SCM Breakout. Kit Builder's Guide for PCB v2.1 4mspedals.com
 4ms SCM Breakout Kit Builder's Guide for PCB v2.1 4mspedals.com Shuffling Clock Multiplier Breakout This guide is for building a Shuffling Clock Multiplier Breakout module (SCMBO) version 2.1 from the
4ms SCM Breakout Kit Builder's Guide for PCB v2.1 4mspedals.com Shuffling Clock Multiplier Breakout This guide is for building a Shuffling Clock Multiplier Breakout module (SCMBO) version 2.1 from the
BGA (Ball Grid Array)
 BGA (Ball Grid Array) National Semiconductor Application Note 1126 November 2002 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Package Overview... 3 PBGA (PLASTIC BGA) CONSTRUCTION... 3 TE-PBGA (THERMALLY ENHANCED
BGA (Ball Grid Array) National Semiconductor Application Note 1126 November 2002 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Package Overview... 3 PBGA (PLASTIC BGA) CONSTRUCTION... 3 TE-PBGA (THERMALLY ENHANCED
3Insert the second rod no. 4
 Yamato: Step-by-step 37 The stern block and searchlight control towers a b c d e f Recommended tools and materials Wood glue Sandpaper (no. 800 grain) Metal file Putty Craft knife For metal: Super Glue
Yamato: Step-by-step 37 The stern block and searchlight control towers a b c d e f Recommended tools and materials Wood glue Sandpaper (no. 800 grain) Metal file Putty Craft knife For metal: Super Glue
Learn to solder electronics with the Maker
 Learn to solder electronics with the Maker Shed Solder Badge! How to assemble the Maker Shed Badge kit. Written By: Alexander ifixit CC BY-NC-SA www.ifixit.com Page 1 of 19 INTRODUCTION The Maker Shed
Learn to solder electronics with the Maker Shed Solder Badge! How to assemble the Maker Shed Badge kit. Written By: Alexander ifixit CC BY-NC-SA www.ifixit.com Page 1 of 19 INTRODUCTION The Maker Shed
Selective Soldering for Interconnection Technology Used in Enterprise Communication Apparatuses
 Selective Soldering for Interconnection Technology Used in Enterprise Communication Apparatuses Mark Woolley, Wesley Brown, and Dr. Jae Choi Avaya Inc. 1300 W 120 th Avenue Westminster, CO 80234 Abstract:
Selective Soldering for Interconnection Technology Used in Enterprise Communication Apparatuses Mark Woolley, Wesley Brown, and Dr. Jae Choi Avaya Inc. 1300 W 120 th Avenue Westminster, CO 80234 Abstract:
Pingable Envelope Generator
 Pingable Envelope Generator Kit Builder's Guide for PCB v1.0.3 4mspedals.com PEG This guide is for building a Pingable Envelope Generator (PEG), which is an intermediate-level kit. You should be confident
Pingable Envelope Generator Kit Builder's Guide for PCB v1.0.3 4mspedals.com PEG This guide is for building a Pingable Envelope Generator (PEG), which is an intermediate-level kit. You should be confident
MINI FM PHONE TRANSMITTER KIT
 MINI FM PHONE TRANSMITTER KIT Description: This is a subminiature FM telephone transmitter capable of transmitting both sides of a telephone conversation to most any FM receiver up to 1/4 mile away. When
MINI FM PHONE TRANSMITTER KIT Description: This is a subminiature FM telephone transmitter capable of transmitting both sides of a telephone conversation to most any FM receiver up to 1/4 mile away. When
Broadband Printing: The New SMT Challenge
 Broadband Printing: The New SMT Challenge Rita Mohanty & Vatsal Shah, Speedline Technologies, Franklin, MA Gary Nicholls, Ron Tripp, Cookson Electronic Assembly Materials Engineered Products, Johnson City,
Broadband Printing: The New SMT Challenge Rita Mohanty & Vatsal Shah, Speedline Technologies, Franklin, MA Gary Nicholls, Ron Tripp, Cookson Electronic Assembly Materials Engineered Products, Johnson City,
USING SIGNATURE IDENTIFICATION FOR RAPID AND EFFECTIVE X-RAY INSPECTION OF BALL GRID ARRAYS
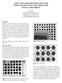 USING SIGNATURE IDENTIFICATION FOR RAPID AND EFFECTIVE X-RAY INSPECTION OF BALL GRID ARRAYS Gil Zweig Glenbrook Technologies, Inc. Randolph, New Jersey USA gzweig@glenbrooktech.com ABSTRACT Although X-ray
USING SIGNATURE IDENTIFICATION FOR RAPID AND EFFECTIVE X-RAY INSPECTION OF BALL GRID ARRAYS Gil Zweig Glenbrook Technologies, Inc. Randolph, New Jersey USA gzweig@glenbrooktech.com ABSTRACT Although X-ray
Working Instruction, Electrical
 Applicable for K700i/K700c Contents 1 Replacement of parts...2 1.1 Battery connector...2 1.2 Board to board connector...3 1.3 FPC connectors...4 1.4 Bending shield can fence...5 1.5 Replacing shield can
Applicable for K700i/K700c Contents 1 Replacement of parts...2 1.1 Battery connector...2 1.2 Board to board connector...3 1.3 FPC connectors...4 1.4 Bending shield can fence...5 1.5 Replacing shield can
Overview of Soldering Assessment Programs
 Overview of Soldering Assessment Programs 1 Objectives Provide a mechanism or program to evaluate the soldering and assembly skills of operators or applicants 2 Goals Provide Customer with the: Ability
Overview of Soldering Assessment Programs 1 Objectives Provide a mechanism or program to evaluate the soldering and assembly skills of operators or applicants 2 Goals Provide Customer with the: Ability
Premium Soldering station
 www.jbctools.com English Premium Soldering station Ref. DIT-D 2 www.jbctools.com Packing List The following items should be included: DI Control Unit... 1 unit Stand... 1 unit Sponge... 1 unit Cartridge...
www.jbctools.com English Premium Soldering station Ref. DIT-D 2 www.jbctools.com Packing List The following items should be included: DI Control Unit... 1 unit Stand... 1 unit Sponge... 1 unit Cartridge...
MA4L Series. Silicon PIN Limiters RoHS Compliant. M/A-COM Products Rev. V12. Features. Chip Outline. Description. Applications
 Features Low Insertion Loss and Noise Figure High Peak and Average Operating Power Various P1dB Compression Powers Low Flat Leakage Power Proven Reliable, Silicon Nitride Passivation Chip Outline A Square
Features Low Insertion Loss and Noise Figure High Peak and Average Operating Power Various P1dB Compression Powers Low Flat Leakage Power Proven Reliable, Silicon Nitride Passivation Chip Outline A Square
LA502 Assembly guide Main PCB Resistors - (2)
 LA502 Assembly guide Safety warning The kits are main powered and use potentially lethal voltages. Under no circumstance should someone undertake the realisation of a kit unless he has full knowledge about
LA502 Assembly guide Safety warning The kits are main powered and use potentially lethal voltages. Under no circumstance should someone undertake the realisation of a kit unless he has full knowledge about
LEARN TO SOLDER CLASS PACK
 TEACHING RESOURCES HOW TO SOLDER GUIDE BUILD INSTRUCIONS HOW THE KIT WORKS DEVELOP YOUR SOLDERING SKILLS WITH THIS LEARN TO SOLDER CLASS PACK Version 1.0 Index of Sheets Introduction... 3 Answers... 4
TEACHING RESOURCES HOW TO SOLDER GUIDE BUILD INSTRUCIONS HOW THE KIT WORKS DEVELOP YOUR SOLDERING SKILLS WITH THIS LEARN TO SOLDER CLASS PACK Version 1.0 Index of Sheets Introduction... 3 Answers... 4
Photo-Etch Demonstration Notes. Presented at the AMPS Central SC August 11, 2011 Meeting
 The basic steps in using PE up-date sets: Photo-Etch Demonstration Notes Presented at the AMPS Central SC August 11, 2011 Meeting 1. Plan Use 2. Cut Part from Fret / Clean up Burrs 3. Bend / Form Part
The basic steps in using PE up-date sets: Photo-Etch Demonstration Notes Presented at the AMPS Central SC August 11, 2011 Meeting 1. Plan Use 2. Cut Part from Fret / Clean up Burrs 3. Bend / Form Part

 !"#$%&'()'*"+,+$&#' *";
!"#$%&'()'*"+,+$&#' *";