Design For Manufacture
|
|
|
- Laurence Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design For Manufacture
2 Brief Part1: The brief for the first part of the design for manufacture module is to understand the fundamental principles of manufacturing in an industry setting, understanding the many processes available and understanding the importance of the link between designing and manufacturing. Many factors have to be taken into consideration when designing a product as this can affect which process is used, the material required to create the product and its necessary finish. By receiving the process of Rotational moulding it allows the group to research the process in which a material becomes a component or a product, what materials are suitable, most commonly used within this process, what products are available from this process and the strengths and weaknesses are. Part2: The second part of the module is a client based project, re-designing an existing mouse using the same key components such as the circuit board and the original optical tracking system. Updating the original design and shape to create a new modern and ergonomic mouse. The design constraints are to not include new buttons and features as they will not be able to be used with the existing circuit board. The second and most important constraint is that the product has to be injection moulded and so this will have to be taken into account. The design will have to be carefully thought through as injection moulding comes with significant problems such as mould design and how the main body will be moulded to allow the battery and components will be accessed.
3 Thermoforming Thermoforming describes the process of heating a material until it is pliable enough to form a specific shape around a mould. Process The process begins with a mould which is typically machined aluminium or cast. 1.The mould is fitted to the machine so that the required shape can be created. Fig2: Vacuum Forming Fig3: Plug Assited Forming 2.The material is then heated up to a point where it is at its most flexible before becoming damaged. The plastic is then stretched around the mould. This is done by using a tool which is either made out of aluminium, nylon, wood or epoxy. 3.Once cooled the waste material is cut from the product. Types: Pressure forming Vacuum forming Plug assited forming. Materials Amorphous thermoforming plastics. Semi Crystalline thermoforming plastics. Other materials include, ABS, PVC, Acrylic, Polycarbonate, Polystyrene, PPS, PET, HDPE, UHMW-PE. Applications Fig4: Plastic Containers Fig5: Thermoformed pond Fig1: Pressure Forming
4 Sand Casting 70% of the products produced by casting are done using sand. There are five steps in total. Process 1. Create the mould required. 2. Fill both halves with sand and pack neatly. 3. Place the two halves of the mould together so they are aligned. 4. Pour the hot molten metal into the mould. 5. Leave the mould to cool and once cooled remove the product. Materials The materials available to sand cast are aluminium, magnesium, steel, grey iron and ductile iron. Tools The tools that are required within this process are; The molten material, tongs, protective clothing, crucible, crucible ring, furnace and a hammer. Applications A widely used process that allows a vast amount of products to be manufactured. Thes include engine parts, gears, signs, small or large ornaments. Fig7: Engine parts Fig8: Ornaments and sand casted parts Fig6: Sand Casting process
5 Rotational Moulding Rotational moulding is the process of placing a plastic powder into a mould and spinning the mould on the x and y axis whilst the mould is being heated. Process There is one basic process that is applied to rotational moulding, however there are slight changes depending on the type of machine that is used. 1. The plastic powder is placed within the mould 2. The mould is then heated. 3. The mould is then spun on an axis and then spun in the opposite direction on the opposite axis. 4. The mould is then removed from the oven and left out to cool. 5. The product is then removed from the mould. There are several types of machines: 1. Rock and Roll machine 2. Leonardo machine 3. Clamshell machine 4. Shuttle machine 5. Carousel machine Tooling Materials Fig9: Carousel machine layout and process 95% of all products are manufactured from Polyethylene. However, others are used as their properties differ slightly such as; Polypropylene, Polyvinylchloride, Polycarbonate and Nylon. Applications A vast amount of products can be rotational moulded and some of those are Kayaks, boats, hospital equipment, bollards, sign posts and many others. The moulds and tools are created either using cast aluminium, fabricated steel or are CNC machined.
6 Rotational Moulding Rototek Visit -Based in Newark. -6million turnover a year. -Second largest output of rotational moulding products in the UK. -Own another sporting company called Teksport. Advantages -Almost any size and shape can be created. -Wall thickness can be selected. -Mouldings are relatively cheap. -Experimentation. -Many colours and textures available. -Little or no waste is achieved from each product. -Virtually stress free products are manufactured. -Plastic or metal inserts can be placed into the mould be manufacture. -No secondary process needed. Disadvantages -Time for each product differs, slowing down production. -Experimentation. Achieving multi-coloured products: -Multi-coloured patterns can be gained prior to the moulding - No pattern is ever the same - Can sometimes feel a different texture Mould is heated Different colour is applied Process continues -Materials are limited to thermoplastics. -Creating right angles can be difficult. -Some shapes can be difficult to manufacture requiring changes to the design.
7 Metal Casting There are three types of metal casting; 1. Die casting using a hot chamber. 2. Die casting using a cold chamber. 3. Investment castings. Process The hot chamber is used when a metal has a low melting point and the cold chamber is used when the metal has a high melting point. Materials Almost any metal can be cast, however many manufacturers choose to use steel as it is cheaper, but a very useful material with many application. Applications As many materials can be used a vast amount of products can be manufactured. Those include car parts, a variety of different ornaments and small components such as nuts and bolts. 1. The die is cleaned and then clamped to the machine. 2. The molten metal is placed into the machine. 3. High pressure push the molten metal into the die until it solidifies. Fig11: Engine Fig13: Gears Fig10: Investment Casting Fig12: Engine parts Fig14: Lost wax casting
8 Metal Pressing and Stamping This is the process of placing large sheets of metal into a machine which contains a stamping die to cut through the metal and create the product or component required. Process There are many types of smaller processes within metal stamping and pressing such as, 1. Embossing 2. Bending 3. Flanging 4. Coining 5. Blanking 6. Punching 7. Stamping Materials The materials available for this process are Brass, Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Aluminium and other steel based alloys. Applications As there are a large amount of processes that can be done within metal stamping and pressing this allows a large amount of products and parts to be manufactured. Some of these products include; 1. Medals 2. Gears 3. Car doors 4. Cutlery 5. Door hinges Fig17: Hinges and Brackets Fig18: Car Body Fig15: Metal Stamping Process Fig16: Metal Stamped Products
9 Metal Milling Metal Milling is the process of using rotary cutter to remove waste material so that the required part and detail can be gained. Process The machine is controlled using numerical control and so it is programmed to do the required job. When started the head of the mill scrapes away the waste material to create the required part. There are several steps to this process; 1. Load the preferred material. 2. Load the tool. 3. Start the mill. 4. Unload the finished product. Materials The materials typically used within this process are; 1. Titanium 2. Aluminium 3. Brass 4. Magnesium 5. Steel Other items/ materials that can be milled include; 1. Metal bars 2. Metal sheets 3. Beams 4. Metal tubes 5. Metal Extrusions Applications A wide variety of products can be metal milled, some of these include, metal bolts, engine parts, car parts and metal ash trays. Fig19: Flat Bed Mill Fig20: Metal Milling Machine Fig21: Milled ash tray Fig22: Milled bolt
10 3/5 Axis Milling 3 and 5 axis machining simply describes how many axis the product and the tool can move on. 5 axis machining allows a much more accurate product to be manufactured as it is able to cut and remove material from areas that may not be accessible on a machine with only 3 axis. This process is usually done by using CNC this allows a highly accurate products to be achieved. Process The chosen material is placed into the machine on a bed which rotates. A CNC file is then uploaded to the machine after being pre-made using a CAD software. The machine is then started and the machine copies the file and creates the product required. Materials Typically it is metals such as stainless steel, titanium and aluminium that are used on a 3/5 axis machines as much more accurate parts can be formed in a much shorter time than if you were to carve the metal by hand. Applications Many accurate and detailed parts can be created using this process. The most common application would be car parts such as engines and fixings. The product is only limited to the size of the machine. Large scale axis machine can produce wind turbines and propellers. Advantages: -Highly accurate -Reduced manual labour -Fast process -Can be used for batch, mass and one-off productions. Disadvantages; -High cost set up -Specialised tools may need to be bought for specific jobs -Using a 3 axis machine limits the applications than using a 5 axis machine. Fig23: 3/5 Axis Machining
11 Laser Cutting Lasercutting is another process that involves using CNC to perform the process. The machine converts the CAD file into a code and the Laser then follows the code creating the product required. Gases are used to create the laser beam which is then focused using lenses and mirrors. The laser reaches a temperature which is then able to cut through a variety of different materials. Gases used; -Hydrogen -Compressed oxygen -Carbon Dioxide -Nitrogen -Helium Laser cutting can be done on both a massive scale and a very small scale such as school laser cutters. This is another process that is only limited to the size of the cutting bed. However, there are levels of laser cutters as some are much more power for industry than others and can cutter much thicker sheets of materials. Blocks of materials or tubes cannot be used within this process which limits the applications. Materials: -MDF -Plywood -Fabrics -Acrylic -Steel -Aluminium -Mild steels Many other materials can be used within this process. It is one of the most common processes industry due to how many materials can be cut. This in turn provides more products and applications. Advantages: -Speed -Variety of materials - Machines can be relatively cheap depending on sizes. -Both large and small scale machines can be bought -Highly accurate Disadvantages: -Industrial machines can be very expensive -The beds have to be replaced over time -The product or component requires a finishing process due to the laser leaving behind a slightly burnt edge. -No mirrored materials can be used -Only 2D products can be manufactured Fig24: Industria Lasercutter Fig25: Lasercutter
12 Injection Moulding Injection moulding is the process of creating plastic products by heating up plastic granules until they form a liquid then forcing the plastic into the mould and creating the specified product. Process The process of injection moulding consists of 5 stages 1. The plastic granules which are pre-coloured and pre-weighed are placed into the hopper of the machine. 2. The polymer is then heated up until it becomes a liquid consistency. 3. A hydraulic ram then pushes the polymer through the machine and into the mould. It is forced through until the mould is full. 4. The mould is then left to cool otherwise warping may occur. 5. The mould is removed from the machine and opened allowing the final product to be achieved. Materials Plastics that are available for injection moulding: -ABS -Nylon -Polypropylene -Polycarbonate -Polystyrene -PET -HIPS Tooling: Moulds for injection moulding have a very high cost. Moulds can be created in both two parts and four parts depending on what product is required and how much detail is necessary. Moulds are tested using a process called flow analysis this determines if the material can freely flow through the mould and cover all surfaces. Certain features have to be taken into account: -Ribbing for strength -Drafts so the product can be removed from the mould. -Wall thickness -Bosses -Sharpness of corners -Webbing Advantages: - Complex shapes can be made - Relatively fast process time. - Variety of colours - Lots of materials available. - Can be used for mass production Disadvantages: -Initial set up can be expensive -Moulds are very expensive -Many materials cannot be recycled - A lot of experimentation may be needed to get the mould and product right.
13 Extrusion The basic type of extrusion is a very similar process to injection moulding however instead of a mould a die with a continuous cross section is used. Process The process of extrusion consists of 4 stages 1. The plastic granules which are pre-coloured and pre-weighed are placed into the hopper of the machine. 2. The polymer is then heated up until it becomes a liquid consistency. 3. A hydraulic ram then pushes the polymer through the machine and into the mould. It is forced through a die. 4. It is then cut to the necessary size. There are several types of extrusion all which differ slightly: -Blow film extrusion -Co-extrusion -Over jacketing extrusion - Tubing extrusion -Sheet/ Film extrusion -Metal extrusion Other types of Extrusion Other types: -Hot extrusion -Cold extrusion -Indirect extrusion -Direct extrusion Hot extrusion consists of working with the material whilst its temperature is above the recrystallisation level. This allows the material to be worked with much easier as well as improve mechanical properties and allows more complex shapes to be created. However, it does affect the surface finish and so components that are manufactured using this process are usually used for structural purposes or will require a finishing process. Cold extrusion is the process of applying no heat to the material whilst the process of extrusion is taking place. This provides a much higher quality finish as no oxidation layer is created. Materials This process allows thermoplastics metals and elastomers to be used. Fig26: Extruded Metal Fig27: Extruded Plastic
14 Forging Forging is the process of using a tool such as a hammer or using a die and using a high impact force, altering the shape of the metal into the required shape. Types of forging: -Hot forging -Cold forging -Rolling ring forging -Drop forging -Closed die forging -Open die forging Hot forging is when the material is heated past the recrystalisation temperature to reduce work hardening. Cold Forging is done at room temperature which causes the material to harden, but lowers the finish. Advantages Typically components that are manufactured using this process are much more durable than that of those that are cast or machined. Disadvantages -A very expensive process to set up -Tools and dies are very expensive to buy. -Not a cost effective process if used for one off production or batch production. Applications Many different industries use forging as a manufacturing process due to the increased strength of the products gained from it. Typically car parts, parts for military vehicles, bridge components, tubing and many others. Drop forging is the process of forcing a ram onto the material which causes it to spread and fill the die to create the required shape. During open die forging, the material is not constrained and is worked into shape by the use of flat faced dies. Rolling ring forging can be done when the material is cold or heated. Extreme forces are used to push the material into a specific shape. Fig28: Metal Forging Fig29: Rolling ring forging
15 Blow Moulding Blow moulding is the process of forcing air into a parison which is then forced into the shape of the chosen mould. Types of blow moulding: -Injection blow moulding -Extrusion blow moulding -Injection stretch blow moulding Injection stretch moulding involves placing an already formed bottle neck into the mould. Where as in ordinary injection blow moulding and extrusion moulding the neck is formed at the same time as the bottle. Fig30: Extrusion blow moulding Advantages -Cost effective in both mass and batch production. - Low pressures are used and so moulds are typically cheaper than those of injection moulding. - Fast production cycle -Many materials can be used. Disadvantages -Initial costs for set-up are high -Oil based plastics are used which aren t environmentally friendly. Fig31: Injection blow moulding Fig32: Blow mould tooling
16 Metal Surface Coating The process of metal surface coating is done to apply a layer that is either for aesthetic purposes or to improve specific mechanical properties. Examples of anodising: Types of metal surface coating: -Electroplating -Anodising -Nickle plating -Zinc and manganese plating -Thermospraying -Electropolishing Advantages: There are many advantages to each individual process such as making the material more durable, wear resistance or just improving the aesthetics. -Metal surface coating makes the material much more wear resistant. -Improves friction performance. -Can improve corrosion/oxidation resistance. -Improved thermal protection. -A large variety of materials can have surface coating finishes. Disadvantages: Each process has its own disadvantages, as many of the processes can be expensive. -Process is usually expensive -Time consuming -It s a finishing process which is expensive as the part will have to be manufactured first. Fig33:Anodised metal Examples of electroplating: Fig35: Electroplated metal part Fig34:Anodised tubing Fig36: Electroplated products
17 Metal Spinning Metal spinning is the process of turning a piece of metal on a lathe and forming a new component over a mandrel. It is the process of transforming a metal sheet without removing material and creating wastage. Typically this process can be done either manually by hand or using a CNC lathe. Both of which have their advantages and disadvantages. As the material is spun only certain shapes can be manufactured: -Spheres -Cones -Funnels -Flanged covers Tools: Materials: Many metals can be used for this process however some are much easier to work with than others. -Copper -Stainless steel -Aluminium -Brass Advantages of Industrial spinning: -Mass production -One continuous process - Lower levels of training needed -Speed of production is improved The mandrel or chuck is one of the key components in metal spinning as this is the shape that the sheet of metal will become. Mandrels can be manufactured out of wood, steel alloys or synthetic materials. Each provide slightly different properties. Metal mandrels provide the best quality finish to the product. The burnisher is another main tool used for spinning. This is the tool in which shapes the material around the mandrel. There are many types of mandrels available, some manufacturers choose to make their own for very specific jobs. Advantages of manual spinning: -Bespoke on-off pieces -Higher quality finish Fig37: CNC metal spinning
18 GRP Glass reinforced plastic is the process of layering up with several materials and adhesives to create a strong durable product. Process: 1. A mould is initially created, it is checked for any imperfections that may affect the outcome of the product. 2. A wax coat is applied in order to create a polished shiny finish to the product. 3. A releasing agent is applied to stop the glass becoming stuck to the mould. 4. A layer of resin is added to the mould to stick to bond the glass layers, this included the chosen coloured pigment that the buyer wishes to have on the outside of the product. 5. Using a roller the reinforcing material is smoothed into place. 6. The process of adding adhesive and reinforcing material is done until the product reaches the required thickness or strength. 7. Once dried the product is removed from the mould with the coloured pigment showing. Moulds can be manufactured from almost any material as long as it provides the strength and support needed and also contains the required amount of detail. Fig38: GRP process Advantages: -Great strength to weight ratio -Durable -Can be moulded into almost any shape -Can be coloured Disadvantages: -There has to be up-keep on the product every few years
19 Lamination Lamination is the process of bonding two or more layers of a flexible material together using an adhesive and gradually bending the wood into shape using clamps which are slowly being tightened. Process: 1. Each layer of wood has a thick layer of adhesive applied to it. 2. The second layer is then applied to the first. 3. The adhesive is then given time to dry. It dries clear so the finish of the final is not ruined. 4. Once the layers are glued together they pieces are then cut evenly as there may have been movement whilst the adhesive was drying. 5. Finally wood is then applied to a pre made guide mould which the wood will be clamped to. The clamps will be gradually tighten until the correct curvature or shape is achieved. Advantages: -The process is quite simple therefore will not cost a lot to set up. -Many woods can be laminated however some are easier than others. -A variety of shapes and products can be created. - The wood can then be varnished in a fireproof coat or coloured if necessary. Disadvantages: -Time consuming - Wood can split or become damaged. -Some woods are harder to work with. -The adhesive can sometimes come unstuck. Fig39: Wood Lamination Fig40: Wood Laminated arches
20 Research Plan Existing Products Reverse Engineering Research Plan Ergonomics Injection Moulding
21 Existing Products By researching existing products this gave an insight into the price, shape, colour and the manufacturing process. It showed what other designers have used in order to hide split lines or make them become a part of the design. Typically many computer mice have a contrast of matte black and a gloss black to create a sophisticated finish. Some had chosen to use silicone over moulds in order to create the grips and hide the split lines.
22 Ergonomics Researching the ergonomic and anthropometric data allows an insight into what hand positions are most comfortable to the user and which can cause discomfort and possibly future health issues. Typically a user is sat at a computer desk for several hours especially if the user has a computer based career. Finding the correct position that the hand and wrist should be in will influence the design of the mouse so that it will also be comfortable. Fig41: Mouse ergonomics Fig42: Theory of computer mice
23 Ergonomics Fig42: Theory of computer mice This research explores the different shapes and styles available and how each affects ergonomics and comfort. This has highlighted areas that can be designed in and what can be explored in much more detail. Fig42: Theory of computer mice
24 Reverse Engineering 2 This is the mouse in which the client has given us to re-design. It is the standard size and shape for a computer mouse. The design constraints are that the circuit board, mouse wheel and LED light housing must be incorporated into the new mouse so that these components can be placed inside and will create a fully functioning computer mouse. Four feet have been added to add a certain level of grip between the surface and the computer whilst still allowing it to move. This allows the user to have more control over the movement of the mouse. It allows raises the mouse slightly so that the plastic surface of the mouse does not become damaged or scratched. It is evident that the design for this mouse has been influenced heavily by ergonomics and anthropometric data. The curvature of the mouse fits into the palm of the hand to allow the most comfort possible when sat at a computer. The curvature reduces the angle the wrist is at, to eliminate cramp and discomfort. The curvature of the side of the body allows comfort for both left and right handed people as it creates grooves that form rests so it is comfortable either way it is held. This is a key part of the design as it allows the product to reach a much larger target market whilst still keeping its comfort levels for everyone. A simple housing has been placed to maintain the switch. It is simple and has been placed on the base of the product so that it does not interfere with the design and also whilst someone is holding the computer mouse. A hollow section has been added to the base of the mouse to allow the tracking system to work and to allow the LED light to shine through. This is a key element within the design of the product as without this feature the mouse would not have the ability to work and so the product would be useless.
25 Reverse Engineering 1 By reverse engineering this mouse it gave the group an insight into the key components of a mouse and how each component is linked. It shows how the body of the mouse has been designed so that once it is injection moulded it houses all the components whilst creating an ergonomic shape to hold. It showed how injection moulding Reverse engineering is a key element in understanding products, how they work, what makes them unique and how designers has overcome issues to create a fully functioning product. It gives an insight into the inner workings of the product to then give a basis to start updating the design of the product or completely re-designing it.
26 Reverse Engineering 3 The mouse consists of three main components that form the outer shell of the product. The top layer has a reduced amount of material which forms the controls. The gap between the top layer and the main body towards the control end is greater than that near the rear, this is both a design and a manufacturing feature as it creates a long flowing curve through the product. The manufacturing feature is that the gap increases to allow the top component to flex allowing the buttons to be pressed without damaging the material. This mouse has a split line that runs through the scroll wheel and half way through the top component. This is a manufacturing feature as this mouse is most likely to be injection moulded out of ABS which is a strong material. However, reducing the material to create a much thinner layer of plastic and adding the split line it transforms the plastic and makes it much more flexible allowing users to press the controls with ease. As this mouse has been designed to be wireless it needs a form of power supply. The designer has chosen to power this mouse using two AAA batteries. This requires a battery cradle to be attached to the product somehow. As evident by reverse engineering the main body of the computer mouse splits into 3 main components. The middle section is injection moulded, this allows the battery cradle to be built into the mould creating a suitable ledge for the batteries. This cradle also forms the main support of the USB so that once the mouse is finished with the USB can be removed from the computer, the top component of the mouse can be removed and then it can be placed inside ready for the next use. The front of the top component has been split and also contains a housing for the wheel. The housing allows the scroll wheel to move freely whilst the computer mouse is in use. As it is not attached to the wheel it also allows the top component to be whole and so the user does not need to remove several pieces in order to place the batteries inside the mouse.
27 Reverse Engineering 4 The base being the key part in the assembly as it holds all the electronic components and keeps them in position. However, one of the most important features being the cradle that both supports the scroll wheel whilst still allowing it to move to be used as a button. The top component holds three main features. One being the extruded sections that link to the circuit board so once the mouse button has been pressed this extrusion presses down on the button performing the required action. The main body of the mouse provides the most support. Without the internal structure of the body the product would not be stable and would not house the other component properly. The battery cradle has added feature such as the boss extrusions which a screw can be placed inside to link the base and the main body together so that it does not fall apart during use. The two final features of the top component are the hook that connects the main body and the top together and the clips that allow the top piece to slide on and off with ease allowing access to the batteries and the USB.
28 Injection Moulding There are several rules and concepts that need to be taken into account when injection moulding otherwise the product that is desired will not be manufactured. The first rule of preventing issues arising is designing with the principles of injection moulding in mind. By keeping these rules in mind will allow a fully working computer mouse to be designed that will have the structural support as well as the high level finish required. Most injection moulds are created in two have which forms one split line down the centre of the product or component. In order to manufacture this mouse it may be necessary to use a four part mould that way a more complex shape can be created and the product will be of a better quality. Rules: 1. Wall thickness must be taken into account when designing as if the walls are too thin they will break easily, however if they are too thick then the product will not mould properly. This could also affect the size of the computer mouse as if the wall thickness is too large then there may not be enough space to it the PCB and the battery holster. 2. Wall thickness should not be used in order to strengthen a product instead ribs should be added to the design as these will increase the strength as well as reduce the weight. 3. A tapered edge should be applied to the design to allow the product or component to be released from the mould without damaging it. 4. Too much material in one area should be avoided as this can cause sink marks to arise on the outside of the product which can affect its durability as well as affect its overall aesthetic appeal. 5. Extruded bosses should meet to allow the screw or pin to locate easily without damaging the screw or the components. This will apply when attaching the battery holster and the bottom component as extruded bosses can be applied to each component and once the components are slotted together the bosses will line up allowing the pieces to be fixed together permanently.
29 Initial Ideas Here are some initial sketches using the same principle of one edge being straight to create a sleek, geometric modern design. The sketches are the start of an exploration into the different shapes, colours, textures, ergonomic grips and sizes.
30 Initial Ideas Further exploration taking a different approach of a much more ergonomic shape. Exploring how the different heights and the curvature of the top of the mouse can affect the comfort levels for users.
31 Modelling For the first initial models three different approaches were taken. The first being a curved ergonomic mouse that fits comfortably in the palm of the hand, the second being a flatter more sleek product and the third being a geometric shaped computer mouse.. This process explores a variety of different style of computer mice to see which route is more effective and the highest quality and comfortable mouse can be designed. Having the large curve at the back allows the mouse to sit comfortably within the palm of the hand. By adding the indents in the side of the mouse this provides finger rests and as both are equal on each side it allows both left and right handers to use the mouse with ease. This makes the mouse design much more inclusive. However the issue with this design is that it is similar to that of the original design and so it would need to be further developed if the design is taken further.
32 Modelling This model is much flatter and has more of a sleek design. The idea behind this is that there is a cut out in the centre of the product, this would reduce weight as well as create an aesthetically pleasing design. However this may be also become an issue as the PCB cannot be altered meaning it would be difficult to fit inside the mouse. One other issue is that the angle at which the wrist is at, after a while it becomes uncomfortable because the mouse is too low. One positive for this model is the flowing curve that flows through the product and down and joins the base. This would lower the visibility of the split that as it would still look like one component than the several it will be.
33 Modelling The third model is a very geometric mouse. It is the correct height for the wrist, but due to the geometric shape it is still uncomfortable to hold for a long period of time. Overall models one and two are the most effective design which can be explored further.
34 Development
35 Development These are a few further explorations into how the circuit board will fit inside the product and how this will affect the overall design. By taking the measurements from the circuit board and forming the first part of the CAD this allowed a template to be created and used to form more shapes and products. The height of the wheel affected the curve and so finding a balance so the wheel is visible as well creating a shape that is comfortable for the user will be difficult.
36 Modelling By taking the long curved edge from the second model, but raising the curve to the height of the first model a much more comfortable product was achieved. The wrist sits at the appropriate height so it will not cause discomfort when being used for long periods of time. It also creates a more appealing design. After the first initial models and exploring different shapes more another model was required to see what else needed to be developed and if the design was going in the right direction. By combining elements of both models one and two a better product was developed. Further development will need to be done to explore how the product will be split, how each part will be moulded, if there will be indents, grips or different textured features on the product.
37 Development Injection moulding requires certain elements to be taken into consideration, such as how the product will be split into separate parts to allow it to be moulded correctly. This sheet is an exploration of how the product can be assembled and how the user can dismantle the product to gain access to the battery and other components. It explores where split lines can be placed to avoid ruining the aesthetics of the product as well as allowing it to be injection moulded.
38 Development These are side profiles to explore possible grips and textured surfaces to make the product much more moulded to the users hand and to improve the grip so the computer mouse is much easier to control. The top left sketch shows a long flowing grip that mirrors the curve of the surface of the mouse. The grip could become indented slightly so users can have somewhere to rest their fingers.
39 Modelling By using the measurements gained from reverse engineering the staples mouse a final model was able to be created. The shaded area represents an indent that will form a finger rest. This will be equal on either side to include both left and right handed people.
40 Development Some initial ideas as to the finish of the top component were done. However the bottom right idea flows more with the design, it would also allow a texture to be added to the surface. This can be added to the mould so that only one section is textured providing more grip and the other can have a gloss finish to improve the visual appeal of the product.
41 Development With almost a finalised idea more development into how the product would split was done. It was decided that there would be three components. The top component that can be slid off to gain access to the batteries and the USB. The second component that forms the main body and houses the battery holster and the main structure and the bottom component that holds the circuit board, switch and light reflector.
42 Development A problem arose when forming the final design. Having used many people to test the comfort levels of the computer mouse, many chose the front wheel to be at the lower sloping edge than that of the higher section of the mouse. It was decided that the position of the wheel would change from the original position to the lower section of the mouse. Many people believed that it was much more comfortable.
43 Final Design This is the final design that will be followed whilst using CAD. These will be the three separate components that will allow the mouse to be taken apart and to access all the components and then have the ability to be put back together. Hooks will be applied to each component to allow them to slot together with ease. There will be grooves along the outer edge to make the mouse much more comfortable to hold and work with over a long period of time.
44 CAD Development These are the three components that the product will be split into. The top section will be detachable to allow the user to unclip it and gain access to the battery cradle as well as the USB holder. There will be a split line down the centre of the top piece to allow the material to flex so that the controls can be pressed. The middle section will form the structure and support of the product as well as being a holster for the batteries and USB. Finally the bottom section will be removable to allow access to the circuit board, LED light and switch.
45 CAD Development In order to manufacture a working mouse an internal structure had to be placed to support the circuit board and house the switch and LED. Using boss extrusions this forms a locator for the screws so that the components can be fixed together to form a solid product. Four other extrusions were placed as these slot into the circuit board to create a fixed position so that it does not move whilst in use. A cradle also had to be added to fix the scroll wheel in place. The circuit board houses all the key components to allow the product to work. It also contains 4 holes in the main board that provide locators so that it can be fixed to the base components of the product.
46 CAD Development The main body was shelled out to allow the housing for the battery to be created as well as make sure that the circuit board does not interfere with any of the components. Finding a balance with the wall thickness was difficult as it has to allow the batteries to fit whilst not affecting or cutting into the curved surface that forms the grip on the side of the mouse. By inserting the circuit board into the finished bas this provided a template to create the structure for the batteries and the supporting frame for the mouse.
47 CAD Development The battery and the battery holster were then added to the product. There was no need for more of an internal structure as the other components such as the wheel are already supported by the circuit board and the top component so they stay in place. The lack of internal structure also reduces weight as it reduces the amount of material used. This also makes the product require a mould which is much simpler and will cost less. The USB holster was added so that the top component can be removed and the USB can be accessed easily. The USB rests on four hooks to again remove material and weight whilst still providing the necessary support.
48 CAD Development To finish the computer mouse several hooks and clips were added to all three components to hold the product together as well as allow the user to take it apart when necessary. Two extrusions were also added to the front of the mouse as this allows the mouse to work correctly. Once the button has been pressed the extrusions are forced down onto the controls on the circuit board which performs the command. A section was cut out to expose the wheel as well as keep it in place while in use. A small section was also removed from the front to allow the top component to flex and so the buttons can be pressed individually.
49 FINAL PRODUCT
50 FINAL PRODUCT
51 E X P L O D E D D R A W I N G
52 Product in Context
53 Orthographic Not to scale 39mm 65.5mm 33mm 65.5mm
54 Orthographic Not to scale 95mm 58mm 95mm 58mm
55 Evaluation Overall the project went to plan, the brief for the first part of the project was to research and understand the fundamental principles of the design process that make up the design industry. Understanding how they influence the choices made during the design process and how certain factors have to be taken into account. Taking into account the process, how long the production time is, how the process can affect the finish of the product and how this may affect your design. Also taking into account which materials are available for each process so this can be taken into account and also what the advantages and disadvantages are as this can affect the outcome and the overall quality of the finished product. The second part of the brief was to re-design a wireless staples mouse using the same components which were in the pre-existing one. Using solidworks to form the finished product cause difficulties as it is a long process and unforeseen circumstances arise which cannot be foreseen on paper, which sends the project backwards and forwards from development. The module on the whole allowed valuable skills to be gained and a wider understanding of how many elements about processes and how this can really affect the design. Elements from injection moulding such as a standard wall thickness, using ribs to provide strength, creating bosses to locate screws to hold the shape of the mouse and others that may affect the outcome. There are several improvements that would be made if the project were to be done again. By exploring a wider range of products this can give a better insight into what is available and further detail into how each individual mouse is manufactured. This will also help provide an insight into how designers have overcome problems with injection moulding and what tricks are used to hide split lines. Time management would be another aspect to improve as more time could be spent in the development stage by exploring certain features of the mouse further to resolve the design to the best of its ability. By doing more development sketches it provides more detail as well as providing more options and paths to take with the mouse.
56 Bibliography Fig1:Pressure Forming (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig2: Vacuum Forming (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig3: Plug Assisted (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig4: Plastic Containers (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig5:Thermoformed pond (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig6: Sand Casting process (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig7: Engine part (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig8: Ornaments and sand casted parts ( Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig9: Carousel machine and process ( Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig10: Investment Casting (Last accessed 17/4/16) Fig11: Engine Fig12: Engine parts Fig13: Gears ( Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig14: Lost wax casting ( Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig15: Metal Stamping Process ( Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig16: Metal Stamped Products ( Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig17: Hinges and Brackets (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig18: Car Body html (Last accessed 17/04/16) Fig19: Flat Bed Mill (Last accessed 18/04/16) Fig20: Metal Milling Machine (Last accessed 18/04/16) Fig21: Milled ash tray CNC-machining/ /Precision-CNC-Milling-Ashtray.htm (Last accessed 18/04/16) Fig22: Milled Bolt CNC-machining/ /Aluminum-CNC-machined-turning-part.htm (Last accessed 18/04/16)
57 Bibliography Fig23: 3/5 Axis Machining (Last Acessed 04/05/16) Fig24; Industrial Lasercutter (Last Acessed 04/05/16) Fig25: Lasercutter aspx (Last Acessed 04/05/16) Fig26: Extruded Metal (Last Acessed 04/05/16) Fig27: Extruded Plastic (Last Acessed 04/05/16) Fig28: Metal Forging (Last Acessed 04/05/16) Fig29: Rolling ring forging (Last Acessed 04/05/16) Fig30: Extrusion blow moulding (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig32: Blow mould tooling (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig33:Anodised metal show=gallery (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig 34 Anodised Tubing show=gallery (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig35: Electroplated metal part (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig36: Electroplated products (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig37: CNC metal spinning (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig38: GRP Process (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig39: Wood Lamination (Last acessed 04/05/16) Fig40: Wood Laminated arches (Last acessed 04/05/16)
58 Bibliography Fig41: Mouse ergonomics (Last accessed 05/05/16) Fig42: Theory of computer mice PACRandom= (Last accessed 05/05/16)
Extrusion. Process. The photo below shows a typical thermoplastic extruder.
 Extrusion This process can be compared to squeezing toothpaste from a tube. It is a continuous process used to produce both solid and hollow products that have a constant cross-section. E.g. window frames,
Extrusion This process can be compared to squeezing toothpaste from a tube. It is a continuous process used to produce both solid and hollow products that have a constant cross-section. E.g. window frames,
Design and Technology Resistant materials Key words and definitions
 Design and Technology Resistant materials Key words and definitions Word Acrylic Definition a type of thermoplastic, which is hard and can be transparent. Used to make shop signs. Perspex is a trade/brand
Design and Technology Resistant materials Key words and definitions Word Acrylic Definition a type of thermoplastic, which is hard and can be transparent. Used to make shop signs. Perspex is a trade/brand
Processes Advantages Disadvantages Identifying features Products
 Plastics Processes Plastics manufacturing processes are mostly mass production processes with high volumes of output. The high cost of machinery and tooling is offset by the speed and volume of production.
Plastics Processes Plastics manufacturing processes are mostly mass production processes with high volumes of output. The high cost of machinery and tooling is offset by the speed and volume of production.
6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 6043/01 Paper 1, maximum
www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 6043/01 Paper 1, maximum
Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
 Introduction to Manufacturing Processes Products and Manufacturing Product Creation Cycle Design Material Selection Process Selection Manufacture Inspection Feedback Typical product cost breakdown Manufacturing
Introduction to Manufacturing Processes Products and Manufacturing Product Creation Cycle Design Material Selection Process Selection Manufacture Inspection Feedback Typical product cost breakdown Manufacturing
TOOLKIT PART 4 MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
 Understanding which manufacturing process has been used to make an object can help you identify its material as different materials are manufactured with different process. Different manufacturing processes
Understanding which manufacturing process has been used to make an object can help you identify its material as different materials are manufactured with different process. Different manufacturing processes
Design and Technology: Resistant Materials Technology Unit 2: Knowledge and Understanding of Resistant Materials Technology
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Design and Technology: Resistant Materials Technology Unit 2: Knowledge and Understanding of Resistant Materials
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Design and Technology: Resistant Materials Technology Unit 2: Knowledge and Understanding of Resistant Materials
6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2008 question paper 6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 6043/01 Paper 1 (Technology),
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2008 question paper 6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 6043/01 Paper 1 (Technology),
Metal Working Processes
 Metal Working Processes Bachelor of Industrial Technology Management with Honours Semester I Session 2013/2014 CLASSIFICATION OF MANUFACTURING PROCESSES TOPIC OUTLINE What is Sheet Metal? Sheet Metalworking
Metal Working Processes Bachelor of Industrial Technology Management with Honours Semester I Session 2013/2014 CLASSIFICATION OF MANUFACTURING PROCESSES TOPIC OUTLINE What is Sheet Metal? Sheet Metalworking
Processing of Non- Metals Dr. Inderdeep Singh Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Processing of Non- Metals Dr. Inderdeep Singh Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 4 Plastics: properties and processing Lecture - 7 Rotational
Processing of Non- Metals Dr. Inderdeep Singh Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 4 Plastics: properties and processing Lecture - 7 Rotational
D E S I G N A N D M A N U F A C T U R E : C O U R S E M A T E R I A L
 exam style 1 a) (i) State two reasons why tubular steel is a suitable material for the frame of the stool. (ii) State a suitable manufacturing process for the thermosetting plastic feet and state a reason
exam style 1 a) (i) State two reasons why tubular steel is a suitable material for the frame of the stool. (ii) State a suitable manufacturing process for the thermosetting plastic feet and state a reason
Injection moulding. Introduction. Typical characteristics of injection moulded parts
 Injection moulding Introduction Injection molding is generally used to produce thermoplastic polymers. It consists of heating of thermo plastic materials until it melts and then injecting into the steel
Injection moulding Introduction Injection molding is generally used to produce thermoplastic polymers. It consists of heating of thermo plastic materials until it melts and then injecting into the steel
Design Guidelines for Injection Molding
 Design Guidelines for Injection Molding TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO INJECTION MOLDING A. Where is it used? B. Importance of prototyping C. Types of prototypes INJECTION MOLDING BASICS A. The machine
Design Guidelines for Injection Molding TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO INJECTION MOLDING A. Where is it used? B. Importance of prototyping C. Types of prototypes INJECTION MOLDING BASICS A. The machine
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2587041388* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/33 Paper 3 Resistant Materials October/November
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2587041388* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/33 Paper 3 Resistant Materials October/November
Factors to Consider in Plastic Molded Design
 9 Factors to Consider in Plastic Molded Design Table Of Contents Introduction 3 Design 4 1. Draft... 4 2. Surface Finish... 5 3. Witness Lines... 6 4. Wall Thickness... 6 5. Support/Straight Ribs Thickness...
9 Factors to Consider in Plastic Molded Design Table Of Contents Introduction 3 Design 4 1. Draft... 4 2. Surface Finish... 5 3. Witness Lines... 6 4. Wall Thickness... 6 5. Support/Straight Ribs Thickness...
Drawing. Fig. 1 Drawing
 Drawing Drawing is a metalworking process which uses tensile forces to stretch metal. It is broken up into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. The specific definition for sheet
Drawing Drawing is a metalworking process which uses tensile forces to stretch metal. It is broken up into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. The specific definition for sheet
Processing of Plastics
 Processing of Plastics Bachelor of Industrial Technology Management with Honours Semester I Session 2013/2014 TOPIC OUTLINE Introduction of Plastics Classification of Plastics Types of Plastic Plastics
Processing of Plastics Bachelor of Industrial Technology Management with Honours Semester I Session 2013/2014 TOPIC OUTLINE Introduction of Plastics Classification of Plastics Types of Plastic Plastics
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2410250691* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/32 Paper 3 Resistant Materials May/June 2018 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2410250691* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/32 Paper 3 Resistant Materials May/June 2018 1 hour Candidates
Materials, tools and processes
 Materials, tools and processes Extension material for Level 1 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide ISBN 978-1-877459-02-3, Page 153 Tools Tools are used to work materials to improve their appearance,
Materials, tools and processes Extension material for Level 1 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide ISBN 978-1-877459-02-3, Page 153 Tools Tools are used to work materials to improve their appearance,
Design Guide: CNC Machining VERSION 3.4
 Design Guide: CNC Machining VERSION 3.4 CNC GUIDE V3.4 Table of Contents Overview...3 Tolerances...4 General Tolerances...4 Part Tolerances...5 Size Limitations...6 Milling...6 Lathe...6 Material Selection...7
Design Guide: CNC Machining VERSION 3.4 CNC GUIDE V3.4 Table of Contents Overview...3 Tolerances...4 General Tolerances...4 Part Tolerances...5 Size Limitations...6 Milling...6 Lathe...6 Material Selection...7
Sabre Series 2 Inspired Design Precision Engineering
 Sabre Series 2 Inspired Design Precision Engineering USER INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for choosing the Keencut Sabre Series 2. Every effort has been made to bring you a precision engineered product with the
Sabre Series 2 Inspired Design Precision Engineering USER INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for choosing the Keencut Sabre Series 2. Every effort has been made to bring you a precision engineered product with the
GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology A.M. TUESDAY, 24 May 2016 2 hours S16-4111-01 For s use Question
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology A.M. TUESDAY, 24 May 2016 2 hours S16-4111-01 For s use Question
LGCSE DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0189 REPORT FOR TEACHERS
 LGCSE DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0189 REPORT FOR TEACHERS The 2016 Design and technology Paper was composed of 16 questions of which 10 of them formed part A and were compulsory and contributed 28 marks. These
LGCSE DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0189 REPORT FOR TEACHERS The 2016 Design and technology Paper was composed of 16 questions of which 10 of them formed part A and were compulsory and contributed 28 marks. These
Clock 35 - Toyland. Construction instructions for Clock 35
 This clock has been designed for children, it is a stand-alone unit and can be positioned on a shelf or cabinet out of the reach of very young hands who may be tempted to touch. The clock is shown in two
This clock has been designed for children, it is a stand-alone unit and can be positioned on a shelf or cabinet out of the reach of very young hands who may be tempted to touch. The clock is shown in two
Two Categories of Metal Casting Processes
 Two Categories of Metal Casting Processes 1. Expendable mold processes - mold is sacrificed to remove part Advantage: more complex shapes possible Disadvantage: production rates often limited by time to
Two Categories of Metal Casting Processes 1. Expendable mold processes - mold is sacrificed to remove part Advantage: more complex shapes possible Disadvantage: production rates often limited by time to
Operating & Maintenance Instructions 320 Dome Blowing Unit
 Operating & Maintenance Instructions 320 Dome Blowing Unit Table of Contents 1. On Delivery... 2 2. General Information... 3 3. Dome Blowing Technique... 4 4. Other Shapes... 6 5. Machine Maintenance...
Operating & Maintenance Instructions 320 Dome Blowing Unit Table of Contents 1. On Delivery... 2 2. General Information... 3 3. Dome Blowing Technique... 4 4. Other Shapes... 6 5. Machine Maintenance...
GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology A.M. WEDNESDAY, 15 May 2013 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS Question
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology A.M. WEDNESDAY, 15 May 2013 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS Question
D E S I G N A N D M A N U F A C T U R E : C O U R S E M A T E R I A L
 UNIT D E S I G N A N D M A N U F A C T U R E : C O U R S E M A T E R I A L metalwork processes Screw Threads The screw thread is a very important detail in engineering. It is used to hold parts together.
UNIT D E S I G N A N D M A N U F A C T U R E : C O U R S E M A T E R I A L metalwork processes Screw Threads The screw thread is a very important detail in engineering. It is used to hold parts together.
Manufacturing Processes (continued)
 Manufacturing (continued) Machining Some other processes Material compatibilities Process (shape) capabilities Manufacturing costs Correct pg 142, question 34i should read Fig 6.18 question 34j should
Manufacturing (continued) Machining Some other processes Material compatibilities Process (shape) capabilities Manufacturing costs Correct pg 142, question 34i should read Fig 6.18 question 34j should
Design and Manufacture. Level 4. Theory homework
 Design and Manufacture Level 4 S3 Theory homework Wood questions Homework 1 1. Briefly explain the term grain when referring to timber. (2) 2. Woods are usually classified into 2 groups, what are they.
Design and Manufacture Level 4 S3 Theory homework Wood questions Homework 1 1. Briefly explain the term grain when referring to timber. (2) 2. Woods are usually classified into 2 groups, what are they.
UNPACK & ASSEMBLY. Done! CAUTION! THE MILL WILL BE VERY HEAVY - GET ASSISTANCE Pepe Tools.
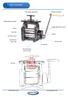 PARTS DIAGRAM T Bar Height adjustment Wooden hand grip Height adjustment gears Frame Height adjustment screws Top roller End Gears cover Handle Brass Bushes (Each side) Bottom roller 4:1 Gearbox Mounting
PARTS DIAGRAM T Bar Height adjustment Wooden hand grip Height adjustment gears Frame Height adjustment screws Top roller End Gears cover Handle Brass Bushes (Each side) Bottom roller 4:1 Gearbox Mounting
6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 6043/01 Paper 1, maximum
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 6043 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 6043/01 Paper 1, maximum
Name: Class: Teacher:..
 Name: Class: Teacher:.. 1 Metals All metals in use today are either PURE METALS or ALLOYS. Copper, iron, tin, lead, gold and silver are all examples of PURE METALS which have been mined from the Earth
Name: Class: Teacher:.. 1 Metals All metals in use today are either PURE METALS or ALLOYS. Copper, iron, tin, lead, gold and silver are all examples of PURE METALS which have been mined from the Earth
Metal Casting Processes CHAPTER 11 PART I
 Metal Casting Processes CHAPTER 11 PART I Topics Introduction Sand casting Shell-Mold Casting Expendable Pattern Casting Plaster-Mold Casting Introduction Metal-Casting Processes First casting were made
Metal Casting Processes CHAPTER 11 PART I Topics Introduction Sand casting Shell-Mold Casting Expendable Pattern Casting Plaster-Mold Casting Introduction Metal-Casting Processes First casting were made
UNPACK & ASSEMBLY. Done! CAUTION! THE MILL WILL BE VERY HEAVY - GET ASSISTANCE Pepe Tools.
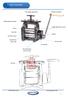 PARTS DIAGRAM T Bar Height adjustment Wooden hand grip Height adjustment gears Frame Height adjustment screws Top roller End Gears cover Handle Brass Bushes (Each side) Bottom roller 4:1 Gearbox Mounting
PARTS DIAGRAM T Bar Height adjustment Wooden hand grip Height adjustment gears Frame Height adjustment screws Top roller End Gears cover Handle Brass Bushes (Each side) Bottom roller 4:1 Gearbox Mounting
Unit IV Drawing of rods, wires and tubes
 Introduction Unit IV Drawing of rods, wires and tubes Drawing is a process in which the material is pulled through a die by means of a tensile force. Usually the constant cross section is circular (bar,
Introduction Unit IV Drawing of rods, wires and tubes Drawing is a process in which the material is pulled through a die by means of a tensile force. Usually the constant cross section is circular (bar,
Javelin Integra Inspired Design Precision Engineering
 Javelin Integra Inspired Design Precision Engineering USER INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for choosing the Keencut Javelin Integra. Every effort has been made to bring you a precision engineered product with the
Javelin Integra Inspired Design Precision Engineering USER INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for choosing the Keencut Javelin Integra. Every effort has been made to bring you a precision engineered product with the
Name: Class: Teacher:..
 Name: Class: Teacher:.. 1 Plastics The basic raw materials used in the manufacture of plastics are oil, natural gas and coal, but contrary to popular belief, plastics are not a new space age material.
Name: Class: Teacher:.. 1 Plastics The basic raw materials used in the manufacture of plastics are oil, natural gas and coal, but contrary to popular belief, plastics are not a new space age material.
Types of moulding sand
 casting Types of moulding sand 1. Green sand: Green sand which is also known as natural sand is the mostly used sand in moulding. It is basically the mixture of sand, clay and water. The clay contain
casting Types of moulding sand 1. Green sand: Green sand which is also known as natural sand is the mostly used sand in moulding. It is basically the mixture of sand, clay and water. The clay contain
CHAPTER FIVE Polymer Forming
 CHAPTER FIVE Polymer Forming Plastic raw materials are available in a variety of forms including Powder, viscous fluids, pellets and granules. Product manufacturers use a wide range of processing machinery
CHAPTER FIVE Polymer Forming Plastic raw materials are available in a variety of forms including Powder, viscous fluids, pellets and granules. Product manufacturers use a wide range of processing machinery
Swift assembly guide
 Swift assembly guide Download the assembly guide at www.scihighmodels.com/swift.pdf Sample kit shown with aluminium bells (available with the Deluxe kit) Shown here without main tanks Version 10/12/2010
Swift assembly guide Download the assembly guide at www.scihighmodels.com/swift.pdf Sample kit shown with aluminium bells (available with the Deluxe kit) Shown here without main tanks Version 10/12/2010
Airframes Instructor Training Manual. Chapter 3 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 Learning Objectives Airframes Instructor Training Manual Chapter 3 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY 1. The purpose of this chapter is to discuss in more detail, the tools and processes technology that is utilised
Learning Objectives Airframes Instructor Training Manual Chapter 3 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY 1. The purpose of this chapter is to discuss in more detail, the tools and processes technology that is utilised
0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/33 Paper 3 (Resistant Materials),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/33 Paper 3 (Resistant Materials),
Mobile Weapons Storage System Specifications
 Mobile Weapons Storage System Specifications Whatever your weapon storage needs, Hi-Density s customized Weapons Storage System will be designed to fit your unique specifications. We recognize that security
Mobile Weapons Storage System Specifications Whatever your weapon storage needs, Hi-Density s customized Weapons Storage System will be designed to fit your unique specifications. We recognize that security
Notes for Making Wood Rings With Stainless Steel Insert Centers
 Notes for Making Wood Rings With Stainless Steel Insert Centers Background These notes describe how to make a ring with a stainless steel (SS) insert and a wood exterior band. They also include information
Notes for Making Wood Rings With Stainless Steel Insert Centers Background These notes describe how to make a ring with a stainless steel (SS) insert and a wood exterior band. They also include information
PLASTIC FURNITURE MANUFACTURING PROCESS I N T D F U R N I T U R E A N D F I T T I N G S
 PLASTIC FURNITURE MANUFACTURING PROCESS I N T D 3 0 1 F U R N I T U R E A N D F I T T I N G S COMMON MANUFACTURING METHODS FOR PLASTIC FURNITURE 1. MOLDING 1. Extrusion molding 2. Injection molding 3.
PLASTIC FURNITURE MANUFACTURING PROCESS I N T D 3 0 1 F U R N I T U R E A N D F I T T I N G S COMMON MANUFACTURING METHODS FOR PLASTIC FURNITURE 1. MOLDING 1. Extrusion molding 2. Injection molding 3.
Clocking a TD-04 Turbo Compressor Housing. Appendix A : AWIC Silicone and Tubing Fitting
 Clocking a TD-04 Turbo Compressor Housing Appendix A : AWIC Silicone and Tubing Fitting Revision A: 7-13-2015 Tools: Metric Sockets (10, 12, 14, 17mm) 5mm Hex Key Large Internal Snap Ring Pliers 3/8 Socket
Clocking a TD-04 Turbo Compressor Housing Appendix A : AWIC Silicone and Tubing Fitting Revision A: 7-13-2015 Tools: Metric Sockets (10, 12, 14, 17mm) 5mm Hex Key Large Internal Snap Ring Pliers 3/8 Socket
Additional Parts List:
 THE TIME MACHINE Additional Parts List: In addition to the cast resin parts enclosed in this kit, there should also be a plastic bag containing the following items needed to complete your time machine
THE TIME MACHINE Additional Parts List: In addition to the cast resin parts enclosed in this kit, there should also be a plastic bag containing the following items needed to complete your time machine
Special Casting. By S K Mondal
 Special Casting By S K Mondal Shell Moulding The sand is mixed with a thermosetting resin is allowed to come in contact with a heated metal pattern (200 0 C). A skin (shell) of about 3.5 mm of sand and
Special Casting By S K Mondal Shell Moulding The sand is mixed with a thermosetting resin is allowed to come in contact with a heated metal pattern (200 0 C). A skin (shell) of about 3.5 mm of sand and
Profiform 200 Profiform 320. Operating manual
 Profiform 200 Profiform 320 Operating manual Profiform 200 / Profiform 320 Operating manual Page 1 Table of contents 1. General information Page 2 2. Profile of the Profiform sheet metal working machines
Profiform 200 Profiform 320 Operating manual Profiform 200 / Profiform 320 Operating manual Page 1 Table of contents 1. General information Page 2 2. Profile of the Profiform sheet metal working machines
Tool & Cutter Grinder
 Tool & Cutter Grinder The Bonelle Tool and Cutter grinder (based on prof. Chaddock s Quorn) can be used to grind most kind of tools from lathe tools to end-mills and reamers. I have been grinding my end-mills
Tool & Cutter Grinder The Bonelle Tool and Cutter grinder (based on prof. Chaddock s Quorn) can be used to grind most kind of tools from lathe tools to end-mills and reamers. I have been grinding my end-mills
Solidification Process(1) - Metal Casting Chapter 9,10
 Solidification Process(1) - Metal Casting Chapter 9,10 Seok-min Kim smkim@cau.ac.kr -1- Classification of solidification processes -2- Casting Process in which molten metal flows by gravity or other force
Solidification Process(1) - Metal Casting Chapter 9,10 Seok-min Kim smkim@cau.ac.kr -1- Classification of solidification processes -2- Casting Process in which molten metal flows by gravity or other force
LocoGear. Technical Bulletin - 14 November 28, 2003 Copyright 2003 by LocoGear LIVE STEAM CASTINGS. Tech Bulletin - 14
 LIVE STEAM CASTINGS LocoGear Tech Bulletin - 14 John D.L. Johnson 3879 Woods Walk Blvd Lake Worth, FL 33467-2359 jjohnson@locogear.com www.locogear.com Technical Bulletin - 14 November 28, 2003 Copyright
LIVE STEAM CASTINGS LocoGear Tech Bulletin - 14 John D.L. Johnson 3879 Woods Walk Blvd Lake Worth, FL 33467-2359 jjohnson@locogear.com www.locogear.com Technical Bulletin - 14 November 28, 2003 Copyright
Permanent Mold Casting Processes. Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Department of Manufacturing & Ind. Eng.
 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Department of Manufacturing & Ind. Eng. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Permanent Mold Casting Processes Gravity die casting Pressure die casting Low pressure High pressure
Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Department of Manufacturing & Ind. Eng. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Permanent Mold Casting Processes Gravity die casting Pressure die casting Low pressure High pressure
Building Rudy Kouhoupt s Walking-Beam Engine
 Building Rudy Kouhoupt s Walking-Beam Engine Some time ago I came across a copy of Rudy Kouhoupt s article: "Build this Walking-Beam Engine" (Popular Mechanics August 1969), and decided to try and make
Building Rudy Kouhoupt s Walking-Beam Engine Some time ago I came across a copy of Rudy Kouhoupt s article: "Build this Walking-Beam Engine" (Popular Mechanics August 1969), and decided to try and make
Qualification: Level 2 Technical Award in Engineering Level 2 Engineering Theory exam (1) June 2018 Marking scheme
 Qualification: 1145-20 Level 2 Technical Award in Engineering 1145-502 Level 2 Engineering Theory exam (1) June 2018 Marking scheme 1a What does the symbol in Figure 1 represent on an orthographic drawing?
Qualification: 1145-20 Level 2 Technical Award in Engineering 1145-502 Level 2 Engineering Theory exam (1) June 2018 Marking scheme 1a What does the symbol in Figure 1 represent on an orthographic drawing?
DESIGNING A PRODUCT IN THE STYLE OF. David Constantine Motivation Multisport Wheelchair. OWEN MACLAREN Innovative Engineer and Designer
 DESIGNING A PRODUCT IN THE STYLE OF David Constantine Motivation Multisport Wheelchair OWEN MACLAREN Innovative Engineer and Designer REVISION BOOKLET BOOKLET DESIGN A DAVID CONSTANTINE / MOTIVATION INSPIRED
DESIGNING A PRODUCT IN THE STYLE OF David Constantine Motivation Multisport Wheelchair OWEN MACLAREN Innovative Engineer and Designer REVISION BOOKLET BOOKLET DESIGN A DAVID CONSTANTINE / MOTIVATION INSPIRED
Design Analysis Process
 Prototype Design Analysis Process Rapid Prototyping What is rapid prototyping? A process that generates physical objects directly from geometric data without traditional tools Rapid Prototyping What is
Prototype Design Analysis Process Rapid Prototyping What is rapid prototyping? A process that generates physical objects directly from geometric data without traditional tools Rapid Prototyping What is
University of Arizona College of Optical Sciences
 University of Arizona College of Optical Sciences Name: Nachiket Kulkarni Course: OPTI521 Topic Plastic Injection Molding Submitted to Prof. J. Burge Date 1. Introduction In daily life, we come across
University of Arizona College of Optical Sciences Name: Nachiket Kulkarni Course: OPTI521 Topic Plastic Injection Molding Submitted to Prof. J. Burge Date 1. Introduction In daily life, we come across
TRAINING MANUAL. Part INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS
 PRESTO INTERNATIONAL UK LTD TRAINING MANUAL Part 2 INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS - 1 - DEFINITION:- A rotary end cutting tool having two or more cutting lips, and having two or more spiral (helical) or
PRESTO INTERNATIONAL UK LTD TRAINING MANUAL Part 2 INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS - 1 - DEFINITION:- A rotary end cutting tool having two or more cutting lips, and having two or more spiral (helical) or
MACKIS. Description A swirling light shade made from sheet material fitted over a cylindrical core. Materials Shade - polyethylene - low density
 This set of storage drawers come in unfinished plywood allowing them to be coloured to suit their surroundings. Case - birch plywood Drawer - birch plywood Label holder - steel / nickel plated Case - laminated
This set of storage drawers come in unfinished plywood allowing them to be coloured to suit their surroundings. Case - birch plywood Drawer - birch plywood Label holder - steel / nickel plated Case - laminated
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0816121761* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/31 Paper 3 Resistant Materials May/June
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0816121761* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/31 Paper 3 Resistant Materials May/June
Uses Fabrications Decoration Signage Artwork Glass alternative
 Acrylic A very popular sheet plastic often sold under the trade name Perspex in a variety of colours and finishes such as opaque, clear and translucent. Tough, versatile and available in many thicknesses,
Acrylic A very popular sheet plastic often sold under the trade name Perspex in a variety of colours and finishes such as opaque, clear and translucent. Tough, versatile and available in many thicknesses,
Screws. Introduction. 1. Nuts, bolts and screws used to clamp things together. Screws are used for two purposes:
 Screws Introduction Screws are used for two purposes: 1. To clamp things together. 2. To control motion. 1. Nuts, bolts and screws used to clamp things together. Nuts, bolts and screws that are used for
Screws Introduction Screws are used for two purposes: 1. To clamp things together. 2. To control motion. 1. Nuts, bolts and screws used to clamp things together. Nuts, bolts and screws that are used for
General Certificate of Education Design and Technology: Product Design 3D
 General Certificate of Education Design and Technology: Product Design 3D PROD1 Report on the Examination 2550 June 2014 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright
General Certificate of Education Design and Technology: Product Design 3D PROD1 Report on the Examination 2550 June 2014 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright
Drivetrain for Vehicles 2018
 Drivetrain for Vehicles 2018 presentation of an innovation RoBoC = Roll Bond Core ADVANTAGES OFFER RoBoC - Keep the stator housing battery housing power unit housing junction box and other similar applications
Drivetrain for Vehicles 2018 presentation of an innovation RoBoC = Roll Bond Core ADVANTAGES OFFER RoBoC - Keep the stator housing battery housing power unit housing junction box and other similar applications
All About Die Casting
 All About Die Casting FAQ Introduction Die casting is a versatile process for producing engineered metal parts by forcing molten metal under high pressure into reusable steel molds. These molds, called
All About Die Casting FAQ Introduction Die casting is a versatile process for producing engineered metal parts by forcing molten metal under high pressure into reusable steel molds. These molds, called
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS GRILLE GUARD RAM 1500 PART # 5058/5058-2
 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS GRILLE GUARD PART # 5058/5058-2 PARTS LIST: Qty Description Qty Description 1 Grille Guard 8 12-1.75mm x 35mm Hex Bolts 2 Upper Frame Mounting s (for trucks without tow hooks
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS GRILLE GUARD PART # 5058/5058-2 PARTS LIST: Qty Description Qty Description 1 Grille Guard 8 12-1.75mm x 35mm Hex Bolts 2 Upper Frame Mounting s (for trucks without tow hooks
DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY Paper 6043/01 Paper 1 General Comments The general performance of candidates was much the same as last year, however, section A was a little below the normal good standard for this
DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY Paper 6043/01 Paper 1 General Comments The general performance of candidates was much the same as last year, however, section A was a little below the normal good standard for this
GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN & TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: RESISTANT MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN & TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: RESISTANT MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. FRIDAY, 25 May 2012 2 hours Question 1 Question
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN & TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: RESISTANT MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. FRIDAY, 25 May 2012 2 hours Question 1 Question
LESMAHAGOW HIGH SCHOOL Technical Department. Design & Manufacture Homework Booklet. Name Class Teacher
 LESMAHAGOW HIGH SCHOOL Technical Department Design & Manufacture Homework Booklet Name_ Class Teacher Q. (a) Explain the design term Problem Identification A 6-8 B - 5 C 8 - F 0-7 Total / 8 S (b) Identify
LESMAHAGOW HIGH SCHOOL Technical Department Design & Manufacture Homework Booklet Name_ Class Teacher Q. (a) Explain the design term Problem Identification A 6-8 B - 5 C 8 - F 0-7 Total / 8 S (b) Identify
1. List or sketch five entirely different forms in which METAL can be supplied to the school workshop.
 Homework 1 - Metals 1&2 1. List or sketch five entirely different forms in which METAL can be supplied to the school workshop. 2. Metals are usually classified as Ferrous and Non-ferrous. Explain what
Homework 1 - Metals 1&2 1. List or sketch five entirely different forms in which METAL can be supplied to the school workshop. 2. Metals are usually classified as Ferrous and Non-ferrous. Explain what
FRIDAY, 27 MAY 9.00 AM AM. Date of birth Day Month Year Scottish candidate number
 FOR OFFICIAL USE F 6/4 Q Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 Total NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 2 FRIDAY, 27 MAY 9. AM. AM CRAFT AND DESIGN STANDARD GRADE Foundation Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below.
FOR OFFICIAL USE F 6/4 Q Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 Total NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 2 FRIDAY, 27 MAY 9. AM. AM CRAFT AND DESIGN STANDARD GRADE Foundation Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2178900346* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/33 Paper 3 Resistant Materials May/June 2016 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2178900346* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/33 Paper 3 Resistant Materials May/June 2016 1 hour Candidates
SHELL MOULDING & INVESTMENT CASTING
 SHELL MOULDING & INVESTMENT CASTING SHELL MOULDING Thisistheprocessinwhichthesandmixedwiththermosettingresinisallowedtocomein contact with the heated metallic pattern plate. This is done so that a thin
SHELL MOULDING & INVESTMENT CASTING SHELL MOULDING Thisistheprocessinwhichthesandmixedwiththermosettingresinisallowedtocomein contact with the heated metallic pattern plate. This is done so that a thin
Myton School Design and Technology Department. Year 7 Resistant Materials. Pewter Casting. Teacher: Personal Target: Target Review:
 Myton School Design and Technology Department Year 7 Resistant Materials Pewter Casting Name: Group: Teacher: Personal Target: Target Review: 0 Criteria Design Ideas Manufacture Level Designing the mould
Myton School Design and Technology Department Year 7 Resistant Materials Pewter Casting Name: Group: Teacher: Personal Target: Target Review: 0 Criteria Design Ideas Manufacture Level Designing the mould
0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/32 Paper 3 (Resistant
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/32 Paper 3 (Resistant
Research task presentation, & PechKucha presentation
 Research task presentation, & PechKucha presentation p.2-20 Jeffrey nyoni Metal coating processes, finishes, & application of graphics JEFFREY NYONI Why include a finishing process on metals? Aesthetic
Research task presentation, & PechKucha presentation p.2-20 Jeffrey nyoni Metal coating processes, finishes, & application of graphics JEFFREY NYONI Why include a finishing process on metals? Aesthetic
Operating & Maintenance Instructions 25 Injection Moulding Machine
 Operating & Maintenance Instructions 25 Injection Moulding Machine Table of Contents 1. Health and Safety Information... 2 2. Upon Receipt... 2 3a. Temperature Controller Settings (Brainchild Controller)...
Operating & Maintenance Instructions 25 Injection Moulding Machine Table of Contents 1. Health and Safety Information... 2 2. Upon Receipt... 2 3a. Temperature Controller Settings (Brainchild Controller)...
Item #28187 EASTWOOD BEAD ROLLER INSTRUCTIONS
 Item #28187 EASTWOOD BEAD ROLLER INSTRUCTIONS The Eastwood Bead Roller is a professional metal fabrication tool for producing strengthening ribs in panels used in creating replacement fl oor pans, fi rewalls,
Item #28187 EASTWOOD BEAD ROLLER INSTRUCTIONS The Eastwood Bead Roller is a professional metal fabrication tool for producing strengthening ribs in panels used in creating replacement fl oor pans, fi rewalls,
Metal Mould System 1. Introduction
 Metal Mould System 1. Introduction Moulds for these purposes can be used many times and are usually made of metal, although semi-permanent moulds of graphite have been successful in some instances. The
Metal Mould System 1. Introduction Moulds for these purposes can be used many times and are usually made of metal, although semi-permanent moulds of graphite have been successful in some instances. The
FULLER CHISELS CUTTING TOOLS
 CUTTING TOOLS Back FULLER CHISELS From the standard Wood Chisel to our top-of-the-line Woodworker s Chisel, FULLER offers the perfect combination of variety and quality in its chisel line-up. Finely honed
CUTTING TOOLS Back FULLER CHISELS From the standard Wood Chisel to our top-of-the-line Woodworker s Chisel, FULLER offers the perfect combination of variety and quality in its chisel line-up. Finely honed
CHAPTER 5: MOULDING PROCESS
 CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER 5: MOULDING PROCESS 5.1 INTRODUCTION 5.2 INJECTION MOULDING 5.3 COMPRESSION AND TRANSFER MOLDING 5.4 BLOW AND ROTATIONAL MOLDING 5.5 PRODUCT DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS 1 5.1 Introduction
CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER 5: MOULDING PROCESS 5.1 INTRODUCTION 5.2 INJECTION MOULDING 5.3 COMPRESSION AND TRANSFER MOLDING 5.4 BLOW AND ROTATIONAL MOLDING 5.5 PRODUCT DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS 1 5.1 Introduction
Design of Jigs, Fixtures, Press Tools and Moulds UNIT - 1 LOCATING AND CLAMPING PRINCIPLES
 Design of Jigs, Fixtures, Press Tools and Moulds UNIT - 1 LOCATING AND CLAMPING PRINCIPLES 1. Define the term Tool design. Tool design is the process of designing and developing the tools, methods, and
Design of Jigs, Fixtures, Press Tools and Moulds UNIT - 1 LOCATING AND CLAMPING PRINCIPLES 1. Define the term Tool design. Tool design is the process of designing and developing the tools, methods, and
joining materials - wood
 UNIT D E S I G N A N D M A N U F A C T U R E : C O U R S E M A T E R I A L Wood joints joining materials - wood The majority of joints used in woodcraft have been designed specifically to attain the maximum
UNIT D E S I G N A N D M A N U F A C T U R E : C O U R S E M A T E R I A L Wood joints joining materials - wood The majority of joints used in woodcraft have been designed specifically to attain the maximum
Special Casting Process. 1. Permanent mould casting
 Special Casting Process 1. Permanent mould casting A permanent mold casting makes use of a mold or metallic die which is permanent.molten metal is poured into the mold under gravity only and no external
Special Casting Process 1. Permanent mould casting A permanent mold casting makes use of a mold or metallic die which is permanent.molten metal is poured into the mold under gravity only and no external
Dicing Through Hard and Brittle Materials in the Micro Electronic Industry By Gideon Levinson, Dicing Tools Product Manager
 Dicing Through Hard and Brittle Materials in the Micro Electronic Industry By Gideon Levinson, Dicing Tools Product Manager A high percentage of micro electronics dicing applications require dicing completely
Dicing Through Hard and Brittle Materials in the Micro Electronic Industry By Gideon Levinson, Dicing Tools Product Manager A high percentage of micro electronics dicing applications require dicing completely
Version 3.0. Genera June Engin. (Spec. Final
 Version 3.0 Genera al Certificate of Secondary Education Engin neering (Double (Spec cification 4850) Unit 1: Written Paper Award) 48501 Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Version 3.0 Genera al Certificate of Secondary Education Engin neering (Double (Spec cification 4850) Unit 1: Written Paper Award) 48501 Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Manufacturing Processes
 Manufacturing Processes Product example Manufacturing process definition Deformation processes Casting processes Sheet metalworking Hammer Forging Video Polymer processing How would we manufacture a mountain
Manufacturing Processes Product example Manufacturing process definition Deformation processes Casting processes Sheet metalworking Hammer Forging Video Polymer processing How would we manufacture a mountain
Installation Guide. Bi-fold Doors
 Installation Guide Bi-fold Doors Installation Guide Components box 1. 6. 2. 3. 7. 5. 4. 8. Contents 1. Fixing plugs 2. Wedge gasket 3. Bottom trolley 4. Top trolley 5. Magnetic keep (x 2 if door height
Installation Guide Bi-fold Doors Installation Guide Components box 1. 6. 2. 3. 7. 5. 4. 8. Contents 1. Fixing plugs 2. Wedge gasket 3. Bottom trolley 4. Top trolley 5. Magnetic keep (x 2 if door height
Rosalina Accessories Tutorial Version March 2011 Martyn
 Rosalina Accessories Tutorial Version 1.0 - March 2011 Martyn Star Brooch Feel free to experiment with these dimensions, you should make a template you are happy with, the method still works. 1) Creating
Rosalina Accessories Tutorial Version 1.0 - March 2011 Martyn Star Brooch Feel free to experiment with these dimensions, you should make a template you are happy with, the method still works. 1) Creating
Building Tips This model can be built using the following types of adhesives:
 Page 1 Building Tips This model can be built using the following types of adhesives: Epoxy (with or without microballons) Odorless cyanoacrylate (CA) with accelerator UHU Creativ for Styrofoam (or UHU
Page 1 Building Tips This model can be built using the following types of adhesives: Epoxy (with or without microballons) Odorless cyanoacrylate (CA) with accelerator UHU Creativ for Styrofoam (or UHU
GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology A.M. TUESDAY, 19 May 2015 2 hours S15-4111-01 For s use Question
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4111/01 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY UNIT 1 FOCUS AREA: Resistant Materials Technology A.M. TUESDAY, 19 May 2015 2 hours S15-4111-01 For s use Question
Locks and Catches Catches and Furniture Bolts
 Magnetic catch with low noise closure Material: Plastic housing Version: with closed surface and internal magnet, magnets no viewable : Press fixing Pull 0. kg, for drilling hole Ø8 mm white 26.01.701
Magnetic catch with low noise closure Material: Plastic housing Version: with closed surface and internal magnet, magnets no viewable : Press fixing Pull 0. kg, for drilling hole Ø8 mm white 26.01.701
CONSTRUCTION TOOLS. Innovation is our mission!
 CONSTRUCTION TOOLS Innovation is our mission! 1 PAGE SCRAPERS & TROWELS 736-738 FLOATS 738-739 2 3 4 5 6 7 JOINTING 739 8 9 SAND SIEVE 739 10 11 CONTAINERS 740 PLUMB LINE 740 SCREW CLAMPS 740-741 12 13
CONSTRUCTION TOOLS Innovation is our mission! 1 PAGE SCRAPERS & TROWELS 736-738 FLOATS 738-739 2 3 4 5 6 7 JOINTING 739 8 9 SAND SIEVE 739 10 11 CONTAINERS 740 PLUMB LINE 740 SCREW CLAMPS 740-741 12 13
PINE WOODS OAK METALS POLYMERS ASH SOFTWOODS CHIPBOARD MAHOGANY MAN MADE HARDWOOD WOODS MDF PLYWOOD BEECH HARDBOARD THERMOSET FERROUS METALS CARBON
 ASH PINE MAHOGANY SOFTWOODS CHIPBOARD HARDWOOD MAN MADE WOODS OAK WOODS MDF PLYWOOD BEECH HARDBOARD RESISTANT METALS MATERIALS ALUMINIUM POLYMERS NON-FERROUS METALS UREA FORMALDEHYDE COPPER ZINC THERMOSET
ASH PINE MAHOGANY SOFTWOODS CHIPBOARD HARDWOOD MAN MADE WOODS OAK WOODS MDF PLYWOOD BEECH HARDBOARD RESISTANT METALS MATERIALS ALUMINIUM POLYMERS NON-FERROUS METALS UREA FORMALDEHYDE COPPER ZINC THERMOSET
SZD-10 bis CZAPLA ASSEMBLY MANUAL IN PICTURES
 1 RUDDER Plan and parts: 2 Assembly steps: Photo above: glue together rudder spar, ribs and trailing edge. Clamp spar to a flat surface (chipboard on the photo) and make sure the straight aligment of the
1 RUDDER Plan and parts: 2 Assembly steps: Photo above: glue together rudder spar, ribs and trailing edge. Clamp spar to a flat surface (chipboard on the photo) and make sure the straight aligment of the
CHAPTER 4: METAL CASTING PROCESS
 CHAPTER 4: METAL CASTING PROCESS CHAPTER OUTLINE 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 EXPANDABLE MOLD CASTING PROCESSES 4.2.1 Sand Casting 4.2.2 Shell Molding 4.2.3 Plaster Mold Casting 4.2.4 Ceramic Mold Casting 4.2.5
CHAPTER 4: METAL CASTING PROCESS CHAPTER OUTLINE 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 EXPANDABLE MOLD CASTING PROCESSES 4.2.1 Sand Casting 4.2.2 Shell Molding 4.2.3 Plaster Mold Casting 4.2.4 Ceramic Mold Casting 4.2.5
Higher Homework MATERIALS & MANUFACTURE
 Higher Homework MATERIALS & MANUFACTURE 1. The Ant and Beluga chairs shown were designed for a similar market. Chair 1 Ant Chair Designed by Arne Jacobsen Price 45 Laminated plywood seat Chrome plated
Higher Homework MATERIALS & MANUFACTURE 1. The Ant and Beluga chairs shown were designed for a similar market. Chair 1 Ant Chair Designed by Arne Jacobsen Price 45 Laminated plywood seat Chrome plated
Pattern Design. Broken Edges. Patterns are generally made from wood however they can be made from metal, plastic or any number of other materials.
 Sand is a process that has been around for over 5000 years. The process itself is fairly simple. A pattern is pressed into a sand mould to leave an impression. The pattern is then removed and the impression
Sand is a process that has been around for over 5000 years. The process itself is fairly simple. A pattern is pressed into a sand mould to leave an impression. The pattern is then removed and the impression
