Estimation of Legibility Distance for Portable Variable Message Signs
|
|
|
- Tyrone Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Estimation of Legibility Distance for Portable Variable Message Signs Tai-Jin Song Graduate Student Researcher Dept. of Transportation Engineering Hanyang University at Ansan 1271,Sa-3 dong, Sangnokgu, Ansan-si Kyunggi-do, Korea, Fax: Taehyung Kim Associate Research Fellow Dept. of Advanced Transportation Research The Korea Transport Institute 1160 Simindaero, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang-si Gyeonggi-do, , Korea Fax: Cheol Oh Assistant Professor Dept. of Transportation Engineering Hanyang University at Ansan 1271,Sa-3 dong, Sangnokgu, Ansan-si Kyunggi-do, Korea, Fax: Ji-Yoon Yeon Associate Research Fellow Dept. of Advanced Transportation Research The Korea Transport Institute 1160 Simindaero, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang-si Gyeonggi-do, , Korea Fax: Abstract: Variable Message Sign (VMS) is one of the major components of intelligent transportation systems (ITS), which is useful for providing real-time information on weather, traffic and highway conditions. In particular, portable variable message signs (PVMS) are very useful in managing traffic events including work zone, special events, and incidents. It is essential that PVMS locations and message operations should be designed with the proper consideration of driver s legibility distance. A variety of factors would affect the legibility distance, such as drivers travel speed and driver characteristics etc. This study aimed at establishing a functional relationship between legibility distance and causal factors based on extensive field experiments. A specially manufactured PVMS was used for the experiment. A 500-meter tangent segment having 4 lanes (2 lanes for each direction) was selected for field experiments at the Hanyang University at Ansan, Korea. A differential global positioning system (DGPS) in a control vehicle was used to obtain drivers legibility distances. Data collection and analysis were undertaken to develop an estimation model for the drivers legibility distances using regression modeling techniques. The proposed model would be greatly useful for ITS designers and planners when making decisions on PVMS locations and message operations for better traffic management. Key Words: Human Factor, Intelligent Transportation Systems, Portable Variable Message Sign, Legibility Distance 1. INTRODUCTION Portable variable message sign (PVMS) is one of the useful tools for managing traffic in real time, which provides various traffic information including incidents, work zone, congestion, and weather etc. PVMS messages should not only be recognizable to drivers, but should also be coherent and legible from a distance. Therefore, installation and message operations considering drivers legibility performance are very important. Drivers legibility distances are dependent on various factors, such as geometric conditions, travel speed, and driver characteristics etc. However, there have not been many efforts to explore the relationship between the drivers legibility distance and the above causal factors.
2 In this study, extensive field experiments were conducted using a specially manufactured PVMS to develop an estimation model for drivers legibility distance. A 500-meter tangent segment having 4 lanes (2 lanes for each direction) was selected for field experiments at the Hanyang University at Ansan, Korea. An in-vehicle Differential global positioning system (DGPS) in a control vehicle was used to obtain drivers legibility distances. We conducted literature review in Chapter 2. Experimental conditions and method to obtain data are discussed in Chapter 3. Statistical data analysis and model development are presented in Chapter 4. Finally, findings are discussed along with future research. 2. LITERATURE REVIEW AND RESEARCH OPPORTUNITY There have been a variety of relevant research studies and experiments on legibility performance for VMS. Armstrong et al (1994) first emphasized reflecting ergonomic factors into designing a VMS, and suggested legibility distance models through experiments that compare legibility of fiber-optic and Light-Emitting Diode(LED) characters. Upchurch et al (1992) released results from a research on legibility distance, which used the Distance Measurement Instrument (DMI) under a target to use three types of VMS, the fip disk, the LED and fiber optics for information expression technology. Carsong and Hawkins (2003) researched and analyzed legibility of general road signs using sheeting technology under actual driving environs instead of applying the VMS under experimental environs. Ullman et al (2005) researched and analyzed legibility distance for the VMS with letters in sizes of 18 or smaller. As for PVMS related research, Ullman et al (2005) analyzed information interpreting ability for various virtual scenarios of the PVMS and VMS, using driving simulators according to each different number, display and form of words in a message. Wang, J. H. and Yon, C. (2005) developed a PVMS information legibility model with number of lanes and number of lines of messages as the main variables, and age and gender as other variables, using driving simulators. Recently, in Korea Oh et al. (2007) performed an on-site investigation on the VMS, and suggested a legibility distance model with the number of lanes, travel speed and heights of letters as independent variables. Also, several studies were conducted for better operation of PVMS to manage traffic flow in the work zone (Finger et al., 2009; Ulman et al., 2007; Anon, 1988). As reviewed above, there have been many studies dealing with legibility for VMS. There have not been many attempts to study legibility performance for PVMS, which is essential for traffic event management. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to develop an estimation model for PVMS legibility distance that would be dependent on various causal factors. 3. EXPERIMENT DESIGN AND DATA ANALYSIS 3.1. Experiment Design and Data Collection A specially manufactured PVMS was used in this study. A 500-meter tangent segment having 4 lanes (2 lanes for each direction) was selected for field experiments at the Hanyang University at Ansan, Korea as shown in <Figure 1>. In this study, 22 message display scenarios (10 sets of letters at a height of 20cm, 4 sets of letters at a height of 30cm, 4 sets of letters at a height of 40cm, and 4 sets of letters at a height of 50cm) were prepared by considering the heights of letters and number of words in messages on the PVMS. An operator and participant drove on the experiment site in an equipped vehicle as shown in
3 <Figure 2>. The operator collected data on the legibility distance and driving patterns can be represented by the change in speed and acceleration. <Figure 1> Experiment Site (a) Equipment (b) Equipped vehicle (c) PVMS(mm) Specification <Figure 2> Experiment Equipment Another operator controlled PVMS messages using a software (PVMS Server: a program which enables to generate and express messages with adjustable variables related to operating a PVMS, such as heights of letters, fonts, colors, messaging frequency etc.). As shown in <Table 1>, scenarios used in the experiments were built such that the number of lines and words in messages differed as heights of letters increased. To measure legibility distance, the investigator recorded the positions using a DGPS device once as the driver passed the reading location, using a DGPS device (at that moment, the driver signaled to the investigator that he would begin reading), and again when the driver passed the PVMS installation, the records of which were used for computation. Travel speed and spot speed of the vehicle, collected every 1 second by the DGPS, were used as traffic parameters. Experiments were conducted from the 23 rd of January to the 1st of February <Figure 3> illustrates the drivers legibility
4 process. <Figure 3> Legibility Process <Table 1> Message Examples for Field Experiment Scenario ID Character height(cm) Information unit Scenario A total of 61 subjects participated in the legibility distance experiment, such as 31 participants for daytime and 30 participants for nighttime experiments. Each participant has a valid Korea driver s license and actual driving experience greater than one year. There were 48 males participants and 13 female participants. More detailed characteristics of the participants are shown in <Figure 4>.
5 (a) Daytime experiment (b) Nighttime experiment <Figure 4> Characteristics of participants <Table 2> Legibility Distances Height of Letters(# of participants) Legibility Distance(m) 20cm(40) 30cm(40) 40cm(40) 50cm(40) Avg. Deviation Avg. Deviation Avg. Deviation Avg. Deviation Overall M(18) F(5) M(4) F(1) M(4) F(4) M(2) F(2) Avg Day M(18) F(5) M(3) F(1) M(2) F(2) M(0) n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a F(1) Avg Night M(17) F(1) M(3) F(0) n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a M(2) F(2) M(2) F(1) Avg
6 Collected PVMS legibility distances were sorted by character heights, and the data from the experiment were separated into day and night sections considering environmental conditions. Legibility distance data are summarized in <Table 2>. The travel speed at the reading location was kph, and the legibility distance ranged from a minimum of 16.56m and a maximum of m with an average of m. PVMS legibility distances were found to range between 100m and 250m Data Analysis Legibility Distance Analysis by Day Daylight Conditions Drivers will have different legibility depending on time of day, thus legibility distance data are divided into overall, day and night categories, and are presented in <Figure 5> by height of message characters. When classifying by day or night, legibility distance tended to be relatively higher during the day. To verify this, we conducted a hypothesis test comparing averages of the population using the t-test. The analyzed results are presented in <Table 3>. The difference of legibility distance between day and night was m and the t-value was 9.44, which indicates statistical significance. Therefore, it is evident that legibility distance during the day is greater than that at night. <Figure 5> Comparison of Legibility Distances for Daylight Conditions Legibility Distance During the Day(m) Legibility Distance During the Night(m) <Table 3> t-test Result (Daytime vs. Nighttime) Avg. N Deviation Paired-sample statistics Avg. : 23.21m Deviation : 60.99m Error of Avg. : 2.46m 95% Confidence Interval : 18.38~28.03 t-value : 9.44 Degree of Freedom : 615 Significance Level : 0.00
7 <Figure 6> Comparison of Legibility Distances for Gender Legibility Distance During the Day(m) Legibility Distance During the Night(m) <Table 4> t-test Result (Gender) Avg. N Deviation Paired-sample statistics Avg. : 26.66m Deviation : 76.25m Error of Avg. : 4.51m 95% Confidence Interval : 17.78~ t-value : 5.91 Degree of Freedom : 285 Significance Level : Legibility Distance Analysis by gender In terms of legibility distance according to gender, as shown in <Figure 6>, male drivers had greater distances of legibility than female drivers. The t-test was conducted to statistically verify the difference according to the gender, results are presented in <Table 4>. The average difference between the two sexes appeared to be m, where the standard deviation was m and the standard error was 4.51m. The t-value was 5.91, which is statistically significant. Hence, male drivers have greater legibility distances than female drivers Legibility Distance Analysis by Age Group Legibility distance was analyzed by different age groups separated into categories ranging from their 20s to 50s. As shown in <Figure 7>, drivers in their 20s to 40s showed similarity in the behavioral aspects, but those in their 50s showed smaller legibility, compared with people in other age groups. To statistically verify legibility distance by age group, we performed an ANOVA (Analysis of variance) and the result is presented in <Table 5>. The ANOVA resulted in an F value of and a p-value of The hypothesis that the averages in different age groups would be the same is rejected. Therefore, legibility distance for different heights of letters may be different in different age groups. As a further analysis, we conducted the Waller-Duncan method to investigate if there is a possibility to distinguish different groups from one another. It was identified that participants in their 50s formed a group and all the others formed another group. This implies that the participants in their 50s had a different average legibility distance from others in other age groups.
8 300 D i s t a n c e m ( ) L e g i b i l i t y s 30s 40s 50s Height of message characters(cm) <Figure 7> Comparison of Legibility Distances for Age Sum of square <Table 5> ANOVA Results (Age) Degree of Mean square freedom F Significance probability Cross-groups In groups Total Legibility Distance Analysis by Driving Experience The participants were divided into three groups such as driving experience of less than three years, from three to less than ten years, and ten years or longer. Drivers of experience of less than three years had the highest legibility distance, where all the others yielded approximately the same result. To statistically verify the difference in legibility distance by driving experience, we used the ANOVA, as shown in <Table 6>. <Table 6> ANOVA Results (Driving Experience) Degree of Sum of square Mean square F freedom Significance probability Cross- groups In groups Total Concerning legibility distance of each driving experience group, the average legibility distance of the group of less than three years was m, while that of three to less than ten years was m, and ten years or longer indicated a value of m. As a result of the ANOVA, the F value was and the p value was 001, thus the hypothesis that the average of drivers with different experience would be approximately the same may be rejected by the indicated p-value. Therefore, legibility distance for different heights of letters may be different in groups with varying experience. It was also identified by the Waller-Duncan
9 method that the participants with experience from three to less than ten years had greater legibility distances compared to others as shown in <Table 7>. Waller-Duncan method is one of the statistical tests to identify the similarity of means based on the statistical significance <Table 7> Result of Waller-Duncan test Subset for alpha=.05 driving experience N 1 2 Greater than 10 years Less than 3 years years <Figure 8> Comparison of Legibility Distance for Driving Experience 4. MODEL DEVELOPMENT A multiple linear regression modeling approach using a stepwise method was used to establish a functional relationship between legibility distance for PVMS and several key independent variables as shown in <Table 8>. Several categorical variables, such as gender (e.g. female = 0, male = 1) and daylight conditions (nighttime = 0, daytime = 1) were represented as dummy variables. <Table 8> Candidates for independent variables Traffic Conditions PVMS message Driver s Daylight conditions display conditions characteristics Spot speed when The number of Age Daytime message is legible words Gender Nighttime Average travel Height of message Driving speed on the test site characters Experience
10 As a result of multiple regression analysis, heights of message characters, time of day, gender, and age were selected for independent variables having statistically significant influence on legibility distance. The results from the multiple regression analysis are summarized in <Table 9>. The height of message character represented highest standardized coefficient, 0.815, which is the influential variable on the legibility distance. <Table 9> Regression Modeling Results Model Legibility distance =4.359 x x x [Adj.R2=0.942F-Value: Sig.Prob:0.000] Variables x x 1 2 x3 x 4 (Character height) (Day Night) (Gender) (Age) B Unstandardized coefficients error ized coefficients t-value Significance probability x 4 Statistics concerning the model built, such as ANOVA and regression coefficients, are presented in <Table 9>. Among standard coefficients in <Table 9>, the height of letters was 0.815, which is relatively high compared with other independent variables, thus it was found to be the most influential variable on legibility distance. The model built in this research, as well as the VMS legibility distance model of PVMS information property variables, indicates longer legibility distance as height of letters increases. Concerning driver aspects, the younger age group appears to have greater legibility distance. This seemed to be affected by the low value of the 50s group presented in <Figure 7>. The differences between day and night, and male and female, which are independent variables inputted as dummy variables, yielded high coefficients. It was also identified that male drivers have greater legibility distance than females, as presented in <Figure 6>. Regarding the daylight conditions, the distance becomes greater during the day than at night. This result complied with a study by Upchurch (1994) reporting that legibility becomes lower at night than during the day. It would be because cone cells in optic nerves, which detect color, are inactive, where only rod-shape cells are active at night, and location of rod-shaped cells is not restricted to retina but is distributed around the yellow spot, requiring more time to accurately recognize images at night than during the day. 5. CONCLUSTION A variety of ITS projects have been implemented to alleviate traffic congestion and enhance driving conditions. Advanced traffic information systems (ATIS), which is a product of such ITS projects, provide useful information to users to support their decision for selecting route, speed, and lane. In particular, PVMS is an important and useful tool for guiding drivers when traffic events including work zone and incident etc. The purpose of this study was to establish a model to estimate legibility distance for PVMS, which is essential for locating PVMS and operating message displays. This study conducted extensive field experiments using specially manufactured portable VMS
11 to obtain data to be analyzed for the model development. A 500-meter road tangent segment having 4 lanes (2 lanes for each direction) was selected to conduct field experiments at the Hanyang University at Ansan in Korea. Data collection and analysis were undertaken to explore the legibility distance and various influential factors. The results of data analysis indicated that the average legibility distance of male drivers was m and that of females was m, clearly indicating a difference. With regard to age group, drivers in their 20s to 40s had an average legibility distance of 160m to 170m, while those in their 50s had a remarkably lower legibility distance of m. Concerning driving experience, drivers of experience of less than three years had m of legibility distance, while from three years less than ten years had 187.3m, while ten years or longer had m. A multiple regression modeling technique using a stepwise independent variable selection method was applied to develop a legibility distance estimation model in this study. It was identified that height of message characters, gender, age, and daylight were significant variables affecting the legibility distance. The PVMS legibility distance model proposed in this research is expected to be utilized as useful material for better installation and management guides of PVMS. However, it should be noted that the limited number of participants could not cover the wide potential range of age groups represented in the driving population. Therefore, more field experiments with larger groups of participants should be conducted to derive more realistic and reliable models. Additionally, there need to be experiments on real roadway conditions to validate the proposed model. REFERENCES Anon. (1988) Portable Bulb-Type Changeable Message Signs for Highway Work Zones, ITE Journal, Vol. 58, No.4, Brooke R. Ullman, Gerald L. Ullman, Conrad L. Dudek and Elizabeth A. Ramirez. (2005) Legibility Distances of Smaller Letters in Changeable Message Signs with Light-Emitting Diodes, Transportation Research Record 1918, 56~62. Brooke R. Ullman, Gerald L. Ullman, Conrad L. Dudek and Alicia A. Wiliams. (2007) Driver Understanding of Sequential Portable Changeable Message Signs in Work Zones, Transportation Research Record 2015, 28~35. Cheol Oh, Won-Gi Kim, Su-Beom Lee, Cheong-Won Lee and Jeong-Wan Kim. (2007) Development of VMS Information Legibility Distance Model Using DGPS, Korean Society of Transportation Magazine, Vol.25, No.5, 23~32. Gerald L. Ullman, Brooke R. Ullman and Conrad L. Dudek. (2007) Evaluation of Alternative Dates for Advance Notification on Portable Changeable Message signs in Work zones, Transportation Research Record 2015, 36~40. Jeffery Dale Armstrong, Jonathan E. Upchurch. (1994) Human Factors design considerations for variable Message Freeway Signs, Journal of Transportation Engineering 120, 264~282. Jonathan E. Upchurch, Jeffery Dale Armstrong, M. Haddi Baaj and Gary B. Thomas. (1992) Evaluation of Variable Message Signs: Target Value, Legibility, and Viewing Comfort, Transportation Research Record 1376, 35~44. Jyh-Hone Wang and Yong Cao. (2005) Assessing Message Display Formats of Portable Variable Message Signs, Transportation Research Record 1937, 113~119. Kristofer Finger, Yong Bai, Yue Li and Umar Firman. (2009) Determining Motorist s
12 Response to Signage in Rural Highway Work Zones, Transportation Research Board 88 th Annual Meeting, Report No Paul J. Carlson and Gene Hawkins. (2003) Legibility of Overhead Guide Signs with Encapsulated Versus Microprismatic Retrore-flective Sheeting, Transportation Research Record 1844, 59~66.
INTERNALLY ILLUMINATED SIGN LIGHTING. Effects on Visibility and Traffic Safety United States Sign Council
 INTERNALLY ILLUMINATED SIGN LIGHTING Effects on Visibility and Traffic Safety 2009 United States Sign Council The Effects of Internally Illuminated On-Premise Sign Brightness on Nighttime Sign Visibility
INTERNALLY ILLUMINATED SIGN LIGHTING Effects on Visibility and Traffic Safety 2009 United States Sign Council The Effects of Internally Illuminated On-Premise Sign Brightness on Nighttime Sign Visibility
A Study on Single Camera Based ANPR System for Improvement of Vehicle Number Plate Recognition on Multi-lane Roads
 Invention Journal of Research Technology in Engineering & Management (IJRTEM) ISSN: 2455-3689 www.ijrtem.com Volume 2 Issue 1 ǁ January. 2018 ǁ PP 11-16 A Study on Single Camera Based ANPR System for Improvement
Invention Journal of Research Technology in Engineering & Management (IJRTEM) ISSN: 2455-3689 www.ijrtem.com Volume 2 Issue 1 ǁ January. 2018 ǁ PP 11-16 A Study on Single Camera Based ANPR System for Improvement
A1 = Chess A2 = Non-Chess B1 = Male B2 = Female
 Chapter IV 4.0Analysis And Interpretation Of The Data In this chapter, the analysis of the data of two hundred chess and non chess players of Hyderabad has been analysed.for this study 200 samples were
Chapter IV 4.0Analysis And Interpretation Of The Data In this chapter, the analysis of the data of two hundred chess and non chess players of Hyderabad has been analysed.for this study 200 samples were
SEQUENTIAL WARNING LIGHT SYSTEM FOR WORK ZONE LANE CLOSURES Paper No
 SEQUENTIAL WARNING LIGHT SYSTEM FOR WORK ZONE LANE CLOSURES Paper No. 01-2293 by Melisa D. Finley Assistant Transportation Researcher Texas Transportation Institute m-finley@tamu.edu Gerald L. Ullman,
SEQUENTIAL WARNING LIGHT SYSTEM FOR WORK ZONE LANE CLOSURES Paper No. 01-2293 by Melisa D. Finley Assistant Transportation Researcher Texas Transportation Institute m-finley@tamu.edu Gerald L. Ullman,
Using Driving Simulator for Advance Placement of Guide Sign Design for Exits along Highways
 Using Driving Simulator for Advance Placement of Guide Sign Design for Exits along Highways Fengxiang Qiao, Xiaoyue Liu, and Lei Yu Department of Transportation Studies Texas Southern University 3100 Cleburne
Using Driving Simulator for Advance Placement of Guide Sign Design for Exits along Highways Fengxiang Qiao, Xiaoyue Liu, and Lei Yu Department of Transportation Studies Texas Southern University 3100 Cleburne
Real-Time Identification and Tracking of Traffic Queues Based on Average Link Speed
 Paper No. 03-3351 Real-Time Identification and Tracking of Traffic Queues Based on Average Link Speed T. Nixon Chan M.A.Sc. Candidate Department of Civil Engineering, University of Waterloo 200 University
Paper No. 03-3351 Real-Time Identification and Tracking of Traffic Queues Based on Average Link Speed T. Nixon Chan M.A.Sc. Candidate Department of Civil Engineering, University of Waterloo 200 University
The Impact of Road Familiarity on the Perception of Traffic Signs Eye Tracking Case Study
 Environmental Engineering 10th International Conference eissn 2029-7092 / eisbn 978-609-476-044-0 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University Lithuania, 27 28 April 2017 Article ID: enviro.2017.131 http://enviro.vgtu.lt
Environmental Engineering 10th International Conference eissn 2029-7092 / eisbn 978-609-476-044-0 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University Lithuania, 27 28 April 2017 Article ID: enviro.2017.131 http://enviro.vgtu.lt
Focus Group Participants Understanding of Advance Warning Arrow Displays used in Short-Term and Moving Work Zones
 Focus Group Participants Understanding of Advance Warning Arrow Displays used in Short-Term and Moving Work Zones Chen Fei See University of Kansas 2160 Learned Hall 1530 W. 15th Street Lawrence, KS 66045
Focus Group Participants Understanding of Advance Warning Arrow Displays used in Short-Term and Moving Work Zones Chen Fei See University of Kansas 2160 Learned Hall 1530 W. 15th Street Lawrence, KS 66045
A Study of Optimal Spatial Partition Size and Field of View in Massively Multiplayer Online Game Server
 A Study of Optimal Spatial Partition Size and Field of View in Massively Multiplayer Online Game Server Youngsik Kim * * Department of Game and Multimedia Engineering, Korea Polytechnic University, Republic
A Study of Optimal Spatial Partition Size and Field of View in Massively Multiplayer Online Game Server Youngsik Kim * * Department of Game and Multimedia Engineering, Korea Polytechnic University, Republic
Reflection and retroreflection
 TECHNICAL NOTE RS 101 Reflection and retro Types of When looking at a reflecting surface, the surface shows an image of the space in front of the surface. The image may be complete blurred as in a surface
TECHNICAL NOTE RS 101 Reflection and retro Types of When looking at a reflecting surface, the surface shows an image of the space in front of the surface. The image may be complete blurred as in a surface
General tips for all graphs Choosing the right kind of graph scatter graph bar graph
 Excerpted and adapted from: McDonald, J.H. 2014. Handbook of Biological Statistics (3rd ed.). Sparky House Publishing, Baltimore, MD. (http://www.biostathandbook.com/graph.html) Guide to fairly good graphs
Excerpted and adapted from: McDonald, J.H. 2014. Handbook of Biological Statistics (3rd ed.). Sparky House Publishing, Baltimore, MD. (http://www.biostathandbook.com/graph.html) Guide to fairly good graphs
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BS
 Rec. ITU-R BS.1350-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BS.1350-1 SYSTEMS REQUIREMENTS FOR MULTIPLEXING (FM) SOUND BROADCASTING WITH A SUB-CARRIER DATA CHANNEL HAVING A RELATIVELY LARGE TRANSMISSION CAPACITY FOR STATIONARY
Rec. ITU-R BS.1350-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BS.1350-1 SYSTEMS REQUIREMENTS FOR MULTIPLEXING (FM) SOUND BROADCASTING WITH A SUB-CARRIER DATA CHANNEL HAVING A RELATIVELY LARGE TRANSMISSION CAPACITY FOR STATIONARY
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SAFETY CAMPAIGN VMS MESSAGES - A DRIVING SIMULATOR INVESTIGATION
 THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SAFETY CAMPAIGN VMS MESSAGES - A DRIVING SIMULATOR INVESTIGATION A. Hamish Jamson and Natasha Merat, Institute for Transport Studies, University of Leeds, U.K. E-mail: a.h.jamson@its.leeds.ac.uk
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SAFETY CAMPAIGN VMS MESSAGES - A DRIVING SIMULATOR INVESTIGATION A. Hamish Jamson and Natasha Merat, Institute for Transport Studies, University of Leeds, U.K. E-mail: a.h.jamson@its.leeds.ac.uk
Development of face safety monitoring system (FSMS) using x-mr control chart
 Development of face safety monitoring system (FSMS) using x-mr control chart Hyun-Seok Yun 1), Seong-Woo Moon 2), Chang-Yong Kim 3), and *Yong-Seok Seo 4) 1), 2), 4) Department of Earth and Environmental
Development of face safety monitoring system (FSMS) using x-mr control chart Hyun-Seok Yun 1), Seong-Woo Moon 2), Chang-Yong Kim 3), and *Yong-Seok Seo 4) 1), 2), 4) Department of Earth and Environmental
ANALYSIS OF DRIVER BEHAVIOR FOR MOBILE WORK ZONES USING A DRIVING SIMULATOR
 Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 00 April, 00, Rolla, Missouri AALYSIS OF DRIVER BEHAVIOR FOR MOBILE WORK ZOES USIG A DRIVIG SIMULATOR Durga Raj Mathur Manoj Vallati Ming C. Leu,
Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 00 April, 00, Rolla, Missouri AALYSIS OF DRIVER BEHAVIOR FOR MOBILE WORK ZOES USIG A DRIVIG SIMULATOR Durga Raj Mathur Manoj Vallati Ming C. Leu,
Tables and Figures. Germination rates were significantly higher after 24 h in running water than in controls (Fig. 4).
 Tables and Figures Text: contrary to what you may have heard, not all analyses or results warrant a Table or Figure. Some simple results are best stated in a single sentence, with data summarized parenthetically:
Tables and Figures Text: contrary to what you may have heard, not all analyses or results warrant a Table or Figure. Some simple results are best stated in a single sentence, with data summarized parenthetically:
Development and Validation of Virtual Driving Simulator for the Spinal Injury Patient
 CYBERPSYCHOLOGY & BEHAVIOR Volume 5, Number 2, 2002 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Development and Validation of Virtual Driving Simulator for the Spinal Injury Patient JEONG H. KU, M.S., 1 DONG P. JANG, Ph.D.,
CYBERPSYCHOLOGY & BEHAVIOR Volume 5, Number 2, 2002 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Development and Validation of Virtual Driving Simulator for the Spinal Injury Patient JEONG H. KU, M.S., 1 DONG P. JANG, Ph.D.,
An Approach to Korean License Plate Recognition Based on Vertical Edge Matching
 An Approach to Korean License Plate Recognition Based on Vertical Edge Matching Mei Yu and Yong Deak Kim Ajou University Suwon, 442-749, Korea Abstract License plate recognition (LPR) has many applications
An Approach to Korean License Plate Recognition Based on Vertical Edge Matching Mei Yu and Yong Deak Kim Ajou University Suwon, 442-749, Korea Abstract License plate recognition (LPR) has many applications
USE OF DRIVING SIMULATOR TO EVALUATE THE EFFECT OF REPETITION ON VARIABLE MESSAGE SIGNS
 USE OF DRIVING SIMULATOR TO EVALUATE THE EFFECT OF REPETITION ON VARIABLE MESSAGE SIGNS Arup Dutta Graduate Research Assistant Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Wisconsin
USE OF DRIVING SIMULATOR TO EVALUATE THE EFFECT OF REPETITION ON VARIABLE MESSAGE SIGNS Arup Dutta Graduate Research Assistant Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Wisconsin
Hazardous Driving Event Detection and Analysis System in Vehicular Networks
 Hazardous Driving Event Detection and Analysis System in Vehicular Networks Methodology and Field Implementation Cheol Oh, Eunbi Jeong, Kyungpyo Kang, and Younsoo Kang This study proposes a novel highway
Hazardous Driving Event Detection and Analysis System in Vehicular Networks Methodology and Field Implementation Cheol Oh, Eunbi Jeong, Kyungpyo Kang, and Younsoo Kang This study proposes a novel highway
A STUDY OF FREEWAY TRAFFIC INFORMATION REPORTED VIA COMMERCIAL RADIO. Conrad L. Dudek. John D. Friebele. and. Roy C. Lautzenheiser
 A STUDY OF FREEWAY TRAFFIC INFORMATION REPORTED VIA COMMERCIAL RADIO by Conrad L. Dudek John D. Friebele and Roy C. Lautzenheiser Research Report Number 139-8 Freeway Control and Information Systems Research
A STUDY OF FREEWAY TRAFFIC INFORMATION REPORTED VIA COMMERCIAL RADIO by Conrad L. Dudek John D. Friebele and Roy C. Lautzenheiser Research Report Number 139-8 Freeway Control and Information Systems Research
A STUDY ON THE CHARACTERISTICS AND PREDICTION METHOD OF NOISE FROM CONCRETE RAILWAY BRIDGE
 11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-12 September 2013 A STUDY ON THE CHARACTERISTICS AND PREDICTION METHOD OF NOISE FROM CONCRETE RAILWAY
11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-12 September 2013 A STUDY ON THE CHARACTERISTICS AND PREDICTION METHOD OF NOISE FROM CONCRETE RAILWAY
Variable Message Sign Trailers
 Variable Message Sign Trailers Frequently Asked Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. What standard are the VMS
Variable Message Sign Trailers Frequently Asked Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. What standard are the VMS
THE EFFECTS OF PC-BASED TRAINING ON NOVICE DRIVERS RISK AWARENESS IN A DRIVING SIMULATOR
 THE EFFECTS OF PC-BASED TRAINING ON NOVICE DRIVERS RISK AWARENESS IN A DRIVING SIMULATOR Anuj K. Pradhan 1, Donald L. Fisher 1, Alexander Pollatsek 2 1 Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
THE EFFECTS OF PC-BASED TRAINING ON NOVICE DRIVERS RISK AWARENESS IN A DRIVING SIMULATOR Anuj K. Pradhan 1, Donald L. Fisher 1, Alexander Pollatsek 2 1 Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
ENTERPRISE Transportation Pooled Fund Study TPF-5 (231)
 ENTERPRISE Transportation Pooled Fund Study TPF-5 (231) Impacts of Traveler Information on the Overall Network FINAL REPORT Prepared by September 2012 i 1. Report No. ENT-2012-2 2. Government Accession
ENTERPRISE Transportation Pooled Fund Study TPF-5 (231) Impacts of Traveler Information on the Overall Network FINAL REPORT Prepared by September 2012 i 1. Report No. ENT-2012-2 2. Government Accession
On-site Safety Management Using Image Processing and Fuzzy Inference
 1013 On-site Safety Management Using Image Processing and Fuzzy Inference Hongjo Kim 1, Bakri Elhamim 2, Hoyoung Jeong 3, Changyoon Kim 4, and Hyoungkwan Kim 5 1 Graduate Student, School of Civil and Environmental
1013 On-site Safety Management Using Image Processing and Fuzzy Inference Hongjo Kim 1, Bakri Elhamim 2, Hoyoung Jeong 3, Changyoon Kim 4, and Hyoungkwan Kim 5 1 Graduate Student, School of Civil and Environmental
Understanding User Privacy in Internet of Things Environments IEEE WORLD FORUM ON INTERNET OF THINGS / 30
 Understanding User Privacy in Internet of Things Environments HOSUB LEE AND ALFRED KOBSA DONALD BREN SCHOOL OF INFORMATION AND COMPUTER SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, IRVINE 2016-12-13 IEEE WORLD FORUM
Understanding User Privacy in Internet of Things Environments HOSUB LEE AND ALFRED KOBSA DONALD BREN SCHOOL OF INFORMATION AND COMPUTER SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, IRVINE 2016-12-13 IEEE WORLD FORUM
DEVELOPMENT OF A MICROSCOPIC TRAFFIC SIMULATION MODEL FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC ENVIRONMENT
 DEVELOPMENT OF A MICROSCOPIC TRAFFIC SIMULATION MODEL FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC ENVIRONMENT Tomoyoshi SHIRAISHI, Hisatomo HANABUSA, Masao KUWAHARA, Edward CHUNG, Shinji TANAKA, Hideki UENO, Yoshikazu OHBA,
DEVELOPMENT OF A MICROSCOPIC TRAFFIC SIMULATION MODEL FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC ENVIRONMENT Tomoyoshi SHIRAISHI, Hisatomo HANABUSA, Masao KUWAHARA, Edward CHUNG, Shinji TANAKA, Hideki UENO, Yoshikazu OHBA,
A Study on Basic VTS Guideline based on Ship s Operator s Consciousness
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 11 Number 4 December 2017 DOI: 10.12716/1001.11.04.04 A Study on Basic VTS Guideline based
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 11 Number 4 December 2017 DOI: 10.12716/1001.11.04.04 A Study on Basic VTS Guideline based
Mindfulness, non-attachment, and emotional well-being in Korean adults
 Vol.87 (Art, Culture, Game, Graphics, Broadcasting and Digital Contents 2015), pp.68-72 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.87.15 Mindfulness, non-attachment, and emotional well-being in Korean adults
Vol.87 (Art, Culture, Game, Graphics, Broadcasting and Digital Contents 2015), pp.68-72 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.87.15 Mindfulness, non-attachment, and emotional well-being in Korean adults
Driving Performance in a Simulator as a Function of Pavement and Shoulder Width, Edge Line Presence, and Oncoming Traffic
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2005 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 29th, 12:00 AM Driving Performance in a Simulator as a Function of Pavement and Shoulder Width,
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2005 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 29th, 12:00 AM Driving Performance in a Simulator as a Function of Pavement and Shoulder Width,
Speed Enforcement Systems Based on Vision and Radar Fusion: An Implementation and Evaluation 1
 Speed Enforcement Systems Based on Vision and Radar Fusion: An Implementation and Evaluation 1 Seungki Ryu *, 2 Youngtae Jo, 3 Yeohwan Yoon, 4 Sangman Lee, 5 Gwanho Choi 1 Research Fellow, Korea Institute
Speed Enforcement Systems Based on Vision and Radar Fusion: An Implementation and Evaluation 1 Seungki Ryu *, 2 Youngtae Jo, 3 Yeohwan Yoon, 4 Sangman Lee, 5 Gwanho Choi 1 Research Fellow, Korea Institute
Sign Legibility Rules Of Thumb
 Sign Legibility Rules Of Thumb UNITED STATES SIGN COUNCIL 2006 United States Sign Council SIGN LEGIBILITY By Andrew Bertucci, United States Sign Council Since 1996, the United States Sign Council (USSC)
Sign Legibility Rules Of Thumb UNITED STATES SIGN COUNCIL 2006 United States Sign Council SIGN LEGIBILITY By Andrew Bertucci, United States Sign Council Since 1996, the United States Sign Council (USSC)
Roadside Range Sensors for Intersection Decision Support
 Roadside Range Sensors for Intersection Decision Support Arvind Menon, Alec Gorjestani, Craig Shankwitz and Max Donath, Member, IEEE Abstract The Intelligent Transportation Institute at the University
Roadside Range Sensors for Intersection Decision Support Arvind Menon, Alec Gorjestani, Craig Shankwitz and Max Donath, Member, IEEE Abstract The Intelligent Transportation Institute at the University
Dynamic Visual Performance of LED with Different Color Temperature
 Vol.9, No.6 (2016), pp.437-446 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.6.38 Dynamic Visual Performance of LED with Different Color Temperature Zhao Jiandong * and Ma Shuo * School of Mechanical and Electronic
Vol.9, No.6 (2016), pp.437-446 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.6.38 Dynamic Visual Performance of LED with Different Color Temperature Zhao Jiandong * and Ma Shuo * School of Mechanical and Electronic
Section 3 Correlation and Regression - Worksheet
 The data are from the paper: Exploring Relationships in Body Dimensions Grete Heinz and Louis J. Peterson San José State University Roger W. Johnson and Carter J. Kerk South Dakota School of Mines and
The data are from the paper: Exploring Relationships in Body Dimensions Grete Heinz and Louis J. Peterson San José State University Roger W. Johnson and Carter J. Kerk South Dakota School of Mines and
I-85 Integrated Corridor Management. Jennifer Portanova, PE, CPM Sreekanth Sunny Nandagiri, PE, PMP
 Jennifer Portanova, PE, CPM Sreekanth Sunny Nandagiri, PE, PMP SDITE Meeting, Columbia, SC March 2017 Agenda The I-85 ICM project in Charlotte will serve as a model to deploy similar strategies throughout
Jennifer Portanova, PE, CPM Sreekanth Sunny Nandagiri, PE, PMP SDITE Meeting, Columbia, SC March 2017 Agenda The I-85 ICM project in Charlotte will serve as a model to deploy similar strategies throughout
Operational and Safety-Based Analyses of Varied Toll Lanes
 Operational and Safety-Based Analyses of Varied Toll Lanes Didier Valdés, PhD, University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez Department of Civil Engineering and Surveying Benjamín Colucci, PhD, University of Puerto
Operational and Safety-Based Analyses of Varied Toll Lanes Didier Valdés, PhD, University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez Department of Civil Engineering and Surveying Benjamín Colucci, PhD, University of Puerto
AN0503 Using swarm bee LE for Collision Avoidance Systems (CAS)
 AN0503 Using swarm bee LE for Collision Avoidance Systems (CAS) 1.3 NA-14-0267-0019-1.3 Document Information Document Title: Document Version: 1.3 Current Date: 2016-05-18 Print Date: 2016-05-18 Document
AN0503 Using swarm bee LE for Collision Avoidance Systems (CAS) 1.3 NA-14-0267-0019-1.3 Document Information Document Title: Document Version: 1.3 Current Date: 2016-05-18 Print Date: 2016-05-18 Document
Design of Traffic Flow Simulation System to Minimize Intersection Waiting Time
 Design of Traffic Flow Simulation System to Minimize Intersection Waiting Time Jang, Seung-Ju Department of Computer Engineering, Dongeui University Abstract This paper designs a traffic simulation system
Design of Traffic Flow Simulation System to Minimize Intersection Waiting Time Jang, Seung-Ju Department of Computer Engineering, Dongeui University Abstract This paper designs a traffic simulation system
Diversion Analysis. Appendix K
 Appendix K Appendix K Appendix K Project Description The Project includes the potential closure of the eastbound direction ramp for vehicular traffic at Washington Street and University Avenue. In addition,
Appendix K Appendix K Appendix K Project Description The Project includes the potential closure of the eastbound direction ramp for vehicular traffic at Washington Street and University Avenue. In addition,
LED-ID Systems Applying the Modulation and Coding Selection Scheme Based on Received Angle
 LED-ID Systems Applying the Modulation and Coding Selection Scheme Based on Received Angle Kyujin Lee 1, Dongho Cha 1, Kyesan Lee 1, 1 Kyung Hee University, 1 Seocheon-dong, Giheung-gu, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do,
LED-ID Systems Applying the Modulation and Coding Selection Scheme Based on Received Angle Kyujin Lee 1, Dongho Cha 1, Kyesan Lee 1, 1 Kyung Hee University, 1 Seocheon-dong, Giheung-gu, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do,
Image Characteristics and Their Effect on Driving Simulator Validity
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2001 Driving Assessment Conference Aug 16th, 12:00 AM Image Characteristics and Their Effect on Driving Simulator Validity Hamish Jamson
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2001 Driving Assessment Conference Aug 16th, 12:00 AM Image Characteristics and Their Effect on Driving Simulator Validity Hamish Jamson
Project: IEEE P Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N
 Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N (WPANs( WPANs) Submission Title: [VLC application :Indoor Navigation / LBS using VLC ] Date Submitted: [13 May, 2008] Source: [Dongjae
Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N (WPANs( WPANs) Submission Title: [VLC application :Indoor Navigation / LBS using VLC ] Date Submitted: [13 May, 2008] Source: [Dongjae
The Impact of Typeface on Future Automotive HMIs
 The Impact of Typeface on Future Automotive HMIs Connected Car USA 2013 September 2013 David.Gould@monotype.com 2 More Screens 3 Larger Screens 4! More Information! 5 Nomadic Devices with Screen Replication
The Impact of Typeface on Future Automotive HMIs Connected Car USA 2013 September 2013 David.Gould@monotype.com 2 More Screens 3 Larger Screens 4! More Information! 5 Nomadic Devices with Screen Replication
Measurement over a Short Distance. Tom Mathew
 Measurement over a Short Distance Tom Mathew Outline Introduction Data Collection Methods Data Analysis Conclusion Introduction Determine Fundamental Traffic Parameter Data Collection and Interpretation
Measurement over a Short Distance Tom Mathew Outline Introduction Data Collection Methods Data Analysis Conclusion Introduction Determine Fundamental Traffic Parameter Data Collection and Interpretation
Evaluation of Real-World Toll Plazas Using Driving Simulation
 Evaluation of Real-World Toll Plazas Using Driving Simulation Mohamed Abdel-Aty, PhD, PI Pegasus Professor, Chair Department of Civil, Environmental and Construction Engineering University of Central Florida
Evaluation of Real-World Toll Plazas Using Driving Simulation Mohamed Abdel-Aty, PhD, PI Pegasus Professor, Chair Department of Civil, Environmental and Construction Engineering University of Central Florida
Lesson Sampling Distribution of Differences of Two Proportions
 STATWAY STUDENT HANDOUT STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The GPS software company, TeleNav, recently commissioned a study on proportions of people who text while they drive. The study suggests that there
STATWAY STUDENT HANDOUT STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The GPS software company, TeleNav, recently commissioned a study on proportions of people who text while they drive. The study suggests that there
IMPACT OF MODERN HEADLAMPS ON THE DESIGN OF SAG VERTICAL CURVES. A Thesis Proposal by Madhuri Gogula
 IMPACT OF MODERN HEADLAMPS ON THE DESIGN OF SAG VERTICAL CURVES A Thesis Proposal by Madhuri Gogula Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
IMPACT OF MODERN HEADLAMPS ON THE DESIGN OF SAG VERTICAL CURVES A Thesis Proposal by Madhuri Gogula Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
PerSec. Pervasive Computing and Security Lab. Enabling Transportation Safety Services Using Mobile Devices
 PerSec Pervasive Computing and Security Lab Enabling Transportation Safety Services Using Mobile Devices Jie Yang Department of Computer Science Florida State University Oct. 17, 2017 CIS 5935 Introduction
PerSec Pervasive Computing and Security Lab Enabling Transportation Safety Services Using Mobile Devices Jie Yang Department of Computer Science Florida State University Oct. 17, 2017 CIS 5935 Introduction
INCHEON 2014 ASIAN PARA GAMES
 MQS Guidelines SANCTION Sanctioned by the Asian Para Tenpin Bowling Federation (APF). EVENTS (14) SINGLES (Mixed) DOUBLES (Mixed) * TPB 1 * TPB 1 + TPB 1 * TPB 2/3 * TPB 2/3 + TPB 2/3 * TPB 8 * TPB 1 +
MQS Guidelines SANCTION Sanctioned by the Asian Para Tenpin Bowling Federation (APF). EVENTS (14) SINGLES (Mixed) DOUBLES (Mixed) * TPB 1 * TPB 1 + TPB 1 * TPB 2/3 * TPB 2/3 + TPB 2/3 * TPB 8 * TPB 1 +
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1.1 INTRODUCTION This document is the Final Evaluation Report for the Genesis Advanced Traveler Information System (ATIS) Field Operational Test (FOT). This test was co-sponsored by
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1.1 INTRODUCTION This document is the Final Evaluation Report for the Genesis Advanced Traveler Information System (ATIS) Field Operational Test (FOT). This test was co-sponsored by
VALIDATION OF LINK TRAVEL TIME USING GPS DATA: A Case Study of Western Expressway, Mumbai
 Map Asia 2005 Jaarta, Indonesia VALIDATION OF LINK TRAVEL TIME USING GPS DATA: A Case Study of Western Expressway, Mumbai Saurabh Gupta 1, Tom V. Mathew 2 Transportation Systems Engineering Department
Map Asia 2005 Jaarta, Indonesia VALIDATION OF LINK TRAVEL TIME USING GPS DATA: A Case Study of Western Expressway, Mumbai Saurabh Gupta 1, Tom V. Mathew 2 Transportation Systems Engineering Department
Verification for Proving the Route Choice Dependence of Motorists Yi Dan 1, a, Shunying Zhu 2, b, Xiaohu Nie 3, c, Yin Chen 4, d, Zipei Zhang 5, e
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-09-04 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 765-767, pp 1427-1430 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.765-767.1427 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Verification for Proving
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-09-04 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 765-767, pp 1427-1430 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.765-767.1427 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Verification for Proving
Traffic Control for a Swarm of Robots: Avoiding Group Conflicts
 Traffic Control for a Swarm of Robots: Avoiding Group Conflicts Leandro Soriano Marcolino and Luiz Chaimowicz Abstract A very common problem in the navigation of robotic swarms is when groups of robots
Traffic Control for a Swarm of Robots: Avoiding Group Conflicts Leandro Soriano Marcolino and Luiz Chaimowicz Abstract A very common problem in the navigation of robotic swarms is when groups of robots
INTEGRATED TUNNEL MONITORING SYSTEM USING WIRELESS AUTOMATED DATA COLLECTION TECHNOLOGY
 INTEGRATED TUNNEL MONITORING SYSTEM USING WIRELESS AUTOMATED DATA COLLECTION TECHNOLOGY Jung-Ryul Kim Researcher KICT, 2311, Daehwadong, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggido, 411-712, jrkim@kict.re.kr Hyun-Suk
INTEGRATED TUNNEL MONITORING SYSTEM USING WIRELESS AUTOMATED DATA COLLECTION TECHNOLOGY Jung-Ryul Kim Researcher KICT, 2311, Daehwadong, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggido, 411-712, jrkim@kict.re.kr Hyun-Suk
Comparing Means. Chapter 24. Case Study Gas Mileage for Classes of Vehicles. Case Study Gas Mileage for Classes of Vehicles Data collection
 Chapter 24 One-Way Analysis of Variance: Comparing Several Means BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 24 1 Comparing Means Chapter 18: compared the means of two populations or the mean responses to two treatments in
Chapter 24 One-Way Analysis of Variance: Comparing Several Means BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 24 1 Comparing Means Chapter 18: compared the means of two populations or the mean responses to two treatments in
Freeway exit ramp traffic flow research based on computer simulation
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2008 Freeway exit ramp traffic flow research based on computer simulation Xu Wang University of South Florida
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2008 Freeway exit ramp traffic flow research based on computer simulation Xu Wang University of South Florida
Traffic Solutions. How to Test FCD Monitoring Solutions: Performance of Cellular-Based Vs. GPS-based systems
 Traffic Solutions How to Test FCD Monitoring Solutions: Performance of Cellular-Based Vs. GPS-based systems About Cellint Israel Based, office in the US Main products NetEyes for quality of RF networks
Traffic Solutions How to Test FCD Monitoring Solutions: Performance of Cellular-Based Vs. GPS-based systems About Cellint Israel Based, office in the US Main products NetEyes for quality of RF networks
Range of Acceptable Illuminance by LED Colors in Indoor Spaces
 Range of Acceptable Illuminance by LED Colors in Indoor Spaces - Focus on Occupants Comfort and Communications in Living Rooms - Taeyon Hwang 1, Dong Gi Lee 2*, Jeong Tai Kim 1 1 Department of Architectural
Range of Acceptable Illuminance by LED Colors in Indoor Spaces - Focus on Occupants Comfort and Communications in Living Rooms - Taeyon Hwang 1, Dong Gi Lee 2*, Jeong Tai Kim 1 1 Department of Architectural
Comparison of Receive Signal Level Measurement Techniques in GSM Cellular Networks
 Comparison of Receive Signal Level Measurement Techniques in GSM Cellular Networks Nenad Mijatovic *, Ivica Kostanic * and Sergey Dickey + * Florida Institute of Technology, Melbourne, FL, USA nmijatov@fit.edu,
Comparison of Receive Signal Level Measurement Techniques in GSM Cellular Networks Nenad Mijatovic *, Ivica Kostanic * and Sergey Dickey + * Florida Institute of Technology, Melbourne, FL, USA nmijatov@fit.edu,
NCSS Statistical Software
 Chapter 147 Introduction A mosaic plot is a graphical display of the cell frequencies of a contingency table in which the area of boxes of the plot are proportional to the cell frequencies of the contingency
Chapter 147 Introduction A mosaic plot is a graphical display of the cell frequencies of a contingency table in which the area of boxes of the plot are proportional to the cell frequencies of the contingency
Optimizing Work Zone Lighting. FINAL REPORT October Submitted by
 NJ-2016-004 Optimizing Work Zone Lighting FINAL REPORT October 2016 Submitted by John D. Bullough Principal Investigator Lighting Research Center Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Mark S. Rea Co-Principal
NJ-2016-004 Optimizing Work Zone Lighting FINAL REPORT October 2016 Submitted by John D. Bullough Principal Investigator Lighting Research Center Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Mark S. Rea Co-Principal
OPPORTUNISTIC TRAFFIC SENSING USING EXISTING VIDEO SOURCES (PHASE II)
 CIVIL ENGINEERING STUDIES Illinois Center for Transportation Series No. 17-003 UILU-ENG-2017-2003 ISSN: 0197-9191 OPPORTUNISTIC TRAFFIC SENSING USING EXISTING VIDEO SOURCES (PHASE II) Prepared By Jakob
CIVIL ENGINEERING STUDIES Illinois Center for Transportation Series No. 17-003 UILU-ENG-2017-2003 ISSN: 0197-9191 OPPORTUNISTIC TRAFFIC SENSING USING EXISTING VIDEO SOURCES (PHASE II) Prepared By Jakob
A NEW SIMULATION FRAMEWORK OF OPERATIONAL EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS FOR UNMANNED GROUND VEHICLE
 A NEW SIMULATION FRAMEWORK OF OPERATIONAL EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS FOR UNMANNED GROUND VEHICLE 1 LEE JAEYEONG, 2 SHIN SUNWOO, 3 KIM CHONGMAN 1 Senior Research Fellow, Myongji University, 116, Myongji-ro,
A NEW SIMULATION FRAMEWORK OF OPERATIONAL EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS FOR UNMANNED GROUND VEHICLE 1 LEE JAEYEONG, 2 SHIN SUNWOO, 3 KIM CHONGMAN 1 Senior Research Fellow, Myongji University, 116, Myongji-ro,
Comparison of Wrap Around Screens and HMDs on a Driver s Response to an Unexpected Pedestrian Crossing Using Simulator Vehicle Parameters
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2017 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 28th, 12:00 AM Comparison of Wrap Around Screens and HMDs on a Driver s Response to an Unexpected
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2017 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 28th, 12:00 AM Comparison of Wrap Around Screens and HMDs on a Driver s Response to an Unexpected
Spatial Judgments from Different Vantage Points: A Different Perspective
 Spatial Judgments from Different Vantage Points: A Different Perspective Erik Prytz, Mark Scerbo and Kennedy Rebecca The self-archived postprint version of this journal article is available at Linköping
Spatial Judgments from Different Vantage Points: A Different Perspective Erik Prytz, Mark Scerbo and Kennedy Rebecca The self-archived postprint version of this journal article is available at Linköping
proc plot; plot Mean_Illness*Dose=Dose; run;
 options pageno=min nodate formdlim='-'; Title 'Illness Related to Dose of Therapeutic Drug'; run; data Lotus; input Dose N; Do I=1 to N; Input Illness @@; output; end; cards; 0 20 101 101 101 104 104 105
options pageno=min nodate formdlim='-'; Title 'Illness Related to Dose of Therapeutic Drug'; run; data Lotus; input Dose N; Do I=1 to N; Input Illness @@; output; end; cards; 0 20 101 101 101 104 104 105
GPS positioning using map-matching algorithms, drive restriction information and road network connectivity
 Extended abstract Submission for GISRUK 2001 GPS positioning using map-matching algorithms, drive restriction information and road network connectivity George Taylor 1, Jamie Uff 2 and Adil Al-Hamadani
Extended abstract Submission for GISRUK 2001 GPS positioning using map-matching algorithms, drive restriction information and road network connectivity George Taylor 1, Jamie Uff 2 and Adil Al-Hamadani
COMMITTEE OF THE WHOLE MEETING JUNE 26, 2017
 REPORT #ENG-2017-37 COMMITTEE OF THE WHOLE MEETING JUNE 26, 2017 INTRODUCTION OF PARKING AND TRAFFIC BY-LAWS IN THE VICINITY OF SIDEROAD 10 AND THE 11TH LINE, TOWN OF NEW TECUMSETH RECOMMENDATION That
REPORT #ENG-2017-37 COMMITTEE OF THE WHOLE MEETING JUNE 26, 2017 INTRODUCTION OF PARKING AND TRAFFIC BY-LAWS IN THE VICINITY OF SIDEROAD 10 AND THE 11TH LINE, TOWN OF NEW TECUMSETH RECOMMENDATION That
High-temperature Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges for On-line Monitoring of Pipe Thinning for FAC Proof Test Facility
 High-temperature Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges for On-line Monitoring of Pipe Thinning for FAC Proof Test Facility Yong-Moo Cheong 1, Se-Beom Oh 1, Kyung-Mo Kim 1, and Dong-Jin Kim 1 1 Nuclear Materials
High-temperature Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges for On-line Monitoring of Pipe Thinning for FAC Proof Test Facility Yong-Moo Cheong 1, Se-Beom Oh 1, Kyung-Mo Kim 1, and Dong-Jin Kim 1 1 Nuclear Materials
Validation of an Economican Fast Method to Evaluate Situationspecific Parameters of Traffic Safety
 Validation of an Economican Fast Method to Evaluate Situationspecific Parameters of Traffic Safety Katharina Dahmen-Zimmer, Kilian Ehrl, Alf Zimmer University of Regensburg Experimental Applied Psychology
Validation of an Economican Fast Method to Evaluate Situationspecific Parameters of Traffic Safety Katharina Dahmen-Zimmer, Kilian Ehrl, Alf Zimmer University of Regensburg Experimental Applied Psychology
Two Factor Full Factorial Design with Replications
 Two Factor Full Factorial Design with Replications Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: 22-1 Overview Model Computation
Two Factor Full Factorial Design with Replications Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: 22-1 Overview Model Computation
Traffic Control for a Swarm of Robots: Avoiding Target Congestion
 Traffic Control for a Swarm of Robots: Avoiding Target Congestion Leandro Soriano Marcolino and Luiz Chaimowicz Abstract One of the main problems in the navigation of robotic swarms is when several robots
Traffic Control for a Swarm of Robots: Avoiding Target Congestion Leandro Soriano Marcolino and Luiz Chaimowicz Abstract One of the main problems in the navigation of robotic swarms is when several robots
Draft Recommended Practice - SAE J-2396
 Draft Recommended Practice - SAE J-2396 Revised 12-98 (Not in SAE document format) Definition and Experimental Measures Related to the Specification of Driver Visual Behavior Using Video Based Techniques
Draft Recommended Practice - SAE J-2396 Revised 12-98 (Not in SAE document format) Definition and Experimental Measures Related to the Specification of Driver Visual Behavior Using Video Based Techniques
ASSESSING THE POTENTIAL FOR THE AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF INCIDENTS ON THE BASIS OF INFORMATION OBTAINED FROM ELECTRONIC TOLL TAGS
 ASSESSING THE POTENTIAL FOR THE AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF INCIDENTS ON THE BASIS OF INFORMATION OBTAINED FROM ELECTRONIC TOLL TAGS Bruce Hellinga Department of Civil Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo,
ASSESSING THE POTENTIAL FOR THE AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF INCIDENTS ON THE BASIS OF INFORMATION OBTAINED FROM ELECTRONIC TOLL TAGS Bruce Hellinga Department of Civil Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo,
Investigating Time-Based Glare Allowance Based On Realistic Short Time Duration
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering July 2018 Investigating Time-Based Glare Allowance Based On Realistic Short Time Duration
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering July 2018 Investigating Time-Based Glare Allowance Based On Realistic Short Time Duration
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors.
 Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Evaluation of Connected Vehicle Technology for Concept Proposal Using V2X Testbed
 AUTOMOTIVE Evaluation of Connected Vehicle Technology for Concept Proposal Using V2X Testbed Yoshiaki HAYASHI*, Izumi MEMEZAWA, Takuji KANTOU, Shingo OHASHI, and Koichi TAKAYAMA ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AUTOMOTIVE Evaluation of Connected Vehicle Technology for Concept Proposal Using V2X Testbed Yoshiaki HAYASHI*, Izumi MEMEZAWA, Takuji KANTOU, Shingo OHASHI, and Koichi TAKAYAMA ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EXTRACTING REAL-TIME DATA FROM A DRIVING SIMULATOR SEYED AMIRHOSSEIN HOSSEINI. Bachelor of Engineering in Civil Engineering QIAU May 2012
 EXTRACTING REAL-TIME DATA FROM A DRIVING SIMULATOR SEYED AMIRHOSSEIN HOSSEINI Bachelor of Engineering in Civil Engineering QIAU May 2012 submitted in partial fulfillment of requirements for the degree
EXTRACTING REAL-TIME DATA FROM A DRIVING SIMULATOR SEYED AMIRHOSSEIN HOSSEINI Bachelor of Engineering in Civil Engineering QIAU May 2012 submitted in partial fulfillment of requirements for the degree
An Application for Driving Simulator Technology: An Evaluation of Traffic Signal Displays for Protected-Permissive Left-Turn Control
 An Application for Driving Simulator Technology: An Evaluation of Traffic Signal Displays for Protected-Permissive Left-Turn Control By Michael A. Knodler Jr. University of Massachusetts Amherst 214C Marston
An Application for Driving Simulator Technology: An Evaluation of Traffic Signal Displays for Protected-Permissive Left-Turn Control By Michael A. Knodler Jr. University of Massachusetts Amherst 214C Marston
Prediction of LOS based Path-Loss in Urban Wireless Sensor Network Environments
 Prediction of LOS based Path-Loss in Urban Wireless Sensor Network Environments Myungnam Bae, Inhwan Lee, Hyochan Bang ETRI, IoT Convergence Research Department, 218 Gajeongno, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 305-700,
Prediction of LOS based Path-Loss in Urban Wireless Sensor Network Environments Myungnam Bae, Inhwan Lee, Hyochan Bang ETRI, IoT Convergence Research Department, 218 Gajeongno, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 305-700,
Characteristics of Routes in a Road Traffic Assignment
 Characteristics of Routes in a Road Traffic Assignment by David Boyce Northwestern University, Evanston, IL Hillel Bar-Gera Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel at the PTV Vision Users Group Meeting
Characteristics of Routes in a Road Traffic Assignment by David Boyce Northwestern University, Evanston, IL Hillel Bar-Gera Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel at the PTV Vision Users Group Meeting
Chapter 25. One-Way Analysis of Variance: Comparing Several Means. BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 24 1
 Chapter 25 One-Way Analysis of Variance: Comparing Several Means BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 24 1 Comparing Means Chapter 18: compared the means of two populations or the mean responses to two treatments in
Chapter 25 One-Way Analysis of Variance: Comparing Several Means BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 24 1 Comparing Means Chapter 18: compared the means of two populations or the mean responses to two treatments in
MOBILITY RESEARCH NEEDS FROM THE GOVERNMENT PERSPECTIVE
 MOBILITY RESEARCH NEEDS FROM THE GOVERNMENT PERSPECTIVE First Annual 2018 National Mobility Summit of US DOT University Transportation Centers (UTC) April 12, 2018 Washington, DC Research Areas Cooperative
MOBILITY RESEARCH NEEDS FROM THE GOVERNMENT PERSPECTIVE First Annual 2018 National Mobility Summit of US DOT University Transportation Centers (UTC) April 12, 2018 Washington, DC Research Areas Cooperative
Enhanced indoor localization using GPS information
 Enhanced indoor localization using GPS information Taegyung Oh, Yujin Kim, Seung Yeob Nam Dept. of information and Communication Engineering Yeongnam University Gyeong-san, Korea a49094909@ynu.ac.kr, swyj90486@nate.com,
Enhanced indoor localization using GPS information Taegyung Oh, Yujin Kim, Seung Yeob Nam Dept. of information and Communication Engineering Yeongnam University Gyeong-san, Korea a49094909@ynu.ac.kr, swyj90486@nate.com,
Naturalistic Flying Study as a Method of Collecting Pilot Communication Behavior Data
 IEEE Cognitive Communications for Aerospace Applications Workshop 2017 Naturalistic Flying Study as a Method of Collecting Pilot Communication Behavior Data Chang-Geun Oh, Ph.D Kent State University Why
IEEE Cognitive Communications for Aerospace Applications Workshop 2017 Naturalistic Flying Study as a Method of Collecting Pilot Communication Behavior Data Chang-Geun Oh, Ph.D Kent State University Why
Designing Service Coverage and Measuring Accessibility and Serviceability
 Designing Service Coverage and Measuring Accessibility and Serviceability INFORMS Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA November 9-12, 2014 EunSu Lee, Ph.D., GISP, CPIM, CSCP Agenda Introduction Objectives
Designing Service Coverage and Measuring Accessibility and Serviceability INFORMS Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA November 9-12, 2014 EunSu Lee, Ph.D., GISP, CPIM, CSCP Agenda Introduction Objectives
Modeling Connectivity of Inter-Vehicle Communication Systems with Road-Side Stations
 Modeling Connectivity of Inter-Vehicle Communication Systems with Road-Side Stations Wen-Long Jin* and Hong-Jun Wang Department of Automation, University of Science and Technology of China, P.R. China
Modeling Connectivity of Inter-Vehicle Communication Systems with Road-Side Stations Wen-Long Jin* and Hong-Jun Wang Department of Automation, University of Science and Technology of China, P.R. China
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
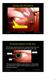 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Use of Dynamic Traffic Assignment in FSUTMS in Support of Transportation Planning in Florida
 Use of Dynamic Traffic Assignment in FSUTMS in Support of Transportation Planning in Florida Requirement Workshop December 2, 2010 Need for Assignment Estimating link flows Estimating zone to zone travel
Use of Dynamic Traffic Assignment in FSUTMS in Support of Transportation Planning in Florida Requirement Workshop December 2, 2010 Need for Assignment Estimating link flows Estimating zone to zone travel
Hypergeometric Probability Distribution
 Hypergeometric Probability Distribution Example problem: Suppose 30 people have been summoned for jury selection, and that 12 people will be chosen entirely at random (not how the real process works!).
Hypergeometric Probability Distribution Example problem: Suppose 30 people have been summoned for jury selection, and that 12 people will be chosen entirely at random (not how the real process works!).
Prices of digital cameras
 Prices of digital cameras The August 2012 issue of Consumer Reports included a report on digital cameras. The magazine listed 60 cameras, all of which were recommended by them, divided into six categories
Prices of digital cameras The August 2012 issue of Consumer Reports included a report on digital cameras. The magazine listed 60 cameras, all of which were recommended by them, divided into six categories
M12/5/MATSD/SP2/ENG/TZ1/XX MATHEMATICAL STUDIES STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2. Friday 4 May 2012 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes. instructions To candidates
 22127404 MATHEMATICAL STUDIES STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Friday 4 May 2012 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes instructions To candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. A graphic display
22127404 MATHEMATICAL STUDIES STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Friday 4 May 2012 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes instructions To candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. A graphic display
Research in Advanced Performance Technology and Educational Readiness
 Research in Advanced Performance Technology and Educational Readiness Enhancing Human Performance with the Right Technology Ronald W. Tarr Program Director RAPTER-IST University of Central Florida 1 Mission
Research in Advanced Performance Technology and Educational Readiness Enhancing Human Performance with the Right Technology Ronald W. Tarr Program Director RAPTER-IST University of Central Florida 1 Mission
How Many Imputations are Really Needed? Some Practical Clarifications of Multiple Imputation Theory
 Prev Sci (2007) 8:206 213 DOI 10.1007/s11121-007-0070-9 How Many Imputations are Really Needed? Some Practical Clarifications of Multiple Imputation Theory John W. Graham & Allison E. Olchowski & Tamika
Prev Sci (2007) 8:206 213 DOI 10.1007/s11121-007-0070-9 How Many Imputations are Really Needed? Some Practical Clarifications of Multiple Imputation Theory John W. Graham & Allison E. Olchowski & Tamika
Power Loss Calculation of High Frequency Transformers
 8 Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, Vol., No., pp. 8~4, 6 Power Loss alculation of High Frequency Transformers Geun-Soo hoi*, Shin-Yong Yoon*, Soo-Hyun Baek** and Kim Yong** Abstract This
8 Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, Vol., No., pp. 8~4, 6 Power Loss alculation of High Frequency Transformers Geun-Soo hoi*, Shin-Yong Yoon*, Soo-Hyun Baek** and Kim Yong** Abstract This
Urban Traffic Bottleneck Identification Based on Congestion Propagation
 Urban Traffic Bottleneck Identification Based on Congestion Propagation Wenwei Yue, Changle Li, Senior Member, IEEE and Guoqiang Mao, Fellow, IEEE State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks,
Urban Traffic Bottleneck Identification Based on Congestion Propagation Wenwei Yue, Changle Li, Senior Member, IEEE and Guoqiang Mao, Fellow, IEEE State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks,
Korean standards of visual grading and establishing allowable properties of softwood structural lumber
 Korean standards of visual grading and establishing allowable properties of softwood structural lumber Park, Moon-Jae 1, Shim, Kug-Bo 1 ABSTRACT Korean standards related to wood products such as "Sizes
Korean standards of visual grading and establishing allowable properties of softwood structural lumber Park, Moon-Jae 1, Shim, Kug-Bo 1 ABSTRACT Korean standards related to wood products such as "Sizes
SIMULATION OF TRAFFIC LIGHTS CONTROL
 SIMULATION OF TRAFFIC LIGHTS CONTROL Krzysztof Amborski, Andrzej Dzielinski, Przemysław Kowalczuk, Witold Zydanowicz Institute of Control and Industrial Electronics Warsaw University of Technology Koszykowa
SIMULATION OF TRAFFIC LIGHTS CONTROL Krzysztof Amborski, Andrzej Dzielinski, Przemysław Kowalczuk, Witold Zydanowicz Institute of Control and Industrial Electronics Warsaw University of Technology Koszykowa
