AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTERS 1 & Worksheet: 1(a, c), 2(a, c), 3a, 4, 5, 10a, 11b, (Solving inequalities)
|
|
|
- Monica Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTERS 1 & 2 1. Worksheet: 1(a, c), 2(a, c), 3a, 4, 5, 10a, 11b, (Solving inequalities) 2. Pg : 1, 3, 7, 13, 14 (Functions. Abs. Val., Piece-wise) Pg : 3, 7, 13, 19, 27, 33 (Linear Functions) 3. Pg : 1, 3, 4, 7, 11, 21, 31, 35, 37, 39, 57, odd (work with functions) Pg. 78: 39, 41 (Trig functions) 4. Pg : 1-14 (Limits-concept visually) 5. Pg : 15-17, 19, 21, 25 (same) 6. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 10, 13, odd, 33, 39 (limits/algebraically) 7. Pg : 2, 4, 11, 29, 33, 40 Pg : 1, 3, 7, 11, 17, 21, 29, 31, 41, 43 (Limits at infinity), 8. Pg : 1, 3, 7, 9, 13, 17, 23, 25, 29, 33 (definition of continuity) 9. Pg : 15, 19, 21, 24, 26, 27, 30, 31, 42, 43 (same) 10. Pg : 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 23, 25, 29, 31, 35, 36, 41, 43 (trig limits) 11. Pg : 3, 7, 11(a, e only), 15, 19, 21, 27, 33, 39, 45, 55, 59 (same) 12. Pg : 1, 3, 7, 9, 13, 19, odd, odd (chapter review) Turn over for answers not in the back of the book.
2 AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTER Pg : 1-21 odd (rates of change/average and instantaneous) 14. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 9, 13, 15, 21, 27 (Definition of derivative) 15. Pg : 7, 19, 23, 25, 29, 31, 41, 43 (graphs f(x), f (x) and differentiability) 16. Worksheet: 1,4,7-13odd,19,25,33(a),35,41,45(copy for your notes only) (same) 17. Pg : 3, 5, 11, 19, 35, 43, 45, 49, 51, odd, 75, 79 (simple power rule) 18. Pg : 7, 9, odd, odd, 67, 76, 77, 84 (product and quotient rules) 19. Pg : 1-9 odd, 15, 19, 25, 29, 35, 39, 41 (trig derivatives) 20. Pg : 1, 5, 7, 9. 13, 17, 19, 21, 27, 37, 43, 55, 61, 65, 69 (chain rule) 21. Pg : 3, 11, 15, 23, 25, 29, 31, 45, 49, 57, 71, 74 (copy into your notes), 77 (same) 22. Pg : 1, 7, 11, 15, 17, 25, 35, 38, 43, 45, 47 (implicit diff.) 23. Pg : 9, 13, 21, 23, 37, 39, 40, 42, 43 (same) 24. Pg : 29, 33, 37, 41, odd (differentials) 25. Pg232-30: 3a, 5, 13, 19, 23, 27 (tangent line approximation) 26. Worksheet: 3, 13, 19, 25, 27, 31, 37, 39, 40, 41, 52 (same) 27. Pg : 1, 3, 9, 11, 13, 17, 19, 31, 39 (chapter review)
3 AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTER Pg : 1, 3, 7, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25 (related rates problems) 29. Pg : 11, 15, 27, 32, 33, 37, 39, 41 (same) 30. Worksheet (same) if needed 31. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 17, 27, 29, 31, 43, 53 (intervals of increase/decrease) 32. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 17, 21, 29, 33, 35, 45, 49 (relative/local extrema) 33. Pg : 2, 7, 11, 13, 23, 27, 31, 39, 47 (Same) 34. Worksheet: Using f and f for analysis 35. Pg : 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 25, 45 (b, c), 49, 53, 55 (Graphs of rational functions) 36. Pg : 3, 9, 23, 27, 29, 33, 37, 43(c), 54 (functional analysis) 37. Pg : 5, 7, 26, 31, 39, 41, 43(d), 45(d), 51, 56 (more of same) 38. Pg : 3, 7, 9, 13, 15, 17, 21, 23, 27, 29, 31, 39 (extreme value theorem) 39. Pg : 5, 11, 19, 25, 30, 33, 34, 35 (same) 40. Pg : 3, 5, 11, 17, 20, 29 (applications/optimization problems) 41. Pg : 8, 9, 19, 47, 49, 55 (same) 42. Pg : 6, 41, 43, 44, 45, 53 (business ideas) 43. Worksheet: 1, 7, 13, 19c, 20, 23, 30, 33, 35, 37, 41 (more business applications) 44. Worksheet: 11, 15, 21, 25, 35, 37, 49 (mixed application review problems) if needed 45. Pg : 1, 5, 9, 11, 15, 19, 21, 23 (Newton s method) 46. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 9, 11, 13, 17, 23, 35, 37, 43, 44 (Mean Value Theorem/Rolle s thm) 47. Worksheet: 1, 3, 11, 17, 23, 29, 31, 33 (same) 48. Pg : 1-3, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, 21, 23, 34 (rectilinear motion) 49. Pg : 4, 6, 13, 18, 25, 27, 31, 37 (same) 50. Pg : 1, 3, 7, 9, 11, 15, 17, 21, 23, 25, 27, 31, 37, 39, 45, 46 (chapter review)
4 AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTER Pg : 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 19, 21, 25, 27, 47, 49 (simple power rule) 52. Pg : 3, 7, 11, 15, 23, 29, 37, 41, 42, 43 (same) 53. Pg : 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, 35, 37, 39 (anti-chain rule/u-substitution) 54. Pg : 3(b, d), 7, 11, 15, 19, 23, 27, 28, 29, 38 (same) 55. Pg : 1, 3-15 odd, 19, 22, 23, 25, 27, 28 (properties of sigma notation) 56. Worksheet on Sigma (if needed) 57. Pg : 29, 31 (use Trapezoids too) (Area approximation) 58. Pg : 32(use Trapezoids too), 37, 39, 41(use easiest method on these 3) (Area by limits) 59. Worksheet on area approximation (if needed) 60. Pg : 1, 3, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, 23, 25 (Riemann sums, definite integral, properties) 61. Pg : 2, 5, 13, 17, 21, 27, 29 (same) 62. Pg :1, 3, 7, 9, 15, 17, 21, 23, 29, 31, 33 (first fundamental theorem) 63. Pg : 5, 11, 13, 19, 25, 27, 30, 32, 35 (same) 64. Pg : odd, (Second Fundamental Thm, MVT) 65. Pg : 1, 3, 7, 11, 13, 19, 21, 25, 29, 31, 33, 39 (u-sub and definite integrals) 66. Pg : 13, 7, 11, 15, 19, 21, 31, 33, 37, 41, 43 (Motion revisited) 67. Pg : 5, 9, 13, 17, 23, 35, 39, 45 (same) 68. Pg : 49-52, 53, 55 (Average value) 69. Worksheet on 2nd Fundamental Theorem, MVT, Average Value (if needed) 70. Pg : 7, 9(a, b), 11, 13, 19, 21, 27, 29, 33, 37, 39, 41, 45, 49 (Chapter review) Turn over for answers not in the back of the book.
5 AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTER Pg : 1, 3, 7, 9, 11, 17, 23, 25, 31 (area between curves) 72. Pg : 5, 8, 12, 14, 16, , 26, 30 (same) 73. Worksheet on Volumes by Cross-sections 74. Worksheet on Volumes by Cross-sections (if needed) 75. Pg : 1, 9, 13, 23, 29, 31, 33 (volumes by discs and washers) 76. Pg : 3, 7, 11, 15, 25, 27, 35 (same) 77. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 9, 13, 15, 17 (volume by shells) 78. Pg : 2, 4, 7, 11, 16, 18, 19 (same) 79. Pg : 3, 6, 7, 18, 19, 20 (chapter review)
6 AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTER Pg : 1c, 3, 11, 13, 15, 21, 23, 25, 35, 37, 43, 45, 53 (function inverses/derivative) 81. Pg : 9, 12, 17, 24, 27, 29, 30, 31, 38, 39, 41, 47 (same) 82. Pg : 1-35 odd, 43 (properties of logarithms/exponential functions) 83. Pg : 2, 6, even, 48 (same) 84. Pg : 1-17 odd, 31, 33, 35, 43, 49, 57 (derivatives of log fnctns/y=ln(u)) 85. Worksheet on integrals of the form du/u: 1-19 odd, 25, 27, 31, Pg : odd, 39, 41, 55, odd (exp functions --derivatives and integrals) 87. Pg : 8, 14, 26, 37, 59, 61, odd (Review of deriv/int of exp/log functions) 88. Worksheet on Review of deriv/int of exp/log functions (if needed) 89. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 11, 15, 19, 27, 29, 35, 39, 43 (graphs of exp/log functions) 90. Pg : 7, 9, 17, 37, 40, 42, 45, 47, 49, 57, 59 (same) 91. Pg : 3, 7, odd, 27, 29, 31, 39, 43 (functions as integrals/review 2nd fund. thm) 92. Pg : 1, 3, 5, 7(do by sep. only), 15, odd (differential equations) 93. Pg : 2, 4, 8(by sep. only), 17, 29, 31, 41, 55 (same) 94. Pg : 1-9 odd, 19 (Slope Fields) Do not write in book. These pages are on a handout. 95. Pg : 3-11 odd, 23 (exponential growth/decay) 96. Pg : 3, 5, 13, 15, odd Pg : 13, 15, 27
7 AP CALCULUS AB - Miscellaneous Chapters/Topics 97. Pg : 1-13 odd, 55, 57 (inverse trig functions) 98. Pg : 2-12 even, 11, 61 (same) 99. Pg : odd, 73 (derivatives inverse trig) 100. Pg : odd, 49, 51, 53, 63, 65, 71 (anti-derivatives inverse trig) 101. Pg. 526: 1-29 odd (Integration techniques) 102. Pg : 1, 5, 9, 11, 15, 19, 25, 33, 37, 47 (integration by parts) 103. Pg : 3, 13, 17, 23, 29, 35, 39, 49, 51 (same) 104. Pg : 1-23 odd, 39, 49 (L Hopital s rule for 0/0, / )
8 105. L Hopital Worksheet: 1-29 odd, 41, Exp/Log Worksheet: 1, 5-17 odd, 22, 35, 43, 47, 49 AP CALCULUS AB - AFTER AP EXAM 107: Same Worksheet: 21, 23, 33, 51, 55, 59, 67, 75, 81, 84, Differential Equation Worksheet: 1, 7, 17, 25, odd, 43, 47, 49, 51, 55, 59, Growth/Decay Worksheet: 1-9 odd, 13, 15, Inverse Trig Worksheet 1: 1-47 every other odd Worksheet 2: 7, 11, 13, 15, odd 111. Inverse Trig Derivatives/Integrals Worksheet: 1-43 odd 112. Integration Techniques Worksheet: 1-63 every other odd, 71, 77, : Same worksheet: 3-65 every other odd, 75, 81, Integration by Parts Worksheet: 1-33 odd
HW#02 (18 pts): All recommended exercises from JIT (1 pt/problem)
 Spring 2011 MthSc103 Course Calendar Page 1 of 7 January W 12 Syllabus/Course Policies BST Review Th 13 Basic Skills Test F 14 JIT 1.1 1.3: Numbers, Fractions, Parentheses JIT 1.1: 2, 6, 8, 9 JIT 1.2:
Spring 2011 MthSc103 Course Calendar Page 1 of 7 January W 12 Syllabus/Course Policies BST Review Th 13 Basic Skills Test F 14 JIT 1.1 1.3: Numbers, Fractions, Parentheses JIT 1.1: 2, 6, 8, 9 JIT 1.2:
MAT 140 SYLLABUS - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND CALCULUS I
 MAT 140 SYLLABUS - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND CALCULUS I ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. Catalog Description: 140-04 Analytic Geometry and Calculus I (Fall 2010) Analytic geometry, functions, limits, derivatives and
MAT 140 SYLLABUS - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND CALCULUS I ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. Catalog Description: 140-04 Analytic Geometry and Calculus I (Fall 2010) Analytic geometry, functions, limits, derivatives and
Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs
 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Accelerated Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Accelerated Pre-Calculus Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Mr. Niedert 1 / 24 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 1 Logarithmic
Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Accelerated Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Accelerated Pre-Calculus Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Mr. Niedert 1 / 24 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 1 Logarithmic
Math Lecture 2 Inverse Functions & Logarithms
 Math 1060 Lecture 2 Inverse Functions & Logarithms Outline Summary of last lecture Inverse Functions Domain, codomain, and range One-to-one functions Inverse functions Inverse trig functions Logarithms
Math 1060 Lecture 2 Inverse Functions & Logarithms Outline Summary of last lecture Inverse Functions Domain, codomain, and range One-to-one functions Inverse functions Inverse trig functions Logarithms
Pre-Calculus. Riemann Sums. Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163. Slide 3 / 163. Slide 4 / 163. Slide 5 / 163. Slide 6 / 163. Intro to Integrals
 Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163 Pre-alculus Intro to Integrals 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 163 Table of ontents Riemann Sums Trapezoid Rule ccumulation Function & efinite Integrals Fundamental Theorem
Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163 Pre-alculus Intro to Integrals 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 163 Table of ontents Riemann Sums Trapezoid Rule ccumulation Function & efinite Integrals Fundamental Theorem
Honors Algebra 2 Assignment Sheet - Chapter 1
 Assignment Sheet - Chapter 1 #01: Read the text and the examples in your book for the following sections: 1.1, 1., and 1.4. Be sure you read and understand the handshake problem. Also make sure you copy
Assignment Sheet - Chapter 1 #01: Read the text and the examples in your book for the following sections: 1.1, 1., and 1.4. Be sure you read and understand the handshake problem. Also make sure you copy
Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.
 MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
Algebra I CC Exam Review #1 H o2m0b1l3v 7KRu9tmal NSIoffrtGwaafrKeB 5LZLhCe.h m na3ldll 3rPiagBhlt8sm 4rEe0sPevr3vKe6dR.S. y x y. ( k ) ( 10) ( ) ( )
 -1-5 b2e0r143a qkxustsah YS3ogfrtFwiazr9e3 BLjLPCQ.W R paslllj LrkiTgphqtysN drzeosqegrqvcezdj.o I YMOaPdyev LwhiVtthR AINnXfriknHirtleD famlwgue4bsryas e2r.j Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC Algebra I CC
-1-5 b2e0r143a qkxustsah YS3ogfrtFwiazr9e3 BLjLPCQ.W R paslllj LrkiTgphqtysN drzeosqegrqvcezdj.o I YMOaPdyev LwhiVtthR AINnXfriknHirtleD famlwgue4bsryas e2r.j Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC Algebra I CC
MATH 105: Midterm #1 Practice Problems
 Name: MATH 105: Midterm #1 Practice Problems 1. TRUE or FALSE, plus explanation. Give a full-word answer TRUE or FALSE. If the statement is true, explain why, using concepts and results from class to justify
Name: MATH 105: Midterm #1 Practice Problems 1. TRUE or FALSE, plus explanation. Give a full-word answer TRUE or FALSE. If the statement is true, explain why, using concepts and results from class to justify
171S5.4p Properties of Logarithmic Functions. November 20, CHAPTER 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Examples. Express as a product.
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 5.1 Inverse Functions 5.2 Exponential Functions and Graphs 5.3 Logarithmic Functions
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 5.1 Inverse Functions 5.2 Exponential Functions and Graphs 5.3 Logarithmic Functions
S56 (5.1) Logs and Exponentials.notebook October 14, 2016
 1. Daily Practice 21.9.2016 Exponential Functions Today we will be learning about exponential functions. A function of the form y = a x is called an exponential function with the base 'a' where a 0. y
1. Daily Practice 21.9.2016 Exponential Functions Today we will be learning about exponential functions. A function of the form y = a x is called an exponential function with the base 'a' where a 0. y
Review Sheet for Math 230, Midterm exam 2. Fall 2006
 Review Sheet for Math 230, Midterm exam 2. Fall 2006 October 31, 2006 The second midterm exam will take place: Monday, November 13, from 8:15 to 9:30 pm. It will cover chapter 15 and sections 16.1 16.4,
Review Sheet for Math 230, Midterm exam 2. Fall 2006 October 31, 2006 The second midterm exam will take place: Monday, November 13, from 8:15 to 9:30 pm. It will cover chapter 15 and sections 16.1 16.4,
MATH 20C: FUNDAMENTALS OF CALCULUS II FINAL EXAM
 MATH 2C: FUNDAMENTALS OF CALCULUS II FINAL EXAM Name Please circle the answer to each of the following problems. You may use an approved calculator. Each multiple choice problem is worth 2 points.. Multiple
MATH 2C: FUNDAMENTALS OF CALCULUS II FINAL EXAM Name Please circle the answer to each of the following problems. You may use an approved calculator. Each multiple choice problem is worth 2 points.. Multiple
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.3 Properties of Logarithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use the change-of-base
5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.3 Properties of Logarithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use the change-of-base
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Properties of Logarithms
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Properties of Logarithms
CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES
 CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 1. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES A) Definition: A function of two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair of real numbers (x,y) in a set D a unique real number
CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 1. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES A) Definition: A function of two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair of real numbers (x,y) in a set D a unique real number
Section 15.3 Partial Derivatives
 Section 5.3 Partial Derivatives Differentiating Functions of more than one Variable. Basic Definitions In single variable calculus, the derivative is defined to be the instantaneous rate of change of a
Section 5.3 Partial Derivatives Differentiating Functions of more than one Variable. Basic Definitions In single variable calculus, the derivative is defined to be the instantaneous rate of change of a
Math 122: Final Exam Review Sheet
 Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
constant EXAMPLE #4:
 Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW
 PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
Aim #35.1: How do we graph using a table?
 A) Take out last night's homework Worksheet - Aim 34.2 B) Copy down tonight's homework Finish aim 35.1 Aim #35.1: How do we graph using a table? C) Plot the following points... a) (-3, 5) b) (4, -2) c)
A) Take out last night's homework Worksheet - Aim 34.2 B) Copy down tonight's homework Finish aim 35.1 Aim #35.1: How do we graph using a table? C) Plot the following points... a) (-3, 5) b) (4, -2) c)
2.1 Partial Derivatives
 .1 Partial Derivatives.1.1 Functions of several variables Up until now, we have only met functions of single variables. From now on we will meet functions such as z = f(x, y) and w = f(x, y, z), which
.1 Partial Derivatives.1.1 Functions of several variables Up until now, we have only met functions of single variables. From now on we will meet functions such as z = f(x, y) and w = f(x, y, z), which
Lecture 19 - Partial Derivatives and Extrema of Functions of Two Variables
 Lecture 19 - Partial Derivatives and Extrema of Functions of Two Variables 19.1 Partial Derivatives We wish to maximize functions of two variables. This will involve taking derivatives. Example: Consider
Lecture 19 - Partial Derivatives and Extrema of Functions of Two Variables 19.1 Partial Derivatives We wish to maximize functions of two variables. This will involve taking derivatives. Example: Consider
Exam 2 Review Sheet. r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t)
 Exam 2 Review Sheet Joseph Breen Particle Motion Recall that a parametric curve given by: r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) can be interpreted as the position of a particle. Then the derivative represents the particle
Exam 2 Review Sheet Joseph Breen Particle Motion Recall that a parametric curve given by: r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) can be interpreted as the position of a particle. Then the derivative represents the particle
Exam 2 Summary. 1. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputes of the function and the range is the set of all outputs.
 Exam 2 Summary Disclaimer: The exam 2 covers lectures 9-15, inclusive. This is mostly about limits, continuity and differentiation of functions of 2 and 3 variables, and some applications. The complete
Exam 2 Summary Disclaimer: The exam 2 covers lectures 9-15, inclusive. This is mostly about limits, continuity and differentiation of functions of 2 and 3 variables, and some applications. The complete
14.2 Limits and Continuity
 14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
5.1N Key Features of Rational Functions
 5.1N Key Features of Rational Functions A. Vocabulary Review Domain: Range: x-intercept: y-intercept: Increasing: Decreasing: Constant: Positive: Negative: Maximum: Minimum: Symmetry: End Behavior/Limits:
5.1N Key Features of Rational Functions A. Vocabulary Review Domain: Range: x-intercept: y-intercept: Increasing: Decreasing: Constant: Positive: Negative: Maximum: Minimum: Symmetry: End Behavior/Limits:
Section 14.3 Partial Derivatives
 Section 14.3 Partial Derivatives Ruipeng Shen March 20 1 Basic Conceptions If f(x, y) is a function of two variables x and y, suppose we let only x vary while keeping y fixed, say y = b, where b is a constant.
Section 14.3 Partial Derivatives Ruipeng Shen March 20 1 Basic Conceptions If f(x, y) is a function of two variables x and y, suppose we let only x vary while keeping y fixed, say y = b, where b is a constant.
Unit 7 Partial Derivatives and Optimization
 Unit 7 Partial Derivatives and Optimization We have learned some important applications of the ordinary derivative in finding maxima and minima. We now move on to a topic called partial derivatives which
Unit 7 Partial Derivatives and Optimization We have learned some important applications of the ordinary derivative in finding maxima and minima. We now move on to a topic called partial derivatives which
Page 1 of 52 Youtube.com/c/StayLearningNewdelhi
 Page 1 of 52 www.vijayadarsh.com Youtube.com/c/StayLearningNewdelhi Contact@vijayAdarsh.com +919268373738 About StayLearning StayLearning (a Division of AASS) believes in educating their students with
Page 1 of 52 www.vijayadarsh.com Youtube.com/c/StayLearningNewdelhi Contact@vijayAdarsh.com +919268373738 About StayLearning StayLearning (a Division of AASS) believes in educating their students with
THE DOMAIN AND RANGE OF A FUNCTION Basically, all functions do is convert inputs into outputs.
 THE DOMAIN AND RANGE OF A FUNCTION Basically, all functions do is convert inputs into outputs. Exercise #1: Consider the function y = f (x) shown on the graph below. (a) Evaluate each of the following:
THE DOMAIN AND RANGE OF A FUNCTION Basically, all functions do is convert inputs into outputs. Exercise #1: Consider the function y = f (x) shown on the graph below. (a) Evaluate each of the following:
Calculus II Fall 2014
 Calculus II Fall 2014 Lecture 3 Partial Derivatives Eitan Angel University of Colorado Monday, December 1, 2014 E. Angel (CU) Calculus II 1 Dec 1 / 13 Introduction Much of the calculus of several variables
Calculus II Fall 2014 Lecture 3 Partial Derivatives Eitan Angel University of Colorado Monday, December 1, 2014 E. Angel (CU) Calculus II 1 Dec 1 / 13 Introduction Much of the calculus of several variables
Radical Expressions and Graph (7.1) EXAMPLE #1: EXAMPLE #2: EXAMPLE #3: Find roots of numbers (Objective #1) Figure #1:
 Radical Expressions and Graph (7.1) Find roots of numbers EXAMPLE #1: Figure #1: Find principal (positive) roots EXAMPLE #2: Find n th roots of n th powers (Objective #3) EXAMPLE #3: Figure #2: 7.1 Radical
Radical Expressions and Graph (7.1) Find roots of numbers EXAMPLE #1: Figure #1: Find principal (positive) roots EXAMPLE #2: Find n th roots of n th powers (Objective #3) EXAMPLE #3: Figure #2: 7.1 Radical
Lesson Plans Week #19, to Monday 7.3 Special Right Triangles 7.7 Positive Rational Roots
 Lesson Plans Week #19, 1-25-16 to 1-29-16 Monday 7.3 Special Right Triangles 7.7 Positive Rational Roots Tuesday 7.4 Trigonometry 7.8 Negative Rational Roots Wednesday 7.4 More on Trigonometry Ch. 7 pretest
Lesson Plans Week #19, 1-25-16 to 1-29-16 Monday 7.3 Special Right Triangles 7.7 Positive Rational Roots Tuesday 7.4 Trigonometry 7.8 Negative Rational Roots Wednesday 7.4 More on Trigonometry Ch. 7 pretest
Definitions and claims functions of several variables
 Definitions and claims functions of several variables In the Euclidian space I n of all real n-dimensional vectors x = (x 1, x,..., x n ) the following are defined: x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x + y,..., x n +
Definitions and claims functions of several variables In the Euclidian space I n of all real n-dimensional vectors x = (x 1, x,..., x n ) the following are defined: x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x + y,..., x n +
Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Math 150 c Lynch 1 of 6 Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions Definition. Let a be any positive number not equal to 1. The logarithm of x to the base a is y if and only if a y = x. The number y is denoted
Math 150 c Lynch 1 of 6 Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions Definition. Let a be any positive number not equal to 1. The logarithm of x to the base a is y if and only if a y = x. The number y is denoted
Trigonometry. An Overview of Important Topics
 Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Similarly, the point marked in red below is a local minimum for the function, since there are no points nearby that are lower than it:
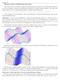 Extreme Values of Multivariate Functions Our next task is to develop a method for determining local extremes of multivariate functions, as well as absolute extremes of multivariate functions on closed
Extreme Values of Multivariate Functions Our next task is to develop a method for determining local extremes of multivariate functions, as well as absolute extremes of multivariate functions on closed
NEW Published in June 2018 CATALOGUE 2019
 NEW Published in June 2018 CATALOGUE 2019 PASS PUBLICATIONS PRIVATE ACADEMIC AND SCIENTIFIC STUDIES LIMITED passpublications.uk@gmail.com +44(0)20 8857 4752 P A S S PUBLICATIONS PASS is an acronym for
NEW Published in June 2018 CATALOGUE 2019 PASS PUBLICATIONS PRIVATE ACADEMIC AND SCIENTIFIC STUDIES LIMITED passpublications.uk@gmail.com +44(0)20 8857 4752 P A S S PUBLICATIONS PASS is an acronym for
The 21 st Century Wireless Classroom Network for AP Calculus
 The 21 st Century Wireless Classroom Network for AP Calculus In this exploratory hands-on workshop, we will be solving Calculus problems with the HP Prime Graphing Calculator and the HP Wireless Classroom
The 21 st Century Wireless Classroom Network for AP Calculus In this exploratory hands-on workshop, we will be solving Calculus problems with the HP Prime Graphing Calculator and the HP Wireless Classroom
4 to find the dimensions of the rectangle that have the maximum area. 2y A =?? f(x, y) = (2x)(2y) = 4xy
 Optimization Constrained optimization and Lagrange multipliers Constrained optimization is what it sounds like - the problem of finding a maximum or minimum value (optimization), subject to some other
Optimization Constrained optimization and Lagrange multipliers Constrained optimization is what it sounds like - the problem of finding a maximum or minimum value (optimization), subject to some other
[f(t)] 2 + [g(t)] 2 + [h(t)] 2 dt. [f(u)] 2 + [g(u)] 2 + [h(u)] 2 du. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus implies that s(t) is differentiable and
![[f(t)] 2 + [g(t)] 2 + [h(t)] 2 dt. [f(u)] 2 + [g(u)] 2 + [h(u)] 2 du. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus implies that s(t) is differentiable and [f(t)] 2 + [g(t)] 2 + [h(t)] 2 dt. [f(u)] 2 + [g(u)] 2 + [h(u)] 2 du. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus implies that s(t) is differentiable and](/thumbs/92/108353356.jpg) Midterm 2 review Math 265 Fall 2007 13.3. Arc Length and Curvature. Assume that the curve C is described by the vector-valued function r(r) = f(t), g(t), h(t), and that C is traversed exactly once as t
Midterm 2 review Math 265 Fall 2007 13.3. Arc Length and Curvature. Assume that the curve C is described by the vector-valued function r(r) = f(t), g(t), h(t), and that C is traversed exactly once as t
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Homework 1. Table 1: 11.1:8 t x y
 MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2 Homework Section., pg. 692: 8, 24, 43. Section.2, pg. 72:, 2 (no graph required), 32, 4. Section.3, pg. 73: 4, 2, 54, 8. Section.4, pg. 79: 6, 35, 46. Solutions.:
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2 Homework Section., pg. 692: 8, 24, 43. Section.2, pg. 72:, 2 (no graph required), 32, 4. Section.3, pg. 73: 4, 2, 54, 8. Section.4, pg. 79: 6, 35, 46. Solutions.:
Intro to Probability Instructor: Alexandre Bouchard
 www.stat.ubc.ca/~bouchard/courses/stat302-sp2017-18/ Intro to Probability Instructor: Alexandre Bouchard Announcements Webwork out Graded midterm available after lecture Regrading policy IF you would like
www.stat.ubc.ca/~bouchard/courses/stat302-sp2017-18/ Intro to Probability Instructor: Alexandre Bouchard Announcements Webwork out Graded midterm available after lecture Regrading policy IF you would like
Properties of Logarithms
 Properties of Logarithms Accelerated Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Accelerated Pre-Calculus Properties of Logarithms Mr. Niedert 1 / 14 Properties of Logarithms 1 Change-of-Base Formula Accelerated Pre-Calculus
Properties of Logarithms Accelerated Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Accelerated Pre-Calculus Properties of Logarithms Mr. Niedert 1 / 14 Properties of Logarithms 1 Change-of-Base Formula Accelerated Pre-Calculus
Logs and Exponentials Higher.notebook February 26, Daily Practice
 Daily Practice 2.2.2015 Daily Practice 3.2.2015 Today we will be learning about exponential functions and logs. Homework due! Need to know for Unit Test 2: Expressions and Functions Adding and subtracng
Daily Practice 2.2.2015 Daily Practice 3.2.2015 Today we will be learning about exponential functions and logs. Homework due! Need to know for Unit Test 2: Expressions and Functions Adding and subtracng
2. Be able to evaluate a trig function at a particular degree measure. Example: cos. again, just use the unit circle!
 Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Logarithms. Since perhaps it s been a while, calculate a few logarithms just to warm up.
 Logarithms Since perhaps it s been a while, calculate a few logarithms just to warm up. 1. Calculate the following. (a) log 3 (27) = (b) log 9 (27) = (c) log 3 ( 1 9 ) = (d) ln(e 3 ) = (e) log( 100) =
Logarithms Since perhaps it s been a while, calculate a few logarithms just to warm up. 1. Calculate the following. (a) log 3 (27) = (b) log 9 (27) = (c) log 3 ( 1 9 ) = (d) ln(e 3 ) = (e) log( 100) =
Calculus 3 Exam 2 31 October 2017
 Calculus 3 Exam 2 31 October 2017 Name: Instructions: Be sure to read each problem s directions. Write clearly during the exam and fully erase or mark out anything you do not want graded. You may use your
Calculus 3 Exam 2 31 October 2017 Name: Instructions: Be sure to read each problem s directions. Write clearly during the exam and fully erase or mark out anything you do not want graded. You may use your
Math 210: 1, 2 Calculus III Spring 2008
 Math 210: 1, 2 Calculus III Spring 2008 Professor: Pete Goetz CRN: 20128/20130 Office: BSS 358 Office Hours: Tuesday 4-5, Wednesday 1-2, Thursday 3-4, Friday 8-9, and by appointment. Phone: 826-3926 Email:
Math 210: 1, 2 Calculus III Spring 2008 Professor: Pete Goetz CRN: 20128/20130 Office: BSS 358 Office Hours: Tuesday 4-5, Wednesday 1-2, Thursday 3-4, Friday 8-9, and by appointment. Phone: 826-3926 Email:
Functions of several variables
 Chapter 6 Functions of several variables 6.1 Limits and continuity Definition 6.1 (Euclidean distance). Given two points P (x 1, y 1 ) and Q(x, y ) on the plane, we define their distance by the formula
Chapter 6 Functions of several variables 6.1 Limits and continuity Definition 6.1 (Euclidean distance). Given two points P (x 1, y 1 ) and Q(x, y ) on the plane, we define their distance by the formula
Comparing Exponential and Logarithmic Rules
 Name _ Date Period Comparing Exponential and Logarithmic Rules Task : Looking closely at exponential and logarithmic patterns ) In a prior lesson you graphed and then compared an exponential function with
Name _ Date Period Comparing Exponential and Logarithmic Rules Task : Looking closely at exponential and logarithmic patterns ) In a prior lesson you graphed and then compared an exponential function with
18 Logarithmic Functions
 18 Logarithmic Functions Concepts: Logarithms (Section 3.3) Logarithms as Functions Logarithms as Exponent Pickers Inverse Relationship between Logarithmic and Exponential Functions. The Common Logarithm
18 Logarithmic Functions Concepts: Logarithms (Section 3.3) Logarithms as Functions Logarithms as Exponent Pickers Inverse Relationship between Logarithmic and Exponential Functions. The Common Logarithm
Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry
 Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry Course Numbers 1206330, 1211300 Lake County School Curriculum Map Released 2010-2011 Page 1 of 33 PREFACE Teams of Lake County teachers created the curriculum maps in order
Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry Course Numbers 1206330, 1211300 Lake County School Curriculum Map Released 2010-2011 Page 1 of 33 PREFACE Teams of Lake County teachers created the curriculum maps in order
Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths. Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project
 Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Authors: Free
Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Authors: Free
College Pre-Calc Lesson Plans
 January 4-8 January 11-15 January 18-22 January 25-29 Sections 9.2 Area of a Triangle Mixed Trig Exercises Section 14.1 Matrix Addition & Scalar Multiplication Section 14.5 Transition Pg 342: 1, 3, 7-13,
January 4-8 January 11-15 January 18-22 January 25-29 Sections 9.2 Area of a Triangle Mixed Trig Exercises Section 14.1 Matrix Addition & Scalar Multiplication Section 14.5 Transition Pg 342: 1, 3, 7-13,
Outcome 9 Review Foundations and Pre-Calculus 10
 Outcome 9 Review Foundations and Pre-Calculus 10 Level 2 Example: Writing an equation in slope intercept form Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + b m = slope b = y-intercept Ex : Write the equation of a line
Outcome 9 Review Foundations and Pre-Calculus 10 Level 2 Example: Writing an equation in slope intercept form Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + b m = slope b = y-intercept Ex : Write the equation of a line
i + u 2 j be the unit vector that has its initial point at (a, b) and points in the desired direction. It determines a line in the xy-plane:
 1 Directional Derivatives and Gradients Suppose we need to compute the rate of change of f(x, y) with respect to the distance from a point (a, b) in some direction. Let u = u 1 i + u 2 j be the unit vector
1 Directional Derivatives and Gradients Suppose we need to compute the rate of change of f(x, y) with respect to the distance from a point (a, b) in some direction. Let u = u 1 i + u 2 j be the unit vector
Study Guide and Review - Chapter 3. Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the graph of each linear function.
 Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the graph of each linear function. 11. The x-intercept is the point at which the y-coordinate is 0, or the line crosses the x-axis. So, the x-intercept is 8. The
Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the graph of each linear function. 11. The x-intercept is the point at which the y-coordinate is 0, or the line crosses the x-axis. So, the x-intercept is 8. The
the input values of a function. These are the angle values for trig functions
 SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
 The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
Perry High School. Algebra 2: Week 9. Note: Don t forget to read the sections before or after we cover them. Also, don t forget the website.
 Algebra 2: Week 9 Monday: 2.8 Absolute Value Functions Tuesday: 2.8 Work Day Wednesday: Review Exam 2, Day 1 Thursday: Professional Day, NO SCHOOL Friday: Fall Break? NO SCHOOL Note: Don t forget to read
Algebra 2: Week 9 Monday: 2.8 Absolute Value Functions Tuesday: 2.8 Work Day Wednesday: Review Exam 2, Day 1 Thursday: Professional Day, NO SCHOOL Friday: Fall Break? NO SCHOOL Note: Don t forget to read
Algebra 2/Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & 2: Trigonometry Mega-Session. The Unit Circle
 Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
The Chain Rule, Higher Partial Derivatives & Opti- mization
 The Chain Rule, Higher Partial Derivatives & Opti- Unit #21 : mization Goals: We will study the chain rule for functions of several variables. We will compute and study the meaning of higher partial derivatives.
The Chain Rule, Higher Partial Derivatives & Opti- Unit #21 : mization Goals: We will study the chain rule for functions of several variables. We will compute and study the meaning of higher partial derivatives.
S56 (5.3) Logs and Exponentials.notebook March 02, 2016
 Daily Practice 22.2.206 Today we will be learning about exponential and logarithmic functions. Homework due tomorrow. Need to know for Unit Test 2: Expressions and Functions Adding and subtracng logs,
Daily Practice 22.2.206 Today we will be learning about exponential and logarithmic functions. Homework due tomorrow. Need to know for Unit Test 2: Expressions and Functions Adding and subtracng logs,
Graphing Exponential Functions Answer Key Algebra 2
 Graphing Answer Key Algebra 2 Free PDF ebook Download: Graphing Answer Key Algebra 2 Download or Read Online ebook graphing exponential functions answer key algebra 2 in PDF Format From The Best User Guide
Graphing Answer Key Algebra 2 Free PDF ebook Download: Graphing Answer Key Algebra 2 Download or Read Online ebook graphing exponential functions answer key algebra 2 in PDF Format From The Best User Guide
Instructor Notes for Chapter 4
 Section 4.1 One to One Functions (Day 1) Instructor Notes for Chapter 4 Understand that an inverse relation undoes the original Understand why the line y = xis a line of symmetry for the graphs of relations
Section 4.1 One to One Functions (Day 1) Instructor Notes for Chapter 4 Understand that an inverse relation undoes the original Understand why the line y = xis a line of symmetry for the graphs of relations
You could identify a point on the graph of a function as (x,y) or (x, f(x)). You may have only one function value for each x number.
 Function Before we review exponential and logarithmic functions, let's review the definition of a function and the graph of a function. A function is just a rule. The rule links one number to a second
Function Before we review exponential and logarithmic functions, let's review the definition of a function and the graph of a function. A function is just a rule. The rule links one number to a second
Arkansas Council of Teachers of Mathematics Regional Algebra I Contest March 3, 2012
 Arkansas Council of Teachers of Mathematics Regional Algebra I Contest March 3, 2012 For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. Make sure that any erasures are cleanly
Arkansas Council of Teachers of Mathematics Regional Algebra I Contest March 3, 2012 For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. Make sure that any erasures are cleanly
Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions
 Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions 7.1 Cycles and Sine Functions Data that is periodic may often be modeled by trigonometric functions. This chapter will help you use Excel to deal with periodic
Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions 7.1 Cycles and Sine Functions Data that is periodic may often be modeled by trigonometric functions. This chapter will help you use Excel to deal with periodic
Absolute Value of Linear Functions
 Lesson Plan Lecture Version Absolute Value of Linear Functions Objectives: Students will: Discover how absolute value affects linear functions. Prerequisite Knowledge Students are able to: Graph linear
Lesson Plan Lecture Version Absolute Value of Linear Functions Objectives: Students will: Discover how absolute value affects linear functions. Prerequisite Knowledge Students are able to: Graph linear
REVIEW SHEET FOR MIDTERM 2: ADVANCED
 REVIEW SHEET FOR MIDTERM : ADVANCED MATH 195, SECTION 59 (VIPUL NAIK) To maximize efficiency, please bring a copy (print or readable electronic) of this review sheet to the review session. The document
REVIEW SHEET FOR MIDTERM : ADVANCED MATH 195, SECTION 59 (VIPUL NAIK) To maximize efficiency, please bring a copy (print or readable electronic) of this review sheet to the review session. The document
GETTING STARTED Have students work in pairs to help determine what points should be plotted and to facilitate discussion of the questions.
 High School/College Example taken from the: Casio PRIZM Lesson Sampler #101 TEACHER S NOTES Area Under A Bridge TOPIC ArEA: Curve fitting to image NCTM STaNdardS: n Create and use representations to organize,
High School/College Example taken from the: Casio PRIZM Lesson Sampler #101 TEACHER S NOTES Area Under A Bridge TOPIC ArEA: Curve fitting to image NCTM STaNdardS: n Create and use representations to organize,
14.4. Tangent Planes. Tangent Planes. Tangent Planes. Tangent Planes. Partial Derivatives. Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations
 14 Partial Derivatives 14.4 and Linear Approximations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Suppose a surface S has equation z = f(x, y), where
14 Partial Derivatives 14.4 and Linear Approximations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Suppose a surface S has equation z = f(x, y), where
POLAR FUNCTIONS. In Precalculus students should have learned to:.
 POLAR FUNCTIONS From the AP Calculus BC Course Description, students in Calculus BC are required to know: The analsis of planar curves, including those given in polar form Derivatives of polar functions
POLAR FUNCTIONS From the AP Calculus BC Course Description, students in Calculus BC are required to know: The analsis of planar curves, including those given in polar form Derivatives of polar functions
Honors Algebra 2 w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals
 Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Algebra Adventure Directions. Format: Individual or Pairs (works best)
 Algebra Adventure Directions Format: Individual or Pairs (works best) Directions: Each student will receive an Algebra Adventure WS that they will keep track of their stations and work. Each pair will
Algebra Adventure Directions Format: Individual or Pairs (works best) Directions: Each student will receive an Algebra Adventure WS that they will keep track of their stations and work. Each pair will
Lesson 8. Diana Pell. Monday, January 27
 Lesson 8 Diana Pell Monday, January 27 Section 5.2: Continued Richter scale is a logarithmic scale used to express the total amount of energy released by an earthquake. The Richter scale gives the magnitude
Lesson 8 Diana Pell Monday, January 27 Section 5.2: Continued Richter scale is a logarithmic scale used to express the total amount of energy released by an earthquake. The Richter scale gives the magnitude
Sect 4.5 Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function
 71 Sect 4. Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function Objective #0: Solving Inequalities using a graph Use the graph to the right to find the following: Ex. 1 a) Find the intervals where f(x) > 0. b) Find
71 Sect 4. Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function Objective #0: Solving Inequalities using a graph Use the graph to the right to find the following: Ex. 1 a) Find the intervals where f(x) > 0. b) Find
Tennessee Senior Bridge Mathematics
 A Correlation of to the Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-130-10 A Correlation of, to the Mathematics Standards Mathematics Standards I. Ways of Looking: Revisiting Concepts
A Correlation of to the Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-130-10 A Correlation of, to the Mathematics Standards Mathematics Standards I. Ways of Looking: Revisiting Concepts
Section 2.3 Task List
 Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Use the Point-Slope Form to Write the Equation of a Line
 Math 90 8.3 "Writing Equations of Lines" Objectives: * Use the point-slope form to write the equation of a line. * Use the slope-intercept form to write the equation of a line. * Use slope as an aid when
Math 90 8.3 "Writing Equations of Lines" Objectives: * Use the point-slope form to write the equation of a line. * Use the slope-intercept form to write the equation of a line. * Use slope as an aid when
Higher. Expressions & Functions. Unit 2 Course Contents. Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher. Higher Higher. Higher Higher. Higher Higher.
 Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher xpressions & unctions Unit 2 Course Contents Higher
Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher Higher xpressions & unctions Unit 2 Course Contents Higher
LEIBNIZ INDIFFERENCE CURVES AND THE MARGINAL RATE OF SUBSTITUTION
 3.2.1 INDIFFERENCE CURVES AND THE MARGINAL RATE OF SUBSTITUTION Alexei cares about his exam grade and his free time. We have seen that his preferences can be represented graphically using indifference
3.2.1 INDIFFERENCE CURVES AND THE MARGINAL RATE OF SUBSTITUTION Alexei cares about his exam grade and his free time. We have seen that his preferences can be represented graphically using indifference
WARM UP. 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) Factor the expression x 2 2x Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing.
 WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
MAT187H1F Lec0101 Burbulla
 Spring 17 What Is A Parametric Curve? y P(x, y) x 1. Let a point P on a curve have Cartesian coordinates (x, y). We can think of the curve as being traced out as the point P moves along it. 3. In this
Spring 17 What Is A Parametric Curve? y P(x, y) x 1. Let a point P on a curve have Cartesian coordinates (x, y). We can think of the curve as being traced out as the point P moves along it. 3. In this
Geometry Chapter 8 8-5: USE PROPERTIES OF TRAPEZOIDS AND KITES
 Geometry Chapter 8 8-5: USE PROPERTIES OF TRAPEZOIDS AND KITES Use Properties of Trapezoids and Kites Objective: Students will be able to identify and use properties to solve trapezoids and kites. Agenda
Geometry Chapter 8 8-5: USE PROPERTIES OF TRAPEZOIDS AND KITES Use Properties of Trapezoids and Kites Objective: Students will be able to identify and use properties to solve trapezoids and kites. Agenda
Math 148 Exam III Practice Problems
 Math 48 Exam III Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 48 Exam III Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Mathematics (Project Maths Phase 2)
 013. M7 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate Examination 013 Mathematics (Project Maths Phase ) Paper 1 Ordinary Level Friday 7 June Afternoon :00 4:30 300 marks
013. M7 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate Examination 013 Mathematics (Project Maths Phase ) Paper 1 Ordinary Level Friday 7 June Afternoon :00 4:30 300 marks
Double Integrals over More General Regions
 Jim Lambers MAT 8 Spring Semester 9-1 Lecture 11 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1. in Stewart and Sections 5.3 and 5.4 in Marsden and Tromba. ouble Integrals over More General Regions We have
Jim Lambers MAT 8 Spring Semester 9-1 Lecture 11 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1. in Stewart and Sections 5.3 and 5.4 in Marsden and Tromba. ouble Integrals over More General Regions We have
11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Just like functions of a single variable, functions of several variables can have local and global extrema,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Just like functions of a single variable, functions of several variables can have local and global extrema,
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
In Exercises 1-12, graph one cycle of the given function. State the period, amplitude, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.
 0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions 809 0.5. Eercises In Eercises -, graph one ccle of the given function. State the period, amplitude, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.. = sin. = sin.
0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions 809 0.5. Eercises In Eercises -, graph one ccle of the given function. State the period, amplitude, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.. = sin. = sin.
Calculus I Handout: Curves and Surfaces in R 3. 1 Curves in R Curves in R 2 1 of 21
 1. Curves in R 2 1 of 21 Calculus I Handout: Curves and Surfaces in R 3 Up until now, everything we have worked with has been in two dimensions. But we can extend the concepts of calculus to three dimensions
1. Curves in R 2 1 of 21 Calculus I Handout: Curves and Surfaces in R 3 Up until now, everything we have worked with has been in two dimensions. But we can extend the concepts of calculus to three dimensions
Practice problems from old exams for math 233
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Lecture 7: Distortion Analysis
 EECS 142 Lecture 7: Distortion Analysis Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 7
EECS 142 Lecture 7: Distortion Analysis Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 7
Algebra. Maureen Steddin
 Algebra Maureen Steddin table of contents To the Student......................... v Part 1: Introduction.................................... 1 General Approach to Math Questions................... 1 Specific
Algebra Maureen Steddin table of contents To the Student......................... v Part 1: Introduction.................................... 1 General Approach to Math Questions................... 1 Specific
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions. By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
MATH 12 CLASS 9 NOTES, OCT Contents 1. Tangent planes 1 2. Definition of differentiability 3 3. Differentials 4
 MATH 2 CLASS 9 NOTES, OCT 0 20 Contents. Tangent planes 2. Definition of differentiability 3 3. Differentials 4. Tangent planes Recall that the derivative of a single variable function can be interpreted
MATH 2 CLASS 9 NOTES, OCT 0 20 Contents. Tangent planes 2. Definition of differentiability 3 3. Differentials 4. Tangent planes Recall that the derivative of a single variable function can be interpreted

 # %
# %