Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry
|
|
|
- Abel Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry Course Numbers , Lake County School Curriculum Map Released Page 1 of 33
2 PREFACE Teams of Lake County teachers created the curriculum maps in order to ensure that all students throughout the district receive a common curriculum. The maps help ensure that all state requirements are taught and that the content is divided into teachable segments with appropriate pacing. The curriculum maps will guide your instruction but provide flexibility based on the individual needs of students. The maps are living documents and feedback is requested of teachers to ensure continuous improvement. All teachers are expected to use the curriculum maps, in conjunction with data, to drive instruction. The maps were designed for the instruction to take place by quarter. There is some flexibility within the quarters for mastery and re-teaching. The expectation is that teachers will finish the content within each quarter in its entirety. The maps have been structured in such a way as to scaffold student learning. Listed below are a few of the new or updated features common to all curriculum maps: Essential Question(s): o Provide application of the skills/concepts o Have more than one right answer which promotes student discourse o Increase the rigor in the classroom, by changing from teacher-centered to student-centered learning o Are referred to at the beginning, middle, and end of the lesson o Require you to make a decision o Promote critical thinking and problem solving o Encourage interdependence o Are open-ended Academic Vocabulary are: o Unfamiliar vocabulary that are essential to understanding new content within explicit instruction o Not necessarily the bold words in the chapter. o Cumulative and continuously used throughout the year. o Integrated into word walls, a research-based strategy that will facilitate vocabulary acquisition. Common Board Configuration Elements (specific layouts may vary by sites, but must include each of these): Purpose: For the student to know what is being taught and what the student will learn o Date o Benchmark o Measurable, student-friendly objective o Essential Question o Bell work o Agenda (Specific daily schedule) o Homework o Exit Strategy/Card Page 2 of 33
3 Lessons that infuse reading, writing, and discussion are imperative components of every subject area. There should be daily: o Teacher to student and student to student discourse utilizing academic vocabulary. o Reading and authentic writing o Writing that includes higher-order thinking o Incorporation of effective reading and writing instructional strategies Maps are organized to include the following: o o o o Pacing Objective Essential questions, content and understanding, benchmarks, and assessment Appendix/ resources Page 3 of 33
4 Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Math Benchmark Coding Scheme MA. 5. A Subject Grade Level Body of Knowledge Big Idea / Supporting Idea Benchmark Body of Knowledge Key A ~ Algebra G ~ Geometry C ~ Calculus P ~ Probability D ~ Discrete Mathematics S ~ Statistics F ~ Financial Literacy T ~ Trigonometry Language Arts Benchmarks LA The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly. LA The student will use background knowledge of subject and related content areas, prereading strategies (e.g., previewing, discussing, generating questions), text features, and text structure to make and confirm complex predictions of content, purpose, and organization of a reading selection. LA The student will identify cause-and-effect relationships in text. LA The student will prewrite by making a plan for writing that addresses purpose, audience, a controlling idea, logical sequence, and time frame for completion. LA The student will prewrite by using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn Diagram, web story map, plot pyramid) to develop a personal organizational style. LA The student will draft writing by establishing a logical organizational pattern with supporting details that are substantial, specific, and relevant. Page 4 of 33
5 Differentiated Instruction Strategies The following differentiated instruction strategies should be incorporated throughout the entire course: Cooperative Groups Computer Assisted Instruction Tiered Assignments Centers Flexible Grouping Curriculum Compacting/Contracts Learning Stations Scaffolding Hands-on Instruction Leveled Texts/Resources Teacher Led Small Groups Web Quest Page 5 of 33
6 Math Pacing Guide for ANALYTIC GEOMETRY/TRIGONOMETRY First Quarter I. Functions and Graphs (4 weeks) A. Solve various types of equations by factoring, completing the square, and by using powers and roots B. Recognize and graph various types of functions, including polynomial, rational, radical, and absolute value functions (with and without calculators) C. Determine sums, differences, products, and quotients of functions D. Determine composites of functions E. Describe the end behavior of polynomial functions First Quarter Second Quarter II. Logarithmic and Exponential Functions (2 weeks) A. Sketch the graphs for exponential and logarithmic functions B. Identify key features of graphs C. Use the rules of logarithms D. Solve exponential and logarithmic equations E. Solve word problems involving applications of logarithmic and exponential functions III. Conic Sections (2 weeks) A. Sketch graphs and determine equations for conic sections (with and without calculators) B. Write the equations of conic sections in standard form (completing the square and using translations as necessary). C. Determine the type of conic section and its geometric properties (foci, asymptotes, eccentricity, etc.). D. Solve applications involving conic sections Second Quarter IV. Parametric Graphs and Equations (1 week) A. Use parametric equations to sketch graphs, indicating the direction of motion. B. Convert from parametric form to rectangular equations C. Solve applications for parametric equations (with and without calculators) Page 6 of 33
7 Math Pacing Guide for ANALYTIC GEOMETRY/TRIGONOMETRY Third Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter Fourth Quarter V. Trigonometric definitions (2 weeks) A. Sketch angles in standard position using protractors B. Identify direction for angles C. Convert between degree and radian measures. D. Identify reference angles and reference triangles and their quadrants E. Determine sine and cosine using the unit circle. F. Find and use exact values of trigonometric functions for special angles (degree and radian measures). G. Evaluate inverse trigonometric functions H. Determine values for trigonometric ratios using a calculator. VI. Trigonometry and Triangles (1 week) A. Use trigonometric ratios to solve right and oblique triangles B. Solve word problems involving right and oblique triangles, including areas. VII. Trigonometric functions (2 weeks) A. Define and graph trigonometric functions using domain, range, intercepts, period, amplitude, phase shift, vertical shift, and asymptotes. B. Sketch graphs of trigonometric functions using graphing calculator C. Solve word problems involving applications of trigonometric functions D. Sketch graphs for inverse trigonometric functions VIII. Trigonometric Identities and Equations (2 weeks) A. Use the reciprocal, ratio, Pythagorean, sum and difference, and double angle identities. B. Use the basic trigonometric identities to verify other identities and simplify expressions C. Solve trigonometric equations and word problems involving trigonometric equations IX. Polar Coordinates and Complex Numbers (1 week) A. Define polar coordinates and relate polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates B. Represent equations given in rectangular coordinates in terms of polar coordinates. C. Graph equations in the polar coordinate plane. D. Define complex numbers, convert complex numbers to trigonometric form, and multiply complex numbers in trigonometric form. E. Apply DeMoivre s Theorem to operations with complex numbers. X. Vectors (1 week) A. Sketch vectors and perform vector operations B. Solve applications involving vectors Page 7 of 33
8 I. Functions and Graphs 4 weeks Objectives: 1. Analyze features in the graphs for selected types of functions by identifying key features and their locations on the graphs. 2. Organize operations with functions. Vocabulary: domain, polynomial, composite, inverse function, intercept, symmetry, asymptote, end behavior Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment What are the techniques commonly used to solve equations? How can one predict the key features of a graph based on a function s algebraic form? What math operations can be applied to functions? A. Solve various types of equations 1. equation balancing 2. factoring and the multiplication property of zero 3. completing the square 4. using roots and powers B. Model and solve A. Recognize and graph various types of functions, including polynomial, rational, radical, and absolute value (with and without calculators) 1. Identify domain and range 2. Locate x and y intercepts 3. Locate vertical and horizontal asymptotes 4. Identify discontinuities in graphs 5. Describe symmetry for the graphs of functions 6. Determine whether functions are even, odd, or neither. 7. Apply transformations to graphing functions. 8. Define, find, and check inverse functions MA.912.A.4.5 MA.912.A.4.9 MA.912.A.4.8 MA.912.A.5.6 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 8 of 33
9 Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment C. Determine sums, differences, products, and quotients of functions D. Determine composites of functions E. Describe the end behavior of polynomial functions Page 9 of 33
10 II. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 2 weeks Objectives: 1. Use exponential and logarithmic patterns to simplifying expressions 2. Illustrate the graphs for exponential and logarithmic functions 3. Calculate the solutions for exponential and logarithmic equations 4. Analyze real world problems using exponential and logarithmic functions and graphs Vocabulary: expression, representation, model, base e, natural logarithm Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment Formal: What are the key features for exponential and logarithmic functions and graphs? What real world issues can be analyzed using exponential and logarithmic functions and graphs? A. Sketch the graphs for exponential and logarithmic functions B. Identify key features of graphs 1. domain and range 2. x and y intercepts 3. asymptotes 4. growth and decay C. Use the rules of logarithms 1. simplify expressions 2. combine logarithms 3. expand expressions D. Solve exponential and logarithmic equations E. Solve word problems involving applications of logarithmic and exponential functions MA.912.A.8.7 Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 10 of 33
11 III. Conic Sections 2 weeks Objectives: 1.Write equations for the conic sections when given key features. 2.Draw graphs for the conics when given the equations. Vocabulary: conic section, eccentricity, focus, directrix, asymptote Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment What are the shapes known as the conic sections? How can equations be used to represent the conic sections? What real-world problems can be modeled using the conics? A. Sketch graphs and determine equations for conic sections (with and without calculators) B. Write the equations of conic sections in standard form (completing the square and using translations as necessary). C. Determine the type of conic section and its geometric properties (foci, asymptotes, eccentricity, etc.). D. Solve applications involving conic sections. MA.912.A.9.2 MA.912.A.9.1 MA.912.D.6.4 MA.912.A.9.3 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 11 of 33
12 IV. Parametric Equations and Graphs 1 week Objectives: 1. Identify key features for parametric functions using graph paper, straightedges, and pencils as well as graphing calculators. 2. Convert from parametric to rectangular form 3. Draw conclusions for applications of parametric equations. Vocabulary: parametric equation, angle, scalar, reflection, arc Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment What alternate methods for graphing exist in mathematics? How do you transform equations to reflect alternate graphical representations? What kinds of applications can be modeled with parametric equations? A. Create a table of values and sketch graphs for parametric relationships (with and without calculators) 1. Identify direction with arrow B. Eliminate parameters to determine rectangular equations for parametric forms and then graph in rectangular form. C. Determine parametric equations for conic sections. D. Solve application problems involving parametric equations. MA.912.D.10.1 MA.912.D.10.2 MA.912.D.10.3 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 12 of 33
13 V. Trigonometric Definitions 2 weeks Objectives: 1. Illustrate trigonometric ratios in the rectangular coordinate system 2. Calculate trigonometric ratios and their inverses using technology Vocabulary: sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant, reference angle Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment What are trigonometric ratios? How can you draw diagrams to determine the values for trigonometric ratios? A. Sketch angles in standard position using protractors B. Identify direction for angles C. Convert between degree and radian measures. D. Identify reference angles and reference triangles and their quadrants E. Determine sine and cosine using the unit circle. F. Find and use exact values of trigonometric functions for special angles (degree and radian measures). G. Evaluate inverse trigonometric functions H. Determine values for trigonometric ratios using a calculator MA.912.T.1.1 MA.912.T.1.5 MA.912.T.1.2 MA.912.T.1.3 MA.912.T.1.4 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Using writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 13 of 33
14 VI. Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios - 1 week Objectives: 1. Formulate strategies for determining sides and angles of right and oblique triangles 2. Analyze real-world problems using triangles and trigonometric ratios Vocabulary: angle of depression, angle of elevation, oblique, representations Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment What is the least amount of information needed to determine all sides and angles for a given triangle? How can trigonometry be used to solve real-world problems? A. Use trigonometric ratios to solve triangles 1. right triangles a. opposite, adjacent, hypotenuse patterns 2. oblique triangles a. Law of Sines b. Law of Cosines B. Solve word problems involving right and oblique triangles, including areas. MA.912.T.2.1 MA.912.T.2.3 MA.912.T.2.2 MA.912.T.2.4 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 14 of 33
15 VII. Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 2weeks Objectives: 1. Sketch graphs for all six trigonometric functions with and without calculators Vocabulary: amplitude, period, phase shift, vertical shift, scale, oscillate Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment What are the key features of the graphs for trigonometric functions? What real-world problems can be modeled by trigonometric functions? A. Graph trigonometric functions on graph paper and identify key features: 1. domain and range 2. intercepts 3. period 4. amplitude 5. phase shift 6. vertical shift 7. vertical asymptotes B. Sketch graphs of trigonometric functions using graphing calculator 1. set appropriate window 2. identify key features C. Solve word problems involving applications of trigonometric functions D. Sketch graphs for inverse trigonometric functions MA.912.T.1.6 MA.912.T.1.8 MA.912.T.1.5 MA.912.T.1.7 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 15 of 33
16 VIII. Trigonometric Identities and Equations 2 weeks Objectives: 1. Create logically valid algebraic steps for verifying trigonometric identities 2. Collect and display solutions for trigonometric equations Vocabulary: equivalent expressions, substitution, identity Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment What are the important relationships among the six trigonometric ratios? How can one use logic to verify when arguments are valid? How can one solve equations involving trigonometric functions? A. Use the reciprocal, ratio, Pythagorean, sum and difference, and double angle identities. 1. find all ratios given one ratio and a quadrant 2. identify equivalent expressions 3. simplify expressions B. Use the basic trigonometric identities to verify other identities 1. rewrite as equivalent expressions 2. construct proofs for identities C. Solve trigonometric equations and word problems involving trigonometric equations MA.912.T.3.1 MA.912.T.3.3 MA.912.T.3.2 MA. 912.T.3.4 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 16 of 33
17 IX. Polar Coordinates and Complex Numbers 1 week Objectives: 1.Sketch graphs in polar coordinates 2.Show rectangular equations in polar form. 3.Organize operations with complex numbers 4. Convert complex numbers to trigonometric form. Vocabulary: complex number, axes, plane, scalar Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment Formal: MA.912.T.4.1 How is graphing in polar coordinates different from graphing in the rectangular system? What are complex numbers and how do you perform operations in the complex number system? A. Define polar coordinates and relate polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates B. Represent equations given in rectangular coordinates in terms of polar coordinates. C. Graph equations in the polar coordinate plane. D. Define complex numbers, convert complex numbers to trigonometric form, and multiply complex numbers in trigonometric form. E. Apply DeMoivre s Theorem to operations with complex numbers. MA.912.T.4.2 MA.912.T.4.3 MA.912.T.4.4 MA.912.T.4.5 Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies to display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 17 of 33
18 X. Vectors 1 week Objective: 1. Sketch graphs for vectors 2. Calculate magnitude for vectors 3. Organize operations involving vectors 4. Investigate real-world problems involving vectors. Vocabulary: vector, magnitude, length, slope Essential Questions Essential Content & Understandings Essential Skills & Benchmarks Assessment How are vectors written and graphed? What kinds of problems can be solved using vectors? A. Sketch vectors and perform vector operations B. Solve applications involving vectors MA.912.D.9.1 MA.912.D.9.2 MA.912.D.9.3 Formal: Chapter Test Vocabulary Test Mini-quizzes Informal: Check for understanding with the use of 5-minute checks FCAT style bell ringers Word Wall activity: Use writing strategies display the connection between the various vocabulary terms. Page 18 of 33
19 Curriculum Map Appendix for High Schools Scope and Sequence Correlated to Textbook Pages State Approved Course Descriptions Page 19 of 33
20 Analytic Geometry Scope and Sequence Correlated to Blitzer, Algebra and Trigonometry 4thed. and NGSSS Topic Chapter Section, resources NGSSS I. Functions and Graphs LA A.Solve various type 1-2 equations by factoring, 1-3 completing the square, and 1-5 by using powers and roots 1-6 B.Recognize and graph various MA.912.A.4.5 types of functions, including MA.912.A.4.8 polynomial, rational, radical, and MA.912.A.5.6 absolute value functions (with and without calculators) 1. Identify domain and range Locate x and y intercepts 2-2 MA.912.A Locate vertical, horizontal, 3-5 and slant asymptotes 4. Identify removable and non-removable discontinuities in graphs 5. Describe symmetry for the graphs of functions Determine whether functions are even, odd, or neither Apply transformations to graphing functions. 2-5 Page 20 of 33
21 Analytic Geometry 8. Define, find, and check inverse functions 2-7 C. Determine sums, differences, products, and quotients of functions 2-.6 D. Determine composites of functions E. Describe the end behavior of polynomial functions II. Logarithmic and Exponential Functions A. Sketch the graphs for exponential and logarithmic functions B. Identify key features of gr domain and range x and y intercepts 3. asymptotes 4. growth and decay C. Use the rules of logarithms simplify expressions 2. combine logarithms 3. expand expressions D. Solve exponential and logarithmic equations 4-4 E. Solve word problems involving applications 4-5 LA of logarithmic and exponential functions MA.912.A.8.7 III. Conic Sections LA A. Sketch graphs and determine equations for 2-8 MA.912.A.9.2 conic sections (with and without calculators) B. Write the equations of conic 10-1 MA.912.A.9.1 Page 21 of 33
22 Analytic Geometry sections in standard form (completing the square and using translations as necessary). C. Determine the type of conic 10-2 MA.912.D.6.4 section and its geometric properties (foci, asymptotes, eccentricity, etc.). D. Solve applications involving conic sections MA.912.A.9.3 IV. Parametric Graphs and Equations 10.5 LA A. Use parametric equations to sketch graphs,. LA indicating the direction of motion. MA.912.D.10.1 B. Convert from parametric form to rectangular equations LA rectangular equations MA.912.D.10.2 C. Solve applications for parametric equations (with and without calculators) MA.912.D.10.3 Page 22 of 33
23 Scope and Sequence Correlated to Blitzer, Algebra and Trigonometry 4thed. and NGSSS Topic Chapter Section, resources NGSSS V. Trigonometric definitions LA A. Convert between decimal degree and DMS supplement B. Convert between degree and MA.912.T.1.1 radian measures. 5-1 C. Sketch angles in standard position using protractors positive and negative rotation 2. degree and radian measure 3. identify quadrants D. Identify reference angles and reference triangles 5-3 E. Determine all six trigonometric MA.912.T.1.2 ratios given: a quadrantal angle 2. one trig ratio 3. a point on the terminal side. F. Determine exact values of MA.912.T.1.3 trigonometric ratios using special MA.912.T.1.5 right triangle patterns in all quadrants 5-3 Page 23 of 33
24 1. degree and radian measure G. Find exact values for inverse trigonometric functions 5-7 H. Determine values for MA.912.T.1.4 trigonometric ratios using a calculator VI. Trigonometry and Triangles A. Use trigonometric ratios to solve triangles right triangles MA.912.T.2.1 a. opposite, adjacent, hypotenuse patterns 2. oblique triangles MA.912.T.2.3 a. Law of Sines 7-1 b. Law of Cosines 7-2 B. Solve word problems MA.912.T.2.2 involving right and oblique MA.912.T.2.4 triangles VII. Trigonometric functions A. Graph trigonometric functions on graph paper and MA.912.T.1.6 identify key features: domain and range 2. intercepts 3. period Page 24 of 33
25 4. amplitude 5. phase shift 6. vertical shift 7. vertical asymptotes B. Sketch graphs of trigonometric functions using graphing calculator set appropriate window 2. identify key features C. Solve word problems 5-4 MA.912.T.1.8 involving applications of 5-5 trigonometric functions 5-6 D. Sketch graphs for inverse MA.912.T.1.7 trigonometric functions 5.7 VIII. Trigonometric Identities and Equations A. Use the reciprocal, ratio, Pythagorean, negative-angle, 5-2 MA.912.T.3.1 and as time permits, the sum and difference, 6-1 MA.912.T.3.3 and double angle identities find all ratios given one ratio and a quadrant 2. identify equivalent expressions 3. simplify expressions B. Use the basic trigonometric identities 6-3 MA.912.T.3.2 to verify other identities 1. rewrite as equivalent expressions 2. construct proofs for identities C. Solve trigonometric equations and word MA.912.T.3.4 problems involving trigonometric equations 6.5 Page 25 of 33
26 IX. Polar coordinates Polar Coordinates and Complex Numbers A. Define polar coordinates and LA relate polar coordinates to MA.912.T.4.1 Cartesian coordinates B. Represent equations given MA.912.T.4.2 in rectangular coordinates 7-4 LA in terms of polar coordinates. Graph equations in the MA.912.T.4.3 polar coordinate plane. C. Define complex numbers, 7-5 MA.912.T.4.4 convert complex numbers to trigonometric form, and multiply complex numbers in trigonometric form. E. Apply DeMoivre s MA.912.T.4.5 Theorem to operations with complex numbers. X. Vectors A. Sketch vectors and LA perform vector operations 7-6 LA B. Solve applications LA involving vectors MA.912.D.9.1 MA.912.D.9.2 MA.912.D.9.3 Page 26 of 33
27 State Approved Analytic Geometry Course Description Course Code Course Category 6-12 Subject Area Mathematics Course Type Core Course Title Analytic Geometry Course Level 3 Course Length One Semester Credit Description 0.5 Abbreviated Title Analytic Geometry RELATED BENCHMARKS (18) : Scheme Descriptor LA The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly; LA LA LA The student will use background knowledge of subject and related content areas, prereading strategies (e.g., previewing, discussing, generating questions), text features, and text structure to make and confirm complex predictions of content, purpose, and organization of a reading selection; The student will identify cause-and-effect relationships in text; The student will prewrite by making a plan for writing that addresses purpose, audience, a controlling idea, logical sequence, and time frame for completion; and Page 27 of 33
28 LA LA MA.912.A.4.5 MA.912.A.4.8 MA.912.A.4.9 MA.912.A.5.6 MA.912.A.8.7 MA.912.A.9.1 MA.912.A.9.2 MA.912.A.9.3 MA.912.D.6.4 The student will prewrite by using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn Diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid) to develop a personal organizational style. The student will draft writing by establishing a logical organizational pattern with supporting details that are substantial, specific, and relevant; and Graph polynomial functions with and without technology and describe end behavior. Describe the relationships among the solutions of an equation, the zeros of a function, the x-intercepts of a graph, and the factors of a polynomial expression, with and without technology. Use graphing technology to find approximate solutions for polynomial equations. Identify removable and non-removable discontinuities, and vertical, horizontal, and oblique asymptotes of a graph of a rational function, find the zeros, and graph the function. Solve applications of exponential growth and decay. Write the equations of conic sections in standard form and general form, in order to identify the conic section and to find its geometric properties (foci, asymptotes, eccentricity, etc.). Graph conic sections with and without using graphing technology. Solve real-world problems involving conic sections Use methods of direct and indirect proof and determine whether a short proof is logically valid. Page 28 of 33
29 MA.912.D.10.1 Sketch the graph of a curve in the plane represented parametrically, indicating the direction of motion. MA.912.D.10.2 Convert from a parametric representation of a plane curve to a rectangular equation, and vice-versa. MA.912.D.10.3 Use parametric equations to model applications of motion in the plane. Page 29 of 33
30 State Approved Trigonometry Course Description Course Code Course Category 6-12 Subject Area Mathematics Course Type Core Course Title Trigonometry Course Level 3 Course Length One Semester Credit Description 0.5 Abbreviated Title Trigonometry RELATED BENCHMARKS (30) : Scheme Descriptor LA The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly; LA LA LA The student will use background knowledge of subject and related content areas, prereading strategies (e.g., previewing, discussing, generating questions), text features, and text structure to make and confirm complex predictions of content, purpose, and organization of a reading selection; The student will identify cause-and-effect relationships in text; The student will prewrite by making a plan for writing that addresses purpose, audience, a controlling idea, logical sequence, and time frame for completion; and Page 30 of 33
31 LA LA MA.912.D.9.1 MA.912.D.9.2 MA.912.D.9.3 MA.912.T.1.1 MA.912.T.1.2 The student will prewrite by using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn Diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid) to develop a personal organizational style. The student will draft writing by establishing a logical organizational pattern with supporting details that are substantial, specific, and relevant; and Demonstrate an understanding of the geometric interpretation of vectors and vector operations including addition, scalar multiplication, dot product and cross product in the plane and in three-dimensional space. Demonstrate an understanding of the algebraic interpretation of vectors and vector operations including addition, scalar multiplication, dot product and cross product in the plane and in three-dimensional space. Use vectors to model and solve application problems. Convert between degree and radian measures. Define and determine sine and cosine using the unit circle. MA.912.T.1.3 State and use exact values of trigonometric functions for special angles, i.e. multiples of and (degree and radian measures) MA.912.T.1.4 MA.912.T.1.5 Find approximate values of trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions using appropriate technology. Make connections between right triangle ratios, trigonometric functions, and circular functions. Page 31 of 33
32 MA.912.T.1.6 MA.912.T.1.7 MA.912.T.1.8 MA.912.T.2.1 MA.912.T.2.2 MA.912.T.2.3 MA.912.T.2.4 Define and graph trigonometric functions using domain, range, intercepts, period, amplitude, phase shift, vertical shift, and asymptotes with and without the use of graphing technology. Define and graph inverse trigonometric relations and functions. Solve real-world problems involving applications of trigonometric functions using graphing technology when appropriate. Define and use the trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant) in terms of angles of right triangles. Solve real-world problems involving right triangles using technology when appropriate. Apply the laws of sines and cosines to solve real-world problems using technology. Use the area of triangles given two sides and an angle or three sides to solve real-world problems. MA.912.T.3.1 Verify the basic Pythagorean identities, e.g., Theorem., and show they are equivalent to the Pythagorean MA.912.T.3.2 MA.912.T.3.3 MA.912.T.3.4 Use basic trigonometric identities to verify other identities and simplify expressions. Use the sum and difference, half-angle and double-angle formulas for sine, cosine, and tangent, when formulas are provided. Solve trigonometric equations and real-world problems involving applications of trigonometric equations using Page 32 of 33
33 technology when appropriate. MA.912.T.4.1 MA.912.T.4.2 MA.912.T.4.3 MA.912.T.4.4 MA.912.T.4.5 Define polar coordinates and relate polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates with and without the use of technology. Represent equations given in rectangular coordinates in terms of polar coordinates. Graph equations in the polar coordinate plane with and without the use of graphing technology. Define the trigonometric form of complex numbers, convert complex numbers to trigonometric form, and multiply complex numbers in trigonometric form. Apply DeMoivre's Theorem to perform operations with complex numbers. Page 33 of 33
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Radian and Degree Measure Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Right Triangle Trigonometry
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Radian and Degree Measure Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Right Triangle Trigonometry
2. Be able to evaluate a trig function at a particular degree measure. Example: cos. again, just use the unit circle!
 Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Tennessee Senior Bridge Mathematics
 A Correlation of to the Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-130-10 A Correlation of, to the Mathematics Standards Mathematics Standards I. Ways of Looking: Revisiting Concepts
A Correlation of to the Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-130-10 A Correlation of, to the Mathematics Standards Mathematics Standards I. Ways of Looking: Revisiting Concepts
Math 1205 Trigonometry Review
 Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 5
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM
 Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Math 122: Final Exam Review Sheet
 Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
Trigonometry Review Page 1 of 14
 Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Basic Trigonometry You Should Know (Not only for this class but also for calculus)
 Angle measurement: degrees and radians. Basic Trigonometry You Should Know (Not only for this class but also for calculus) There are 360 degrees in a full circle. If the circle has radius 1, then the circumference
Angle measurement: degrees and radians. Basic Trigonometry You Should Know (Not only for this class but also for calculus) There are 360 degrees in a full circle. If the circle has radius 1, then the circumference
Trigonometry. An Overview of Important Topics
 Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Algebra 2/Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & 2: Trigonometry Mega-Session. The Unit Circle
 Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
Lesson Plan Mr. Baglos Course: Honors Algebra II As of: 4/2/18. After School: 2:30-3:30 Room 2232
 Lesson Plan Mr. Baglos Course: Honors Algebra II As of: 4/2/18 After School: 2:30-3:30 Room 2232 HW: Finish all notes for the day, do the assignment from your HMH workbook, Gizmos, your Math Journal, and
Lesson Plan Mr. Baglos Course: Honors Algebra II As of: 4/2/18 After School: 2:30-3:30 Room 2232 HW: Finish all notes for the day, do the assignment from your HMH workbook, Gizmos, your Math Journal, and
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
Trigonometry Review Tutorial Shorter Version
 Author: Michael Migdail-Smith Originally developed: 007 Last updated: June 4, 0 Tutorial Shorter Version Avery Point Academic Center Trigonometric Functions The unit circle. Radians vs. Degrees Computing
Author: Michael Migdail-Smith Originally developed: 007 Last updated: June 4, 0 Tutorial Shorter Version Avery Point Academic Center Trigonometric Functions The unit circle. Radians vs. Degrees Computing
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School
 AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure. Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles?
 Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
Unit Circle: Sine and Cosine
 Unit Circle: Sine and Cosine Functions By: OpenStaxCollege The Singapore Flyer is the world s tallest Ferris wheel. (credit: Vibin JK /Flickr) Looking for a thrill? Then consider a ride on the Singapore
Unit Circle: Sine and Cosine Functions By: OpenStaxCollege The Singapore Flyer is the world s tallest Ferris wheel. (credit: Vibin JK /Flickr) Looking for a thrill? Then consider a ride on the Singapore
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet
 Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
Chapter 1 and Section 2.1
 Chapter 1 and Section 2.1 Diana Pell Section 1.1: Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles Angles Degree Measure Angles that measure 90 are called right angles. Angles that measure between 0 and 90 are called
Chapter 1 and Section 2.1 Diana Pell Section 1.1: Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles Angles Degree Measure Angles that measure 90 are called right angles. Angles that measure between 0 and 90 are called
constant EXAMPLE #4:
 Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW
 PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Math + 4 (Red) SEMESTER 1. { Pg. 1 } Unit 1: Whole Number Sense. Unit 2: Whole Number Operations. Unit 3: Applications of Operations
 Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs
 Mathematics IV Frameworks Student Edition Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs 1 st Edition Table of Contents INTRODUCTION:... 3 What s Your Temperature? Learning Task... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Mathematics IV Frameworks Student Edition Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs 1 st Edition Table of Contents INTRODUCTION:... 3 What s Your Temperature? Learning Task... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
Trigonometric Equations
 Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Instructor Notes for Chapter 4
 Section 4.1 One to One Functions (Day 1) Instructor Notes for Chapter 4 Understand that an inverse relation undoes the original Understand why the line y = xis a line of symmetry for the graphs of relations
Section 4.1 One to One Functions (Day 1) Instructor Notes for Chapter 4 Understand that an inverse relation undoes the original Understand why the line y = xis a line of symmetry for the graphs of relations
Unit 8 Trigonometry. Math III Mrs. Valentine
 Unit 8 Trigonometry Math III Mrs. Valentine 8A.1 Angles and Periodic Data * Identifying Cycles and Periods * A periodic function is a function that repeats a pattern of y- values (outputs) at regular intervals.
Unit 8 Trigonometry Math III Mrs. Valentine 8A.1 Angles and Periodic Data * Identifying Cycles and Periods * A periodic function is a function that repeats a pattern of y- values (outputs) at regular intervals.
COURSE SYLLABUS. Course Title: Introduction to Quality and Continuous Improvement
 COURSE SYLLABUS Course Number: TBD Course Title: Introduction to Quality and Continuous Improvement Course Pre-requisites: None Course Credit Hours: 3 credit hours Structure of Course: 45/0/0/0 Textbook:
COURSE SYLLABUS Course Number: TBD Course Title: Introduction to Quality and Continuous Improvement Course Pre-requisites: None Course Credit Hours: 3 credit hours Structure of Course: 45/0/0/0 Textbook:
MAT 140 SYLLABUS - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND CALCULUS I
 MAT 140 SYLLABUS - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND CALCULUS I ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. Catalog Description: 140-04 Analytic Geometry and Calculus I (Fall 2010) Analytic geometry, functions, limits, derivatives and
MAT 140 SYLLABUS - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND CALCULUS I ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. Catalog Description: 140-04 Analytic Geometry and Calculus I (Fall 2010) Analytic geometry, functions, limits, derivatives and
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Properties of Logarithms
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Properties of Logarithms
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934)
 HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934) Presented by Shelley Kriegler President, Center for Mathematics and Teaching shelley@mathandteaching.org Fall 2014 8.F.1 8.G.1a
HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934) Presented by Shelley Kriegler President, Center for Mathematics and Teaching shelley@mathandteaching.org Fall 2014 8.F.1 8.G.1a
Mathematics UNIT FIVE Trigonometry II. Unit. Student Workbook. Lesson 1: Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days
 Mathematics 0- Student Workbook Unit 5 Lesson : Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric Identities I Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric
Mathematics 0- Student Workbook Unit 5 Lesson : Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric Identities I Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric
Big Ideas Math: A Common Core Curriculum Geometry 2015 Correlated to Common Core State Standards for High School Geometry
 Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Special Right Triangles and Right Triangle Trigonometry
 Special Right Triangles and Right Triangle Trigonometry Reporting Category Topic Triangles Investigating special right triangles and right triangle trigonometry Primary SOL G.8 The student will solve real-world
Special Right Triangles and Right Triangle Trigonometry Reporting Category Topic Triangles Investigating special right triangles and right triangle trigonometry Primary SOL G.8 The student will solve real-world
Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I
 MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Chapter 3, Part 1: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions
 Haberman MTH 11 Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter 3, Part 1: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions In Example 4 in Section I: Chapter, we observed that a circle rotating about its center (i.e.,
Haberman MTH 11 Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter 3, Part 1: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions In Example 4 in Section I: Chapter, we observed that a circle rotating about its center (i.e.,
Honors Algebra 2 w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals
 Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3)
 You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
Geometry. Teacher s Guide
 Geometry Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
Geometry Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
TenMarks Curriculum Alignment Guide: EngageNY/Eureka Math, Grade 7
 EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory
 Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
13-1 Trigonometric Identities. Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. SOLUTION: 2. If, find cos θ.
 Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 2. If, find cos θ. Since is in the first quadrant, is positive. Thus,. 3. If, find sin θ. Since is in the first quadrant,
Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 2. If, find cos θ. Since is in the first quadrant, is positive. Thus,. 3. If, find sin θ. Since is in the first quadrant,
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE. Algebra I MATHEMATICS G R E A T E R C L A R K C O U N T Y S C H O O L S
 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Algebra I MATHEMATICS 2014-2015 G R E A T E R C L A R K C O U N T Y S C H O O L S ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Quarter/Learning Check Days (Approx) Q1/LC1 11 Concept/Skill
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Algebra I MATHEMATICS 2014-2015 G R E A T E R C L A R K C O U N T Y S C H O O L S ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Quarter/Learning Check Days (Approx) Q1/LC1 11 Concept/Skill
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12. Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the. Externally set task 2017
 Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
Grade 4 Mathematics Indiana Academic Standards Crosswalk
 Grade 4 Mathematics Indiana Academic Standards Crosswalk 2014 2015 The Process Standards demonstrate the ways in which students should develop conceptual understanding of mathematical content and the ways
Grade 4 Mathematics Indiana Academic Standards Crosswalk 2014 2015 The Process Standards demonstrate the ways in which students should develop conceptual understanding of mathematical content and the ways
Unit 5. Algebra 2. Name:
 Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
One of the classes that I have taught over the past few years is a technology course for
 Trigonometric Functions through Right Triangle Similarities Todd O. Moyer, Towson University Abstract: This article presents an introduction to the trigonometric functions tangent, cosecant, secant, and
Trigonometric Functions through Right Triangle Similarities Todd O. Moyer, Towson University Abstract: This article presents an introduction to the trigonometric functions tangent, cosecant, secant, and
NEW Published in June 2018 CATALOGUE 2019
 NEW Published in June 2018 CATALOGUE 2019 PASS PUBLICATIONS PRIVATE ACADEMIC AND SCIENTIFIC STUDIES LIMITED passpublications.uk@gmail.com +44(0)20 8857 4752 P A S S PUBLICATIONS PASS is an acronym for
NEW Published in June 2018 CATALOGUE 2019 PASS PUBLICATIONS PRIVATE ACADEMIC AND SCIENTIFIC STUDIES LIMITED passpublications.uk@gmail.com +44(0)20 8857 4752 P A S S PUBLICATIONS PASS is an acronym for
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals
 Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS Ferris Wheel Height As a Function of Time The London Eye Ferris Wheel measures 450 feet in diameter and turns continuously, completing a single rotation once every
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS Ferris Wheel Height As a Function of Time The London Eye Ferris Wheel measures 450 feet in diameter and turns continuously, completing a single rotation once every
Introduction to Trigonometry. Algebra 2
 Introduction to Trigonometry Algebra 2 Angle Rotation Angle formed by the starting and ending positions of a ray that rotates about its endpoint Use θ to represent the angle measure Greek letter theta
Introduction to Trigonometry Algebra 2 Angle Rotation Angle formed by the starting and ending positions of a ray that rotates about its endpoint Use θ to represent the angle measure Greek letter theta
Trigonometry LESSON ONE - Degrees and Radians Lesson Notes
 8 = 6 Trigonometry LESSON ONE - Degrees and Radians Example : Define each term or phrase and draw a sample angle. Angle in standard position. b) Positive and negative angles. Draw. c) Reference angle.
8 = 6 Trigonometry LESSON ONE - Degrees and Radians Example : Define each term or phrase and draw a sample angle. Angle in standard position. b) Positive and negative angles. Draw. c) Reference angle.
College Pre-Calc Lesson Plans
 January 4-8 January 11-15 January 18-22 January 25-29 Sections 9.2 Area of a Triangle Mixed Trig Exercises Section 14.1 Matrix Addition & Scalar Multiplication Section 14.5 Transition Pg 342: 1, 3, 7-13,
January 4-8 January 11-15 January 18-22 January 25-29 Sections 9.2 Area of a Triangle Mixed Trig Exercises Section 14.1 Matrix Addition & Scalar Multiplication Section 14.5 Transition Pg 342: 1, 3, 7-13,
6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions. The smallest number p with the above property is called the period of the function.
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
1 Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Identify a unit circle and describe
1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Identify a unit circle and describe
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
In this section, you will learn the basic trigonometric identities and how to use them to prove other identities.
 4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
Section 8.1 Radians and Arc Length
 Section 8. Radians and Arc Length Definition. An angle of radian is defined to be the angle, in the counterclockwise direction, at the center of a unit circle which spans an arc of length. Conversion Factors:
Section 8. Radians and Arc Length Definition. An angle of radian is defined to be the angle, in the counterclockwise direction, at the center of a unit circle which spans an arc of length. Conversion Factors:
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions. By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
JMG. Review Module 1 Lessons 1-20 for Mid-Module. Prepare for Endof-Unit Assessment. Assessment. Module 1. End-of-Unit Assessment.
 Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
(3,4) focus. y=1 directrix
 Math 153 10.5: Conic Sections Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas Parabolas: Definition: A parabola is the set of all points in a plane such that its distance from a fixed point F (called the focus) is equal
Math 153 10.5: Conic Sections Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas Parabolas: Definition: A parabola is the set of all points in a plane such that its distance from a fixed point F (called the focus) is equal
1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
 1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Strand Measurement and Geometry Overall Expectations MGV.02: solve problems involving the measurements of two-dimensional shapes and the volumes of three-dimensional figures;
1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Strand Measurement and Geometry Overall Expectations MGV.02: solve problems involving the measurements of two-dimensional shapes and the volumes of three-dimensional figures;
The reciprocal identities are obvious from the definitions of the six trigonometric functions.
 The Fundamental Identities: (1) The reciprocal identities: csc = 1 sec = 1 (2) The tangent and cotangent identities: tan = cot = cot = 1 tan (3) The Pythagorean identities: sin 2 + cos 2 =1 1+ tan 2 =
The Fundamental Identities: (1) The reciprocal identities: csc = 1 sec = 1 (2) The tangent and cotangent identities: tan = cot = cot = 1 tan (3) The Pythagorean identities: sin 2 + cos 2 =1 1+ tan 2 =
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions
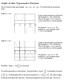 Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content. Pennsylvania Department of Education
 Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION General Introduction to the Keystone Exam Assessment
Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION General Introduction to the Keystone Exam Assessment
13-1 Trigonometric Identities. Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. ANSWER: 2. If, find cos θ.
 Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 8. CCSS PERSEVERANCE When unpolarized light passes through polarized sunglass lenses, the intensity of the light is cut
Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 8. CCSS PERSEVERANCE When unpolarized light passes through polarized sunglass lenses, the intensity of the light is cut
10.1 Curves defined by parametric equations
 Outline Section 1: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 1.1 Curves defined by parametric equations 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves 1.3 Polar Coordinates 1.4 Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
Outline Section 1: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 1.1 Curves defined by parametric equations 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves 1.3 Polar Coordinates 1.4 Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas
 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Connected Mathematics 2, 6th Grade Units (c) 2006 Correlated to: Utah Core Curriculum for Math (Grade 6)
 Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Trigonometric identities
 Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review. Fall 2017
 MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
D.3. Angles and Degree Measure. Review of Trigonometric Functions
 APPENDIX D. Review of Trigonometric Functions D7 APPENDIX D. Review of Trigonometric Functions Angles and Degree Measure Radian Measure The Trigonometric Functions Evaluating Trigonometric Functions Solving
APPENDIX D. Review of Trigonometric Functions D7 APPENDIX D. Review of Trigonometric Functions Angles and Degree Measure Radian Measure The Trigonometric Functions Evaluating Trigonometric Functions Solving
Pennsylvania System of School Assessment
 Mathematics, Grade 04 Pennsylvania System of School Assessment The Assessment Anchors, as defined by the Eligible Content, are organized into cohesive blueprints, each structured with a common labeling
Mathematics, Grade 04 Pennsylvania System of School Assessment The Assessment Anchors, as defined by the Eligible Content, are organized into cohesive blueprints, each structured with a common labeling
Students will be able to:
 GRADE 4 UNIT 5 MEASURE AND CLASSIFY GEOMETRIC FIGURES Established Goals: Standards 4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. 4.MD.5 Recognize angles as geometric
GRADE 4 UNIT 5 MEASURE AND CLASSIFY GEOMETRIC FIGURES Established Goals: Standards 4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. 4.MD.5 Recognize angles as geometric
HPS Scope Sequence Last Revised June SUBJECT: Math GRADE: 7. Michigan Standard (GLCE) Code & Language. What this Standard means:
 Number and Numeration MA.7.NS.1 (Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical
Number and Numeration MA.7.NS.1 (Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical
5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Objectives: 1. Graph the sine and cosine functions. 2. Determine the amplitude, period and phase shift of the sine and cosine functions. 3. Find equations
5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Objectives: 1. Graph the sine and cosine functions. 2. Determine the amplitude, period and phase shift of the sine and cosine functions. 3. Find equations
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE. Grade 4 Mathematics GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS
 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Grade 4 Mathematics 2014-2015 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Learning Old Format New Format Q1LC1 4.NBT.1, 4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.3, (4.1.1, 4.1.2,
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Grade 4 Mathematics 2014-2015 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Learning Old Format New Format Q1LC1 4.NBT.1, 4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.3, (4.1.1, 4.1.2,
BIG IDEA 1: Develop an understanding of and fluency with multiplication and division of fractions and decimals BIG IDEA 1:
 BIG IDEA 1: Develop an understanding of and fluency with multiplication and division of fractions and decimals Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Explain the difference between an exact answer and an estimated
BIG IDEA 1: Develop an understanding of and fluency with multiplication and division of fractions and decimals Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Explain the difference between an exact answer and an estimated
Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
University of North Georgia Department of Mathematics
 University of North Georgia Department of Mathematics Instructor: Berhanu Kidane Course: College Algebra Math 1111 Text Book: For this course we use the free e book by Stitz and Zeager with link: http://www.stitz-zeager.com/szca07042013.pdf
University of North Georgia Department of Mathematics Instructor: Berhanu Kidane Course: College Algebra Math 1111 Text Book: For this course we use the free e book by Stitz and Zeager with link: http://www.stitz-zeager.com/szca07042013.pdf
Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.
 MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
 The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards
 Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
GRADE 4. M : Solve division problems without remainders. M : Recall basic addition, subtraction, and multiplication facts.
 GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
and Transitional Comprehensive Curriculum. Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships
 Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships Time Frame: Approximately three weeks Unit Description This unit demonstrates the basic role played by Euclid s fifth postulate in geometry. Euclid
Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships Time Frame: Approximately three weeks Unit Description This unit demonstrates the basic role played by Euclid s fifth postulate in geometry. Euclid
C.3 Review of Trigonometric Functions
 C. Review of Trigonometric Functions C7 C. Review of Trigonometric Functions Describe angles and use degree measure. Use radian measure. Understand the definitions of the si trigonometric functions. Evaluate
C. Review of Trigonometric Functions C7 C. Review of Trigonometric Functions Describe angles and use degree measure. Use radian measure. Understand the definitions of the si trigonometric functions. Evaluate
Chino Valley Unified School District High School Course Description #5U01
 CONTACTS 1. School Information: School: Chino Valley Unified School District Street Address: 5130 Riverside Dr., Chino, CA 91710 Mailing Address: 5130 Riverside Dr., Chino, CA 91710 Phone: (909) 628-1201
CONTACTS 1. School Information: School: Chino Valley Unified School District Street Address: 5130 Riverside Dr., Chino, CA 91710 Mailing Address: 5130 Riverside Dr., Chino, CA 91710 Phone: (909) 628-1201
Table of Contents. Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x
 Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
SPIRIT 2.0 Lesson: How Far Am I Traveling?
 SPIRIT 2.0 Lesson: How Far Am I Traveling? ===============================Lesson Header ============================ Lesson Title: How Far Am I Traveling? Draft Date: June 12, 2008 1st Author (Writer):
SPIRIT 2.0 Lesson: How Far Am I Traveling? ===============================Lesson Header ============================ Lesson Title: How Far Am I Traveling? Draft Date: June 12, 2008 1st Author (Writer):
Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions
 Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the other four trigonometric functions. We will start by examining the tangent
Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the other four trigonometric functions. We will start by examining the tangent
Estimating Tolerance Accuracy (Rounding, including sig. fig.) Scientific notation
 S3 Pathways for learning in Maths Pathway 1 (Lower) Pathway 2 (Middle) Pathway 3 (Upper) Targets Complete coverage of level 3 experiences and outcomes in Mathematics Cover level 4 experiences and outcomes
S3 Pathways for learning in Maths Pathway 1 (Lower) Pathway 2 (Middle) Pathway 3 (Upper) Targets Complete coverage of level 3 experiences and outcomes in Mathematics Cover level 4 experiences and outcomes
Geometry Problem Solving Drill 11: Right Triangle
 Geometry Problem Solving Drill 11: Right Triangle Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? Question #01 A. (1/2, 1/2) B. (1/2, 2/2) C. ( 2/2, 2/2) D. ( 2/2, 3/2) The
Geometry Problem Solving Drill 11: Right Triangle Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? Question #01 A. (1/2, 1/2) B. (1/2, 2/2) C. ( 2/2, 2/2) D. ( 2/2, 3/2) The
Chapter 2: Functions and Graphs Lesson Index & Summary
 Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
Module Guidance Document. Geometry Module 2
 Geometry Module 2 Topic A Scale Drawings 5 days Topic B Dilations 5 days Topic C Similarity and Dilations 15 days Topic D Applying Similarity to Right 7 days Triangles Topic D Trigonometry 13 days Just
Geometry Module 2 Topic A Scale Drawings 5 days Topic B Dilations 5 days Topic C Similarity and Dilations 15 days Topic D Applying Similarity to Right 7 days Triangles Topic D Trigonometry 13 days Just
Section 2.3 Task List
 Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions.notebook. Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2

 # %
# %