DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 2013 REGULATION 2MARKS UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
|
|
|
- Shon Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 2013 REGULATION 2MARKS UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal. 2. What are the types of analog modulation? (i) Amplitude modulation. (ii)angle Modulation 1. Frequency modulation 2. Phase modulation. 3.Define the term modulation index for AM. Modulation index is the ratio of amplitude of modulating signal (Em) to amplitude of carrier (Ec) i.e.m = mec 4. What are the degrees of modulation? a) Under modulation (m < 1) b) Critical modulation (m=1) c) Over modulation(m>1) 5. What is the need formodulation? Needs for modulation: a) Ease of transmission b) Multiplexing c) Reduced noise d) Narrow bandwidth e) Frequency assignment f) Reduce the equipments limitations. 6.Give the Classification of Modulation. There are two types of modulation. TheyAnalog modulation is classified as follows (i)continuous wave modulation (ii)pulse modulation Continuous wave modulation is classified as follows (i)amplitude modulation (ii)double side band suppressed carrier (iii)single side band suppressed carrier (iv)vestigial side band suppressed carrier Angle modulation (i)frequency modulation (ii)phase Pulse modulation is classified as follows (i)pulse amplitude modulation is classified as follows ii)pulse position modulation (iii)pulse duration modulation (iv)pulse code modulation Digital modulation
2 (i) Amplitude shift keying (ii) (ii)phase shift keying (iii) Frequency shift keyin
3 7. What is the difference between high level and low level modulation? In high level modulation, the modulator amplifier operates at high power levels and delivers power directly to the antenna. In low level modulation, the modulator amplifier performs modulation at relatively low power levels. The modulated signal is then amplified to high power level by class B power amplifier. The amplifier feeds power to antenna. 8. Define Detection. Detection is the process of extracting modulating signal from the modulated carrier. Different types of detectors are used for different types of modulations. 9. Define Amplitude Modulation. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of a carrier signal is varied according to variations in amplitude of modulating signal. The AM signal can be represented mathematically as, eam = (Ec + Em sinωmt ) sinωct and the modulation index is given as,m = Em EC 10. What is Super Heterodyne Receiver? The super heterodyne receiver converts all incoming RF frequencies to a fixed lower frequency, called intermediate frequency (IF). This IF is then amplitude and detected to get the original signal. 11. What is single tone and multi tone modulation? If modulation is performed for a message signal with more than one frequency component then the modulation is called multi tone modulation. If modulation is performed for a message signal with one frequency component then the modulation is called single tone modulation. 12. Compare AM with DSB-SC and SSB-SC. S.No AM signal DSB-SC SSB-SC 1 Bandwidth = 2fm Bandwidth = 2fm Bandwidth = fm 2 Contains USB,LSB,Carrier Contains USB,LSB USB,LSB 3 More Power is required for Power required is less than Power required is less than transmission that of AM. AM &DSB-SC 13. What are the advantages of VSB-AM? 1. It has bandwidth greater than SSB but less than DSB system. 2. Power transmission greater than DSB but less than SSB system. 3. No low frequency component lost. Hence it avoids phase distortion. 14. How will you generating DSBSC-AM? There are two ways of generating DSBSC-AM such as a).balanced modulator
4 15. What are advantages of ring modulator? a).its output is stable. b). It requires no external power source to activate the diodes. c).virtually no maintenance. d). Long life. b).ring modulators
5 16. Define Demodulation. Demodulation or detection is the process by which modulating voltage is recovered from the modulated signal. It is the reverse process of modulation. The devices used for demodulation or detection are called demodulators or detectors. For amplitude modulation, detectors or demodulators are categorized as, a) Square-law detectors b) Envelope detectors 17. Define Multiplexing. Multiplexing is defined as the process of transmitting several message signals Simultaneously over a single channel. 18. Define Frequency Division Multiplexing. Frequency division multiplexing is definedas many signals are transmitted simultaneously with each signal occupying a different frequency slot within a common bandwidth. 19. Define Guard Band. Guard Bands are introduced in the spectrum of FDM in order to avoid any interference between the adjacent channels. Wider the guard bands, Smaller the interference. 20. Define SSB-SC. (i) SSB-SC stands for Single Side Band Suppressed Carrier (ii) When only one sideband is transmitted, the modulation is referred to as Single side band modulation. It is also called as SSB or SSB-SC. 21. Define DSB-SC. After modulation, the process of transmitting the sidebands (USB, LSB) alone and suppressing the carrier is called as Double Side Band-Suppressed Carrier. 22. What are the disadvantages of DSB-FC? (i) Power wastage takes place in DSB-FC (ii) DSB-FC is bandwidth inefficient system. 23. Define Coherent Detection. During Demodulation carrier is exactly coherent or synchronized in both the frequency and phase, with the original carrier wave used to generate the DSB-SC wave. This method of detection is called as coherent detection or synchronous detection. 24. What is Vestigial Side Band Modulation? Vestigial Sideband Modulation is defined as a modulation in which one of the sideband is partially suppressed and the vestige of the other sideband is transmitted to compensate for that suppression. 25. What are the advantages of signal sideband transmission? a) Power consumption b) Bandwidth conservation c) Noise reduction 26. What are the disadvantages of single side band transmission?
6 a)complex receivers: Single side band systems requiremore complex and expensive receivers thn conventiaonal AM transmission. b)tuning difficulties: Single side band receiversrequire more complex and precise tunig than conventional AM receivers.
7 27. Compare linear and non-linear modulators? S.No Linear Modulators Non Linear Modulators 1. Heavy filtering is not required. Heavy filtering is required. 2. These modulators are used in high These modulators are used in low level level modulation. modulation. The carrier voltage is very much The modulating signal voltage is very much 3. greater than modulating signal greater than the carrier signal voltage. voltage. 28. What is frequency translation? Suppose that a signal is band limited to the frequency range extending from a frequency f1 to a frequency f2. The process of frequency translation is one in which the original signal is replaced with a new signal whose spectral range extends from f1 and f2 and which new signal bears, in recoverable form the same information as was borne by the original signal. 29. What are the two situations identified in frequency translations? a) Up Conversion: In this case the translated carrier frequency is greater than the incoming carrier b) Down Conversion: In this case the translated carrier frequency is smaller than the increasing carrier frequency. Thus, a narrowband FM signal requires essentially the same transmission bandwidth as the AM signal. 30. What is BW for AM wave? The difference between these two extreme frequencies is equal to the bandwidth of the AM wave. Therefore, Bandwidth, B = (ωc + ωm) - (ωc - ωm) B = 2ωm 31. What is the BW of DSB-SC signal? Bandwidth, B = (ωc + ωm) - (ωc - ωm) B = 2ω It is obvious that the bandwidth of DSB-SC modulation is same as that of general AM waves. 32.What are the demodulation methods for DSB-SC signals? The DSB-SC signal may be demodulated by following two methods: (i) Synchronous detection method. (ii) Using envelope detector after carrier reinsertion. 33. Write the applications of Hilbert transform? (i) For generation of SSB signals, (ii) For designing of minimum phase type filters, (iii) (iii) For representation of band pass signals. 34. What are the methods for generating SSB-SC signal? SSB-SC signals may be generated by two methods as under: (i)frequency discrimination method or filter method. (ii)phase discrimination method
8 or phase-shift method.
9 UNIT-II ANGLE MODULATION 2Marks Questions andanswers 1. What do you understand by narrowband FM? When the modulation index is less than 1, the angle modulated systems are called low index. The bandwidth requirement of low index systems is approximately twice of the modulating. 2. Define frequency modulation. Frequency modulation is defined as the process by which the frequency of the carrier wave is varied in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating or message signal. 3. Define modulation index of frequency modulation. It is defined as the ratio of maximum frequency deviation to the modulating β = δ f f m 4. What do you meant by multitone modulation? Modulation done for the message signal with more than one frequency component is called multitone modulation. 5. Define phase modulation. Phase modulation is defined as the process of changing the phase of the carrier signal in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal. 6. What are the types of Frequency Modulation? Based on the modulation index FM can be divided into types. They are Narrow band FM and Wide band FM. If the modulation index is greater than one then it is wide band FM and if the modulation index is less than one then it is Narrow band FM 7. What is the basic difference between an AM signal and a narrowband FM signal? In the case of sinusoidal modulation, the basic difference between an AM signal and a narrowband FM signal is that the algebraic sign of the lower side frequency in the narrow band FM is reversed. 8. What are the two methods of producing an FM wave? Basically there are two methods of producing an FM wave. They are, i) Direct method: In this method the transmitter originates a wave whose frequency varies as function of the modulating source. It is used for the generation of NBFM ii) Indirect method: In this method the transmitter originates a wave whose phase is a function of the modulation. Normally it is used for the generation of WBFM where WBFM is generated from NBFM 9. Compare WBFM and NBFM. S.NO WBFM NBFM Modulation index is greater Modulation index less than 1 1 than 1
10 2 Frequency deviation 75 KHz Frequency deviation 5 KHz 3 Bandwidth 15 times NBFM Bandwidth 2fm 4 Noise is more suppressed Less suppressing of noise
11 10. List the properties of the Bessel function. The properties of the Bessel function is given by, (i) J n (β )= ( 1)n J for all n, both positive and negative. n β (ii) For small values of the modulation index β, we have J 0 (β ) =1 J1 (β ) = β 2J n (β ) = 0, n f 2 (iii) J 2 n (β )= 1 n = 11. Give the average power of an FM signal. The amplitude of the frequency modulated signal is constant.the power of the FM signal is same as that of the carrier power. P =1 2 E 2c 12. Define phase deviation. The maximum phase deviation of the total angle from the carrier angle is called phase deviation. 13. Define frequency Deviation. The maximum departure of the instantaneous frequency from the carrier frequency is called frequency deviation. 14. State the Carson s rule. An approximate rule for the transmission bandwidth of an FM Signal generated by a single tone-modulating signal of frequency f m (max) is defined as ] BW=2[δ + f m(max) 15. Define the deviation ratio D for non-sinusoidal modulation. The deviation ratio D is defined as the ratio of the frequency deviation f, which Corresponds to the maximum possible amplitude of the modulation signal m (t), to the highest modulation frequency.d = f f m 16. What is the use of crystal controlled oscillator? The crystal-controlled oscillator always produces a constant carrier frequency there by enhancing frequency stability. 17. What are the disadvantages of FM system? 1. A much wider channel is required by FM. 2.FM transmitting and receiving equipments tend to be more complex and hence it is expensive. 18. How will you generate message from frequency-modulated signals? First the frequency-modulated signals are converted into corresponding amplitude-modulated signal using frequency dependent circuits. Then the original signal is recovered from this AM signal.
12 19. What are the types of FM detectors? The types of FM detectors are (i) Slope detector and (ii) Phase discriminator. 20. What are the types of phase discriminator? The types of phase discriminator are (i) Foster seeley discriminator and (ii) Ratio detector. 21. What are the disadvantages of balanced slope detector? 1. Amplitude limiting cannot be provided 2. Linearity is not sufficient 3. It is difficult to align because of three different frequency to which various tuned circuits to be tuned. 4. The tuned circuit is not purely band limited. 22. Write the advantages and disadvantages of foster-seely discrimination method? Advantages: a) It is much easier to design b) Only two tuned circuits are necessary and they are tuned to same frequency c) Linearity is better Disadvantages: a) It requires Amplitude limiting circuit. 23. What are the applications of phase locked loop? Phase locked loops are used for various purposes in AM and FM communication. (i)automatic frequency correction in FM transmitter uses PLL to keep carrier frequency constant. (ii)pll is used direct FM Tramitter uses PLL to keep carrier frequency constant. (iii) PLL is also used in FM demodulators. 24. Differentiate phase and frequency modulation. S.No Phase Modulation Frequency Modulation 1 Phase of the carrier varies as per Frequency of the carrier varies as per amplitude variations of modulating amplitude variations of modulating signal. signals. 2 Instantaneous phase deviation, Instantaneous frequency deviation, θ (t ) = k em (t ) θ ' (t ) = d [ω t + θ (t )] dt C 3 Modulation index = k Em Modulation index = k1 Em Ωm 25. What is diversity reception? Diversity reception is used when the signal fades into noise level. There are two types of
13 diversity reception: a) Space diversity b) Frequency diversity. a) Space diversity: It uses two or more receiving antennas separated by nine or more wavelengths. These are separate receivers for each antenna. The receiver with strongest signal is selected. b) Frequency diversity: It uses single receiving antenna which works for two or more frequencies. The frequency which has strong signal is selected. UNIT-III RANDOM PROCESS 2 Marks Questions and Answers 1. Define noise. Noise is defined as any unwanted form of energy, which tends to interfere with proper reception and reproduction of wanted signal. 2. Give the classification of noise. Noise is broadly classified into two types. They are (i)external noise (ii)internal noise. 3. What are the types of External noise? External noise can be classified into 1. Atmospheric noise 2. Extraterrestrial noises 3. Man made noises or industrial noises 4. What are types of internal noise? Internal noise can be classified into 1. Thermal noise 2. Shot noise 3. Transit time noise 4. Miscellaneous internal noise 5. What are the types of extraterrestrial noise and write their origin? The two type of extraterrestrial noise are solar noise and cosmic noise Solar noise is the electrical noise emanating from the sun.cosmic noise is the noise received from the center part of our galaxy, other distant galaxies and other virtual point sources. 6. Define transit time of a transistor. Transit time is defined as the time taken by the electron to travel from emitter to the collector. 7. Define flicker noise. Flicker noise is the one appearing in transistors operating at low audio frequencies. Flicker noise is proportional to the emitter current and junction temperature and inversely proportional to the frequency. 8. State the reasons for higher noise in mixers.
14 1. Conversion transconductance of mixers is much lower than the transconductance of amplifiers. 2. If image frequency rejection is inadequate, the noise associated with the image frequency also gets accepted. 9. Define signal to noise ratio. Signal to noise ratio is the ratio of signal power to the noise power at the same point in a system. 10. Define noise figure. Noise figure is decibel representation of Noise factor. i.e, Noise figure = (Noise factor) db Available SPower ratio at the input
15 =N db Available S N Power ratio at the ouput Where, S/N = Signal -Noise ratio 11. Define thermal noise. Give the expression for the thermal noise voltage across a resistor. The electrons in a conductor possess varying amounts of energy. A small fluctuation in this energy produces small noise voltages in the conductor. These random fluctuations produced by thermal agitation of the electrons is called thermal noise. 12. Define noise temperature. (In terms of hypothetical temperature) The available noise power is directly proportional to temperature and it is independent of value of resistance. This power specified in terms of temperature is called as noise temperature. It is denoted by Te. It is given as,te = (F 1 )T 13. What is shot noise? When current flows in electronic device, the fluctuations number of electrons or holes generates the noise. It is called shot noise. Shot noise also depends upon operating conditions of the device. 14. Give the expression for noise voltage in a resistor. The Mean Square value of thermal noise voltage is given by, Vn 2 = 4 k TBR K Boltz man constant, R Resistance T Obsolute temperature, B Bandwidth 15. What is White Noise? Many types of noise sources are Gaussian and have flat spectral density over a wide frequency range. Such spectrum has all frequency components in equal portion, and is therefore called white noise. The power spectral density of white noise is independent of the operating frequency. The Power spectral density of White Noise is given as, S ( f ) = N What is narrowband noise? The receiver of a communication system usually includes some provision for preprocessing the received signal. The preprocessing may take the form of a narrowband filter whose bandwidth is large enough to pass modulated component of the received signal essentially undistorted but not so large as to admit excessive noise through the receiver. The noise process appearing at the output of such filter is called narrow band noise. 17. Define noise equivalent bandwidth. The noise equivalent bandwidth of the filter is defined as the bandwidth of an ideal filter at which the noise power passed by real filter and ideal filter is same. 18. Define noise factor. Noise factor (F) is defined as the ratio of signal to noise power ratio at the input to signal to noise power ratio at the output
16 19. Give the characteristics of shot noise. (i) Shot noise is generated due to fluctuations in the number of electrons or holes. (ii) Shot noise has uniform spectral density. (iii) Mean square noise current depends upon direct component of current. (iv) Shot noise depends upon operating conditions of the device. UNIT-IV NOISE CHARACTERIZATION 2 marks questions and answers 1. What is FM threshold effect? As the carrier to noise ratio is reduced, clicks are heard in the receiver output. As the carrier to noise ratio reduces further, crackling, or sputtering sound appears at the receiver output. Near the breaking point, the theoretically calculated output signal to noise ratio becomes large, but its actual value is very small. This phenomenon is called threshold effect. 2. What is capture effect in FM? When the noise interference is stronger than FM signal, then FM receiver locks to interference. This suppresses FM signal. When the noise interference as well as FM signal are of equal strength, then the FM receiver locking fluctuates between them. This phenomenon is called capture effect. 3. What is meant by figure of merit of a receiver? The ratio of output signals to noise ratio to channel signal to noise ratio is called figure of merit., 4. What is the Purpose of re-emphasis and de-emphasis in FM? The PSD of noise at the output of FM receiver sally increases rapidly at high frequencies but the PSD of message signal falls off at higher frequencies. This means the message signal doesn t utilize the frequency band in efficient manner. Such more efficient use of frequency band and improved noise performance can be obtained with the help of re-emphasis and de-emphasis. 5. What are extended threshold demodulators? Threshold extension s also called threshold reduction. It is achieved with the help of FMFB demodulator. In the local oscillator is replaced by voltage controlled oscillator (VCO).The VC frequency changes as per low frequency variations of demodulated signal. Thus the receiver responds only to narrow band of noise centered around instantaneous carrier frequency. This reduces the threshold of FMFB receiver. 6. What is threshold effect with respect to noise? When the carrier to noise ratio reduces below certain value, the message information is lost. The performance of the envelope detector deteriorates rapidly and it has no proportion with carrier to noise ratio. This is called threshold effect. 7. Define pre-emphasis and de-emphasis. Pre-emphasis: It artificially emphasizes the high frequency components before modulation. This
17 equalizes the low frequency and high frequency portions of the PSD and complete band is occupied. De-emphasis: This circuit attenuates the high frequency components. The attenuation characteristic is exactly opposite to that of pre-emphasis circuit. De-emphasis restores the power distribution of the original signal. The signal to noise ratio is improved because of pre-emphasis and de-emphasis circuits. 9. Write the expression of the SNR for a synchronous detector. DSB-SC receiver uses synchronous detection. Its signal to noise ratio is given as, S = PiN N 0 f M
18 10. Define superheterodyne principle. It can be defined as the process of operation of modulated waves to obtain similarly modulated waves of different frequency. This process uses a locally generated carrier wave, which determines the change of frequency. 11. Define signal to noise ratio. Signal to noise ratio is the ratio of signal power to the noise power at the same point in a system. 12. Compare the Noise performance of an AM and FM system? The figure of merit of AM system is 1 3 when the modulation is 100 percent and that of FM is (3 2)m 2 f. The use of FM offers improved noise performance over AM when (3 2)m f 2 f1 modulation index in FM 3 m f 13. What is threshold effect in an envelope detector? Explain. When a noise is large compared to the signal at the input of the envelope detector, the detected output has a message signal completely mingled with noise. It means that if the input SNR is below a certain level, called threshold level, the noise dominates over the message signal, threshold is defined as value of the input signal to noise ratio (So/No) below which the output signal to noise ratio (Si/Ni) deteriorates much more rapidly than the input signal to noise ratio. The threshold effect in an envelope detector whenever the carrier power-to-noise power ratio approaches unity or less. 14.State the disadvantages of FM. i) Bandwidth requirement of FM is much higher. ii) FM transmitting and receiving equipment is more complex and costly. iii) Distance of reception is limited only to line of sight. 15.What do you understand by FM stereo multiplexing? FM stereo multiplexing is used for stereo transmission. It is basically frequency division multiplexing. It is used for FM radio broadcasting. The left and right channel signals are used to generate sum and difference signals. The difference signal frequency modulates the carrier. The difference signal, FM difference signal, FM difference signal and carrier are combined together and sent. Such FM multiplexed signal can be coherently received by stereo as well as mono receiver.
19 UNIT-V INFORMATION THEORY 2 Marks Questions and Answers 1. What is entropy? Entropy is also called average information per message. It is the ratio of total information to number of messages. i.e., Entropy, H = Total inf ormation Number of messages 2. What is channel redundancy? Redundancy (γ) = 1 code efficiency Redundancy should be as low as possible. 3. Name the two source coding techniques. The source coding techniques are, a) prefix coding b) Shannon-fano coding c) Huffman coding 4. When is the average information delivered by a source of alphabet size 2, maximum? Average information is maximum, when the two messages are equally likely, i.e., 1 Then the maximum average information is given as, 2 p1 = p2 5.What is memory less source? Give an example. The alphabets emitted by memory less source do not depend upon previous alphabets. Every alphabet is independent. For example a character generated by keyboard represents memory less source. 6.Explain the significance of the entropy H(X/Y) of a communication system where X is the transmitter and Y is the receiver. a) H(X/Y) is called conditional entropy. It represents uncertainty of X, on average, when Y is known. b) In other words H(X/Y) is an average measure of uncertainty in X after Y is received. H(X/Y) represents the information lost in the noisy channel 7.What is prefix code? In prefix code, no codeword is the prefix of any other codeword. It is variable length code. The binary digits (codewords) are assigned to the messages as per their probabilities of occurrence. 8. Define information rate. Information rate(r) is represented in average number of bits of information per second. It is calculated as,r = r H Information bits / sec 9. Calculate the entropy of source with a symbol set containing 64 symbols each with a probability pi =1 64. Here, there are M = 64 equally likely symbols. Hence entropy of such source is given as,h
20 = log 2 M = log 2 64 = 6 bits / symbol 10.State any four properties of entropy. a) For sure event or impossible event entropy is zero. b) For M number of equally H max = log 2 M likely symbols, entropy is log2 M c) Upper bound on entropy is b) Entropy is lower bound on average number of bits per symbol 12.Give the expressions for channel capacity of a Gaussian channel. Channel capacity of a Gaussian channel is given as, C = B log 1+S 2 bits / sec N Here B is Channalbandwidth S is signal power N is total noise power within the channel bandwidth. 13. State the channel coding theorem for a discrete memory less channel. Statement of the theorem: Given a source of M equally likely messages, with M >>1, which is generating information at a rate. Given channel with capacity C. Then if,r C There exits a coding technique such that the output of the source may be transmitted over the channel with a probability of error in the received message which may be made arbitrarily small. Explanation: This theorem says that if R C ; it is possible to transmit information without any error even if noise is present. Coding techniques are used to detect and correct the errors. 14. What is information theory? Information theory deals with the mathematical modeling and analysis of a communication system rather than with physical sources and physical channels 15. State Shannon Hartley theorem. Channel capacity C of a Gaussian channel is given as, C = B log 1+ Here B is Channel bandwidth S/N Signal to noise ratio. S 2 bits / sec N 16. Explain Shannon-Fano coding. An efficient code can be obtained by the following simple procedure, known as Shannon Fano algorithm. Step 1: List the source symbols in order of decreasing probability. Step 2: Partition the set into two sets that are as close to equiprobable as possible, and sign 0 to the upper set and 1 to the lower set.
21 Step: Continue this process, each time partitioning the sets with as nearly equal probabilities as possible until further partitioning is not possible. 17. Define bandwidth efficiency. The ratio of channel capacity to bandwidth is called bandwidth efficiency. i.e, Bandwidth efficiency = Channel capacity (C ) Bandwidth (B) 18. Define channel capacity of the discrete memory less channel. The channel capacity of the discrete memory less channel is given as maximum average mutual information. The maximization is taken with respect to input probabilities p(xi ) i.e.,
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
15.Calculate the local oscillator frequency if incoming frequency is F1 and translated carrier frequency
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME:COMMUNICATION THEORY YEAR/SEM: II/IV SUBJECT CODE: EC 6402 UNIT I:l (AMPLITUDE MODULATION) PART A 1. Compute the bandwidth of the AMP
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME:COMMUNICATION THEORY YEAR/SEM: II/IV SUBJECT CODE: EC 6402 UNIT I:l (AMPLITUDE MODULATION) PART A 1. Compute the bandwidth of the AMP
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
 UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK UNIT IV PART-A
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
Angle Modulated Systems
 Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
SKP Engineering College
 SKP Engineering College Tiruvannamalai 606611 A Course Material on Communication Theory By K.Vijayalakshmi Assistant Professor Electronics and Communication Engineering Department Electronics and CommunicationEngineering
SKP Engineering College Tiruvannamalai 606611 A Course Material on Communication Theory By K.Vijayalakshmi Assistant Professor Electronics and Communication Engineering Department Electronics and CommunicationEngineering
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam
 V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY III YEAR / VI SEMESTER ACADEMIC YEAR 2015-16(EVEN)
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY III YEAR / VI SEMESTER ACADEMIC YEAR 2015-16(EVEN)
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems
 CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System
 UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, Kumaracoil DEPARTMENT OF ECE 2 MARKS & QUESTION- ANSWERS
 NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, Kumaracoil DEPARTMENT OF ECE 2 MARKS & QUESTION- ANSWERS EC 1301 Communication Theory Class : S5 ECE Prepared by :E.P.Kannan ECE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, Kumaracoil DEPARTMENT OF ECE 2 MARKS & QUESTION- ANSWERS EC 1301 Communication Theory Class : S5 ECE Prepared by :E.P.Kannan ECE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
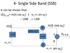 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks)
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
two computers. 2- Providing a channel between them for transmitting and receiving the signals through it.
 1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
Chapter 3. Question Mar No
 Chapter 3 Sr Question Mar No k. 1 Write any two drawbacks of TRF radio receiver 1. Instability due to oscillatory nature of RF amplifier.. Variation in bandwidth over tuning range. 3. Insufficient selectivity
Chapter 3 Sr Question Mar No k. 1 Write any two drawbacks of TRF radio receiver 1. Instability due to oscillatory nature of RF amplifier.. Variation in bandwidth over tuning range. 3. Insufficient selectivity
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
 ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Angle Modulation. Frequency Modulation
 Angle Modulation Contrast to AM Generalized sinusoid: v(t)=v max sin(ωt+φ) Instead of Varying V max, Vary (ωt+φ) Angle and Pulse Modulation - 1 Frequency Modulation Instantaneous Carrier Frequency f i
Angle Modulation Contrast to AM Generalized sinusoid: v(t)=v max sin(ωt+φ) Instead of Varying V max, Vary (ωt+φ) Angle and Pulse Modulation - 1 Frequency Modulation Instantaneous Carrier Frequency f i
Modulation Methods Frequency Modulation
 Modulation Methods Frequency Modulation William Sheets K2MQJ Rudolf F. Graf KA2CWL The use of frequency modulation (called FM) is another method of adding intelligence to a carrier signal. While simple
Modulation Methods Frequency Modulation William Sheets K2MQJ Rudolf F. Graf KA2CWL The use of frequency modulation (called FM) is another method of adding intelligence to a carrier signal. While simple
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques. Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur
 Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN
 SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN Course Code : EC0210 Course Title : COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester : IV
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN Course Code : EC0210 Course Title : COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester : IV
Module 8 Theory. dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain. Functional Blocks Parameters. IRTS Region 4
 Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Time division multiplexing The block diagram for TDM is illustrated as shown in the figure
 CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise
 Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]
![Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER] Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]](/thumbs/90/103239233.jpg) Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS
 J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
 UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALOG COMMUNICATION Introduction In the Microbroadcasting services, a reliable radio communication system is of vital importance. The swiftly moving operations of modern communities
UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALOG COMMUNICATION Introduction In the Microbroadcasting services, a reliable radio communication system is of vital importance. The swiftly moving operations of modern communities
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT. Semester: III Max.Marks: 100
 NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
FM THRESHOLD AND METHODS OF LIMITING ITS EFFECT ON PERFORMANCE
 FM THESHOLD AND METHODS OF LIMITING ITS EFFET ON PEFOMANE AHANEKU, M. A. Lecturer in the Department of Electronic Engineering, UNN ABSTAT This paper presents the outcome of the investigative study carried
FM THESHOLD AND METHODS OF LIMITING ITS EFFET ON PEFOMANE AHANEKU, M. A. Lecturer in the Department of Electronic Engineering, UNN ABSTAT This paper presents the outcome of the investigative study carried
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) Frequency Shift Keying Objectives To appreciate the principle of frequency shift keying and its relationship to analogue
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) Frequency Shift Keying Objectives To appreciate the principle of frequency shift keying and its relationship to analogue
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter
 SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals
 Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN
 Course Code Course Title Semester SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN : EC0210 : COMMUNICATION THEORY : IV
Course Code Course Title Semester SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN : EC0210 : COMMUNICATION THEORY : IV
The Digital Linear Amplifier
 The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS
 PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER
 LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER APPARATUS: Oscilloscope DSB/SSB Traine Power supply Connecting leads THEORY: A
LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER APPARATUS: Oscilloscope DSB/SSB Traine Power supply Connecting leads THEORY: A
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
Frequency Modulation
 Frequency Modulation transferred to the microwave carrier by means of FM. Instead of being done in one step, this modulation usually takes place at an intermediate frequency. signal is then frequency multiplied
Frequency Modulation transferred to the microwave carrier by means of FM. Instead of being done in one step, this modulation usually takes place at an intermediate frequency. signal is then frequency multiplied
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad
 Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
Downloaded from 1
 VII SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004 Attempt ALL questions. Q. [1] How does Digital communication System differ from Analog systems? Draw functional block diagram of DCS and explain the significance of
VII SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004 Attempt ALL questions. Q. [1] How does Digital communication System differ from Analog systems? Draw functional block diagram of DCS and explain the significance of
3.1 Introduction 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3 Double Sideband-Suppressed Carrier Modulation 3.4 Quadrature-Carrier Multiplexing 3.
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
 DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC8453 - LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question Bank (II-ECE) UNIT I BASICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART A 1.Mention the
DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC8453 - LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question Bank (II-ECE) UNIT I BASICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART A 1.Mention the
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation
 Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Communications I (ELCN 306)
 Communications I (ELCN 306) c Samy S. Soliman Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department Cairo University, Egypt Email: samy.soliman@cu.edu.eg Website: http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/samysoliman
Communications I (ELCN 306) c Samy S. Soliman Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department Cairo University, Egypt Email: samy.soliman@cu.edu.eg Website: http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/samysoliman
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System
 Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
AM, PM and FM mo m dula l ti t o i n
 AM, PM and FM modulation What is amplitude modulation In order that a radio signal can carry audio or other information for broadcasting or for two way radio communication, it must be modulated or changed
AM, PM and FM modulation What is amplitude modulation In order that a radio signal can carry audio or other information for broadcasting or for two way radio communication, it must be modulated or changed
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING. Radar Signal Processing Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti. Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti
 Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Block Diagram of FM Receiver
 FM Receivers FM receivers, like AM receivers, utilize the superheterodyne principle, but they operate at uch higher frequencies (88-108 MHz). A liiter is often used to ensure the received signal is constant
FM Receivers FM receivers, like AM receivers, utilize the superheterodyne principle, but they operate at uch higher frequencies (88-108 MHz). A liiter is often used to ensure the received signal is constant
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035)
 EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
LBI-30398N. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS. Page. DESCRIPTION...
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
Communication Systems
 Electrical Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
Electrical Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
OBJECTIVES EQUIPMENT LIST
 1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. A. Introduction. A. Introduction
 1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Amplitude Modulation
 Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002
 Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
4/29/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Signals and Emissions. SignalSignals and Emissionsissions. Subelement G8
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G8 Signals and Emissions 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G8 Signals and Emissions 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ERICSSONZ LBI-30398P. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
Electronics Interview Questions
 Electronics Interview Questions 1. What is Electronic? The study and use of electrical devices that operate by controlling the flow of electrons or other electrically charged particles. 2. What is communication?
Electronics Interview Questions 1. What is Electronic? The study and use of electrical devices that operate by controlling the flow of electrons or other electrically charged particles. 2. What is communication?
