Made of semiconducting materials: silicon, gallium arsenide, indium phosphide, gallium nitride, etc. (EE 332 stuff.)
|
|
|
- Shannon Russell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diodes Simple two-terminal electronic devices. Made of semiconducting materials: silicon, gallium arsenide, indium phosphide, gallium nitride, etc. (EE 332 stuff.) Semiconductors are interesting because their electrical properties can be varied over many order of magnitude: resistivity as high as 10 7 Ω-m (almost an insulator) or as low as 10 6 Ω-m (almost a conductor). Also, semiconductors can be made in two different varieties : either n- type in which current is carried by electrons (as usual) or p-type which current is carried by positive charges called holes. A diode consists of a p-type layer of semiconductor joined to a n-type layer, and so is also known as a p-n junction. Current flowing across this junction exhibits a very asymmetric, non-linear i-v characteristic. The non-linearity will force us to change the way we analyze circuits. EE 201 diodes 1
2 Diode applications Rectification cutting off the top half or bottom half of a voltage signal. Voltage regulation providing a steady voltage reference in a circuit. light-emitting diodes for indicators light-emitting diodes for illumination lasers - DVD players, fiber-optic communication, surgery photodetectors sense presence of light, especially low levels or fast pulses photovoltaics (solar cells) green electrical power generation building block for transistors EE 201 diodes 2
3 rectifying diode (switching or small-signal) made of silicon LEDs various materials (not silicon). Different material different colors. laser solar cell LED lighting usually gallium nitride (UV light) that excites a phosphor. EE 201 diodes 3
4 Diode anode i d i d anode v d v d cathode cathode think funnel it flows in one direction EE 201 diodes 4
5 diode i-v characteristic ideal diode equation i d v d / Extremely non-linear. Will cause lots of problems in analyzing, but offers many opportunities for applications. I S is a parameter of the diode, known as saturation current or scale current. Different for every diode. (Like R for a resistor.) Typical: I S A. kt is the thermal energy. k (Boltzmann s constant 1.38x10 23 J/K), T temperature in kelvin (K). q is the charge on one electron; kt/q is the thermal voltage. At 300K ( 27 C, approximately room temperature), kt/q 25.8 mv. EE 201 diodes 5
6 diode: forward and reverse conduction i d / v d If v D is positive, v D >> kt/q. / Lots of current can flow. Increases rapidly as v D increases. Forward bias or forward conduction. If v D is negative. almost zero. Independent of the A very small trickle of current flows, voltage. Reverse bias or reverse conduction. The asymmetry between forward and reverse conduction is the basis for rectification current can flow only one way (essentially). (Again, think funnel.) EE 201 diodes 6
7 I D (A) I D (A) V D (V) V D (V) Diode i-v I S A T 300 K Same diode Forward voltage only semi-log plot EE 201 diodes 7
8 diodes in circuit The non-linear behavior has some significant effects. Basic notions are still valid: KCL and KCL, energy and power Some techniques are invalid with non-linear elements: superposition, Thevenin. Node-voltage and mesh-current techniques are still applicable, but the result is a set of non-linear equations, which are difficult to solve. With non-linear elements, we will rely on: Approximating the device behavior with linear elements. This requires some guessing and then checking of the results. Of course, it is only approximate. SPICE EE 201 diodes 8
9 diodes in circuits Important: When working with diodes, don t EVER apply a forward voltage directly across the diode. The result is usually a dead diode. VS 1.5 V vd id IS 1014 A room temp: kt/q 25.8 mv. vd VS /... This is absolutely absurd. Of course, what really happens is that the diode would burn up (due to instant heating) when the current hits 1 A or so. There must always be a current-limiting resistor in series. EE 201 diodes 9
10 R 1 k! VS 1.5 V id vd IS 1014 A room temp: kt/q 25.8 mv. / ln VS vr vd 1st guess EE 201 / ln ln??? Can t be solved in closed form. Transcendental equation. Must use iteration. (Trial-and-error.) 1.00 ma ma ma ma ma. (. ) ln id ma vd V diodes 10
11 a VS D1 R1 b R2 c D2 R3 / / / 3 non-linear equations in 3 unknowns Good luck with that!! EE 201 diodes 11
12 V S R 1 k! i D v D / ln When the diode is reverse-biased (V S < 0, so v D < 0), the diode behaves essentially like an open circuit, i D 0. When the diode is forward-biased (V S > 0, so v D > 0), the diode voltage is roughly constant at 0.6 V V. V S (V) v D (V) i D (ma) V V V V V v v EE 201 diodes 12
13 piecewise diode model The results of the previous slide suggest the following approximate model. When the diode is reverse-biased, we can treat it as if it is an opencircuit When the diode is forward-biased, we treat it like an ideal source with a value of 0.7 V. Reverse (v D < 0) Forward (v D > 0) i D 0 i D 0 v D < 0 v D i D i D v D > V To use the models. Guess forward or reverse Insert the corresponding model Solve for voltage/current using model Check the result: for reverse, v D < 0, for forward, i D flows in correct direction Note that the diode is NOT a voltage source. It does not provide power to the circuit. It simply behaves as if it were a small voltage source or battery that is absorbing power. EE 201 diodes 13
14 V S R 1 k! V S (V) v D (V) i D (ma) i D v D Reverse (v D < 0 when V S < 0) R 1 k! V S i D 0 v D V S Forward (v D > 0 when V S > 0) V S i D v D 0.7 V R 1 k! V V V V V v v compare to slide 12 very similar EE 201 diodes 14
15 a b 1 k! R2 2 k! D1 VS 5V R1 c D2 Since VS is positive, we might guess that both diodes are forward-biased. R3 3 k! id1 va VS 0.7 V 4.3 V. vc vb 0.7 V. VS a id2 R1 0.7 V b R2 Example c 0.7 V R3 check:. vb 2.47 V. EE Both currents are positive, consistent with forward conducting diodes. The guesses were correct. diodes 15
Chapter #3: Diodes. from Microelectronic Circuits Text by Sedra and Smith Oxford Publishing
 Chapter #3: Diodes from Microelectronic Circuits Text by Sedra and Smith Oxford Publishing Introduction IN THIS CHAPTER WE WILL LEARN the characteristics of the ideal diode and how to analyze and design
Chapter #3: Diodes from Microelectronic Circuits Text by Sedra and Smith Oxford Publishing Introduction IN THIS CHAPTER WE WILL LEARN the characteristics of the ideal diode and how to analyze and design
Microelectronic Circuits, Kyung Hee Univ. Spring, Chapter 3. Diodes
 Chapter 3. Diodes 1 Introduction IN THIS CHAPTER WE WILL LEARN the characteristics of the ideal diode and how to analyze and design circuits containing multiple ideal diodes together with resistors and
Chapter 3. Diodes 1 Introduction IN THIS CHAPTER WE WILL LEARN the characteristics of the ideal diode and how to analyze and design circuits containing multiple ideal diodes together with resistors and
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits. Electrical Enginnering Departement. By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben. Instructor: Eng.
 Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
ENG2210 Electronic Circuits. Chapter 3 Diodes
 ENG2210 Electronic Circuits Mokhtar A. Aboelaze York University Chapter 3 Diodes Objectives Learn the characteristics of ideal diode and how to analyze and design circuits containing multiple diodes Learn
ENG2210 Electronic Circuits Mokhtar A. Aboelaze York University Chapter 3 Diodes Objectives Learn the characteristics of ideal diode and how to analyze and design circuits containing multiple diodes Learn
EE/COE 152: Basic Electronics. Lecture 3. A.S Agbemenu. https://sites.google.com/site/agbemenu/courses/ee-coe-152
 EE/COE 152: Basic Electronics Lecture 3 A.S Agbemenu https://sites.google.com/site/agbemenu/courses/ee-coe-152 Books: Microelcetronic Circuit Design (Jaeger/Blalock) Microelectronic Circuits (Sedra/Smith)
EE/COE 152: Basic Electronics Lecture 3 A.S Agbemenu https://sites.google.com/site/agbemenu/courses/ee-coe-152 Books: Microelcetronic Circuit Design (Jaeger/Blalock) Microelectronic Circuits (Sedra/Smith)
Diodes. Introduction. Silicon p-n junction diodes. Structure
 Diodes ntroduction A diode is a two terminal circuit element that allows current flow in one direction only. Diodes are thus non-linear circuit elements because the current through them is not proportional
Diodes ntroduction A diode is a two terminal circuit element that allows current flow in one direction only. Diodes are thus non-linear circuit elements because the current through them is not proportional
Light Emitting Diodes
 Light Emitting Diodes Topics covered in this presentation: LED operation LED Characteristics Display devices Protection and limiting 1 of 9 Light Emitting Diode - LED A special type of diode is the Light
Light Emitting Diodes Topics covered in this presentation: LED operation LED Characteristics Display devices Protection and limiting 1 of 9 Light Emitting Diode - LED A special type of diode is the Light
Lecture 5: Diode, Rectifier and Capacitor. Bo Wang Division of Information & Computing Technology Hamad Bin Khalifa University
 Lecture 5: Diode, Rectifier and Capacitor Bo Wang Division of Information & Computing Technology Hamad Bin Khalifa University bwang@hbku.edu.qa 1 Why Rectifying? Voltage and current delivered from the
Lecture 5: Diode, Rectifier and Capacitor Bo Wang Division of Information & Computing Technology Hamad Bin Khalifa University bwang@hbku.edu.qa 1 Why Rectifying? Voltage and current delivered from the
Analog Electronic Circuits
 Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
The George Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 20 - LAB
 The George Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 20 - LAB Components: Experiment # 1 Solid State Diodes Testing & Characterization
The George Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 20 - LAB Components: Experiment # 1 Solid State Diodes Testing & Characterization
EDC Lecture Notes UNIT-1
 P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram
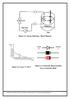 Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica. Analogue Electronics. Paolo Colantonio A.A.
 Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
EE70 - Intro. Electronics
 EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells
 LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
Lecture 2 p-n junction Diode characteristics. By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood
 Electronic I Lecture 2 p-n junction Diode characteristics By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood THE p-n JUNCTION DIODE The pn junction diode is formed by fabrication of a p-type semiconductor region in intimate
Electronic I Lecture 2 p-n junction Diode characteristics By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood THE p-n JUNCTION DIODE The pn junction diode is formed by fabrication of a p-type semiconductor region in intimate
Lab VIII Photodetectors ECE 476
 Lab VIII Photodetectors ECE 476 I. Purpose The electrical and optical properties of various photodetectors will be investigated. II. Background Photodiode A photodiode is a standard diode packaged so that
Lab VIII Photodetectors ECE 476 I. Purpose The electrical and optical properties of various photodetectors will be investigated. II. Background Photodiode A photodiode is a standard diode packaged so that
Chapter #4: Diodes. from Microelectronic Circuits Text by Sedra and Smith Oxford Publishing
 Chapter #4: Diodes from Microelectronic Circuits Text by Sedra and Smith Oxford Publishing Introduction IN THIS CHAPTER WE WILL LEARN the characteristics of the ideal diode and how to analyze and design
Chapter #4: Diodes from Microelectronic Circuits Text by Sedra and Smith Oxford Publishing Introduction IN THIS CHAPTER WE WILL LEARN the characteristics of the ideal diode and how to analyze and design
Intrinsic Semiconductor
 Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
Diodes (non-linear devices)
 C H A P T E R 4 Diodes (non-linear devices) Ideal Diode Figure 4.2 The two modes of operation of ideal diodes and the use of an external circuit to limit (a) the forward current and (b) the reverse voltage.
C H A P T E R 4 Diodes (non-linear devices) Ideal Diode Figure 4.2 The two modes of operation of ideal diodes and the use of an external circuit to limit (a) the forward current and (b) the reverse voltage.
Diode. Diode. Diode - mode of operation. AMN in the direction of conventional current (opposite to electron flow)
 Diode Diode Chapter 1 2 A diode is a single p-n junction device with conductive contacts wire leads co each region. The n region is called cathode, p region is called anode. The a Diode packages Diode
Diode Diode Chapter 1 2 A diode is a single p-n junction device with conductive contacts wire leads co each region. The n region is called cathode, p region is called anode. The a Diode packages Diode
EECE251 Circuit Analysis I Set 6: Diodes
 EECE251 Circuit Analysis I Set 6: Diodes Shahriar Mirabbasi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Thanks to Dr. Linares and Dr. Yan for sharing
EECE251 Circuit Analysis I Set 6: Diodes Shahriar Mirabbasi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Thanks to Dr. Linares and Dr. Yan for sharing
 FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 PHY301- Circuit Theory (Session - 2) Time: 120 min Marks: 70 Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Charge of 2c and 5c will attract each other repel each other
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 PHY301- Circuit Theory (Session - 2) Time: 120 min Marks: 70 Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Charge of 2c and 5c will attract each other repel each other
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits
 EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture IIII James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Defined some terminology
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture IIII James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Defined some terminology
10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional)
 EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
semiconductor p-n junction Potential difference across the depletion region is called the built-in potential barrier, or built-in voltage:
 Chapter four The Equilibrium pn Junction The Electric field will create a force that will stop the diffusion of carriers reaches thermal equilibrium condition Potential difference across the depletion
Chapter four The Equilibrium pn Junction The Electric field will create a force that will stop the diffusion of carriers reaches thermal equilibrium condition Potential difference across the depletion
PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. Diodes and Transistors 1
 Part I Diodes Purpose PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. In this experiment, you will investigate the current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode and examine the applications of
Part I Diodes Purpose PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. In this experiment, you will investigate the current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode and examine the applications of
Introduction to Photovoltaics
 Introduction to Photovoltaics PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 24, 2015 Only solar energy Of all the possible sources
Introduction to Photovoltaics PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 24, 2015 Only solar energy Of all the possible sources
Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits
 Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
Downloaded from
 SOLID AND SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES (EASY AND SCORING TOPIC) 1. Distinction of metals, semiconductor and insulator on the basis of Energy band of Solids. 2. Types of Semiconductor. 3. PN Junction formation
SOLID AND SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES (EASY AND SCORING TOPIC) 1. Distinction of metals, semiconductor and insulator on the basis of Energy band of Solids. 2. Types of Semiconductor. 3. PN Junction formation
Diode as a Temperature Sensor
 M.B. Patil, IIT Bombay 1 Diode as a Temperature Sensor Introduction A p-n junction obeys the Shockley equation, I D = I s e V a/v T 1 ) I s e Va/V T for V a V T, 1) where V a is the applied voltage, V
M.B. Patil, IIT Bombay 1 Diode as a Temperature Sensor Introduction A p-n junction obeys the Shockley equation, I D = I s e V a/v T 1 ) I s e Va/V T for V a V T, 1) where V a is the applied voltage, V
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Diode conducts when V anode > V cathode. Positive current flow. Diodes (and transistors) are non-linear device: V IR!
 Diodes: What do we use diodes for? Lecture 5: Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double
Diodes: What do we use diodes for? Lecture 5: Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS. Class XII : PHYSICS WORKSHEET
 SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
CHAPTER 1 DIODE CIRCUITS. Semiconductor act differently to DC and AC currents
 CHAPTER 1 DIODE CIRCUITS Resistance levels Semiconductor act differently to DC and AC currents There are three types of resistances 1. DC or static resistance The application of DC voltage to a circuit
CHAPTER 1 DIODE CIRCUITS Resistance levels Semiconductor act differently to DC and AC currents There are three types of resistances 1. DC or static resistance The application of DC voltage to a circuit
UNIT IX ELECTRONIC DEVICES
 UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
Circle the one best answer for each question. Five points per question.
 ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 1 September 11, 2001 Instructor (circle one) Talavage Gray This exam consists of 16 multiple choice questions and one workout problem. Record all answers to the multiple choice questions
ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 1 September 11, 2001 Instructor (circle one) Talavage Gray This exam consists of 16 multiple choice questions and one workout problem. Record all answers to the multiple choice questions
Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits
 Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits Circuits which are used to clip off portions of signal voltages above or below certain levels are called limiters or clippers. Types of Clippers Positive Clipper Negative
Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits Circuits which are used to clip off portions of signal voltages above or below certain levels are called limiters or clippers. Types of Clippers Positive Clipper Negative
Unit 2 Semiconductor Devices. Lecture_2.5 Opto-Electronic Devices
 Unit 2 Semiconductor Devices Lecture_2.5 Opto-Electronic Devices Opto-electronics Opto-electronics is the study and application of electronic devices that interact with light. Electronics (electrons) Optics
Unit 2 Semiconductor Devices Lecture_2.5 Opto-Electronic Devices Opto-electronics Opto-electronics is the study and application of electronic devices that interact with light. Electronics (electrons) Optics
Lecture -1: p-n Junction Diode
 Lecture -1: p-n Junction Diode Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor to
Lecture -1: p-n Junction Diode Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor to
Exam Below are two schematics of current sources implemented with MOSFETs. Which current source has the best compliance voltage?
 Exam 2 Name: Score /90 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. Below are two schematics of current sources implemented with MOSFETs. Which current source has the best compliance
Exam 2 Name: Score /90 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. Below are two schematics of current sources implemented with MOSFETs. Which current source has the best compliance
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting AC to DC
 EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
Page 1. Date 15/02/2013
 Page 1 Date 15/02/2013 Final Term Examination Fall 2012 Phy301-Circuit Theory 1. State kirchhoff s current law (KCL) Marks: 2: Answer: (PAGE 42) KIRCHHOF S CURRENT LAW Sum of all the currents entering
Page 1 Date 15/02/2013 Final Term Examination Fall 2012 Phy301-Circuit Theory 1. State kirchhoff s current law (KCL) Marks: 2: Answer: (PAGE 42) KIRCHHOF S CURRENT LAW Sum of all the currents entering
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Homework Assignment True or false. For both the inverting and noninverting op-amp configurations, V OS results in
 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each. Homework Assignment 02 1. An op-amp has input bias current I B = 1 μa. Make an estimate for the input offset current I OS. Answer. I OS is normally an order of
Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each. Homework Assignment 02 1. An op-amp has input bias current I B = 1 μa. Make an estimate for the input offset current I OS. Answer. I OS is normally an order of
Physics 15b, Lab 3: The Capacitor... and a glimpse of Diodes
 Phys 15b: Lab 3, Sprng 2007 1 Due Friday, March 23, 2007. Physics 15b, Lab 3: The Capacitor... and a glimpse of Diodes REV0 1 ; March 14, 2007 NOTE that this is the first of the labs that you are invited
Phys 15b: Lab 3, Sprng 2007 1 Due Friday, March 23, 2007. Physics 15b, Lab 3: The Capacitor... and a glimpse of Diodes REV0 1 ; March 14, 2007 NOTE that this is the first of the labs that you are invited
ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 1 (Fall 2016 SOLUTIONS)
 SOLUTIONS ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 1 (Fall 2016 SOLUTIONS) Problem 1 (20 points) We know that a pn junction diode has an exponential I-V behavior when forward biased. The diode equation relating
SOLUTIONS ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 1 (Fall 2016 SOLUTIONS) Problem 1 (20 points) We know that a pn junction diode has an exponential I-V behavior when forward biased. The diode equation relating
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2-6. Current, Voltage, & Resistors DIODES
 26.1 26.2 Learning Outcomes Spiral 26 Semiconductor Material MOS Theory I underst why a diode conducts current under forward bias but does not under reverse bias I underst the three modes of operation
26.1 26.2 Learning Outcomes Spiral 26 Semiconductor Material MOS Theory I underst why a diode conducts current under forward bias but does not under reverse bias I underst the three modes of operation
Exercise 12. Semiconductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Introduction to semiconductors. The diode
 Exercise 12 Semiconductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. You will learn how to use a diode to rectify ac voltage to produce
Exercise 12 Semiconductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. You will learn how to use a diode to rectify ac voltage to produce
Applications of diodes
 Applications of diodes Learners should be able to: (a) describe the I V characteristics of a silicon diode (b) describe the use of diodes for component protection in DC circuits and half-wave rectification
Applications of diodes Learners should be able to: (a) describe the I V characteristics of a silicon diode (b) describe the use of diodes for component protection in DC circuits and half-wave rectification
OFCS OPTICAL DETECTORS 11/9/2014 LECTURES 1
 OFCS OPTICAL DETECTORS 11/9/2014 LECTURES 1 1-Defintion & Mechanisms of photodetection It is a device that converts the incident light into electrical current External photoelectric effect: Electrons are
OFCS OPTICAL DETECTORS 11/9/2014 LECTURES 1 1-Defintion & Mechanisms of photodetection It is a device that converts the incident light into electrical current External photoelectric effect: Electrons are
EE 105. Diode Circuits. Prof. Ali M. Niknejad and Prof. Rikky Muller. March 2, U.C. Berkeley Copyright 2017 by Ali M.
 EE 105 Diode Circuits Prof. Ali M. Niknejad and Prof. Rikky Muller U.C. Berkeley Copyright 2017 by Ali M. Niknejad March 2, 2017 1/ 23 Diode Introduction A diode is a non-linear element. To a very good
EE 105 Diode Circuits Prof. Ali M. Niknejad and Prof. Rikky Muller U.C. Berkeley Copyright 2017 by Ali M. Niknejad March 2, 2017 1/ 23 Diode Introduction A diode is a non-linear element. To a very good
Ideal Diode Summary. p-n Junction. Consequently, characteristics curve of the ideal diode is given by. Ideal diode state = OF F, if V D < 0
 Course Contents ELE230 Electronics I http://www.ee.hacettepe.edu.tr/ usezen/ele230/ Dr. Umut Sezen & Dr. Dinçer Gökcen Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Hacettepe University and Diode
Course Contents ELE230 Electronics I http://www.ee.hacettepe.edu.tr/ usezen/ele230/ Dr. Umut Sezen & Dr. Dinçer Gökcen Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Hacettepe University and Diode
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES
 KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
Electronic Instrumentation. Experiment 8: Diodes (continued) Project 4: Optical Communications Link
 Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 8: Diodes (continued) Project 4: Optical Communications Link Agenda Brief Review: Diodes Zener Diodes Project 4: Optical Communication Link Why optics? Understanding
Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 8: Diodes (continued) Project 4: Optical Communications Link Agenda Brief Review: Diodes Zener Diodes Project 4: Optical Communication Link Why optics? Understanding
The preferred Exercise is shown in Exercises 5B or 5C.
 ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 5A The preferred Exercise is shown in Exercises 5B or 5C. Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Validate the Schottky diode equation. Calculate the dc and dynamic (ac) resistance
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 5A The preferred Exercise is shown in Exercises 5B or 5C. Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Validate the Schottky diode equation. Calculate the dc and dynamic (ac) resistance
Electrical and Electronic Laboratory Faculty of Engineering Chulalongkorn University. Semiconductor Diode (SD)
 2141274 Electrical and Electronic Laboratory Faculty of Engineering Chulalongkorn University Semiconductor Diode (SD) Contents A. Introduction 1. History 2. Thermionic or gaseous state diodes 3. Semiconductor
2141274 Electrical and Electronic Laboratory Faculty of Engineering Chulalongkorn University Semiconductor Diode (SD) Contents A. Introduction 1. History 2. Thermionic or gaseous state diodes 3. Semiconductor
Chapter 3: Resistive Network Analysis Instructor Notes
 Chapter 3: Resistive Network Analysis Instructor Notes Chapter 3 presents the principal topics in the analysis of resistive (DC) circuits The presentation of node voltage and mesh current analysis is supported
Chapter 3: Resistive Network Analysis Instructor Notes Chapter 3 presents the principal topics in the analysis of resistive (DC) circuits The presentation of node voltage and mesh current analysis is supported
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit,
The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit,
Diodes. Sections
 iodes Sections 3.3.1 3.3.8 1 Modeling iode Characteristics Exponential model nonlinearity makes circuit analysis difficult. Two common approaches are graphical analysis and iterative analysis For simple
iodes Sections 3.3.1 3.3.8 1 Modeling iode Characteristics Exponential model nonlinearity makes circuit analysis difficult. Two common approaches are graphical analysis and iterative analysis For simple
Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes
 Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Diodes The diode is a 2-terminal device. A diode ideally conducts in only one direction. 2 Diode Characteristics Conduction Region Non-Conduction Region The voltage across
Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Diodes The diode is a 2-terminal device. A diode ideally conducts in only one direction. 2 Diode Characteristics Conduction Region Non-Conduction Region The voltage across
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
 Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 10 - Junction Device Wrap-up - Outline Announcements IES
 6.012 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 10 - Junction Device Wrap-up - Outline Announcements Handout - Lecture Outline and Summary First Hour Exam - Tomorrow!! Rm. 34-101, 7:30-9:30 pm Recitations
6.012 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 10 - Junction Device Wrap-up - Outline Announcements Handout - Lecture Outline and Summary First Hour Exam - Tomorrow!! Rm. 34-101, 7:30-9:30 pm Recitations
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo Section s7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s7ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
The University of Toledo Section s7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s7ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
Diodes. Analog Electronics Lesson 4. Objectives and Overview:
 Analog Electronics Lesson 4 Diodes Objectives and Overview: This lesson will introduce p- and n-type material, how they form a junction that rectifies current, and familiarize you with basic p-n junction
Analog Electronics Lesson 4 Diodes Objectives and Overview: This lesson will introduce p- and n-type material, how they form a junction that rectifies current, and familiarize you with basic p-n junction
Structure. Symbol. physical structure. directions for current and voltage. circuit symbol
 iodes 1/18 Structure. Symbol physical structure circuit symbol directions for current and voltage The arrow in the diode s symbol points in the direction of forward current flow 2 / 5 Current voltage characteristic
iodes 1/18 Structure. Symbol physical structure circuit symbol directions for current and voltage The arrow in the diode s symbol points in the direction of forward current flow 2 / 5 Current voltage characteristic
FINALTERM EXAMINATION. Spring PHY301- Circuit Theory
 Date 14/2/2013 Eini FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 PHY301- Circuit Theory Time: 90 min Marks: 60 Question No: 1 If we connect 3 capacitors in parallel, the combined effect of all these capacitors will
Date 14/2/2013 Eini FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 PHY301- Circuit Theory Time: 90 min Marks: 60 Question No: 1 If we connect 3 capacitors in parallel, the combined effect of all these capacitors will
CHAPTER SEMI-CONDUCTING DEVICES QUESTION & PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 Solutions--Ch. 15 (Semi-conducting Devices) CHAPTER 15 -- SEMI-CONDUCTING DEVICES QUESTION & PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 15.1) What is the difference between a conductor and a semi-conductor? Solution: A conductor
Solutions--Ch. 15 (Semi-conducting Devices) CHAPTER 15 -- SEMI-CONDUCTING DEVICES QUESTION & PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 15.1) What is the difference between a conductor and a semi-conductor? Solution: A conductor
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
Experiment 8: Semiconductor Devices
 Name/NetID: Experiment 8: Semiconductor Devices Laboratory Outline In today s experiment you will be learning to use the basic building blocks that drove the ability to miniaturize circuits to the point
Name/NetID: Experiment 8: Semiconductor Devices Laboratory Outline In today s experiment you will be learning to use the basic building blocks that drove the ability to miniaturize circuits to the point
1) A silicon diode measures a low value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, is
 1) A silicon diode measures a low value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, is A [ ]) the diode is open. B [ ]) the diode is shorted to ground. C [v]) the diode is
1) A silicon diode measures a low value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, is A [ ]) the diode is open. B [ ]) the diode is shorted to ground. C [v]) the diode is
ELEN-325. Introduction to Electronic Circuits: Design Approach. ELEN-325. Part IV. Diode s Applications
 Jose SilvaMartinez ELEN325. Part I. Diode s Applications 1. The PN junction (diode). The diode is a unidirectional device with two modes of operation: Forward bias when current can flow through the device
Jose SilvaMartinez ELEN325. Part I. Diode s Applications 1. The PN junction (diode). The diode is a unidirectional device with two modes of operation: Forward bias when current can flow through the device
EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES
 EXPERIMENT 9 EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES Semiconductor Diodes Structure 91 Introduction Objectives 92 Basics of Semiconductors Revisited 93 A p-n Junction Operation of a p-n Junction A Forward
EXPERIMENT 9 EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES Semiconductor Diodes Structure 91 Introduction Objectives 92 Basics of Semiconductors Revisited 93 A p-n Junction Operation of a p-n Junction A Forward
Diodes Rectifiers, Zener diodes light emitting diodes, laser diodes photodiodes, optocouplers
 Diodes Rectifiers, Zener diodes light emitting diodes, laser diodes photodiodes, optocouplers Prepared by Scott Robertson Fall 2007 Physics 3330 1 Impurity-doped semiconductors Semiconductors (Ge, Si)
Diodes Rectifiers, Zener diodes light emitting diodes, laser diodes photodiodes, optocouplers Prepared by Scott Robertson Fall 2007 Physics 3330 1 Impurity-doped semiconductors Semiconductors (Ge, Si)
Question. 1 (2 points. (a) (b) 10 khz (c) (d) 10.4 khz. (a) (b) khz (c) (d) 100 khz. 3. The. (a) (c) Fall What is the 3-dB. 1 nf?
 Homework Assignment 02 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if 2.5K, 100K, 40 ms, and 1 nf? (a) 65.25 khz (b) 10 khz (c) 1.59 khz
Homework Assignment 02 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if 2.5K, 100K, 40 ms, and 1 nf? (a) 65.25 khz (b) 10 khz (c) 1.59 khz
Battery Charger Circuit Using SCR
 Battery Charger Circuit Using SCR Introduction to SCR: SCR is abbreviation for Silicon Controlled Rectifier. SCR has three pins anode, cathode and gate as shown in the below figure. It is made up of there
Battery Charger Circuit Using SCR Introduction to SCR: SCR is abbreviation for Silicon Controlled Rectifier. SCR has three pins anode, cathode and gate as shown in the below figure. It is made up of there
Lecture 4. pn Junctions (Diodes) Wednesday 27/9/2017 pn junctions 1-1
 Lecture 4 n Junctions (Diodes) Wednesday 27/9/2017 n junctions 1-1 Agenda Continue n junctions Equilibrium (zero bias) Deletion rejoins Built-in otential Reverse and forward bias I-V characteristics Bias
Lecture 4 n Junctions (Diodes) Wednesday 27/9/2017 n junctions 1-1 Agenda Continue n junctions Equilibrium (zero bias) Deletion rejoins Built-in otential Reverse and forward bias I-V characteristics Bias
2 MARKS EE2203 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT 1
 2 MARKS EE2203 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT 1 1. Define PN junction. When a p type semiconductor is joined to a N type semiconductor the contact surface is called PN junction. 2. What is an ideal
2 MARKS EE2203 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT 1 1. Define PN junction. When a p type semiconductor is joined to a N type semiconductor the contact surface is called PN junction. 2. What is an ideal
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology Available Online at:
 MODELLING LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING SPICE Dattaprasad Madur 1, Najib Ghatte 2, init Pereira 3, Tushar Surwadkar 4 1 2 3 4 Department of Electronics Fr. Conceicao Rodrigues College of Engineering Fr. Agnel
MODELLING LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING SPICE Dattaprasad Madur 1, Najib Ghatte 2, init Pereira 3, Tushar Surwadkar 4 1 2 3 4 Department of Electronics Fr. Conceicao Rodrigues College of Engineering Fr. Agnel
Electronic Circuits I. Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud
 Electronic Circuits I Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud alaa_y_emam@hotmail.com Chapter 27 Diode and diode application Outline: Semiconductor Materials The P-N Junction Diode Biasing P-N Junction Volt-Ampere
Electronic Circuits I Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud alaa_y_emam@hotmail.com Chapter 27 Diode and diode application Outline: Semiconductor Materials The P-N Junction Diode Biasing P-N Junction Volt-Ampere
FET Channel. - simplified representation of three terminal device called a field effect transistor (FET)
 FET Channel - simplified representation of three terminal device called a field effect transistor (FET) - overall horizontal shape - current levels off as voltage increases - two regions of operation 1.
FET Channel - simplified representation of three terminal device called a field effect transistor (FET) - overall horizontal shape - current levels off as voltage increases - two regions of operation 1.
PN Junction Diode Table of Contents. What Are Diodes Made Out Of?
 PN Junction iode Table of Contents What are diodes made out of?slide 3 N-type materialslide 4 P-type materialslide 5 The pn junctionslides 6-7 The biased pn junctionslides 8-9 Properties of diodesslides
PN Junction iode Table of Contents What are diodes made out of?slide 3 N-type materialslide 4 P-type materialslide 5 The pn junctionslides 6-7 The biased pn junctionslides 8-9 Properties of diodesslides
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION 17215
 MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION 17215 Subject Title: Elements of Electronics Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION 17215 Subject Title: Elements of Electronics Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
DESIGN OF AN ANALOG FIBER OPTIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
 DESIGN OF AN ANALOG FIBER OPTIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM OBJECTIVE To design and build a complete analog fiber optic transmission system, using light emitting diodes and photodiodes. INTRODUCTION A fiber optic
DESIGN OF AN ANALOG FIBER OPTIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM OBJECTIVE To design and build a complete analog fiber optic transmission system, using light emitting diodes and photodiodes. INTRODUCTION A fiber optic
Three Terminal Devices
 Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
An Introduction to Rectifier Circuits
 TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION An Introduction to Rectifier Circuits An important application of the diode is one that takes place in the design of the rectifier circuit. Simply put, this circuit converts alternating
TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION An Introduction to Rectifier Circuits An important application of the diode is one that takes place in the design of the rectifier circuit. Simply put, this circuit converts alternating
What Is An SMU? SEP 2016
 What Is An SMU? SEP 2016 Agenda SMU Introduction Theory of Operation (Constant Current/Voltage Sourcing + Measure) Cabling : Triax vs Coax Advantages in Resistance Applications (vs. DMMs) Advantages in
What Is An SMU? SEP 2016 Agenda SMU Introduction Theory of Operation (Constant Current/Voltage Sourcing + Measure) Cabling : Triax vs Coax Advantages in Resistance Applications (vs. DMMs) Advantages in
Experiments in Photonics
 Experiments in Photonics Section 3: Electronics & Photonics An integrated electronic/photonic device. Photograph courtesy of Quantum Optics Group, Australian National University Minilabs 2006 1 Electronics
Experiments in Photonics Section 3: Electronics & Photonics An integrated electronic/photonic device. Photograph courtesy of Quantum Optics Group, Australian National University Minilabs 2006 1 Electronics
12/01/2009. Practice with past exams
 EE40 Final Exam Review Prof. Nathan Cheung 12/01/2009 Practice with past exams http://hkn.eecs.berkeley.edu/exam/list/?examcourse=ee%2040 Slide 1 Overview of Course Circuit components: R, C, L, sources
EE40 Final Exam Review Prof. Nathan Cheung 12/01/2009 Practice with past exams http://hkn.eecs.berkeley.edu/exam/list/?examcourse=ee%2040 Slide 1 Overview of Course Circuit components: R, C, L, sources
Lecture 9: Limiting and Clamping Diode Circuits. Voltage Doubler. Special Diode Types.
 Whites, EE 320 Lecture 9 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 9: Limiting and Clamping Diode Circuits. Voltage Doubler. Special Diode Types. We ll finish up our discussion of diodes in this lecture by consider a few more
Whites, EE 320 Lecture 9 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 9: Limiting and Clamping Diode Circuits. Voltage Doubler. Special Diode Types. We ll finish up our discussion of diodes in this lecture by consider a few more
Mechatronics Chapter 3-1 Semiconductor devices Diode
 MEMS1082 Mechatronics Chapter 3-1 Semiconductor devices Diode Semiconductor: Si Semiconductor N-type and P-type Semiconductors There are two types of impurities: N-type - In N-type doping, phosphorus or
MEMS1082 Mechatronics Chapter 3-1 Semiconductor devices Diode Semiconductor: Si Semiconductor N-type and P-type Semiconductors There are two types of impurities: N-type - In N-type doping, phosphorus or
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:041 Electronic Circuits Chapter 1 & 2 A. Kruger Diode Review, Page-1 Semiconductors licon () atoms have 4 electrons in valence band and form strong covalent bonds with surrounding atoms. Section 1.1.2
55:041 Electronic Circuits Chapter 1 & 2 A. Kruger Diode Review, Page-1 Semiconductors licon () atoms have 4 electrons in valence band and form strong covalent bonds with surrounding atoms. Section 1.1.2
Digital Electronics. By: FARHAD FARADJI, Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Electrical and Computer Engineering, K. N. Toosi University of Technology
 K. N. Toosi University of Technology Chapter 7. Field-Effect Transistors By: FARHAD FARADJI, Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Electrical and Computer Engineering, K. N. Toosi University of Technology http://wp.kntu.ac.ir/faradji/digitalelectronics.htm
K. N. Toosi University of Technology Chapter 7. Field-Effect Transistors By: FARHAD FARADJI, Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Electrical and Computer Engineering, K. N. Toosi University of Technology http://wp.kntu.ac.ir/faradji/digitalelectronics.htm
Homework Assignment 01
 Homework Assignment 01 In this homework set students review some basic circuit analysis techniques, as well as review how to analyze ideal op-amp circuits. Numerical answers must be supplied using engineering
Homework Assignment 01 In this homework set students review some basic circuit analysis techniques, as well as review how to analyze ideal op-amp circuits. Numerical answers must be supplied using engineering
Diode Characteristics and Applications
 Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Electric Circuit Fall 2017 Lab3 LABORATORY 3. Diode. Guide
 LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
Homework Assignment 02
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) 1. Is the following circuit an STC circuit? Homework Assignment 02 (a) Yes (b) No (c) Need additional information Answer: There is one reactive element
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) 1. Is the following circuit an STC circuit? Homework Assignment 02 (a) Yes (b) No (c) Need additional information Answer: There is one reactive element
