MEDIUM SPEED ANALOG-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
|
|
|
- Gilbert Pearson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMOS Analog IC Design Page MEDIUM SPEED ANALOG-DIGITAL CONVERTERS INTRODUCTION Successive Approximation Algorithm: 1.) Start with the MSB bit and work toward the LSB bit. 2.) Guess the MSB bit as 1. 3.) Apply the digital word to a DAC. 4.) Compare the DAC output with the sampled analog input voltage. 5.) If the DAC output is greater, keep the guess of 1. If the DAC output is less, change the guess to 0. 6.) Repeat for the next MSB. If the number of bits is N, the time for conversion will be NT where T is the clock period. Illustration:
2 CMOS Analog IC Design Page BLOCK DIAGRAM OF A SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC R. Hnatek, A User's Handbook of D/A and A/D Converters, JohnWiley and Sons, Inc., New York, NY, 1976.
3 CMOS Analog IC Design Page BIT SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC
4 CMOS Analog IC Design Page m-bit VOLTAGE-SCALING, k-bit CHARGE-SCALING SUCCESSIVE APPROX. ADC Implementation: Operation: 1.) With the two S F switches closed, all capacitors are paralleled and connected to V in * which autozeros the comparator offset voltage. 2.) With all capacitors still in parallel, a successive approximation search is performed to find the resistor segment in which the analog signal lies.
5 CMOS Analog IC Design Page ) Finally, a successive approximation search is performed on charge scaling subdac to establish the analog output voltage.
6 CMOS Analog IC Design Page VOLTAGE-SCALING, CHARGE-SCALING SUCCESSIVE APPROX. DAC - CONTINUED Autozero Step Removes the influence of the offset voltage of the comparator. The voltage across the capacitor is given as, v C = V in * - V OS Successive Approximation Search on the Resistor String The voltage at the comparator input is v comp = V Ri - V in * If v comp > 0, then V Ri > V in * If v comp < 0, then V Ri < V in * Successive Approximation Search on the Capacitor SubDAC The input to the comparator is written as, v comp = (V Ri+1 - V * in ) C eq 2 k C + (V Ri - V* in ) 2k C-C eq 2 k C However, Combining gives, V Ri+1 = V Ri + 2 -m V REF v comp = (V Ri + 2 -m V REF -V * IN ) C eq 2 k C + (V Ri -V * IN ) 2k C-C eq 2 k C
7 CMOS Analog IC Design Page = V Ri - V * IN + 2-m V REF C eq 2 k C
8 CMOS Analog IC Design Page A SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC USING A SERIAL DAC Implementation: Conversion Sequence: Digital-analog Number of Digital-analog Input Word Comparator Conversion Charging Number d 1 d 2 d 3... d N-1 d N Output Steps 1 1 a N a N a N a N-1 a N d 1 a N N 1 a 2 a 3... a N-1 a N a 1 2N Total number of charging steps = N(N+1)
9 CMOS Analog IC Design Page A SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC USING A SERIAL DAC - CONTINUED Example: Analog input is 13/16. Digital word out is b 0 = 1, b 1 = 1, b 2 = 0, and b 3 = 1.
10 CMOS Analog IC Design Page PIPELINE ANALOG-DIGITAL ALGORITHMIC CONVERTER Implementation: Operation: Each stage muliplies its input by 2 and adds or subtracts V REF depending upon the sign of the input. i-th stage, V i = 2V i-1 - b i V REF where b i is given as b i = +1 if V i-1 >0-1 if V i-1 <0
11 CMOS Analog IC Design Page EXAMPLE Illustration of the Operation of the Pipeline Algorithmic ADC Assume that the sampled analog input to a 4-bit pipeline algorithmic analog-digital converter is 2.00 V. If V REF is equal to 5 V, find the digital output word and the analog equivalent voltage. Solution Illustration: Stage Ouputs normalized to V REF Stage 4 Stage No. Input to the ith stage, V i-1 V i-1 > 0? Bit i 1 2V Yes 1 2 (2V 2) - 5 = -1V No 0 3 (-1V 2) + 5 = 3V Yes 1 4 (3V 2) - 5 = 1V Yes 1 Stage 3 Stage 2 Stage V * /VREF in V analog = = 5(0.4375) = where b i = +1 if the ith-bit is 1 and b i = -1 if the ith bit is 0
12 CMOS Analog IC Design Page ACHIEVING THE HIGH SPEED POTENTIAL OF THE PIPELINE ALGORITHMIC ADC If shift registers are used to store the output bits and align them in time, the pipeline ADC can output a digital word at every clock cycle with a latency of NT. Illustration:
13 CMOS Analog IC Design Page ERRORS IN THE PIPELINE ALGORITHMIC ADC The output voltage for the N-th stage can be written as, i=1 V N = A i V in - N i=1 Σ N N-1 j = i+1 A j b j + b N ) V REF where A i (A j ) is the actual gain of 2 for the i-th ( j-th) stage. Errors include: 1.) Gain errors - x2 amplifier or summing junctions 2.) Offset errors - comparator or summing junctions i-th stage including errors, where V i = A i V i-1 + V OSi - b i A si V REF b i = = +1 if V i-1 >V OCi = -1 if V i-1 <V OCi A i is the gain of 2 amplifier for the i-th stage V OSi is the system offset errors of the i-th stage A si is the gain of 1 summer for the i-th stage V OCi is the comparator offset voltage of the i-th stage
14 CMOS Analog IC Design Page ERRORS IN THE PIPELINE ALGORITHMIC ADC - CONTINUED Illustration of the errors Example of an error analysis for a 4-bit pipeline algorithmic ADC The output of the 4th stage can be written as, V 4 = 2 4 V in - (2 3 b b b b 4 )V REF The difference between the actual, V 4, and the ideal, V 4, can be written as, V 4 -V 4 = 2 3 A 1 V in An error will occur in the output of stage 4 if V 4 -V 4 > V REF. A 1 V REF 2 3 V in The smallest value of A 1 occurs when V in = V REF which gives Α 1 A It can be shown that the tolerance of A 2 will be half of the tolerance of A 1, and so forth.
15 CMOS Analog IC Design Page Generally, Α 1 A N, V OS1 V REF 2 N, and V OC1 V REF 2 N
16 CMOS Analog IC Design Page EXAMPLE Accuracy requirements for a 5-bit pipeline algorithmic ADC Show that if V in = V REF, that the pipeline algorithmic ADC will have an error in the 5th bit if the gain of the first stage is 2-(1/8) =1.875 which corresponds to when an error will occur. Show the influence of V in on this result for values of V in of 0.65V REF and 0.22V REF. Solution For V in = V REF, we get the following results shown in the table below. The input to the fifth stage is 0V which means that the bit is uncertain. If A 1 was slightly less than 1.875, the fifth bit would be 0 which would be in error. This result of course assumes that all stages but the first are ideal. i V i (ideal) Bit i (ideal) V i (A 1 =1.875) Bit i (A 1 =1.875) ? Now let us repeat the above results for V in = 0.65V REF. The results are shown below. We see that now an error occurs in the fourth bit. i V i (ideal) Bit i (ideal) V i (A 1 =1.875) Bit i (A 1 =1.875)
17 CMOS Analog IC Design Page EXAMPLE CONTINUED Next, we repeat for the results for V in = 0.22V REF. The results are shown below. We see that no errors occur. i V i (ideal) Bit i (ideal) V i (A 1 =1.875) Bit i (A 1 =1.875) Note the influence of V in in the fact that an error occurs for A 1 = for V in = 0.65V REF but not for V in = 0.22V REF. Why? Note on the plot for the output of each stage, that for V in = 0.65V REF, the output of the fourth stage is close to 0V so any small error will cause problems. However, for V in = 0.22V REF, the output of the fourth stage is at 0.65V REF which is further away from 0V and is less sensitive to errors. The most robust values of V in will be near -V REF, 0 and +V REF. or when each stage output is furthest from the comparator threshold, 0V.
18 CMOS Analog IC Design Page ITERATIVE (CYCLIC) ALGORITHMIC ANALOG-DIGITAL CONVERTER The pipeline algorithmic ADC can be reduced to a single stage that cycles the output back to the input. Implementation: Operation: 1.) Sample the input by connecting switch S1 to V in *. 2.) Multiply V in * by 2. 3.) If V a, is greater than V REF set the corresponding bit = 1 and subtract V REF from V a. If V a, is less than V REF set the corresponding bit = 0 and add zero to V a. 4.) Repeat until all N bits have been converted.
19 CMOS Analog IC Design Page EXAMPLE Conversion Process of an Iterative, Algorithmic Analog-Digital Converter The iterative, algorithmic analog-digital converter is to be used to convert an analog signal of 0.8V REF. The figure below shows the waveforms for V a and V b during the process. T is the time for one iteration cycle. 1.) The analog input of 0.8V REF givesv a = 1.6V REF and a value of V b = 0.6V REF and the MSB as 1. 2.) V b is multiplied by two to give V a = 1.2V REF. Thus the next bit is also 1 and V b = 0.2V REF.. 3.) The third iteration givesv a = 0.4V REF, making the next bit 0 and V b = 0.4V REF. 4.) The fourth iteration gives V a = 0.8V REF, which gives V b = 0.8V REF and the fourth bit as 0. 5.) The fifth iteration gives V a = 1.6V REF, V b = 0.6V REF and the fifth bit as 1. The digital word after the fifth iteration is and is equivalent to an analog voltage of V REF.
20 CMOS Analog IC Design Page SELF-CALIBRATING ANALOG-DIGITAL CONVERTERS Self-calibration architecture for a m-bit charge scaling, k-bit voltage scaling successive approximation ADC Comments: Self-calibration can be accomplished during a calibration cycle or at start-up In the above scheme, the LSB bits are not calibrated Calibration can extend the resolution to 2-4 bits more that without calibration
21 CMOS Analog IC Design Page
22 CMOS Analog IC Design Page SELF-CALIBRATING ANALOG-DIGITAL CONVERTERS - CONTINUED Self-calibration procedure starting with the MSB bit: 1.) Connect C 1 to V REF and the remaining capacitors (C 2 +C 3 + +C m +C m = C 1 ) to ground with S F closed. 2.) Next, connect C 1 to ground and C 1 to V REF. 3.) The result will be V x1 = C 1 -C 1 C 1 + C 1 V REF. If C 1 = C 1, then V x1 = 0. 4.) If V x1 0, then the comparator output will be either high or low. Depending on the comparator output, the calibration circuitry makes a correction through the calibration DAC until the comparator output changes. At this point the MSB is calibrated and the MSB correction voltage, V ε1 is stored. 5.) Proceed to the next MSB with C 1 out of the array and repeat for C 2 and C 2. Store the correction voltage, V ε2, in the data register. 6.) Repeat for C 3 with C 1 and C 2 out of the array. Continue until all of the capacitors of the MSB DAC have been corrected.
23 CMOS Analog IC Design Page Note that for any combination of MSB bits the calibration circuit adds the correct combined correction voltage during normal operation.
24 CMOS Analog IC Design Page SUMMARY OF MEDIUM SPEED ANALOG-DIGITAL CONVERTERS Medium speed ADCs generally use some form of successive approximation. Type of ADC Advantage Disadvantage Voltage-scaling, charge-scaling successive approximation ADC Successive approximation using a serial DAC High resolution Simple Requires considerable digital control circuitry Slow Pipeline algorithmic ADC Fast after initial latency of NT Accuracy depends on input Iterative algorithmic ADC Simple Requires other digital circuitry Successive approximation ADCs also can be calibrated extending their resolution 2-4 bits more than without calibration.
Lecture 370 Testing of ADCs and Moderate Speed Nyquist ADCs (3/29/10) Page 370-1
 Lecture 37 Testing of ADs and Moderate Speed Nyquist ADs (3/9/) Page 37 LETURE 37 TESTING OF ADS AND MODERATE SPEED NYQUIST ADS LETURE ORGANIZATION Outline Introduction Testing of ADs Serial ADs Successive
Lecture 37 Testing of ADs and Moderate Speed Nyquist ADs (3/9/) Page 37 LETURE 37 TESTING OF ADS AND MODERATE SPEED NYQUIST ADS LETURE ORGANIZATION Outline Introduction Testing of ADs Serial ADs Successive
Summary Last Lecture
 EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page 1 Summary Last
EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page 1 Summary Last
CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World
 CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World 11.1 (a) Analog output = (K) x (digital input) (b) Smallest change that can occur in the analog output as a result of a change in the digital input. (c)
CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World 11.1 (a) Analog output = (K) x (digital input) (b) Smallest change that can occur in the analog output as a result of a change in the digital input. (c)
Summary Last Lecture
 EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page Summary Last
EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page Summary Last
P a g e 1. Introduction
 P a g e 1 Introduction 1. Signals in digital form are more convenient than analog form for processing and control operation. 2. Real world signals originated from temperature, pressure, flow rate, force
P a g e 1 Introduction 1. Signals in digital form are more convenient than analog form for processing and control operation. 2. Real world signals originated from temperature, pressure, flow rate, force
CMOS ADC & DAC Principles
 CMOS ADC & DAC Principles Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESAT-MICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 10-05 201 Table of contents Definitions Digital-to-analog converters Resistive Capacitive
CMOS ADC & DAC Principles Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESAT-MICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 10-05 201 Table of contents Definitions Digital-to-analog converters Resistive Capacitive
Lab Exercise 6: Digital/Analog conversion
 Lab Exercise 6: Digital/Analog conversion Introduction In this lab exercise, you will study circuits for analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion Preparation Before arriving at the lab, you should
Lab Exercise 6: Digital/Analog conversion Introduction In this lab exercise, you will study circuits for analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion Preparation Before arriving at the lab, you should
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL AND DIGITAL- TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci Fall 2018 OUTLINE Nyquist-Rate DAC Thermometer-Code Converter Hybrid
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL AND DIGITAL- TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci Fall 2018 OUTLINE Nyquist-Rate DAC Thermometer-Code Converter Hybrid
Tuesday, March 1st, 9:15 11:00. Snorre Aunet Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo.
 Nyquist Analog to Digital it Converters Tuesday, March 1st, 9:15 11:00 Snorre Aunet (sa@ifi.uio.no) Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo 3.1 Introduction 3.1.1 DAC applications
Nyquist Analog to Digital it Converters Tuesday, March 1st, 9:15 11:00 Snorre Aunet (sa@ifi.uio.no) Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo 3.1 Introduction 3.1.1 DAC applications
Electronics A/D and D/A converters
 Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
CMOS High Speed A/D Converter Architectures
 CHAPTER 3 CMOS High Speed A/D Converter Architectures 3.1 Introduction In the previous chapter, basic key functions are examined with special emphasis on the power dissipation associated with its implementation.
CHAPTER 3 CMOS High Speed A/D Converter Architectures 3.1 Introduction In the previous chapter, basic key functions are examined with special emphasis on the power dissipation associated with its implementation.
The need for Data Converters
 The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs)
 ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FSR 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input
ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FSR 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input
Another way to implement a folding ADC
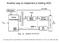 Another way to implement a folding ADC J. Van Valburg and R. van de Plassche, An 8-b 650 MHz Folding ADC, IEEE JSSC, vol 27, #12, pp. 1662-6, Dec 1992 Coupled Differential Pair J. Van Valburg and R. van
Another way to implement a folding ADC J. Van Valburg and R. van de Plassche, An 8-b 650 MHz Folding ADC, IEEE JSSC, vol 27, #12, pp. 1662-6, Dec 1992 Coupled Differential Pair J. Van Valburg and R. van
Data Converters. Lecture Fall2013 Page 1
 Data Converters Lecture Fall2013 Page 1 Lecture Fall2013 Page 2 Representing Real Numbers Limited # of Bits Many physically-based values are best represented with realnumbers as opposed to a discrete number
Data Converters Lecture Fall2013 Page 1 Lecture Fall2013 Page 2 Representing Real Numbers Limited # of Bits Many physically-based values are best represented with realnumbers as opposed to a discrete number
CONTINUOUS DIGITAL CALIBRATION OF PIPELINED A/D CONVERTERS
 CONTINUOUS DIGITAL CALIBRATION OF PIPELINED A/D CONVERTERS By Alma Delić-Ibukić B.S. University of Maine, 2002 A THESIS Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of
CONTINUOUS DIGITAL CALIBRATION OF PIPELINED A/D CONVERTERS By Alma Delić-Ibukić B.S. University of Maine, 2002 A THESIS Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of
Mixed-Signal-Electronics
 1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Analog-to-Digital Converter Families Architecture Variant Speed Precision Counting Operation
1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Analog-to-Digital Converter Families Architecture Variant Speed Precision Counting Operation
Data Converters. Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT
 Data Converters Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT Purpose To convert digital values to analog voltages V OUT Digital Value Reference Voltage Digital Value DAC Analog Voltage Analog Quantity:
Data Converters Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT Purpose To convert digital values to analog voltages V OUT Digital Value Reference Voltage Digital Value DAC Analog Voltage Analog Quantity:
Analog-to-Digital i Converters
 CSE 577 Spring 2011 Analog-to-Digital i Converters Jaehyun Lim, Kyusun Choi Department t of Computer Science and Engineering i The Pennsylvania State University ADC Glossary DNL (differential nonlinearity)
CSE 577 Spring 2011 Analog-to-Digital i Converters Jaehyun Lim, Kyusun Choi Department t of Computer Science and Engineering i The Pennsylvania State University ADC Glossary DNL (differential nonlinearity)
IMPLEMENTING THE 10-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC
 98 CHAPTER 5 IMPLEMENTING THE 0-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC 99 5.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter is devoted to describe the implementation of a 0-bit, 50MS/sec pipelined ADC with different stage resolutions
98 CHAPTER 5 IMPLEMENTING THE 0-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC 99 5.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter is devoted to describe the implementation of a 0-bit, 50MS/sec pipelined ADC with different stage resolutions
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) 2 1. DAC In an electronic circuit, a combination of high voltage (+5V) and low voltage (0V) is usually used to represent a binary
1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) 2 1. DAC In an electronic circuit, a combination of high voltage (+5V) and low voltage (0V) is usually used to represent a binary
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Final Exam EECS 247 H. Khorramabadi Tues., Dec. 14, 2010 FALL 2010 Name: SID: Total number of
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Final Exam EECS 247 H. Khorramabadi Tues., Dec. 14, 2010 FALL 2010 Name: SID: Total number of
Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Outline
 Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Lecture 9 SAR and Cyclic (Algorithmic) Analog-to-Digital Converters Ayman H. Ismail Integrated Circuits Laboratory Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt ayman.hassan@eng.asu.edu.eg
Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Lecture 9 SAR and Cyclic (Algorithmic) Analog-to-Digital Converters Ayman H. Ismail Integrated Circuits Laboratory Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt ayman.hassan@eng.asu.edu.eg
Embedded Control. Week 3 (7/13/11)
 Embedded Control Week 3 (7/13/11) Week 3 15:00 Lecture Overview of analog signals Digital-to-analog conversion Analog-to-digital conversion 16:00 Lab NXT analog IO Overview of Analog Signals Continuous
Embedded Control Week 3 (7/13/11) Week 3 15:00 Lecture Overview of analog signals Digital-to-analog conversion Analog-to-digital conversion 16:00 Lab NXT analog IO Overview of Analog Signals Continuous
Data Acquisition: A/D & D/A Conversion
 Data Acquisition: A/D & D/A Conversion Mark Colton ME 363 Spring 2011 Sampling: A Review In order to store and process measured variables in a computer, the computer must sample the variables 10 Continuous
Data Acquisition: A/D & D/A Conversion Mark Colton ME 363 Spring 2011 Sampling: A Review In order to store and process measured variables in a computer, the computer must sample the variables 10 Continuous
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Mixed-Signal-Electronics
 1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Pipelined ADC 2 4 High-Speed ADC: Pipeline Processing Stephan Henzler Advanced Integrated
1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Pipelined ADC 2 4 High-Speed ADC: Pipeline Processing Stephan Henzler Advanced Integrated
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
Design Of A Comparator For Pipelined A/D Converter
 Design Of A Comparator For Pipelined A/D Converter Ms. Supriya Ganvir, Mr. Sheetesh Sad ABSTRACT`- This project reveals the design of a comparator for pipeline ADC. These comparator is designed using preamplifier
Design Of A Comparator For Pipelined A/D Converter Ms. Supriya Ganvir, Mr. Sheetesh Sad ABSTRACT`- This project reveals the design of a comparator for pipeline ADC. These comparator is designed using preamplifier
ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs)
 ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FS 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input V
ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FS 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input V
The counterpart to a DAC is the ADC, which is generally a more complicated circuit. One of the most popular ADC circuit is the successive
 1 The counterpart to a DAC is the ADC, which is generally a more complicated circuit. One of the most popular ADC circuit is the successive approximation converter. 2 3 The idea of sampling is fully covered
1 The counterpart to a DAC is the ADC, which is generally a more complicated circuit. One of the most popular ADC circuit is the successive approximation converter. 2 3 The idea of sampling is fully covered
RESIDUE AMPLIFIER PIPELINE ADC
 RESIDUE AMPLIFIER PIPELINE ADC A direct-conversion ADC designed only with Op-Amps Abstract This project explores the design of a type of direct-conversion ADC called a Residue Amplifier Pipeline ADC. Direct-conversion
RESIDUE AMPLIFIER PIPELINE ADC A direct-conversion ADC designed only with Op-Amps Abstract This project explores the design of a type of direct-conversion ADC called a Residue Amplifier Pipeline ADC. Direct-conversion
ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC)
 COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC) Connecting digital circuitry to sensor devices
COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC) Connecting digital circuitry to sensor devices
EE247 Lecture 23. EECS 247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs 2008 H.K. Page 1. Pipeline ADC Block Diagram DAC ADC. V res2. Stage 2 B 2.
 EE247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs (continued) Effect gain stage, sub-dac non-idealities on overall ADC performance Digital calibration (continued) Correction for inter-stage gain nonlinearity Implementation
EE247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs (continued) Effect gain stage, sub-dac non-idealities on overall ADC performance Digital calibration (continued) Correction for inter-stage gain nonlinearity Implementation
SUCCESSIVE approximation register (SAR) analog-todigital
 426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 62, NO. 5, MAY 2015 A Novel Hybrid Radix-/Radix-2 SAR ADC With Fast Convergence and Low Hardware Complexity Manzur Rahman, Arindam
426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 62, NO. 5, MAY 2015 A Novel Hybrid Radix-/Radix-2 SAR ADC With Fast Convergence and Low Hardware Complexity Manzur Rahman, Arindam
A-D and D-A Converters
 Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
Chapter 2 Basics of Digital-to-Analog Conversion
 Chapter 2 Basics of Digital-to-Analog Conversion This chapter discusses basic concepts of modern Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs). The basic generic DAC functionality and specifications are discussed,
Chapter 2 Basics of Digital-to-Analog Conversion This chapter discusses basic concepts of modern Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs). The basic generic DAC functionality and specifications are discussed,
Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall Lecture Outline
 Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 07 October 17, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Administrative Detailed Technical Discussions Digital to Analog Conversion Lab
Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 07 October 17, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Administrative Detailed Technical Discussions Digital to Analog Conversion Lab
CENG4480 Lecture 04: Analog/Digital Conversions
 CENG4480 Lecture 04: Analog/Digital Conversions Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: October 3, 2018) Fall 2018 1 / 31 Overview Preliminaries Comparator Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Analog
CENG4480 Lecture 04: Analog/Digital Conversions Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: October 3, 2018) Fall 2018 1 / 31 Overview Preliminaries Comparator Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Analog
Data Acquisition & Computer Control
 Chapter 4 Data Acquisition & Computer Control Now that we have some tools to look at random data we need to understand the fundamental methods employed to acquire data and control experiments. The personal
Chapter 4 Data Acquisition & Computer Control Now that we have some tools to look at random data we need to understand the fundamental methods employed to acquire data and control experiments. The personal
Working with ADCs, OAs and the MSP430
 Working with ADCs, OAs and the MSP430 Bonnie Baker HPA Senior Applications Engineer Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda An Overview of the MSP430 Data Acquisition System SAR Converters
Working with ADCs, OAs and the MSP430 Bonnie Baker HPA Senior Applications Engineer Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda An Overview of the MSP430 Data Acquisition System SAR Converters
8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with track/hold function ADC0820
 8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with DESCRIPTION By using a half-flash conversion technique, the 8-bit CMOS A/D offers a 1.5µs conversion time while dissipating a maximum 75mW of power.
8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with DESCRIPTION By using a half-flash conversion technique, the 8-bit CMOS A/D offers a 1.5µs conversion time while dissipating a maximum 75mW of power.
Digital to Analog Converters (DAC) 15 March 2006 Doug Hinckley Lee Huynh Dooroo Kim
 Digital to Analog Converters (DAC) 5 March 006 Doug Hinckley Lee Huynh Dooroo Kim What is a DAC? A digital to analog converter (DAC) converts a digital signal to an analog voltage or current output. 000
Digital to Analog Converters (DAC) 5 March 006 Doug Hinckley Lee Huynh Dooroo Kim What is a DAC? A digital to analog converter (DAC) converts a digital signal to an analog voltage or current output. 000
Advantages of Analog Representation. Varies continuously, like the property being measured. Represents continuous values. See Figure 12.
 Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
EE 435. Lecture 32. DAC Design. Parasitic Capacitances. The String DAC
 EE 435 Lecture 32 DAC Design The String DAC Parasitic Capacitances . eview from last lecture. DFT Simulation from Matlab . eview from last lecture. Summary of time and amplitude quantization assessment
EE 435 Lecture 32 DAC Design The String DAC Parasitic Capacitances . eview from last lecture. DFT Simulation from Matlab . eview from last lecture. Summary of time and amplitude quantization assessment
Linear Integrated Circuits
 Linear Integrated Circuits Single Slope ADC Comparator checks input voltage with integrated reference voltage, V REF At the same time the number of clock cycles is being counted. When the integrator output
Linear Integrated Circuits Single Slope ADC Comparator checks input voltage with integrated reference voltage, V REF At the same time the number of clock cycles is being counted. When the integrator output
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall Class # 07. October 16, 2008
 DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
System on a Chip. Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft
 System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
L9: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A)
 L9: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A) Acknowledgement: Dave Wentzloff Introduction to Operational Amplifiers DC Model Typically very high input resistance ~ 300KΩ v id in a v id out High DC gain
L9: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A) Acknowledgement: Dave Wentzloff Introduction to Operational Amplifiers DC Model Typically very high input resistance ~ 300KΩ v id in a v id out High DC gain
University of Pennsylvania. Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering. ESE Undergraduate Laboratory. Analog to Digital Converter
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE Undergraduate Laboratory Analog to Digital Converter PURPOSE The purpose of this lab is to design and build a simple Digital-to-Analog
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE Undergraduate Laboratory Analog to Digital Converter PURPOSE The purpose of this lab is to design and build a simple Digital-to-Analog
Algorithmic Pipeline ADC
 Algorithmic Pipeline ADC Ivan Perić's new current-mode ADC design Tim Armbruster tim.armbruster@ziti.uni-heidelberg.de 13th CBM CM Darmstadt Schaltungstechnik und 1.03.009 ADC Overview and Application
Algorithmic Pipeline ADC Ivan Perić's new current-mode ADC design Tim Armbruster tim.armbruster@ziti.uni-heidelberg.de 13th CBM CM Darmstadt Schaltungstechnik und 1.03.009 ADC Overview and Application
Analog to Digital Converters
 Analog to Digital Converters By: Byron Johns, Danny Carpenter Stephanie Pohl, Harry Bo Marr http://ume.gatech.edu/mechatronics_course/fadc_f05.ppt (unless otherwise marked) Presentation Outline Introduction:
Analog to Digital Converters By: Byron Johns, Danny Carpenter Stephanie Pohl, Harry Bo Marr http://ume.gatech.edu/mechatronics_course/fadc_f05.ppt (unless otherwise marked) Presentation Outline Introduction:
ADS9850 Signal Generator Module
 1. Introduction ADS9850 Signal Generator Module This module described here is based on ADS9850, a CMOS, 125MHz, and Complete DDS Synthesizer. The AD9850 is a highly integrated device that uses advanced
1. Introduction ADS9850 Signal Generator Module This module described here is based on ADS9850, a CMOS, 125MHz, and Complete DDS Synthesizer. The AD9850 is a highly integrated device that uses advanced
12-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit A/D Converter AD ADC80
 a 2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit A/D Converter FEATURES True 2-Bit Operation: Max Nonlinearity.2% Low Gain T.C.: 3 ppm/ C Max Low Power: 8 mw Fast Conversion Time: 25 s Precision 6.3
a 2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit A/D Converter FEATURES True 2-Bit Operation: Max Nonlinearity.2% Low Gain T.C.: 3 ppm/ C Max Low Power: 8 mw Fast Conversion Time: 25 s Precision 6.3
Reading: Schwarz and Oldham (light on non-ideal) and comparator viewgraphs. Lecture 14: October 17, 2001
 Lecture 4: October 7, 00 Op-Amp Circuits and Comprators A)Cascade Op-Amps B)Integration/Differentiation Op-Amps C)I vs. V of Op-Amps Source Limits D)Comparator Circuits E)D to A Converters Reading: The
Lecture 4: October 7, 00 Op-Amp Circuits and Comprators A)Cascade Op-Amps B)Integration/Differentiation Op-Amps C)I vs. V of Op-Amps Source Limits D)Comparator Circuits E)D to A Converters Reading: The
High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters. ELCT 1003:High Speed ADCs
 High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters Ann Kotkat Barbara Georgy Mahmoud Tantawi Ayman Sakr Heidi El-Feky Nourane Gamal 1 Outline Introduction. Process of ADC. ADC Specifications. Flash ADC. Pipelined
High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters Ann Kotkat Barbara Georgy Mahmoud Tantawi Ayman Sakr Heidi El-Feky Nourane Gamal 1 Outline Introduction. Process of ADC. ADC Specifications. Flash ADC. Pipelined
EE247 Lecture 14. EE247 Lecture 14
 EE47 Lecture 14 Administrative issues Midterm exam postponed to Thurs. Nov. 5th o You can only bring one 8x11 paper with your own written notes (please do not photocopy) o No books, class or any other
EE47 Lecture 14 Administrative issues Midterm exam postponed to Thurs. Nov. 5th o You can only bring one 8x11 paper with your own written notes (please do not photocopy) o No books, class or any other
ROTRONIC HygroClip Digital Input / Output
 ROTRONIC HygroClip Digital Input / Output OEM customers that use the HygroClip have the choice of using either the analog humidity and temperature output signals or the digital signal input / output (DIO).
ROTRONIC HygroClip Digital Input / Output OEM customers that use the HygroClip have the choice of using either the analog humidity and temperature output signals or the digital signal input / output (DIO).
L10: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A)
 L10: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A) Acknowledgement: Dave Wentzloff 1 Introduction to Operational Amplifiers DC Model Typically very high input resistance ~ 300KΩ v id in a v id out v out High
L10: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A) Acknowledgement: Dave Wentzloff 1 Introduction to Operational Amplifiers DC Model Typically very high input resistance ~ 300KΩ v id in a v id out v out High
L10: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A)
 L10: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A) Acknowledgement: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Dave Wentzloff 1 Introduction to Operational
L10: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps,, A/D, D/A) Acknowledgement: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Dave Wentzloff 1 Introduction to Operational
Lecture 9, ANIK. Data converters 1
 Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
W H I T E P A P E R. Analog Signal Chain Calibration
 W H I T E P A P E R Gautam Das G, Applications Engineer & Praveen Sekar, Applications Engineer Senior Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Analog Signal Chain Calibration Abstract Analog signal chains are prone
W H I T E P A P E R Gautam Das G, Applications Engineer & Praveen Sekar, Applications Engineer Senior Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Analog Signal Chain Calibration Abstract Analog signal chains are prone
High Precision 10 V IC Reference AD581
 High Precision 0 V IC Reference FEATURES Laser trimmed to high accuracy 0.000 V ±5 mv (L and U models) Trimmed temperature coefficient 5 ppm/ C maximum, 0 C to 70 C (L model) 0 ppm/ C maximum, 55 C to
High Precision 0 V IC Reference FEATURES Laser trimmed to high accuracy 0.000 V ±5 mv (L and U models) Trimmed temperature coefficient 5 ppm/ C maximum, 0 C to 70 C (L model) 0 ppm/ C maximum, 55 C to
How do ADCs work? Martin Rowe, Senior Technical Editor -- 7/1/2002 Test & Measurement World

A 14b 40Msample/s Pipelined ADC with DFCA
 A 14b 40Msample/s Pipelined ADC with DFCA Paul Yu, Shereef Shehata, Ashutosh Joharapurkar, Pankaj Chugh, Alex Bugeja, Xiaohong Du, Sung-Ung Kwak, Yiannis Papantonopoulos, Turker Kuyel Texas Instruments,
A 14b 40Msample/s Pipelined ADC with DFCA Paul Yu, Shereef Shehata, Ashutosh Joharapurkar, Pankaj Chugh, Alex Bugeja, Xiaohong Du, Sung-Ung Kwak, Yiannis Papantonopoulos, Turker Kuyel Texas Instruments,
A Digitally Enhanced 1.8-V 15-b 40- Msample/s CMOS Pipelined ADC
 A Digitally Enhanced.8-V 5-b 4- Msample/s CMOS d ADC Eric Siragusa and Ian Galton University of California San Diego Now with Analog Devices San Diego California Outline Conventional PADC Example Digitally
A Digitally Enhanced.8-V 5-b 4- Msample/s CMOS d ADC Eric Siragusa and Ian Galton University of California San Diego Now with Analog Devices San Diego California Outline Conventional PADC Example Digitally
L9: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps, A/D, D/A)
 L9: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps, A/D, D/A) Courtesy of Dave Wentzloff. Used with permission. 1 Introduction to Operational Amplifiers v id in DC Model a v id LM741 Pinout out 10 to 15V Typically very
L9: Analog Building Blocks (OpAmps, A/D, D/A) Courtesy of Dave Wentzloff. Used with permission. 1 Introduction to Operational Amplifiers v id in DC Model a v id LM741 Pinout out 10 to 15V Typically very
Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers
 Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers Rabeeh Majidi ECE Department, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester MA USA rabeehm@ece.wpi.edu Abstract: This paper presents low power design
Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers Rabeeh Majidi ECE Department, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester MA USA rabeehm@ece.wpi.edu Abstract: This paper presents low power design
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN109 Microprocessor-compatible DACs Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
Transfer Function DAC architectures/examples Calibrations
 Welcome to 046188 Winter semester 2012 Mixed Signal Electronic Circuits Instructor: Dr. M. Moyal Lecture 06 DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS Transfer Function DAC architectures/examples Calibrations www.gigalogchip.com
Welcome to 046188 Winter semester 2012 Mixed Signal Electronic Circuits Instructor: Dr. M. Moyal Lecture 06 DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS Transfer Function DAC architectures/examples Calibrations www.gigalogchip.com
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign
 Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 13 Building Blocks (Multipliers) Register Adder Shift Register Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Acknowledgement This lecture note has been summarized and categorized
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 13 Building Blocks (Multipliers) Register Adder Shift Register Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Acknowledgement This lecture note has been summarized and categorized
Analog I/O. ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Winter 2016
 Analog I/O ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Introduction Anytime we need to monitor or control analog signals with a digital system, we require analogto-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
Analog I/O ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Introduction Anytime we need to monitor or control analog signals with a digital system, we require analogto-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
Implementing a 5-bit Folding and Interpolating Analog to Digital Converter
 Implementing a 5-bit Folding and Interpolating Analog to Digital Converter Zachary A Pfeffer (pfefferz@colorado.edu) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder CO
Implementing a 5-bit Folding and Interpolating Analog to Digital Converter Zachary A Pfeffer (pfefferz@colorado.edu) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder CO
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion 02534567998 6 4 2 3 4 5 6 ANALOG to DIGITAL CONVERSION Analog variation (Continuous, smooth variation) Digitized Variation (Discrete set of points) N2 N1 Digitization applied
Analog to Digital Conversion 02534567998 6 4 2 3 4 5 6 ANALOG to DIGITAL CONVERSION Analog variation (Continuous, smooth variation) Digitized Variation (Discrete set of points) N2 N1 Digitization applied
A Novel Architecture For An Energy Efficient And High Speed Sar Adc
 A Novel Architecture For An Energy Efficient And High Speed Sar Adc Ms.Vishnupriya Iv 1, Ms. Prathibha Varghese 2 1 (Electronics And Communication dept. Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering,
A Novel Architecture For An Energy Efficient And High Speed Sar Adc Ms.Vishnupriya Iv 1, Ms. Prathibha Varghese 2 1 (Electronics And Communication dept. Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering,
12-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit ADC ADADC80
 2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit ADC FEATURES True 2-bit operation: maximum nonlinearity ±.2% Low gain temperature coefficient (TC): ±3 ppm/ C maximum Low power: 8 mw Fast conversion time:
2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit ADC FEATURES True 2-bit operation: maximum nonlinearity ±.2% Low gain temperature coefficient (TC): ±3 ppm/ C maximum Low power: 8 mw Fast conversion time:
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Data Converters. Springer FRANCO MALOBERTI. Pavia University, Italy
 Data Converters by FRANCO MALOBERTI Pavia University, Italy Springer Contents Dedicat ion Preface 1. BACKGROUND ELEMENTS 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 The Ideal Data Converter Sampling 1.2.1 Undersampling
Data Converters by FRANCO MALOBERTI Pavia University, Italy Springer Contents Dedicat ion Preface 1. BACKGROUND ELEMENTS 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 The Ideal Data Converter Sampling 1.2.1 Undersampling
A 130nm CMOS Evaluation Digitizer Chip for Silicon Strips readout at the ILC
 A 130nm CMOS Evaluation Digitizer Chip for Silicon Strips readout at the ILC Jean-Francois Genat Thanh Hung Pham on behalf of W. Da Silva 1, J. David 1, M. Dhellot 1, D. Fougeron 2, R. Hermel 2, J-F. Huppert
A 130nm CMOS Evaluation Digitizer Chip for Silicon Strips readout at the ILC Jean-Francois Genat Thanh Hung Pham on behalf of W. Da Silva 1, J. David 1, M. Dhellot 1, D. Fougeron 2, R. Hermel 2, J-F. Huppert
EE247 Lecture 15. EE247 Lecture 15
 EE47 Lecture 5 Administrative issues Midterm exam postponed to Tues. Oct. 8th o You can only bring one 8x paper with your own written notes (please do not photocopy) o No books, class or any other kind
EE47 Lecture 5 Administrative issues Midterm exam postponed to Tues. Oct. 8th o You can only bring one 8x paper with your own written notes (please do not photocopy) o No books, class or any other kind
SPT BIT, 100 MWPS TTL D/A CONVERTER
 FEATURES 12-Bit, 100 MWPS digital-to-analog converter TTL compatibility Low power: 640 mw 1/2 LSB DNL 40 MHz multiplying bandwidth Industrial temperature range Superior performance over AD9713 Improved
FEATURES 12-Bit, 100 MWPS digital-to-analog converter TTL compatibility Low power: 640 mw 1/2 LSB DNL 40 MHz multiplying bandwidth Industrial temperature range Superior performance over AD9713 Improved
ON-CHIP TOUCH SENSOR READOUT CIRCUIT USING PASSIVE SIGMA-DELTA MODULATOR CAPACITANCE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER. A Thesis. Presented to
 ON-CHIP TOUCH SENSOR READOUT CIRCUIT USING PASSIVE SIGMA-DELTA MODULATOR CAPACITANCE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER A Thesis Presented to The Graduate Faculty of The University of Akron In Partial Fulfillment of
ON-CHIP TOUCH SENSOR READOUT CIRCUIT USING PASSIVE SIGMA-DELTA MODULATOR CAPACITANCE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER A Thesis Presented to The Graduate Faculty of The University of Akron In Partial Fulfillment of
Behavioral Simulator of Analog-to-Digital Converters
 Behavioral Simulator of Analog-to-Digital Converters Grzegorz Zareba Olgierd. A. Palusinski University of Arizona Outline Introduction and Motivation Behavioral Simulator of Analog-to-Digital Converters
Behavioral Simulator of Analog-to-Digital Converters Grzegorz Zareba Olgierd. A. Palusinski University of Arizona Outline Introduction and Motivation Behavioral Simulator of Analog-to-Digital Converters
Fundamentals of Data Converters. DAVID KRESS Director of Technical Marketing
 Fundamentals of Data Converters DAVID KRESS Director of Technical Marketing 9/14/2016 Analog to Electronic Signal Processing Sensor (INPUT) Amp Converter Digital Processor Actuator (OUTPUT) Amp Converter
Fundamentals of Data Converters DAVID KRESS Director of Technical Marketing 9/14/2016 Analog to Electronic Signal Processing Sensor (INPUT) Amp Converter Digital Processor Actuator (OUTPUT) Amp Converter
Digital to Analog Conversion. Data Acquisition
 Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
Towards an ADC for the Liquid Argon Electronics Upgrade
 1 Towards an ADC for the Liquid Argon Electronics Upgrade Gustaaf Brooijmans Upgrade Workshop, November 10, 2009 2 Current LAr FEB Existing FEB (radiation tolerant for LHC, but slhc?) Limits L1 latency
1 Towards an ADC for the Liquid Argon Electronics Upgrade Gustaaf Brooijmans Upgrade Workshop, November 10, 2009 2 Current LAr FEB Existing FEB (radiation tolerant for LHC, but slhc?) Limits L1 latency
Administrative. No office hour on Thurs. this week Instead, office hour 3 to 4pm on Wed.
 Administrative No office hour on Thurs. this week Instead, office hour 3 to 4pm on Wed. EECS 247 Lecture 2 Nyquist Rate ADC: Architecture & Design 27 H.K. Page EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters Sampling (continued)
Administrative No office hour on Thurs. this week Instead, office hour 3 to 4pm on Wed. EECS 247 Lecture 2 Nyquist Rate ADC: Architecture & Design 27 H.K. Page EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters Sampling (continued)
SWITCHED-CURRENTS an analogue technique for digital technology
 SWITCHED-CURRENTS an analogue technique for digital technology Edited by С Toumazou, ]. B. Hughes & N. C. Battersby Supported by the IEEE Circuits and Systems Society Technical Committee on Analog Signal
SWITCHED-CURRENTS an analogue technique for digital technology Edited by С Toumazou, ]. B. Hughes & N. C. Battersby Supported by the IEEE Circuits and Systems Society Technical Committee on Analog Signal
Tel: Fax:
 B Tel: 78.39.4700 Fax: 78.46.33 SPECIFICATIONS (T A = +5 C, V+ = +5 V, V = V or 5 V, all voltages measured with respect to digital common, unless otherwise noted) AD57J AD57K AD57S Model Min Typ Max Min
B Tel: 78.39.4700 Fax: 78.46.33 SPECIFICATIONS (T A = +5 C, V+ = +5 V, V = V or 5 V, all voltages measured with respect to digital common, unless otherwise noted) AD57J AD57K AD57S Model Min Typ Max Min
20-Stage Pipelined ADC with Radix-Based Calibration. by Chong Kyu Yun A THESIS. submitted to. Oregon State University
 20-Stage Pipelined ADC with Radix-Based Calibration by Chong Kyu Yun A THESIS submitted to Oregon State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Presented
20-Stage Pipelined ADC with Radix-Based Calibration by Chong Kyu Yun A THESIS submitted to Oregon State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Presented
A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah
 A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah 1 Master of Technology,Dept. of VLSI &Embedded Systems,Sardar Vallabhbhai National
A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah 1 Master of Technology,Dept. of VLSI &Embedded Systems,Sardar Vallabhbhai National
CHAPTER 10 DIGITAL-ANALOG AND ANALOG-DIGITAL CONVERTERS INTRODUCTION
 Chapter DigitalAnalog and AnalogDigital Converters 5/2/4 CHAPTER DIGITALANALOG AND ANALOGDIGITAL CONVERTERS Section. Introduction Section. Characterization of DigitalAnalog Converters Section.2 Parallel
Chapter DigitalAnalog and AnalogDigital Converters 5/2/4 CHAPTER DIGITALANALOG AND ANALOGDIGITAL CONVERTERS Section. Introduction Section. Characterization of DigitalAnalog Converters Section.2 Parallel
Chapter 2 Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion
 09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
Chapter 2 ADC Architecture
 Chapter 2 ADC Architecture 2.1 Introduction While lots of Nyquist-rate ADCs are proposed to resolve resolutions at different speeds throughout the years, there are three types of architectures most widely
Chapter 2 ADC Architecture 2.1 Introduction While lots of Nyquist-rate ADCs are proposed to resolve resolutions at different speeds throughout the years, there are three types of architectures most widely
Microprocessors & Interfacing
 Lecture overview Microprocessors & Interfacing /Output output PMW Digital-to- (D/A) Conversion input -to-digital (A/D) Conversion Lecturer : Dr. Annie Guo S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9 1 S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9
Lecture overview Microprocessors & Interfacing /Output output PMW Digital-to- (D/A) Conversion input -to-digital (A/D) Conversion Lecturer : Dr. Annie Guo S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9 1 S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
The Design and Characterization of an 8-bit ADC for 250 o C Operation
 The Design and Characterization of an 8-bit ADC for 25 o C Operation By Lynn Reed, John Hoenig and Vema Reddy Tekmos, Inc. 791 E. Riverside Drive, Bldg. 2, Suite 15, Austin, TX 78744 Abstract Many high
The Design and Characterization of an 8-bit ADC for 25 o C Operation By Lynn Reed, John Hoenig and Vema Reddy Tekmos, Inc. 791 E. Riverside Drive, Bldg. 2, Suite 15, Austin, TX 78744 Abstract Many high
Lec. 8: Subranging/Two-step ADCs
 In The Name of Almighty Lec. 8: Subranging/Two-step ADCs Lecturer: Hooman Farkhani Department of Electrical Engineering Islamic Azad University of Najafabad Feb. 2016. Email: H_farkhani@yahoo.com General
In The Name of Almighty Lec. 8: Subranging/Two-step ADCs Lecturer: Hooman Farkhani Department of Electrical Engineering Islamic Azad University of Najafabad Feb. 2016. Email: H_farkhani@yahoo.com General
EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation
 University of Turkish Aeronautical Association Faculty of Engineering EEE department EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation Digital Electronic meters BY Ankara March 2017 1 Introduction The digital
University of Turkish Aeronautical Association Faculty of Engineering EEE department EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation Digital Electronic meters BY Ankara March 2017 1 Introduction The digital
A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in. Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California
 A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in 0.35 µm CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California 1 Outline Background Chip Architecture
A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in 0.35 µm CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California 1 Outline Background Chip Architecture
