COURSE INFORMATION. Course Prefix/Number: EET 231. Lecture Hours/Week: 3.0 Lab Hours/Week: 3.0 Credit Hours/Semester: 4.0
|
|
|
- Laurence Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COURSE INFORMATION Course Prefix/Number: EET 231 Course Title: Industrial Electronics Lecture Hours/Week: 3.0 Lab Hours/Week: 3.0 Credit Hours/Semester: 4.0 VA Statement/Distance Learning Attendance Textbook Information Student Code and Grievance Policy Attendance Statement (Page 51) COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is a survey of topics related to industrial application of electronic devices and circuits. The course covers switches, DC and AC motor controls, sensors and transducers, open and closed-loop control circuits, and voltage converting interfaces. Circuits are constructed and tested. COURSE COMPETENCIES Upon successful completion of this course, the student should be competent to perform the following tasks Module 1: Introduction/Logic Gates/Instrumentation Amplifier Describe the characteristics of the open and closed loop systems Describe the characteristics of the following types of control circuits Time driven Process control o Batch o Sequential Control o Direct digital Control o Distributed Control o Continuous o Motion Control o Numerical Control Identify the parts of open and closed loop systems Describe feedback control Describe feed forward control Identify the following terms o Lag time o Dead time o Signal conditioning Transfer function (TF) Ground loop o Single point ground Current loop EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
2 List the characteristics of an ideal and practical op-amp. Determine the output of the following op-amp configurations o Inverting amplifier o Non-inverting amplifier o Summing amplifier o Difference amplifier Module 2: Sensors/Transducers/Switches Temperature/Humidity Define the three scales most commonly used to measure temperature. Describe the construction and operation of the following temperature detection devices: o Bimetallic Thermometer o Filled Thermal System o Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) o Thermocouples Explain how intermediate metals can affect the operation of a thermocouple. Explain the effect of connecting thermocouples in series and in parallel to measure State how to determine the polarity of a thermocouple temperature. Describe the importance of reference junction compensation when using a thermocouple to measure temperature. Explain the purpose of using an "ice bath" when checking the operation of a thermocouple. Describe the operation of the following humidity sensors o Hygrometers o Hair Sorption Resistance Capacitive o Psychrometers o Microwave absorption Pressure/force o Define the relationship between pressure, force, and area. o Describe the relationship between atmospheric pressure, absolute pressure vacuum pressure, and gauge pressure. o Describe the units commonly used to measure pressure. o Given a list of pressure units, Convert the pressure units from one form to another. o Explain hydrostatic pressure measurement. o Describe the construction and operation of the following pressure measuring devices Manometers. Elastic deformation devices to include: Bourdon Tube Diaphragm (Capsule) Bellows Capacitance Strain Gauge LVDT s o Describe how elastic deformation sensors can be used to provide remote indication and control. o Describe the effect a water leg (reference) has on pressure measurements. o Flow/velocity/acceleration/jerk EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
3 o Describe the characteristics and physical properties associated with fluids and fluid flow. o Describe the relationship between pressure and flow with respect to fluid flow through a restriction. o Define the terms Laminar Flow and Turbulent flow o Define the terms Flow Rate and Total Flow. o Describe five restrictor type (non-linear) devices used to measure flow to include the following: Orifice Plate Venturi Tube Flow Nozzle Pitot Tube Elbow Tap o Describe four linear type devices used to measure flow to include the following: Rotameter Magnetic Flowmeter Turbine Flowmeter Ultrasonic Flowmeter o Describe how the following types of flow meters are used to measure flow Doppler Capacitive Piezoelectric Accelerometers Tachometers Potentiometers Cantilever Heat transfer Describe the function of a square root extractor in a flow measuring system. Level o Describe the characteristics of liquids that affect liquid level measurement. o Define the term Specific Gravity and describe its effect on liquid level measurements. o Describe the relationship between pressure and level with respect to liquid level measurements. o Describe the operation of conductivity, capacitance, and ultrasonic probes used for level measurement. o Describe the operation of a Bubbler System used to measure level. o Describe the operation of displacer level measuring device. o Explain the operation of differential pressure level measurement devices. o Describe the operation of a differential pressure type level measurement for the following: Open Tank Closed/Pressurized Tank Position o Magnetism o Light Module 3: Motors Generators State how AC and DC generators are different. Explain three methods of excitation used on AC generators. EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
4 Explain how three-phase power is generated. State how AC generators are rated. Discuss the synchronization of a generator to another generator. Discuss how voltage and speed are controlled on generators that are NOT paralleled with other generators. Discuss how voltage and speed are controlled on generators that ARE paralleled with other generators List the three requirements for inducing a voltage Discuss Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction State the function of a Generator Explain the operation of AC generators Explain the purpose of the commutator and brushes on a DC generator DC Motors State the purpose of the brushes, stator and rotor of a DC Motor Explain the basic operating principles of DC Motors. Describe what speed and torque characteristics are associated with DC Motors. Identify how counter EMF (CEMF) effects DC motor operation. Explain why starting resistors are needed on large DC Motors. State the effects of operating a DC Motor with no load applied. Identify the advantages and disadvantages of DC Motors. Describe how to reverse the rotation of a DC Motor. Identify brush problems and brush maintenance practices in DC Motors. Explain how to identify commutator problems in DC Motors. Disassemble and assemble a DC Motor in accordance with requirements of the lab exercise Measure current, speed, insulation resistance, and winding resistance on a DC Motor in accordance with the lab exercise. Identify applications of DC Motors. AC Motors Single Phase State the purpose of the stator and rotor of an AC motor Describe the operation of a single-phase induction motor. Explain why most single-phase induction motors require starting assist devices. Define the term slip as it relates to induction motors. Describe the following types of single-phase motors including their integral parts: o Shaded-Pole Induction Motor o Split-Phase Induction Motors o Wound Rotor o Capacitor Start/Capacitor Run Explain how to reverse rotational direction of the following single-phase motors: o Shaded-Pole Induction Motor o Split-Phase Induction Motor o Wound Rotor o Capacitor Start/Capacitor Run State the resultant failure for each of the following motor problems: o Shorted or open capacitor o Centrifugal switch stuck open o Centrifugal switch stuck closed Given a motor nameplate wiring diagram, Determine the following: EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
5 o Voltage and Amperage Ratings o Low voltage Connections o High Voltage Connections Disassemble and assemble a Single-Phase AC Motor in accordance with requirements of the Lab Exercise. Measure current, speed, insulation resistance, and winding resistance on a Single-Phase AC Motor in accordance with the Lab Exercise. Identify applications of single-phase AC Motors. AC Motors Three Phase Explain the basic operating principles of three-phase AC motors. Explain why a three-phase motor self-starts. Define Synchronous Speed. Explain why starting current is higher than running current on a three-phase motor Describe the operation of the following three-phase motors and the characteristics of each. o Squirrel Cage Induction Motor o Synchronous Motor Describe the term single-phasing and how to recognize this condition Define the term Breakdown Torque. Discuss the advantages of using three-phase motors vs. single-phase motors. Explain how direction of rotation is reversed in a three-phase motor. State when and how the phase rotation meter should be used in three-phase motor applications. Explain the term wye configuration in reference to three-phase motor applications. Explain the term delta configuration in reference to three-phase motor applications Demonstrate the ability to measure current, insulation resistance, and winding resistance on a Three-Phase AC Motor in accordance with the appropriate plant procedure and lab. Identify applications of three-phase AC Motors. Stepper Motors Explain the basic operating principles of stepper motors. Identify applications of Stepper Motors. Describe the operation of the following stepper motors: o Permanent Magnet o Variable Reluctance o Hybrid Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each of the stepper motors. Define the following terms: o Holding torque o Détente torque o Residual torque o Bipolar o Step angle o Multi stack steppers o Step rate o Unipolar Universal Motors Describe the operation of a Universal Motor EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
6 State the purpose of brushes in the Universal Motor Discuss the purpose of the compensating winding Compare the torque characteristics of the universal motor running under DC to those of the motor running under AC Identify applications of Universal Motors. MINIMAL STANDARDS/PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES Module 1: Introduction/Logic Gates/Instrumentation Amplifier Given parts and instructions, the student must build, test and demonstrate an Instrumentation Amplifier (IA) using common operational amplifiers within 80% of expected values. Given parts and instructions, the student must build, test and demonstrate an IA circuit using an integrated IA with 100% accuracy. Given lectures and notes, the student must attain the competencies listed in above with 80% accuracy. Module 2: Sensors/Transducers/Switches Given an IC Op Amp and various types of transducers, construct circuits utilizing the sensors and Op Amp working with an 80% accuracy Given a heat source, determine the temperature using a thermocouple and a DVM. Module 3: Motors Given a dissectible motor, assemble and disassemble a DC Motor with 100% accuracy. Given instruction and components, construct a powered DC motor, measure current, speed, voltage, power and winding resistance with 90 % accuracy. Given a motor nameplate wiring diagram, determine the following: o Voltage and Amperage Ratings o Low voltage Connections High Voltage Connections Given a dissectible motor, disassemble and assemble a Single-Phase AC Motor with 100% accuracy. Given instruction and components, construct a powered single phase AC motor, measure current, speed, voltage, power and winding resistance with 90% accuracy. Given instruction and components construct a powered three-phase AC motor, measure current, speed, voltage, and power with 90% accuracy. Given instruction and components, construct a powered universal motor, measure current, speed, voltage, and power with 90% accuracy. Given instruction and components, construct a powered Stepper motor that will work with 100% accuracy. COURSE REQUIREMENTS Students are responsible for attaining competencies through completion of the following course requirements: Academic Integrity The policies stated in the York Technical College Handbook will be enforced. Any student violating these policies will be subject to academic discipline. EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
7 METHOD OF INSTRUCTION This course may be offered in either a traditional or a hybrid format. In the traditional format, this course consists of 48 hours of in-class lecture and 48 hours of laboratory time each for each course. The class instruction includes lectures, discussions, problem-solving sessions, and tests. The lectures are administered using the chalkboard, PowerPoint, and video tapes. The discussions consist of student-student and student-instructor dialogue. The problemsolving sessions consist of students working problems on the chalkboard or at their desks while the instructor checks their work. The laboratory experiments follow and complement the class lectures. The students are given instructions before the laboratory begins so they can perform the experiment. In the hybrid format, the students will be responsible for the basic material by reading the text book, by reviewing the online notes and PowerPoint s. Labs will follow the traditional format. In the hybrid format, the students should spend at least two hours per week accessing the on-line learning material. STUDENTS ARE EXPECTED TO PARTICIPATE IN CLASS DISCUSSIONS, SOLVE PROBLEMS, COMPLETE: 1) ASSIGNED HOMEWORK, 2) COMPUTER PROGRAMS, 3) SIMULATIONS, 4) LAB EXPERIMENTS AND 5) REPORTS. Laboratory Requirements Laboratory experiment worksheets will be handed out each week, completed by the student, and submitted by the next laboratory period. All data taken during the experiment and observations noted by the student will be part of the laboratory report. Any questions will be answered and a hard copy of all computer simulations will be attached to the laboratory report prior to submission. EVALUATION STRATEGIES/GRADING The following scale will be the standard: Grade Range A B C D F Below 60 Final grades will be determined as follows: Each module will have equal weight and contribute 25% toward the final grade. Grades for each module will be determined as follows: Major Tests (minimum of 1)... 50% Laboratory (minimum of 1)... 25% Instructor Options... 15% Affective Skills... 10% Attendance at 95% or more of the classes and labs. Dependability (No tardiness). Acceptable student conduct as defined in the College Catalog. The instructor options will be discussed with the students during the first week of class. These EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
8 options may include homework, spot quizzes, projects, or written reports. Students are expected to "conduct themselves with dignity and to maintain high standards of responsible citizenship." (York Technical College Catalog, Student Life Section, "Student Conduct"). Points will be deducted for disruptive behavior that violates the principles of acceptable conduct. ENTRY LEVEL SKILLS The student must be able to build and test a basic electronic circuit starting with a schematic diagram. PREREQUISITE EET 111 or equivalent with minimum grade of C CO-REQUISITE EET 112 or equivalent, MAT 110 DISABILITIES STATEMENT Any student who feels s/he may need an accommodation based on the impact of a disability should contact the Special Resources Office (SRO) at in the 300 area of Student Services. The SRO coordinates reasonable accommodations for students with documented disabilities. EET of 8 Revised 12/2015
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS
 M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
ECET 211 Electrical Machines and Controls
 ECET 211 Electrical Machines and Controls 2016/4/27 Class Review and Wrapping Up Comprehensive Exam, Friday, 1:00-3:00 PM, May 6, 2016 Close books/allow 1-page (8 x 11 and ½) hand-written review note,
ECET 211 Electrical Machines and Controls 2016/4/27 Class Review and Wrapping Up Comprehensive Exam, Friday, 1:00-3:00 PM, May 6, 2016 Close books/allow 1-page (8 x 11 and ½) hand-written review note,
1. Explain in detail the constructional details and working of DC motor.
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
COURSE INFORMATION COURSE PREFIX/NO.: RAD 121 LEC HRS/WK: 4.0 LAB HRS/WK: 0.0 CREDIT HRS/SEMESTER: 4.0
 COURSE INFORMATION COURSE PREFIX/NO.: RAD 121 COURSE TITLE: RADIOGRAPHIC PHYSICS LEC HRS/WK: 4.0 LAB HRS/WK: 0.0 CREDIT HRS/SEMESTER: 4.0 Distance Learning Attendance/VA Statement Textbook Information
COURSE INFORMATION COURSE PREFIX/NO.: RAD 121 COURSE TITLE: RADIOGRAPHIC PHYSICS LEC HRS/WK: 4.0 LAB HRS/WK: 0.0 CREDIT HRS/SEMESTER: 4.0 Distance Learning Attendance/VA Statement Textbook Information
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements
 Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Upon successful completion of this course, the student should be competent to perform the following tasks:
 COURSE INFORMATION COURSE PREFIX/NO. : EET 112 COURSE TITLE: ALTERNATING CURRENT CIRCUITS LEC HRS/WK: 3.0 LAB HRS/WK: 3.0 CREDIT HRS/SEMESTER: 4.0 Distance Learning Attendance/VA Statement Textbook Information
COURSE INFORMATION COURSE PREFIX/NO. : EET 112 COURSE TITLE: ALTERNATING CURRENT CIRCUITS LEC HRS/WK: 3.0 LAB HRS/WK: 3.0 CREDIT HRS/SEMESTER: 4.0 Distance Learning Attendance/VA Statement Textbook Information
 VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
Lesson Plan. Name of the Faculty : Discipline : Electrical Engineering Semester : 4 th Semester. Lesson Plan Duration : Week
 Lesson Plan Name of the Faculty : Discipline : Electrical Engineering Semester : 4 th Semester Subject : ELECTRICAL MACHINES - I Lesson Plan Duration : 15-16 Week Week Theory Practical Lecture Topic (including
Lesson Plan Name of the Faculty : Discipline : Electrical Engineering Semester : 4 th Semester Subject : ELECTRICAL MACHINES - I Lesson Plan Duration : 15-16 Week Week Theory Practical Lecture Topic (including
Placement Paper For Electrical
 Placement Paper For Electrical Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is (A) conductively linked. (B) inductively linked. (C) not linked at all. (D) electrically linked. Ans : B Q.2 A salient pole synchronous
Placement Paper For Electrical Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is (A) conductively linked. (B) inductively linked. (C) not linked at all. (D) electrically linked. Ans : B Q.2 A salient pole synchronous
EE 350: Electric Machinery Fundamentals
 EE 350: Electric Machinery Fundamentals Lecture Schedule See Time Table Course Type, Semester Fundamental Engineering, Fifth Credit Hours Three + One Pre-requisite Physics Instructor Dr. Muhammad Asghar
EE 350: Electric Machinery Fundamentals Lecture Schedule See Time Table Course Type, Semester Fundamental Engineering, Fifth Credit Hours Three + One Pre-requisite Physics Instructor Dr. Muhammad Asghar
PART A. 1. List the types of DC Motors. Give any difference between them. BTL 1 Remembering
 UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
Electrical Machine Design
 ET-401E Electrical Machine Design 3 1 0 External : 70 Marks Credit 3.5 DURATION OF EXAM: 3 HRS UNIT I GENERAL : General features & limitations of electrical machine design, types of enclosures, heat dissipation,
ET-401E Electrical Machine Design 3 1 0 External : 70 Marks Credit 3.5 DURATION OF EXAM: 3 HRS UNIT I GENERAL : General features & limitations of electrical machine design, types of enclosures, heat dissipation,
ABET Course Syllabus Template
 1. Course number and name ECE341: Energy Conversion ABET Course Syllabus Template 2. Credits and contact hours 3 credit hours, 3 contact hours (including 20 minutes breaks) 3. Instructor s or course coordinator
1. Course number and name ECE341: Energy Conversion ABET Course Syllabus Template 2. Credits and contact hours 3 credit hours, 3 contact hours (including 20 minutes breaks) 3. Instructor s or course coordinator
Process Measurement, Instrumentation & Process Control: Principles & Best Practices
 Process Measurement, Instrumentation & Process Control: Principles & Best Practices SECTOR / ENGINEERING NON-TECHNICAL & CERTIFIED TRAINING COURSE This is a hands-on, practical training course and where
Process Measurement, Instrumentation & Process Control: Principles & Best Practices SECTOR / ENGINEERING NON-TECHNICAL & CERTIFIED TRAINING COURSE This is a hands-on, practical training course and where
Continuous Sensors Accuracy Resolution Repeatability Linearity Precision Range
 Continuous Sensors A sensor element measures a process variable: flow rate, temperature, pressure, level, ph, density, composition, etc. Much of the time, the measurement is inferred from a second variable:
Continuous Sensors A sensor element measures a process variable: flow rate, temperature, pressure, level, ph, density, composition, etc. Much of the time, the measurement is inferred from a second variable:
Department of Mechatronics Engineering
 Department of Mechatronics Engineering COURSES COVERED CONTROL SYSTEM POWER ELECTRONICS ELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEM SENSORS AND INTRUMENTATION LAB SUPERVISOR: ENGR. MOEZ UL HASSAN NI ELVIS II The NI Educational
Department of Mechatronics Engineering COURSES COVERED CONTROL SYSTEM POWER ELECTRONICS ELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEM SENSORS AND INTRUMENTATION LAB SUPERVISOR: ENGR. MOEZ UL HASSAN NI ELVIS II The NI Educational
Inductance, capacitance and resistance
 Inductance, capacitance and resistance As previously discussed inductors and capacitors create loads on a circuit. This is called reactance. It varies depending on current and frequency. At no frequency,
Inductance, capacitance and resistance As previously discussed inductors and capacitors create loads on a circuit. This is called reactance. It varies depending on current and frequency. At no frequency,
Measurement and Instrumentation
 Measurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application Alan S. Morris Reza Langari ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic
Measurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application Alan S. Morris Reza Langari ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic
CRN: MET-487 Instrumentation and Automatic Control June 28, 2010 August 5, 2010 Professor Paul Lin
 CRN: 32030 MET-487 Instrumentation and Automatic Control June 28, 2010 August 5, 2010 Professor Paul Lin Course Description: Class 2, Lab 2, Cr. 3, Junior class standing and 216 Instrumentation for pressure,
CRN: 32030 MET-487 Instrumentation and Automatic Control June 28, 2010 August 5, 2010 Professor Paul Lin Course Description: Class 2, Lab 2, Cr. 3, Junior class standing and 216 Instrumentation for pressure,
Course outline: 231 AC Machines G006A UEENEEG006A - Solve problems in single and three phase low voltage machines
 RTO Code 41319 Course outline: 231 AC Machines G006A UEENEEG006A - Solve problems in single and three phase low voltage machines Qualification: Applicable to: Unit of competency: Related policies: Monitor
RTO Code 41319 Course outline: 231 AC Machines G006A UEENEEG006A - Solve problems in single and three phase low voltage machines Qualification: Applicable to: Unit of competency: Related policies: Monitor
Quantity available (A) Quantity required (R) Sl. No. Deficiency (R - A) Description of Equipment
 . 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
Ballari Institute of Technology & Management Ballari Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. Vision & Mission of the Institute
 Ballari Institute of Technology & Management Ballari Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Vision & Mission of the Institute Vision We will be a top notch educational Institution that provides
Ballari Institute of Technology & Management Ballari Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Vision & Mission of the Institute Vision We will be a top notch educational Institution that provides
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 4-2 Motor Control Devices: Lecture 4 Motor Control Devices
 ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 4-2 Motor Control Devices: Part 3. Sensors, Part 4. Actuators Text Book: Electric Motors and Control Systems, by Frank D. Petruzella, published by McGraw Hill,
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 4-2 Motor Control Devices: Part 3. Sensors, Part 4. Actuators Text Book: Electric Motors and Control Systems, by Frank D. Petruzella, published by McGraw Hill,
Page ENSC387 - Introduction to Electro-Mechanical Sensors and Actuators: Simon Fraser University Engineering Science
 Motor Driver and Feedback Control: The feedback control system of a dc motor typically consists of a microcontroller, which provides drive commands (rotation and direction) to the driver. The driver is
Motor Driver and Feedback Control: The feedback control system of a dc motor typically consists of a microcontroller, which provides drive commands (rotation and direction) to the driver. The driver is
Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3)
 Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3) Example 1.2 Measurement System Digital Thermometer (p. 5) Figure 2.2 Electric circuit terminology (p. 13) Table 2.2 Resistor color band codes (p. 18) Figure
Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3) Example 1.2 Measurement System Digital Thermometer (p. 5) Figure 2.2 Electric circuit terminology (p. 13) Table 2.2 Resistor color band codes (p. 18) Figure
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER EI6402 ELECTRICAL MACHINES Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER EI6402 ELECTRICAL MACHINES Regulation 2013 Academic
Three-Phase Induction Motors. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg332:-Electrical Machine I
 Three-Phase Induction Motors 1 2 3 Classification of AC Machines 1. According to the type of current Single Phase and Three phase 2. According to Speed Constant Speed, Variable Speed and Adjustable Speed
Three-Phase Induction Motors 1 2 3 Classification of AC Machines 1. According to the type of current Single Phase and Three phase 2. According to Speed Constant Speed, Variable Speed and Adjustable Speed
Electromechanical Technology /Electromechanical Engineering Technology CIP Task Grid
 1 Secondary Task List 100 DEMONSTRATE KNOWLEDGE OF TECHNICAL REPORTS 101 Identify components of technical reports. 102 Demonstrate knowledge of the common components of technical documents. 103 Maintain
1 Secondary Task List 100 DEMONSTRATE KNOWLEDGE OF TECHNICAL REPORTS 101 Identify components of technical reports. 102 Demonstrate knowledge of the common components of technical documents. 103 Maintain
Remote Laboratory Operation: Web Technology Successes
 Remote Laboratory Operation: Web Technology Successes Masoud Naghedolfeizi 1, Jim Henry 2, Sanjeev Arora 3 Abstract National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has awarded Fort Valley State University
Remote Laboratory Operation: Web Technology Successes Masoud Naghedolfeizi 1, Jim Henry 2, Sanjeev Arora 3 Abstract National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has awarded Fort Valley State University
IE062: Principles and Best Practices of Process Measurement, Instrumentation & Control in Process Industry
 IE062: Principles and Best Practices of Process Measurement, Instrumentation & Control in Process Industry IE062 Rev.001 CMCT COURSE OUTLINE Page 1 of 6 Training Description: In an industrial situation
IE062: Principles and Best Practices of Process Measurement, Instrumentation & Control in Process Industry IE062 Rev.001 CMCT COURSE OUTLINE Page 1 of 6 Training Description: In an industrial situation
Industrial Electrician Level 3
 Industrial Electrician Level 3 Industrial Electrician Unit: C1 Industrial Electrical Code I Level: Three Duration: 77 hours Theory: Practical: 77 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide
Industrial Electrician Level 3 Industrial Electrician Unit: C1 Industrial Electrical Code I Level: Three Duration: 77 hours Theory: Practical: 77 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide
Training Fees 3,300$ per participant including Materials/Handouts, Tea/Coffee Refreshments & International Buffet Lunch.
 Training Title POWER TRANSFORMERS Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Power transformers 5 20-24 May $3,300 Abu Dhabi In any of the 5 star hotel. The exact venue will be informed soon. Training
Training Title POWER TRANSFORMERS Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Power transformers 5 20-24 May $3,300 Abu Dhabi In any of the 5 star hotel. The exact venue will be informed soon. Training
ET475 Electronic Circuit Design I [Onsite]
![ET475 Electronic Circuit Design I [Onsite] ET475 Electronic Circuit Design I [Onsite]](/thumbs/89/98281525.jpg) ET475 Electronic Circuit Design I [Onsite] Course Description: This course covers the analysis and design of electronic circuits, and includes a laboratory that utilizes computer-aided software tools for
ET475 Electronic Circuit Design I [Onsite] Course Description: This course covers the analysis and design of electronic circuits, and includes a laboratory that utilizes computer-aided software tools for
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 I INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad-500043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Course Code : AEE018
I INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad-500043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Course Code : AEE018
Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement. Documentation item: Secondary Competency Task List Coversheet
 Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement Documentation item: Secondary Task List Coversheet The Secondary School agrees to: A. Implement the approved PDE Program(s) of Study. B. Provide assessment of student
Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement Documentation item: Secondary Task List Coversheet The Secondary School agrees to: A. Implement the approved PDE Program(s) of Study. B. Provide assessment of student
OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES
 Training Title OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Operation Skills Enhancement - Measurement & Instrument For
Training Title OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Operation Skills Enhancement - Measurement & Instrument For
ACTUATORS AND SENSORS. Joint actuating system. Servomotors. Sensors
 ACTUATORS AND SENSORS Joint actuating system Servomotors Sensors JOINT ACTUATING SYSTEM Transmissions Joint motion low speeds high torques Spur gears change axis of rotation and/or translate application
ACTUATORS AND SENSORS Joint actuating system Servomotors Sensors JOINT ACTUATING SYSTEM Transmissions Joint motion low speeds high torques Spur gears change axis of rotation and/or translate application
PART 2 - ACTUATORS. 6.0 Stepper Motors. 6.1 Principle of Operation
 6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
EE401,EC401,DEE19,DETE19
 EE401,EC401,DEE19,DETE19 IV SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY 2013 LINEAR & DIGITAL ICs Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What is
EE401,EC401,DEE19,DETE19 IV SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY 2013 LINEAR & DIGITAL ICs Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What is
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Lesson 1 Introducing the Course on Basic Electrical Contents 1 Introducing the course (Lesson-1) 4 Introduction... 4 Module-1 Introduction... 4 Module-2 D.C. circuits.. 4 Module-3
Module 1 Introduction Lesson 1 Introducing the Course on Basic Electrical Contents 1 Introducing the course (Lesson-1) 4 Introduction... 4 Module-1 Introduction... 4 Module-2 D.C. circuits.. 4 Module-3
Process Measurement, Instrumentation & Process Control Principles & Best Practices Jul 2017, Dubai Nov 2017, Dubai
 09-13 Jul 2017, Dubai 12-16 Nov 2017, Dubai Introduction Objectives In an industrial situation where it is required to measure and control some aspect of a process, it is often the application of the knowledge
09-13 Jul 2017, Dubai 12-16 Nov 2017, Dubai Introduction Objectives In an industrial situation where it is required to measure and control some aspect of a process, it is often the application of the knowledge
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY Subject Code: (EC303ES) Regulations : R6 JNTUH Class :II Year B.Tech ECE I Semester Department of Electronics and communication Engineering BHARAT INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY Subject Code: (EC303ES) Regulations : R6 JNTUH Class :II Year B.Tech ECE I Semester Department of Electronics and communication Engineering BHARAT INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
Electrical Machines (EE-343) For TE (ELECTRICAL)
 PRACTICALWORKBOOK Electrical Machines (EE-343) For TE (ELECTRICAL) Name: Roll Number: Year: Batch: Section: Semester: Department: N.E.D University of Engineering &Technology, Karachi Electrical Machines
PRACTICALWORKBOOK Electrical Machines (EE-343) For TE (ELECTRICAL) Name: Roll Number: Year: Batch: Section: Semester: Department: N.E.D University of Engineering &Technology, Karachi Electrical Machines
STRAIN, FORCE, PRESSURE, AND FLOW MEASUREMENTS
 SECTION 4 STRAIN,, PRESSURE, AND FLOW MEASUREMENTS Walt Kester STRAIN GAGES The most popular electrical elements used in force measurements include the resistance strain gage, the semiconductor strain
SECTION 4 STRAIN,, PRESSURE, AND FLOW MEASUREMENTS Walt Kester STRAIN GAGES The most popular electrical elements used in force measurements include the resistance strain gage, the semiconductor strain
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS)
 Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A30203 : II B.
Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A30203 : II B.
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Actuators. EECS461, Lecture 5, updated September 16,
 Actuators The other side of the coin from sensors... Enable a microprocessor to modify the analog world. Examples: - speakers that transform an electrical signal into acoustic energy (sound) - remote control
Actuators The other side of the coin from sensors... Enable a microprocessor to modify the analog world. Examples: - speakers that transform an electrical signal into acoustic energy (sound) - remote control
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
Assembly Language. Topic 14 Motion Control. Stepper and Servo Motors
 Assembly Language Topic 14 Motion Control Stepper and Servo Motors Objectives To gain an understanding of the operation of a stepper motor To develop a means to control a stepper motor To gain an understanding
Assembly Language Topic 14 Motion Control Stepper and Servo Motors Objectives To gain an understanding of the operation of a stepper motor To develop a means to control a stepper motor To gain an understanding
1. (a) Determine the value of Resistance R and current in each branch when the total current taken by the curcuit in figure 1a is 6 Amps.
 Code No: 07A3EC01 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production
Code No: 07A3EC01 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production
Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors
 ME 3200 Mechatronics Laboratory Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors Introduction In this laboratory exercise, you will explore some of the properties of stepper and servomotors. These actuators are
ME 3200 Mechatronics Laboratory Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors Introduction In this laboratory exercise, you will explore some of the properties of stepper and servomotors. These actuators are
An Instrumentation System
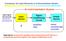 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Syllabus for ENGR065-01: Circuit Theory
 Syllabus for ENGR065-01: Circuit Theory Fall 2017 Instructor: Huifang Dou Designation: Catalog Description: Text Books and Other Required Materials: Course Objectives Student Learning Outcomes: Course
Syllabus for ENGR065-01: Circuit Theory Fall 2017 Instructor: Huifang Dou Designation: Catalog Description: Text Books and Other Required Materials: Course Objectives Student Learning Outcomes: Course
ESE 230 Syllabus Prof. D. L. Rode
 ESE 230 Syllabus Prof. D. L. Rode Course Description: ESE 230. "Introduction to Electrical & Electronic Circuits" Electron and ion motion, electrical current and voltage. Electrical energy, current, voltage,
ESE 230 Syllabus Prof. D. L. Rode Course Description: ESE 230. "Introduction to Electrical & Electronic Circuits" Electron and ion motion, electrical current and voltage. Electrical energy, current, voltage,
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK PRESSURE Hydraulic Pressure (Gauge) Hewett Road Gapton Hall Industrial Estate Great Yarmouth Norfolk NR31 0NN Contact: Mr J Gunn Tel: +44
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK PRESSURE Hydraulic Pressure (Gauge) Hewett Road Gapton Hall Industrial Estate Great Yarmouth Norfolk NR31 0NN Contact: Mr J Gunn Tel: +44
Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]
![Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405] Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]](/thumbs/95/124646158.jpg) UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
Position Sensors. The Potentiometer.
 Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
L T P EE 441: Analog Electronics (EE/IE) (3 1 3) Theory Marks =100 Sessional Marks = 50 Laboratory Marks = 50 Time = 3 hours
 EE 441: Analog Electronics (EE/IE) (3 1 3) 1. Bond Model of silicon crystal: Intrinsic carrier concentration, Effect of doping on carrier concentration. Holes and electrons, Majority and Minority carriers,
EE 441: Analog Electronics (EE/IE) (3 1 3) 1. Bond Model of silicon crystal: Intrinsic carrier concentration, Effect of doping on carrier concentration. Holes and electrons, Majority and Minority carriers,
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
ELECTRONIC CONTROL OF A.C. MOTORS
 CONTENTS C H A P T E R46 Learning Objectives es Classes of Electronic AC Drives Variable Frequency Speed Control of a SCIM Variable Voltage Speed Control of a SCIM Chopper Speed Control of a WRIM Electronic
CONTENTS C H A P T E R46 Learning Objectives es Classes of Electronic AC Drives Variable Frequency Speed Control of a SCIM Variable Voltage Speed Control of a SCIM Chopper Speed Control of a WRIM Electronic
ICE065 Practical Process Control & Instrumentation:
 ICE065 Practical Process Control & Instrumentation: Measurement & Sensors H.H. Sheikh Sultan Tower (0) Floor Corniche Street Abu Dhabi U.A.E www.ictd.ae ictd@ictd.ae Course Introduction: Globalization
ICE065 Practical Process Control & Instrumentation: Measurement & Sensors H.H. Sheikh Sultan Tower (0) Floor Corniche Street Abu Dhabi U.A.E www.ictd.ae ictd@ictd.ae Course Introduction: Globalization
GRAAD 12 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 GRAAD 12 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY EXEMPLAR 2014 MEMORANDUM MARKS: 200 This memorandum consists of 13 pages. Electrical Technology 2 DBE/2014 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE MARKERS
GRAAD 12 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY EXEMPLAR 2014 MEMORANDUM MARKS: 200 This memorandum consists of 13 pages. Electrical Technology 2 DBE/2014 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE MARKERS
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS
 SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS Page: 1 Contents 1. Capacitive sensors 2. Temperature measurements 3. Signal processing and data analysis using LabVIEW 4. Load measurements 5. Noise and noise reduction
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS Page: 1 Contents 1. Capacitive sensors 2. Temperature measurements 3. Signal processing and data analysis using LabVIEW 4. Load measurements 5. Noise and noise reduction
Contents. Acknowledgments. About the Author
 Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
MG Electrical Machine. 68 _ ED Co.,Ltd. > EXPERIMENTS > SPECIFICATIONS
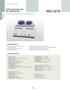 Electrical Machine 1/1 REPULSION MOTOR/ DC GENERATOR Starting and drive characteristics of repulsion induction motor Lad characteristics of separately excited DC shunt wound generator MG-5216 > EXPERIMENTS
Electrical Machine 1/1 REPULSION MOTOR/ DC GENERATOR Starting and drive characteristics of repulsion induction motor Lad characteristics of separately excited DC shunt wound generator MG-5216 > EXPERIMENTS
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Examination.
 Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2002 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2002 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Synchronous Machines Study Material
 Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
MICROCONTROLLERS Stepper motor control with Sequential Logic Circuits
 PH-315 MICROCONTROLLERS Stepper motor control with Sequential Logic Circuits Portland State University Summary Four sequential digital waveforms are used to control a stepper motor. The main objective
PH-315 MICROCONTROLLERS Stepper motor control with Sequential Logic Circuits Portland State University Summary Four sequential digital waveforms are used to control a stepper motor. The main objective
Sensors. Chapter 3. Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems Pearson Education Limited 2004 OHT 3.1
 Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY
 CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS 1 Electric Circuit Principles 2 Electronic Circuit Principles 3 Generation 4 Distribution 5 Utilisation The expected learning outcome is
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS 1 Electric Circuit Principles 2 Electronic Circuit Principles 3 Generation 4 Distribution 5 Utilisation The expected learning outcome is
Basic NC and CNC. Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur
 Basic NC and CNC Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Outline 1. Introduction to CNC machine 2. Component
Basic NC and CNC Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Outline 1. Introduction to CNC machine 2. Component
Sensors & transducers
 Sensors & transducers Prof. H. Arya DEPT. OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING IIT BOMBAY Sensors Sensors - A device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. Sensors are also
Sensors & transducers Prof. H. Arya DEPT. OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING IIT BOMBAY Sensors Sensors - A device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. Sensors are also
Houston Community College CAREER AND TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING COURSE SYLLABUS
 Houston Community College CAREER AND TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING COURSE SYLLABUS COURSE NUMBER: Hart 1301 COURSE TITLE: Basic Electricity Principles CREDITS: # (2 lectures,
Houston Community College CAREER AND TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING COURSE SYLLABUS COURSE NUMBER: Hart 1301 COURSE TITLE: Basic Electricity Principles CREDITS: # (2 lectures,
LabVIEW Based Instrumentation and Experimental Methods Course
 Session 2259 LabVIEW Based Instrumentation and Experimental Methods Course Chi-Wook Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering University of the Pacific Stockton, CA 95211 Abstract Instrumentation and Experimental
Session 2259 LabVIEW Based Instrumentation and Experimental Methods Course Chi-Wook Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering University of the Pacific Stockton, CA 95211 Abstract Instrumentation and Experimental
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction By Sintayehu Challa
 Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS. M.D. Desai Professor of Instrumentation and Control Engineering Institute of Technology Nirma University Ahmedabad
 CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS M.D. Desai Professor of Instrumentation and Control Engineering Institute of Technology Nirma University Ahmedabad New Delhi-110001 2008 CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS M.D. Desai 2008
CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS M.D. Desai Professor of Instrumentation and Control Engineering Institute of Technology Nirma University Ahmedabad New Delhi-110001 2008 CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS M.D. Desai 2008
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS
 Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
MEASUREMENT, TRANSMITTERS AND FILTERING
 MEASUREMENT DEVICE CHE302 LECTURE II MEASUREMENT, TRANSMITTERS AND ILTERING Professor Dae Ryook Yang all 2001 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University CHE302ProcessDynamicsandControl
MEASUREMENT DEVICE CHE302 LECTURE II MEASUREMENT, TRANSMITTERS AND ILTERING Professor Dae Ryook Yang all 2001 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University CHE302ProcessDynamicsandControl
Objective: Study of self-excitation characteristics of an induction machine.
 Objective: Study of self-excitation characteristics of an induction machine. Theory: The increasing importance of fuel saving has been responsible for the revival of interest in so-called alternative source
Objective: Study of self-excitation characteristics of an induction machine. Theory: The increasing importance of fuel saving has been responsible for the revival of interest in so-called alternative source
REQUIRED SKILLS AND KNOWLEDGE UEENEEG101A. Electromagnetic devices and circuits. Topic and Description NIDA Lesson CARD # Magnetism encompassing:
 REQUIRED SKILLS AND KNOWLEDGE UEENEEG101A KS01-EG101A Electromagnetic devices and circuits T1 Magnetism encompassing: Topic and Description NIDA Lesson CARD # magnetic field pattern of bar and horse-shoe
REQUIRED SKILLS AND KNOWLEDGE UEENEEG101A KS01-EG101A Electromagnetic devices and circuits T1 Magnetism encompassing: Topic and Description NIDA Lesson CARD # magnetic field pattern of bar and horse-shoe
L E C T U R E R, E L E C T R I C A L A N D M I C R O E L E C T R O N I C E N G I N E E R I N G
 P R O F. S L A C K L E C T U R E R, E L E C T R I C A L A N D M I C R O E L E C T R O N I C E N G I N E E R I N G G B S E E E @ R I T. E D U B L D I N G 9, O F F I C E 0 9-3 1 8 9 ( 5 8 5 ) 4 7 5-5 1 0
P R O F. S L A C K L E C T U R E R, E L E C T R I C A L A N D M I C R O E L E C T R O N I C E N G I N E E R I N G G B S E E E @ R I T. E D U B L D I N G 9, O F F I C E 0 9-3 1 8 9 ( 5 8 5 ) 4 7 5-5 1 0
Electrical Engineering / Electromagnetics
 Electrical Engineering / Electromagnetics. Plot voltage versus time and current versus time for the circuit with the following substitutions: A. esistor B. Capacitor C. Inductor t = 0 A/B/C A. I t t B.
Electrical Engineering / Electromagnetics. Plot voltage versus time and current versus time for the circuit with the following substitutions: A. esistor B. Capacitor C. Inductor t = 0 A/B/C A. I t t B.
AC : INTRODUCTION OF NEW AND COST EFFECTIVE TECHNOLOGIES IN THE ENT POWER LABORATORY
 AC 2007-473: INTRODUCTION OF NEW AND COST EFFECTIVE TECHNOLOGIES IN THE ENT POWER LABORATORY Alireza Rahrooh, University of Central Florida ALIREZA RAHROOH Alireza Rahrooh is an Associate Professor of
AC 2007-473: INTRODUCTION OF NEW AND COST EFFECTIVE TECHNOLOGIES IN THE ENT POWER LABORATORY Alireza Rahrooh, University of Central Florida ALIREZA RAHROOH Alireza Rahrooh is an Associate Professor of
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EECE 365: Applied Electronics and Electromechanics
 THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 365: Applied Electronics and Electromechanics Final Exam / Sample-Practice Exam Spring 2008 April 23 Topics Covered:
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 365: Applied Electronics and Electromechanics Final Exam / Sample-Practice Exam Spring 2008 April 23 Topics Covered:
3. What is hysteresis loss? Also mention a method to minimize the loss. (N-11, N-12)
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE 6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I UNIT I : MAGNETIC CIRCUITS AND MAGNETIC MATERIALS Part A (2 Marks) 1. List
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE 6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I UNIT I : MAGNETIC CIRCUITS AND MAGNETIC MATERIALS Part A (2 Marks) 1. List
DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS
 Unit 4 AC s UNIT OBJECTIVE After completing this unit, you will be able to demonstrate and explain the operation of ac induction motors using the Squirrel-Cage module and the Capacitor-Start Motor module.
Unit 4 AC s UNIT OBJECTIVE After completing this unit, you will be able to demonstrate and explain the operation of ac induction motors using the Squirrel-Cage module and the Capacitor-Start Motor module.
1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M]
![1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M] 1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M]](/thumbs/95/125538661.jpg) Subject Code: 17435 Model Answer Page 1 of 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17435 Model Answer Page 1 of 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Q.1 a) Attempt any SIX of the following: 12M. (i) Give comparison between active transducer and passive transducer. Ans:- (Any Two) 1M each
 Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
combine regular DC-motors with a gear-box and an encoder/potentiometer to form a position control loop can only assume a limited range of angular
 Embedded Control Applications II MP10-1 Embedded Control Applications II MP10-2 week lecture topics 10 Embedded Control Applications II - Servo-motor control - Stepper motor control - The control of a
Embedded Control Applications II MP10-1 Embedded Control Applications II MP10-2 week lecture topics 10 Embedded Control Applications II - Servo-motor control - Stepper motor control - The control of a
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2I03
 Student Name: Student ID: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2I03 DAY CLASS Duration 2 hours McMaster University Practice Exam Dr. M. Thompson The final test includes 60 questions on 12 pages. This test paper must be
Student Name: Student ID: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2I03 DAY CLASS Duration 2 hours McMaster University Practice Exam Dr. M. Thompson The final test includes 60 questions on 12 pages. This test paper must be
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN1221 Switched-mode drives for DC motors. Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr.
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. 1988 Dec Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate the use of integrated switched-mode controllers, generally
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. 1988 Dec Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate the use of integrated switched-mode controllers, generally
MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Exam. December 11, 2006
 MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Exam December 11, 2006 o Closed Book and Notes o No Calculators 1. Fill in your name on side 2 of the scoring sheet (Last name first!) 2. Fill
MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Exam December 11, 2006 o Closed Book and Notes o No Calculators 1. Fill in your name on side 2 of the scoring sheet (Last name first!) 2. Fill
EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
 EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V: TRANSDUCERS Temperature transducers-rtd, thermistor, Thermocouple-Displacement transducer-inductive, capacitive, LVDT, Pressure transducer Bourdon tube,
EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V: TRANSDUCERS Temperature transducers-rtd, thermistor, Thermocouple-Displacement transducer-inductive, capacitive, LVDT, Pressure transducer Bourdon tube,
