FLATE Hillsborough Community College - Brandon (813)
|
|
|
- Clementine King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Florida Advanced Technological Education (FLATE) Center wishes to make available, for educational and noncommercial purposes only, materials relevant to the EST1830 Introduction to Alternative/Renewable Energy course comprised of images, texts, facilitator s notes, and other demonstration materials. This instructional resource forms part of FLATE s outreach efforts to facilitate a connection between students and teachers throughout the State of Florida. We trust that these activities and materials will add value to your teaching and/or presentations. FLATE Hillsborough Community College - Brandon E Columbus Dr., Tampa, FL (813) This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No and a Florida Energy Systems Consortium Grant. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation or the Florida Energy Systems Consortium. 1
2 Introduction to Alternative and Renewable Energy EST1830 2
3 3. Energy Production 3.1 Renewable Energy Technologies Solar Energy 3
4 3. Energy Production Solar Energy 3.1.1a Sun s Position 3.1.1b Sun Path 3.1.1c Sun Path Charts 3.1.1d Solar Panel Positioning Photovoltaics Solar Thermal a Low Temperature Collectors b Medium Temperature Collectors c High Temperature Collectors 4
5 Photovoltaics a. Review of energy in light b. Operation of solar cells c. Types of solar cells Excellent resource for further study online: 5
6 a Light energy Light from the sun is a mixture of different wavelengths. The different wavelengths that are visible to the eye show up as different colors. 6
7 a Light energy Speed of light c= λν Speed of light: c (m/s) Wavelength: λ(m) Frequency: ν(1/s) High Energy Photon for Blue Light Higher frequency Energy of a Photon E=hν Or also Low Energy Photon for Red Light Lower frequency Planck s Constant: h= Joule second Typically, when dealing with particles such as photons or electrons the units to use are electron volts (ev). But, we will stick to Joules. 7
8 Remember our study of Air Mass a Air Mass 8
9 Visible spectrum is between the wavelength range of nm 9
10 a Radiant energy Solar cells respond differently to the different wavelengths of light. For example, crystalline silicon (Si) can use the entire visible spectrum, plus some part of the infrared spectrum. But energy in part of the infrared spectrum, as well as longer-wavelength radiation, is too low to produce current flow. Higher-energy radiation can produce current flow, but much of this energy is not usable. In summary, light that is too high or low in energy is not usable by a cell to produce electricity. It is transformed into heat. 10
11 a Radiant energy The spectral response is the ratio of the current generated (A) by the solar cell to the power (W) incident on the solar cell. Si W A The spectral response of a silicon solar cell under glass. At short wavelengths below 400 nm the glass absorbs most of the light and the cell response is very low. At intermediate wavelengths the cell approaches the ideal. At long wavelengths the response fall back to zero. Note: Silicon is an indirect band gap semiconductor so there is not a sharp cut off at the wavelength corresponding to the band gap (E g = 1.12 ev). 11
12 About 80-90% of solar cells are made of crystalline Silicon These are the first generation type of solar cells. There are other types: Gen 2 and Gen 3 that will be mentioned briefly. Simplified schematic of solar cell operation. 12
13 All matter is composed of atoms, which are made up of positively charged protons, negatively charged electrons, and neutral neutrons. As depicted in this simplified diagram, silicon has 14 electrons. The four electrons that orbit the nucleus in the outermost "valence" energy level are given to, accepted from, or shared with other atoms. Large numbers of silicon atoms bond with each other by means of their valence electrons to form a crystal. In a crystalline solid, each silicon atom normally shares one of its four valence electrons in a covalent bond with each of four neighboring silicon atoms. The solid thus consists of basic units of five silicon atoms: the original atom plus the four other atoms with which it shares valence electrons. 13
14 Si Si Si Si Si Si Schematic of covalent bonds in a Silicon crystal lattice Solar Cells are made of semi-conductor material, meaning that the material doesn t have the conductivity of metals but it is also not insulating material. The atomic characteristics are such that electrons straddle between the conductor and insulator states. External energy is needed to move the electrons into a conductive state. In the case of solar cells, this external energy is provided by Photons from sunlight. When the electron gets knocked into the conductive state (or free state), it leaves a space in the covalent bond which could be thought of as a hole. Many free electrons are what create electric currents when connected to a load. Electrons have negative charge (-) Holes have positive charge (+) 14
15 P-N Junction The n-type (negative) region has a high electron concentration..this is due to doping with electron donor elements. P-njunctions are formed by joining n-type and p-type semiconductor materials. The p-type (positive) region has a high hole concentration this is due to doping with electron acceptor elements. 15
16 P-N Junction On the n-type side, positive ion cores are exposed electrons diffuse from the n-type side to the p-type side in a p-njunction, when the electrons and holes move to the other side of the junction, they leave behind exposed charges on dopantatom sites, which are fixed in the crystal lattice and are unable to move P-njunction An electric field Ê forms between the positive ion cores in the n-type material and negative ion cores in the p-type material. holes flow by diffusion from the p-type side to the n-type side On the p-type side, negative ion cores are exposed 16
17 P-N Junction On the n-type side, positive ion cores are exposed electrons diffuse from the n-type side to the p-type side In equilibrium, the net current from the device is zero. P-njunction A "built in" potential V bi due to Ê is formed at the junction holes flow by diffusion from the p-type side to the n-type side On the p-type side, negative ion cores are exposed 17
18 P-N Junction Electrons in the n-type region want to continue to recombine with the holes in the p-type region. (-)(+) In equilibrium, the net current from the device is zero. Zero voltage with no light. P-njunction But, the electric field in the depletion region prevents recombination. However, there are still some electrons or holes that go across the depletion region through diffusion or drift. The electron drift and diffusion current exactly balance out (if they did not there would be a net buildup of electrons on either one side or the other of the device). Similarly, the hole drift and diffusion current also balance each other out. 18
19 1. As we learned before, when photons from sunlight hit the solar cell, valence electrons are knocked free to become conductive. The Photovoltaic Effect Light generates extra carriers. P-njunction The collection of lightgenerated carriers does not by itself give rise to power generation. In order to generate power, a voltage must be generated as well as a current The collection of lightgenerated carriers causes an increase in the number of electrons on the n-type side of the p-njunction and a similar increase in holes in the p-type material 19
20 The Photovoltaic Effect (-) 3. Since there is an excess of electrons in the n-type material and an excess of holes in the p-type material a separation of charges occurs. That charge separation leads to the formation of a voltage across thep-n junction. This is the open circuit voltage: V oc Light generates extra carriers. P-njunction (+) V oc This is DC voltage!! 20
21 4. When the terminals are connected, a current flows proportional to the light intensity. This is the short-circuit current: I sc The Photovoltaic Effect Light generates extra carriers. P-njunction (-) (+) I sc Voltage is Zero This is also maximum current from solar cell. This is DC current!! Electrons recombine with holes to complete the circuit. 21
22 Influence of irradiance on the I-V Characteristics of a Solar Cell at T=25 o C This is DC current!! Volker Quaschning - Understanding Renewable Energy Systems - Earthscan, London,
23 The basic photovoltaic or solar cell typically produces only a small amount of power. To produce more power, cells can be interconnected to form modules (also called panels), which can in turn be connected into arrays to produce yet more power. Because of this modularity, PV systems can be designed to meet any electrical requirement, no matter how large or how small. 23
24 This is DC current!! Don t pay attention to the resistance lines. A single silicon photovoltaic cell produces an open-circuit voltage of slightly over 0.55 volts. The voltage produced by a photovoltaic panel is a function of how many cells are connected in series. In the case of the panel described above, there must be about 36 photovoltaic cells connected in series in order to produce over 20 volts. 24
25 Influence of Temperature on the I-V Characteristics of a Solar Cell Volker Quaschning - Understanding Renewable Energy Systems - Earthscan, London, 2005 V oc decreases at a faster rate with rising temperature than the I sc increases. Therefore, the solar cell s maximum power and the cell efficiency decrease with rising temperature. For most cells, a temperature rise of 25 C causes a power drop of about 10%. Unfortunately, the higher the temperature of the cell, the lower the voltage output. Cold, Sunny days are the best. 25
26 The solar cell generates its maximum power at a certain voltage Current Power Current Voltage Line Power Voltage Line This graph shows the current voltageand power voltagecharacteristics. It shows clearly that the power curve has a point of maximum power called the maximum power point, MPP. The maximum power point voltage, V MPP, is less than V oc The current I MPP is lower than I sc. At the MPP, current and voltage have nearly the same relation to irradiance and temperature as the short circuit current and open circuit voltage. Volker Quaschning - Understanding Renewable Energy Systems - Earthscan, London,
27 The solar cell generates its maximum power at a certain voltage To make solar cells and modules comparable, MPP power is measured under standard test conditions (STC): Irradiance at 1000 W/m2 : Temperature of 25 C: Air mass (AM) 1.5. Power generated by the solar modules in real weather conditions is usually lower, hence STC power has the unit W p (Watt peak). This is the rating you will typically see on commercial solar cells. In terms of dependence on irradiance, the current dominates the device s behavior, so that the MPP power is nearly proportional to the irradiance. Solar cell efficiency is the ratio of the maximum electrical solar cell power to the radiant power on the solar cell area. η = P MPP /E*A where E=irradiance; A=solar cell area Commercial crystalline solar cells now reach efficiencies up to almost 20%, but in the laboratory, efficiencies of more than 25% are possible. Efficiencies of thin-film solar cells are lower. Volker Quaschning - Understanding Renewable Energy Systems - Earthscan, London,
28 The solar cell generates its maximum power at a certain voltage So we have seen that P MPP is nearly proportional to the irradiance, so that Solar cell efficiency is the ratio of maximum power point power to irradiance. But, Maximum power point voltage varies with irradiance and temperature. So that efficiency varies. One solution: Maximum Power Point Tracker 28
29 The solar cell generates its maximum power at a certain voltage Maximum Power Point Tracker High efficiency DC to DC converter which operates by taking the DC input current, changing it to AC, running it through a transformer (usually a toroid, a doughnut looking transformer), and then rectifying it back to DC. It tracks the instantaneous power by continually measuring the voltage and current through a microprocessor Uses this information to dynamically adjust the load so the maximum power is alwaystransferred, regardless of the variation in temperature and irradiance. The microprocessor tries to maximize the watts delivered to the load from the solar panel by controlling the step down ratio to keep the solar panel operating at its Maximum Power Point. A load that may represent an end-user, or an energy storage element, or a power grid-interface. Outback Power FLEXmax80 MPPT Solar Charge Controller Maximum Solar Array: 12 VDC systems 1250 Watts / 24 VDC systems 2500 Watts / 48 VDC systems 5000 Watts / 60 VDC Systems 7500 Watts 29
30 b Solar Operation Another way to maximize power is to maximize irradiance by having the panels (or arrays) track the sun. This is Panel/Array Tracking. These are mainly used in commercial applications. Azimuth-Altitude Dual Axis Tracker - 2 axis solar tracker, Toledo, Spain Horizontal Single Axis Trackers Single Axis Trackers Two Axis Tracker, Alamosa, CO January 27, 2011 One Axis Tracker, Alamosa, CO 30
31 b Irradiation Data 31
32 We have seen that solar cells generate DC current/voltage. But, most commercial appliances use AC current/voltage. Inverters must be used. Most have MPP tracking capability. 32
33 Mimics AC current by using square waves. A reasonable AC current is obtained through superposition of square waves, but it is not perfect. DC to AC Inverters modify DC signals, which are constant, to AC signals, which as we have seen vary in a sinusoidal pattern. Volker Quaschning - Understanding Renewable Energy Systems - Earthscan, London,
34 c Types of Solar Cells First Generation Single crystal; multicrisytalline Silicon These solar cells, using silicon wafers, account for 86% of the solar cell market. High efficiency, long life But, high material and manufacturing costs Fragile and Rigid Second Generation Thin-film solar cells, are significantly cheaper to produce than first generation cells but have lower efficiencies Amorphous Si, CdTe, CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide) Flexible Third Generation Still in research phase Do not need P-n junction Wide range of potential solar innovations Organic and dye sensitized (Grätzel cells) Polymer solar cells Nanocrystalline solar cells Light absorbing dye attached to nanoscale titania. 34
35 c Types of Solar Cells Best Research-Cell Efficiencies AS OF 5/27/10 Efficiency (% %) Multijunction Concentrators Three-junction (2-terminal, monolithic) Two-junction (2-terminal, monolithic) Crystalline Si Cells Single crystal Multicrystalline Thin Si Thin Film Technologies Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 CdTe Amorphous Si:H (stabilized) Masushita RCA Emerging PV Organic cells Monosolar Boeing Boeing 1980 Kodak University of Maine RCA RCA RCA RCA Westinghouse No. Carolina State University RCA ARCO Kodak Boeing RCA Solarex Spire 1985 Solarex Stanford ARCO AstroPower Varian AMETEK Boeing Spire UNSW Georgia Tech University So. Florida Photon Energy 1990 Boeing NREL UNSW Sharp Japan Energy NREL UNSW Euro-CIS 1995 UNSW Georgia Tech NREL United Solar UNSW NREL/ Spectrolab Spectrolab 2000 Spectrolab NREL Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 14x concentration UNSW NREL University Konstanz NREL AstroPower United Solar NREL NREL University California Berkeley NREL Princeton NREL
36 Photovoltaic Cost Trends Source: Bullis, Kevin, Technology Review, Vol. 113, Solar's Great Leap Forward No. 4, July/August Today the solar panels themselves account for less than half the total cost of the technology. Additional costs are: Installation costs inverters sales and marketing by installers and financing. Source: Photon Consulting *For the lowest-cost manufacturers in each country Credit: Tommy McCall 36
37 Photovoltaics a. Review of energy in light b. Operation of solar cells c. Types of solar cells Excellent resource for further study online: 37
CHAPTER-2 Photo Voltaic System - An Overview
 CHAPTER-2 Photo Voltaic System - An Overview 15 CHAPTER-2 PHOTO VOLTAIC SYSTEM -AN OVERVIEW 2.1 Introduction With the depletion of traditional energies and the increase in pollution and greenhouse gases
CHAPTER-2 Photo Voltaic System - An Overview 15 CHAPTER-2 PHOTO VOLTAIC SYSTEM -AN OVERVIEW 2.1 Introduction With the depletion of traditional energies and the increase in pollution and greenhouse gases
10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional)
 EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell?
 What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell? GT CRC Roof-Mounted PV System Largest single PV structure at the time of it s construction for the 1996 Olympic games Produced more than 1 billion watt hrs. of
What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell? GT CRC Roof-Mounted PV System Largest single PV structure at the time of it s construction for the 1996 Olympic games Produced more than 1 billion watt hrs. of
Chapter Semiconductor Electronics
 Chapter Semiconductor Electronics Q1. p-n junction is said to be forward biased, when [1988] (a) the positive pole of the battery is joined to the p- semiconductor and negative pole to the n- semiconductor
Chapter Semiconductor Electronics Q1. p-n junction is said to be forward biased, when [1988] (a) the positive pole of the battery is joined to the p- semiconductor and negative pole to the n- semiconductor
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells
 LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
Fall 2004 Dawn Hettelsater, Yan Zhang and Ali Shakouri, 05/09/2002
 University of California at Santa Cruz Jack Baskin School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE-145L: Properties of Materials Laboratory Lab 6: Solar Cells Fall 2004 Dawn Hettelsater, Yan
University of California at Santa Cruz Jack Baskin School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE-145L: Properties of Materials Laboratory Lab 6: Solar Cells Fall 2004 Dawn Hettelsater, Yan
10/14/2009. Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell
 PHOTOVOLTAICS Fundamentals PV FUNDAMENTALS Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell SEMICONDUCTOR BASICS Allowed energy bands Valence and conduction band Fermi
PHOTOVOLTAICS Fundamentals PV FUNDAMENTALS Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell SEMICONDUCTOR BASICS Allowed energy bands Valence and conduction band Fermi
Electronic devices-i. Difference between conductors, insulators and semiconductors
 Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
CHAPTER 5 CIRCUIT MODELING METHODOLOGY FOR THIN-FILM PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULES
 106 CHAPTER 5 CIRCUIT MODELING METHODOLOGY FOR THIN-FILM PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULES 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this Chapter, the constructional details of various thin-film modules required for modeling are given.
106 CHAPTER 5 CIRCUIT MODELING METHODOLOGY FOR THIN-FILM PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULES 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this Chapter, the constructional details of various thin-film modules required for modeling are given.
Modelling and simulation of PV module for different irradiation levels Balachander. K Department of EEE, Karpagam University, Coimbatore.
 6798 Available online at www.elixirpublishers.com (Elixir International Journal) Electrical Engineering Elixir Elec. Engg. 43 (2012) 6798-6802 Modelling and simulation of PV module for different irradiation
6798 Available online at www.elixirpublishers.com (Elixir International Journal) Electrical Engineering Elixir Elec. Engg. 43 (2012) 6798-6802 Modelling and simulation of PV module for different irradiation
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica. Analogue Electronics. Paolo Colantonio A.A.
 Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics
 Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács BME DED 17/09/2015 1 / 37 The basic properties of semiconductors Range of conductivity [Source: http://www.britannica.com]
Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács BME DED 17/09/2015 1 / 37 The basic properties of semiconductors Range of conductivity [Source: http://www.britannica.com]
Lecture 7:PN Junction. Structure, Depletion region, Different bias Conditions, IV characteristics, Examples
 Lecture 7:PN Junction Structure, Depletion region, Different bias Conditions, IV characteristics, Examples PN Junction The diode (pn junction) is formed by dopping a piece of intrinsic silicon, such that
Lecture 7:PN Junction Structure, Depletion region, Different bias Conditions, IV characteristics, Examples PN Junction The diode (pn junction) is formed by dopping a piece of intrinsic silicon, such that
Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit
 9 Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit 9.1 External solar cell parameters The main parameters that are used to characterise the performance of solar cells are the peak power P max, the short-circuit
9 Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit 9.1 External solar cell parameters The main parameters that are used to characterise the performance of solar cells are the peak power P max, the short-circuit
Key Questions ECE 340 Lecture 28 : Photodiodes
 Things you should know when you leave Key Questions ECE 340 Lecture 28 : Photodiodes Class Outline: How do the I-V characteristics change with illumination? How do solar cells operate? How do photodiodes
Things you should know when you leave Key Questions ECE 340 Lecture 28 : Photodiodes Class Outline: How do the I-V characteristics change with illumination? How do solar cells operate? How do photodiodes
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
CHAPTER 3 PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM MODEL WITH CHARGE CONTROLLERS
 34 CHAPTER 3 PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM MODEL WITH CHARGE CONTROLLERS Solar photovoltaics are used for the direct conversion of solar energy into electrical energy by means of the photovoltaic effect, that is,
34 CHAPTER 3 PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM MODEL WITH CHARGE CONTROLLERS Solar photovoltaics are used for the direct conversion of solar energy into electrical energy by means of the photovoltaic effect, that is,
Intrinsic Semiconductor
 Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
IENGINEERS- CONSULTANTS LECTURE NOTES SERIES ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING 1 YEAR UPTU. Lecture-4
 2 P-n Lecture-4 20 Introduction: If a junction is formed between a p-type and a n-type semiconductor this combination is known as p-n junction diode and has the properties of a rectifier 21 Formation of
2 P-n Lecture-4 20 Introduction: If a junction is formed between a p-type and a n-type semiconductor this combination is known as p-n junction diode and has the properties of a rectifier 21 Formation of
Electronic Circuits I. Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud
 Electronic Circuits I Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud alaa_y_emam@hotmail.com Chapter 27 Diode and diode application Outline: Semiconductor Materials The P-N Junction Diode Biasing P-N Junction Volt-Ampere
Electronic Circuits I Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud alaa_y_emam@hotmail.com Chapter 27 Diode and diode application Outline: Semiconductor Materials The P-N Junction Diode Biasing P-N Junction Volt-Ampere
Laboratory 2: PV Module Current-Voltage Measurements
 Laboratory 2: PV Module Current-Voltage Measurements Introduction and Background The current-voltage (I-V) characteristic is the basic descriptor of photovoltaic device performance. A fundamental understanding
Laboratory 2: PV Module Current-Voltage Measurements Introduction and Background The current-voltage (I-V) characteristic is the basic descriptor of photovoltaic device performance. A fundamental understanding
 Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
Week 10 Power Electronics Applications to Photovoltaic Power Generation
 ECE1750, Spring 2017 Week 10 Power Electronics Applications to Photovoltaic Power Generation 1 Photovoltaic modules Photovoltaic (PV) modules are made by connecting several PV cells. PV arrays are made
ECE1750, Spring 2017 Week 10 Power Electronics Applications to Photovoltaic Power Generation 1 Photovoltaic modules Photovoltaic (PV) modules are made by connecting several PV cells. PV arrays are made
Presented in Electrical & Computer Engineering University of New Brunswick Fredericton, NB, Canada The Photovoltaic Cell
 Presented in Electrical & Computer Engineering University of New Brunswick Fredericton, NB, Canada Introduction The The concept and PVA Characteristics Modeling Operating principles Control strategies
Presented in Electrical & Computer Engineering University of New Brunswick Fredericton, NB, Canada Introduction The The concept and PVA Characteristics Modeling Operating principles Control strategies
ISSN: Page 465
 Modelling of Photovoltaic using MATLAB/SIMULINK Varuni Agarwal M.Tech (Student), Dit University Electrical and Electronics Department Dr.Gagan Singh Hod,Dit University Electrical and Electronics Department
Modelling of Photovoltaic using MATLAB/SIMULINK Varuni Agarwal M.Tech (Student), Dit University Electrical and Electronics Department Dr.Gagan Singh Hod,Dit University Electrical and Electronics Department
An Analysis of a Photovoltaic Panel Model
 An Analysis of a Photovoltaic Panel Model Comparison Between Measurements and Analytical Models Ciprian Nemes, Florin Munteanu Faculty of Electrical Engineering Technical University of Iasi Iasi, Romania
An Analysis of a Photovoltaic Panel Model Comparison Between Measurements and Analytical Models Ciprian Nemes, Florin Munteanu Faculty of Electrical Engineering Technical University of Iasi Iasi, Romania
UNIT IX ELECTRONIC DEVICES
 UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
Introduction to Photovoltaics
 Introduction to Photovoltaics PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 24, 2015 Only solar energy Of all the possible sources
Introduction to Photovoltaics PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 24, 2015 Only solar energy Of all the possible sources
Modelling and Analysis of Four-Junction Tendem Solar Cell in Different Environmental Conditions Mr. Biraju J. Trivedi 1 Prof. Surendra Kumar Sriwas 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 08, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Modelling and Analysis of Four-Junction Tendem Solar Cell in Different Environmental
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 08, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Modelling and Analysis of Four-Junction Tendem Solar Cell in Different Environmental
EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES
 EXPERIMENT 9 EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES Semiconductor Diodes Structure 91 Introduction Objectives 92 Basics of Semiconductors Revisited 93 A p-n Junction Operation of a p-n Junction A Forward
EXPERIMENT 9 EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES Semiconductor Diodes Structure 91 Introduction Objectives 92 Basics of Semiconductors Revisited 93 A p-n Junction Operation of a p-n Junction A Forward
1 Semiconductor-Photon Interaction
 1 SEMICONDUCTOR-PHOTON INTERACTION 1 1 Semiconductor-Photon Interaction Absorption: photo-detectors, solar cells, radiation sensors. Radiative transitions: light emitting diodes, displays. Stimulated emission:
1 SEMICONDUCTOR-PHOTON INTERACTION 1 1 Semiconductor-Photon Interaction Absorption: photo-detectors, solar cells, radiation sensors. Radiative transitions: light emitting diodes, displays. Stimulated emission:
Design, construction and characterization of a steady state solar simulator
 Design, construction and characterization of a steady state solar simulator T.V. Mthimunye, E.L Meyer and M. Simon Fort Hare Institute of Technology, University Of Fort Hare, Alice Tmthimunye@ufh.ac.za
Design, construction and characterization of a steady state solar simulator T.V. Mthimunye, E.L Meyer and M. Simon Fort Hare Institute of Technology, University Of Fort Hare, Alice Tmthimunye@ufh.ac.za
Downloaded from
 SOLID AND SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES (EASY AND SCORING TOPIC) 1. Distinction of metals, semiconductor and insulator on the basis of Energy band of Solids. 2. Types of Semiconductor. 3. PN Junction formation
SOLID AND SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES (EASY AND SCORING TOPIC) 1. Distinction of metals, semiconductor and insulator on the basis of Energy band of Solids. 2. Types of Semiconductor. 3. PN Junction formation
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics Materials Devices And Simple Circuits
 Class XII Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics Materials Devices And Simple Circuits Physics Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers
Class XII Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics Materials Devices And Simple Circuits Physics Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers
Semiconductor Devices
 About the Tutorial The electronic components exploiting the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, are termed as semiconductor devices. This tutorial discusses the functional operation of semiconductor
About the Tutorial The electronic components exploiting the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, are termed as semiconductor devices. This tutorial discusses the functional operation of semiconductor
 SEMICONDUCTOR EECTRONICS MATERIAS, DEVICES AND SIMPE CIRCUITS Important Points: 1. In semiconductors Valence band is almost filled and the conduction band is almost empty. The energy gap is very small
SEMICONDUCTOR EECTRONICS MATERIAS, DEVICES AND SIMPE CIRCUITS Important Points: 1. In semiconductors Valence band is almost filled and the conduction band is almost empty. The energy gap is very small
Lesson 08. Name and affiliation of the author: Professor L B D R P Wijesundera Department of Physics, University of Kelaniya.
 Lesson 08 Title of the Experiment: Identification of active components in electronic circuits and characteristics of a Diode, Zener diode and LED (Activity number of the GCE Advanced Level practical Guide
Lesson 08 Title of the Experiment: Identification of active components in electronic circuits and characteristics of a Diode, Zener diode and LED (Activity number of the GCE Advanced Level practical Guide
Performance and Loss Analyses of High-Efficiency CBD-ZnS/Cu(In 1-x Ga x )Se 2 Thin-Film Solar Cells
 Performance and Loss Analyses of High-Efficiency CBD-ZnS/Cu(In 1-x Ga x )Se 2 Thin-Film Solar Cells Alexei Pudov 1, James Sites 1, Tokio Nakada 2 1 Department of Physics, Colorado State University, Fort
Performance and Loss Analyses of High-Efficiency CBD-ZnS/Cu(In 1-x Ga x )Se 2 Thin-Film Solar Cells Alexei Pudov 1, James Sites 1, Tokio Nakada 2 1 Department of Physics, Colorado State University, Fort
COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT COMMERCIAL SOLAR
 WU YUANYUAN COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT COMMERCIAL SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULES Master of science thesis Examiner: Professor Seppo Valkealahti the examiner and topic of the thesis were approved by the Council
WU YUANYUAN COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT COMMERCIAL SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULES Master of science thesis Examiner: Professor Seppo Valkealahti the examiner and topic of the thesis were approved by the Council
PHYS 3050 Electronics I
 PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
Measurements and simulations of the performance of the PV systems at the University of Gävle
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Department of Building, Energy and Environmental Engineering Measurements and simulations of the performance of the PV systems at the University of Gävle
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Department of Building, Energy and Environmental Engineering Measurements and simulations of the performance of the PV systems at the University of Gävle
Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
 PV systems are comprised of building blocks of cells, modules and arrays to form a DC power generating unit with specified electrical output. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p. 115-118 Reference: Photovoltaic
PV systems are comprised of building blocks of cells, modules and arrays to form a DC power generating unit with specified electrical output. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p. 115-118 Reference: Photovoltaic
Multiband Solar Concentrator using Transmissive Dichroic Beamsplitting
 Multiband Solar Concentrator using Transmissive Dichroic Beamsplitting Jason H. Karp and Joseph E. Ford Photonics Systems Integration Lab University of California, San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering
Multiband Solar Concentrator using Transmissive Dichroic Beamsplitting Jason H. Karp and Joseph E. Ford Photonics Systems Integration Lab University of California, San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering
Optimization of Different Solar Cell Arrangements Using Matlab/Simulink for Small Scale Systems
 Optimization of Different Solar Cell Arrangements Using Matlab/Simulink for Small Scale Systems Sunil Kumar Saini, Shelly Vadhera School of Renewable Energy & Efficiency, NIT-Kurukshetra, Haryana, India
Optimization of Different Solar Cell Arrangements Using Matlab/Simulink for Small Scale Systems Sunil Kumar Saini, Shelly Vadhera School of Renewable Energy & Efficiency, NIT-Kurukshetra, Haryana, India
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits. Electrical Enginnering Departement. By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben. Instructor: Eng.
 Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Chapter 4. Impact of Dust on Solar PV Module: Experimental Analysis
 Chapter 4 Impact of Dust on Solar PV Module: Experimental Analysis 53 CHAPTER 4 IMPACT OF DUST ON SOLAR PV MODULE: EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS 4.1 INTRODUCTION: On a bright, sunny day the sun shines approximately
Chapter 4 Impact of Dust on Solar PV Module: Experimental Analysis 53 CHAPTER 4 IMPACT OF DUST ON SOLAR PV MODULE: EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS 4.1 INTRODUCTION: On a bright, sunny day the sun shines approximately
Understanding Solar Energy Teacher Page
 Understanding Solar Energy Teacher Page Photovoltaic Power Output & I-V Curves Student Objective The student: will be able to determine the voltage, current and power of a given PV module given the efficiency,
Understanding Solar Energy Teacher Page Photovoltaic Power Output & I-V Curves Student Objective The student: will be able to determine the voltage, current and power of a given PV module given the efficiency,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa
 Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa SEMICONDUCTORS What is a Semiconductor? What is a Semiconductor? Microprocessors LED Transistors Capacitors Range of Conduciveness The semiconductors
Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa SEMICONDUCTORS What is a Semiconductor? What is a Semiconductor? Microprocessors LED Transistors Capacitors Range of Conduciveness The semiconductors
ANALYSIS OF MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF PV MODULE USING MATLAB/SIMULINK ENVIRONMENT: REVIEW
 ANALYSIS OF MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF PV MODULE USING MATLAB/SIMULINK ENVIRONMENT: REVIEW 1 NISHA PATEL, 2 Hardik Patel, 3 Ketan Bariya 1 M.E. Student, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Assistant Professor 1 Electrical
ANALYSIS OF MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF PV MODULE USING MATLAB/SIMULINK ENVIRONMENT: REVIEW 1 NISHA PATEL, 2 Hardik Patel, 3 Ketan Bariya 1 M.E. Student, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Assistant Professor 1 Electrical
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 1 The Diode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following
Exercise 1 The Diode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following
BASIC ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 BASIC ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Objective Questions UNIT 1: DIODES AND CIRCUITS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 The process by which impurities are added to a pure semiconductor is A. Diffusing B. Drift C. Doping
BASIC ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Objective Questions UNIT 1: DIODES AND CIRCUITS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 The process by which impurities are added to a pure semiconductor is A. Diffusing B. Drift C. Doping
Downloaded from
 Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
IMPLEMENTATION OF MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING ALGORITHM USING RASPBERRY PI
 IMPLEMENTATION OF MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING ALGORITHM USING RASPBERRY PI B. Evangeline kiruba K.Gerard Joe Nigel PG Scholar Department of Electrical Technology Karunya University, Coimbatore, India
IMPLEMENTATION OF MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING ALGORITHM USING RASPBERRY PI B. Evangeline kiruba K.Gerard Joe Nigel PG Scholar Department of Electrical Technology Karunya University, Coimbatore, India
Unit 2 Semiconductor Devices. Lecture_2.5 Opto-Electronic Devices
 Unit 2 Semiconductor Devices Lecture_2.5 Opto-Electronic Devices Opto-electronics Opto-electronics is the study and application of electronic devices that interact with light. Electronics (electrons) Optics
Unit 2 Semiconductor Devices Lecture_2.5 Opto-Electronic Devices Opto-electronics Opto-electronics is the study and application of electronic devices that interact with light. Electronics (electrons) Optics
HipoCIGS: enamelled steel as substrate for thin film solar cells
 HipoCIGS: enamelled steel as substrate for thin film solar cells Lecturer D. Jacobs*, Author S. Efimenko, Co-author C. Schlegel *:PRINCE Belgium bvba, Pathoekeweg 116, 8000 Brugge, Belgium, djacobs@princecorp.com
HipoCIGS: enamelled steel as substrate for thin film solar cells Lecturer D. Jacobs*, Author S. Efimenko, Co-author C. Schlegel *:PRINCE Belgium bvba, Pathoekeweg 116, 8000 Brugge, Belgium, djacobs@princecorp.com
13. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
 Synopsis: 13. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES 1. Solids are classified into two categories. a) Crystalline solids b) Amorphous solids 2. Crystalline solids : Crystalline solids have orderly arrangement of atoms
Synopsis: 13. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES 1. Solids are classified into two categories. a) Crystalline solids b) Amorphous solids 2. Crystalline solids : Crystalline solids have orderly arrangement of atoms
Wallace Hall Academy. CfE Higher Physics. Unit 3 - Electricity Notes Name
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 3 - Electricity Notes Name 1 Electrons and Energy Alternating current and direct current Alternating current electrons flow back and forth several times per
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 3 - Electricity Notes Name 1 Electrons and Energy Alternating current and direct current Alternating current electrons flow back and forth several times per
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram
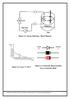 Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
STAND ALONE SOLAR TRACKING SYSTEM
 STAND ALONE SOLAR TRACKING SYSTEM Rajendra Ghivari 1, Prof. P.P Revankar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, AITM, Savagaon Road, Belgaum, Karnataka, (India)
STAND ALONE SOLAR TRACKING SYSTEM Rajendra Ghivari 1, Prof. P.P Revankar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, AITM, Savagaon Road, Belgaum, Karnataka, (India)
ECE 340 Lecture 29 : LEDs and Lasers Class Outline:
 ECE 340 Lecture 29 : LEDs and Lasers Class Outline: Light Emitting Diodes Lasers Semiconductor Lasers Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is an LED and how does it work? How does a
ECE 340 Lecture 29 : LEDs and Lasers Class Outline: Light Emitting Diodes Lasers Semiconductor Lasers Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is an LED and how does it work? How does a
Key Questions. What is an LED and how does it work? How does a laser work? How does a semiconductor laser work? ECE 340 Lecture 29 : LEDs and Lasers
 Things you should know when you leave Key Questions ECE 340 Lecture 29 : LEDs and Class Outline: What is an LED and how does it How does a laser How does a semiconductor laser How do light emitting diodes
Things you should know when you leave Key Questions ECE 340 Lecture 29 : LEDs and Class Outline: What is an LED and how does it How does a laser How does a semiconductor laser How do light emitting diodes
Grid Connected photovoltaic system based on Chain cell converter Using Simulink
 Grid Connected photovoltaic system based on Chain cell converter Using Simulink Problem statement To prove Chain cell converter performance superior when compared with the traditional Pulse width modulation
Grid Connected photovoltaic system based on Chain cell converter Using Simulink Problem statement To prove Chain cell converter performance superior when compared with the traditional Pulse width modulation
Class XII - Physics Semiconductor Electronics. Chapter-wise Problems
 lass X - Physics Semiconductor Electronics Materials, Device and Simple ircuit hapter-wise Problems Multiple hoice Question :- 14.1 The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature
lass X - Physics Semiconductor Electronics Materials, Device and Simple ircuit hapter-wise Problems Multiple hoice Question :- 14.1 The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature
PN Junction Diode Table of Contents. What Are Diodes Made Out Of?
 PN Junction iode Table of Contents What are diodes made out of?slide 3 N-type materialslide 4 P-type materialslide 5 The pn junctionslides 6-7 The biased pn junctionslides 8-9 Properties of diodesslides
PN Junction iode Table of Contents What are diodes made out of?slide 3 N-type materialslide 4 P-type materialslide 5 The pn junctionslides 6-7 The biased pn junctionslides 8-9 Properties of diodesslides
Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS
 Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS 3. Optical sources and Detectors 3.1 Introduction: The success of light wave communications and optical fiber sensors is due to the result of two technological breakthroughs.
Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS 3. Optical sources and Detectors 3.1 Introduction: The success of light wave communications and optical fiber sensors is due to the result of two technological breakthroughs.
SILICON NANOWIRE HYBRID PHOTOVOLTAICS
 SILICON NANOWIRE HYBRID PHOTOVOLTAICS Erik C. Garnett, Craig Peters, Mark Brongersma, Yi Cui and Mike McGehee Stanford Univeristy, Department of Materials Science, Stanford, CA, USA ABSTRACT Silicon nanowire
SILICON NANOWIRE HYBRID PHOTOVOLTAICS Erik C. Garnett, Craig Peters, Mark Brongersma, Yi Cui and Mike McGehee Stanford Univeristy, Department of Materials Science, Stanford, CA, USA ABSTRACT Silicon nanowire
EDC Lecture Notes UNIT-1
 P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
A Circuit Model for Polymer Solar Cells. Shamica Green. Faculty advisor: Dr. Selman Hershfield. Abstract
 A Circuit Model for Polymer Solar Cells Shamica Green Faculty advisor: Dr. Selman Hershfield Abstract In this simulation a polymer solar cell is modeled by resistors and diodes in a circuit. Voltage outputs
A Circuit Model for Polymer Solar Cells Shamica Green Faculty advisor: Dr. Selman Hershfield Abstract In this simulation a polymer solar cell is modeled by resistors and diodes in a circuit. Voltage outputs
Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits
 Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits Circuits which are used to clip off portions of signal voltages above or below certain levels are called limiters or clippers. Types of Clippers Positive Clipper Negative
Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits Circuits which are used to clip off portions of signal voltages above or below certain levels are called limiters or clippers. Types of Clippers Positive Clipper Negative
Solar Cells, Modules, Arrays, and Characterization
 ... energizing Ohio for the 21st Century Solar Cells, Modules, Arrays, and Characterization April 17, 2014 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles and Varieties
... energizing Ohio for the 21st Century Solar Cells, Modules, Arrays, and Characterization April 17, 2014 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles and Varieties
PV Module Fundamentals
 ESS 032 Intermediate Photovoltaic Systems PV Module Fundamentals ESS 034 Advanced Photovoltaic Systems Lesson Plan Review midterm exam Solar Energy Fundamentals any questions? NABCEP Learning Objectives:
ESS 032 Intermediate Photovoltaic Systems PV Module Fundamentals ESS 034 Advanced Photovoltaic Systems Lesson Plan Review midterm exam Solar Energy Fundamentals any questions? NABCEP Learning Objectives:
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode
 CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
Teacher Page. Understanding Solar Energy. Photovoltaic Power Output & I-V Curves. Student Objective
 Understanding Solar Energy Teacher Page Photovoltaic Power Output & I-V Curves Student Objective The student: current and power of a given PV module will be able to determine the size of the array necessary
Understanding Solar Energy Teacher Page Photovoltaic Power Output & I-V Curves Student Objective The student: current and power of a given PV module will be able to determine the size of the array necessary
IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY OF SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER SYSTEM
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Open Access Master's Theses 2013 IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY OF SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER SYSTEM Henry A. Aribisala University of Rhode Island, aribisala@yahoo.com
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Open Access Master's Theses 2013 IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY OF SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER SYSTEM Henry A. Aribisala University of Rhode Island, aribisala@yahoo.com
PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS(ECE3540) APPLICATIONS OF PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS PART I
 PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS(ECE3540) APPLICATIONS OF PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS PART I Tennessee Technological University Monday, October 28, 2013 1 Introduction In the following slides, we will discuss the summary
PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS(ECE3540) APPLICATIONS OF PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS PART I Tennessee Technological University Monday, October 28, 2013 1 Introduction In the following slides, we will discuss the summary
Florida State University Libraries
 Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2006 Analysis, Modeling and Simulation of Optimal Power Tracking of Multiple- Modules of Paralleled
Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2006 Analysis, Modeling and Simulation of Optimal Power Tracking of Multiple- Modules of Paralleled
Optodevice Data Book ODE I. Rev.9 Mar Opnext Japan, Inc.
 Optodevice Data Book ODE-408-001I Rev.9 Mar. 2003 Opnext Japan, Inc. Section 1 Operating Principles 1.1 Operating Principles of Laser Diodes (LDs) and Infrared Emitting Diodes (IREDs) 1.1.1 Emitting Principles
Optodevice Data Book ODE-408-001I Rev.9 Mar. 2003 Opnext Japan, Inc. Section 1 Operating Principles 1.1 Operating Principles of Laser Diodes (LDs) and Infrared Emitting Diodes (IREDs) 1.1.1 Emitting Principles
420 Intro to VLSI Design
 Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering 420 Intro to VLSI Design Lecture 0: Course Introduction and Overview Valencia M. Joyner Spring 2005 Getting Started Syllabus About the Instructor Labs, Problem
Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering 420 Intro to VLSI Design Lecture 0: Course Introduction and Overview Valencia M. Joyner Spring 2005 Getting Started Syllabus About the Instructor Labs, Problem
semiconductor p-n junction Potential difference across the depletion region is called the built-in potential barrier, or built-in voltage:
 Chapter four The Equilibrium pn Junction The Electric field will create a force that will stop the diffusion of carriers reaches thermal equilibrium condition Potential difference across the depletion
Chapter four The Equilibrium pn Junction The Electric field will create a force that will stop the diffusion of carriers reaches thermal equilibrium condition Potential difference across the depletion
Printable Organic Solar Cells Challenges and Opportunities in Technology Transfer from Lab to Market
 Power Plastic R Printable Organic Solar Cells Challenges and Opportunities in Technology Transfer from Lab to Market Alan J. Heeger Chief Scientist and Co-Founder 116 John Street, Lowell, MA 01852 Plastic
Power Plastic R Printable Organic Solar Cells Challenges and Opportunities in Technology Transfer from Lab to Market Alan J. Heeger Chief Scientist and Co-Founder 116 John Street, Lowell, MA 01852 Plastic
2nd Asian Physics Olympiad
 2nd Asian Physics Olympiad TAIPEI, TAIWAN Experimental Competition Thursday, April 26, 21 Time Available : 5 hours Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the front side of the answer
2nd Asian Physics Olympiad TAIPEI, TAIWAN Experimental Competition Thursday, April 26, 21 Time Available : 5 hours Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the front side of the answer
Sharjah Indian School, Sharjah ELECTRONIC DEVICES - Class XII (Boys Wing) Page 01
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES - Class XII (Boys Wing) Page 01 Electronics is the fast developing branch of Physics. Before the discovery of transistors in 1948, vacuum tubes (thermionic valves) were used as the building
ELECTRONIC DEVICES - Class XII (Boys Wing) Page 01 Electronics is the fast developing branch of Physics. Before the discovery of transistors in 1948, vacuum tubes (thermionic valves) were used as the building
Investigation of Photovoltaic Properties of In:ZnO/SiO 2 /p- Si Thin Film Devices
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Investigation of Photovoltaic Properties of In:ZnO/SiO 2 /p- Si Thin Film Devices Kay Thi Soe 1, Moht Moht Than 2 and Win Win Thar 3 Abstract This study
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Investigation of Photovoltaic Properties of In:ZnO/SiO 2 /p- Si Thin Film Devices Kay Thi Soe 1, Moht Moht Than 2 and Win Win Thar 3 Abstract This study
The Solar Resource. Energy Systems Research Laboratory, FIU
 The Solar Resource Before we can talk about solar power, we need to talk about the sun Need to know how much sunlight is available Can predict where the sun is at any time Insolation :solar radiation Want
The Solar Resource Before we can talk about solar power, we need to talk about the sun Need to know how much sunlight is available Can predict where the sun is at any time Insolation :solar radiation Want
Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits
 Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
I D = I so e I. where: = constant T = junction temperature [K] I so = inverse saturating current I = photovoltaic current
![I D = I so e I. where: = constant T = junction temperature [K] I so = inverse saturating current I = photovoltaic current I D = I so e I. where: = constant T = junction temperature [K] I so = inverse saturating current I = photovoltaic current](/thumbs/83/87981810.jpg) H7. Photovoltaics: Solar Power I. INTRODUCTION The sun is practically an endless source of energy. Most of the energy used in the history of mankind originated from the sun (coal, petroleum, etc.). The
H7. Photovoltaics: Solar Power I. INTRODUCTION The sun is practically an endless source of energy. Most of the energy used in the history of mankind originated from the sun (coal, petroleum, etc.). The
15 - SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Page 1
 15.1 Introduction MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Page 1 The word electronics is coined from the words electron mechanics. The subject of electronics deals with the study of devices in which specific
15.1 Introduction MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Page 1 The word electronics is coined from the words electron mechanics. The subject of electronics deals with the study of devices in which specific
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES
 KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
LED lecture. Wei Chih Wang University of Washington
 LED lecture Wei Chih Wang University of Washington Linear and Nonlinear electronics current voltage Vaccum tube (i.e. type 2A3) voltage Thermistor (large negative temperature coefficient of resistivity)
LED lecture Wei Chih Wang University of Washington Linear and Nonlinear electronics current voltage Vaccum tube (i.e. type 2A3) voltage Thermistor (large negative temperature coefficient of resistivity)
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis. Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng
 EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng 1.1 Prof. Zhuo Feng Office: EERC 730 Phone: 487-3116 Email: zhuofeng@mtu.edu Class Website http://www.ece.mtu.edu/~zhuofeng/ee4800fall2010.html
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng 1.1 Prof. Zhuo Feng Office: EERC 730 Phone: 487-3116 Email: zhuofeng@mtu.edu Class Website http://www.ece.mtu.edu/~zhuofeng/ee4800fall2010.html
STUDY OF A PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM WITH MPPT USING MATLAB TM
 STUDY OF A PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM WITH MPPT USING MATLAB TM Dumitru POP, Radu TÎRNOVAN, Liviu NEAMŢ, Dorin SABOU Technical University of Cluj Napoca dan.pop@enm.utcluj.ro Key words: photovoltaic system, solar
STUDY OF A PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM WITH MPPT USING MATLAB TM Dumitru POP, Radu TÎRNOVAN, Liviu NEAMŢ, Dorin SABOU Technical University of Cluj Napoca dan.pop@enm.utcluj.ro Key words: photovoltaic system, solar
EE Solar Cell Opreation. Y. Baghzouz Professor of Electrical Engineering
 EE 495-695 4.2 Solar Cell Opreation Y. Baghzouz Professor of Electrical Engineering Characteristic Resistance The characteristic resistance of a solar cell is the output resistance of the solar cell at
EE 495-695 4.2 Solar Cell Opreation Y. Baghzouz Professor of Electrical Engineering Characteristic Resistance The characteristic resistance of a solar cell is the output resistance of the solar cell at
Traditional PWM vs. Morningstar s TrakStar MPPT Technology
 Traditional PWM vs. Morningstar s TrakStar MPPT Technology Introduction: Morningstar MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) controllers utilize Morningstar s own advanced TrakStar Maximum Power Point Tracking
Traditional PWM vs. Morningstar s TrakStar MPPT Technology Introduction: Morningstar MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) controllers utilize Morningstar s own advanced TrakStar Maximum Power Point Tracking
Discuss the basic structure of atoms Discuss properties of insulators, conductors, and semiconductors
 Discuss the basic structure of atoms Discuss properties of insulators, conductors, and semiconductors Discuss covalent bonding Describe the properties of both p and n type materials Discuss both forward
Discuss the basic structure of atoms Discuss properties of insulators, conductors, and semiconductors Discuss covalent bonding Describe the properties of both p and n type materials Discuss both forward
Lecture 18: Photodetectors
 Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Sliding Mode Control based Maximum Power Point Tracking of PV System
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 4 Ver. II (July Aug. 2015), PP 58-63 www.iosrjournals.org Sliding Mode Control based
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 4 Ver. II (July Aug. 2015), PP 58-63 www.iosrjournals.org Sliding Mode Control based
The Effect of Photon Flux Density and Module Temperature on Power Output of Photovoltaic Array
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 34 (2013 ) 430 438 10th Eco-Energy and Materials Science and Engineering (EMSES2012) The Effect of Photon Flux Density and Module Temperature on
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 34 (2013 ) 430 438 10th Eco-Energy and Materials Science and Engineering (EMSES2012) The Effect of Photon Flux Density and Module Temperature on
Lecture 2 p-n junction Diode characteristics. By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood
 Electronic I Lecture 2 p-n junction Diode characteristics By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood THE p-n JUNCTION DIODE The pn junction diode is formed by fabrication of a p-type semiconductor region in intimate
Electronic I Lecture 2 p-n junction Diode characteristics By Asst. Prof Dr. Jassim K. Hmood THE p-n JUNCTION DIODE The pn junction diode is formed by fabrication of a p-type semiconductor region in intimate
Comparative Study of P&O and InC MPPT Algorithms
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-12, pp-402-408 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Comparative Study of P&O and InC MPPT Algorithms
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-12, pp-402-408 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Comparative Study of P&O and InC MPPT Algorithms
