A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION IN SCINTILLATORS
|
|
|
- Magdalene Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, Oct 2005, PO (2005) A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION IN SCINTILLATORS M. Riva, B. Esposito, D. Marocco Associazione Euratom-ENEA sulla Fusione, C.R. Frascati, CP 65, Frascati, Italy. ABSTRACT During the last years, extensive experimental work has been carried out by ENEA in the framework of Nuclear Fusion activities, in particular in Frascati Tokamak Upgrade (FTU) and Joint European Torus (JET) tokamaks, to demonstrate the possibility of digitally acquiring the -ray and neutron pulses generated in scintillators, separating neutrons from -rays and calculating the pulse height spectra (PHS). This has been done using a commercially available high speed (200 MSamples/s, 12- bit) digital acquisition board, equipped with a PC workstation hosting the board and suitable software for acquiring and elaborating data. Although the results have been promising, showing the capability of the post-processing software of correctly separating -rays from neutrons and produce the PHS, several limitations have appeared (e.g.: short time acquisition, excessive amount of stored data). Therefore, we have decided to start the design of a new front-end digital acquisition system (200 MSamples/s, 14-bit, FPGA-based), capable of overcoming these limitations and also able to perform on-line signal pre-elaboration and to produce real-time outputs (i.e.: count rates) for feedback purposes. In the article, we will describe the results obtained using the previous system, showing its limits and drawbacks, and the new system, describing its main characteristics and the first tests we have performed. PROBLEM DESCRIPTION In neutron measurements for nuclear fusion experiments, organic scintillators (e.g.: NE213) coupled to photomultipliers are normally used to detect -rays and neutrons. The slight difference in the pulses generated from the scintillator is used to discriminate between -rays ( and neutrons (n), see Fig. 1: this is called Pulse Shape Discrimination (PSD). A typical n/ PSD method is based on charge comparison: integrating the pulse for two different intervals t F and t S, we obtain respectively the integrals Q S and Q F. Since neutron pulses have larger slow components, the ratio Q S / Q F identifies, regardless of the pulse amplitude, a neutron or a -ray event. In JET, for example, 19 analogue PSD modules are used and they normally operate up to 200 KHz output count rate [1]. The main drawback of such modules is that they do not allow any kind of data reprocessing, as they do not have any storage capability and therefore it is necessary to take particular care in the hardware set-up of the systems. Figure 1: Difference between neutron and -ray pulses.
2 10th ICALEPCS 2005; M. Riva, B. Esposito, D. Marocco et al. : A Novel FPGA-based Digital Approach to Ne... 2 of 6 In this article we will show how we have replaced an analogue PSD module with a Digital Pulse Shape Discrimination system (DSPD), which in a first phase was simply a commercial fast analogue to digital (A/D) transient recorder coupled with a personal computer equipped with a suitable software to perform the n/ discrimination. Due to various limitations of this system, we decided to start the design and development of a new DSPD system, based on a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) and two 100 MSamples/s A/D converter, able to overcome the difficulties and providing data preelaboration and real-time capabilities. The article will also describe this new system and its first results. PAST EXPERIENCE The first DSPD system we tested on tokamak experiments [1,2] is based on a commercial 200 MSamples/s 12-bit A/D transient recorder PCI board (Strategic Test model UF 3025) which digitizes the scintillator pulses. The board can operate in several modalities, but we used mainly two: the first is to acquire continuously, after a trigger signal, until the 512 MBytes memory board is filled. The second is to acquire a pre-programmed time window each time the signal is over a given threshold. The first modality is optimal in acquisitions where we do not want to lose any data. As soon as the trigger arrives, the acquisition starts and continues without any interruption until the memory is full. After that, the elaboration software, written in LabVIEW, performs the n/ separation and calculates the PHS by integration of the pulses. The main drawback of this method is the insufficient physical memory of the board: it takes about 1.3 s to fill the 512 Mbytes RAM, regardless of the pulse frequency. This is largely inadequate to cover the s needed in tokamak experiments like JET. The second modality is more flexible, due to the fact that we acquire only the triggered pulse signals, taking for each pulse a fixed time window [3,4]. In this way, by choosing the correct number of pre-triggers and post-triggers we can store all pulses for longer time intervals using the 512 MBytes RAM. However, there are limitations also using this technique, the main one being on the hardware side. In order to operate fixed time windows a buffer-mode feature of the board must be used. Once a pre-programmed memory size is filled, data and timing information (a time stamp for each pulse) are sent to the computer memory (via PCI). Unfortunately, during the data transfer no acquisition takes place and, therefore, a temporal gap in the data stream is experienced: in laboratory tests, we measured about 4 ms of lost data each buffer sent (see Figure 2). Figure 2: Showing the temporal gap due to the PCI transfer in three cases at different pulse rates ( KHz). This can be acceptable or not, depending on the application. In this case, the total count rate can be obviously given at time resolution > 4 ms. In addition, having a fixed window, also complicates the software analysis in presence of pile-ups (i.e.: multiple or overlapping events in a given window): for example, when a rising pulse in the tail of the window is cut due the fixed time window duration this pulse as well as the subsequent one would be probably rejected.
3 10th ICALEPCS 2005; M. Riva, B. Esposito, D. Marocco et al. : A Novel FPGA-based Digital Approach to Ne... 3 of 6 THE NEW SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE Our experience with the commercial 12-bit board drove us towards a new system capable of overcoming the limitations discussed above. We decided to find a general solution to the pile-up problem with fixed time windows. The simplest solution we found was to relax the constraint on the length, allowing it to dynamically increase/decrease depending on the pulse shape. This allowed us to reduce at minimum the acquired data per pulse. On the other hand, the acquisition file structure is a little bit more complex than in the previous system, as the actual pulse length plus the time stamp must be stored. With this solution we store only the meaningful data, performing a strong data compression. For example, in case of a pulse rate of 1 MHz, acquiring 32 samples per pulse, we obtain about an 84% data compression. In this way, data can be stored continuously to the PC, because the reduced bandwidth is compatible with the PCI bus throughput. This solved the second problem we had: the temporal gap between data as shown in Figure 2. The general layout of the new system is given in Figure 3. Analogue input 14 bit A/D 14 bit A/D Acquisition block Clock Dynamic Window Data Acquisition Data Packing High speed Digital acquisition PCI board On-line Elaboration module Timing FPGA PC Ethernet and/or ATM External gate 14 bit D/A Analogue outputs Figure 3. General system architecture. The analogue signal coming from the photomultiplier is acquired by the 14-bit ADC block. This is a 200 MSamples/s acquisition block and it is formed by two 100 MSamples/s, 14-bit Analog Devices ADC, coupled in interleaved mode. Preliminary results on the prototype have shown for the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and Effective Numbers Of Bits (ENOB) values of about 75 db and 12.2 bits respectively. This is a good result, because the real values will be certainly better, due to the fact that we did not use a pure sine wave generator with low Noise/Distortion for this measurement. The 14-bit data go to the Dynamic Window Data Acquisition (DWDA). This block acquires a pre-programmed number of samples, unless another pulse arrives during the time window. In this case the length is automatically increased to include the new pulse. This feature can be disabled, returning to the standard fixed length window. The window data are sent in parallel to two blocks: the On-line Elaboration module performs calculations on the data, as approximate integrals, count rate, etc.; the Data Packing completes the data packet adding the time stamp information to the data. Finally, the packed data go to the digital acquisition board on the PC which collects and stores data on memory. On the other side, data go to the D/A block from the online side and analogue signal can be used for real-time purposes.
4 10th ICALEPCS 2005; M. Riva, B. Esposito, D. Marocco et al. : A Novel FPGA-based Digital Approach to Ne... 4 of 6 For the prototype, we used an evaluation board mounting an Altera FPGA 1S25, equipped with two D/A 14-bit channel. The digital acquisition board is a National Instrument high speed PCI I/O 6534, allowing a fast continuous bandwidth to the PC memory. The software running on the PC was written in C++, using National Instrument libraries to access the PCI digital I/O board. It manages the initial board parameter set-up (e.g.: buffer length) and acquires the blocks arriving from the board as soon as they are ready. The board operates in First In-First Out (FIFO) mode. When half buffer is full it is sent to the PC via the PCI bus, while the board continues data acquisition in the second half buffer. In this operational mode no data are lost, up to a total throughput of 80 MBytes/s. After the acquisition is finished, data are written on disk in the correct format, containing, for each pulse, the time stamp data, the pulse length and all the pulse samples. A parallel software module is under study to perform on-line data elaboration, in order to calculate relevant quantities to be sent digitally to a real time control system. FIRST RESULTS A LabVIEW program has been written for post-acquisition data elaboration and analysis (Figure 4). Starting from the stream of acquired and formatted data, the software performs the analysis as follows: each single pulse above a preset threshold is selected and two outputs are produced according to whether single or pile-up pulses are identified in any time window. Pile-up events are defined as multiple or overlapping pulses above threshold in any given time window. Single events are further processed for n/ separation and PHS analysis. Figure 4. LabVIEW program. The total count rate is produced (sum of pile-up plus single pulses), as well as, separately, single, neutron and -ray count rates. The n/ separation is performed, as described above, using Q S = 25 ns and Q F = 120 ns, starting from the peak of each pulse: a graphical output is produced (Figure 5) and the separation line can be adjusted in order to reach the best separation according to the experimental conditions. The PHS analysis (Figure 6) is performed by digital integration of the single pulses over their full time window. It has been found that the pulse baseline determination is crucial for the achievement of the best energy resolution in the PHS: the software is capable of determining the baseline for each single pulse.
5 10th ICALEPCS 2005; M. Riva, B. Esposito, D. Marocco et al. : A Novel FPGA-based Digital Approach to Ne... 5 of 6 Figure 5: Graphical output of n/ separation algorithm. Total count rates up to 1 MHz have been handled in laboratory tests with a periodic pulse generator, using time windows of 32 samples. The system has also been preliminarily tested in experimental conditions with -ray calibration sources as well as 2.5 and 14 MeV neutron sources showing good overall performance. Using a minimum of 96 samples per time window, count rates over 240 khz have been handled without problems in 14 MeV operation. Figures 5 and 6 refer to 2.5 MeV operation total neutron counts channel Figure 6: Result of PHS analysis.
6 10th ICALEPCS 2005; M. Riva, B. Esposito, D. Marocco et al. : A Novel FPGA-based Digital Approach to Ne... 6 of 6 CONCLUSIONS AND PLANNED WORK In this paper, we presented a new FPGA-based approach to the digital acquisition of neutron and ray pulses coming from scintillators (the same approach can be obviously used in any other application with similar pulse characteristics). We called it Dynamic Windows Data Acquisition (DWDA). It allows acquisition of any pulse type without pulse truncation due to fixed length window. The first tests showed promising results. We are currently working on a new version of the system in which we will remove the high speed PCI fast digital acquisition board and will introduce several optimisations, in order to simplify the system and have a cost reduction. Another improvement under study is a series of on-line algorithms to make various signals available for real time control purposes. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors would like to thank the staff of PTB (Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt in Braunschweig (Germany)) accelerator, where the first experimental tests of the new system have been carried out, together with H. Klein, H. Schumacher, A. Zimbal (PTB) and L. Bertalot, A. Pensa, S. Lupini (ENEA) for their help in the experiment. REFERENCES [1] B. Esposito et al., Nucl. Instrum. Phys. Res. A 518 (2004) 626. [2] B. Esposito et al., Rev. Sci. Instr. 75 (2004) [3] L. Bertalot et al., in Proceedings of the 9th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors, Siena (2004), Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) in press (2006). [4] S. Vitulli et al., to be submittted to Nucl. Instrum. Phys. Res. A
FAST DIGITIZING TECHNIQUES APPLIED TO SCINTILLATION DETECTORS
 9 th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors 23-26 May 2004 Siena, Italy FAST DIGITIZING TECHNIQUES APPLIED TO SCINTILLATION DETECTORS L. Bertalot 1, B. Esposito 1, Y. Kaschuck 2,
9 th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors 23-26 May 2004 Siena, Italy FAST DIGITIZING TECHNIQUES APPLIED TO SCINTILLATION DETECTORS L. Bertalot 1, B. Esposito 1, Y. Kaschuck 2,
Neutron Measurements on JET using an NE213 Scintillator with Digital Pulse Shape Discrimination
 EFDA JET CP(04)01/12 B. Esposito, Y. Kaschuck, L. Bertalot, A. Zimbal, M. Reginatto, D. Marocco, M. Riva, D. Skopintsev, J.M. Adams, A. Murari, H. Schuhmacher and JET-EFDA Contributors Neutron Measurements
EFDA JET CP(04)01/12 B. Esposito, Y. Kaschuck, L. Bertalot, A. Zimbal, M. Reginatto, D. Marocco, M. Riva, D. Skopintsev, J.M. Adams, A. Murari, H. Schuhmacher and JET-EFDA Contributors Neutron Measurements
Digital coincidence acquisition applied to portable β liquid scintillation counting device
 Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 030401 Digital coincidence acquisition applied to portable β liquid scintillation counting device REN Zhongguo 1,2 HU Bitao 1 ZHAO Zhiping 2 LI Dongcang 1,* 1 School
Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 030401 Digital coincidence acquisition applied to portable β liquid scintillation counting device REN Zhongguo 1,2 HU Bitao 1 ZHAO Zhiping 2 LI Dongcang 1,* 1 School
Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1]
![Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1] Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1]](/thumbs/75/72878980.jpg) Giuliano Mini Viareggio April 22, 2010 Introduction The aim of this paper is to compare the energy resolution of two gamma ray spectroscopy setups based on two different acquisition chains; the first chain
Giuliano Mini Viareggio April 22, 2010 Introduction The aim of this paper is to compare the energy resolution of two gamma ray spectroscopy setups based on two different acquisition chains; the first chain
Real Time Pulse Pile-up Recovery in a High Throughput Digital Pulse Processor
 Real Time Pulse Pile-up Recovery in a High Throughput Digital Pulse Processor Paul A. B. Scoullar a, Chris C. McLean a and Rob J. Evans b a Southern Innovation, Melbourne, Australia b Department of Electrical
Real Time Pulse Pile-up Recovery in a High Throughput Digital Pulse Processor Paul A. B. Scoullar a, Chris C. McLean a and Rob J. Evans b a Southern Innovation, Melbourne, Australia b Department of Electrical
A digital method for separation and reconstruction of pile-up events in germanium detectors. Abstract
 A digital method for separation and reconstruction of pile-up events in germanium detectors M. Nakhostin a), Zs. Podolyak, P. H. Regan, P. M. Walker Department of Physics, University of Surrey, Guildford
A digital method for separation and reconstruction of pile-up events in germanium detectors M. Nakhostin a), Zs. Podolyak, P. H. Regan, P. M. Walker Department of Physics, University of Surrey, Guildford
Digital trigger system for the RED-100 detector based on the unit in VME standard
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Digital trigger system for the RED-100 detector based on the unit in VME standard To cite this article: D Yu Akimov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Digital trigger system for the RED-100 detector based on the unit in VME standard To cite this article: D Yu Akimov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Overview 256 channel Silicon Photomultiplier large area using matrix readout system The SensL Matrix detector () is the largest area, highest channel
 技股份有限公司 wwwrteo 公司 wwwrteo.com Page 1 Overview 256 channel Silicon Photomultiplier large area using matrix readout system The SensL Matrix detector () is the largest area, highest channel count, Silicon
技股份有限公司 wwwrteo 公司 wwwrteo.com Page 1 Overview 256 channel Silicon Photomultiplier large area using matrix readout system The SensL Matrix detector () is the largest area, highest channel count, Silicon
PACS codes: Qx, Nc, Kv, v Keywords: Digital data acquisition, segmented HPGe detectors, clock and trigger distribution
 Clock and Trigger Synchronization between Several Chassis of Digital Data Acquisition Modules W. Hennig, H. Tan, M. Walby, P. Grudberg, A. Fallu-Labruyere, W.K. Warburton, XIA LLC, 31057 Genstar Road,
Clock and Trigger Synchronization between Several Chassis of Digital Data Acquisition Modules W. Hennig, H. Tan, M. Walby, P. Grudberg, A. Fallu-Labruyere, W.K. Warburton, XIA LLC, 31057 Genstar Road,
Enhanced neutron diagnostics data acquisition system based on a time digitizer and transient recorder hybrid module
 Fusion Engineering and Design 81 (2006) 1873 1877 Enhanced neutron diagnostics data acquisition system based on a time digitizer and transient recorder hybrid module R.C. Pereira a,, A. Combo a, N. Cruz
Fusion Engineering and Design 81 (2006) 1873 1877 Enhanced neutron diagnostics data acquisition system based on a time digitizer and transient recorder hybrid module R.C. Pereira a,, A. Combo a, N. Cruz
INDEX. Firmware for DPP (Digital Pulse Processing) DPP-PSD Digital Pulse Processing for Pulse Shape Discrimination
 Firmware for DPP (Digital Pulse Processing) Thanks to the powerful FPGAs available nowadays, it is possible to implement Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) algorithms directly on the acquisition boards and
Firmware for DPP (Digital Pulse Processing) Thanks to the powerful FPGAs available nowadays, it is possible to implement Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) algorithms directly on the acquisition boards and
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer
 Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
A user-friendly fully digital TDPAC-spectrometer
 Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-010-0201-8 A user-friendly fully digital TDPAC-spectrometer M. Jäger K. Iwig T. Butz Springer Science+Business Media B.V. 2010 Abstract A user-friendly fully digital
Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-010-0201-8 A user-friendly fully digital TDPAC-spectrometer M. Jäger K. Iwig T. Butz Springer Science+Business Media B.V. 2010 Abstract A user-friendly fully digital
Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
Simulation of Algorithms for Pulse Timing in FPGAs
 2007 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record M13-369 Simulation of Algorithms for Pulse Timing in FPGAs Michael D. Haselman, Member IEEE, Scott Hauck, Senior Member IEEE, Thomas K. Lewellen, Senior
2007 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record M13-369 Simulation of Algorithms for Pulse Timing in FPGAs Michael D. Haselman, Member IEEE, Scott Hauck, Senior Member IEEE, Thomas K. Lewellen, Senior
CAEN Tools for Discovery
 Viareggio 5 September 211 Introduction In recent years CAEN has developed a complete family of digitizers that consists of several models differing in sampling frequency, resolution, form factor and other
Viareggio 5 September 211 Introduction In recent years CAEN has developed a complete family of digitizers that consists of several models differing in sampling frequency, resolution, form factor and other
nanomca 80 MHz HIGH PERFORMANCE, LOW POWER DIGITAL MCA Model Numbers: NM0530 and NM0530Z
 datasheet nanomca 80 MHz HIGH PERFORMANCE, LOW POWER DIGITAL MCA Model Numbers: NM0530 and NM0530Z I. FEATURES Finger-sized, high performance digital MCA. 16k channels utilizing smart spectrum-size technology
datasheet nanomca 80 MHz HIGH PERFORMANCE, LOW POWER DIGITAL MCA Model Numbers: NM0530 and NM0530Z I. FEATURES Finger-sized, high performance digital MCA. 16k channels utilizing smart spectrum-size technology
Development of a 256-channel Time-of-flight Electronics System For Neutron Beam Profiling
 JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. 14, NO. 8, AUGUST 2015 1 Development of a 256-channel Time-of-flight Electronics System For Neutron Beam Profiling Haolei Chen, Changqing Feng, Jiadong Hu, Laifu Luo,
JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. 14, NO. 8, AUGUST 2015 1 Development of a 256-channel Time-of-flight Electronics System For Neutron Beam Profiling Haolei Chen, Changqing Feng, Jiadong Hu, Laifu Luo,
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip
 The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment. Conference Report. Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2017/349 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 09 October 2017 (v4, 10 October 2017)
Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2017/349 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 09 October 2017 (v4, 10 October 2017)
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors
 A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
Beam Condition Monitors and a Luminometer Based on Diamond Sensors
 Beam Condition Monitors and a Luminometer Based on Diamond Sensors Wolfgang Lange, DESY Zeuthen and CMS BRIL group Beam Condition Monitors and a Luminometer Based on Diamond Sensors INSTR14 in Novosibirsk,
Beam Condition Monitors and a Luminometer Based on Diamond Sensors Wolfgang Lange, DESY Zeuthen and CMS BRIL group Beam Condition Monitors and a Luminometer Based on Diamond Sensors INSTR14 in Novosibirsk,
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 Nov 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 Nov 2015](/thumbs/75/71497215.jpg) Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION arxiv:1511.08385v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 Nov 2015 The Data Acquisition System for LZ Eryk Druszkiewicz a, for the LZ Collaboration a Department of Physics
Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION arxiv:1511.08385v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 Nov 2015 The Data Acquisition System for LZ Eryk Druszkiewicz a, for the LZ Collaboration a Department of Physics
The software and hardware for the ground testing of ALFA- ELECTRON space spectrometer
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The software and hardware for the ground testing of ALFA- ELECTRON space spectrometer To cite this article: A G Batischev et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The software and hardware for the ground testing of ALFA- ELECTRON space spectrometer To cite this article: A G Batischev et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf.
FPGA-BASED PULSED-RF PHASE AND AMPLITUDE DETECTOR AT SLRI
 doi:10.18429/jacow-icalepcs2017- FPGA-BASED PULSED-RF PHASE AND AMPLITUDE DETECTOR AT SLRI R. Rujanakraikarn, Synchrotron Light Research Institute, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand Abstract In this paper, the
doi:10.18429/jacow-icalepcs2017- FPGA-BASED PULSED-RF PHASE AND AMPLITUDE DETECTOR AT SLRI R. Rujanakraikarn, Synchrotron Light Research Institute, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand Abstract In this paper, the
Data Compression and Analysis Methods for High- Throughput Radiation Detector Systems
 1 Data Compression and Analysis Methods for High- Throughput Radiation Detector Systems John Mattingly Associate Professor, Nuclear Engineering North Carolina State University 2 Introduction The capabilities
1 Data Compression and Analysis Methods for High- Throughput Radiation Detector Systems John Mattingly Associate Professor, Nuclear Engineering North Carolina State University 2 Introduction The capabilities
Development and Application of 500MSPS Digitizer for High Resolution Ultrasonic Measurements
 Indian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Hyderabad Chapter Proc. National Seminar on Non-Destructive Evaluation Dec. 7-9, 2006, Hyderabad Development and Application of 500MSPS Digitizer for High Resolution
Indian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Hyderabad Chapter Proc. National Seminar on Non-Destructive Evaluation Dec. 7-9, 2006, Hyderabad Development and Application of 500MSPS Digitizer for High Resolution
Detection of Radio Pulses from Air Showers with LOPES
 Detection of Radio Pulses from Air Showers with LOPES Andreas Horneffer for the LOPES Collaboration Radboud University Nijmegen Radio Emission from Air Showers air showers are known since 1965 to emit
Detection of Radio Pulses from Air Showers with LOPES Andreas Horneffer for the LOPES Collaboration Radboud University Nijmegen Radio Emission from Air Showers air showers are known since 1965 to emit
FTMS Booster X1 High-performance data acquisition system for FT-ICR MS
 FTMS Booster X1 High-performance data acquisition system for FT-ICR MS What is FTMS Booster? The Spectroswiss FTMS Booster X1 is a high-performance data acquisition and analysis system based on state-of-the-art
FTMS Booster X1 High-performance data acquisition system for FT-ICR MS What is FTMS Booster? The Spectroswiss FTMS Booster X1 is a high-performance data acquisition and analysis system based on state-of-the-art
USB4. Encoder Data Acquisition USB Device Page 1 of 8. Description. Features
 USB4 Page 1 of 8 The USB4 is a data acquisition device designed to record data from 4 incremental encoders, 8 digital inputs and 4 analog input channels. In addition, the USB4 provides 8 digital outputs
USB4 Page 1 of 8 The USB4 is a data acquisition device designed to record data from 4 incremental encoders, 8 digital inputs and 4 analog input channels. In addition, the USB4 provides 8 digital outputs
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 614 (2010) 308 312 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 614 (2010) 308 312 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
How different FPGA firmware options enable digitizer platforms to address and facilitate multiple applications
 How different FPGA firmware options enable digitizer platforms to address and facilitate multiple applications 1 st of April 2019 Marc.Stackler@Teledyne.com March 19 1 Digitizer definition and application
How different FPGA firmware options enable digitizer platforms to address and facilitate multiple applications 1 st of April 2019 Marc.Stackler@Teledyne.com March 19 1 Digitizer definition and application
LV-Link 3.0 Software Interface for LabVIEW
 LV-Link 3.0 Software Interface for LabVIEW LV-Link Software Interface for LabVIEW LV-Link is a library of VIs (Virtual Instruments) that enable LabVIEW programmers to access the data acquisition features
LV-Link 3.0 Software Interface for LabVIEW LV-Link Software Interface for LabVIEW LV-Link is a library of VIs (Virtual Instruments) that enable LabVIEW programmers to access the data acquisition features
nanodpp datasheet I. FEATURES
 datasheet nanodpp I. FEATURES Ultra small size high-performance Digital Pulse Processor (DPP). 16k channels utilizing smart spectrum-size technology -- all spectra are recorded and stored as 16k spectra
datasheet nanodpp I. FEATURES Ultra small size high-performance Digital Pulse Processor (DPP). 16k channels utilizing smart spectrum-size technology -- all spectra are recorded and stored as 16k spectra
Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO
 Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO Abstract The ALICE Time of Flight Detector system comprises about 176.000 channels and covers an area of more than 100 m 2. The timing resolution
Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO Abstract The ALICE Time of Flight Detector system comprises about 176.000 channels and covers an area of more than 100 m 2. The timing resolution
Development of front-end readout electronics for silicon strip. detectors
 Development of front-end readout electronics for silicon strip detectors QIAN Yi( 千奕 ) 1 SU Hong ( 苏弘 ) 1 KONG Jie( 孔洁 ) 1,2 DONG Cheng-Fu( 董成富 ) 1 MA Xiao-Li( 马晓莉 ) 1 LI Xiao-Gang ( 李小刚 ) 1 1 Institute
Development of front-end readout electronics for silicon strip detectors QIAN Yi( 千奕 ) 1 SU Hong ( 苏弘 ) 1 KONG Jie( 孔洁 ) 1,2 DONG Cheng-Fu( 董成富 ) 1 MA Xiao-Li( 马晓莉 ) 1 LI Xiao-Gang ( 李小刚 ) 1 1 Institute
Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on LHC)
 Lecture 2! Introduction! Data handling requirements for LHC! Design issues: Architectures! Front-end, event selection levels! Trigger! Upgrades! Conclusion Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on
Lecture 2! Introduction! Data handling requirements for LHC! Design issues: Architectures! Front-end, event selection levels! Trigger! Upgrades! Conclusion Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on
Considerations on the ICARUS read-out and on data compression
 ICARUS-TM/2002-05 May 16, 2002 Considerations on the ICARUS read-out and on data compression S. Amerio, M. Antonello, B. Baiboussinov, S. Centro, F. Pietropaolo, W. Polchlopek, S. Ventura Dipartimento
ICARUS-TM/2002-05 May 16, 2002 Considerations on the ICARUS read-out and on data compression S. Amerio, M. Antonello, B. Baiboussinov, S. Centro, F. Pietropaolo, W. Polchlopek, S. Ventura Dipartimento
Nyquist filter FIFO. Amplifier. Impedance matching. 40 MHz sampling ADC. DACs for gain and offset FPGA. clock distribution (not yet implemented)
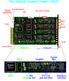 The Digital Gamma Finder (DGF) Firewire clock distribution (not yet implemented) DSP One of four channels Inputs Camac for 4 channels 2 cm System FPGA Digital part Analog part FIFO Amplifier Nyquist filter
The Digital Gamma Finder (DGF) Firewire clock distribution (not yet implemented) DSP One of four channels Inputs Camac for 4 channels 2 cm System FPGA Digital part Analog part FIFO Amplifier Nyquist filter
Image processing with the HERON-FPGA Family
 HUNT ENGINEERING Chestnut Court, Burton Row, Brent Knoll, Somerset, TA9 4BP, UK Tel: (+44) (0)1278 760188, Fax: (+44) (0)1278 760199, Email: sales@hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunt-dsp.com
HUNT ENGINEERING Chestnut Court, Burton Row, Brent Knoll, Somerset, TA9 4BP, UK Tel: (+44) (0)1278 760188, Fax: (+44) (0)1278 760199, Email: sales@hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunt-dsp.com
Physics Experiment N -17. Lifetime of Cosmic Ray Muons with On-Line Data Acquisition on a Computer
 Introduction Physics 410-510 Experiment N -17 Lifetime of Cosmic Ray Muons with On-Line Data Acquisition on a Computer The experiment is designed to teach the techniques of particle detection using scintillation
Introduction Physics 410-510 Experiment N -17 Lifetime of Cosmic Ray Muons with On-Line Data Acquisition on a Computer The experiment is designed to teach the techniques of particle detection using scintillation
ADQ108. Datasheet. Features. Introduction. Applications. Software support. ADQ Development Kit. Ordering information
 ADQ18 is a single channel high speed digitizer in the ADQ V6 Digitizer family. The ADQ18 has an outstanding combination of dynamic range and unique bandwidth, which enables demanding measurements such
ADQ18 is a single channel high speed digitizer in the ADQ V6 Digitizer family. The ADQ18 has an outstanding combination of dynamic range and unique bandwidth, which enables demanding measurements such
Amptek Silicon Drift Diode (SDD) at High Count Rates
 Amptek Silicon Drift Diode (SDD) at High Count Rates A silicon drift diode (SDD) is functionally similar to a SiPIN photodiode but its unique electrode structure reduces the electronic noise at short peaking
Amptek Silicon Drift Diode (SDD) at High Count Rates A silicon drift diode (SDD) is functionally similar to a SiPIN photodiode but its unique electrode structure reduces the electronic noise at short peaking
GFT bit High Speed Digitizer
 FEATURES Up to 4 analog channels in only 1U space Up to 2GS/s sampling rate per channel 14 bits vertical resolution DC coupled with up to 1GHz bandwidth Programmable DC offset Internal and external clock
FEATURES Up to 4 analog channels in only 1U space Up to 2GS/s sampling rate per channel 14 bits vertical resolution DC coupled with up to 1GHz bandwidth Programmable DC offset Internal and external clock
Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on LHC)
 Lecture 2 Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on LHC) Introduction Data handling requirements for LHC Design issues: Architectures Front-end, event selection levels Trigger Future evolutions Conclusion
Lecture 2 Data acquisition and Trigger (with emphasis on LHC) Introduction Data handling requirements for LHC Design issues: Architectures Front-end, event selection levels Trigger Future evolutions Conclusion
A Prototype Amplifier-Discriminator Chip for the GLAST Silicon-Strip Tracker
 A Prototype Amplifier-Discriminator Chip for the GLAST Silicon-Strip Tracker Robert P. Johnson Pavel Poplevin Hartmut Sadrozinski Ned Spencer Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics The GLAST Project
A Prototype Amplifier-Discriminator Chip for the GLAST Silicon-Strip Tracker Robert P. Johnson Pavel Poplevin Hartmut Sadrozinski Ned Spencer Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics The GLAST Project
Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator. Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator
 Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator Sandeep Mukthavaram August 23, 1999 Thesis Defense for the Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering
Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator Sandeep Mukthavaram August 23, 1999 Thesis Defense for the Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering
Picosecond time measurement using ultra fast analog memories.
 Picosecond time measurement using ultra fast analog memories. Dominique Breton a, Eric Delagnes b, Jihane Maalmi a acnrs/in2p3/lal-orsay, bcea/dsm/irfu breton@lal.in2p3.fr Abstract The currently existing
Picosecond time measurement using ultra fast analog memories. Dominique Breton a, Eric Delagnes b, Jihane Maalmi a acnrs/in2p3/lal-orsay, bcea/dsm/irfu breton@lal.in2p3.fr Abstract The currently existing
Development of a Multi-Channel Integrated Circuit for Use in Nuclear Physics Experiments Where Particle Identification is Important
 Development of a Multi-Channel Integrated Circuit for Use in Nuclear Physics Experiments Where Particle Identification is Important Michael Hall Southern Illinois University Edwardsville IC Design Research
Development of a Multi-Channel Integrated Circuit for Use in Nuclear Physics Experiments Where Particle Identification is Important Michael Hall Southern Illinois University Edwardsville IC Design Research
COMPENDIUM OF FRONT-END ELECTRONICS
 COMPENDIUM OF FRONT-END ELECTRONICS F. MESSI Division of Nuclear Physics, Lund University and European Spallation Source ERIC Lund, Sweden Email: francesco.messi@nuclear.lu.se Abstract Our world is changing
COMPENDIUM OF FRONT-END ELECTRONICS F. MESSI Division of Nuclear Physics, Lund University and European Spallation Source ERIC Lund, Sweden Email: francesco.messi@nuclear.lu.se Abstract Our world is changing
GA A23281 EXTENDING DIII D NEUTRAL BEAM MODULATED OPERATIONS WITH A CAMAC BASED TOTAL ON TIME INTERLOCK
 GA A23281 EXTENDING DIII D NEUTRAL BEAM MODULATED OPERATIONS WITH A CAMAC BASED TOTAL ON TIME INTERLOCK by D.S. BAGGEST, J.D. BROESCH, and J.C. PHILLIPS NOVEMBER 1999 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared
GA A23281 EXTENDING DIII D NEUTRAL BEAM MODULATED OPERATIONS WITH A CAMAC BASED TOTAL ON TIME INTERLOCK by D.S. BAGGEST, J.D. BROESCH, and J.C. PHILLIPS NOVEMBER 1999 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared
A PC104 Multiprocessor DSP System for Radiation Spectroscopy Applications
 A PC104 Multiprocessor DSP System for Radiation Spectroscopy Applications J. Basílio Simões, João Cardoso, Nuno Cruz, and Carlos M. B. A. Correia Instrumentation Center, Physics Department of the University
A PC104 Multiprocessor DSP System for Radiation Spectroscopy Applications J. Basílio Simões, João Cardoso, Nuno Cruz, and Carlos M. B. A. Correia Instrumentation Center, Physics Department of the University
nanomca-sp datasheet I. FEATURES
 datasheet nanomca-sp 80 MHz HIGH PERFORMANCE, LOW POWER DIGITAL MCA WITH BUILT IN PREAMPLIFIER Model Numbers: SP0534A/B to SP0539A/B Standard Models: SP0536B and SP0536A I. FEATURES Built-in preamplifier
datasheet nanomca-sp 80 MHz HIGH PERFORMANCE, LOW POWER DIGITAL MCA WITH BUILT IN PREAMPLIFIER Model Numbers: SP0534A/B to SP0539A/B Standard Models: SP0536B and SP0536A I. FEATURES Built-in preamplifier
Amptek Inc. Page 1 of 7
 OPERATING THE DP5 AT HIGH COUNT RATES The DP5 with the latest firmware (Ver 6.02) and Amptek s new 25 mm 2 SDD are capable of operating at high rates, with an OCR greater than 1 Mcps. Figure 1 shows a
OPERATING THE DP5 AT HIGH COUNT RATES The DP5 with the latest firmware (Ver 6.02) and Amptek s new 25 mm 2 SDD are capable of operating at high rates, with an OCR greater than 1 Mcps. Figure 1 shows a
The Liquid Argon Jet Trigger of the H1 Experiment at HERA. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction. 3 Jet Trigger Algorithm
 The Liquid Argon Jet Trigger of the H1 Experiment at HERA Bob Olivier Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut) Föhringer Ring 6, D-80805 München, Germany 1 Abstract The Liquid Argon
The Liquid Argon Jet Trigger of the H1 Experiment at HERA Bob Olivier Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut) Föhringer Ring 6, D-80805 München, Germany 1 Abstract The Liquid Argon
THE Hadronic Tile Calorimeter (TileCal) is the central
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL 53, NO 4, AUGUST 2006 2139 Digital Signal Reconstruction in the ATLAS Hadronic Tile Calorimeter E Fullana, J Castelo, V Castillo, C Cuenca, A Ferrer, E Higon,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL 53, NO 4, AUGUST 2006 2139 Digital Signal Reconstruction in the ATLAS Hadronic Tile Calorimeter E Fullana, J Castelo, V Castillo, C Cuenca, A Ferrer, E Higon,
ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System
 ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System Elements of a Data Acquisition System 2 Analog Signal Data Acquisition Hardware Your Signal Data Acquisition DAQ Device System Computer Cable Terminal Block Data Acquisition
ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System Elements of a Data Acquisition System 2 Analog Signal Data Acquisition Hardware Your Signal Data Acquisition DAQ Device System Computer Cable Terminal Block Data Acquisition
FTMS Booster X1 High-performance data acquisition system for Orbitrap FTMS
 FTMS Booster X1 High-performance data acquisition system for Orbitrap FTMS What is FTMS Booster? The Spectroswiss FTMS Booster X1 is a high-performance data acquisition and analysis system based on state-of-the-art
FTMS Booster X1 High-performance data acquisition system for Orbitrap FTMS What is FTMS Booster? The Spectroswiss FTMS Booster X1 is a high-performance data acquisition and analysis system based on state-of-the-art
Prototype of a Compact Imaging System for GEM Detectors Tomohisa Uchida, Member, IEEE, Yowichi Fujita, Manobu Tanaka, Member, IEEE, and Shoji Uno
 2698 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 55, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2008 Prototype of a Compact Imaging System for GEM Detectors Tomohisa Uchida, Member, IEEE, Yowichi Fujita, Manobu Tanaka, Member, IEEE,
2698 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 55, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2008 Prototype of a Compact Imaging System for GEM Detectors Tomohisa Uchida, Member, IEEE, Yowichi Fujita, Manobu Tanaka, Member, IEEE,
50 MHz Voltage-to-Frequency Converter
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS 50 MHz Voltage-to-Frequency Converter To cite this article: T Madden and J Baldwin 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 493 012008 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS 50 MHz Voltage-to-Frequency Converter To cite this article: T Madden and J Baldwin 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 493 012008 View the article online for updates
PX4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
 PX4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) What is the PX4? The PX4 is a component in the complete signal processing chain of a nuclear instrumentation system. It replaces many different components in a traditional
PX4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) What is the PX4? The PX4 is a component in the complete signal processing chain of a nuclear instrumentation system. It replaces many different components in a traditional
PROGRESS in TOF PET timing resolution continues to
 Combined Analog/Digital Approach to Performance Optimization for the LAPET Whole-Body TOF PET Scanner W. J. Ashmanskas, Member, IEEE, Z. S. Davidson, B. C. LeGeyt, F. M. Newcomer, Member, IEEE, J. V. Panetta,
Combined Analog/Digital Approach to Performance Optimization for the LAPET Whole-Body TOF PET Scanner W. J. Ashmanskas, Member, IEEE, Z. S. Davidson, B. C. LeGeyt, F. M. Newcomer, Member, IEEE, J. V. Panetta,
MI.31xx - 8 channel 12 bit A/D up to 25 MS/s
 Standard PCI format 12 bit A/D converter board 1 MS/s, 10 Ms/s or 25 MS/s 2, 4 or 8 channels per board Simultaneously sampling on all channels 8 input ranges: ±50 mv up to ± 10 V Up to 256 MSample memory
Standard PCI format 12 bit A/D converter board 1 MS/s, 10 Ms/s or 25 MS/s 2, 4 or 8 channels per board Simultaneously sampling on all channels 8 input ranges: ±50 mv up to ± 10 V Up to 256 MSample memory
nanomca datasheet I. FEATURES
 datasheet nanomca I. FEATURES Finger-sized, high performance digital MCA. 16k channels utilizing smart spectrum-size technology -- all spectra are recorded and stored as 16k spectra with instant, distortion-free
datasheet nanomca I. FEATURES Finger-sized, high performance digital MCA. 16k channels utilizing smart spectrum-size technology -- all spectra are recorded and stored as 16k spectra with instant, distortion-free
When to use an FPGA to prototype a controller and how to start
 When to use an FPGA to prototype a controller and how to start Mark Corless, Principal Application Engineer, Novi MI Brad Hieb, Principal Application Engineer, Novi MI 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 When to
When to use an FPGA to prototype a controller and how to start Mark Corless, Principal Application Engineer, Novi MI Brad Hieb, Principal Application Engineer, Novi MI 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 When to
Multi-channel front-end board for SiPM readout
 Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION Multi-channel front-end board for SiPM readout arxiv:1606.02290v1 [physics.ins-det] 7 Jun 2016 M. Auger, A. Ereditato, D. Goeldi, I. Kreslo, D. Lorca, M.
Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION Multi-channel front-end board for SiPM readout arxiv:1606.02290v1 [physics.ins-det] 7 Jun 2016 M. Auger, A. Ereditato, D. Goeldi, I. Kreslo, D. Lorca, M.
Multi-Channel Time Digitizing Systems
 454 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITY, VOL. 13, NO. 2, JUNE 2003 Multi-Channel Time Digitizing Systems Alex Kirichenko, Saad Sarwana, Deep Gupta, Irwin Rochwarger, and Oleg Mukhanov Abstract
454 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITY, VOL. 13, NO. 2, JUNE 2003 Multi-Channel Time Digitizing Systems Alex Kirichenko, Saad Sarwana, Deep Gupta, Irwin Rochwarger, and Oleg Mukhanov Abstract
Contents. Why waveform? Waveform digitizer : Domino Ring Sampler CEX Beam test autumn 04. Summary
 Contents Why waveform? Waveform digitizer : Domino Ring Sampler CEX Beam test data @PSI autumn 04 Templates and time resolution Pulse Shape Discrimination Pile-up rejection Summary 2 In the MEG experiment
Contents Why waveform? Waveform digitizer : Domino Ring Sampler CEX Beam test data @PSI autumn 04 Templates and time resolution Pulse Shape Discrimination Pile-up rejection Summary 2 In the MEG experiment
A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS
 A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS M. Belluso 1, G. Bonanno 1, A. Calì 1, A. Carbone 3, R. Cosentino 1, A. Modica 4, S. Scuderi 1, C. Timpanaro 1, M. Uslenghi 2 1- I.N.A.F.-Osservatorio
A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS M. Belluso 1, G. Bonanno 1, A. Calì 1, A. Carbone 3, R. Cosentino 1, A. Modica 4, S. Scuderi 1, C. Timpanaro 1, M. Uslenghi 2 1- I.N.A.F.-Osservatorio
Measuring Voltage and Time Quantities of a Signal Through a Virtual Oscilloscope
 AASCIT Journal of Physics 2017; 3(2): 5-12 http://www.aascit.org/journal/physics ISSN: 2381-1358 (Print); ISSN: 2381-1366 (Online) Measuring Voltage and Time Quantities of a Signal Through a G. Tektas
AASCIT Journal of Physics 2017; 3(2): 5-12 http://www.aascit.org/journal/physics ISSN: 2381-1358 (Print); ISSN: 2381-1366 (Online) Measuring Voltage and Time Quantities of a Signal Through a G. Tektas
SPD VERY FRONT END ELECTRONICS
 10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, 10 14 Oct 2005, PO2.0684 (2005) SPD VERY FRONT END ELECTRONICS S. Luengo 1, J. Riera 1, S. Tortella 1, X. Vilasis
10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, 10 14 Oct 2005, PO2.0684 (2005) SPD VERY FRONT END ELECTRONICS S. Luengo 1, J. Riera 1, S. Tortella 1, X. Vilasis
Design and performance of LLRF system for CSNS/RCS *
 Design and performance of LLRF system for CSNS/RCS * LI Xiao 1) SUN Hong LONG Wei ZHAO Fa-Cheng ZHANG Chun-Lin Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China Abstract:
Design and performance of LLRF system for CSNS/RCS * LI Xiao 1) SUN Hong LONG Wei ZHAO Fa-Cheng ZHANG Chun-Lin Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China Abstract:
BANDWIDTH EFFICIENT TURBO CODING FOR HIGH SPEED MOBILE SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS
 BANDWIDTH EFFICIENT TURBO CODING FOR HIGH SPEED MOBILE SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS S. Adrian BARBULESCU, Wade FARRELL Institute for Telecommunications Research, University of South Australia, Warrendi Road,
BANDWIDTH EFFICIENT TURBO CODING FOR HIGH SPEED MOBILE SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS S. Adrian BARBULESCU, Wade FARRELL Institute for Telecommunications Research, University of South Australia, Warrendi Road,
ADQ214. Datasheet. Features. Introduction. Applications. Software support. ADQ Development Kit. Ordering information
 ADQ214 is a dual channel high speed digitizer. The ADQ214 has outstanding dynamic performance from a combination of high bandwidth and high dynamic range, which enables demanding measurements such as RF/IF
ADQ214 is a dual channel high speed digitizer. The ADQ214 has outstanding dynamic performance from a combination of high bandwidth and high dynamic range, which enables demanding measurements such as RF/IF
Coincidence Rates. QuarkNet. summer workshop June 24-28, 2013
 Coincidence Rates QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 Example Pulse input Threshold level (-10 mv) Discriminator output Once you have a digital logic pulse, you can analyze it using digital electronics
Coincidence Rates QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 Example Pulse input Threshold level (-10 mv) Discriminator output Once you have a digital logic pulse, you can analyze it using digital electronics
NIM. ADCs (Peak Sensing) Analog Pulse Processors Amplifiers (Fast) Amplifiers (Spectroscopy) Attenuators Coincidence/Logic/Trigger Units
 The NIM-Nuclear Instrumentation Module standard is a very popular form factor widely used in experimental Particle and Nuclear Physics setups. Defined the first time by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission
The NIM-Nuclear Instrumentation Module standard is a very popular form factor widely used in experimental Particle and Nuclear Physics setups. Defined the first time by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission
Positron Emission Tomography
 Positron Emission Tomography UBC Physics & Astronomy / PHYS 409 1 Introduction Positron emission tomography (PET) is a non-invasive way to produce the functional 1 image of a patient. It works by injecting
Positron Emission Tomography UBC Physics & Astronomy / PHYS 409 1 Introduction Positron emission tomography (PET) is a non-invasive way to produce the functional 1 image of a patient. It works by injecting
DAQ & Electronics for the CW Beam at Jefferson Lab
 DAQ & Electronics for the CW Beam at Jefferson Lab Benjamin Raydo EIC Detector Workshop @ Jefferson Lab June 4-5, 2010 High Event and Data Rates Goals for EIC Trigger Trigger must be able to handle high
DAQ & Electronics for the CW Beam at Jefferson Lab Benjamin Raydo EIC Detector Workshop @ Jefferson Lab June 4-5, 2010 High Event and Data Rates Goals for EIC Trigger Trigger must be able to handle high
Multi-Channel Charge Pulse Amplification, Digitization and Processing ASIC for Detector Applications
 1.0 Multi-Channel Charge Pulse Amplification, Digitization and Processing ASIC for Detector Applications Peter Fischer for Tim Armbruster, Michael Krieger and Ivan Peric Heidelberg University Motivation
1.0 Multi-Channel Charge Pulse Amplification, Digitization and Processing ASIC for Detector Applications Peter Fischer for Tim Armbruster, Michael Krieger and Ivan Peric Heidelberg University Motivation
Spectrum Detector for Cognitive Radios. Andrew Tolboe
 Spectrum Detector for Cognitive Radios Andrew Tolboe Motivation Currently in the United States the entire radio spectrum has already been reserved for various applications by the FCC. Therefore, if someone
Spectrum Detector for Cognitive Radios Andrew Tolboe Motivation Currently in the United States the entire radio spectrum has already been reserved for various applications by the FCC. Therefore, if someone
GAMMA-GAMMA CORRELATION Latest Revision: August 21, 2007
 C1-1 GAMMA-GAMMA CORRELATION Latest Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: decay event? What is the angular correlation between two gamma rays emitted by a single INTRODUCTION & THEORY:
C1-1 GAMMA-GAMMA CORRELATION Latest Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: decay event? What is the angular correlation between two gamma rays emitted by a single INTRODUCTION & THEORY:
Firmware development and testing of the ATLAS IBL Read-Out Driver card
 Firmware development and testing of the ATLAS IBL Read-Out Driver card *a on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration a University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering, Seattle, WA 98195, U.S.A.
Firmware development and testing of the ATLAS IBL Read-Out Driver card *a on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration a University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering, Seattle, WA 98195, U.S.A.
Final Results from the APV25 Production Wafer Testing
 Final Results from the APV Production Wafer Testing M.Raymond a, R.Bainbridge a, M.French b, G.Hall a, P. Barrillon a a Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London, UK b Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
Final Results from the APV Production Wafer Testing M.Raymond a, R.Bainbridge a, M.French b, G.Hall a, P. Barrillon a a Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London, UK b Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
Design of the Front-End Readout Electronics for ATLAS Tile Calorimeter at the slhc
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 60, NO. 2, APRIL 2013 1255 Design of the Front-End Readout Electronics for ATLAS Tile Calorimeter at the slhc F. Tang, Member, IEEE, K. Anderson, G. Drake, J.-F.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 60, NO. 2, APRIL 2013 1255 Design of the Front-End Readout Electronics for ATLAS Tile Calorimeter at the slhc F. Tang, Member, IEEE, K. Anderson, G. Drake, J.-F.
FREIA Facility for Research Instrumentation and Accelerator Development Infrastructure and Control Architecture
 FREIA Facility for Research Instrumentation and Accelerator Development Infrastructure and Control Architecture Konrad Gajewski 10 September 2013, Uppsala Why FREIA? Several circumstances test stand for
FREIA Facility for Research Instrumentation and Accelerator Development Infrastructure and Control Architecture Konrad Gajewski 10 September 2013, Uppsala Why FREIA? Several circumstances test stand for
Real-time use of GPUs in High-Energy Physics experiments
 Real-time use of GPUs in High-Energy Physics experiments Marco S. Sozzi University of Pisa Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare CERN With: G. Lamanna, J. Pinzino, F. Pantaleo (Pisa U. and CERN) The frontiers
Real-time use of GPUs in High-Energy Physics experiments Marco S. Sozzi University of Pisa Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare CERN With: G. Lamanna, J. Pinzino, F. Pantaleo (Pisa U. and CERN) The frontiers
CAEN. Electronic Instrumentation DPP-PSD. Rev July Digital Pulse Processing for Pulse Shape Discrimination. User Manual UM2580
 Tools for Discovery n Rev 4-21 July 2014 User Manual UM2580 DPP-PSD Digital Pulse Processing for Pulse Shape Discrimination Rev 8 - September 29th, 2016 Purpose of this Manual This User Manual contains
Tools for Discovery n Rev 4-21 July 2014 User Manual UM2580 DPP-PSD Digital Pulse Processing for Pulse Shape Discrimination Rev 8 - September 29th, 2016 Purpose of this Manual This User Manual contains
Activities in Electronics Lab Associates are: Mrs. Arti Gupta, K.S.Golda, S.Muralithar & Dr.R.K.Bhowmik
 Activities in Electronics Lab. 2006 Associates are: Mrs. Arti Gupta, K.S.Golda, S.Muralithar & Dr.R.K.Bhowmik Nuclear Electronics (INGA, NAND) Pulse Shape Discriminator Electronics for NAND National Array
Activities in Electronics Lab. 2006 Associates are: Mrs. Arti Gupta, K.S.Golda, S.Muralithar & Dr.R.K.Bhowmik Nuclear Electronics (INGA, NAND) Pulse Shape Discriminator Electronics for NAND National Array
PoS(ICRC2017)449. First results from the AugerPrime engineering array
 First results from the AugerPrime engineering array a for the Pierre Auger Collaboration b a Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay, INP-CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, 9106 Orsay
First results from the AugerPrime engineering array a for the Pierre Auger Collaboration b a Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay, INP-CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, 9106 Orsay
Multiple Instrument Station Module
 Multiple Instrument Station Module Digital Storage Oscilloscope Vertical Channels Sampling rate Bandwidth Coupling Input impedance Vertical sensitivity Vertical resolution Max. input voltage Horizontal
Multiple Instrument Station Module Digital Storage Oscilloscope Vertical Channels Sampling rate Bandwidth Coupling Input impedance Vertical sensitivity Vertical resolution Max. input voltage Horizontal
CAEN. Electronic Instrumentation. CAEN Silicon Photomultiplier Kit
 CAEN Tools for Discovery Electronic Instrumentation CAEN Silicon Photomultiplier Kit CAEN realized a modular development kit dedicated to Silicon Photomultipliers, representing the state-of-the art in
CAEN Tools for Discovery Electronic Instrumentation CAEN Silicon Photomultiplier Kit CAEN realized a modular development kit dedicated to Silicon Photomultipliers, representing the state-of-the art in
Method for digital particle spectrometry Khryachkov Vitaly
 Method for digital particle spectrometry Khryachkov Vitaly Institute for physics and power engineering (IPPE) Obninsk, Russia The goals of Analog Signal Processing Signal amplification Signal filtering
Method for digital particle spectrometry Khryachkov Vitaly Institute for physics and power engineering (IPPE) Obninsk, Russia The goals of Analog Signal Processing Signal amplification Signal filtering
THE PERFORMANCE TEST OF THE AD CONVERTERS EMBEDDED ON SOME MICROCONTROLLERS
 THE PERFORMANCE TEST OF THE AD CONVERTERS EMBEDDED ON SOME MICROCONTROLLERS R. Holcer Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, Technical University of Košice, Park Komenského 13, SK-04120 Košice,
THE PERFORMANCE TEST OF THE AD CONVERTERS EMBEDDED ON SOME MICROCONTROLLERS R. Holcer Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, Technical University of Košice, Park Komenského 13, SK-04120 Košice,
A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter
 A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter Quentin Diduck, Martin Margala * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department 526 Computer Studies Bldg., PO Box 270231 University
A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter Quentin Diduck, Martin Margala * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department 526 Computer Studies Bldg., PO Box 270231 University
Computer-Based Digital Signal Processing for Nuclear Scintillator Detectors NCRRT, AEA Abstract I. Introduction.
 Computer-Based Digital Signal Processing for Nuclear Scintillator Detectors M. A. Ashour, A. M. Abo Shosha NCRRT, AEA P.O.B. 29, Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt. Fax: ++22-2749298 Abstract This article addresses
Computer-Based Digital Signal Processing for Nuclear Scintillator Detectors M. A. Ashour, A. M. Abo Shosha NCRRT, AEA P.O.B. 29, Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt. Fax: ++22-2749298 Abstract This article addresses
Moller DAQ with the FADC250 B 2. Figure M1 CR SR CL SL FADC SD_FP. VME64x FLEX_I/O ROC CR: CALORIMETER RIGHT [1-4] SR: SCINTILLATOR RIGHT [1-4]
![Moller DAQ with the FADC250 B 2. Figure M1 CR SR CL SL FADC SD_FP. VME64x FLEX_I/O ROC CR: CALORIMETER RIGHT [1-4] SR: SCINTILLATOR RIGHT [1-4] Moller DAQ with the FADC250 B 2. Figure M1 CR SR CL SL FADC SD_FP. VME64x FLEX_I/O ROC CR: CALORIMETER RIGHT [1-4] SR: SCINTILLATOR RIGHT [1-4]](/thumbs/90/102643912.jpg) Moller DAQ with the F5 CR: CALORIMETER RIGHT [1-] CR SR CL SL F SR: SCINTILLATOR RIGHT [1-] CL: CALORIMETER LEFT [1-] SL: SCINTILLATOR LEFT [1-] A b a SD_FP A: [ HELICITY, HELICITY_FLIP ] (NIM or ECL)
Moller DAQ with the F5 CR: CALORIMETER RIGHT [1-] CR SR CL SL F SR: SCINTILLATOR RIGHT [1-] CL: CALORIMETER LEFT [1-] SL: SCINTILLATOR LEFT [1-] A b a SD_FP A: [ HELICITY, HELICITY_FLIP ] (NIM or ECL)
A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 2 journal of August 2005 physics pp. 273 283 A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator S K GUPTA a, Y HAYASHI b, A JAIN a, S KARTHIKEYAN
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 2 journal of August 2005 physics pp. 273 283 A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator S K GUPTA a, Y HAYASHI b, A JAIN a, S KARTHIKEYAN
Fast first practical help -- detailed instructions will follow- preliminary Experiment F80
 Fast first practical help -- detailed instructions will follow- preliminary Experiment F80 Measurement Methods of Nuclear and Particle Physics Introduction: This experiment is going to introduce you to
Fast first practical help -- detailed instructions will follow- preliminary Experiment F80 Measurement Methods of Nuclear and Particle Physics Introduction: This experiment is going to introduce you to
A CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FOR PULSE-SHAPE DISCRIMINATION*
 A CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FOR PULSE-SHAPE DISCRIMINATION* S. S. Frank, M. N. Ericson, M. L. Simpson, R. A. Todd, and D. P. Hutchinson Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 3783 1 Abstract and Summary
A CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FOR PULSE-SHAPE DISCRIMINATION* S. S. Frank, M. N. Ericson, M. L. Simpson, R. A. Todd, and D. P. Hutchinson Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 3783 1 Abstract and Summary
Summary. Introduction
 Performance of an Enhanced Throughput Feature in a High-Count Rate System Ronald M Keyser, Senior Member, and Rex C Trammell, Senior Member ORTEC 801 South Illinois Avenue Oak Ridge, TN 37831-0895 Summary
Performance of an Enhanced Throughput Feature in a High-Count Rate System Ronald M Keyser, Senior Member, and Rex C Trammell, Senior Member ORTEC 801 South Illinois Avenue Oak Ridge, TN 37831-0895 Summary
