Design And Development Of Magnetron Power Source From Three Phase Supply Madhukesh Heggannavar, 2 Prakash Mugali and 3 Shashidhar M.
|
|
|
- Shannon Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design And Development Of Magnetron Power Source From Three Supply Madhukesh Heggannavar, 2 Prakash Mugali and 3 Shashidhar M. Patil 1 Student, BEC Bagalkot, Karnataka, India. 2 Managing Director, Enerzi Microwave Systems Pvt.Ltd., Belgaum, India. 3 Professor - E&E dept, BEC Bagalkot, Karnataka, India. ABSTRACT: Electromagnetic radiations are phenomena that takes the form of self propagating waves in a vacuum or in matter. Microwaves are a part of the electro-magnetic (EM) radiation spectrum, with a frequency range of 300Mhz to 300Ghz.Microwave heating applications ceramics, Metallic powder, Food products, Wood, Polymers, Rubber, Textile & Paper. Various sources of microwaves include the Magnetron, Klystron, Travelling-wave tube (TWT) and gyrotron. These devices work in the density modulated mode rather than the current modulated mode. This means that they work on the basis of clumps of electrons flying through them, rather than using a continuous stream. The scope of this project work requires us to focus on such device namely Magnetron. Microwave wave heating has advantages over the conventional heating due to which it is finding applications in industries for heating. The heart of every microwave oven is a high voltage system whose purpose is to generate Microwaves. This high voltage system is called as Magnetron power supply. Three phase supply design for magnetron power source by providing gate firing signal using control scheme to the thyristors can be achieved by using the power scheme design respectively. In power scheme design three identical thyristors are connected in each phase of the three phase line supply and of the three thyristors are connected to the star connected load. Control scheme design is formed by using the comparators, diode and logic gate. In control scheme design input is taken from the mains supply and of the control card which can be used for gate triggering pulses for thyristors. The objective is to design control pulses for the gate triggering signals, and also monitoring various parameters such as voltage, current and total power control for various applications. Using a three phase supply we can achieve high power to the magnetron power source as compared to the single phase control in single phase supply with much better ripple characteristics. Thus high power magnetron source for industrial and practical applications is conveniently used. KEYWORDS: Microwaves, Magnetron, Power supply card, Control card, Thyristor card. I. INTRODUCTION Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz (0.3 GHz) and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF (Ultra High Frequency) and EHF (Extremely high frequency) (millimetre waves), and various sources use different boundaries. In all cases, microwave includes the entire SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum, with RF engineering often putting the lower boundary at 1 GHz (30 cm), and the upper around 100 GHz (3mm). Fig.1.1: Electromagnetic Spectrum The applications of microwaves are vast. The microwaves are used in various fields like, Communications, radar systems, radio astronomy, navigation etc. Microwave heating is used in industrial processes for drying and curing products heating. Microwave heating is finding a wide application in industry for Ceramics, Metallic Powder, Food Products, Wood / Bamboo, Polymers / Rubber, Textile / Paper. 1.1 Microwave Heating When materials are exposed to microwave radiation, it gets reflected(r),absorbed(a)or transmitted (T) depending on the dielectric properties of the material permittivity (ε) and permeability (μ),which is a function of composition, size and temperature. Practically all the three phenomena are present partially when a material is exposed to microwaves. The absorbed portion (A) of the incident microwave, heats the material by polarization of the atomic / molecular structure. As the microwave travel through the material, it gets attenuated, resulting in volumetric heating. 1549
2 For most industrial heating applications the microwave frequencies are restricted to: MHz, MHz and MHz the rest of the frequency range is mostly reserved for communication purposes. Advantages of Microwave Heating: Volumetric heating Eco-Friendly No exhaust gases Energy Efficient Low Operational Cost Uniform heating Microwave Sources: Magnetron, klystron, traveling-wave tube (TWT), and gyrotron operate on the ballistic motion of electrons in a vacuum under the influence of controlled electric or magnetic fields. These devices work in the density modulated mode, rather than the current modulated mode. This means that they work on the basis of clumps of electrons flying ballistically through them, rather than using a continuous stream. Low power microwave sources use solid-state devices such as the field-effect transistor (at least at lower frequencies), tunnel diodes, Gunn diodes, and IMPATT diodes. The heart of every microwave oven is the high voltage system. Its purpose is to generate microwave energy. The high-voltage components accomplish this by stepping up AC line voltage to high voltage, which is then changed to an even higher DC voltage. This DC power is then converted to the RF energy that cooks the food. II.MAGNETRON the grid. While the external configurations of different magnetrons will vary, the basic internal structures are the same; these include the anode, the filament/cathode, the antenna, and the magnets. The ANODE (or plate) is a hollow cylinder of iron from which an even number of anode vanes extends inward. The open trapezoidal shaped areas between each of the vanes are resonant cavities that serve as tuned circuits and determine the frequency of the tube. The anode operates in such a way that alternate segments must be connected, or strapped, so that each segment is opposite in polarity to the segment on either side. In effect, the cavities are connected in parallel with regard to the. This will become easier to understand as the description of operation is considered. The FILAMENT (also called heater), which also serves as the cathode of the tube, is located in the canter of the magnetron, and is supported by the large and rigid filament leads, which are carefully sealed into the tube and shielded. The ANTENNA is a probe or loop that is connected to the anode and extends into one of the tuned cavities. The antenna is coupled to the waveguide, a hollow metal enclosure, into which the antenna transmits the RF energy. The MAGNETIC FIELD is provided by strong permanent magnets, which are mounted around the magnetron so that the magnetic field is parallel with the axis of the cathode. Fig.2.1: (a) A magnetron and (b) schematic cross-sectional view of the magnetron cavity 2.1 Basic Magnetron Structure The nucleus of the high-voltage system is the magnetron tube. The magnetron is a diode-type electron tube which is used to produce the required 2450 MHz of microwave energy. It is classed as a diode because it has no grid just like an ordinary electron tube. A magnetic field imposed on the space between the anode (plate) and the cathode serves as Fig.2.2: Structure of Magnetron This paper discusses about design and development of the three phase power supply circuits for Magnetron power source for industrial microwave systems which require consistent, maintenance free, long life and superior controls for required parameters through controlled design input parameters. The power supply to the magnetron is achieved in the project by using a three phase input. The three phase input is given to the power scheme consisting 1550
3 of three thyristors, These thyristors are fired using a control scheme. The of the power scheme design is given to the load. III. METHODOLOGY 3.1. Power Supply Design Concept The Paper scope includes design of power supply for a magnetron power source. The block diagram of the power supply is as shown Fig 3.1. Once the electrons are emitted they start forming electron clouds around the filament, and need an extra energy to move towards the anode. This extra energy is provided by the electrostatic field produced by the high voltage DC power supply connected between anode and cathode. 3.2 Final Block Diagram of Modules Fig.3.1: Block diagram of the power supply design for magnetron Power supply card Input to the power supply card is three phase 220vac and it converts AC to DC supplies the necessary power 5v,+12v,-12v to the control card Control card Output of the power supply card is given to the control card to provide the proper supply to the control cad components such as comparator, diodes and AND gate which operates on low supply voltages. By design of control card gate triggering signals will be formed and of this is given to the gate triggering and switching thyristor block Thyristor Block Solid state switches used to control the flow of electric current often used for circuit protection. The input to the power supply is the three phase mains 415Volts/50Hz, the mains is stabilized. The microcontroller based power controllers control the power to be delivered by the magnetron by controlling the two power supplies connected to the magnetron. One is the high current power supply with approximate rating of 20A/3.8V and the other is the high voltage DC power supply with approximate rating of 4KV/450mA. The filament of the magnetron requires a high current power supply to emit electrons by the process of thermionic emission. The high current supplied to the filament can be AC or DC, here the alternating current is selected as it is the simplest method. Fig.3.2:Final Block Diagram of Modules Final diagram of Modules as shown in the Fig.3.2 consists of a four pole MCB, control cards, stepdown transformer, power supply card and thyristor card. Three phase Input from the MCB is given to the step-down transformers. Input to each step-down transformer is 230Vac and its secondary is 5Vac.Output of the step-down transformer is given to the input of the control card because control card components operate on low supply voltages. Power supply gives the necessary dc supply of +12v,- 12v,+5v, and com to the control cards. Output of the control card is given to the thyristor cards and input to the thyrisor card taken from three line supply. Output of the thyristor cards is given to the star connected load. 3.3 Power scheme design 1551
4 Fig.3.3: Power scheme diagram Power scheme diagram consists of three identical thyristors which are connected in each phase as shown in the above Fig.3.3. Output of the each thyristor is connected to the load. 3.4 Control scheme design Fig.3.4: control Scheme Control scheme design consists of comparator, diode and AND gate. Control scheme design as shown in the figure. and neutral are the two inputs to the comparator. Output of the comparator is given to the diode which conducts only in forward direction and blocks the reverse current flow of current in the circuit. Output of the diode is given to pin number 2 of the AND gate and pin numbers 1 and 14 are shorted, Output of this AND gate is given to the thyristor gate signals. IV. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS For the load each of 500W sodium vapor lamps star connected was tested for variations in the input mains supply voltage from 415 Volts, to check the repeatability and consistency. The readings are tabulated and plotted. Power Setting The following readings of anode current are recorded when the power supply is operated at 415Vac mains supply and the current and voltage readings are tabulated for the same. Table 4.1: Readings for voltage, Current and Output power for input voltage V in =415 V ac input Y - input input Y- (amps) (amps) Y- (amps) (watts) (watts) Y- (watts) 10% % % % % % % % % % Fig.4.1: Voltage graph Above graph voltage v/s power setting shows that as the power setting increases voltages in each phase also increases. Fig.4.2: Current graph 1552
5 Above graph current v/s power setting shows that as the power setting increases current in each phase also increases. Fig.4.6:Output at 80% Fig.4.3: Output Power graph 4.2 Voltage waveforms on CRO Above graph power v/s power setting shows that as the power setting increases power in each phase also increases. 4.1 Current Waveforms on CRO Fig.4.7:Output at 50% Fig.4.4:Output at 10% Fig.4.8:Output at 80% Fig.4.5:Output at 50% Fig.4.9:Output at 100% 1553
6 CONCLUSION Three phase supply design for magnetron power source by providing gate firing signal to the thyristors is achieved by using the power scheme, control scheme design respectively. The various parameters were monitored such as voltage, current and the power. Therefore using the three phase supply we are able to provide phase to phase supply and balance the load. Three phase-phase control has significant advantages over single phase firing and this was observed and confirmed through the readings as tabulated in the report. Three phase firing has provided the advantage of low ripple in the dc quantity. We have also observed better smooth control of power delivered to load as compared to the single phase firing. Three phase supply design provides low losses and more accurate firing angles compared to single phase supply. Low ripple and high performance are the major advantages. Thus the three phase power to the magnetron power source is achieved and high power magnetron source can be conveniently used for industrial applications. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Authors place on record the colleagues and friends at Enerzi Microwave systems Pvt. Ltd., Belgaum and the professors and lecturers at BEC, Bagalkot for their endless support and help. REFERENCES Books: [1]A.C.Metaxas and Roger J.Meredith, Industrial Microwave heating, Sec ond Edition, IET, [2]Von M. A. Laughton,D. F. Warne, Electrical Engineer s Reference book, Sixteenth Edition, Newnes, [3]Ned Mohan/Undeland/Robins, Power Electronics, Second Edition, Wiley, [4]P.S.Bimbra Power Electronics KhannaPuplishers,New Delhi,2002. [5]David A.Bell, Operational Amplifiers and Linear IC's, 2nd edition, PHI/Pearson, [6]Ramakanth A. Gayakwad Op-Amps and Linear Integrated Circuits, Fourth Edition,2004. BIBILOGRAPHY Mr. Madhukesh Heggannavar: was born in Belgaum, Karnataka, India on December 29, He obtained B.E (Electrical and Electronics) from Veshwesvaraya Techhnological University, Belgaum in He is currently persuing M.Tech. Degree in Power and Energy Systems in Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Basaveshwar Engineering College, Bagalkot, India. id madhukesh016@gmail.com Mr. Prakash S. Mugali: was born in Belgaum, Karnataka, India on July 19, He obtained his B.E (Electronics) degree from Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum in 2002 and MBA from Symbiosys Pune. His areas of interest include Radiation Heating, Wind and Solar Systems, Power Systems, Automation and Energy Conservation. He possesses more than 10years of Experience in Industrial Electronics and Electro-mechanical Equipment Manufacturing. Having got an opportunity to work with many eminent scientists of the country and abroad he has been leading M/s. Enerzi Microwave Systems Pvt. Ltd. to develop various markets for different microwave applications. He currently serves as the Chairman and Managing Director of this company. id prakash@enerzi.co Prof. Shashidhar M.Patil: was born in Gudadur, in Raichur Dist, on 16 th January He Obtained his B.E. (Electrical and Electronics Engg.) degree from P.D.A College of Engineering, Gulbarga in 1985 and M.tech (Machine Drives and Power Electronics) from IIT Kharagpur in Presently he is working as a lecturer (selection grade) in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering at Basaveshwar Engineering College,Bagalkot. id smpatil@yahoo.co.in 1554
Magnetron. Physical construction of a magnetron
 anode block interaction space cathode filament leads Magnetron The magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that works as self-excited microwave oscillator. Crossed electron and magnetic fields are used
anode block interaction space cathode filament leads Magnetron The magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that works as self-excited microwave oscillator. Crossed electron and magnetic fields are used
Highly efficient water heaters using magnetron effects
 Highly efficient water heaters using magnetron effects Technical task of this project is maximum heat output and minimum electric input of power. This research project has several stages of development.
Highly efficient water heaters using magnetron effects Technical task of this project is maximum heat output and minimum electric input of power. This research project has several stages of development.
COURSE: ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PROCESSES. Module No. 5: OTHER PROCESSES
 COURSE: ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Module No. 5: OTHER PROCESSES Lecture No-3 Microwave Processing of Materials Microwave processing is a relatively new and emerging area in material processing.
COURSE: ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Module No. 5: OTHER PROCESSES Lecture No-3 Microwave Processing of Materials Microwave processing is a relatively new and emerging area in material processing.
MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER
 1 MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDERGARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
1 MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDERGARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Module IV, Lecture 2 DNP experiments and hardware
 Module IV, Lecture 2 DNP experiments and hardware tunnel diodes, Gunn diodes, magnetrons, traveling-wave tubes, klystrons, gyrotrons Dr Ilya Kuprov, University of Southampton, 2013 (for all lecture notes
Module IV, Lecture 2 DNP experiments and hardware tunnel diodes, Gunn diodes, magnetrons, traveling-wave tubes, klystrons, gyrotrons Dr Ilya Kuprov, University of Southampton, 2013 (for all lecture notes
Experiment-4 Study of the characteristics of the Klystron tube
 Experiment-4 Study of the characteristics of the Klystron tube OBJECTIVE To study the characteristics of the reflex Klystron tube and to determine the its electronic tuning range EQUIPMENTS Klystron power
Experiment-4 Study of the characteristics of the Klystron tube OBJECTIVE To study the characteristics of the reflex Klystron tube and to determine the its electronic tuning range EQUIPMENTS Klystron power
-31- VII. MAGNETRON DEVELOPMENT. Prof. S. T. Martin V. Mayper D. L. Eckhardt R. R. Moats S. Goldberg R. Q. Twiss
 VII. MAGNETRON DEVELOPMENT Prof. S. T. Martin V. Mayper D. L. Eckhardt R. R. Moats S. Goldberg R. Q. Twiss The activities associated with this project may be divided into two groups; (a) development of
VII. MAGNETRON DEVELOPMENT Prof. S. T. Martin V. Mayper D. L. Eckhardt R. R. Moats S. Goldberg R. Q. Twiss The activities associated with this project may be divided into two groups; (a) development of
Wireless Charging of Mobile Phones using Microwaves K. E. CH. VIDHYA SAGAR 1, S. V. SRINIVASA RAJU 2
 www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.01, January-2014, Pages:0192-0196 Wireless Charging of Mobile Phones using Microwaves K. E. CH. VIDHYA SAGAR 1, S. V. SRINIVASA RAJU 2 1 Asst
www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.01, January-2014, Pages:0192-0196 Wireless Charging of Mobile Phones using Microwaves K. E. CH. VIDHYA SAGAR 1, S. V. SRINIVASA RAJU 2 1 Asst
LESSON PLAN. LESSON PLAN DURATION : - 15 weeks (from JULY 2018 to NOVEMBER 2018)
 LESSON PLAN NAME OF THE FACULTY DISCIPLINE SEMESTER SUBJECT : - HIMANSHU YADAV : - ECE : - FIFTH : - MICROWAVE ENGG LESSON PLAN DURATION : - 15 weeks (from JULY 2018 to NOVEMBER 2018) WORK LOAD (LECTURE/PRACTICAL)
LESSON PLAN NAME OF THE FACULTY DISCIPLINE SEMESTER SUBJECT : - HIMANSHU YADAV : - ECE : - FIFTH : - MICROWAVE ENGG LESSON PLAN DURATION : - 15 weeks (from JULY 2018 to NOVEMBER 2018) WORK LOAD (LECTURE/PRACTICAL)
R.K.YADAV. 2. Explain with suitable sketch the operation of two-cavity Klystron amplifier. explain the concept of velocity and current modulations.
 Question Bank DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-603) Unit-III 1. What are the high frequency limitations of conventional tubes? Explain clearly. 2. Explain
Question Bank DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-603) Unit-III 1. What are the high frequency limitations of conventional tubes? Explain clearly. 2. Explain
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II. Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS
 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS 1. Explain microwave power measurement. 2. Why we can not use ordinary diode and transistor in microwave detection and microwave amplification? 3.
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS 1. Explain microwave power measurement. 2. Why we can not use ordinary diode and transistor in microwave detection and microwave amplification? 3.
7. Experiment K: Wave Propagation
 7. Experiment K: Wave Propagation This laboratory will be based upon observing standing waves in three different ways, through coaxial cables, in free space and in a waveguide. You will also observe some
7. Experiment K: Wave Propagation This laboratory will be based upon observing standing waves in three different ways, through coaxial cables, in free space and in a waveguide. You will also observe some
Physics 4BL: Electricity and Magnetism Lab manual. UCLA Department of Physics and Astronomy
 Physics 4BL: Electricity and Magnetism Lab manual UCLA Department of Physics and Astronomy Last revision April 16, 2017 1 Lorentz Force Laboratory 2: Lorentz Force In 1897, only 120 years ago, J.J. Thomson
Physics 4BL: Electricity and Magnetism Lab manual UCLA Department of Physics and Astronomy Last revision April 16, 2017 1 Lorentz Force Laboratory 2: Lorentz Force In 1897, only 120 years ago, J.J. Thomson
ECRH on the Levitated Dipole Experiment
 ECRH on the Levitated Dipole Experiment S. Mahar, J. Kesner, A.C. Boxer, J.E. Ellsworth, I. Karim, A. Roach MIT PSFC A.K. Hansen, D.T. Garnier, M.E. Mauel, E.E.Ortiz Columbia University Presented at the
ECRH on the Levitated Dipole Experiment S. Mahar, J. Kesner, A.C. Boxer, J.E. Ellsworth, I. Karim, A. Roach MIT PSFC A.K. Hansen, D.T. Garnier, M.E. Mauel, E.E.Ortiz Columbia University Presented at the
Lecture 19 Optical Characterization 1
 Lecture 19 Optical Characterization 1 1/60 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June). Homework 6/6: Will be online
Lecture 19 Optical Characterization 1 1/60 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June). Homework 6/6: Will be online
EC 1402 Microwave Engineering
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC 1402 Microwave Engineering
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC 1402 Microwave Engineering
Overview of experiments and projects
 Overview of experiments and projects Pathways: Experiments Experiment EE ECE Media Eng D: Op Amps 1 1 F: Digital Communications 1 1 1 S: Pulses and Bandwidth 1 J: Transformers 1 K: Wave Propagation 1 Software
Overview of experiments and projects Pathways: Experiments Experiment EE ECE Media Eng D: Op Amps 1 1 F: Digital Communications 1 1 1 S: Pulses and Bandwidth 1 J: Transformers 1 K: Wave Propagation 1 Software
Navy Electricity and Electronics Training Series
 NONRESIDENT TRAINING COURSE Navy Electricity and Electronics Training Series Module 11 Microwave Principles NAVEDTRA 14183 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
NONRESIDENT TRAINING COURSE Navy Electricity and Electronics Training Series Module 11 Microwave Principles NAVEDTRA 14183 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
MICROWAVE MICROWAVE TRAINING BENCH COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS:
 Microwave section consists of Basic Microwave Training Bench, Advance Microwave Training Bench and Microwave Communication Training System. Microwave Training System is used to study all the concepts of
Microwave section consists of Basic Microwave Training Bench, Advance Microwave Training Bench and Microwave Communication Training System. Microwave Training System is used to study all the concepts of
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II
 Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY
 BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY
 BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
BASIC ELECTRICITY/ APPLIED ELECTRICITY PREAMBLE This examination syllabus has been evolved from the Senior Secondary School Electricity curriculum. It is designed to test candidates knowledge and understanding
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad 500014. Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SUB: MICROWAVE ENGINEERING SECTION: ECE IV A & B NAME OF THE FACULTY: S RAVI KUMAR,T.SUDHEER
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad 500014. Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SUB: MICROWAVE ENGINEERING SECTION: ECE IV A & B NAME OF THE FACULTY: S RAVI KUMAR,T.SUDHEER
10 GHz Microwave Link
 10 GHz Microwave Link Project Project Objectives System System Functionality Testing Testing Procedures Cautions and Warnings Problems Encountered Recommendations Conclusion PROJECT OBJECTIVES Implement
10 GHz Microwave Link Project Project Objectives System System Functionality Testing Testing Procedures Cautions and Warnings Problems Encountered Recommendations Conclusion PROJECT OBJECTIVES Implement
Chapter 21. Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal
EE320L Electronics I. Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #4. Diode Rectifiers and Power Supply Circuits. Angsuman Roy
 EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #4 Diode Rectifiers and Power Supply Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective:
EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #4 Diode Rectifiers and Power Supply Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective:
LNB and its ham radio usage
 http://ea4eoz.blogspot.gr/2012/09/lnb-and-its-ham-radio-usage.html LNB and its ham radio usage The letters LNB means Low Noise Block, but we must call it LNC, this is Low Noise Converter, because a LNB
http://ea4eoz.blogspot.gr/2012/09/lnb-and-its-ham-radio-usage.html LNB and its ham radio usage The letters LNB means Low Noise Block, but we must call it LNC, this is Low Noise Converter, because a LNB
Maltase cross tube. D. Senthilkumar P a g e 1
 Thermionic Emission Maltase cross tube Definition: The emission of electrons when a metal is heated to a high temperature Explanation: In metals, there exist free electrons which are able to move around
Thermionic Emission Maltase cross tube Definition: The emission of electrons when a metal is heated to a high temperature Explanation: In metals, there exist free electrons which are able to move around
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL BANK Name : MICROWAVE ENGINEERING Code : A70442 Class : IV B. Tech I
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL BANK Name : MICROWAVE ENGINEERING Code : A70442 Class : IV B. Tech I
Projects in microwave theory 2009
 Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Intermediate Physics PHYS102
 Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
UNIT - V WAVEGUIDES. Part A (2 marks)
 Part A (2 marks) UNIT - V WAVEGUIDES 1. What is the need for guide termination? (Nov / Dec 2011) To avoid reflection loss. The termination should provide a wave impedance equal to that of the transmission
Part A (2 marks) UNIT - V WAVEGUIDES 1. What is the need for guide termination? (Nov / Dec 2011) To avoid reflection loss. The termination should provide a wave impedance equal to that of the transmission
Circuit Components Lesson 4 From: Emergency Management Ontario
 4.1 Amplifier Fundamentals The role of a amplifier is to produce an output which is an enlarged reproduction of the features of the signal fed into the input. The increase in signal by an amplifier is
4.1 Amplifier Fundamentals The role of a amplifier is to produce an output which is an enlarged reproduction of the features of the signal fed into the input. The increase in signal by an amplifier is
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR. By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Third Edition by J.
 PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
S-band Magnetron. Tuner revolutions to cover frequency range 4.75 (note 3) Mounting position (note 4) Any Cooling (note 5) Water
 S-band Magnetron GENERAL DESCRIPTION is a mechanical tuned pulsed type S-band magnetron intended primarily for linear accelerator. It is water cooled and has circle waveguide output type. It is designed
S-band Magnetron GENERAL DESCRIPTION is a mechanical tuned pulsed type S-band magnetron intended primarily for linear accelerator. It is water cooled and has circle waveguide output type. It is designed
Analysis and Minimizing Strategies for Conducted Emission from Power Supply Cable of GPS Based Vehicle Tracking System
 Analysis and Minimizing Strategies for Conducted Emission from Power Supply Cable of GPS Based Vehicle Tracking System Shreenivas Jog and M. S. Sutaone Dept. of E and TC, College of Engineering, Pune,
Analysis and Minimizing Strategies for Conducted Emission from Power Supply Cable of GPS Based Vehicle Tracking System Shreenivas Jog and M. S. Sutaone Dept. of E and TC, College of Engineering, Pune,
Renewable Energy Based Interleaved Boost Converter
 Renewable Energy Based Interleaved Boost Converter Pradeepakumara V 1, Nagabhushan patil 2 PG Scholar 1, Professor 2 Department of EEE Poojya Doddappa Appa College of Engineering, Kalaburagi, Karnataka,
Renewable Energy Based Interleaved Boost Converter Pradeepakumara V 1, Nagabhushan patil 2 PG Scholar 1, Professor 2 Department of EEE Poojya Doddappa Appa College of Engineering, Kalaburagi, Karnataka,
EMC Amplifiers Going Beyond the Basics to Ensure Successful Immunity Tests
 EMC Amplifiers Going Beyond the Basics to Ensure Successful Immunity Tests Paul Denisowski, Application Engineer Broadband amplifiers are used to generate the high field strengths required by EMC radiated
EMC Amplifiers Going Beyond the Basics to Ensure Successful Immunity Tests Paul Denisowski, Application Engineer Broadband amplifiers are used to generate the high field strengths required by EMC radiated
CHAPTER 6 EMI EMC MEASUREMENTS AND STANDARDS FOR TRACKED VEHICLES (MIL APPLICATION)
 147 CHAPTER 6 EMI EMC MEASUREMENTS AND STANDARDS FOR TRACKED VEHICLES (MIL APPLICATION) 6.1 INTRODUCTION The electrical and electronic devices, circuits and systems are capable of emitting the electromagnetic
147 CHAPTER 6 EMI EMC MEASUREMENTS AND STANDARDS FOR TRACKED VEHICLES (MIL APPLICATION) 6.1 INTRODUCTION The electrical and electronic devices, circuits and systems are capable of emitting the electromagnetic
Chapter 3 SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODE
 Chapter 3 SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODE 1 Inventor of Zener Diode Clarence Melvin Zener was a professor at Carnegie Mellon University in the department of Physics. He developed the Zener Diode in 1950 and employed
Chapter 3 SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODE 1 Inventor of Zener Diode Clarence Melvin Zener was a professor at Carnegie Mellon University in the department of Physics. He developed the Zener Diode in 1950 and employed
Revised April Unit/Standard Number. Proficiency Level Achieved: (X) Indicates Competency Achieved to Industry Proficiency Level
 Unit/Standard Number Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of state,
Unit/Standard Number Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of state,
SHORT QUESTIONS MICROWAVE ENGINEERING UNIT I
 SHORT QUESTIONS MICROWAVE ENGINEERING UNIT I 1. Define Microwave. Microwaves are generally described as electromagnetic waves with frequencies that range from approximately 1GHz to 300 GHz. Therefore,
SHORT QUESTIONS MICROWAVE ENGINEERING UNIT I 1. Define Microwave. Microwaves are generally described as electromagnetic waves with frequencies that range from approximately 1GHz to 300 GHz. Therefore,
The Electro-Magnetic Spectrum
 The Electro-Magnetic Spectrum Part Three In This Issue: All about Tubes How a diode rectifier works How a triode amplifier works How the mixer in your receiver works Dear Friends: For quite some time I
The Electro-Magnetic Spectrum Part Three In This Issue: All about Tubes How a diode rectifier works How a triode amplifier works How the mixer in your receiver works Dear Friends: For quite some time I
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING
 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING SANJEEVA GUPTA B.Sc. (Electrical) Electronics Engineering DINESH ARORA B.Sc. (Electrical) Electronics Engineering SATYA BHUSHAN SARNA B.Sec. (Electrical)Electronics Engineering PRASHANT
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING SANJEEVA GUPTA B.Sc. (Electrical) Electronics Engineering DINESH ARORA B.Sc. (Electrical) Electronics Engineering SATYA BHUSHAN SARNA B.Sec. (Electrical)Electronics Engineering PRASHANT
REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING
 1 REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING INTRODUCTION EMI Testing 1. Whether a product is intended for military, industrial, commercial or residential use, while it must perform its intended function in
1 REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING INTRODUCTION EMI Testing 1. Whether a product is intended for military, industrial, commercial or residential use, while it must perform its intended function in
Learning Material Ver 1.1
 SCR Triggering Circuits Scientech 2702 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100,
SCR Triggering Circuits Scientech 2702 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100,
Revised April Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018
 Unit/Standard Number High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018 Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100
Unit/Standard Number High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018 Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100
Exercise 1-4. The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS
 Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Electron Spin Resonance v2.0
 Electron Spin Resonance v2.0 Background. This experiment measures the dimensionless g-factor (g s ) of an unpaired electron using the technique of Electron Spin Resonance, also known as Electron Paramagnetic
Electron Spin Resonance v2.0 Background. This experiment measures the dimensionless g-factor (g s ) of an unpaired electron using the technique of Electron Spin Resonance, also known as Electron Paramagnetic
Turn off all electronic devices
 Radio 1 Radio 2 Observations about Radio Radio It can transmit sound long distances wirelessly It involve antennas It apparently involves electricity and magnetism Its reception depends on antenna positioning
Radio 1 Radio 2 Observations about Radio Radio It can transmit sound long distances wirelessly It involve antennas It apparently involves electricity and magnetism Its reception depends on antenna positioning
Note 2 Electromagnetic waves N2/EMWAVES/PHY/XII/CHS2012
 ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic waves include visible light waves, X-rays, gamma rays, radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet and infrared waves. The classification of em waves according to frequency
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic waves include visible light waves, X-rays, gamma rays, radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet and infrared waves. The classification of em waves according to frequency
Technician Licensing Class T6
 Technician Licensing Class T6 Amateur Radio Course Monroe EMS Building Monroe, Utah January 11/18, 2014 January 22, 2014 Testing Session Valid dates: July 1, 2010 June 30, 2014 Amateur Radio Technician
Technician Licensing Class T6 Amateur Radio Course Monroe EMS Building Monroe, Utah January 11/18, 2014 January 22, 2014 Testing Session Valid dates: July 1, 2010 June 30, 2014 Amateur Radio Technician
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Why can t conventional tubes be used at microwave frequencies? Conventional tubes can t be used at microwave frequencies because of transit time effect.
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Why can t conventional tubes be used at microwave frequencies? Conventional tubes can t be used at microwave frequencies because of transit time effect.
Unit/Standard Number. LEA Task # Alignment
 1 Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding
1 Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
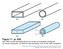 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Ground. Input: 0-24VDC
 High Voltage Power Supply General Description The high voltage power supplies are designed to provide very high output voltages. They provide isolated outputs of up 50 kv with power levels to 20 Watts
High Voltage Power Supply General Description The high voltage power supplies are designed to provide very high output voltages. They provide isolated outputs of up 50 kv with power levels to 20 Watts
Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research
 International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2, March 2016 Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research Bowen Li and Yongsheng Dai Abstract
International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2, March 2016 Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research Bowen Li and Yongsheng Dai Abstract
FCC Technician License Course
 FCC Technician License Course 2014-2018 FCC Element 2 Technician Class Question Pool Presented by: Tamiami Amateur Radio Club (TARC) WELCOME To the SECOND of 4, 3-hour classes presented by TARC to prepare
FCC Technician License Course 2014-2018 FCC Element 2 Technician Class Question Pool Presented by: Tamiami Amateur Radio Club (TARC) WELCOME To the SECOND of 4, 3-hour classes presented by TARC to prepare
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) Proceedings of the 2 nd International Conference on Current Trends in Engineering and Management ICCTEM -2014 ISSN 0976 6545(Print)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) Proceedings of the 2 nd International Conference on Current Trends in Engineering and Management ICCTEM -2014 ISSN 0976 6545(Print)
Technician License Course Chapter 2 Radio and Signals Fundamentals
 Technician License Course Chapter 2 Radio and Signals Fundamentals Handling Large and Small Numbers Electronics and Radio use a large range of sizes, i.e., 0.000000000001 to 1000000000000. Scientific Notation
Technician License Course Chapter 2 Radio and Signals Fundamentals Handling Large and Small Numbers Electronics and Radio use a large range of sizes, i.e., 0.000000000001 to 1000000000000. Scientific Notation
MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS
 MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS M. Hawley 1, S. Farhat 1, B. Shanker 2, L. Kempel 2 1 Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Michigan State University;
MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS M. Hawley 1, S. Farhat 1, B. Shanker 2, L. Kempel 2 1 Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Michigan State University;
Hidden Active Cellphone Detector.
 Hidden Active Cellphone Detector Introduction: It is a handy, pocket-size mobile transmission detector or sniffer. It is a circuit for a mobile transmission detector which can detect use of a mobile phone
Hidden Active Cellphone Detector Introduction: It is a handy, pocket-size mobile transmission detector or sniffer. It is a circuit for a mobile transmission detector which can detect use of a mobile phone
Γ L = Γ S =
 TOPIC: Microwave Circuits Q.1 Determine the S parameters of two port network consisting of a series resistance R terminated at its input and output ports by the characteristic impedance Zo. Q.2 Input matching
TOPIC: Microwave Circuits Q.1 Determine the S parameters of two port network consisting of a series resistance R terminated at its input and output ports by the characteristic impedance Zo. Q.2 Input matching
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth
 Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One
 MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
IJSER. Abstract. transfer electrical power from a source to a device without the aid of wires. Introduction
 Wireless Power Transfer : The future 942 Abstract AGUBOSHIM, Emmanuel Chukwujioke Postgraduate student, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Anambra State, Nigeria. aguboshimec@gmail.com The technology for
Wireless Power Transfer : The future 942 Abstract AGUBOSHIM, Emmanuel Chukwujioke Postgraduate student, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Anambra State, Nigeria. aguboshimec@gmail.com The technology for
Normal-conducting high-gradient rf systems
 Normal-conducting high-gradient rf systems Introduction Motivation for high gradient Order of 100 GeV/km Operational and state-of-the-art SwissFEL C-band linac: Just under 30 MV/m CLIC prototypes: Over
Normal-conducting high-gradient rf systems Introduction Motivation for high gradient Order of 100 GeV/km Operational and state-of-the-art SwissFEL C-band linac: Just under 30 MV/m CLIC prototypes: Over
6 Experiment II: Law of Reflection
 Lab 6: Microwaves 3 Suggested Reading Refer to the relevant chapters, 1 Introduction Refer to Appendix D for photos of the apparatus This lab allows you to test the laws of reflection, refraction and diffraction
Lab 6: Microwaves 3 Suggested Reading Refer to the relevant chapters, 1 Introduction Refer to Appendix D for photos of the apparatus This lab allows you to test the laws of reflection, refraction and diffraction
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
 LECTURE:2 ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic waves: In an electromagnetic wave the electric and magnetic fields are mutually perpendicular. They are also both perpendicular
LECTURE:2 ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic waves: In an electromagnetic wave the electric and magnetic fields are mutually perpendicular. They are also both perpendicular
Ground Penetrating Radar
 Ground Penetrating Radar Begin a new section: Electromagnetics First EM survey: GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) Physical Property: Dielectric constant Electrical Permittivity EOSC 350 06 Slide Di-electric
Ground Penetrating Radar Begin a new section: Electromagnetics First EM survey: GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) Physical Property: Dielectric constant Electrical Permittivity EOSC 350 06 Slide Di-electric
Ionization (gas filled) tubes
 Ionization (gas filled) tubes So far, we've explored tubes which are totally "evacuated" of all gas and vapor inside their glass envelopes, properly known as vacuum tubes. With the addition of certain
Ionization (gas filled) tubes So far, we've explored tubes which are totally "evacuated" of all gas and vapor inside their glass envelopes, properly known as vacuum tubes. With the addition of certain
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE: MICROWAVE & RADAR ENGINEERING (COURSE CODE: )
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE: MICROWAVE & RADAR ENGINEERING (COURSE CODE: 3351103) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics and
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE: MICROWAVE & RADAR ENGINEERING (COURSE CODE: 3351103) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics and
An acousto-electromagnetic sensor for locating land mines
 An acousto-electromagnetic sensor for locating land mines Waymond R. Scott, Jr. a, Chistoph Schroeder a and James S. Martin b a School of Electrical and Computer Engineering b School of Mechanical Engineering
An acousto-electromagnetic sensor for locating land mines Waymond R. Scott, Jr. a, Chistoph Schroeder a and James S. Martin b a School of Electrical and Computer Engineering b School of Mechanical Engineering
The Principle V(SWR) The Result. Mirror, Mirror, Darkly, Darkly
 The Principle V(SWR) The Result Mirror, Mirror, Darkly, Darkly 1 Question time!! What do you think VSWR (SWR) mean to you? What does one mean by a transmission line? Coaxial line Waveguide Water pipe Tunnel
The Principle V(SWR) The Result Mirror, Mirror, Darkly, Darkly 1 Question time!! What do you think VSWR (SWR) mean to you? What does one mean by a transmission line? Coaxial line Waveguide Water pipe Tunnel
LECTURE 20 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 20 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 20 2 25.6 The photon model of electromagnetic waves 25.7 The electromagnetic spectrum Radio waves and microwaves Infrared, visible light,
LECTURE 20 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 20 2 25.6 The photon model of electromagnetic waves 25.7 The electromagnetic spectrum Radio waves and microwaves Infrared, visible light,
Radar. Radio. Electronics. Television. .104f 4E011 UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES LOUISVILLE
 Electronics Radio Television.104f Radar UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES LOUISVILLE KENTUCKY REVISED 1967 4E011 1:1111E111611 COPYRIGHT 1956 UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES POWER SUPPLIES ASSIGNMENT 23
Electronics Radio Television.104f Radar UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES LOUISVILLE KENTUCKY REVISED 1967 4E011 1:1111E111611 COPYRIGHT 1956 UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES POWER SUPPLIES ASSIGNMENT 23
T6A4. Electrical components; fixed and variable resistors, capacitors, and inductors; fuses, switches, batteries
 Amateur Radio Technician Class Element Course Presentation ti ELEMENT SUB-ELEMENTS Technician Licensing Class Supplement T Electrical/Electronic Components Exam Questions, Groups T - FCC Rules, descriptions
Amateur Radio Technician Class Element Course Presentation ti ELEMENT SUB-ELEMENTS Technician Licensing Class Supplement T Electrical/Electronic Components Exam Questions, Groups T - FCC Rules, descriptions
Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and
 Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and optics p. 4 Communication systems p. 6 Radar systems p.
Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and optics p. 4 Communication systems p. 6 Radar systems p.
TAP 313-1: Polarisation of waves
 TAP 313-1: Polarisation of waves How does polarisation work? Many kinds of polariser filter out waves, leaving only those with a polarisation along the direction allowed by the polariser. Any kind of transverse
TAP 313-1: Polarisation of waves How does polarisation work? Many kinds of polariser filter out waves, leaving only those with a polarisation along the direction allowed by the polariser. Any kind of transverse
Crossed-Field Amplifier (Amplitron)
 Crossed-Field Amplifier (Amplitron) Figure 1: water-cooled Crossed-Field Amplifier L 4756A in its transport case Figure 2: Subset of the cycloidal electron paths into a Crossed-Field Amplifier Also other
Crossed-Field Amplifier (Amplitron) Figure 1: water-cooled Crossed-Field Amplifier L 4756A in its transport case Figure 2: Subset of the cycloidal electron paths into a Crossed-Field Amplifier Also other
Digital PWM Techniques and Commutation for Brushless DC Motor Control Applications: Review
 Digital PWM Techniques and Commutation for Brushless DC Motor Control Applications: Review Prof. S.L. Tade 1, Ravindra Sor 2 & S.V. Kinkar 3 Professor, Dept. of E&TC, PCCOE, Pune, India 1 Scientist, ARDE-DRDO,
Digital PWM Techniques and Commutation for Brushless DC Motor Control Applications: Review Prof. S.L. Tade 1, Ravindra Sor 2 & S.V. Kinkar 3 Professor, Dept. of E&TC, PCCOE, Pune, India 1 Scientist, ARDE-DRDO,
SAR REDUCTION IN SLOTTED PIFA FOR MOBILE HANDSETS USING RF SHIELD
 SAR REDUCTION IN SLOTTED PIFA FOR MOBILE HANDSETS USING RF SHIELD T. Anita Jones Mary 1 and C. S. Ravichandran 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication, Karunya University, Coimbatore, India 2 SSK
SAR REDUCTION IN SLOTTED PIFA FOR MOBILE HANDSETS USING RF SHIELD T. Anita Jones Mary 1 and C. S. Ravichandran 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication, Karunya University, Coimbatore, India 2 SSK
4/30/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Circuit CoCircuit Componentsmponents. Subelement G6. 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP Task Grid
 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Correlation Between Measured and Simulated Parameters of a Proposed Transfer Standard
 Correlation Between Measured and Simulated Parameters of a Proposed Transfer Standard Jim Nadolny AMP Incorporated ABSTRACT Total radiated power of a device can be measured using a mode stirred chamber
Correlation Between Measured and Simulated Parameters of a Proposed Transfer Standard Jim Nadolny AMP Incorporated ABSTRACT Total radiated power of a device can be measured using a mode stirred chamber
Projects in microwave theory 2017
 Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2017 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2017 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Study of 1-phase AC to DC controlled converter (both fully controlled And half controlled)
 Study of 1-phase AC to DC controlled converter (both fully controlled And half controlled) Object: To study the performances of single phase half-controlled bridge Rectifier. A. In configuration A. B.
Study of 1-phase AC to DC controlled converter (both fully controlled And half controlled) Object: To study the performances of single phase half-controlled bridge Rectifier. A. In configuration A. B.
Thermal Management of Solid-State RF Cooking Appliances
 Abstract Thermal Management of Solid-State RF Cooking Appliances Ben Zickel CTO, Goji Research Ltd., Kfar Sava, Israel E-mail: benz@gojisolutions.com Recent advances in solid state LDMOS and GaN power
Abstract Thermal Management of Solid-State RF Cooking Appliances Ben Zickel CTO, Goji Research Ltd., Kfar Sava, Israel E-mail: benz@gojisolutions.com Recent advances in solid state LDMOS and GaN power
The ETO-Alpha 89 ETO-Alpha 89
 ETO-Alpha 89 The 89 was produced from 12/92 to 9/2000, 408 units were built during this time. These units were much like the 86, but with many updates and refinements. The 89 uses a pair of 3CX800A7 triodes
ETO-Alpha 89 The 89 was produced from 12/92 to 9/2000, 408 units were built during this time. These units were much like the 86, but with many updates and refinements. The 89 uses a pair of 3CX800A7 triodes
070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE
 070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The trade will be examined under the following components or subject grouping: Electronic Devices and Circuit, Radio Communication and Television. EXAMINATION
070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The trade will be examined under the following components or subject grouping: Electronic Devices and Circuit, Radio Communication and Television. EXAMINATION
A NOVEL DUAL-BAND PATCH ANTENNA FOR WLAN COMMUNICATION. E. Wang Information Engineering College of NCUT China
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 6, 93 102, 2009 A NOVEL DUAL-BAND PATCH ANTENNA FOR WLAN COMMUNICATION E. Wang Information Engineering College of NCUT China J. Zheng Beijing Electro-mechanical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 6, 93 102, 2009 A NOVEL DUAL-BAND PATCH ANTENNA FOR WLAN COMMUNICATION E. Wang Information Engineering College of NCUT China J. Zheng Beijing Electro-mechanical
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS. Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum
 PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
Simulation of the Near-field of a Ferrite Antenna
 Simulation of the Near-field of a Ferrite Antenna Alexey A. Kalmykov, Kirill D. Shaidurov, and Stanislav O. Polyakov Ural Federal University named after the first President of Russia B.N.Yeltsin Ekaterinburg,
Simulation of the Near-field of a Ferrite Antenna Alexey A. Kalmykov, Kirill D. Shaidurov, and Stanislav O. Polyakov Ural Federal University named after the first President of Russia B.N.Yeltsin Ekaterinburg,
Microwave Circuit Design and Measurements Lab. INTRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS: DETECTION OF RF POWER AND STANDING WAVES Lab #2
 EE 458/558 Microwave Circuit Design and Measurements Lab INTRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS: DETECTION OF RF POWER AND STANDING WAVES Lab #2 The purpose of this lab is to gain a basic understanding
EE 458/558 Microwave Circuit Design and Measurements Lab INTRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS: DETECTION OF RF POWER AND STANDING WAVES Lab #2 The purpose of this lab is to gain a basic understanding
Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION. Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti. Radar Signal Processing 1. Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti
 Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION 1 Radar Introduction. A brief history. Simplified Radar Block Diagram. Two basic Radar Types. Radar Wave Modulation. 2 RADAR The term radar is an acronym for the phrase RAdio Detection
Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION 1 Radar Introduction. A brief history. Simplified Radar Block Diagram. Two basic Radar Types. Radar Wave Modulation. 2 RADAR The term radar is an acronym for the phrase RAdio Detection
Developme nt of Active Phased Array with Phase-controlled Magnetrons
 Developme nt of Active Phased Array with Phase-controlled Magnetrons Naoki SHINOHARA, Junsuke FUJIWARA, and Hiroshi MATSUMOTO Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 611-0011,
Developme nt of Active Phased Array with Phase-controlled Magnetrons Naoki SHINOHARA, Junsuke FUJIWARA, and Hiroshi MATSUMOTO Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 611-0011,
Experiment 12: Microwaves
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 OBJECTIVES Experiment 12: Microwaves To observe the polarization and angular dependence of radiation from a microwave generator
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 OBJECTIVES Experiment 12: Microwaves To observe the polarization and angular dependence of radiation from a microwave generator
List of Figures. Sr. no.
 List of Figures Sr. no. Topic No. Topic 1 1.3.1 Angle Modulation Graphs 11 2 2.1 Resistor 13 3 3.1 Block Diagram of The FM Transmitter 15 4 4.2 Basic Diagram of FM Transmitter 17 5 4.3 Circuit Diagram
List of Figures Sr. no. Topic No. Topic 1 1.3.1 Angle Modulation Graphs 11 2 2.1 Resistor 13 3 3.1 Block Diagram of The FM Transmitter 15 4 4.2 Basic Diagram of FM Transmitter 17 5 4.3 Circuit Diagram
Pulsed 5 MeV standing wave electron linac for radiation processing
 PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 7, 030101 (2004) Pulsed 5 MeV standing wave electron linac for radiation processing L. Auditore, R. C. Barnà, D. De Pasquale, A. Italiano,
PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 7, 030101 (2004) Pulsed 5 MeV standing wave electron linac for radiation processing L. Auditore, R. C. Barnà, D. De Pasquale, A. Italiano,
