TX ENABLE TX PS V BIAS TX DATA DATA RETIME & LEVEL SHIFT CLOCK DIVIDER RX CIRCUIT CONTROL FILTER
|
|
|
- Loreen Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
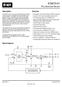
1 COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS DATA BULLETIN MX589 Features Data Rates from 4kbps to 64kbps Full or Half Duplex Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) Operation Selectable BT: (0.3 or 0.5) Low Power 3.0V, 20kbps, 1.5mA typ. 5.0V, 64kbps, 4.0mA typ. Low Current Non-DSP Solution Small TSSOP size fits PCMCIA / PC CARDs Applications Point of Sale Terminals Low Power Wireless Data Link for PCs, Laptops, and Printers Data for GPS/Differential GPS Portable Wireless Data Applications Cellular Digital Packet Data (CDPD) Mobitex Mobile Data System TX ENABLE TX PS V BIAS V BIAS TX DATA XTAL/CLOCK XTAL ClkDIVA ClkDIVB BT V DD RXHold PLLacq RXDCacq DATA RETIME & LEVEL SHIFT CLOCK DIVIDER RX CIRCUIT CONTROL TX FILTER RX DATA DETECTION RX S/N DETECTION RX CLOCK TX OUT TX CLK RX DATA RX S/N RX CLK RX PS RX SIGNAL IN RX FEEDBACK V BIAS + - RX FILTER RX DC LEVEL MEASURE DOC1 DOC2 V SS V BIAS The MX589 is a single-chip synchronous modem designed for Wireless Data Applications. Employing Gaussian Minimum shift Keying (GMSK) baseband modulation, the MX589 features a wide range of available data rates: 4k to 64kbps. Data Rates and the choice of BT (0.3 or 0.5) are pin programmable to provide for different system requirements. The Tx and Rx digital data interfaces are bit serial, synchronized to Tx and Rx data clocks generated by the modem. Separate Tx and Rx Powersave inputs allow full or half-duplex operation. Rx input levels can be set by suitable AC and DC level adjusting circuitry built with external components around an on-chip Rx Input Amplifier. Acquisition, Lock, and Hold of Rx data signals are made easier and faster by the use of Rx Control Inputs to clamp, detect, and /or hold input data levels and can be set by the μprocessor as required. The Rx S/N output provides an indication of the quality of the received signal. The MX589 may be used with a 3.0V to 5.5V power supply and is available in the following packages: 24-pin TSSOP (MX589TN), 24-pin SOIC (MX589DW), and 24-pin PDIP (MX589P).
2 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 2 of 20 MX589 Section Contents Page 1 Block Diagram Signal List External Components General Description Clock Oscillator Divider Receive Rx Signal Path Description Rx Circuit Control Modes Rx Clock Extraction Rx Data Extraction Rx S/N Detection Rx Signal Quality Transmit TX Signal Path Description Data Formats Acquisition and Hold Modes Application Radio Channel Requirements Bit Rate, BT, and Bandwidth FM Modulator, Demodulator and IF Two-Point Modulation AC Coupling of Tx and Rx Signals Performance Specifications Electrical Specifications Absolute Maximum Limits Operating Limits Operating Characteristics Packages...19 MXCOM, Inc. reserves the right to change specifications at any time without notice.
3 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 3 of 20 MX589 1 Block Diagram TX ENABLE TX PS V BIAS V BIAS TX DATA XTAL/CLOCK XTAL ClkDIVA ClkDIVB BT V DD RXHold PLLacq RXDCacq DATA RETIME & LEVEL SHIFT CLOCK DIVIDER RX CIRCUIT CONTROL TX FILTER RX DATA DETECTION RX S/N DETECTION RX CLOCK TX OUT TX CLK RX DATA RX S/N RX CLK RX PS RX SIGNAL IN RX FEEDBACK V BIAS + - RX FILTER RX DC LEVEL MEASURE DOC1 DOC2 V SS V BIAS Figure 1: Block Diagram RX Frequency Discriminator Frequency Modulator DC Level Adjust RX Sig In RX Filter and Gain RX Feedback Signal and DC Level Adjustment RX circuits TX circuits TX Out ucontroller or UART RXD RXC TXD TXC RX Data RX Clock TX Data TX Clock MX589 GMSK MODEM TX Out Filter Figure 2: System Block Diagram
4 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 4 of 20 MX589 2 Signal List Pin No. Signal Type Description TN/DW/P 1 XTAL output The output of the on-chip clock oscillator. 2 XTAL/CLOCK input The input to the on-chip Xtal oscillator. A Xtal, or externally derived clock (f XTAL ) pulse input should be connected here. If an externally generated clock is to be used, it should be connected to this pin and the XTAL pin left unconnected. Note: Operation of the MX589 without a suitable Xtal or clock input may cause device damage. 3 ClkDivA input Logic level inputs control the internal clock divider and therefore, the transmit and receive data rate. See Table 4. 4 ClkDivB input Logic level inputs control the internal clock divider and therefore, the transmit and receive data rate. See Table 4. 5 Rx HOLD input A logic 0 applied to this input will freeze the Clock Extraction and Level Measurement circuits unless they are in Acquire mode. 6 RxDCacq input A logic 1 applied to this input will set the RX Level Measurement circuitry to the Acquire mode. 7 PLLacq input A logic 1 applied to this input will set the RX Clock Extraction circuitry to the Acquire mode. See Table 5. 8 Rx PSAVE input A logic 1 applied to this input will powersave all receive circuits except for RXCLK output (which will continue at the set bit-rate) and cause the RX Data and RX S/N outputs to go to a logic 0. 9 V BIAS The internal circuitry bias line, held at V DD /2. This pin must be bypassed to V SS by a capacitor mounted close to the pin. 10 Rx FB Output of the RX Input Amplifier. 11 Rx Signal In input Input to RX input amplifier. 12 V SS power Negative supply (GND). 13 DOC1 Connections to the RX Level Measurement Circuitry. A capacitor should be connected from each pin to V SS. 14 DOC2 Connections to the RX Level Measurement Circuitry. A capacitor should be connected from each pin to V SS. 15 BT A logic level to select the modem BT (the ratio of the TX Filter's -3dB frequency to the Bit-Rate). A logic 1 = BT of 0.5 and a logic 0 = BT of Tx Out output The TX signal output from the MX589 GMSK Modem. 17 Tx Enable input A logic 1 applied to this input, enables the transmit data path, through the TX Filter to the TX Out pin. A logic 0 will place the TX Out pin to VBIAS via a high impedance. 18 Tx PSAVE input A logic 1 applied to this input will powersave all transmit circuits except for the TX Clock. 19 Tx Data input The logic level input for the data to be transmitted. This data should be synchronous with TX CLK. 20 Rx Data output A logic level output carrying the received data, synchronous with RX CLK. 21 Rx CLK output A logic level clock output at the received data bit-rate. 22 Tx CLK output A logic level clock output at the transmit-data rate. 23 Rx S/N output A logic level output which may be used as an indication of the quality of the received signal. 24 V DD power Positive supply. A single 5.0V power supply is required. Levels and voltages within this modem are dependent upon this supply. This pin should be bypassed to V SS by a capacitor mounted close to the pin. Table 1: Signal List
5 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 5 of 20 MX589 3 External Components XTAL C3 X1 R2 C2 XTAL/CLOCK C5 R4 R3 1 2 C6 XTAL XTAL/CLOCK ClkDivA ClkDivB RX HOLD RXDCacq PLLacq RX PSAVE V BIAS RX FB RX SIGNAL IN V SS MX V DD RX S/N TXCLK RXCLK RXDATA TXDATA TXPSAVE TXENABLE TXOUT BT DOC1 DOC2 R1 C4 V DD C7 C8 C1 Figure 3: Recommended External Components Component Notes Value Tolerance Component Notes Value Tolerance R1 Note 1 ±5% C4 0.1µF ±20% R2 1.0MΩ ±10% C5 1.0µF ±20% R3 Note 2 ±10% C6 22.0pF ±20% R4 100kΩ ±10% C7 Note 4 C1 Note 1 ±10% C8 Note 4 C2 Note 3 C3 Note 3 X1 Note 5 Table 2: Recommended External Components
6 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 6 of 20 MX589 Recommended External Component Notes: 1. The RC network formed by R1 and C1 is required between the TX Out pin and the input to the modulator. This network, which can form part of any DC level shifting and gain adjustment circuitry, forms an important part of the transmit signal filtering. The ground connection to the capacitor C1 should be positioned to give maximum attenuation of high-frequency noise into the modulator. The component values should be chosen so that the product of the resistance and the capacitance is: For a BT of 0.3 For a BT of 0.5 R1C1 = 0.34/bit rate (bps) R1C1 = 0.22/bit rate (bps) Data Rates BT =- 0.3 BT = 0.5 (bps) R1 C1 R1 C kΩ 680pF 120kΩ 470pF kΩ 680pF 100kΩ 470pF kΩ 470pF 120kΩ 220pF kΩ 390pF 47kΩ 470pF kΩ 470pF 91kΩ 150pF kΩ 180pF 91kΩ 120pF 32,000 47kΩ 220pF 47kΩ 150pF 38,400 * 47kΩ 180pF 47kΩ 120pF 64,000 * 56kΩ 100pF 51kΩ 68pF * V DD 4.5V Table 3: Data Rate vs. BT and Selected External Component Values Note: In all cases, the value of R1 should not be less than 20.0kΩ, and that the calculated value of C1 includes calculated parasitic capacitance. 2. R3, R4 and C6 form the gain components for the RX Input signal. R3 should be chosen as required by the signal input level. 3. The values chosen for C2 and C3 (including stray capacitance), should be suitable for the applied V DD and the frequency of X1. As a guide: C2 = C3 = 33pF at 1.0MHz falling to 18pF at the maximum frequency. At 3.0V, C2 = C3 = 33pF falling to 18pF at 5.0MHz the equivalent series resistance of X1 should be less than 2.0KΩ falling to 150Ω at the maximum frequency. Stray capacitance on the Xtal/Clock circuit pins must be minimized. 4. C7 and C8 should both be.015μf for a data rate of 8kbps, and inversely proportional to the data rate for other data rates, e.g..030μf at 4kbps, 1800pF at 64kbps. 5. The MX589 can operate correctly with the Xtal/Clock frequencies between 1.0MHz and 8.2MHz (V DD = 5.0V) and 1.0MHz to 5.0MHz (V DD = 3.0V) see Table 1 for examples. For best results, a crystal oscillator design should drive the clock inverter input with signal levels of at least 40% of V DD, peak to peak. Tuning fork crystals generally cannot meet this requirement. To obtain crystal oscillator design assistance, consult your crystal manufacturer. Operation of this device without a Xtal or Clock input may cause device damage.
7 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 7 of 20 MX589 4 General Description 4.1 Clock Oscillator Divider The TX and (nominal) RX data rates are determined by division of the frequency present at the Xtal pin, which may be generated by the on-chip Xtal oscillator or derived from an external source. Any Xtal/Clock frequency in the range of 1.0MHz to 5.0MHz for V DD = 3.0V, or 1.0MHz to 8.2MHz for V DD = 5.0V may be used, depending on the desired data rate. The division ratio is controlled by the logic level inputs on ClkDivA and ClkDivB pins as shown in Table 4, together with an indication of how various standard data rates may be derived from common µp Xtal frequencies. Data Rate = Xtal/Clk Frequency Division Ratio (ClkDiv Xtal/Clock Frequency (MHz) Inputs Division Ratio / / /3 ClkDivA ClkDivB Xtal Frequency Data Rate Data Rate (bps) * 38400* * V DD 4.5V Table 4: Clock/Data Rates Note: The device operation is not guaranteed above 64kbps or below 4kbps at the relevant supply voltage. A/B) MHz SETTINGS: D/RATE 4800 bps -BT Rx and Tx Enabled XTAL/CLOCK V DD XTAL Tx Enable SERIAL I/O PORT μcontroller RxD RxC TxD TxC Rx DATA Rx CLOCK Tx ClOCK Tx DATA PLLacq RxDCacq MX589 GMSK MODEM ClkDIVA ClkDIVB BT RxHOLD Rx S/N Tx PS Rx PS Figure 4: Minimum μcontroller System Connections 4.2 Receive Rx Signal Path Description The function of the RX circuitry is to: 1. Set the incoming signal to a usable level. 2. Clean the signal by filtering. 3. Provide DC level thresholds for clock and data extraction. 4. Provide clock timing information for data extraction and external circuits. 5. Provide RX data in a binary form. 6. Assess signal quality and provide Signal-to-Noise information.
8 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 8 of 20 MX589 The output of the radio receiver's Frequency Discriminator should be fed to the MX589's RX Filter by a suitable gain and DC level adjusting circuit. This circuit can be built with external components around the onchip RX Input Amplifier. The gain should be set so that the signal level at the RX Feedback pin is nominally 1V peak to peak (for V DD =5.0V) centered around V BIAS when receiving a continuous data pattern. Positive going signal excursions at RX Feedback pin will produce a logic 0 at the RX Data Output. Negative going excursions will produce a logic 1. The received signal is fed through the lowpass RX Filter, which has a -3dB corner frequency of 0.56 times the data bit-rate, before being applied to the Level Measure and Clock and Data extraction blocks. The Level Measuring block consists of two voltage detectors, one of which measures the amplitude of the positive parts of the received signal. The other measures the amplitude of the negative portions. (Positive refers to signal levels higher than V DD /2, and negative to levels lower than V DD /2.) External capacitors are used by these detectors, via the Doc1 & Doc2 pins, to form voltage hold or integrator circuits. These two levels are then used to establish the optimum DC level decision-thresholds for the Clock and Data extraction, depending upon the RX signal amplitude and any DC offset Rx Circuit Control Modes The operating characteristics of the Rx Level Measurement and Clock Extraction circuits are controlled, as shown in Table 5, by logic level inputs applied to the PLLacq, Rx HOLD, and RxDCacq pins to suit a particular application, or to cope with changing reception conditions, reference Figure 5. In general, a data transmission will begin with a preamble, for example, , to allow the receive modem to establish timing and level-lock as quickly as possible. After the Rx carrier has been detected, and during the time that the preamble is expected, the RxDCacq and PLLacq Inputs should be switched from a logic 0 to a logic 1 so that the Level Measuring and Clock Extraction modes are operated and sequenced as shown. The Rx HOLD input should normally be held at a logic 1 while data is being received, but may be driven to a logic 0 to freeze the Level Measuring Clock Extraction circuits during a fade. If a fade lasts for less than 200 bit periods, normal operation can be resumed by returning the Rx HOLD input to a logic 1 at the end of the fade. For longer fades, it may be better to reset the Level Measuring circuits by placing the RxDCacq to a logic 1 for 10 to 20 bit periods. Rx HOLD has no effect on the Level Measuring circuits while RxDCacq is at a logic 1, and has no effect on the PLL while PLLacq is at a logic 1. A logic 0 on Rx HOLD does not disable the Rx Clock output, and the Rx Data Extraction and S/N Detector circuits will continue to operate. Rx Signal Input PREAMBLE DATA Rx CARRIER DET (RSSI) Input RxDCacq Rx LEVEL MEASURE MODE CLAMP FAST PEAK DETECT AVERAGING PEAK DETECT PLLacq CLOCK EXTRACTION CCT MODE ACQUIRE 30 BITS MEDIUM BANDWIDTH NARROW BANDWIDTH Figure 5: Rx Mode Control Diagram
9 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 9 of 20 MX589 PLLacq Rx HOLD PLL Action 1 1 Acquire Sets the PLL bandwidth wide enough to allow a lock to the received signal in less than 8 zero crossings. This mode will operate as long as PLLacq is a logic 1. 1 to 0 1 Medium Bandwidth 0 1 Narrow Bandwidth The correction applied to the extracted clock is limited to a maximum of ±1/16th bit-period for every two received zero-crossings. The PLL operates in this mode for a period of about 30 bits immediately following a 1 to 0 transition of the PLLacq input, provided that the Rx HOLD input is a logic 1. The correction applied to the extracted clock is limited to a maximum of ±1/64th bit-period for every two received zero-crossings. The PLL operates in this mode whenever the Rx HOLD Input is a logic 1 and PLLacq has been a logic 0 for at least 30 bit periods (after Medium Bandwidth operation for instance). 0 0 Hold The PLL feedback loop is broken, allowing the RX Clock to freewheel during signal fade periods. RxDCacq Rx HOLD Rx Level Measure Action 0 to 1 X Clamp Operates for one bit-time after a 0 to 1 transition of the RXDCacq input. The external capacitors are rapidly charged towards a voltage mid-way between the received signal input level and VBIAS, with the charge time-constant being of the order of 0.5bit-time. 1 X Fast Peak Detect 0 1 Averaging Peak Detect The voltage detectors act as peak-detectors, one capacitor is used to capture the positive-going signal peaks of the RX Filter output signal and the other capturing the negative-going peaks. The detectors operate in this mode whenever the RXDCacq input is at a logic 1, except for the initial 1-bit Clamp-mode time. Provides a slower but more accurate measurement of the signal peak amplitudes. 0 0 Hold The capacitor charging circuits are disabled so that the outputs of the voltage detectors remain substantially at the last readings (discharging very slowly [time-constant approx. 2,000 bits] towards VBIAS). X = Do not care Table 5: PLL and Rx Level Measurement Operational Modes Rx Clock Extraction Synchronized by a PLL circuit to zero-crossings of the incoming data, the Rx Clock Extraction circuitry controls the Rx Clock output. The Rx Clock is also used internally by the Data Extraction circuitry. The PLL parameters can be varied by the Rx Circuit Control inputs PLLacq and Rx HOLD to operate in one of four PLL modes as described in Table Rx Data Extraction The RX Data Extraction circuit decides whether each received bit is a 1 or 0 by sampling the received signal, after filtering, and comparing the sample values to an adaptive threshold derived from the Level Measuring circuit. This threshold is adapted from bit to bit to compensate for intersymbol interference caused by the bandlimiting of the overall transmission path and the Gaussian premodulation filter. Extracted data is output from the RX Data pin, and should be sampled externally on the rising edge of the RX CLK.
10 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 10 of 20 MX Rx S/N Detection The RX S/N Detector system classifies the incoming zero-crossings as GOOD or BAD depending upon the time when each crossing actually occurs with respect to its expected time as determined by the Clock Extraction PLL. This information is then processed to provide a logic level output at the RX S/N pin. A high level indicates a series of GOOD crossings; a low level indicates a BAD crossing. By averaging this output, it is possible to derive a measure of the Signal-to-Noise-Ratio and hence the Bit- Error-Rate of the received signal BER 10-4 MX589 BT = BT = 1.0 (Theoretical) MX589 BT = S/N (db) [Noise Bandwidth = Bit Rate] Figure 6: Typical Bit-Error-Rate Performance Rx Signal Quality The effect of input Rx Signal quality on the Rx S/N output is shown in Figure 7. % High Time BT = 0.5 BT = S/N (db) Figure 7: Typical Rx S/N Output High time (%) vs. Input S/N
11 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 11 of 20 MX Transmit TX Signal Path Description The binary data applied to the TX Data input is retimed within the chip on each rising edge of the TX Clock and then converted to a 1-volt peak-to-peak binary signal centered at V BIAS (for V DD = 5.0V) If the TX Enable input is high, then this internal binary signal will be connected to the input of the lowpass TX Filter, and the output of the filter connected to the TX Out pin. Tx Enable Tx Filter Input Tx Out Pin 1 V DD /5V P-P Data Filtered Data 0 V BIAS V BIAS via 500kΩ A low input to the TX Enable will connect the input of the TX Filter to V BIAS, and disconnect the TX Out pin from the filter, connecting it instead to V BIAS through a high resistance (nominally 500kΩ). The TX Filter has a lowpass frequency response, which is approximately gaussian in shape, as shown in Figure 9, to minimize amplitude and phase distortion of the binary signal while providing sufficient attenuation of the high frequency-components which would otherwise cause interference into adjacent radio channels. The actual filter bandwidth to be used in any particular application will be determined by the overall system requirements. The attenuation- vs. -frequency response of the transmit filtering provided by the MX589 has been designed to meet the specifications for most GMSK modem systems that are -3dB bandwidth switchable between 0.3 and 0.5 times the data bit-rate (BT). Note: An external RC network is required between the TX Out pin and the input to the Frequency Modulator (see Figure 2 and Figure 3). This network, which can form part of any DC level shifting and gain adjustment circuitry, forms an important part of the transmit signal filtering. The ground connection to capacitor C1 should be positioned to give maximum attenuation of high-frequency noise into the modulator. The signal at Tx Out is centered around V BIAS, going positive for logic 1 (high) level inputs to the Tx Data input and negative for logic 0 (low) inputs. When the transmit circuits are put into a powersave mode (by a logic 1 to the Tx PS pin) the output voltage of the Tx Filter will be undefined. When power is subsequently restored to the Tx filter, its output will take several bit-times to settle. The Tx Enable input can be used to prevent these abnormal voltages from appearing at the Tx Out pin. 1 BIT PERIOD TX DATA SAMPLED BY THE MX589 AT THESE INSTANCES TX CLOCK AND RX CLOCK OUTPUTS (MARK/SPACE) DUTY CYCLE NOMINALLY 50%. TX CLK 1.0 μs Min. 1.0 μs Min. DON'T CARE DATA MUST BE VALID TX Data RX Data 1.0 μs Max. 1.0 μs Max. DATA INVALID DATA VALID RX CLK EXTERNAL CIRCUITS SHOULD SAMPLE RX DATA AT THIS TIME Figure 8: Rx and Tx Clock Data Timings
12 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 12 of 20 MX BT = 0.3 BT = Gain (db) Frequency/Bitrate 1 10 Figure 9: Tx Filter Response BT = 0.3 BT = 0.5 Figure 10: Typical Transmit Eye Patterns BT = 0.3 BT = 0.5 Gain (db) Frequency/Bitrate Figure 11: Tx Output Spectrum (Random Data)
13 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 13 of 20 MX Data Formats The receive section of the MX589 works best with data which has a reasonably random structure --the data should contain approximately the same number of ones as zeroes with no long sequences (>100 bits) of consecutive ones or zeroes. Also, long sequences (>100 bits) of patterns should be avoided. For this reason, it is recommended that data be made random in some manner before transmission, for example by exclusive-oring it with the output of a binary pseudo-random pattern generator. Where data is transmitted in bursts, each burst should be preceded by a preamble designed to allow the receive modem to establish timing and level lock as quickly as possible. This preamble for BT=0.3 should be at least 16 bits long, and should preferably consist of alternating pairs of ones and zeros i.e ; the eye of pattern has the most gradual slope and will yield poor peak levels for the RX circuits. For BT=0.5 the eye pattern of has reduced intersymbol interference and may be used as the preamble (DC Acq pin should be held high during preamble). See Fig Acquisition and Hold Modes The RXDCacq and PLLacq inputs must be pulsed High for about 16 bits at the start of reception to ensure that the DC measurement and timing extraction circuits lock-on to the received signal correctly. Once lock has been achieved, the above inputs should be taken Low again. In most applications, there will be a DC step in the output voltage from the receiver FM discriminator due to carrier frequency offsets as channels are changed or when the remote transmitter is turned on. The MX589 can tolerate DC offsets in the received signal of at least ±0.5V with respect to V BIAS, (measured at the RX Feedback pin). However, to ensure that the DC offset compensation circuit operates correctly and with minimum delay, the Low to High transition of the RXDCacq and PLLacq inputs should occur after the mean input voltage to the MX589 has settled to within about 0.1V of its final value. Note: This can place restrictions on the value of any series signal coupling capacitor. As well as using the RX Hold input to freeze the Level Measuring and Clock Extraction circuits during a signal fade, it may also be used in systems which use a continuously transmitting control channel to freeze the RX circuitry during transmission of a data packet, allowing reception to resume afterwards without losing bit synchronization. To achieve this, the MX589 Xtal clock needs to be accurate enough that the derived RXClock output does not drift by more than about 0.1 bit time from the actual received data-rate during the time that the RXHold input is Low. However; the RXDCacq input may need to be pulsed High for 2 bit durations to re-establish the level measurements if the RXHold input is Low for more that a few hundred bit-times (exact number depends on system crystal tolerances). The voltages on the Doc1 and Doc2 pins reflect the average peak positive and negative excursions of the (filtered) receive signal, and could therefore be used to derive a measure of the data signal amplitude. Note: These pins are driven from very high-impedance circuits, so that the DC load presented by any external circuitry should exceed 10MΩ to V BIAS.
14 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 14 of 20 MX589 5 Application 5.1 Radio Channel Requirements To achieve legal adjacent channel performance at high bit-rates, a radio with an accurate carrier frequency and an accurate modulation index is required. For optimum channel utilization, (e.g. low BER and high datarates) attention must be paid to the phase and frequency response of both the IF and baseband circuitry Bit Rate, BT, and Bandwidth The maximum data rate that can be transmitted over a radio channel depends on the following: Channel spacing Allowable adjacent channel interference TX filter bandwidth Peak carrier deviation (Modulation Index) TX and RX carrier frequency accuracies Modulator and Demodulator linearity RX IF filter frequency and phase characteristics Use of error correction techniques Acceptable error-rate As a guide to MOBITEX operation, a raw data-rate of 8kbps at 12.5kHz channel spacing may be achievable - depending on local regulatory requirements- using a ±2kHz maximum deviation, a BT of 0.3, and no more than 1.5kHz discrepancy between Tx & Rx carrier frequencies. Forward error correction (FEC) could then be used with interleaving to reduce the effect of burst errors. Reducing the data-rate to 4.8kbps would allow the BT to be increased to 0.5, improving the error-rate performance FM Modulator, Demodulator and IF For optimum performance, the eye pattern of the received signal (when receiving random data) applied to the MX589 should be as close as possible to the Transmit eye pattern examples shown in Figure 10. Of particular importance are general symmetry, cleanliness of the zero-crossings, and for a BT of 0.3, the relative amplitude of the inner eye opening. To achieve this, attention must be paid to: Linearity and frequency/phase response of the Tx frequency modulator. Unless the transmit data is especially encoded to remove low frequency components, the modulator frequency response should extend down to a few hertz. This is because two-point modulation is necessary for synthesized radios. Bandwidth & phase response of the RX IF filters. Accuracy of the Tx and Rx carrier frequencies -any difference will shift the received signal towards one of the skirts of the IF filter response. Ideally, the Rx demodulator should be DC coupled to the MX589 RX Signal In pin (with a DC bias added to center the signal at the RX Feedback pin at V DD /2 [V BIAS ]). However, AC coupling can be used provided that: The 3dB cut-off frequency is 20Hz or below (i.e. a 0.1μF capacitor in series with 100kΩ). The data does not contain long sequences of consecutive ones or zeroes. Sufficient time is allowed after a step change at the discriminator output (resulting from channel changing or the appearance of a RF carrier) for the voltage into the MX589 to settle before the RXDCacq line is strobed.
15 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 15 of 20 MX Two-Point Modulation When designing the MX589 into a radio that uses a frequency synthesizer, a two-point modulation technique is recommended. This is both to prevent the radio's PLL circuitry from counteracting the modulation process, and to provide a clean flat modulation response down to DC. Figure 12 shows a suggested basic configuration to provide a two-point modulation drive from the MX589 TX Output using MX-COM's MX019 Digitally Controlled Quad Amplifier Array. The MX019 elements provide individual set-up, calibration and dynamic control of modulation levels. Level setting control of the amplifiers/attenuators of the MX019 is via an 8-bit data word. With reference to Figure 12: The buffer amplifier is required to prevent loading of the MX589 external RC circuit. Stage B, with R1/R2, provides suitable signal and DC levels for the VCO varactor; C1 is RF decoupling. The drive level should be adjusted (digitally) to provide the desired deviation. Stage C, with R3/R4, provides the Reference Oscillator drive (application dependent). This parameter is set by adjusting for minimum AC signal on the PLL control voltage with a low-frequency modulating signal (inside the PLL bandwidth) applied. Stage D could be used with the components shown if a negative reference drive is required. Stage A provides buffering and overall level control. CONTROL MX589 TX OUT +14dB V SS External RC See Fig.3 Buffer A to -14dB With reference to the MX019 Data Sheet Stage A = MX019 Channel 4 Stage B = MX019 Channel 1 Stage C = MX019 Channel 2 Stage D = MX019 Channel 3 Note: 1. All stages of the MX019 are 'inverting' stages. 2. Components R1-R6 should produce the proper output signal levels for interface into the modulator. B C D +3dB to -3dB R1 R2 +3dB to -3dB TX VCO +3dB to -3dB To TX REF Osc (+) R3 V REF(+) R4 R5 R6 V VCO V (-) REF C1 To TX REF Osc (-) Figure 12: An Example of Two-Point Modulation Drive with Individual Adjustment Using the MX019
16 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 16 of 20 MX AC Coupling of Tx and Rx Signals In practical applications, it is possible to arrange AC coupling between the MX589 Tx Output and the frequency modulator to cut-off at a very low frequency, such as 5.0Hz. AC coupling between the receive discriminator and the input of the MX589 may need a shorter time-constant to avoid problems from voltage steps at the output of the discriminator when changing channels or when the distant transmitter turns on. For these reasons, as well as to maintain reasonable BER, the optimum 3dB cut-off frequencies are around 5.0Hz in the Tx path and 20.0Hz in the Rx path. Figure 13 shows the typical static Bit-Error-Rate performance of the MX589 operating under nominal conditions for various degrees of AC coupling at the Rx input and the Tx output. Data Rate = 8kbps V DD = 5.0V T AMB = 25C Tx BT = BER 10-3 TX and RX DC coupled TX 5Hz, RX DC coupled 10-4 TX 5Hz, RX 10Hz TX 5Hz, RX 30Hz 10-5 TX 5Hz, RX 100Hz S/N (db) (noise in 8kHz bandwidth) Figure 13: Effect of AC Coupling on Typical Bit-Error Rate Any AC Coupling at the receive input will transform any step in the voltage at the discriminator output to a slowly decaying pulse which can confuse the modem s level measuring circuits. As illustrated in Figure 14, the time for this step to decay to 37% of its original value is RC where: 1 RC = 2π(the 3dB cutoff frequency of the RC network) which is 32ms, or 256 bit times at 8kbps, for a 5Hz network. Figure 14: Decay time-ac Coupling
17 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 17 of 20 MX589 6 Performance Specifications 6.1 Electrical Specifications Absolute Maximum Limits Exceeding these maximum ratings can result in damage to the device. General Notes Min. Typ. Max. Units Supply (V DD- V SS ) V Voltage on any pin to V SS -0.3 V DD V Current V DD ma V SS ma Any other pin ma DW / P Packages Total allowable Power dissipation at T AMB = 25 C 800 mw Derating above 25 C 13 mw/ C above 25 C Operating Temperature C Storage Temperature C TN Package Total allowable Power dissipation at T AMB = 25 C 550 mw Derating above 25 C 9 mw/ C above 25 C Operating Temperature C Storage Temperature C Table 6: Absolute Maximum Ratings Operating Limits Correct Operation of the device outside these limits is not implied. Notes Min. Typ. Max. Units Supply (V DD -V SS ) / V Operating Temperature C Rx and Tx Data Rate V DD 3.0V 4 20 kbps V DD 4.5V 4 64 kbps Xtal Frequency V DD 3.0V MHz V DD 4.5V MHz High Pulse Width 1 40 Ns Low Pulse Width 1 40 ns Table 7: Operating Limits Operating Limits Notes 1. Timing for an external clock input to the Xtal/Clock pin.
18 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 18 of 20 MX Operating Characteristics For the following conditions unless otherwise specified. V DD = T AMB = 25 C Xtal/Clock Frequency = 4.096MHz, Data Rate = 8kbps, Noise Bandwidth = Bit Rate Static Values Notes Min. Typ. Max. Units Supply Current Tx PS Rx PS 1 I DD (V DD = 3.0V) ma ma ma ma I DD (V DD = 5.0V) ma ma ma ma Input Logic Level Logic 1 Input Level 3.5 V Logic 0 Input Level 1.5 V Logic Input Current μa Logic 1 Output Level (I OL = 120μA) 4.6 V Logic 0 Output Level (I OL = -120μA) 0.4 V Transmit Parameters Tx OUT, Output Impedance kω Tx Out, Level 4, V P-P Output DC Offset V Tx Data Delay BT = bit-periods BT = bit-periods Tx PS to Output-Stable time bit-periods Receive Parameters Rx Amplifier Input Impedance 1.0 MΩ Output Impedance KΩ Voltage Gain 50.0 db Rx Filter Signal Input Level 8, V P-P Rx Time Delay bit-periods On-Chip Xtal Oscillator R IN 10.0 MΩ R OUT kω Voltage Gain db Table 8: Operating Characteristics
19 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 19 of 20 MX589 Operating Characteristics Notes: 1. Not including current drawn from the MX589 pins by external circuitry. See Absolute Maximum Ratings. 2. For V IN in the range V SS to V DD. 3. For a load of 10KΩ or greater. Tx PS input at logic 0; Tx Enable = Data pattern of Measured between the rising edge of Tx Clock and the center of the corresponding bit at Tx Out. 6. Time between the falling edge of the Tx PS and the Tx Out voltage stabilizing to normal output levels. 7. For a load of 10kΩ or greater. Rx PS input at logic For optimum performance, Measured at the Rx Feedback pin for an pattern. 9. Measured between the center of bit at Rx Signal In and corresponding rising edge of the Rx Clock. 10. Levels are proportional to applied V DD 11. Small signal measurement at 1.0kHz with no load on Xtal output. 12. (Tx OUT enabled DC level) (Tx Out disabled DC level) when transmitting a repeating bit pattern. 6.2 Packages A Package Tolerances DIM. MIN. TYP. MAX. ALTERNATIVE PIN LOCATION MARKING PIN 1 H Y J P C B E T L A B C E H J L P T Y (7.70) (7.90) (4.30) (4.50) (1.20) (6.30) (6.50) (0.05) (0.15) (0.17) (0.30) (0.50) (0.75) (0.65) (0.08) (0.20) 0 8 NOTE : All dimensions in inches (mm.) Angles are in degrees Figure 15: 24-pin TSSOP Mechanical Outline: Order as part no. MX589TN Package Tolerances ALTERNATIVE PIN LOCATION MARKING PIN 1 H Y J A P C B K E W X T L Z DIM. A B C E H J K L P T W X Y Z MIN. TYP. MAX (15.16) (15.57) (7.26) (7.59) (2.36) (2.67) (9.90) (10.64) (0.08) (0.51) (0.33) (0.51) (0.91) (1.17) (0.41) (1.27) (1.27) (0.23) (0.32) NOTE : All dimensions in inches (mm.) Angles are in degrees Figure 16: 24-pin SOIC Mechanical Outline: Order as part no. MX589DW
20 High Speed GMSK Modem 4k to 64kbps Page 20 of 20 MX589 A Package Tolerances PIN1 K H L J J1 P B C E1 Y T E DIM. A B C E E1 H MIN. TYP (30.48) (12.70) (3.84) (15.24) MAX (32.26) (14.04) (5.59) (17.02) (14.99) (15.88) (0.38) (1.14) J (0.38) (0.58) J (1.02) (1.65) K (1.67) (1.88) L (3.07) (4.05) P (2.54) T (0.20) (0.38) Y 7 NOTE : All dimensions in inches (mm.) Angles are in degrees Figure 17: 24-pin PDIP Mechanical Outline: Order as part no. MX589P
CMX589A. GMSK Modem. CML Microcircuits. Features and Applications
 查询 供应商 CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS D/589A/4 April 2002 Features and Applications Data Rates from 4kbps to 200kbps Full or Half Duplex Gaussian Filter and Data Recovery for Minimum Shift
查询 供应商 CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS D/589A/4 April 2002 Features and Applications Data Rates from 4kbps to 200kbps Full or Half Duplex Gaussian Filter and Data Recovery for Minimum Shift
Half Duplex GMSK Modem
 CML Semiconductor Products Half Duplex GMSK Modem D/579/4 Sept 1995 1.0 Features Provisional Issue Half Duplex GMSK Modem for FM Radio Data Links Acquire Pin to assist with the acquisition of Rx Data signals
CML Semiconductor Products Half Duplex GMSK Modem D/579/4 Sept 1995 1.0 Features Provisional Issue Half Duplex GMSK Modem for FM Radio Data Links Acquire Pin to assist with the acquisition of Rx Data signals
MX614 MX614. Telephone. Line Line. Interface PRELIMINARY INFORMATION
 COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS DATA BULLETIN Features 1200bps - 1800bps half duplex Bell 202 Compatible Modem Optional 1200bps Data Retiming Facility can eliminate external UART Optional 5bps and 150bps
COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS DATA BULLETIN Features 1200bps - 1800bps half duplex Bell 202 Compatible Modem Optional 1200bps Data Retiming Facility can eliminate external UART Optional 5bps and 150bps
4 x 10 bit Free Run A/D 4 x Hi Comparator 4 x Low Comparator IRQ on Compare MX839. C-BUS Interface & Control Logic
 DATA BULLETIN MX839 Digitally Controlled Analog I/O Processor PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features x 4 input intelligent 10 bit A/D monitoring subsystem 4 High and 4 Low Comparators External IRQ Generator
DATA BULLETIN MX839 Digitally Controlled Analog I/O Processor PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features x 4 input intelligent 10 bit A/D monitoring subsystem 4 High and 4 Low Comparators External IRQ Generator
MX633 Call Progress Tone Detector
 DATA BULLETIN MX633 Call Progress Tone Detector PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features Worldwide Tone Compatibility Single and Dual Tones Detected U.S. Busy-Detect Output Voice-Detect Output Wide Dynamic Range
DATA BULLETIN MX633 Call Progress Tone Detector PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features Worldwide Tone Compatibility Single and Dual Tones Detected U.S. Busy-Detect Output Voice-Detect Output Wide Dynamic Range
CML Semiconductor Products
 CML Semiconductor Products Bell 202 Compatible Modem 1.0 Features D/614/4 October 1997 Advance Information 1200bits/sec 1/2 Duplex Bell 202 compatible Modem with: Optional 5bits/sec and 150bits/sec Back
CML Semiconductor Products Bell 202 Compatible Modem 1.0 Features D/614/4 October 1997 Advance Information 1200bits/sec 1/2 Duplex Bell 202 compatible Modem with: Optional 5bits/sec and 150bits/sec Back
SERIAL OUTPUT PORT (6-BITS) LATCH COUNT FREQUENCY COUNTER RESET DECODE ON / OFF LOGIC RESET TIME. TIMER LO = 39.4ms HI = 13.16ms
 DATA BULLETIN MX613 Global Call Progress Detector PRELIMINARY INFORMATION MX COM MiXed Signal CMOS Covers Worldwide Call Progress Frequencies (300Hz TO 2150Hz) Decode Single or Modulated Tones Analog In
DATA BULLETIN MX613 Global Call Progress Detector PRELIMINARY INFORMATION MX COM MiXed Signal CMOS Covers Worldwide Call Progress Frequencies (300Hz TO 2150Hz) Decode Single or Modulated Tones Analog In
CTCSS FAST CTCSS. Tx MOD1 SELCALL. Tx MOD2 DCS RSSI CARRIER DETECT TIMER. ANALOG Rx LEVEL CONTROL AUDIO FILTER AUDIO SIGNALS MX828
 DATA BULLETIN MX828 CTCSS/DCS/SelCall Processor PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features Fast CTCSS Detection Full Duplex CTCSS and SelCall Full 23/24 Bit DCS Codec SelCall Codec Non Predictive Tone Detection
DATA BULLETIN MX828 CTCSS/DCS/SelCall Processor PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features Fast CTCSS Detection Full Duplex CTCSS and SelCall Full 23/24 Bit DCS Codec SelCall Codec Non Predictive Tone Detection
DATA BULLETIN MX315A. Programmed Clocks. TX Tone Square Wave
 DATA BULLETIN MX315A CTCSS Encoder Features Field Programmable Tone Encoder 40 CTCSS Frequencies Crystal-Controlled Frequency Stability Low Distortion Sinewave Output Few External Components Required CMOS
DATA BULLETIN MX315A CTCSS Encoder Features Field Programmable Tone Encoder 40 CTCSS Frequencies Crystal-Controlled Frequency Stability Low Distortion Sinewave Output Few External Components Required CMOS
FSK DEMODULATOR / TONE DECODER
 FSK DEMODULATOR / TONE DECODER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a monolithic phase-locked loop (PLL) system especially designed for data communications. It is particularly well suited for FSK modem applications,
FSK DEMODULATOR / TONE DECODER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a monolithic phase-locked loop (PLL) system especially designed for data communications. It is particularly well suited for FSK modem applications,
HART Modem DS8500. Features
 Rev 1; 2/09 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE General Description The is a single-chip modem with Highway Addressable Remote Transducer (HART) capabilities and satisfies the HART physical layer requirements. The
Rev 1; 2/09 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE General Description The is a single-chip modem with Highway Addressable Remote Transducer (HART) capabilities and satisfies the HART physical layer requirements. The
CDPD Wireless Modem Data Pump
 CML Semiconductor Products CDPD Wireless Modem Data Pump 1.0 Features Obsolete Product 'For Information Only' MES Full Duplex Operation 19.2kb/s GMSK Modulation Forward Channel Decoding Sleep Timer Included
CML Semiconductor Products CDPD Wireless Modem Data Pump 1.0 Features Obsolete Product 'For Information Only' MES Full Duplex Operation 19.2kb/s GMSK Modulation Forward Channel Decoding Sleep Timer Included
Features +5V ASK DATA INPUT. 1.0pF. 8.2pF. 10nH. 100pF. 27nH. 100k. Figure 1
 QwikRadio UHF ASK Transmitter Final General Description The is a single chip Transmitter IC for remote wireless applications. The device employs s latest QwikRadio technology. This device is a true data-in,
QwikRadio UHF ASK Transmitter Final General Description The is a single chip Transmitter IC for remote wireless applications. The device employs s latest QwikRadio technology. This device is a true data-in,
FX623 FX623. CML Semiconductor Products PRODUCT INFORMATION. Call Progress Tone Decoder
 CML Semiconductor Products PRODUCT INFORMATION FX623 Call Progress Tone Decoder Features Measures Call Progress Tone Frequencies [ Busy, Dial, Fax-Tone etc.] Telephone, PABX, Fax and Dial-Up Modem Applications
CML Semiconductor Products PRODUCT INFORMATION FX623 Call Progress Tone Decoder Features Measures Call Progress Tone Frequencies [ Busy, Dial, Fax-Tone etc.] Telephone, PABX, Fax and Dial-Up Modem Applications
CLOCK OUT CLOCK IN V DD BUFFER. Ch 1 COMPARATOR PULSE GENERATOR AND DIVIDER PULSE MEASUREMENT LOGIC CHANNEL 1 INTERNAL COMPARATOR THRESHOLD
 COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS DATA BULLETIN MX641 Dual SPM Detector PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features Two (12kHz / 16kHz) SPM Detectors on a Single Chip Detects 12 or 16kHz SPM Frequencies Controlled (µc)
COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS DATA BULLETIN MX641 Dual SPM Detector PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features Two (12kHz / 16kHz) SPM Detectors on a Single Chip Detects 12 or 16kHz SPM Frequencies Controlled (µc)
Low voltage LNA, mixer and VCO 1GHz
 DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
FX375. CML Semiconductor Products PRODUCT INFORMATION FX375 Private Squelch Circuit. Features
 CML Semiconductor Products PRODUCT INFORMATION FX375 Private Squelch Circuit Features Tone Operated Private/Clear Switching CTCSS Tone Encode/Decode Separate Rx/Tx Speech Paths Fixed Frequency Speech Inversion
CML Semiconductor Products PRODUCT INFORMATION FX375 Private Squelch Circuit Features Tone Operated Private/Clear Switching CTCSS Tone Encode/Decode Separate Rx/Tx Speech Paths Fixed Frequency Speech Inversion
Peak Reducing EMI Solution
 Peak Reducing EMI Solution Features Cypress PREMIS family offering enerates an EMI optimized clocking signal at the output Selectable input to output frequency Single 1.% or.% down or center spread output
Peak Reducing EMI Solution Features Cypress PREMIS family offering enerates an EMI optimized clocking signal at the output Selectable input to output frequency Single 1.% or.% down or center spread output
1GHz low voltage LNA, mixer and VCO
 DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
Low-Jitter, 8kHz Reference Clock Synthesizer Outputs MHz
 19-3530; Rev 0; 1/05 Low-Jitter, 8kHz Reference General Description The low-cost, high-performance clock synthesizer with an 8kHz input reference clock provides six buffered LVTTL clock outputs at 35.328MHz.
19-3530; Rev 0; 1/05 Low-Jitter, 8kHz Reference General Description The low-cost, high-performance clock synthesizer with an 8kHz input reference clock provides six buffered LVTTL clock outputs at 35.328MHz.
Spread Spectrum Frequency Timing Generator
 Spread Spectrum Frequency Timing Generator Features Maximized EMI suppression using Cypress s Spread Spectrum technology Generates a spread spectrum copy of the provided input Selectable spreading characteristics
Spread Spectrum Frequency Timing Generator Features Maximized EMI suppression using Cypress s Spread Spectrum technology Generates a spread spectrum copy of the provided input Selectable spreading characteristics
NTE980 Integrated Circuit CMOS, Micropower Phase Locked Loop (PLL)
 NTE980 Integrated Circuit CMOS, Micropower Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Description: The NTE980 CMOS Micropower Phase Locked Loop (PLL) consists of a low power, linear voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) and
NTE980 Integrated Circuit CMOS, Micropower Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Description: The NTE980 CMOS Micropower Phase Locked Loop (PLL) consists of a low power, linear voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) and
CMX969 MOTIENT SM /ARDIS SM RD-LAP TM MDC4800 Modem
 COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS DATA BULLETIN CMX969 MOTIENT SM /ARDIS SM RD-LAP TM MDC4800 Modem Advance Information Features Autonomous Frame Sync Detection for SFR operation Full Packet Data Framing Powersave
COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS DATA BULLETIN CMX969 MOTIENT SM /ARDIS SM RD-LAP TM MDC4800 Modem Advance Information Features Autonomous Frame Sync Detection for SFR operation Full Packet Data Framing Powersave
Phase-locked loop PIN CONFIGURATIONS
 NE/SE DESCRIPTION The NE/SE is a versatile, high guaranteed frequency phase-locked loop designed for operation up to 0MHz. As shown in the Block Diagram, the NE/SE consists of a VCO, limiter, phase comparator,
NE/SE DESCRIPTION The NE/SE is a versatile, high guaranteed frequency phase-locked loop designed for operation up to 0MHz. As shown in the Block Diagram, the NE/SE consists of a VCO, limiter, phase comparator,
ODUCTCEMENT CA3126 OBSOLETE PR NO RECOMMENDED REPLA
 May OBSOLETE PRODUCT NO RECOMMENDED REPLACEMENT Call Central Applications -800-44-7747 or email: centapp@harris.com TV Chroma Processor [ /Title (CA3 6) /Subject (TV Chrom a Processor) /Autho r () /Keywords
May OBSOLETE PRODUCT NO RECOMMENDED REPLACEMENT Call Central Applications -800-44-7747 or email: centapp@harris.com TV Chroma Processor [ /Title (CA3 6) /Subject (TV Chrom a Processor) /Autho r () /Keywords
ISO 2 -CMOS MT8840 Data Over Voice Modem
 SO 2 -CMOS Data Over Voice Modem Features Performs ASK (amplitude shift keyed) modulation and demodulation 32 khz carrier frequency Up to 2 kbit/s full duplex data transfer rate On-chip oscillator On-chip
SO 2 -CMOS Data Over Voice Modem Features Performs ASK (amplitude shift keyed) modulation and demodulation 32 khz carrier frequency Up to 2 kbit/s full duplex data transfer rate On-chip oscillator On-chip
Maximum data rate: 50 MBaud Data rate range: ±15% Lock-in time: 1 bit
 MONOLITHIC MANCHESTER ENCODER/DECODER (SERIES 3D7503) FEATURES 3D7503 data 3 delay devices, inc. PACKAGES All-silicon, low-power CMOS technology CIN 1 14 Encoder and decoder function independently Encoder
MONOLITHIC MANCHESTER ENCODER/DECODER (SERIES 3D7503) FEATURES 3D7503 data 3 delay devices, inc. PACKAGES All-silicon, low-power CMOS technology CIN 1 14 Encoder and decoder function independently Encoder
Synchronous Buck Converter Controller
 Product is End of Life 3/204 Synchronous Buck Converter Controller Si950 DESCRIPTION The Si950 synchronous buck regulator controller is ideally suited for high-efficiency step down converters in battery-powered
Product is End of Life 3/204 Synchronous Buck Converter Controller Si950 DESCRIPTION The Si950 synchronous buck regulator controller is ideally suited for high-efficiency step down converters in battery-powered
Improved Second Source to the EL2020 ADEL2020
 Improved Second Source to the EL ADEL FEATURES Ideal for Video Applications.% Differential Gain. Differential Phase. db Bandwidth to 5 MHz (G = +) High Speed 9 MHz Bandwidth ( db) 5 V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling
Improved Second Source to the EL ADEL FEATURES Ideal for Video Applications.% Differential Gain. Differential Phase. db Bandwidth to 5 MHz (G = +) High Speed 9 MHz Bandwidth ( db) 5 V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling
OSC2 Selector Guide appears at end of data sheet. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 9-3697; Rev 0; 4/05 3-Pin Silicon Oscillator General Description The is a silicon oscillator intended as a low-cost improvement to ceramic resonators, crystals, and crystal oscillator modules as the clock
9-3697; Rev 0; 4/05 3-Pin Silicon Oscillator General Description The is a silicon oscillator intended as a low-cost improvement to ceramic resonators, crystals, and crystal oscillator modules as the clock
Dual-Rate Fibre Channel Repeaters
 9-292; Rev ; 7/04 Dual-Rate Fibre Channel Repeaters General Description The are dual-rate (.0625Gbps and 2.25Gbps) fibre channel repeaters. They are optimized for use in fibre channel arbitrated loop applications
9-292; Rev ; 7/04 Dual-Rate Fibre Channel Repeaters General Description The are dual-rate (.0625Gbps and 2.25Gbps) fibre channel repeaters. They are optimized for use in fibre channel arbitrated loop applications
781/ /
 781/329-47 781/461-3113 SPECIFICATIONS DC SPECIFICATIONS J Parameter Min Typ Max Units SAMPLING CHARACTERISTICS Acquisition Time 5 V Step to.1% 25 375 ns 5 V Step to.1% 2 35 ns Small Signal Bandwidth 15
781/329-47 781/461-3113 SPECIFICATIONS DC SPECIFICATIONS J Parameter Min Typ Max Units SAMPLING CHARACTERISTICS Acquisition Time 5 V Step to.1% 25 375 ns 5 V Step to.1% 2 35 ns Small Signal Bandwidth 15
SYN501R Datasheet. ( MHz Low Voltage ASK Receiver) Version 1.0
 SYN501R Datasheet (300-450MHz Low Voltage ASK Receiver) Version 1.0 Contents 1. General Description... 1 2. Features... 1 3. Applications... 1 4. Typical Application... 2 5. Pin Configuration... 2 6. Pin
SYN501R Datasheet (300-450MHz Low Voltage ASK Receiver) Version 1.0 Contents 1. General Description... 1 2. Features... 1 3. Applications... 1 4. Typical Application... 2 5. Pin Configuration... 2 6. Pin
HM9270C HM9270D HM 9270C/D DTMF RECEIVER. General Description. Features. Pin Configurations. * Connect to V SS. V DD St/GT ESt StD Q4 Q3 Q2 Q1 TOE
 General Description The HM 9270C/D is a complete DTMF receiver integrating both the bandsplit filter and digital decoder functions. The filter section uses switched capacitor techniques for high- and low-group
General Description The HM 9270C/D is a complete DTMF receiver integrating both the bandsplit filter and digital decoder functions. The filter section uses switched capacitor techniques for high- and low-group
ICS PLL BUILDING BLOCK
 Description The ICS673-01 is a low cost, high performance Phase Locked Loop (PLL) designed for clock synthesis and synchronization. Included on the chip are the phase detector, charge pump, Voltage Controlled
Description The ICS673-01 is a low cost, high performance Phase Locked Loop (PLL) designed for clock synthesis and synchronization. Included on the chip are the phase detector, charge pump, Voltage Controlled
SA620 Low voltage LNA, mixer and VCO 1GHz
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Low voltage LNA, mixer and VCO 1GHz Supersedes data of 1993 Dec 15 2004 Dec 14 DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Low voltage LNA, mixer and VCO 1GHz Supersedes data of 1993 Dec 15 2004 Dec 14 DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance
Universal Input Switchmode Controller
 Universal Input Switchmode Controller Si9120 FEATURES 10- to 0- Input Range Current-Mode Control 12-mA Output Drive Internal Start-Up Circuit Internal Oscillator (1 MHz) and DESCRIPTION The Si9120 is a
Universal Input Switchmode Controller Si9120 FEATURES 10- to 0- Input Range Current-Mode Control 12-mA Output Drive Internal Start-Up Circuit Internal Oscillator (1 MHz) and DESCRIPTION The Si9120 is a
MM5452/MM5453 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers
 MM5452/MM5453 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers General Description The MM5452 is a monolithic integrated circuit utilizing CMOS metal gate, low threshold enhancement mode devices. It is available in a 40-pin
MM5452/MM5453 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers General Description The MM5452 is a monolithic integrated circuit utilizing CMOS metal gate, low threshold enhancement mode devices. It is available in a 40-pin
ML4818 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller
 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Tel: Fax:
 B Tel: 78.39.4700 Fax: 78.46.33 SPECIFICATIONS (T A = +5 C, V+ = +5 V, V = V or 5 V, all voltages measured with respect to digital common, unless otherwise noted) AD57J AD57K AD57S Model Min Typ Max Min
B Tel: 78.39.4700 Fax: 78.46.33 SPECIFICATIONS (T A = +5 C, V+ = +5 V, V = V or 5 V, all voltages measured with respect to digital common, unless otherwise noted) AD57J AD57K AD57S Model Min Typ Max Min
CMX865A Telecom Signalling Device
 Telecom Signalling Device D/865A/3 February 2007 Provisional Issue DTMF CODEC AND TELECOM SIGNALLING COMBO Features V.23 1200/75, 1200/1200, 75, 1200 bps FSK Bell 202 1200/150, 1200/1200, 150, 1200 bps
Telecom Signalling Device D/865A/3 February 2007 Provisional Issue DTMF CODEC AND TELECOM SIGNALLING COMBO Features V.23 1200/75, 1200/1200, 75, 1200 bps FSK Bell 202 1200/150, 1200/1200, 150, 1200 bps
DS275S. Line-Powered RS-232 Transceiver Chip PIN ASSIGNMENT FEATURES ORDERING INFORMATION
 Line-Powered RS-232 Transceiver Chip FEATURES Low power serial transmitter/receiver for battery-backed systems Transmitter steals power from receive signal line to save power Ultra low static current,
Line-Powered RS-232 Transceiver Chip FEATURES Low power serial transmitter/receiver for battery-backed systems Transmitter steals power from receive signal line to save power Ultra low static current,
ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R PRECISION INTEGRATING ANALOG PROCESSOR WITH PRECISION VOLTAGE REFERENCE
 ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R PRECISION INTEGRATING ANALOG PROCESSOR WITH PRECISION VOLTAGE REFERENCE APPLICATIONS 4 1/2 digits to 5 1/2 digits plus sign measurements Precision
ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R PRECISION INTEGRATING ANALOG PROCESSOR WITH PRECISION VOLTAGE REFERENCE APPLICATIONS 4 1/2 digits to 5 1/2 digits plus sign measurements Precision
CD V Low Power Subscriber DTMF Receiver. Description. Features. Ordering Information. Pinouts CD22204 (PDIP) TOP VIEW. Functional Diagram
 Semiconductor January Features No Front End Band Splitting Filters Required Single Low Tolerance V Supply Three-State Outputs for Microprocessor Based Systems Detects all Standard DTMF Digits Uses Inexpensive.4MHz
Semiconductor January Features No Front End Band Splitting Filters Required Single Low Tolerance V Supply Three-State Outputs for Microprocessor Based Systems Detects all Standard DTMF Digits Uses Inexpensive.4MHz
APPLICATION NOTE 3671 Data Slicing Techniques for UHF ASK Receivers
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Basestations/Wireless Infrastructure > APP 3671 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Basestations/Wireless Infrastructure > APP 3671 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP
Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > User Guides > APP 3910 Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System USER GUIDE 3910 User's
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > User Guides > APP 3910 Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System USER GUIDE 3910 User's
Power supply IA Ordinary current ID operation Input *1 I IL V I = 0 V leakage current I IH V I = V D
 Data Pack H Issued March 1997 232-2756 Data Sheet Modem IC 6929 CCITT V21 data format RS stock number 630-976 The 6926 is 300 bit per second chip modem designed to transmit and receive serial binary data
Data Pack H Issued March 1997 232-2756 Data Sheet Modem IC 6929 CCITT V21 data format RS stock number 630-976 The 6926 is 300 bit per second chip modem designed to transmit and receive serial binary data
RX3400 Low Power ASK Receiver IC. Description. Features. Applications. Block Diagram
 Low Power ASK Receiver IC Princeton Technology Corp. reserves the right to change the product described in this datasheet. All information contained in this datasheet is subject to change without prior
Low Power ASK Receiver IC Princeton Technology Corp. reserves the right to change the product described in this datasheet. All information contained in this datasheet is subject to change without prior
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
PRECISION INTEGRATING ANALOG PROCESSOR
 ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD500AU/ALD500A/ALD500 PRECISION INTEGRATING ANALOG PROCESSOR APPLICATIONS 4 1/2 digits to 5 1/2 digits plus sign measurements Precision analog signal processor Precision
ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD500AU/ALD500A/ALD500 PRECISION INTEGRATING ANALOG PROCESSOR APPLICATIONS 4 1/2 digits to 5 1/2 digits plus sign measurements Precision analog signal processor Precision
SG2525A SG3525A REGULATING PULSE WIDTH MODULATORS
 SG2525A SG3525A REGULATING PULSE WIDTH MODULATORS 8 TO 35 V OPERATION 5.1 V REFERENCE TRIMMED TO ± 1 % 100 Hz TO 500 KHz OSCILLATOR RANGE SEPARATE OSCILLATOR SYNC TERMINAL ADJUSTABLE DEADTIME CONTROL INTERNAL
SG2525A SG3525A REGULATING PULSE WIDTH MODULATORS 8 TO 35 V OPERATION 5.1 V REFERENCE TRIMMED TO ± 1 % 100 Hz TO 500 KHz OSCILLATOR RANGE SEPARATE OSCILLATOR SYNC TERMINAL ADJUSTABLE DEADTIME CONTROL INTERNAL
Low Cost, General Purpose High Speed JFET Amplifier AD825
 a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
6-Bit A/D converter (parallel outputs)
 DESCRIPTION The is a low cost, complete successive-approximation analog-to-digital (A/D) converter, fabricated using Bipolar/I L technology. With an external reference voltage, the will accept input voltages
DESCRIPTION The is a low cost, complete successive-approximation analog-to-digital (A/D) converter, fabricated using Bipolar/I L technology. With an external reference voltage, the will accept input voltages
SYN500R Datasheet. ( MHz ASK Receiver) Version 1.0
 SYN500R Datasheet (300-450MHz ASK Receiver) Version 1.0 Contents 1. General Description... 1 2. Features... 1 3. Applications... 1 4. Typical Application... 2 5. Pin Configuration... 2 6. Pin Description...
SYN500R Datasheet (300-450MHz ASK Receiver) Version 1.0 Contents 1. General Description... 1 2. Features... 1 3. Applications... 1 4. Typical Application... 2 5. Pin Configuration... 2 6. Pin Description...
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
XR-2211 FSK Demodulator/ Tone Decoder
 ...the analog plus company TM XR- FSK Demodulator/ Tone Decoder FEATURES APPLICATIONS June 997-3 Wide Frequency Range, 0.0Hz to 300kHz Wide Supply Voltage Range, 4.5V to 0V HCMOS/TTL/Logic Compatibility
...the analog plus company TM XR- FSK Demodulator/ Tone Decoder FEATURES APPLICATIONS June 997-3 Wide Frequency Range, 0.0Hz to 300kHz Wide Supply Voltage Range, 4.5V to 0V HCMOS/TTL/Logic Compatibility
DS1267 Dual Digital Potentiometer Chip
 Dual Digital Potentiometer Chip www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Ultra-low power consumption, quiet, pumpless design Two digitally controlled, 256-position potentiometers Serial port provides means for setting
Dual Digital Potentiometer Chip www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Ultra-low power consumption, quiet, pumpless design Two digitally controlled, 256-position potentiometers Serial port provides means for setting
CD22202, CD DTMF Receivers/Generators. 5V Low Power DTMF Receiver. Features. Description. Ordering Information. Pinout. Functional Diagram
 SEMICONDUCTOR DTMF Receivers/Generators CD0, CD0 January 1997 5V Low Power DTMF Receiver Features Description Central Office Quality No Front End Band Splitting Filters Required Single, Low Tolerance,
SEMICONDUCTOR DTMF Receivers/Generators CD0, CD0 January 1997 5V Low Power DTMF Receiver Features Description Central Office Quality No Front End Band Splitting Filters Required Single, Low Tolerance,
MK LOW PHASE NOISE T1/E1 CLOCK GENERATOR. Features. Description. Block Diagram DATASHEET. Pullable Crystal
 DATASHEET LOW PHASE NOISE T1/E1 CLOCK ENERATOR MK1581-01 Description The MK1581-01 provides synchronization and timing control for T1 and E1 based network access or multitrunk telecommunication systems.
DATASHEET LOW PHASE NOISE T1/E1 CLOCK ENERATOR MK1581-01 Description The MK1581-01 provides synchronization and timing control for T1 and E1 based network access or multitrunk telecommunication systems.
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET. TDA1596 IF amplifier/demodulator for FM radio receivers. Product specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 April 1991 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The provides IF amplification, symmetrical quadrature demodulation and level detection for quality home
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 April 1991 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The provides IF amplification, symmetrical quadrature demodulation and level detection for quality home
315MHz Low-Power, +3V Superheterodyne Receiver
 General Description The MAX1470 is a fully integrated low-power CMOS superheterodyne receiver for use with amplitude-shiftkeyed (ASK) data in the 315MHz band. With few required external components, and
General Description The MAX1470 is a fully integrated low-power CMOS superheterodyne receiver for use with amplitude-shiftkeyed (ASK) data in the 315MHz band. With few required external components, and
Package and Pin Assignment SSOP-6 (0.64mm pitch) OSCIN OSCOUT TXEN 3 VSS 4 TXOUT 5 VSS 6 7 MODIN 8 HiMARK SW DO RES RESB VREFP VSS Symbol
 Low Power ASK Transmitter IC HiMARK Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change the product described in this datasheet. All information contained in this datasheet is subject to change without prior
Low Power ASK Transmitter IC HiMARK Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change the product described in this datasheet. All information contained in this datasheet is subject to change without prior
LM148/LM248/LM348 Quad 741 Op Amps
 Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series is a true quad 741. It consists of four independent, high gain, internally compensated, low power operational amplifiers which have been designed to
Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series is a true quad 741. It consists of four independent, high gain, internally compensated, low power operational amplifiers which have been designed to
CY520 Datasheet. 300M-450MHz ASK Receiver. General Description. Features. Applications CY520
 CY520 Datasheet 300M-450MHz ASK Receiver General Description The CY520 is a general purpose, 3.3-5V ASK Receiver that operates from 300M to 450MHz with typical sensitivity of -109dBm. The CY520 functions
CY520 Datasheet 300M-450MHz ASK Receiver General Description The CY520 is a general purpose, 3.3-5V ASK Receiver that operates from 300M to 450MHz with typical sensitivity of -109dBm. The CY520 functions
Single Supply, Rail to Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD820
 a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
LM565/LM565C Phase Locked Loop
 LM565/LM565C Phase Locked Loop General Description The LM565 and LM565C are general purpose phase locked loops containing a stable, highly linear voltage controlled oscillator for low distortion FM demodulation,
LM565/LM565C Phase Locked Loop General Description The LM565 and LM565C are general purpose phase locked loops containing a stable, highly linear voltage controlled oscillator for low distortion FM demodulation,
8-Bit A/D Converter AD673 REV. A FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
 a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit A/D Converter with Reference, Clock and Comparator 30 s Maximum Conversion Time Full 8- or 16-Bit Microprocessor Bus Interface Unipolar and Bipolar Inputs No Missing Codes Over
a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit A/D Converter with Reference, Clock and Comparator 30 s Maximum Conversion Time Full 8- or 16-Bit Microprocessor Bus Interface Unipolar and Bipolar Inputs No Missing Codes Over
PIN CONFIGURATIONS FEATURES APPLICATION ORDERING INFORMATION. FE, N Packages
 DESCRIPTION The are monolithic sample-and-hold circuits which utilize high-voltage ion-implant JFET technology to obtain ultra-high DC accuracy with fast acquisition of signal and low droop rate. Operating
DESCRIPTION The are monolithic sample-and-hold circuits which utilize high-voltage ion-implant JFET technology to obtain ultra-high DC accuracy with fast acquisition of signal and low droop rate. Operating
CD4541BC Programmable Timer
 CD4541BC Programmable Timer General Description The CD4541BC Programmable Timer is designed with a 16-stage binary counter, an integrated oscillator for use with an external capacitor and two resistors,
CD4541BC Programmable Timer General Description The CD4541BC Programmable Timer is designed with a 16-stage binary counter, an integrated oscillator for use with an external capacitor and two resistors,
12-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit ADC ADADC80
 2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit ADC FEATURES True 2-bit operation: maximum nonlinearity ±.2% Low gain temperature coefficient (TC): ±3 ppm/ C maximum Low power: 8 mw Fast conversion time:
2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit ADC FEATURES True 2-bit operation: maximum nonlinearity ±.2% Low gain temperature coefficient (TC): ±3 ppm/ C maximum Low power: 8 mw Fast conversion time:
Type Ordering Code Package TDA Q67000-A5168 P-DIP-18-5
 Video Modulator for FM-Audio TDA 5666-5 Preliminary Data Bipolar IC Features FM-audio modulator Sync level clamping of video input signal Controlling of peak white value Continuous adjustment of modulation
Video Modulator for FM-Audio TDA 5666-5 Preliminary Data Bipolar IC Features FM-audio modulator Sync level clamping of video input signal Controlling of peak white value Continuous adjustment of modulation
XR-2207 Voltage-Controlled Oscillator
 ...the analog plus company TM Voltage-Controlled Oscillator FETURES Excellent Temperature Stability (20ppm/ C) Linear Frequency Sweep djustable Duty Cycle (0.% to.%) Two or Four Level FSK Capability Wide
...the analog plus company TM Voltage-Controlled Oscillator FETURES Excellent Temperature Stability (20ppm/ C) Linear Frequency Sweep djustable Duty Cycle (0.% to.%) Two or Four Level FSK Capability Wide
FX806A AUDIO PROCESSOR
 FX86A AUDIO PROCESSOR CALIBRATION INPUT (TX) MIC. IN INPUT PROCESS (RX) AUDIO IN POWER SUPPLY MIC. & AMPS LOW & HIGHPASS FILTERS DE-EMPHASIS FILTER CHIP SELECT SENSE GAIN SET SERIAL CLOCK C-BUS INTERFACE
FX86A AUDIO PROCESSOR CALIBRATION INPUT (TX) MIC. IN INPUT PROCESS (RX) AUDIO IN POWER SUPPLY MIC. & AMPS LOW & HIGHPASS FILTERS DE-EMPHASIS FILTER CHIP SELECT SENSE GAIN SET SERIAL CLOCK C-BUS INTERFACE
SERIALLY PROGRAMMABLE CLOCK SOURCE. Features
 DATASHEET ICS307-02 Description The ICS307-02 is a versatile serially programmable clock source which takes up very little board space. It can generate any frequency from 6 to 200 MHz and have a second
DATASHEET ICS307-02 Description The ICS307-02 is a versatile serially programmable clock source which takes up very little board space. It can generate any frequency from 6 to 200 MHz and have a second
Low-Jitter, Precision Clock Generator with Two Outputs
 19-2456; Rev 0; 11/07 E V A L U A T I O N K I T A V A I L A B L E Low-Jitter, Precision Clock Generator Ethernet Networking Equipment General Description The is a low-jitter precision clock generator optimized
19-2456; Rev 0; 11/07 E V A L U A T I O N K I T A V A I L A B L E Low-Jitter, Precision Clock Generator Ethernet Networking Equipment General Description The is a low-jitter precision clock generator optimized
IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC. Technical Data. HSDL pc, tape and reel HSDL-7001# pc, 50/tube
 IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC Technical Data HSDL-7001-2500 pc, tape and reel HSDL-7001#100-100pc, 50/tube Features Compliant with IrDA 1.0 Physical Layer Specs Interfaces with IrDA 1.0 Compliant IR Transceivers
IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC Technical Data HSDL-7001-2500 pc, tape and reel HSDL-7001#100-100pc, 50/tube Features Compliant with IrDA 1.0 Physical Layer Specs Interfaces with IrDA 1.0 Compliant IR Transceivers
NTE7047 Integrated Circuit TV Color Small Signal Sub System
 NTE7047 Integrated Circuit TV Color Small Signal Sub System Features: Vision IF Amplifier with Synchronous Demodulator Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Detector Suitable for Negative Modulation AGC Tuner Automatic
NTE7047 Integrated Circuit TV Color Small Signal Sub System Features: Vision IF Amplifier with Synchronous Demodulator Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Detector Suitable for Negative Modulation AGC Tuner Automatic
Low-Voltage IF Transceiver with Limiter/RSSI and Quadrature Modulator
 19-1296; Rev 2; 1/1 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL FOLLOWS DATA SHEET Low-Voltage IF Transceiver with General Description The is a highly integrated IF transceiver for digital wireless applications. It operates
19-1296; Rev 2; 1/1 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL FOLLOWS DATA SHEET Low-Voltage IF Transceiver with General Description The is a highly integrated IF transceiver for digital wireless applications. It operates
ISM Band FSK Receiver IC ADF7902
 ISM Band FSK Receiver IC FEATURES Single-chip, low power UHF receiver Companion receiver to ADF7901 transmitter Frequency range: 369.5 MHz to 395.9 MHz Eight RF channels selectable with three digital inputs
ISM Band FSK Receiver IC FEATURES Single-chip, low power UHF receiver Companion receiver to ADF7901 transmitter Frequency range: 369.5 MHz to 395.9 MHz Eight RF channels selectable with three digital inputs
6500V/µs, Wideband, High-Output-Current, Single- Ended-to-Differential Line Drivers with Enable
 99 Rev ; /99 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 65V/µs, Wideband, High-Output-Current, Single- General Description The // single-ended-todifferential line drivers are designed for high-speed communications. Using
99 Rev ; /99 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 65V/µs, Wideband, High-Output-Current, Single- General Description The // single-ended-todifferential line drivers are designed for high-speed communications. Using
TDA 4700 TDA Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
 Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4700 Features Feed-forward control (line hum suppression) Symmetry inputs for push-pull converter (TDA 4700) Push-pull
Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4700 Features Feed-forward control (line hum suppression) Symmetry inputs for push-pull converter (TDA 4700) Push-pull
DS1867 Dual Digital Potentiometer with EEPROM
 Dual Digital Potentiometer with EEPROM www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Nonvolatile version of the popular DS1267 Low power consumption, quiet, pumpless design Operates from single 5V or ±5V supplies Two digitally
Dual Digital Potentiometer with EEPROM www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Nonvolatile version of the popular DS1267 Low power consumption, quiet, pumpless design Operates from single 5V or ±5V supplies Two digitally
HA7210, HA kHz to 10MHz, Low Power Crystal Oscillator. Description. Features. Ordering Information. Applications. Typical Application Circuits
 SEMICONDUCTOR HA, HA November 99 khz to MHz, Low Power Crystal Oscillator Features Description Single Supply Operation at khz.......... V to V Operating Frequency Range........ khz to MHz Supply Current
SEMICONDUCTOR HA, HA November 99 khz to MHz, Low Power Crystal Oscillator Features Description Single Supply Operation at khz.......... V to V Operating Frequency Range........ khz to MHz Supply Current
RF Basics 15/11/2013
 27 RF Basics 15/11/2013 Basic Terminology 1/2 dbm is a measure of RF Power referred to 1 mw (0 dbm) 10mW(10dBm), 500 mw (27dBm) PER Packet Error Rate [%] percentage of the packets not successfully received
27 RF Basics 15/11/2013 Basic Terminology 1/2 dbm is a measure of RF Power referred to 1 mw (0 dbm) 10mW(10dBm), 500 mw (27dBm) PER Packet Error Rate [%] percentage of the packets not successfully received
CMX860 Telephone Signalling Transceiver
 CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS Telephone Signalling Transceiver D/860/7 April 2008 Features V.23 & Bell 202 FSK Tx and Rx DTMF/Tones Transmit and Receive Line and Phone Complementary Drivers
CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS Telephone Signalling Transceiver D/860/7 April 2008 Features V.23 & Bell 202 FSK Tx and Rx DTMF/Tones Transmit and Receive Line and Phone Complementary Drivers
DATASHEET HSP Features. Description. Applications. Ordering Information. Block Diagram. Digital QPSK Demodulator. FN4162 Rev 3.
 DATASHEET HSP50306 Digital QPSK Demodulator Features 25.6MHz or 26.97MHz Clock Rates Single Chip QPSK Demodulator with 10kHz Tracking Loop Square Root of Raised Cosine ( = 0.4) Matched Filtering 2.048
DATASHEET HSP50306 Digital QPSK Demodulator Features 25.6MHz or 26.97MHz Clock Rates Single Chip QPSK Demodulator with 10kHz Tracking Loop Square Root of Raised Cosine ( = 0.4) Matched Filtering 2.048
12-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit A/D Converter AD ADC80
 a 2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit A/D Converter FEATURES True 2-Bit Operation: Max Nonlinearity.2% Low Gain T.C.: 3 ppm/ C Max Low Power: 8 mw Fast Conversion Time: 25 s Precision 6.3
a 2-Bit Successive-Approximation Integrated Circuit A/D Converter FEATURES True 2-Bit Operation: Max Nonlinearity.2% Low Gain T.C.: 3 ppm/ C Max Low Power: 8 mw Fast Conversion Time: 25 s Precision 6.3
SYN113 Datasheet. ( MHz ASK Transmitter) Version 1.0
 Datasheet (300 450MHz ASK Transmitter) Version 1.0 Contents 1. General Description... 1 2. Features... 1 3. Applications... 1 4. Typical Application... 2 5. Pin Configuration... 2 6. Pin Description...
Datasheet (300 450MHz ASK Transmitter) Version 1.0 Contents 1. General Description... 1 2. Features... 1 3. Applications... 1 4. Typical Application... 2 5. Pin Configuration... 2 6. Pin Description...
ericssonz LBI-38640E MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR VHF TRANSMITTER SYNTHESIZER MODULE 19D902780G1 DESCRIPTION
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR VHF TRANSMITTER SYNTHESIZER MODULE 19D902780G1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION........................................... Front Cover GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS...................................
MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR VHF TRANSMITTER SYNTHESIZER MODULE 19D902780G1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION........................................... Front Cover GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS...................................
XR-215A Monolithic Phase Locked Loop
 ...the analog plus company TM XR-21A Monolithic Phase Locked Loop FEATURES APPLICATIONS June 1997-3 Wide Frequency Range: 0.Hz to 2MHz Wide Supply Voltage Range: V to 26V Wide Dynamic Range: 300V to 3V,
...the analog plus company TM XR-21A Monolithic Phase Locked Loop FEATURES APPLICATIONS June 1997-3 Wide Frequency Range: 0.Hz to 2MHz Wide Supply Voltage Range: V to 26V Wide Dynamic Range: 300V to 3V,
KM4110/KM mA, Low Cost, +2.7V & +5V, 75MHz Rail-to-Rail Amplifiers
 + + www.fairchildsemi.com KM411/KM41.5mA, Low Cost, +.7V & +5V, 75MHz Rail-to-Rail Amplifiers Features 55µA supply current 75MHz bandwidth Power down to I s = 33µA (KM41) Fully specified at +.7V and +5V
+ + www.fairchildsemi.com KM411/KM41.5mA, Low Cost, +.7V & +5V, 75MHz Rail-to-Rail Amplifiers Features 55µA supply current 75MHz bandwidth Power down to I s = 33µA (KM41) Fully specified at +.7V and +5V
CD4046BM/CD4046BC Micropower Phase-Locked Loop
 CD4046BM/CD4046BC Micropower Phase-Locked Loop General Description The CD4046B micropower phase-locked loop (PLL) consists of a low power, linear, voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), a source follower,
CD4046BM/CD4046BC Micropower Phase-Locked Loop General Description The CD4046B micropower phase-locked loop (PLL) consists of a low power, linear, voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), a source follower,
ZL30111 POTS Line Card PLL
 POTS Line Card PLL Features Synchronizes to 8 khz, 2.048 MHz, 8.192 MHz or 19.44 MHz input Provides a range of clock outputs: 2.048 MHz, 4.096 MHz and 8.192 MHz Provides 2 styles of 8 khz framing pulses
POTS Line Card PLL Features Synchronizes to 8 khz, 2.048 MHz, 8.192 MHz or 19.44 MHz input Provides a range of clock outputs: 2.048 MHz, 4.096 MHz and 8.192 MHz Provides 2 styles of 8 khz framing pulses
FHP3350, FHP3450 Triple and Quad Voltage Feedback Amplifiers
 FHP335, FHP345 Triple and Quad Voltage Feedback Amplifiers Features.dB gain flatness to 3MHz.7%/.3 differential gain/phase error 2MHz full power -3dB bandwidth at G = 2,V/μs slew rate ±55mA output current
FHP335, FHP345 Triple and Quad Voltage Feedback Amplifiers Features.dB gain flatness to 3MHz.7%/.3 differential gain/phase error 2MHz full power -3dB bandwidth at G = 2,V/μs slew rate ±55mA output current
Low Power. Video Op Amp with Disable AD810 REV. A. Closed-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency, G = +2, R L = 150, R F = 715 Ω
 CLOSED-LOOP db SHIFT Degrees DIFFERENTIAL % DIFFERENTIAL Degrees a FEATURES High Speed MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling Time to.% ( = V Step) Ideal for Video
CLOSED-LOOP db SHIFT Degrees DIFFERENTIAL % DIFFERENTIAL Degrees a FEATURES High Speed MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling Time to.% ( = V Step) Ideal for Video
PART MAX4144ESD MAX4146ESD. Typical Application Circuit. R t IN- IN+ TWISTED-PAIR-TO-COAX CABLE CONVERTER
 9-47; Rev ; 9/9 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE General Description The / differential line receivers offer unparalleled high-speed performance. Utilizing a threeop-amp instrumentation amplifier architecture,
9-47; Rev ; 9/9 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE General Description The / differential line receivers offer unparalleled high-speed performance. Utilizing a threeop-amp instrumentation amplifier architecture,
ADC0808/ADC Bit µp Compatible A/D Converters with 8-Channel Multiplexer
 ADC0808/ADC0809 8-Bit µp Compatible A/D Converters with 8-Channel Multiplexer General Description The ADC0808, ADC0809 data acquisition component is a monolithic CMOS device with an 8-bit analog-to-digital
ADC0808/ADC0809 8-Bit µp Compatible A/D Converters with 8-Channel Multiplexer General Description The ADC0808, ADC0809 data acquisition component is a monolithic CMOS device with an 8-bit analog-to-digital
XR FSK Modem Filter FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM GENERAL DESCRIPTION FEATURES ORDERING INFORMATION APPLICATIONS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
 FSK Modem Filter GENERAL DESCRIPTION FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM The XR-2103 is a Monolithic Switched-Capacitor Filter designed to perform the complete filtering function necessary for a Bell 103 Compatible
FSK Modem Filter GENERAL DESCRIPTION FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM The XR-2103 is a Monolithic Switched-Capacitor Filter designed to perform the complete filtering function necessary for a Bell 103 Compatible
Single chip 433MHz RF Transceiver
 Single chip 433MHz RF Transceiver RF0433 FEATURES True single chip FSK transceiver On chip UHF synthesiser, 4MHz crystal reference 433MHz ISM band operation Few external components required Up to 10mW
Single chip 433MHz RF Transceiver RF0433 FEATURES True single chip FSK transceiver On chip UHF synthesiser, 4MHz crystal reference 433MHz ISM band operation Few external components required Up to 10mW
MGM 3000X Q67000-A5179 P-DSO-20-1 (SMD) MGM 3000X Q67006-A5179 P-DSO-20-1 Tape & Reel (SMD)
 Video Modulator for FM/AM-Audio MGM 3000X Bipolar IC Features FM- and AM-audio modulator Audio carrier output for suppression of harmonics Sync level clamping of video input signal Controlling of peak
Video Modulator for FM/AM-Audio MGM 3000X Bipolar IC Features FM- and AM-audio modulator Audio carrier output for suppression of harmonics Sync level clamping of video input signal Controlling of peak
