Section 9 Glossary, Unit Conversions & Kulite Reports
|
|
|
- Earl Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 9 Glossary, Unit Conversions & Kulite Reports 9.1. Glossary of Terms A Acceleration Sensitivity (Error) The maximum difference at any measurand value between the output with and without the application of a specified constant acceleration along specified axes. Normally specified in transverse and perpendicular directions. (% FSO/g) Accuracy The ratio of error to Full Scale Output often expressed in percent of Full Scale output. (%FSO) Acceptor A material added as a dopant to a semiconductor to make it p-type by accept-in valence electrons and leaving holes behind that can conduct electric charges. Normally Boron is used for doping Silicon. A/D Abbreviation for analogue to digital A/D Converter An electronic device used to convert an analogue voltage to a digital signal. Altitude The vertical distance above a specified reference datum such as sea level. Ambient Conditions The conditions (Pressure, temperature, etc.) of the device's environment. Analogue Output An output of analogue voltage derived from processing of digital and/or analogue input to circuitry within an (electronic) device. Normally a continuous function of the measurand except as modified by device resolution. Angstrom A unit for Ultra-high frequencies equal to ten raised to the power -10 meters. Annealing A heating process that reverse damage to the crystal structure or to activate dopant. Attitude Error The error due to the orientation of the device relative to direction of the force of gravity on the transducer. B Bandwidth The highest frequency signal component that can pass through input amplifiers without being attenuated. Best Fit Straight Line A line midway between two parallel straight lines closest together and enclosing all output points of the instrumentation between zero load and full scale. Breakdown Voltage Rating The voltage (AC or DC) which can be applied across the transducer insulation without causing arcing or conduction above a specified current. Bridge Resistance Resistance of the transducer bridge elements ( input or output impedance). Burst Pressure Rating The pressure which may be applied to the sensing element or the transducer case just prior to rupture of either. A minimum number of applications and time duration are also often specified. C Calibration A test to determine the output signal of the device with a steady input excitation and known values of the parameter under controlled conditions Calibration Curve A graphical representation of the device output vs. measurand under controlled conditions. 123 Semiconductor Products, Inc. Page 9-1
2 Calibration Cycle The application of controlled values of a parameter proving an output signal over the full range of the instrument in ascending and descending order. Compensated Temperature Range Range of Temperatures over which the transducer has been corrected by the addition of a circuit to correct the output for errors induced by changes in bridge resistance due to temperature. Compensation Addition of supplemental device, circuit, or special materials to reverse known source of errors. Combined Linearity and Hysteresis Square of the sums of squares of error due to non-linearity and that of and hysteresis non-linearity. D D/A Abbreviation for Digital to Analogue. D/A Converter A device for converting a digital signal to an analogue signal. Damping An energy absorbing factor that in conjunction with the natural frequency determines the limit of frequency response and the response time characteristics of a transducer. In response to a step function of the parameter a periodic (underdamped) system oscillates about the voltage level before stabilising at its final steady output; an aperiodic (overdamped) system comes to the final steady output without overshooting; and a critically damped system is defined as one that is at the point of changing from a periodic to a aperiodic system. Dead Volume Total volume of the pressure port cavity of a transducer with room barometric pressure applied. Decibel A unit of logarithmic measure based on the ratio of power related quantities such as sound, volts, or watts to a specified reference in same units. Deposition The procedure of deposit materials onto a substrate by means of vacuum, electrical, screening, or vapour techniques. Dice or Die A section of a processed wafer, usually rectangular, which contains one functional circuit. Dielectric An insulating layer. A material that has high resistance. Dielectric Strength Same as breakdown voltage. Diffusion A process used in semiconductor production by adding small amounts of impurities or dopants to a semiconductor. Digital Output Transducer output that represents the magnitude of the parameter measured in terms of discrete quantities or codes in a system of notation. 0 and 1 are commonly used. Digital and analogue are common output types. Donor A material added as a dopant to a semiconductor to make it n-type by donating valence electrons which can conduct electric charge. An example is phosphorus. Dopant A material added in minute quantities to a semiconductor to alter it's electrical conducting characteristics. They may be donors or acceptors. Doping The process of adding a dopant to semiconductor material. Drift A undesired change of a reading with no charge in the input signal or operating conditions. Dynamic Characteristics The characteristics of a transducer which describes its response to variations in measurand pressure over time. E Electrical Connection The portion of the transducer assembly used to connect, disconnect, and reconnect the electrical wiring that carries excitation voltage, signal or current to and from the transducer. Page Semiconductor Products, Inc.
3 Environmental Conditions Specific external conditions, such as shock, vibration, temperature, moisture, etc. to which a transducer may be exposed during normal operations. End Point Output signal at upper and lower limits of the transducer range. End Point Line Line drawn between the end points of a transducer calibration. Environmental Conditions Specified external conditions,such as shock, vibration, temperature, moisture, etc. to which a transducer may be exposed during normal operations. Environmental Conditions, Operating Specified external conditions,such as shock, vibration, temperature, moisture, etc. when a transducer is exposed to must perform as specified. Error The mathematical difference between the indicated value and the true value of the parameter signal. Error Band The band of maximum deviations of output values from a specified reference line or curve due to those causes attributable to the transducer. Usually described as plus or minus some value of transducer full scale output. Excitation The external electrical voltage and/or current applied to a sensor assembly to initiate the proportional output. Usually expressed in ranges the transducer may subjected to without damage. The value of this voltage is set by calibration and any serious deviation from this value will negate the calibration. Extrinsic Semiconductor A semiconductor that has been doped either n-type or p-type. Electrons and holes are present in unequal proportions (by 4 to 8 orders of magnitude). F Frequency Modulated Output An output in the form of frequency deviations from a centre frequency, where the deviation is a function of the measured parameter. Frequency Output An output in the form of frequency which varies as a function of the applied measurand. Frequency, Natural The frequency of free (not forced) oscillations of the sensing element of a fully assembled transducer. Frequency, Resonant The input frequency at which a transducer responds with maximum output amplitude. If there is more than one frequency the lowest is the resonant frequency Frequency Response The change with frequency of the output/parameter amplitude ratio( and of the phase difference between the output and the parameter) for sinusoidal varying measurand applied to a transducer within a specified range. It is normal consider at plus or minus 3 db and is given by the approximation. F.R.= 1/2pt Freq. Response = 1 divided by 2 times Pi times time constant Full Scale Output The value of transducer output at the maximum rated load minus the output at the minimum rated load. G Gage Factor A measure of the ratio of the relative change of resistance to the relative change in length of a resistance strain transducer (strain gage). 123 Semiconductor Products, Inc. Page 9-3
4 H Hysteresis The maximum difference in output, at any measurand value within the specified range, when the value is approached first with increasing and then decreasing measurand. Normally expressed in % FSO. I IEEE Abbreviation for Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Input Measurand signal (and/or exciting voltage or current). Input Impedance The impedance (presented to the excitation source) measured across the excitation terminals of the transducer. Unless otherwise specified the impedance is measured at room temperature, etc. Insulation Resistance The resistance measured between specified insulated portions of a transducer when a specified DC voltage is applied at ambient conditions- room temperature etc. Ion The result of an atom losing an electron and becoming positive or gaining an electron and becoming negative. J, K, L Leakage Rate The maximum rate at which a fluid is observed or permitted to leak through a seal. The type of fluid, differential pressure across the seal, and the direction of flow should be specified. Units are normally volume or pressure drop per unit of time. Least Squares Line The straight line for which the sum of the squares of the residuals( deviations) is minimised. Life, Cycle The specified number of full and/or partial range excursions over which a device will operate within specified performance criteria. Life, Operating The length of time over which device will operate to a specified performance. Life, Storage The length of time over which device can be stored at specified conditions and still operate to a specified performance. Linearity The closeness of a calibration curve to a specified straight line expressed as % FSO. Load Impedance The impedance presented to the output terminals of the transducer by the external circuitry connected to the device. M Maximum Ambient Temperature The value of the highest (and the lowest) ambient temperatures that a (Minimum) transducer can be exposed to with or without excitation applied, without being damaged and subsequently suffering performance degradation. Maximum Excitation Value of excitation voltage or current that can be applied to the transducer at room conditions without causing damage or performance degradation. Measurand (Parameter) A physical quantity, property, or condition, which is measured, Sometimes called input, parameter, or variable. Measured Fluid The fluid that comes in contact with the sensing element. Chemical and/or physical properties of this fluid may be specified to insure proper transducer operation and life. Page Semiconductor Products, Inc.
5 Mounting Error An error due to mechanical deformation of the transducer caused by mounting the device and/or making the electrical connection. N Natural Frequency See Frequency, Natural Non-Linearity See Linearity. Normally expressed as % FSO. Non-Operating Conditions Any conditions outside of operating conditions that might cause transducer to malfunction. Non-Repeatability Breakdown of the transducer characteristics of repeatability a small amount of which is contained in an acceptable error band. Usually expressed as % FSO. Null A condition, such as of balance, which results in a minimum absolute value of output. O Operation Mode A description of how the transducer is used to provide a usable signal representing a measurand variation. Operating Conditions See environmental conditions. Operating Temperature Range Temperature range the operating transducer will be subjected to. Output The electrical quantity produced by the transducer which is a function of the applied measurand. Output Impedance The impedance across the output terminals of a transducer presented by the transducer to the associated external circuitry. Output Noise The RMS or peak to peak, as specified, ac component of a transducer's DC output in the absence of measurand variations. Output Range Design band of output for specified input. Overload The maximum value of a measurand that can be applied to a transducer without damage or change in performance beyond a specified tolerance. Over Pressure See Overload. P Pressure Range Lowest to the highest pressures to be measured by a specific transducer. Pressure Media See measured fluid. Proof Pressure The maximum pressure, which may be applied to the sensing element without a change in the transducer performance beyond specified tolerances. Differential pressure transducers must have the reference pressure specified and whether the reverse pressure is applicable. Q, R Range The measurand values over which a transducer is designed to measure. Indicated by upper and lower values. 123 Semiconductor Products, Inc. Page 9-5
6 Rated Electrical Excitation The electrical voltage supply the transducer sensing element for normal operation given the specified output with the application of a known measurand. Reference Pressure The pressure applied to the opposite side of the sensing element- ambient pressure for gage and perfect vacuum for absolute designs. Reference Pressure Error The error in transducer output resulting from errors in the reference pressure value within a specified reference pressure range. Reference Pressure Range The range of pressures that can be applied to the backside of a sensing element without changing the pressure transducer's performance beyond specified tolerances. If no tolerance is specified, none is allowed. Reference Pressure Sensitivity Shift The sensitivity shift resulting from variations of a differential pressure transducer's reference pressure within specified limits. Repeatability The ability of a transducer to reproduce output values when the same measurand value is applied repeatedly under the same conditions and in the same direction. Reproducibility See Repeatability Residual Unbalance Zero measurand sensing element output Resolution The magnitude of output step changes as measurand is continuously varied over the range. Resonance Amplified vibrations of transducer components, within a narrow frequency band, observable in the output as a vibration applied along a specific transducer axis. Resonant Frequency The input frequency at which a transducer responds with maximum output amplitude. If there is more than one frequency the lowest is the resonant frequency Response Time The length of time required for the output of a transducer to rise to a value normally specified as 98 % of the value of a step change in measurand expressed in milliseconds. Rise Time The length of time required for the output of a transducer to rise from a small specified percentage of it's final value to a large specified percentage of it's final value as a result of a step change in the measurand. Room Conditions Normal specified ambient conditions. Normally 77 F + or - 18 F, 90 % RH, and 29 + or - 3 in Hg. S Self-Heating Internal heating as a result of electrical energy dissipated within the transducer. Sensing Element The part of the sensing element that responds directly to the measurand. Sensitivity The ratio of the change in transducer output to a change in the value of the measurand. Sensitivity Shift A change in the slope of the calibration curve due to a change in sensitivity. Sensor Instrumentation device, such as transducer. Sound Pressure Level (SPL) A unit that is 20 times the logarithm to the base 10 of the ratio of the pressure of the measured sound to the reference pressure of 20 micronewtons per square meter. Span The algebraic difference between the limits of range. Stability The ability of a transducer to retain its performance characteristics for relatively long period of time. Normally expressed in % FSO. Static Calibration A calibration performed under room conditions and in the absence of any vibration, shock, or acceleration. Static Error Band See Error Band. T Temperature Error Band The error band applicable to increased or decrease environmental temperature usually expressed in % FSO/ 100 F. Page Semiconductor Products, Inc.
7 Temperature Range, Compensated See Temperature range, operating. Compensated temperature range is the interval of temperature range that was considered when designing compensation module for a specific transducer. Temperature Range, Fluid The rang for temperatures of the measured fluid, when it is not the ambient within which operation of the transducer is intended, and all specific tolerances for the temperature error band apply. Temperature Range, Operating The range of temperatures, given by their extremes, within which the transducer is designed to operate with no permanent damage to the transducer. Thermal Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) The relative change in resistance of a conductor or semiconductor per unit change in temperature over a stated range of temperature normally expressed in ohms per degree F or C. Thermal Compensation The addition of circuitry to alter output changed by temperature error back toward specified values at room temperature. Thermal Sensitivity Shift The sensitivity change due to changes of the ambient temperature from room temperature (design conditions) toward the limits of the operating temperature range. Thermal Zero Shift The zero measurand transducer output shift due to changes of the ambient temperature from room temperature to the specified limits of the operating temperature range. Transducer A device which provides a usable output in response to a specified measurand. Transient Response The response of a transducer to a step change in measurand. It is indicated by Time Constant, Ringing Period, and Response Time. Transverse Acceleration An acceleration perpendicular to the sensitive axis of the transducer. U, V Vibration Error The maximum change in output, at any measurand value within the specified range, when vibration levels of specified amplitude and range of frequencies are applied to the transducer along specified axes. Vibration Sensitivity See Vibration error. W, X, Y, Z Warm-up Period The period of time required from the time the excitation voltage is applied to the transducer until the output of the unit is within the specified tolerances for the applied measurand. Weight Weight of the transducer normally not including any portion that varies such as cables. 123 Semiconductor Products, Inc. Page 9-7
8 9.2 Pressure Unit Conversions Units of Measurement Decibel Formulae Page Semiconductor Products, Inc.
9 9.3 Kulite Reports Andrew Bemis High Pressure Transducers Dr. A. D. Kurtz, A. A. Ned, Glenn Beheim 6H-SiC Pressure Sensor for High Temperature, Low Pressure Applications Dr. A. D. Kurtz, Boaz Kochman Dual Resonant Beam Pressure Transducer Joe VanDe Weert Fuel Pump Transducer Adam Kane Miniature combination Pressure/ Temperature Sensors with Redundant Capability Wolf Landmann Solid State Replacements for Electro-Mechanical Pressure Transducers Dr. A. D. Kurtz, Dr. J. W. H. Chivers, A. A. Ned (Kulite) & Professor A. H. Epstein (MIT) Sensor Requirements for Active Gas Turbine Engine Control Adam Kane High Accuracy DC Combustion Transducers Andrew Schwartz Subminiature Load Cells Dr. A. D. Kurtz, Joseph VanDe Weert & Boaz Kochman Static Pitot Transducer Semiconductor Products, Inc. Page Kulite Semiconductor Products, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Pressure Transducer Handbook
 123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
Introduction to Measurement Systems
 MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
DavidsonSensors. Fiber Optic Sensing System Definitions. Davidson Fiber Optic Sensing System
 DavidsonSensors October 2007 Fiber Optic Sensing System Davidson Fiber Optic Sensing System DavidsonSensors Measure Temperature, Pressure, Vacuum, Flow, Level, and Vibration DavidsonSensors Transmit Intrinsically
DavidsonSensors October 2007 Fiber Optic Sensing System Davidson Fiber Optic Sensing System DavidsonSensors Measure Temperature, Pressure, Vacuum, Flow, Level, and Vibration DavidsonSensors Transmit Intrinsically
Section 7 - Measurement of Transient Pressure Pulses
 Section 7 - Measurement of Transient Pressure Pulses Special problems are encountered in transient pressure pulse measurement, which place stringent requirements on the measuring system. Some of these
Section 7 - Measurement of Transient Pressure Pulses Special problems are encountered in transient pressure pulse measurement, which place stringent requirements on the measuring system. Some of these
Section 6 - Electronics
 Section 6 - Electronics 6.1. Power for Excitation Piezoresistive transducers are passive devices and require an external power supply to provide the necessary current (I x ) or voltage excitation (E x
Section 6 - Electronics 6.1. Power for Excitation Piezoresistive transducers are passive devices and require an external power supply to provide the necessary current (I x ) or voltage excitation (E x
Miniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C TP 301
 Miniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C TP 301 Model 8540 miniature pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C Abstract A miniature,
Miniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C TP 301 Model 8540 miniature pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C Abstract A miniature,
GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR PROCESS CONTROL
 Y1900SS-1a 1 GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR PROCESS CONTROL Accuracy Conformity of an indicated value to an accepted standard value, or true value. Accuracy, Reference A number or quantity which defines the limit
Y1900SS-1a 1 GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR PROCESS CONTROL Accuracy Conformity of an indicated value to an accepted standard value, or true value. Accuracy, Reference A number or quantity which defines the limit
Miniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C
 Miniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C PMiniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C Abstract A miniature,
Miniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C PMiniature silicon-on-insulator pressure transducer for absolute pressure measurement at 260 C Abstract A miniature,
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES
 KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
An Explanation of GP:50 Performance Specifications
 Introduction: The performance specifications of GP:50 pressure transducers are typically identified on the sales literature or datasheet for the particular model type. Performance specifications include
Introduction: The performance specifications of GP:50 pressure transducers are typically identified on the sales literature or datasheet for the particular model type. Performance specifications include
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Technical Information
 Technical Information Introduction to force sensors Driving long cable lengths Conversions, article reprints, glossary INTRODUCTION TO QUARTZ FORCE SENSORS Quartz Force Sensors are well suited for dynamic
Technical Information Introduction to force sensors Driving long cable lengths Conversions, article reprints, glossary INTRODUCTION TO QUARTZ FORCE SENSORS Quartz Force Sensors are well suited for dynamic
Anthony Chu. Basic Accelerometer types There are two classes of accelerometer in general: AC-response DC-response
 Engineer s Circle Choosing the Right Type of Accelerometers Anthony Chu As with most engineering activities, choosing the right tool may have serious implications on the measurement results. The information
Engineer s Circle Choosing the Right Type of Accelerometers Anthony Chu As with most engineering activities, choosing the right tool may have serious implications on the measurement results. The information
 Page 1 of 6 A Historical Perspective From Aristotle to Hawking Force & Its Effects Measurement Limitations The Strain Gage Sensor Designs Measuring Circuits Application & Installation Process Pressure
Page 1 of 6 A Historical Perspective From Aristotle to Hawking Force & Its Effects Measurement Limitations The Strain Gage Sensor Designs Measuring Circuits Application & Installation Process Pressure
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Examination.
 Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2003 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2003 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES
 EXPERIMENT 9 EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES Semiconductor Diodes Structure 91 Introduction Objectives 92 Basics of Semiconductors Revisited 93 A p-n Junction Operation of a p-n Junction A Forward
EXPERIMENT 9 EXPERIMENTS USING SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES Semiconductor Diodes Structure 91 Introduction Objectives 92 Basics of Semiconductors Revisited 93 A p-n Junction Operation of a p-n Junction A Forward
Materials (other materials see WIKA diaphragm seal program) Model S-10
 2.0 Specifications WIKA Tronic catalog pages and data sheets have a consistent layout of technical information that is required to select the correct transmitter. The second page of the data sheet lists
2.0 Specifications WIKA Tronic catalog pages and data sheets have a consistent layout of technical information that is required to select the correct transmitter. The second page of the data sheet lists
INDEX IEC:
 60050-300 IEC:2001 173 INDEX A absolute absolute error... 311-01-05 (absolute) frequency deviation... 314-08-07 accessory accessory (of a measuring instrument)... 312-03-01 accessory of limited interchangeability...
60050-300 IEC:2001 173 INDEX A absolute absolute error... 311-01-05 (absolute) frequency deviation... 314-08-07 accessory accessory (of a measuring instrument)... 312-03-01 accessory of limited interchangeability...
Freescale Semiconductor Data Sheet: Technical Data
 Freescale Semiconductor Data Sheet: Technical Data Media Resistant and High Temperature Accuracy Integrated Silicon Sensor for Measuring Absolute, On-Chip Signal Conditioned, Temperature Compensated and
Freescale Semiconductor Data Sheet: Technical Data Media Resistant and High Temperature Accuracy Integrated Silicon Sensor for Measuring Absolute, On-Chip Signal Conditioned, Temperature Compensated and
EC T34 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 RAJIV GANDHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY PONDY-CUDDALORE MAIN ROAD, KIRUMAMPAKKAM-PUDUCHERRY DEPARTMENT OF ECE EC T34 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II YEAR Mr.L.ARUNJEEVA., AP/ECE 1 PN JUNCTION
RAJIV GANDHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY PONDY-CUDDALORE MAIN ROAD, KIRUMAMPAKKAM-PUDUCHERRY DEPARTMENT OF ECE EC T34 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II YEAR Mr.L.ARUNJEEVA., AP/ECE 1 PN JUNCTION
MIL-STD-202G SHOCK (SPECIFIED PULSE)
 SHOCK (SPECIFIED PULSE) 1. PURPOSE. This test is conducted for the purpose of determining the suitability of component parts and subassemblies of electrical and electronic components when subjected to
SHOCK (SPECIFIED PULSE) 1. PURPOSE. This test is conducted for the purpose of determining the suitability of component parts and subassemblies of electrical and electronic components when subjected to
AN5E Application Note
 Metra utilizes for factory calibration a modern PC based calibration system. The calibration procedure is based on a transfer standard which is regularly sent to Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)
Metra utilizes for factory calibration a modern PC based calibration system. The calibration procedure is based on a transfer standard which is regularly sent to Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)
bar, Type 413xA..., 414xA... Technical Data (based on Tref = 25 C; power supply 1 ma constant) Type 413xA... 0,2... 0,
 Pressure SUNSTAR 传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 E-MAIL: OEM Pressure Sensors for Relative and Absolute Pressure of 0,2... 200 bar Type 413xA..., 414xA... OEM pressure sensors of Type
Pressure SUNSTAR 传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 E-MAIL: OEM Pressure Sensors for Relative and Absolute Pressure of 0,2... 200 bar Type 413xA..., 414xA... OEM pressure sensors of Type
CHOOSING THE RIGHT TYPE OF ACCELEROMETER
 As with most engineering activities, choosing the right tool may have serious implications on the measurement results. The information below may help the readers make the proper accelerometer selection.
As with most engineering activities, choosing the right tool may have serious implications on the measurement results. The information below may help the readers make the proper accelerometer selection.
PHYS 3050 Electronics I
 PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2I03
 Student Name: Student ID: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2I03 DAY CLASS Duration 2 hours McMaster University Practice Exam Dr. M. Thompson The final test includes 60 questions on 12 pages. This test paper must be
Student Name: Student ID: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2I03 DAY CLASS Duration 2 hours McMaster University Practice Exam Dr. M. Thompson The final test includes 60 questions on 12 pages. This test paper must be
Load cell system fault finding guide (Application Note: Number AN1)
 Load cell system fault finding guide (Application Note: Number AN1) Table of Contents Basic checks 3 Basic load cell system............................ 3 Basic load cell resistance checks......................
Load cell system fault finding guide (Application Note: Number AN1) Table of Contents Basic checks 3 Basic load cell system............................ 3 Basic load cell resistance checks......................
FEATURES. V out VSH144. Interloop Capacitance Reduction in Series. Mutual Inductance Reduction due to Opposing Current in Adjacent Lines
 Bulk Metal Foil Technology Low Profile Conformally Coated High Precision Voltage Divider Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0.5 ppm/ C and Tolerance Match to 0.01 % (100 ppm) APPLICATIONS Instrumentation amplifiers
Bulk Metal Foil Technology Low Profile Conformally Coated High Precision Voltage Divider Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0.5 ppm/ C and Tolerance Match to 0.01 % (100 ppm) APPLICATIONS Instrumentation amplifiers
Capacitive Versus Thermal MEMS for High-Vibration Applications James Fennelly
 Capacitive Versus Thermal MEMS for High-Vibration Applications James Fennelly Design engineers involved in the development of heavy equipment that operate in high shock and vibration environments need
Capacitive Versus Thermal MEMS for High-Vibration Applications James Fennelly Design engineers involved in the development of heavy equipment that operate in high shock and vibration environments need
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
Ultrasonic. Advantages
 Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 20
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 20 Photo-Detectors and Detector Noise Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept.
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 20 Photo-Detectors and Detector Noise Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept.
PN Junction Diode Table of Contents. What Are Diodes Made Out Of?
 PN Junction iode Table of Contents What are diodes made out of?slide 3 N-type materialslide 4 P-type materialslide 5 The pn junctionslides 6-7 The biased pn junctionslides 8-9 Properties of diodesslides
PN Junction iode Table of Contents What are diodes made out of?slide 3 N-type materialslide 4 P-type materialslide 5 The pn junctionslides 6-7 The biased pn junctionslides 8-9 Properties of diodesslides
Experiment 9. PID Controller
 Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
AD596/AD597 SPECIFICATIONS +60 C and V S = 10 V, Type J (AD596), Type K (AD597) Thermocouple,
 AD597 SPECIFICATIONS (@ +60 C and V S = 10 V, Type J (AD596), Type K (AD597) Thermocouple, unless otherwise noted) Model AD596AH AD597AH AD597AR Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM
AD597 SPECIFICATIONS (@ +60 C and V S = 10 V, Type J (AD596), Type K (AD597) Thermocouple, unless otherwise noted) Model AD596AH AD597AH AD597AR Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Chapter 1. Introduction Basic Architecture for an Electronic/Optoelectronic Instrumentation Measurement System. Definitions. Sensors and Categories of Sensor by Input Mechanisms
Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Chapter 1. Introduction Basic Architecture for an Electronic/Optoelectronic Instrumentation Measurement System. Definitions. Sensors and Categories of Sensor by Input Mechanisms
SX Series Pressure sensors
 FEATURES 0...1 to 0...300 psi Absolute, differential and gage devices High impedance bridge Low power consumption for battery operation APPLICATIONS Industrial controls Pneumatic controls Medical instrumentation
FEATURES 0...1 to 0...300 psi Absolute, differential and gage devices High impedance bridge Low power consumption for battery operation APPLICATIONS Industrial controls Pneumatic controls Medical instrumentation
Thermocouple Conditioner and Setpoint Controller AD596*/AD597*
 a FEATURES Low Cost Operates with Type J (AD596) or Type K (AD597) Thermocouples Built-In Ice Point Compensation Temperature Proportional Operation 10 mv/ C Temperature Setpoint Operation ON/OFF Programmable
a FEATURES Low Cost Operates with Type J (AD596) or Type K (AD597) Thermocouples Built-In Ice Point Compensation Temperature Proportional Operation 10 mv/ C Temperature Setpoint Operation ON/OFF Programmable
Temperature References for Highest Accuracy Industrial Thermocouple Measurements
 Publication #531 Temperature References for Highest Accuracy Industrial Thermocouple Measurements Obtaining high-accuracy thermocouple temperature measurements requires instrumentation designed to minimize
Publication #531 Temperature References for Highest Accuracy Industrial Thermocouple Measurements Obtaining high-accuracy thermocouple temperature measurements requires instrumentation designed to minimize
EDC Lecture Notes UNIT-1
 P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
Heavy Duty Pressure Transducers. PX2 Series 1 bar to 46 bar 100 kpa to 4.6 MPa 15 psi to 667 psi. Datasheet
 PX2 Series bar to 46 bar 00 kpa to 4.6 MPa 5 psi to 667 psi Datasheet Table. Electrical Specifications Characteristic Ratiometric Regulated Transfer Function Order Code (See Figure 5.) AA AB AC AD CH BC
PX2 Series bar to 46 bar 00 kpa to 4.6 MPa 5 psi to 667 psi Datasheet Table. Electrical Specifications Characteristic Ratiometric Regulated Transfer Function Order Code (See Figure 5.) AA AB AC AD CH BC
Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics
 Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács BME DED 17/09/2015 1 / 37 The basic properties of semiconductors Range of conductivity [Source: http://www.britannica.com]
Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács BME DED 17/09/2015 1 / 37 The basic properties of semiconductors Range of conductivity [Source: http://www.britannica.com]
UNIT-VI FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR. 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s.
 UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
MEAS Silicon MEMS Piezoresistive Accelerometer and its Benefits
 MEAS Silicon MEMS Piezoresistive Accelerometer and its Benefits Piezoresistive Accelerometers 1. Bonded Strain Gage type (Gages bonded to metal seismic mass using epoxy) Undamped circa 1950 s Fluid (oil)
MEAS Silicon MEMS Piezoresistive Accelerometer and its Benefits Piezoresistive Accelerometers 1. Bonded Strain Gage type (Gages bonded to metal seismic mass using epoxy) Undamped circa 1950 s Fluid (oil)
Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa
 Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa SEMICONDUCTORS What is a Semiconductor? What is a Semiconductor? Microprocessors LED Transistors Capacitors Range of Conduciveness The semiconductors
Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa SEMICONDUCTORS What is a Semiconductor? What is a Semiconductor? Microprocessors LED Transistors Capacitors Range of Conduciveness The semiconductors
Digital Panel Meter Glossary
 Glossary RS-232C (Recommended Standard 232C) RS-232C is a modem interface standard for serial communications defined by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA). It defines the electrical specifications,
Glossary RS-232C (Recommended Standard 232C) RS-232C is a modem interface standard for serial communications defined by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA). It defines the electrical specifications,
The units of vibration depend on the vibrational parameter, as follows:
 Vibration Measurement Vibration Definition Basically, vibration is oscillating motion of a particle or body about a fixed reference point. Such motion may be simple harmonic (sinusoidal) or complex (non-sinusoidal).
Vibration Measurement Vibration Definition Basically, vibration is oscillating motion of a particle or body about a fixed reference point. Such motion may be simple harmonic (sinusoidal) or complex (non-sinusoidal).
Data sheet. P3 Top Class BlueLine. P3MBP BlueLine. Ultra-high pressure transducers to 15,000 bar. Special features
 Ultra-high pressure transducers to 1,000 bar Data sheet Special features P Top Class BlueLine PMBP BlueLine - For static and dynamic pressure variance, pressure peaks and pressure fluctuations - Principle
Ultra-high pressure transducers to 1,000 bar Data sheet Special features P Top Class BlueLine PMBP BlueLine - For static and dynamic pressure variance, pressure peaks and pressure fluctuations - Principle
up to 200 C, 4007B... Technical Data 4007B, General Measuring range bar Overload bar Power supply ma* 1 Output signal (FS
 Pressure SUNSTAR 传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 E-MAIL: High Temperature Pressure Sensor 5 and 20 bar Version for Temperatures up to 200 C 4007B... Rugged pressure sensor for the measurement
Pressure SUNSTAR 传感与控制 http://www.sensor-ic.com/ TEL:0755-83376549 E-MAIL: High Temperature Pressure Sensor 5 and 20 bar Version for Temperatures up to 200 C 4007B... Rugged pressure sensor for the measurement
OX-043 Low g-sensitivity Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator
 OX-043 Low g-sensitivity Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator OX-043 Features Applications Ultra Low g-sensitivity Low Phase Noise High Stability Frequency Range: 8 MHZ to 15 MHZ Standard Frequency 10 MHz
OX-043 Low g-sensitivity Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator OX-043 Features Applications Ultra Low g-sensitivity Low Phase Noise High Stability Frequency Range: 8 MHZ to 15 MHZ Standard Frequency 10 MHz
AUTOMOTIVE CURRENT SENSOR DHAB S/18. Datasheet
 AUTOMOTIVE CURRENT SENSOR DHAB S/18 Datasheet 070720/1 Page 1/6 Introduction The DHAB family is best suited for DC, AC or pulse current measurement in high power and low voltage automotive applications.
AUTOMOTIVE CURRENT SENSOR DHAB S/18 Datasheet 070720/1 Page 1/6 Introduction The DHAB family is best suited for DC, AC or pulse current measurement in high power and low voltage automotive applications.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
AUTOMOTIVE CURRENT SENSOR DHAB S/25. Datasheet
 AUTOMOTIVE CURRENT SENSOR DHAB S/25 Datasheet Page 1/6 Introduction The DHAB family is best suited for DC, AC or pulse current measurement in high power and low voltage automotive applications. It s contains
AUTOMOTIVE CURRENT SENSOR DHAB S/25 Datasheet Page 1/6 Introduction The DHAB family is best suited for DC, AC or pulse current measurement in high power and low voltage automotive applications. It s contains
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
BARTINGTON INSTRUMENTS. How to use this Manual... 3 Symbols Glossary Introduction to the Mag Vector Measurements and Conventions...
 Table of Contents How to use this Manual... 3 Symbols Glossary... 3 Introduction to the Mag648... 4 Vector Measurements and Conventions... 4 Installing the Mag648... 5 Siting the Magnetometer (Environment
Table of Contents How to use this Manual... 3 Symbols Glossary... 3 Introduction to the Mag648... 4 Vector Measurements and Conventions... 4 Installing the Mag648... 5 Siting the Magnetometer (Environment
MPXM2051G, 0 to 50 kpa, Gauge Compensated Pressure Sensors
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: Data Sheet: Technical Data Rev. 3.0, 11/2015, 0 to 50 kpa, Gauge Compensated Pressure The device is a silicon piezoresistive pressure sensor providing a highly
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: Data Sheet: Technical Data Rev. 3.0, 11/2015, 0 to 50 kpa, Gauge Compensated Pressure The device is a silicon piezoresistive pressure sensor providing a highly
10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional)
 EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Exam. December 11, 2006
 MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Exam December 11, 2006 o Closed Book and Notes o No Calculators 1. Fill in your name on side 2 of the scoring sheet (Last name first!) 2. Fill
MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Exam December 11, 2006 o Closed Book and Notes o No Calculators 1. Fill in your name on side 2 of the scoring sheet (Last name first!) 2. Fill
High Pressure OEM Sensor RHU50
 Pressure High Pressure OEM Sensor RHU50 for Absolute Pressures from 100... 3 000 bar Type RHU50... Unlike many other pressure transducers, the series RH high pressure/high temperature sensors can directly
Pressure High Pressure OEM Sensor RHU50 for Absolute Pressures from 100... 3 000 bar Type RHU50... Unlike many other pressure transducers, the series RH high pressure/high temperature sensors can directly
Achieving accurate measurements of large DC currents
 Achieving accurate measurements of large DC currents Victor Marten, Sendyne Corp. - April 15, 2014 While many instruments are available to accurately measure small DC currents (up to 3 A), few devices
Achieving accurate measurements of large DC currents Victor Marten, Sendyne Corp. - April 15, 2014 While many instruments are available to accurately measure small DC currents (up to 3 A), few devices
Aero Support Ltd, 70 Weydon Hill Road, Farnham, Surrey, GU9 8NY, U.K.
 4-170 Piezoelectric Accelerometer The CEC 4-170 accelerometer is a self-generating, piezoelectric accelerometer designed for medium temperature vibration measurement applications. This instrument provides
4-170 Piezoelectric Accelerometer The CEC 4-170 accelerometer is a self-generating, piezoelectric accelerometer designed for medium temperature vibration measurement applications. This instrument provides
SCX Series Precision compensated pressure sensors
 FEATURES 0...1 psi to 0...150 psi Precision temperature compensation Calibrated zero and span Small size Low noise High accuracy High impedance for low power applications APPLICATIONS Medical equipment
FEATURES 0...1 psi to 0...150 psi Precision temperature compensation Calibrated zero and span Small size Low noise High accuracy High impedance for low power applications APPLICATIONS Medical equipment
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Sensing and Sensors: Fundamental Concepts
 Sensing and Sensors: Fundamental Concepts Sensitivity Range Precision Accuracy Resolution Offset Hysteresis Response Time Source: sensorwebs.jpl.nasa.gov Sensor: a device the receives and responds to a
Sensing and Sensors: Fundamental Concepts Sensitivity Range Precision Accuracy Resolution Offset Hysteresis Response Time Source: sensorwebs.jpl.nasa.gov Sensor: a device the receives and responds to a
Electronic Circuits I. Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud
 Electronic Circuits I Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud alaa_y_emam@hotmail.com Chapter 27 Diode and diode application Outline: Semiconductor Materials The P-N Junction Diode Biasing P-N Junction Volt-Ampere
Electronic Circuits I Instructor: Dr. Alaa Mahmoud alaa_y_emam@hotmail.com Chapter 27 Diode and diode application Outline: Semiconductor Materials The P-N Junction Diode Biasing P-N Junction Volt-Ampere
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
Rakon Product Proposal
 RTX5032A -- SMD Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator -- -- High performance TCXO offering excellent Phase Noise, Frequency Stability and VCO tilt compensation. -- Product description -- The RTX5032A
RTX5032A -- SMD Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator -- -- High performance TCXO offering excellent Phase Noise, Frequency Stability and VCO tilt compensation. -- Product description -- The RTX5032A
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica. Analogue Electronics. Paolo Colantonio A.A.
 Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
Improved Low Cost ±5 g Dual-Axis Accelerometer with Ratiometric Analog Outputs MXR7305VF
 Improved Low Cost ±5 g Dual-Axis Accelerometer with Ratiometric Analog Outputs MXR7305VF FEATURES Dual axis accelerometer fabricated on a single CMOS IC Monolithic design with mixed mode signal processing
Improved Low Cost ±5 g Dual-Axis Accelerometer with Ratiometric Analog Outputs MXR7305VF FEATURES Dual axis accelerometer fabricated on a single CMOS IC Monolithic design with mixed mode signal processing
MXD7210GL/HL/ML/NL. Low Cost, Low Noise ±10 g Dual Axis Accelerometer with Digital Outputs
 FEATURES Low cost Resolution better than 1milli-g at 1Hz Dual axis accelerometer fabricated on a monolithic CMOS IC On chip mixed signal processing No moving parts; No loose particle issues >50,000 g shock
FEATURES Low cost Resolution better than 1milli-g at 1Hz Dual axis accelerometer fabricated on a monolithic CMOS IC On chip mixed signal processing No moving parts; No loose particle issues >50,000 g shock
Coast and Ship Station Single Sideband Radiotelephone Transmitters and Receivers Operating in the 1,605-28,000 khz Band
 Issue 1 April 1, 1971 Spectrum Management Radio Standards Specification Coast and Ship Station Single Sideband Radiotelephone Transmitters and Receivers Operating in the 1,605-28,000 khz Band Aussi disponible
Issue 1 April 1, 1971 Spectrum Management Radio Standards Specification Coast and Ship Station Single Sideband Radiotelephone Transmitters and Receivers Operating in the 1,605-28,000 khz Band Aussi disponible
Amateur Extra Manual Chapter 9.4 Transmission Lines
 9.4 TRANSMISSION LINES (page 9-31) WAVELENGTH IN A FEED LINE (page 9-31) VELOCITY OF PROPAGATION (page 9-32) Speed of Wave in a Transmission Line VF = Velocity Factor = Speed of Light in a Vacuum Question
9.4 TRANSMISSION LINES (page 9-31) WAVELENGTH IN A FEED LINE (page 9-31) VELOCITY OF PROPAGATION (page 9-32) Speed of Wave in a Transmission Line VF = Velocity Factor = Speed of Light in a Vacuum Question
An Instrumentation System
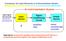 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
I P. /dt. di p V S Applications. Standards 1) IEC : 2007; IEC : ) IEC : 2016; IEC : 2017
 Ref: ART-B22-D70, ART-B22-D125, ART-B22-D175, ART-B22-D300 Flexible clip-around Rogowski coil for the electronic measurement of AC current with galvanic separation between the primary circuit (power) and
Ref: ART-B22-D70, ART-B22-D125, ART-B22-D175, ART-B22-D300 Flexible clip-around Rogowski coil for the electronic measurement of AC current with galvanic separation between the primary circuit (power) and
Intrinsic Semiconductor
 Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
I P. /dt. di p V S+ Applications. Standards. 1) IEC ed1.0: 2007; IEC : ed1.0: 2012
 Ref: ART-B22-D70, ART-B22-D125, ART-B22-D175 Flexible clip-around Rogowski coil for the electronic measurement of AC current with galvanic separation between the primary circuit (power) and the secondary
Ref: ART-B22-D70, ART-B22-D125, ART-B22-D175 Flexible clip-around Rogowski coil for the electronic measurement of AC current with galvanic separation between the primary circuit (power) and the secondary
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Examination.
 Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2002 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2002 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Inductive Sensors. Fig. 1: Geophone
 Inductive Sensors A voltage is induced in the loop whenever it moves laterally. In this case, we assume it is confined to motion left and right in the figure, and that the flux at any moment is given by
Inductive Sensors A voltage is induced in the loop whenever it moves laterally. In this case, we assume it is confined to motion left and right in the figure, and that the flux at any moment is given by
Glossary of VCO terms
 Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
SPECIFICATION FOR APPROVAL. 1/2W, 0603, Low Resistance Chip Resistor (Lead / Halogen free)
 PAGE : 1 OF 7 1/2W, 0603, Low Resistance Chip Resistor (Lead / Halogen free) 1. Scope This specification applies to 0.8mm x 1.6mm size 1/2W, fixed metal film chip resistors rectangular type for use in
PAGE : 1 OF 7 1/2W, 0603, Low Resistance Chip Resistor (Lead / Halogen free) 1. Scope This specification applies to 0.8mm x 1.6mm size 1/2W, fixed metal film chip resistors rectangular type for use in
Selecting Piezoresistive vs. Piezoelectric Pressure Transducers
 APPLICATION NOTE: AN-102 Selecting Piezoresistive vs. Piezoelectric Pressure Transducers (General Measurement) Authors: Steve Carter, Alex Ned, John Chivers, Andy Bemis Introduction This application note
APPLICATION NOTE: AN-102 Selecting Piezoresistive vs. Piezoelectric Pressure Transducers (General Measurement) Authors: Steve Carter, Alex Ned, John Chivers, Andy Bemis Introduction This application note
INDUSTRIAL VIBRATION SENSOR SELECTION MADE EASY
 SENSORS FOR RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT WHITE PAPER #28 INDUSTRIAL VIBRATION SENSOR SELECTION MADE EASY NINE QUESTIONS TO SUCCESSFULLY IDENTIFY THE SOLUTION TO YOUR APPLICATION www.pcb.com info@pcb.com 800.828.8840
SENSORS FOR RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT WHITE PAPER #28 INDUSTRIAL VIBRATION SENSOR SELECTION MADE EASY NINE QUESTIONS TO SUCCESSFULLY IDENTIFY THE SOLUTION TO YOUR APPLICATION www.pcb.com info@pcb.com 800.828.8840
MODEL 5002 PHASE VERIFICATION BRIDGE SET
 CLARKE-HESS COMMUNICATION RESEARCH CORPORATION clarke-hess.com MODEL 5002 PHASE VERIFICATION BRIDGE SET TABLE OF CONTENTS WARRANTY i I BASIC ASSEMBLIES I-1 1-1 INTRODUCTION I-1 1-2 BASIC ASSEMBLY AND SPECIFICATIONS
CLARKE-HESS COMMUNICATION RESEARCH CORPORATION clarke-hess.com MODEL 5002 PHASE VERIFICATION BRIDGE SET TABLE OF CONTENTS WARRANTY i I BASIC ASSEMBLIES I-1 1-1 INTRODUCTION I-1 1-2 BASIC ASSEMBLY AND SPECIFICATIONS
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) 1. JUNCTION FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (JFET)
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. Although there
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. Although there
ASC IMU 7.X.Y. Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) Description.
 Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) 6-axis MEMS mini-imu Acceleration & Angular Rotation analog output 12-pin connector with detachable cable Aluminium housing Made in Germany Features Acceleration rate: ±2g
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) 6-axis MEMS mini-imu Acceleration & Angular Rotation analog output 12-pin connector with detachable cable Aluminium housing Made in Germany Features Acceleration rate: ±2g
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
 CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION Broadly speaking, system identification is the art and science of using measurements obtained from a system to characterize the system. The characterization
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION Broadly speaking, system identification is the art and science of using measurements obtained from a system to characterize the system. The characterization
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Manual Supplement. This supplement contains information necessary to ensure the accuracy of the above manual.
 Manual Title: 550A Getting Started Supplement Issue: Part Number: 415509 Issue Date: 9/18 Print Date: November 01 Page Count: 19 Revision/Date: This supplement contains information necessary to ensure
Manual Title: 550A Getting Started Supplement Issue: Part Number: 415509 Issue Date: 9/18 Print Date: November 01 Page Count: 19 Revision/Date: This supplement contains information necessary to ensure
OX-046 VHF low g-sensitivity Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator
 OX-046 VHF low g-sensitivity Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator OX-046 Features Ultra Low G-Sensitivity Low Phase Noise Very High Frequency Frequency Range: 50 MHZ to 250 MHZ Standard Frequency: 100 MHz
OX-046 VHF low g-sensitivity Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator OX-046 Features Ultra Low G-Sensitivity Low Phase Noise Very High Frequency Frequency Range: 50 MHZ to 250 MHZ Standard Frequency: 100 MHz
IMPORTANCE OF INSULATION RESISTANCE
 IMPORTANCE OF INSULATION RESISTANCE What is Good Insulation? Every electric wire in your plant whether it s in a motor, generator, cable, switch, transformer, etc., is carefully covered with some form
IMPORTANCE OF INSULATION RESISTANCE What is Good Insulation? Every electric wire in your plant whether it s in a motor, generator, cable, switch, transformer, etc., is carefully covered with some form
VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE
 RFS21 December 1991 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO APPARATUS: VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE USING AMPLITUDE MODULATION WITH 12.5 khz CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION Communications Division Ministry of Commerce
RFS21 December 1991 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO APPARATUS: VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE USING AMPLITUDE MODULATION WITH 12.5 khz CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION Communications Division Ministry of Commerce
Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale
 Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION Sound level meters Sonomètres OIML R 58 Edition 1998 (E) CONTENTS Foreword... 3 1 Scope... 4 2 Construction and maximum permissible
Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION Sound level meters Sonomètres OIML R 58 Edition 1998 (E) CONTENTS Foreword... 3 1 Scope... 4 2 Construction and maximum permissible
MXD2125J/K. Ultra Low Cost, ±2.0 g Dual Axis Accelerometer with Digital Outputs
 Ultra Low Cost, ±2.0 g Dual Axis Accelerometer with Digital Outputs MXD2125J/K FEATURES RoHS Compliant Dual axis accelerometer Monolithic CMOS construction On-chip mixed mode signal processing Resolution
Ultra Low Cost, ±2.0 g Dual Axis Accelerometer with Digital Outputs MXD2125J/K FEATURES RoHS Compliant Dual axis accelerometer Monolithic CMOS construction On-chip mixed mode signal processing Resolution
Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals
 1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
Electro - Principles I
 The PN Junction Diode Introduction to the PN Junction Diode Note: In this chapter we consider conventional current flow. Page 11-1 The schematic symbol for the pn junction diode the shown in Figure 1.
The PN Junction Diode Introduction to the PN Junction Diode Note: In this chapter we consider conventional current flow. Page 11-1 The schematic symbol for the pn junction diode the shown in Figure 1.
Analog Electronic Circuits
 Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
Microelectronic Circuits Fourth Edition Adel S. Sedra, Kenneth C. Smith, 1998 Oxford University Press
 Diodes ELZ 206 - Elektronik I Microelectronic Circuits Fourth Edition Adel S. Sedra, Kenneth C. Smith, 1998 Oxford University Press Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Dicle University
Diodes ELZ 206 - Elektronik I Microelectronic Circuits Fourth Edition Adel S. Sedra, Kenneth C. Smith, 1998 Oxford University Press Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Dicle University
