The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 3
|
|
|
- Rafe Wade
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (July 1993) The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 3 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last two issues, we described how a projection system forms an image of a mask: diffraction of light by the mask, collection of a portion of the diffracted light by the objective lens, and recombination of the diffracted light to form an image. Examining this process in more detail, the diffraction pattern is described by the Fourier Transform of the mask transmittance and is expressed in terms of spatial frequencies, which is just a scaled coordinate system in the plane of the diffraction pattern. In general, this diffraction pattern will extend throughout this plane in all directions. However, any lens of finite size will only collect a portion of this infinitely big diffraction pattern. Thinking of the entrance to the lens as an aperture which collects only the light that falls inside the aperture, light with too large a spatial frequency will not make it into the lens and thus will be lost. The radius of this lens aperture is described by its numerical aperture (NA), defined as the sine of the maximum half-angle of light that can pass through the aperture. Finally, the lens acts as a second Fourier Transform acting on the portion of the diffraction pattern entering the aperture. The result is an image of the mask, degraded due to the lost information of the high frequency portion of the diffraction pattern. Although we have built up a basic knowledge of how an image is formed, there is one important piece still missing: how does defocus affect the aerial image? Over the last several years, depth-of-focus (DOF) has become a limiting factor in our ability to push optical lithography to smaller and smaller geometries. Why do smaller features have less DOF than larger features? Can we quantify the effects of defocus? What can be done about it? Before answering these and other questions, we must first gain a solid understanding of how defocus affects the imaging process. Consider a perfect spherical wave converging (i.e., focusing) down to a point. An ideal projection system would create such a wave coming out of the lens aperture (called the exit pupil), as shown in Figure 1a. If the wafer to be printed were placed in the same plane as the focal point of this wave, we would say that the wafer was in focus. What happens if the wafer were removed from this plane by some distance δ, called the defocus distance? Figure 1b shows such a situation. The spherical wave with the solid line represents the actual wave focused to a point a distance δ away from the wafer. If, however, the wave had a different shape, as given by the dotted curve, then the wafer would be in focus. Note that the only difference between these two different waves is the radius of curvature. Since the dotted curve is the wavefront we want for the given wafer position, we can say that the actual wavefront is in error because it does not
2 focus where the wafer is located. (This is just a variation of the customer is always right attitude - the wafer is always right, it is the optical wavefront that is out of focus.) By viewing the actual wavefront as having an error in curvature relative to the desired wavefront (i.e., the one that focuses on the wafer), we can quantify the effect of defocus. Looking at Figure 1b, it is apparent that the distance from the desired to the defocused wavefront goes from zero at the center of the exit pupil and increases as we approach the edge of the pupil. This distance between wavefronts is called the optical path difference (OPD). The OPD is a function of the defocus distance and the position within the pupil and can be obtained from the geometry shown in Figure. (The following description necessarily becomes a bit mathematical, but the results are worth the effort.) Describing the position within the exit pupil by an angle θ, the optical path difference is given by OPD = δ ( 1 cos θ) As we have seen before, the spatial frequency and the numerical aperture define positions within the pupil as the sine of an angle. Thus, the above expression for optical path difference would be much more useful if expressed as a function of sinθ : sin θ sin θ OPD = δ( 1 cos θ) = δ sin θ where the final approximation is true for relatively small angles. 1 δsin θ So how does this optical path difference affect the formation of an image? For light, the path length traveled is equivalent to a change in phase. Thus, the OPD can be expressed as a phase error, φ, due to defocus: φ = kopd= πδsin θ / λ where k = π/λ = the propagation constant. We are now ready to see how defocus affects the diffraction pattern and the resulting image. Our interpretation of defocus is that it causes a phase error as a function of radial position within the aperture. Light in the center of the aperture has no error, light at the edge of the aperture has the greatest phase error. This is very important when we remember what a diffraction pattern looks like as it enters the lens aperture. Figure 3 shows such a diffraction pattern for the simple case of equal lines and spaces. Recall that diffraction by periodic patterns results in discrete diffraction orders: the zero order is the undiffracted light passing through the center of the lens, higher orders contain information necessary to reconstruct the image. In this case, only the zero and the ±1 diffraction orders make it through the lens. Thus, the effect of defocus is to add a phase error to the higher order diffracted light relative to the zero order. When the lens recombines these orders to form an image, this phase error will result in a degraded image.
3 With this basic understanding of how defocus affects the diffraction pattern, we can now explore one of the most important aspects of high resolution imaging: how depth-of-focus changes with feature size. Recall that the position of the diffraction orders within the aperture varies inversely with the pitch of the pattern being printed. In fact, the diffraction angle θ for the first orders is given by λ sinθ = p where p is the pitch of the equal line/space pattern. As a result, the phase error can be expressed as a function of the mask feature: φ = πδλ / p A smaller line/space pitch results in a greater phase error for a given amount of defocus. Since it is the phase error which degrades the image, one would expect there to be some maximum tolerable phase error (φ max ) equivalent to the maximum tolerable defocus (called the depth-offocus, DOF). Thus, p DOF = = K p φ max πλ λ where K is just a constant for a given amount of image degradation. This result is extremely important and is the main reason for our discussion. The DOF scales as the square of the feature size being printed. If we cut our minimum feature size in half, our DOF will be reduced by a factor of four! No wonder the industry is working so hard to improve DOF as we move to smaller production linewidths. Also notice that for a given feature size, reducing the wavelength increases the DOF. The motivation for moving to i-line (λ=365nm) and then deep-uv (λ=48nm) is obvious. I should make clear, however, that the above equation really only applies to coherent illumination when only the zero and first diffraction orders enter the lens. In any case, it does give us a good physical understanding of the relationship of feature size and wavelength to the effects of defocus. Next time we ll briefly look at phase-shifting masks and off-axis illumination from the limited perspective of how they relate to this discussion on focus effects and to resolution.
4 Exit Pupil Wafer Wafer δ (a) (b) Figure 1. Focusing of light can be thought of as a converging spherical wave: a) in focus, and b) out of focus by a distance δ. OPD θ δ Figure. Geometry relating the optical path difference (OPD) to the defocus distance δ and the angle θ.
5 Mask Pattern (equal lines and spaces) Diffraction Pattern Lens Aperture Figure 3. Typical diffraction pattern entering an objective lens aperture (assuming coherent illumination and a mask pattern of equal lines and spaces).
The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 2
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (April 1993) The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 2 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last issue, we began to described how a projection system
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (April 1993) The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 2 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last issue, we began to described how a projection system
More on the Mask Error Enhancement Factor
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Fall 1999) More on the Mask Error Enhancement Factor Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In a previous edition of this column (Winter, 1999) I described
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Fall 1999) More on the Mask Error Enhancement Factor Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In a previous edition of this column (Winter, 1999) I described
Using the Normalized Image Log-Slope, part 2
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Spring ) Using the Normalized Image Log-Slope, part Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, A Division of KLA-Tencor, Austin, Texas As we saw in part of this column,
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Spring ) Using the Normalized Image Log-Slope, part Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, A Division of KLA-Tencor, Austin, Texas As we saw in part of this column,
Optical Projection Printing and Modeling
 Optical Projection Printing and Modeling Overview of optical lithography, concepts, trends Basic Parameters and Effects (1-14) Resolution Depth of Focus; Proximity, MEEF, LES Image Calculation, Characterization
Optical Projection Printing and Modeling Overview of optical lithography, concepts, trends Basic Parameters and Effects (1-14) Resolution Depth of Focus; Proximity, MEEF, LES Image Calculation, Characterization
Depth of Focus and the Alternating Phase Shift Mask
 T h e L i t h o g r a h y E x e r t (November 4) Deth of Focus and the Alternating Phase Shift Mask Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas One of the biggest advantages of the use of
T h e L i t h o g r a h y E x e r t (November 4) Deth of Focus and the Alternating Phase Shift Mask Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas One of the biggest advantages of the use of
Horizontal-Vertical (H-V) Bias
 Tutor51.doc: Version 8/11/05 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (November 005) Horizontal-Vertical (H-V) Bias Chris A. Mack, Austin, Texas A nanometer here, a nanometer there. Before long, you ve
Tutor51.doc: Version 8/11/05 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (November 005) Horizontal-Vertical (H-V) Bias Chris A. Mack, Austin, Texas A nanometer here, a nanometer there. Before long, you ve
Purpose: Explain the top 10 phenomena and concepts. BPP-1: Resolution and Depth of Focus (1.5X)
 Basic Projection Printing (BPP) Modules Purpose: Explain the top 10 phenomena and concepts key to understanding optical projection printing BPP-1: Resolution and Depth of Focus (1.5X) BPP-2: Bragg condition
Basic Projection Printing (BPP) Modules Purpose: Explain the top 10 phenomena and concepts key to understanding optical projection printing BPP-1: Resolution and Depth of Focus (1.5X) BPP-2: Bragg condition
Phase Contrast Lithography
 Phase Contrast Lithography Chris A. Mack FINLE Technologies, Austin, TX 78716 Abstract This paper analyzes theoretically the potential for a novel approach to lithographic imaging: Phase Contrast Lithography.
Phase Contrast Lithography Chris A. Mack FINLE Technologies, Austin, TX 78716 Abstract This paper analyzes theoretically the potential for a novel approach to lithographic imaging: Phase Contrast Lithography.
Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts
 Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts The fundamental feature of any optical system is the aperture stop. Thus, the most fundamental optical system is the pinhole camera. The image
Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts The fundamental feature of any optical system is the aperture stop. Thus, the most fundamental optical system is the pinhole camera. The image
APPLICATION NOTE
 THE PHYSICS BEHIND TAG OPTICS TECHNOLOGY AND THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF APPLICATION NOTE 12-001 USING SOUND TO SHAPE LIGHT Page 1 of 6 Tutorial on How the TAG Lens Works This brief tutorial explains the
THE PHYSICS BEHIND TAG OPTICS TECHNOLOGY AND THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF APPLICATION NOTE 12-001 USING SOUND TO SHAPE LIGHT Page 1 of 6 Tutorial on How the TAG Lens Works This brief tutorial explains the
( ) Deriving the Lens Transmittance Function. Thin lens transmission is given by a phase with unit magnitude.
 Deriving the Lens Transmittance Function Thin lens transmission is given by a phase with unit magnitude. t(x, y) = exp[ jk o ]exp[ jk(n 1) (x, y) ] Find the thickness function for left half of the lens
Deriving the Lens Transmittance Function Thin lens transmission is given by a phase with unit magnitude. t(x, y) = exp[ jk o ]exp[ jk(n 1) (x, y) ] Find the thickness function for left half of the lens
Copyright 2000 by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers.
 Copyright by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in the proceedings of Optical Microlithography XIII, SPIE Vol. 4, pp. 658-664. It is made available as an electronic
Copyright by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in the proceedings of Optical Microlithography XIII, SPIE Vol. 4, pp. 658-664. It is made available as an electronic
Line End Shortening. T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Spring 2000) Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas
 Tutor29.doc: Version 2/15/00 Line End Shortening Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Spring 2000) Historically, lithography engineering has focused
Tutor29.doc: Version 2/15/00 Line End Shortening Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Spring 2000) Historically, lithography engineering has focused
Tutor43.doc; Version 8/15/03 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (November 2003)
 Tutor43.doc; Version /15/03 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (November 2003) Scattering Bars Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas Resolution enhancement technologies refer to
Tutor43.doc; Version /15/03 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (November 2003) Scattering Bars Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas Resolution enhancement technologies refer to
Properties of optical instruments. Projection optical systems
 Properties of optical instruments Projection optical systems Instruments : optical systems designed for a specific function Projection systems: : real image (object real or at infinity) Examples: videoprojector,,
Properties of optical instruments Projection optical systems Instruments : optical systems designed for a specific function Projection systems: : real image (object real or at infinity) Examples: videoprojector,,
Why is There a Black Dot when Defocus = 1λ?
 Why is There a Black Dot when Defocus = 1λ? W = W 020 = a 020 ρ 2 When a 020 = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at full aperture (ρ = 1) = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at ρ = 0.707 = 0.5λ Area of the pupil from ρ =
Why is There a Black Dot when Defocus = 1λ? W = W 020 = a 020 ρ 2 When a 020 = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at full aperture (ρ = 1) = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at ρ = 0.707 = 0.5λ Area of the pupil from ρ =
Lithography. 3 rd. lecture: introduction. Prof. Yosi Shacham-Diamand. Fall 2004
 Lithography 3 rd lecture: introduction Prof. Yosi Shacham-Diamand Fall 2004 1 List of content Fundamental principles Characteristics parameters Exposure systems 2 Fundamental principles Aerial Image Exposure
Lithography 3 rd lecture: introduction Prof. Yosi Shacham-Diamand Fall 2004 1 List of content Fundamental principles Characteristics parameters Exposure systems 2 Fundamental principles Aerial Image Exposure
Simulation of coherent multiple imaging by means of pupil-plane filtering in optical microlithography
 Erdélyi et al. Vol. 16, No. 8/August 1999/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1909 Simulation of coherent multiple imaging by means of pupil-plane filtering in optical microlithography M. Erdélyi and Zs. Bor Department
Erdélyi et al. Vol. 16, No. 8/August 1999/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1909 Simulation of coherent multiple imaging by means of pupil-plane filtering in optical microlithography M. Erdélyi and Zs. Bor Department
Resolution. T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Winter 1997) Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Winter 1997) Resolution Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In past editions of this column (Spring and Summer, 1995), we defined quite carefully what
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Winter 1997) Resolution Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In past editions of this column (Spring and Summer, 1995), we defined quite carefully what
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution
 Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Astronomical Observing Techniques Lecture 6: Op:cs
 Astronomical Observing Techniques Lecture 6: Op:cs Christoph U. Keller keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Outline 1. Geometrical Op
Astronomical Observing Techniques Lecture 6: Op:cs Christoph U. Keller keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Outline 1. Geometrical Op
Collimation Tester Instructions
 Description Use shear-plate collimation testers to examine and adjust the collimation of laser light, or to measure the wavefront curvature and divergence/convergence magnitude of large-radius optical
Description Use shear-plate collimation testers to examine and adjust the collimation of laser light, or to measure the wavefront curvature and divergence/convergence magnitude of large-radius optical
Mirrors and Lenses. Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses.
 Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
Synthesis of projection lithography for low k1 via interferometry
 Synthesis of projection lithography for low k1 via interferometry Frank Cropanese *, Anatoly Bourov, Yongfa Fan, Andrew Estroff, Lena Zavyalova, Bruce W. Smith Center for Nanolithography Research, Rochester
Synthesis of projection lithography for low k1 via interferometry Frank Cropanese *, Anatoly Bourov, Yongfa Fan, Andrew Estroff, Lena Zavyalova, Bruce W. Smith Center for Nanolithography Research, Rochester
Properties of optical instruments. Visual optical systems part 2: focal visual instruments (microscope type)
 Properties of optical instruments Visual optical systems part 2: focal visual instruments (microscope type) Examples of focal visual instruments magnifying glass Eyepieces Measuring microscopes from the
Properties of optical instruments Visual optical systems part 2: focal visual instruments (microscope type) Examples of focal visual instruments magnifying glass Eyepieces Measuring microscopes from the
Image Manipulation. Chris A. Mack Department of Defense Fort Meade, MD ABSTRACT
 An Algorithm for Optimizing Stepper Performance Through Image Manipulation Chris A. Mack Department of Defense Fort Meade, MD 20755 ABSTRACT The advent offlexible steppers, allowing variation in the numericalaperture,
An Algorithm for Optimizing Stepper Performance Through Image Manipulation Chris A. Mack Department of Defense Fort Meade, MD 20755 ABSTRACT The advent offlexible steppers, allowing variation in the numericalaperture,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY. 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Practice Problems Posted May 11, 2014
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Practice Problems Posted May 11, 2014 1. (Pedrotti 13-21) A glass plate is sprayed with uniform opaque particles. When a distant point
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Practice Problems Posted May 11, 2014 1. (Pedrotti 13-21) A glass plate is sprayed with uniform opaque particles. When a distant point
Modulation Transfer Function
 Modulation Transfer Function The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is a useful tool in system evaluation. t describes if, and how well, different spatial frequencies are transferred from object to image.
Modulation Transfer Function The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is a useful tool in system evaluation. t describes if, and how well, different spatial frequencies are transferred from object to image.
Photolithography II ( Part 2 )
 1 Photolithography II ( Part 2 ) Chapter 14 : Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by M. Quirk & J. Serda Saroj Kumar Patra, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Norwegian University of Science
1 Photolithography II ( Part 2 ) Chapter 14 : Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by M. Quirk & J. Serda Saroj Kumar Patra, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Norwegian University of Science
OPC Scatterbars or Assist Features
 OPC Scatterbars or Assist Features Main Feature The isolated main pattern now acts somewhat more like a periodic line and space pattern which has a higher quality image especially with focus when off-axis
OPC Scatterbars or Assist Features Main Feature The isolated main pattern now acts somewhat more like a periodic line and space pattern which has a higher quality image especially with focus when off-axis
Purpose: Explain the top advanced issues and concepts in
 Advanced Issues and Technology (AIT) Modules Purpose: Explain the top advanced issues and concepts in optical projection printing and electron-beam lithography. h AIT-1: LER and Chemically Amplified Resists
Advanced Issues and Technology (AIT) Modules Purpose: Explain the top advanced issues and concepts in optical projection printing and electron-beam lithography. h AIT-1: LER and Chemically Amplified Resists
OPTICAL IMAGE FORMATION
 GEOMETRICAL IMAGING First-order image is perfect object (input) scaled (by magnification) version of object optical system magnification = image distance/object distance no blurring object distance image
GEOMETRICAL IMAGING First-order image is perfect object (input) scaled (by magnification) version of object optical system magnification = image distance/object distance no blurring object distance image
Copyright 1997 by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers.
 Copyright 1997 by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in the proceedings of Microlithographic Techniques in IC Fabrication, SPIE Vol. 3183, pp. 14-27. It is
Copyright 1997 by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in the proceedings of Microlithographic Techniques in IC Fabrication, SPIE Vol. 3183, pp. 14-27. It is
12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes
 330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
Optimization of the Spatial Properties of Illumination for Improved Lithographic Response
 Optimization of the Spatial Properties of llumination for mproved Lithographic Response Chris A. Mack FNLE Technologies, Austin, TX 78716 Abstract Using computer simulations of the lithographic process,
Optimization of the Spatial Properties of llumination for mproved Lithographic Response Chris A. Mack FNLE Technologies, Austin, TX 78716 Abstract Using computer simulations of the lithographic process,
MICRO AND NANOPROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES
 MICRO AND NANOPROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 4 Optical lithography Concepts and processes Lithography systems Fundamental limitations and other issues Photoresists Photolithography process Process parameter
MICRO AND NANOPROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 4 Optical lithography Concepts and processes Lithography systems Fundamental limitations and other issues Photoresists Photolithography process Process parameter
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Rays. Wavefronts. Aberrations. Outline
 Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Optical Requirements
 Optical Requirements Transmission vs. Film Thickness A pellicle needs a good light transmission and long term transmission stability. Transmission depends on the film thickness, film material and any anti-reflective
Optical Requirements Transmission vs. Film Thickness A pellicle needs a good light transmission and long term transmission stability. Transmission depends on the film thickness, film material and any anti-reflective
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN
 Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
Lecture Notes 10 Image Sensor Optics. Imaging optics. Pixel optics. Microlens
 Lecture Notes 10 Image Sensor Optics Imaging optics Space-invariant model Space-varying model Pixel optics Transmission Vignetting Microlens EE 392B: Image Sensor Optics 10-1 Image Sensor Optics Microlens
Lecture Notes 10 Image Sensor Optics Imaging optics Space-invariant model Space-varying model Pixel optics Transmission Vignetting Microlens EE 392B: Image Sensor Optics 10-1 Image Sensor Optics Microlens
Diffraction. Interference with more than 2 beams. Diffraction gratings. Diffraction by an aperture. Diffraction of a laser beam
 Diffraction Interference with more than 2 beams 3, 4, 5 beams Large number of beams Diffraction gratings Equation Uses Diffraction by an aperture Huygen s principle again, Fresnel zones, Arago s spot Qualitative
Diffraction Interference with more than 2 beams 3, 4, 5 beams Large number of beams Diffraction gratings Equation Uses Diffraction by an aperture Huygen s principle again, Fresnel zones, Arago s spot Qualitative
Immersion Lithography Micro-Objectives
 Immersion Lithography Micro-Objectives James Webb and Louis Denes Corning Tropel Corporation, 60 O Connor Rd, Fairport, NY 14450 (U.S.A.) 585-388-3500, webbj@corning.com, denesl@corning.com ABSTRACT The
Immersion Lithography Micro-Objectives James Webb and Louis Denes Corning Tropel Corporation, 60 O Connor Rd, Fairport, NY 14450 (U.S.A.) 585-388-3500, webbj@corning.com, denesl@corning.com ABSTRACT The
EE-527: MicroFabrication
 EE-57: MicroFabrication Exposure and Imaging Photons white light Hg arc lamp filtered Hg arc lamp excimer laser x-rays from synchrotron Electrons Ions Exposure Sources focused electron beam direct write
EE-57: MicroFabrication Exposure and Imaging Photons white light Hg arc lamp filtered Hg arc lamp excimer laser x-rays from synchrotron Electrons Ions Exposure Sources focused electron beam direct write
What s So Hard About Lithography?
 What s So Hard About Lithography? Chris A. Mack, www.lithoguru.com, Austin, Texas Optical lithography has been the mainstay of semiconductor patterning since the early days of integrated circuit production.
What s So Hard About Lithography? Chris A. Mack, www.lithoguru.com, Austin, Texas Optical lithography has been the mainstay of semiconductor patterning since the early days of integrated circuit production.
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 20 at the start of class
 PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
Optical Proximity Effects
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Spring 1996) Optical Proximity Effects Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas Proximity effects are the variations in the linewidth of a feature (or the
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Spring 1996) Optical Proximity Effects Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas Proximity effects are the variations in the linewidth of a feature (or the
Study on Imaging Quality of Water Ball Lens
 2017 2nd International Conference on Mechatronics and Information Technology (ICMIT 2017) Study on Imaging Quality of Water Ball Lens Haiyan Yang1,a,*, Xiaopan Li 1,b, 1,c Hao Kong, 1,d Guangyang Xu and1,eyan
2017 2nd International Conference on Mechatronics and Information Technology (ICMIT 2017) Study on Imaging Quality of Water Ball Lens Haiyan Yang1,a,*, Xiaopan Li 1,b, 1,c Hao Kong, 1,d Guangyang Xu and1,eyan
Properties of Structured Light
 Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
Opti 415/515. Introduction to Optical Systems. Copyright 2009, William P. Kuhn
 Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
CHAPTER 1 Optical Aberrations
 CHAPTER 1 Optical Aberrations 1.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the concepts of aperture stop and entrance and exit pupils of an optical imaging system. Certain special rays, such as the chief
CHAPTER 1 Optical Aberrations 1.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the concepts of aperture stop and entrance and exit pupils of an optical imaging system. Certain special rays, such as the chief
Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design
 Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design Computer Aided Design Several CAD tools use Ray Tracing (see
Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design Computer Aided Design Several CAD tools use Ray Tracing (see
Physics 3340 Spring Fourier Optics
 Physics 3340 Spring 011 Purpose Fourier Optics In this experiment we will show how the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern or spatial Fourier transform of an object can be observed within an optical system.
Physics 3340 Spring 011 Purpose Fourier Optics In this experiment we will show how the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern or spatial Fourier transform of an object can be observed within an optical system.
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Today. Defocus. Deconvolution / inverse filters. MIT 2.71/2.710 Optics 12/12/05 wk15-a-1
 Today Defocus Deconvolution / inverse filters MIT.7/.70 Optics //05 wk5-a- MIT.7/.70 Optics //05 wk5-a- Defocus MIT.7/.70 Optics //05 wk5-a-3 0 th Century Fox Focus in classical imaging in-focus defocus
Today Defocus Deconvolution / inverse filters MIT.7/.70 Optics //05 wk5-a- MIT.7/.70 Optics //05 wk5-a- Defocus MIT.7/.70 Optics //05 wk5-a-3 0 th Century Fox Focus in classical imaging in-focus defocus
Advanced Lens Design
 Advanced Lens Design Lecture 3: Aberrations I 214-11-4 Herbert Gross Winter term 214 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 1 21.1. Basics Paraxial optics, imaging, Zemax handling 2 28.1. Optical systems
Advanced Lens Design Lecture 3: Aberrations I 214-11-4 Herbert Gross Winter term 214 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 1 21.1. Basics Paraxial optics, imaging, Zemax handling 2 28.1. Optical systems
Explanation of Aberration and Wavefront
 Explanation of Aberration and Wavefront 1. What Causes Blur? 2. What is? 4. What is wavefront? 5. Hartmann-Shack Aberrometer 6. Adoption of wavefront technology David Oh 1. What Causes Blur? 2. What is?
Explanation of Aberration and Wavefront 1. What Causes Blur? 2. What is? 4. What is wavefront? 5. Hartmann-Shack Aberrometer 6. Adoption of wavefront technology David Oh 1. What Causes Blur? 2. What is?
Exam Preparation Guide Geometrical optics (TN3313)
 Exam Preparation Guide Geometrical optics (TN3313) Lectures: September - December 2001 Version of 21.12.2001 When preparing for the exam, check on Blackboard for a possible newer version of this guide.
Exam Preparation Guide Geometrical optics (TN3313) Lectures: September - December 2001 Version of 21.12.2001 When preparing for the exam, check on Blackboard for a possible newer version of this guide.
Section 2: Lithography. Jaeger Chapter 2. EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1
 Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1 The lithographic process EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-2 Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered with silicon
Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1 The lithographic process EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-2 Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered with silicon
Optical Lithography. Here Is Why. Burn J. Lin SPIE PRESS. Bellingham, Washington USA
 Optical Lithography Here Is Why Burn J. Lin SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Contents Preface xiii Chapter 1 Introducing Optical Lithography /1 1.1 The Role of Lithography in Integrated Circuit Fabrication
Optical Lithography Here Is Why Burn J. Lin SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Contents Preface xiii Chapter 1 Introducing Optical Lithography /1 1.1 The Role of Lithography in Integrated Circuit Fabrication
Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1
 Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1 Short answer 1.) Sketch a pechan prism. Name a possible application of this prism., write the mirror matrix for this prism (or any other common
Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1 Short answer 1.) Sketch a pechan prism. Name a possible application of this prism., write the mirror matrix for this prism (or any other common
Applied Optics. , Physics Department (Room #36-401) , ,
 Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
Chapter 3. Introduction to Zemax. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Zemax
 Chapter 3 Introduction to Zemax 3.1 Introduction Ray tracing is practical only for paraxial analysis. Computing aberrations and diffraction effects are time consuming. Optical Designers need some popular
Chapter 3 Introduction to Zemax 3.1 Introduction Ray tracing is practical only for paraxial analysis. Computing aberrations and diffraction effects are time consuming. Optical Designers need some popular
INTRODUCTION TO ABERRATIONS IN OPTICAL IMAGING SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO ABERRATIONS IN OPTICAL IMAGING SYSTEMS JOSE SASIÄN University of Arizona ШШ CAMBRIDGE Щ0 UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Acknowledgements Harold H. Hopkins Roland V. Shack Symbols 1 Introduction
INTRODUCTION TO ABERRATIONS IN OPTICAL IMAGING SYSTEMS JOSE SASIÄN University of Arizona ШШ CAMBRIDGE Щ0 UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Acknowledgements Harold H. Hopkins Roland V. Shack Symbols 1 Introduction
Reducing Proximity Effects in Optical Lithography
 INTERFACE '96 This paper was published in the proceedings of the Olin Microlithography Seminar, Interface '96, pp. 325-336. It is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of Olin Microelectronic
INTERFACE '96 This paper was published in the proceedings of the Olin Microlithography Seminar, Interface '96, pp. 325-336. It is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of Olin Microelectronic
Condition Mirror Refractive Lens Concave Focal Length Positive Focal Length Negative. Image distance positive
 Comparison between mirror lenses and refractive lenses Condition Mirror Refractive Lens Concave Focal Length Positive Focal Length Negative Convex Focal Length Negative Focal Length Positive Image location
Comparison between mirror lenses and refractive lenses Condition Mirror Refractive Lens Concave Focal Length Positive Focal Length Negative Convex Focal Length Negative Focal Length Positive Image location
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
A New Hybrid Diffractive Photo-mask Technology
 University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) A New Hybrid Diffractive Photo-mask Technology 2005 Jin Won Sung University of Central Florida Find
University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) A New Hybrid Diffractive Photo-mask Technology 2005 Jin Won Sung University of Central Florida Find
optical and photoresist effects
 Focus effects in submicron optical lithography, optical and photoresist effects Chris A. Mack and Patricia M. Kaufman Department of Defense Fort Meade, Maryland 20755 Abstract This paper gives a review
Focus effects in submicron optical lithography, optical and photoresist effects Chris A. Mack and Patricia M. Kaufman Department of Defense Fort Meade, Maryland 20755 Abstract This paper gives a review
Lecture 3: Geometrical Optics 1. Spherical Waves. From Waves to Rays. Lenses. Chromatic Aberrations. Mirrors. Outline
 Lecture 3: Geometrical Optics 1 Outline 1 Spherical Waves 2 From Waves to Rays 3 Lenses 4 Chromatic Aberrations 5 Mirrors Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 3: Geometrical
Lecture 3: Geometrical Optics 1 Outline 1 Spherical Waves 2 From Waves to Rays 3 Lenses 4 Chromatic Aberrations 5 Mirrors Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 3: Geometrical
Comparison of an Optical-Digital Restoration Technique with Digital Methods for Microscopy Defocused Images
 Comparison of an Optical-Digital Restoration Technique with Digital Methods for Microscopy Defocused Images R. Ortiz-Sosa, L.R. Berriel-Valdos, J. F. Aguilar Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica Óptica y
Comparison of an Optical-Digital Restoration Technique with Digital Methods for Microscopy Defocused Images R. Ortiz-Sosa, L.R. Berriel-Valdos, J. F. Aguilar Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica Óptica y
MALA MATEEN. 1. Abstract
 IMPROVING THE SENSITIVITY OF ASTRONOMICAL CURVATURE WAVEFRONT SENSOR USING DUAL-STROKE CURVATURE: A SYNOPSIS MALA MATEEN 1. Abstract Below I present a synopsis of the paper: Improving the Sensitivity of
IMPROVING THE SENSITIVITY OF ASTRONOMICAL CURVATURE WAVEFRONT SENSOR USING DUAL-STROKE CURVATURE: A SYNOPSIS MALA MATEEN 1. Abstract Below I present a synopsis of the paper: Improving the Sensitivity of
OPTICAL LITHOGRAPHY INTO THE MILLENNIUM: SENSITIVITY TO ABERRATIONS, VIBRATION AND POLARIZATION
 OPTICAL LITHOGRAPHY INTO THE MILLENNIUM: SENSITIVITY TO ABERRATIONS, VIBRATION AND POLARIZATION Donis G. Flagello a, Jan Mulkens b, and Christian Wagner c a ASML, 8555 S. River Parkway, Tempe, AZ 858,
OPTICAL LITHOGRAPHY INTO THE MILLENNIUM: SENSITIVITY TO ABERRATIONS, VIBRATION AND POLARIZATION Donis G. Flagello a, Jan Mulkens b, and Christian Wagner c a ASML, 8555 S. River Parkway, Tempe, AZ 858,
Evaluation of Performance of the Toronto Ultra-Cold Atoms Laboratory s Current Axial Imaging System
 Page 1 5/7/2007 Evaluation of Performance of the Toronto Ultra-Cold Atoms Laboratory s Current Axial Imaging System Vincent Kan May 7, 2007 University of Toronto Department of Physics Supervisor: Prof.
Page 1 5/7/2007 Evaluation of Performance of the Toronto Ultra-Cold Atoms Laboratory s Current Axial Imaging System Vincent Kan May 7, 2007 University of Toronto Department of Physics Supervisor: Prof.
 Telecentric Imaging Object space telecentricity stop source: edmund optics The 5 classical Seidel Aberrations First order aberrations Spherical Aberration (~r 4 ) Origin: different focal lengths for different
Telecentric Imaging Object space telecentricity stop source: edmund optics The 5 classical Seidel Aberrations First order aberrations Spherical Aberration (~r 4 ) Origin: different focal lengths for different
3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools:
 3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools: Alignment equipment The alignment telescope and its use The laser autostigmatic cube (LACI) interferometer A pin -- and how to find the center of curvature
3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools: Alignment equipment The alignment telescope and its use The laser autostigmatic cube (LACI) interferometer A pin -- and how to find the center of curvature
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Mechanical Engineering Department. 2.71/2.710 Final Exam. May 21, Duration: 3 hours (9 am-12 noon)
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Mechanical Engineering Department 2.71/2.710 Final Exam May 21, 2013 Duration: 3 hours (9 am-12 noon) CLOSED BOOK Total pages: 5 Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Mechanical Engineering Department 2.71/2.710 Final Exam May 21, 2013 Duration: 3 hours (9 am-12 noon) CLOSED BOOK Total pages: 5 Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH
EUV Plasma Source with IR Power Recycling
 1 EUV Plasma Source with IR Power Recycling Kenneth C. Johnson kjinnovation@earthlink.net 1/6/2016 (first revision) Abstract Laser power requirements for an EUV laser-produced plasma source can be reduced
1 EUV Plasma Source with IR Power Recycling Kenneth C. Johnson kjinnovation@earthlink.net 1/6/2016 (first revision) Abstract Laser power requirements for an EUV laser-produced plasma source can be reduced
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II. + 1 s i. = 1 f
 Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
An Indian Journal FULL PAPER. Trade Science Inc. Parameters design of optical system in transmitive star simulator ABSTRACT KEYWORDS
 [Type text] [Type text] [Type text] ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 10 Issue 23 BioTechnology 2014 An Indian Journal FULL PAPER BTAIJ, 10(23), 2014 [14257-14264] Parameters design of optical system in transmitive
[Type text] [Type text] [Type text] ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 10 Issue 23 BioTechnology 2014 An Indian Journal FULL PAPER BTAIJ, 10(23), 2014 [14257-14264] Parameters design of optical system in transmitive
Optical Proximity Effects, part 3
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Autumn 1996) Optical Proximity Effects, part 3 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last two editions of the Lithography Expert, we examined
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Autumn 1996) Optical Proximity Effects, part 3 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last two editions of the Lithography Expert, we examined
Extending SMO into the lens pupil domain
 Extending SMO into the lens pupil domain Monica Kempsell Sears*, Germain Fenger, Julien Mailfert, Bruce Smith Rochester Institute of Technology, Microsystems Engineering, 77 Lomb Memorial Drive, Rochester,
Extending SMO into the lens pupil domain Monica Kempsell Sears*, Germain Fenger, Julien Mailfert, Bruce Smith Rochester Institute of Technology, Microsystems Engineering, 77 Lomb Memorial Drive, Rochester,
Physics 4. Diffraction. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 4 Diffraction Diffraction When light encounters an obstacle it will exhibit diffraction effects as the light bends around the object or passes through a narrow opening. Notice the alternating bright
Physics 4 Diffraction Diffraction When light encounters an obstacle it will exhibit diffraction effects as the light bends around the object or passes through a narrow opening. Notice the alternating bright
Understanding focus effects in submicrometer optical lithography: a review
 Understanding focus effects in submicrometer optical lithography: a review Chris A. Mack, MEMBER SPIE FINLE Technologies P.O. Box 171 Austin, Texas 7871 Abstract. A review is presented on focus effects
Understanding focus effects in submicrometer optical lithography: a review Chris A. Mack, MEMBER SPIE FINLE Technologies P.O. Box 171 Austin, Texas 7871 Abstract. A review is presented on focus effects
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008
 ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
Resolution Enhancement Technologies
 Tutor4.doc; Version 2/9/3 T h e L i t h o g r a h y E x e r t (May 23) Resolution Enhancement Technologies Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas Classically seaking, otical lithograhy
Tutor4.doc; Version 2/9/3 T h e L i t h o g r a h y E x e r t (May 23) Resolution Enhancement Technologies Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas Classically seaking, otical lithograhy
High Resolution Microlithography Applications of Deep-UV Excimer Lasers
 Invited Paper High Resolution Microlithography Applications of Deep-UV Excimer Lasers F.K. Tittel1, M. Erdélyi2, G. Szabó2, Zs. Bor2, J. Cavallaro1, and M.C. Smayling3 1Department of Electrical and Computer
Invited Paper High Resolution Microlithography Applications of Deep-UV Excimer Lasers F.K. Tittel1, M. Erdélyi2, G. Szabó2, Zs. Bor2, J. Cavallaro1, and M.C. Smayling3 1Department of Electrical and Computer
In the Figure above, the fringe at point P on the screen will be:
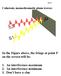 Coherent, monochromatic plane waves: In the Figure above, the fringe at point P on the screen will be: 1. An interference maximum 2. An interference minimum 3. Don t have a clue Answer: 2. Interference
Coherent, monochromatic plane waves: In the Figure above, the fringe at point P on the screen will be: 1. An interference maximum 2. An interference minimum 3. Don t have a clue Answer: 2. Interference
Fiber Optic Communications
 Fiber Optic Communications ( Chapter 2: Optics Review ) presented by Prof. Kwang-Chun Ho 1 Section 2.4: Numerical Aperture Consider an optical receiver: where the diameter of photodetector surface area
Fiber Optic Communications ( Chapter 2: Optics Review ) presented by Prof. Kwang-Chun Ho 1 Section 2.4: Numerical Aperture Consider an optical receiver: where the diameter of photodetector surface area
Topography effects and wave aberrations in advanced PSM-technology
 Header for SPIE use Topography effects and wave aberrations in advanced PSM-technology Andreas Erdmann Fraunhofer Institute of Integrated Circuits, Device Technology Division (IIS-B), Schottkystrasse 1,
Header for SPIE use Topography effects and wave aberrations in advanced PSM-technology Andreas Erdmann Fraunhofer Institute of Integrated Circuits, Device Technology Division (IIS-B), Schottkystrasse 1,
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN
 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN Pantazis Mouroulis Associate Professor Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology John Macdonald Senior Lecturer Physics Department University of
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN Pantazis Mouroulis Associate Professor Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology John Macdonald Senior Lecturer Physics Department University of
Practical Flatness Tech Note
 Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Line End Shortening, part 2
 Tutor31.doc: Version 8/17/00 Line End Shortening, part 2 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Fall 2000) Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, A Division of KLA-Tencor, Austin, Texas As discussed in the
Tutor31.doc: Version 8/17/00 Line End Shortening, part 2 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (Fall 2000) Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, A Division of KLA-Tencor, Austin, Texas As discussed in the
Astronomy 80 B: Light. Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson
 Astronomy 80 B: Light Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson Sensitive Countries LLNL field trip 2003 April 29 80B-Light 2 Topics for Today Optical illusion Reflections
Astronomy 80 B: Light Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson Sensitive Countries LLNL field trip 2003 April 29 80B-Light 2 Topics for Today Optical illusion Reflections
Introduction to Light Microscopy. (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps)
 Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Optical transfer function shaping and depth of focus by using a phase only filter
 Optical transfer function shaping and depth of focus by using a phase only filter Dina Elkind, Zeev Zalevsky, Uriel Levy, and David Mendlovic The design of a desired optical transfer function OTF is a
Optical transfer function shaping and depth of focus by using a phase only filter Dina Elkind, Zeev Zalevsky, Uriel Levy, and David Mendlovic The design of a desired optical transfer function OTF is a
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Measurement of low-order aberrations with an autostigmatic microscope
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Measurement of low-order aberrations with an autostigmatic microscope William P. Kuhn Measurement of low-order aberrations with
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Measurement of low-order aberrations with an autostigmatic microscope William P. Kuhn Measurement of low-order aberrations with
Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102 28 March 2002 Lecture 6 28 Mar 2002 Physics 102 Lecture 6 1 Light waves and light rays Last time we showed: Time varying B fields E fields B fields to create
Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102 28 March 2002 Lecture 6 28 Mar 2002 Physics 102 Lecture 6 1 Light waves and light rays Last time we showed: Time varying B fields E fields B fields to create
