Chapter 2 Visual Perception: Basic Processes
|
|
|
- Edward Miller
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cognitve Psychology A Students s Handbook 1. Mai 2002 Chapter 2 Visual Perception: Basic Processes CHAPTER OVERVIEW (SUMMARY) 1. Perceptional organisation: The Gestalt psychologists identified several laws, eg: - law of similarity, - law of proximity, - law of good continuation, - law of closure, - law of common fate determing which elements of a visual display will be grouped together. They focused on lines and shapes and tried unsuccessfully to explain visual organisation in terms of electrical field forces in the brain. 2. Depth and size perception: - Monocular cues: linear perspective, aerial perspective, texture, interposition, shading, familiar size, motion parallax - Oculomotor cues: convergence, accomodation (both very limited usefull) - Binocular cues: stereopsis (very important) involves establishing correspondences between the information presented to the one eye and the information presented to the other eye Information from th various depth cues is additively combined to minimise errors in depth perception. Size constancy depends mainly on perceived distance, but familiar size is also important. 3. Brain systems: Anatomically distinct systems in the visual cortex which are specialised for processing different kinds of information, eg: form, motion, colour: V3: motion processing, exspecially processing of dynamic form and obtaining 3-dimens. Structure from motion V4: colour processing V3,V4,IT and other: form perception V5: motion processing INTRODUCTION Roth s definition of perception: The term perception refers to the means by which information acquired from the environment via the sense organs is transformed into experiences of objects, events sounds, tastes, etc. 1. PERCEPTUAL ORGANISATION 1
2 Although the basic visual information available to us consists of simple elements such as edges, lines and blobs we perceive an organised world consisting of people and objects. We are able to work out, which parts of the visual information belong together and so to form seperate objects: perceptual segregation. Gestaltist approach The Gestaltists made the first systematic attempt to study perceptual segregation and perceptional organisation: fundamental principle of perceptional organisation: law of Prägnanz Of several geometrically possible organisations that one will actually occur, which possesses the best, simplest and most stable shape. Other laws (subsumed under the law of Prägnanz): law of proximity: elements that are close to each other are grouped together law of similarity: elements that are similar to each other are grouped together law of good continuation: elements requiering the fewest changes or interuption are grouped together in straight or smoothly curving lines (remember: Kreuz wird als bestehend aus zwei geschwungenen Linien wahrgenommen, nicht als zwei sich im Scheitel berührende Winkel) law of closure: missing parts of a figure are filled in to compete it And: law of common fate: elements, that appear to move together are grouped together Gestalt laws are descriptive statements possessing little or no explanatory power Doctrine of isomorphism: assumed, there are electrical field forces in the brain to produce the experience of a stable perceptual organisation when we look at our visual environment Section summary The great strength of the Gestaltist approach: indentification of several important phenomena. The important weaknesses: no experiments to find limitations and inadequacies of their theory and no real explanation ot the phenomena they had discovered. And: Though they emphased (betonen) the importance of the law of Prägnanz, according to which the perceptual world is organised into the simplest and best shape, they could not say which shape is the simplest and best. Subsequent theories Restle s (1979) way of clarifying the notion of simplicity: studied the perception of moving dots: complicated approach: to treat each dot as completely seperated from all the other dots and to calculate starting position, speed, direction but what is possible: to treat the dots as belonging to groups, especially if they move together in the same direction with the same speed greater amount of processing or computation when dots are treated seperatly than as members of groups main finding: whatever moving dots in a display would involve the least calculation generally correponds to what is actually perceived 2
3 Julesz (1975) identified grouping processes based on basic stimulus properties such as brightness, wavelength and granularity: extended the Gestaltists work by sudying the effects of brightness and colour: a visual display is perceived at consisting of two regions if the average brightness in each region differs considerably but: no perceived difference if detailed pattern of brightness in each region was different but there was only a modest difference in the average brightness a visual display is perceived as consisting of two regions if it consists of coloured squares and the average wavelength of light in each region is clearly different discovered some exceptions to the notion that average brightness or wavelength is crucial in determining wether a display is perceived as consisting of two regions: another important factor: granularity (way in which the elements in a region are distributed) a visual display in which the overall brightness is the same but the granularity is greater in one half than the other is perceived as consisting of two regions Suggest: processes involved in perceptual organisation occur very early in visual perception Proposition of the theory of textons (basic elements of early vision): textons consist of elongated blobs or line segments and their termination they coorespond directly to the representations found in the raw primal sketch the raw primal sketch contains only basic information about a visual display -> the initial perceptual organisation does not take account of subtle (fein) variations in texture Full primal sketch Workers in artificial intelligence made some progress in telling us in detail about processes involved in perceptual organisation, as Marr (1976, 1982) for example: noted that basic perceptual organisation is achieved already at the level of the twodimensional primal sketch the raw primal sketch contains information about light intensity changes in the form of edges, blobs, bars and terminations, it is typically ambiguous used two general principles to design a program to achieve perceptual organisation: principle of explicit naming: give a name or symbol to a set of grouped elements that is used to describe other sets of grouped elements all of which can form a larger grouping principle of least commitment: ambiguities are resolved only when there is evidence as to the appropriate solution assigned place tokens to small regions of the raw primal sketch, such as the position of a blob or edge or the termination of a longer blob or edge various edge points are incorporated into a single place token place tokens than are grouped together in various ways: Clustering: place tokens that are close together are combined ti form higher-order place tokens Curvilinear aggregation: place tokens that are alined in the same direction are joined to form a contour Section summary Why Marr s visual processing program was so successful: the grouping principles applied to place tokens reflect what is generally the case in the real world 3
4 it does not rely (sich verlassen auf) on object knowledge or expectations but works well nevertheless The greatest limitation of Marr s appoach: his assumption, that grouping is based on 2-dimensional representations; in general this is the case, but grouping can also be based on 3-dimensional representations 2. DEPTH PERCEPTION How is the 2-dimensional retina image transformad into perception of a 3-dimensional world? Different senses of the term depth perception : absolute distance: distance from the observer that an object is located relative distance: distance between two objects (used when fitting a slize of bread into a toaster) Judgements of relative distance are often more accurate than judgements of absolute distance. Cues to depth are often provided by movement either of the object or of the observer but here we focus on monocular cues and binocular and oculumotor cues that are available even if nothing move. Monocular cues Only require the use of one eye, but can be used with both eyes open as wel. Include: linear perspective: parallel lines pointing directly away appear closer together as they recede into the distance (Schienen) arial perspective: because of light scattering more distant objects lose contrast and appear hazy (verschwommen) -> objects with less contrast appear to be more distant texture: textured objects (cobble-stoned road) slanting away have a texture gradient, density (Dichte) increases with distance interposition: a nearer object hides a part of more distant object (remeber: vier Kreise, denen je ein Viertel fehlt scheinen wie von Quadrat verdeckt) shading: a shade provides evidence that there must be a 3-dimensional object as 2- dimensional objects do not have shades familiar size: use of retinal image size of an object to provide an accurate estimate of its distance, only possible if actual size of the object is known motion parallax: refers to the movement of an object s image over the retina (caused by the move of the object as well as by the move of the observer s eye), motion parallax can generate depth information without all other cues Binocular and oculomotor cues Involve both eyes being used together, are effictive only in facilitating depth perception over short distances, include: Oculomotor cues (less important): convergence: eyes turn inwards to focus on an object to a greater extent close with a very close object than with one that is further away accomodation: tickening of the lens of the eye when focusing on a close object Binocular cue (more important): stereopsis: stereoscopic vision depending on the disparity in the images projected on the retinas of the two eyes 4
5 Three rules to match up information from the two eyes: Comptibility constraint: elements from the input of each eye are matched with each other only if they are campatible (eg: same colour) Uniqueness constraint: each element in one image can match with only one element in the other image Continuity constraint: matches between to elements are prefered where the disparities between the two images are similar to the disparities between nearby matches on the same surface... This is the least adequate constraint. Integrating cue information How is the information from the various cues combined and integrated? Additivity: all the information from different cues is added together. Exceptions: there can be a situation where one depth cue is overhelmed by another, which then is ignored, eg: experiment where the interposition overhelms the cue of familiar size Size constancy is the tendency for any given object to appear the same size whether its size in the retinal image is large or small (imagine someone walking towards you, their retinal images increases but their size seems to remain the same). Why is it important? we take account of an objects s apparent distance when judging its size size distance invariance hypothesis : for a given size of retinal image, the perceived size of an object is proportional to its perceived distance example: size constancy is often not shown when we look down at objects from a high building or a plane because it is hard to estaimate the distance In sum size constancy depends on many factors including perceived distance, size familiarity, the horizon and so on. 3. BRAIN SYSTEMS more than 30 visual areas in the cortex in retina: great majority of M (magnocellular or largebodied) and P (parvocellular or smallbodied) cells their axons form the optic nerve which projects on the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) the LGN is organised in 6 layers: layer 1 and 2 receive input from M ganglion cells -> Magno layers: movement detection layers 3-6 receive input from P ganglion cells -> Parvo layers: colour, fine textures, detailed objects ipsilateral projections (from the eye at the same side) terminate in layers 2, 3 and 5 contralateral projections (from the eye at the other side) terminate in layers 1, 4 and 6 neurons from the P layers and from the M layers mainly project to the primary visual cortex, V1 5
6 after having passed V2 there are two pathways proceeding further into the cortex: parietal pathway: mainly concerned with movement processing ( Where pathway for action) temporal pathway: concerned with colour and form processing ( What pathway for perception) different parts of the cortex are specialised for different visual functions: V1 and V2: colour and form, contain pigeonholes (Ablegefach) into which the different signals are assembled before being relayed to the specialised visual areas V3, V3A, (V4) and IT (inferotemporal cortex): form (especially the shapes of objects in motion) but not colour (V1 and) V4: mainly colour, many cells are also responsive to line orientation V5: visual motion Blindsight Partial or total damages in V1 cause a loss of vision in part or all of the visual field, in spite of this loss of conscious vision, some of these patients can make accurate judgements and discriminations about visual stimuli. (Anm. d. Red.:) No real explanation seems to exist. Intagration of information the binding problem Gazzaniga: Visual perception is a devide-and-conquer strategy. : each area provides its own limited analysis -> processing is distributed and specialised How is information about colour, form and motion combined? An approach: oscillation-binding theory: neurons sometimes exhibit oscillatory activity, in which there are alternating bursts of high and low rates of firing, they could tend to oscillate in a synchronised way when they are responding to the same abject -> produce an integrated percept of the object problem with this theory: oscillation only seems to occur with moving stimuli! What about static stimuli? Oscillations develop too slowly and last for too long Tovée: not such a binding problem : there is only high visual acuity for stimuli presented to the fovea of the retina -> tunnel vision effect, where only the visual information from the centre of the visual field is fully sampled and analysed, the different features of an object are probably integrated or combined in a subsequent higher integrative cortical area. 6
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Today. Pattern Recognition. Introduction. Perceptual processing. Feature Integration Theory, cont d. Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
 Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Sensation. Perception. Perception
 Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception
 Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception Fritz Perls Father of Gestalt theory and Gestalt Therapy Movement in experimental psychology which began prior to WWI. We perceive objects as well-organized patterns
Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception Fritz Perls Father of Gestalt theory and Gestalt Therapy Movement in experimental psychology which began prior to WWI. We perceive objects as well-organized patterns
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
the dimensionality of the world Travelling through Space and Time Learning Outcomes Johannes M. Zanker
 Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Occlusion. Atmospheric Perspective. Height in the Field of View. Seeing Depth The Cue Approach. Monocular/Pictorial
 Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych
 Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych Perception: is the study of how we integrate sensory information into percepts of objects and how we then use these percepts to get around in the world (a percept is
Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych Perception: is the study of how we integrate sensory information into percepts of objects and how we then use these percepts to get around in the world (a percept is
Module 2. Lecture-1. Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation.
 Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2)
 Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Lecture Outline. Basic Definitions
 Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision: Distance & Size Perception
 Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness )
 Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
3D Space Perception. (aka Depth Perception)
 3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Vision III. How We See Things (short version) Overview of Topics. From Early Processing to Object Perception
 Vision III From Early Processing to Object Perception Chapter 10 in Chaudhuri 1 1 Overview of Topics Beyond the retina: 2 pathways to V1 Subcortical structures (LGN & SC) Object & Face recognition Primary
Vision III From Early Processing to Object Perception Chapter 10 in Chaudhuri 1 1 Overview of Topics Beyond the retina: 2 pathways to V1 Subcortical structures (LGN & SC) Object & Face recognition Primary
Perceptual Organization
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Lecture 5. The Visual Cortex. Cortical Visual Processing
 Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Chapter 6: Perception
 Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Perceptual Organization. Unit 3 RG 4e
 Perceptual Organization Unit 3 RG 4e Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Perceptual Illusions To understand how perception is organized, illusions
Perceptual Organization Unit 3 RG 4e Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Perceptual Illusions To understand how perception is organized, illusions
CHAPTER 4. Sensation & Perception. Lecture Overview. Introduction to Sensation & Perception PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Understanding Sensation
 CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ. Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. Topics
 Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning
 Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Perception. Selective Attention focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. Cocktail Party Effect
 Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture
 59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
Outline. The visual pathway. The Visual system part I. A large part of the brain is dedicated for vision
 The Visual system part I Patrick Kanold, PhD University of Maryland College Park Outline Eye Retina LGN Visual cortex Structure Response properties Cortical processing Topographic maps large and small
The Visual system part I Patrick Kanold, PhD University of Maryland College Park Outline Eye Retina LGN Visual cortex Structure Response properties Cortical processing Topographic maps large and small
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION. Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K.
 THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K. Simpson The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute Ann
THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K. Simpson The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute Ann
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Overview
 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June
 An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 8 Depth Perception 8.1 Stereoscopic Depth Perception When we observe the three dimensional
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 8 Depth Perception 8.1 Stereoscopic Depth Perception When we observe the three dimensional
CS 534: Computer Vision
 CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes
 Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neural development and visual system Lecture 2 Topics Development Gastrulation Neural
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neural development and visual system Lecture 2 Topics Development Gastrulation Neural
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
Visual Perception of Spatial Subjects
 DIR 2007 - International Symposium on Digital industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography, June 25-27, 2007, Lyon, France Visual Perception of Spatial Subjects Kurt R. S. Osterloh 1, Uwe Ewert 1 1 Federal
DIR 2007 - International Symposium on Digital industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography, June 25-27, 2007, Lyon, France Visual Perception of Spatial Subjects Kurt R. S. Osterloh 1, Uwe Ewert 1 1 Federal
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
The Ecological View of Perception. Lecture 14
 The Ecological View of Perception Lecture 14 1 Ecological View of Perception James J. Gibson (1950, 1966, 1979) Eleanor J. Gibson (1967) Stimulus provides information Perception involves extracting this
The Ecological View of Perception Lecture 14 1 Ecological View of Perception James J. Gibson (1950, 1966, 1979) Eleanor J. Gibson (1967) Stimulus provides information Perception involves extracting this
Introduction to Visual Perception
 The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL OVERVIEW 1
 OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
IN VISION, AS IN OTHER mental operations, we experience
 Chapter 28 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form 549 28 A Stripes in area 8 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form lnterblob Blob V2 V The Parvocellular and Magnocellular Pathways Feed nto Two Processing
Chapter 28 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form 549 28 A Stripes in area 8 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form lnterblob Blob V2 V The Parvocellular and Magnocellular Pathways Feed nto Two Processing
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
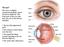 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Face Perception. The Thatcher Illusion. The Thatcher Illusion. Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Face Inversion Effect
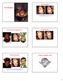 The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception
 Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
Definitions Sensation Sensation and perception Perception
 Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
3 THE VISUAL BRAIN. No Thing to See. Copyright Worth Publishers 2013 NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
 3 THE VISUAL BRAIN No Thing to See In 1988 a young woman who is known in the neurological literature as D.F. fell into a coma as a result of carbon monoxide poisoning at her home. (The gas was released
3 THE VISUAL BRAIN No Thing to See In 1988 a young woman who is known in the neurological literature as D.F. fell into a coma as a result of carbon monoxide poisoning at her home. (The gas was released
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
Cortical sensory systems
 Cortical sensory systems Motorisch Somatosensorisch Sensorimotor Visuell Sensorimotor Visuell Visuell Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Mensch Katze Ratte Primary Visual Cortex
Cortical sensory systems Motorisch Somatosensorisch Sensorimotor Visuell Sensorimotor Visuell Visuell Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Mensch Katze Ratte Primary Visual Cortex
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 3: Visual Perception of Objects
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 3: Visual Perception of Objects www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 What is after V1?... 2 Assembling Simple Features into Objects... 4 Illusory Contours...
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 3: Visual Perception of Objects www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 What is after V1?... 2 Assembling Simple Features into Objects... 4 Illusory Contours...
Segregation of Form, Color, Movement, and Depth: Anatomy, Physiology, and Perception
 Segregation of Form, Color, Movement, and Depth: Anatomy, Physiology, and Perception Anatomical and physiological observations in monkeys indicate that the primate visual system consists of several separate
Segregation of Form, Color, Movement, and Depth: Anatomy, Physiology, and Perception Anatomical and physiological observations in monkeys indicate that the primate visual system consists of several separate
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
A Fraser illusion without local cues?
 Vision Research 40 (2000) 873 878 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Rapid communication A Fraser illusion without local cues? Ariella V. Popple *, Dov Sagi Neurobiology, The Weizmann Institute of Science,
Vision Research 40 (2000) 873 878 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Rapid communication A Fraser illusion without local cues? Ariella V. Popple *, Dov Sagi Neurobiology, The Weizmann Institute of Science,
Perceiving Motion and Events
 Perceiving Motion and Events Chienchih Chen Yutian Chen The computational problem of motion space-time diagrams: image structure as it changes over time 1 The computational problem of motion space-time
Perceiving Motion and Events Chienchih Chen Yutian Chen The computational problem of motion space-time diagrams: image structure as it changes over time 1 The computational problem of motion space-time
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects
 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
