ENGAGE. Daily Routines Common Core. Essential Question
|
|
|
- Cecil O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LESSON 10.1 Algebra Area of Parallelograms FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 6.G.A.1 Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Find the area of parallelograms. Also 6.EE.A., 6.EE.B.7 MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES (See ematical Practices in GO! in the Planning Guide for full text.) MP Model with mathematics. MP5 Use appropriate tools strategically. MP6 Attend to precision. MP8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. F C R Coherence: Language Objective Students draw a four-panel picture poster showing how to find the area of parallelograms. Materials Board, Grid Paper (see Teacher Resources), scissors, straightedge, number cubes Standards Across the Grades Before Grade 6 After 5.NF.B.b 6.G.A.1 7.G.A.1 7.G.B.6 F C R Rigor: Level 1: Understand Concepts...Share and Show ( Checked Items) Level : Procedural Skills and Fluency...On Your Own, Practice and Homework Level 3: Applications...Think Smarter and Go Deeper F C R For more about how GO! fosters Coherence within the Content Standards and ematical Progressions for this chapter, see page 531J. About the Professional Development If Students Ask Students may not understand how a parallelogram and rectangle can have the same area when the parallelogram extends farther in one direction than the rectangle. Students may not understand that the height is perpendicular to the base. They may use the side lengths in the formula for area rather than the base and height. In this lesson, students cut out a parallelogram and examine its relationship to a rectangle with the same base and height. This will reinforce that the height of a parallelogram is different from a side length. Professional Development Videos 533A Chapter 10 Interactive Student Edition Personal Trainer on the Spot Video itools: Geometry HMH Mega
2 Daily Routines Common Core Problem of the Day 10.1 Mrs. Hanson bought 1.6 pounds of grapes. The grapes cost $.50 per pound. How much did she pay for the grapes? $.00 Vocabulary area, parallelogram Interactive Student Edition Multimedia Glossary e 1 3 Fluency Builder Materials eteacher Resources pages TR13 TR135 Operations Find the quotient. Write the remainder with an r. 1. 1, r8. 3, r , r35 Common Core Fluency Standard 6.NS.B. 1 ENGAGE with the Interactive Student Edition Essential Question How can you find the area of a parallelogram? Making Connections Draw a rectangle and review how to find its perimeter. What formula do you use? P = l + w, where l and w are the length and width of the rectangle Learning Activity Discuss the relationship between an equation and a formula. Focus on the area formula for a rectangle. What two measures of a rectangle are needed to calculate the area? length and width Is it possible to compute the length if you know the area and the width? yes What operation would you use? division Literacy and ematics Visit the lesson opener with the students. Have students brainstorm common applications of how area of a figure is used in their everyday lives. Have students write a real-world problem that involves finding the area of a rectangle.. 56, r , r Pages in Strategies and Practice for Skills and Facts Fluency provide additional fluency support for this lesson. Literature Connection From the Grab-and-Go TM Differentiated Centers Kit Students read about using area to find the amount of paint and the tile needed for a room. How can you find the area of a parallelogram? Room Makeover: Serving the Community 533B
3 LESSON 10.1 EXPLORE Discuss the definition of area. Have students count the number of grid squares, or unit squares, inside the -by-3 rectangle. Students should connect the number of grid squares with the product of the dimensions. Students may be familiar with the formula A = bh rather than A = lw. Explain that these formulas are equivalent for rectangles. Unlock the Problem MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES Explain that the area of the quilt piece is measured in square centimeters because it is the product of two dimensions that are measured in centimeters. MP Reason abstractly and quantitatively. What characteristics affect the area of a parallelogram? the length of a base and the height Talk Use Talk to expand on students understanding of parallelograms. DEEPER Remind students that the height of a parallelogram is the length of a segment that forms a 90º angle with the base and extends to the opposite side. MP8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Why is the area of the rectangle the same as the area of the parallelogram? Possible answer: Since the number of grid squares covered by the two shapes is the same, the area of the shapes must be the same. ELL Strategy: Restate Restate the steps of the process for finding the area of a parallelogram using familiar language. Be sure to use simplified language to explain what are parallelograms, rectangles, and quadrilaterals. Use real objects or drawings to demonstrate area and height. 533 Chapter 10 6.G.A.1 Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Image Credits: (r) Roman Soumar/Corbis Area of Parallelograms Essential Question How can you find the area of parallelograms? connect The area of a figure is the measure of the number of unit squares needed to cover it without any gaps or overlaps. The area of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width. The rectangle shown has an area of 1 square units. For a rectangle with length l and width w, A = l w, or A = lw. Recall that a rectangle is a special type of parallelogram. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. Algebra Area of Parallelograms The formula for the area of a parallelogram is the product of the base and height. height 5 h base 5 b Find the area. A 5 bh A 5 s Step 1 Identify the figure. 1 mi 13 m 1 mi yd 5 1 yd side 5 s The figure is a parallelogram, so use the formula A 5 bh. Step Substitute 5 1_ for b and for h. A 5 5 1_ 3 Step 3 Multiply. A 5 1_ _ So, the area of the parallelogram is 11 yd. Find the area. 1. Figure:.7 m Formula: A The formula for the area of a square is the square of one of its sides. parallelogram bh A m 3 yd yd 1 3_ 5 mi yd Chapter Resources Unlock the Problem Victoria is making a quilt. She is using material in the shape of parallelograms to form the pattern. The base of each parallelogram measures 9 cm and the height measures cm. What is the area of each parallelogram? See below. Activity Use the area of a rectangle to find the area of the parallelogram. Materials grid paper scissors Draw the parallelogram on grid paper and cut it out. Cut along the dashed line to remove a triangle. Move the triangle to the right side of the figure to form a rectangle. What is the area of the rectangle? 36 sq cm What is the area of the parallelogram? 36 sq cm base of parallelogram = length of rectangle height of parallelogram = width of rectangle area of parallelogram = area of rectangle For a parallelogram with base b and height h, A = bh or b h Area of parallelogram = b h = 9 cm cm = _ 36 sq cm So, the area of each parallelogram in the quilt is _ 36 sq cm. Problem Type: Area Unknown Product Reteach Differentiated Enrich Instruction Reteach 10-5 Reteach All Aboard Parallelogram and Square Express Find the areas of the train cars below. Write the shape of the car and the formula you used to find the area. (Do not include the wheels as part of the area.) 73 yd Figure: Car D 13 1 yd Train Car A Formula for the Area: Area: Figure: Train Car C Formula for the Area: Area: Car C 36. ft 3.3 ft parallelogram A 5 bh,318 ft parallelogram A 5 bh 83.6 ft 1. Stretch Your Thinking Add another car to the train. Draw and label the car. Then find the area. Check students drawings and answers. Chapter Resources width (w) cm ALGEBRA Geometry 6.G.A.1 Also 6.EE.A.c, 6.EE.B.7 MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES MP, MP5, MP6 Talk 3 Car B 0.6 ft Figure: 0.6 ft Car A 61 ft 38 ft Train Car B Formula for the Area: Area: Figure: Train Car D Formula for the Area: Area: height (h) cm base (b) 9 cm length (l) 9 cm The height of a parallelogram forms a 90º angle with the base. The parallelogram can be cut along the height and put back together to form the rectangle, so the areas are the same. MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES 6 Explain how you know that the area of the parallelogram is the same as the area of the rectangle. Chapter Enrich square A 5 s 1,68.36 ft parallelogram A 5 bh yd. Stretch Your Thinking If the unshaded triangles in Train Car C are removed, the figure is a square. What is the area of the shaded section of Train Car C? 5.89 ft 10-6 Enrich
4 Example 1 of the parallelogram. Write the formula. Replace b and h with their values. Multiply. A = bh A = A = 13.3 So, the area of the parallelogram is _ 13.3 square meters. A square is a special rectangle in which the length and width are equal. For a square with side length s, A = l w = s s = s, or A = s. Example Find the area of a square with sides measuring 9.5 cm. Write the formula. Substitute 9.5 for s. Simplify. Use the formula A = bh to find the area A = s So, the area of the square is 90.5 cm. A = ( ) 9.5 = 90.5 Example 3 A parallelogram has an area of 98 square feet and a base of 1 feet. What is the height of the parallelogram? Write the formula. Replace A and b with their values. Use the Division Property of Equality. 98 Solve for h. A = bh 98 1 = h = 1h = h So, the height of the parallelogram is 7 feet..1 m 6.3 m? 9.5 cm 9.5 cm Area 5 98 ft 1 ft Problem Type: Area Unknown Product Example 1 What are the dimensions of a rectangle with the same area as this parallelogram? Possible answer: 6.3 meters long by.1 meters wide Example Why is the area measured in square centimeters? Possible answer: because each side is measured in centimeters and area is measured in square units. Example 3 Why did you use division to find the width? Possible answer: Since multiplication and division are inverse operations, and area is the product of length and width, you can divide the area by the length to find the width. DEEPER MP3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Can you use the formula for the area of a parallelogram to find the area of a rectangle? Explain. Yes; a rectangle is a special type of parallelogram. The length of the rectangle is the base, and the width of the rectangle is the height, because the sides of a rectangle are perpendicular. MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE 6 Compare Explain the difference between the height of a rectangle and the height of a parallelogram. Possible answer: The height of a rectangle is the length of one side of the rectangle. The height of a parallelogram is the length of a perpendicular line segment drawn from the base to an opposite side or to a line segment extended from the opposite side. If the parallelogram is a rectangle, the height will be the length of a side of the parallelogram. 53 Advanced Learners Logical / ematical Partners Materials Grid Paper (see eteacher Resources), number cubes labeled 1 to 6 Give each pair of students grid paper, two number cubes, and the following instructions. Take turns rolling the number cubes and finding the product of the numbers rolled. The product represents the area of a parallelogram. Find the dimensions of a figure with this area. On the grid paper, draw the figure with the area and dimensions found above. Figures may share sides but may not overlap. Make an identifying mark, such as initials, inside the figure and record the figure s area. When there is no more room to draw parallelograms, the game is over. The player with the greatest total area wins. COMMON ERRORS Error When finding the area of a parallelogram, students may incorrectly identify the height from a drawing. Example A = bh 1 in. 1 A = 15 in. 1 A = 195 in. 15 in. Springboard to Learning Remind students that the height, h, of a parallelogram forms a right angle with its base, b. 53
5 3 If Then EXPLAIN Share and Show The first problem connects to the learning model. Have students use the Board to explain their thinking. Talk Quick Check MATH MATH BOARD Use Talk to focus on students understanding of area of parallelograms. MP8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. If you know the area and height of a parallelogram, how can you calculate the base? Divide the area by the height. Use the checked exercises for Quick Check. Students should show their answers for the Quick Check on the Board. 3 1 Rt I a student misses the checked exercises Differentiate Instruction with Reteach 10.1 Personal Trainer 6.G.A.1, 6.EE.A.c RtI Tier 1 Activity (online) Share and Show 1. A = bh 1. m. 8.3 m 6 ft A = ft A = m.5 mm 9.1 m.5 mm 5. Area = 11 yd yd On Your Own? yd 1 5 yd Find the area of the parallelogram m MATH BOARD Find the area of the parallelogram or square. 6.5 mm Find the unknown measurement for the parallelogram.. ft 3 3 ft 8 ft ft ft yd 1 ft m Find the unknown measurement for the figure. 9. square A = 5 ft s = 15 ft 10. parallelogram A = 3 m b = m h = 8 m 6. Area = 3 yd Possible answer: The area of a parallelogram with no right angles is the same as the area of a rectangle that has the same base (length) and height (width). 13. The height of a parallelogram is four times the base. The base measures 3 1_ ft. Find the area of the parallelogram. 9 f t 8. 8 yd 11. parallelogram Talk A = 51 1_ in. b = 8 1_ 5 in. 6 h = 1_ in.? yd MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES Reasoning Explain how the areas of some parallelograms and rectangles are related. ft 1. parallelogram A = 11 mm b = 11 mm h = 11 mm Chapter 10 Lesson _ On Your Own You may wish to provide grid paper to students to help them solve Exercises Ask for volunteers to share their solutions for Exercise 13. As a class, compare the various methods the volunteers used. MP6 Attend to precision. Describe a method you can use to determine if your answer is reasonable. Possible answer: Estimation. I can round the base and the height and multiply. Additional Example Kelly made an enclosed square garden with a side length of 5.5 feet. Write and evaluate an expression for the area of the garden using an exponent. A = 5.5 ; 30.5 square feet PROBLEM TYPE SITUATIONS Addition and Subtraction Put Together/Take Apart Total Unknown Exercise: 15 Multiplication and Division Area Unknown Product Exercises: 13, 1, 15, 16 Area Unknown Factor Exercise: Chapter 10
6 MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES M 1. Jane s backyard is shaped like a parallelogram. The base of the parallelogram is 90 feet, and the height is 5 feet. What is the area of Jane s backyard? ELABORATE,50 ft 15. Jack made a parallelogram by putting together two congruent triangles and a square, like the figures shown at the right. The triangles have the same height as the square. What is the area of Jack s parallelogram? 10 cm 16. DEEPER The base of a parallelogram is times the parallelogram s height. If the base is 1 inches, what is the area? 7 in. 5 cm 8 cm 5 cm Problem Solving Applications MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES Exercise 15 requires students to use higher order thinking skills. Students must infer that the area of the parallelogram is the sum of the areas of two congruent triangles and a square. 17. MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE 3 Verify the Reasoning of Others Li Ping says that a square with 3-inch sides has a greater area than a parallelogram that is not a square but has sides that have the same length. Does Li Ping s statement make sense? Explain. Yes; possible explanation: A parallelogram with sides that are each 3 inches does not have a on the Spot Video Tutor Use this video to help students model and solve this type of Think Smarter problem. height of 3 inches. Its height will be less than 3 inches, and its area will be less than that of the on the Spot videos are in the Interactive Student Edition and at square, which is 9 square inches. 18. Find the area of the parallelogram. 536 The area is _ 60 in. 5 in. 1 in. DIFFERENTIATED INSTRUCTION 6 in. INDEPENDENT ACTIVITIES Exercise 18 assesses a student s ability to use the formula to find the area of a parallelogram. Students must find the area by multiplying the base and the height. Students who answer 7 square inches have used the side dimension, 6 inches, rather than the 5-inch height. Students who multiply all three numbers may not have known the formula. 5 EVALUATE Formative Assessment Activities Risky Rectangles Differentiated Centers Kit Activities Areas of Parallelograms and Trapezoids Literature Room Makeover: Serving the Community Essential Question Using the Language Objective Reflect Have students draw a four-panel picture poster to answer the essential question. How can you find the area of a parallelogram? Possible answer: To find the area of a parallelogram, multiply its base by its height. Students complete orange Activity Card 3 by drawing and measuring rectangles. Students complete online blue Activity Card 19 by finding the area of parallelograms and trapezoids. Students read about using area to find the amount of paint and tile needed for a room. Journal WRITE Copy the two triangles and the square in Exercise 15. Show how you found the area of each piece. Draw the parallelogram formed when the three figures are put together. Calculate its area using the formula for the area of a parallelogram. 536
7 Area of Parallelograms Practice and Homework Practice and Homework Use the Practice and Homework pages to provide students with more practice of the concepts and skills presented in this lesson. Students master their understanding as they complete practice items and then challenge their critical thinking skills with Problem Solving. Use the Write section to determine student s understanding of content for this lesson. Encourage students to use their Journals to record their answers. Find the area of the figure. 1. A = bh 7 ft A = A = 16 ft 18 ft Find the unknown measurement for the figure. 3. parallelogram A = 9.18 m b =.7 m h = 3. m. parallelogram 9 A = m b = 3 10 m h = 1 10 m. 5 cm 7 cm 35 cm 5. square A = 1,5 cm s = 35 cm COMMON CORE STANDARD 6.G.A.1 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume. 6. parallelogram A = 6.3 mm b = 7 mm h = 0.9 mm Problem Solving 7. Ronna has a sticker in the shape of a parallelogram. The sticker has a base of 6.5 cm and a height of 10.1 cm. What is the area of the sticker? 8. A parallelogram-shaped tile has an area of 8 in.. The base of the tile measures 1 in. What is the measure of its height? cm 9. WRITE Copy the two triangles and the square in Exercise 15 on page 536. Show how you found the area of each piece. Draw the parallelogram formed when the three figures are put together. Calculate its area using the formula for the area of a parallelogram. Check students work. in. Chapter Cross-Curricular Cartographers, or mapmakers, make maps and globes. In the past, they used pen and paper, but today, with the help of computers, they can make quicker work of mapmaking. They often begin with an estimate of the area of a continent, country, state, or town. Then they apply more precise computer techniques to make the map a true model of the actual area. Use a map of your town to make an estimate of the area of your town. Explain your reasoning. Check students work. SOCIAL STUDIES The game of chess has its ancestry in a game from sixth-century India called chaturanga, which literally means having four parts. This refers to the four-part army of elephant brigades, chariots, cavalry, and foot soldiers, corresponding to the modern-day chess pieces bishops, rooks, knights, and pawns, respectively. The square chessboard contains 6 smaller squares. If each of those squares on a particular chessboard has sides that are 1 1_ inches long, what is the area of the chessboard? 1 i n Image Credits: PhotoDisc/Getty Images 537 Chapter 10
8 Lesson Check (6.G.A.1, 6.EE.A.c, 6.EE.B.7) 1. Cougar Park is shaped like a parallelogram and has an area of 1 16 square mile. Its base is 3_ 8 mile. What is its height? 1_ 6 mile. Square County is a square-shaped county divided into 16 equal-sized square districts. If the side length of each district is miles, what is the area of Square County? 56 square miles Continue concepts and skills practice with Lesson Check. Use Spiral Review to engage students in previously taught concepts and to promote content retention. Common Core standards are correlated to each section. Spiral Review (6.EE.B.5, 6.EE.B.8, 6.EE.C.9) 3. Which of the following values of y make the inequality y < true? y = y = 6 y = 0 y = 8 y =. On a winter s day, 9 F is the highest temperature recorded. Write an inequality that represents the temperature t in degrees Fahrenheit at any time on this day. y = 6 and y = 8 t 9 5. In seconds, an elevator travels 0 feet. In 3 seconds, the elevator travels 60 feet. In seconds, the elevator travels 80 feet. Write an equation that gives the relationship between the number of seconds x and the distance y the elevator travels. 538 y = 0x 6. The linear equation y = x represents the number of bracelets y that Jolene can make in x hours. Which ordered pair lies on the graph of the equation? Students answers will vary, but the y-value of the ordered pair should be times as great as the x-value. Possible answers are (1, ), (, 8), and (3, 1). FOR MORE PRACTICE GO TO THE Personal Trainer Connecting and Science Mean, Median, Mode, and Range You can analyze both the measures of central tendency and the variability of data using mean, median, mode, and range. Tutorial Orbit eccentricity measures how oval-shaped the elliptical orbit is. The closer a value is to 0, the closer the orbit is to a circle. Examine the eccentricity values below. Orbit Eccentricities of Planets in the Solar System Mercury 0.05 Jupiter 0.09 Venus Saturn Earth Uranus 0.06 Mars 0.09 Neptune Mean The mean is the sum of all of the values in a data set divided by the total number of values in the data set. The mean is also called the average. Median The median is the value of the middle item when data are arranged in numerical order. If there is an odd number of values, the median is the middle value. If there is an even number of values, the median is the mean of the two middle values. Mode The mode is the value or values that occur most frequently in a data set. Order the values to find the mode. If all values occur with the same frequency, the data set is said to have no mode. Range The range is the difference between the greatest value and the least value of a data set. 66 Unit 8 The Solar System Add up all of the values. Divide the sum by the number of values. mean = Order the values. The median is the middle value if there is an odd number of values. If there is an even number of values, calculate the mean of the two middle values. median = Order the values. Find the value or values that occur most frequently. mode = none Subtract the least value from the greatest value. range = Do the Mean, Median, Mode, and Range Develop Vocabulary S.T.E.M. Activity Chapter Define the following terms in your own words. Mean (Average): Possible answer: The mean is the sum of all of the values in a data set divided by the total Do the! number of values in the data set. 3. The data table below shows the masses and densities of the planets. Develop Concepts Use with ScienceFusion pages g Planets Mass ( 10 kg) Density ( cm 3 ) Median: Mercury Possible answer: The median is the value of the middle item when data are arranged in Venus numerical order. If there is an odd number of values, the median is the middle value. If there Earth is an even number of values, the median is the mean of the two middle values. Mars Mode: Jupiter 1, Possible answer: The mode is the value or values that occur most frequently Saturn in a data set Uranus Order the values to find the mode. If all values occur with the same frequency, the data set Neptune is said to have no mode.. Find the mean, median, mode, and range for the density of the planets. Range: Show your work. Possible answer: The range is the difference between the greatest value and the least value Mean: of a data set. ( ) 8 = 3.06 cm 3. A planet has an orbit eccentricity of Is the orbit circular? Mode: Possible answer: No. A planet s orbit has to have an eccentricity close to 0 for No density appears more than once. The data has no mode. it to be circular. Range: Range is 5.5 g cm g cm 3 =.83 g cm 3. S.T.E.M. Activity 67 Summarize 68 Median: from smallest to largest: 0.69, 1.7, 1.33, 1.6, 3.3, 5., 5.3, 5.5. Since there is an even ( ) number of values, I take the average of 1.6 and 3.3. =.9 g cm Why is it important to know the mean, median, mode, and range of data? Possible answer: so that scientists can identify the central tendency of the data and how much the data varies In Chapter 10, students extend their understanding of area, by performing calculations with multiple values. These same topics are used often in the development of various science concepts and process skills. Help students make the connection between math and science through the S.T.E.M. activities and activity worksheets found at In Chapter 10, students connect math and science with the S.T.E.M. Activity Mean, Median, Mode, and Range and the accompanying worksheets (pages 67 and 68). Through this S.T.E.M. Activity, students will connect the GO! Chapter 10 concepts and skills with various problems about mass and density, including finding the mean density of the planets in our solar system. It is recommended that this S.T.E.M. Activity be used after. 538
Investigate Model with Arrays
 LESSON 6.6 Progress to Algebra Investigate Model with Arrays FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 3.OA.A.3 Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve
LESSON 6.6 Progress to Algebra Investigate Model with Arrays FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 3.OA.A.3 Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve
Describe Plane Shapes
 LESSON 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses,
LESSON 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses,
Classify Quadrilaterals
 LESSON 10.4 Classify Quadrilaterals FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 4.G.A.2 Classify two-dimensional figures based on the presence or
LESSON 10.4 Classify Quadrilaterals FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 4.G.A.2 Classify two-dimensional figures based on the presence or
Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms
 NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
Activity Model and record the factors of 24. Materials square tiles
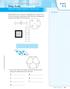
 Name Model Factors Essential Question How can you use models to find factors? Unlock the Problem Lesson 5.1 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4.OA.B.4 MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES MP1, MP4 A factor is a number
Name Model Factors Essential Question How can you use models to find factors? Unlock the Problem Lesson 5.1 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4.OA.B.4 MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES MP1, MP4 A factor is a number
16.2. Use Area Models. Are You Ready? Lesson Opener Making Connections. Resources. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills.
 6.? Essential Question Why can you multiply to find the area of a rectangle? Why can you multiply to find the area of a rectangle? Lesson Opener Making Connections Invite students to tell you what they
6.? Essential Question Why can you multiply to find the area of a rectangle? Why can you multiply to find the area of a rectangle? Lesson Opener Making Connections Invite students to tell you what they
9.1. Formulas for Area and Perimeter. Are You Ready? Lesson Opener Making Connections. Resources. Essential Question
 9.1 Formulas for Area and Perimeter? Essential Question How can you use formulas to find the area and perimeter of shapes? How can you use formulas to find the area and perimeter of shapes? Lesson Opener
9.1 Formulas for Area and Perimeter? Essential Question How can you use formulas to find the area and perimeter of shapes? How can you use formulas to find the area and perimeter of shapes? Lesson Opener
UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Model Perimeter. So, the perimeter of the figure is 16 units. centimeters. centimeters. centimeters. centimeters
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Model Perimeter Perimeter is the distance around a figure. Find the perimeter of the figure. Step 1 Choose a unit to begin counting and label it 1. 1 1 unit Step 2 Count each unit around
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Model Perimeter Perimeter is the distance around a figure. Find the perimeter of the figure. Step 1 Choose a unit to begin counting and label it 1. 1 1 unit Step 2 Count each unit around
GRADE LEVEL: FOURTH GRADE SUBJECT: MATH DATE: Read (in standard form) whole numbers. whole numbers Equivalent Whole Numbers
 CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION 1 GRADE LEVEL: FOURTH GRADE SUBJECT: MATH DATE: 2019 2020 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 MASTER COPY 1 20 19 NUMBER SENSE Whole Numbers 4.NS.1: Read and write whole
CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION 1 GRADE LEVEL: FOURTH GRADE SUBJECT: MATH DATE: 2019 2020 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 MASTER COPY 1 20 19 NUMBER SENSE Whole Numbers 4.NS.1: Read and write whole
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE. Grade 4 Mathematics GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS
 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Grade 4 Mathematics 2014-2015 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Learning Old Format New Format Q1LC1 4.NBT.1, 4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.3, (4.1.1, 4.1.2,
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Grade 4 Mathematics 2014-2015 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Learning Old Format New Format Q1LC1 4.NBT.1, 4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.3, (4.1.1, 4.1.2,
AIMS Common Core Math Standards Alignment
 AIMS Common Core Math Standards Alignment Third Grade Operations and Algebraic Thinking (.OA) 1. Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 7 as the total number of objects in groups of 7 objects
AIMS Common Core Math Standards Alignment Third Grade Operations and Algebraic Thinking (.OA) 1. Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 7 as the total number of objects in groups of 7 objects
Applications. 60 Covering and Surrounding
 Applications For Exercises 7, find the area and perimeter of each parallelogram. Give a brief explanation of your reasoning for Exercises, 6, and 7... 4. 3. 7. 5. 6. 60 Covering and Surrounding 8. On the
Applications For Exercises 7, find the area and perimeter of each parallelogram. Give a brief explanation of your reasoning for Exercises, 6, and 7... 4. 3. 7. 5. 6. 60 Covering and Surrounding 8. On the
SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 10 AREA AND PERIMETER TOPICS COVERED:
 SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 10 AREA AND PERIMETER TOPICS COVERED: Perimeter of Polygons Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of a Trapezoid Area of Irregular Figures Activity 10-1: Sixth Grade
SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 10 AREA AND PERIMETER TOPICS COVERED: Perimeter of Polygons Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of a Trapezoid Area of Irregular Figures Activity 10-1: Sixth Grade
Northern York County School District Curriculum
 Northern York County School District Curriculum Course Name Grade Level Mathematics Fourth grade Unit 1 Number and Operations Base Ten Time Frame 4-5 Weeks PA Common Core Standard (Descriptor) (Grades
Northern York County School District Curriculum Course Name Grade Level Mathematics Fourth grade Unit 1 Number and Operations Base Ten Time Frame 4-5 Weeks PA Common Core Standard (Descriptor) (Grades
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
The Grade 6 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6)
 LESSON Name 1 Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6) A number line shows numbers in order from least to greatest. The number line has zero at the center. Numbers to the right of zero are
LESSON Name 1 Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6) A number line shows numbers in order from least to greatest. The number line has zero at the center. Numbers to the right of zero are
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6. Student Book
 TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
Standards for Mathematical Practice
 Common Core State Standards Mathematics Student: Teacher: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Standards for Mathematical Practice 3. Construct
Common Core State Standards Mathematics Student: Teacher: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Standards for Mathematical Practice 3. Construct
Perimeters of Composite Figures
 8. Perimeters of Composite Figures How can you find the perimeter of a composite figure? ACTIVITY: Finding a Pattern Work with a partner. Describe the pattern of the perimeters. Use your pattern to find
8. Perimeters of Composite Figures How can you find the perimeter of a composite figure? ACTIVITY: Finding a Pattern Work with a partner. Describe the pattern of the perimeters. Use your pattern to find
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies?
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Measuring Parallelograms
 4 Measuring Parallelograms In this unit, you have developed ways to find the area and perimeter of rectangles and of triangles. In this investigation you will develop ways to find the area and perimeter
4 Measuring Parallelograms In this unit, you have developed ways to find the area and perimeter of rectangles and of triangles. In this investigation you will develop ways to find the area and perimeter
Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Perimeter and Area
 Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Perimeter and Area Objective: Students will be able to: Distinguish between area and perimeter. Calculate the perimeter of a polygon whose side lengths are given or can be determined.
Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Perimeter and Area Objective: Students will be able to: Distinguish between area and perimeter. Calculate the perimeter of a polygon whose side lengths are given or can be determined.
Covering and Surrounding Practice Answers
 Investigation Additional Practice. a. units, Area 8 square units b. 8 units, Area 33 square units c. 3 units, Area 33 square units d. units, 7 Area 7 square units 8. a. Students should draw and label a
Investigation Additional Practice. a. units, Area 8 square units b. 8 units, Area 33 square units c. 3 units, Area 33 square units d. units, 7 Area 7 square units 8. a. Students should draw and label a
Find the value of the expressions. 3 x = 3 x = = ( ) 9 = 60 (12 + 8) 9 = = 3 9 = 27
 PreAlgebra Concepts Important Concepts exponent In a power, the number of times a base number is used as a factor order of operations The rules which tell which operation to perform first when more than
PreAlgebra Concepts Important Concepts exponent In a power, the number of times a base number is used as a factor order of operations The rules which tell which operation to perform first when more than
Area of Composite Figures. ESSENTIAL QUESTION do you find the area of composite figures? 7.9.C
 ? LESSON 9.4 Area of Composite Figures ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? Equations, expressions, and relationships Determine the area of composite figures containing combinations
? LESSON 9.4 Area of Composite Figures ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? Equations, expressions, and relationships Determine the area of composite figures containing combinations
Core Connections, Course 2 Checkpoint Materials
 Core Connections, Course Checkpoint Materials Notes to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn exactly the same way at the same time. At
Core Connections, Course Checkpoint Materials Notes to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn exactly the same way at the same time. At
Grade 3 Area and Perimeter Unit Overview
 Grade 3 Area and Perimeter Unit Overview Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and to addition. 3.MD.C.5 Recognize area as an attribute of plane figures and
Grade 3 Area and Perimeter Unit Overview Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and to addition. 3.MD.C.5 Recognize area as an attribute of plane figures and
4 th Grade Curriculum Map
 4 th Grade Curriculum Map 2017-18 MONTH UNIT/ CONTENT CORE GOALS/SKILLS STANDARDS WRITTEN ASSESSMENTS ROUTINES RESOURCES VOCABULARY September Chapter 1 8 days NUMBERS AND OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN WORKING
4 th Grade Curriculum Map 2017-18 MONTH UNIT/ CONTENT CORE GOALS/SKILLS STANDARDS WRITTEN ASSESSMENTS ROUTINES RESOURCES VOCABULARY September Chapter 1 8 days NUMBERS AND OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN WORKING
AREA See the Math Notes box in Lesson for more information about area.
 AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
ENGAGE. Daily Routines Common Core. Essential Question. Making Connections Invite students to tell you what they know about parking lots.
 LESSON 10.3 Parallel Lines and Perpendicular Lines LESSON T GLNE R ocus: ommon ore State Standards Learning Objective 4.G..1 raw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular
LESSON 10.3 Parallel Lines and Perpendicular Lines LESSON T GLNE R ocus: ommon ore State Standards Learning Objective 4.G..1 raw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular
Unit 6, Activity 1, Measuring Scavenger Hunt
 Unit 6, Activity 1, Measuring Scavenger Hunt Name: Measurement Descriptions Object 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Blackline Masters, Mathematics, Grade 7 Page 6-1 Unit 6, Activity 4, Break it Down Name
Unit 6, Activity 1, Measuring Scavenger Hunt Name: Measurement Descriptions Object 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Blackline Masters, Mathematics, Grade 7 Page 6-1 Unit 6, Activity 4, Break it Down Name
Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem
 UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
All About That Base... and Height
 All About That Base... and Height Area of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 2 WARM UP Write 3 different expressions to describe the total area of this rectangle. LEARNING GOALS State and compare the attributes
All About That Base... and Height Area of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 2 WARM UP Write 3 different expressions to describe the total area of this rectangle. LEARNING GOALS State and compare the attributes
Math Pacing Guide. 2 nd Grade
 Unit 1: Extending Base 10 Understanding 5, 10 5 weeks Instructional Days August 8 September 9, 2016 Understand place value. MGSE2.NBT.1 Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent
Unit 1: Extending Base 10 Understanding 5, 10 5 weeks Instructional Days August 8 September 9, 2016 Understand place value. MGSE2.NBT.1 Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
4th Grade Mathematics Mathematics CC
 Course Description In Grade 4, instructional time should focus on five critical areas: (1) attaining fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
Course Description In Grade 4, instructional time should focus on five critical areas: (1) attaining fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
Lesson 5: The Area of Polygons Through Composition and Decomposition
 Lesson 5: The Area of Polygons Through Composition and Decomposition Student Outcomes Students show the area formula for the region bounded by a polygon by decomposing the region into triangles and other
Lesson 5: The Area of Polygons Through Composition and Decomposition Student Outcomes Students show the area formula for the region bounded by a polygon by decomposing the region into triangles and other
Formative type assessment (i.e. windshield check, dry erase boards, exit tickets, multiple choice, journals, checklists, etc.
 Jones County School District Assessment Blueprint 2013-2014 Grade/Subject Level: 3rd Grade Math Team Members: A. Mobley, K. Husser, R. Sims, S. Clark, K. Knight, J. Hall Creating Summative / District Benchmark
Jones County School District Assessment Blueprint 2013-2014 Grade/Subject Level: 3rd Grade Math Team Members: A. Mobley, K. Husser, R. Sims, S. Clark, K. Knight, J. Hall Creating Summative / District Benchmark
One Way Draw a model. Another Way Use division. Lesson q w 3 2
 Name Factors and Divisibility Essential Question How can you tell whether one number is a factor of another number? Unlock the Problem Lesson 5.2 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4.OA.B.4 MATHEMATICAL
Name Factors and Divisibility Essential Question How can you tell whether one number is a factor of another number? Unlock the Problem Lesson 5.2 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4.OA.B.4 MATHEMATICAL
Geometry. Warm Ups. Chapter 11
 Geometry Warm Ups Chapter 11 Name Period Teacher 1 1.) Find h. Show all work. (Hint: Remember special right triangles.) a.) b.) c.) 2.) Triangle RST is a right triangle. Find the measure of angle R. Show
Geometry Warm Ups Chapter 11 Name Period Teacher 1 1.) Find h. Show all work. (Hint: Remember special right triangles.) a.) b.) c.) 2.) Triangle RST is a right triangle. Find the measure of angle R. Show
11.2 Areas of Trapezoids,
 11. Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Goal p Find areas of other types of quadrilaterals. Your Notes VOCABULARY Height of a trapezoid THEOREM 11.4: AREA OF A TRAPEZOID b 1 The area of a trapezoid
11. Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Goal p Find areas of other types of quadrilaterals. Your Notes VOCABULARY Height of a trapezoid THEOREM 11.4: AREA OF A TRAPEZOID b 1 The area of a trapezoid
Number Models for Area
 Number Models for Area Objectives To guide children as they develop the concept of area by measuring with identical squares; and to demonstrate how to calculate the area of rectangles using number models.
Number Models for Area Objectives To guide children as they develop the concept of area by measuring with identical squares; and to demonstrate how to calculate the area of rectangles using number models.
Standards for Mathematical Practice
 Common Core State Standards Mathematics Student: Teacher: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Standards for Mathematical Practice 3. Construct
Common Core State Standards Mathematics Student: Teacher: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Standards for Mathematical Practice 3. Construct
Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd
 Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd Materials, Texts Needed, or advanced preparation: Lap tops or computer with Geogebra if possible
Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd Materials, Texts Needed, or advanced preparation: Lap tops or computer with Geogebra if possible
1 inch 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch. 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch 1 inch
 Name Customary Units of Length Essential Question How can you use models to compare customary units of length? Lesson 2.2 Measurement and Data 4.MD.A. Also 4.MD.A.2 MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES MP, MP2, MP5
Name Customary Units of Length Essential Question How can you use models to compare customary units of length? Lesson 2.2 Measurement and Data 4.MD.A. Also 4.MD.A.2 MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES MP, MP2, MP5
Grade 4 Mathematics Indiana Academic Standards Crosswalk
 Grade 4 Mathematics Indiana Academic Standards Crosswalk 2014 2015 The Process Standards demonstrate the ways in which students should develop conceptual understanding of mathematical content and the ways
Grade 4 Mathematics Indiana Academic Standards Crosswalk 2014 2015 The Process Standards demonstrate the ways in which students should develop conceptual understanding of mathematical content and the ways
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA
 UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
Essential Mathematics Practice Problems for Exam 5 Chapter 8
 Math 254B Essential Mathematics Practice Problems for Eam 5 Chapter 8 Name Date This eam is closed book and closed notes, ecept for the Geometry Formula sheet that is provided by the instructor. You can
Math 254B Essential Mathematics Practice Problems for Eam 5 Chapter 8 Name Date This eam is closed book and closed notes, ecept for the Geometry Formula sheet that is provided by the instructor. You can
5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work
 NAME: 5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work DATE: 1.) 26.) 51.) 76.) 2.) 27.) 52.) 77.) 3.) 28.) 53.) 78.) 4.) 29.) 54.) 79.) 5.) 30.) 55.) 80.) 6.) 31.) 56.) 81.) 7.) 32.) 57.)
NAME: 5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work DATE: 1.) 26.) 51.) 76.) 2.) 27.) 52.) 77.) 3.) 28.) 53.) 78.) 4.) 29.) 54.) 79.) 5.) 30.) 55.) 80.) 6.) 31.) 56.) 81.) 7.) 32.) 57.)
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES.
 AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
Mathematics Success Level F
 T598 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the perimeter and area of rectangles and triangles. [MATERIALS] Student pages S204 S212 Transparencies T612, T614, T616, T618, T620, T622 Ruler Scissors Gridded index
T598 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the perimeter and area of rectangles and triangles. [MATERIALS] Student pages S204 S212 Transparencies T612, T614, T616, T618, T620, T622 Ruler Scissors Gridded index
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Accelerated 7 th Grade Math Second Quarter Unit 3: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic C: Ratios and Rates Involving Fractions In Topic C,
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Accelerated 7 th Grade Math Second Quarter Unit 3: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic C: Ratios and Rates Involving Fractions In Topic C,
h r c On the ACT, remember that diagrams are usually drawn to scale, so you can always eyeball to determine measurements if you get stuck.
 ACT Plane Geometry Review Let s first take a look at the common formulas you need for the ACT. Then we ll review the rules for the tested shapes. There are also some practice problems at the end of this
ACT Plane Geometry Review Let s first take a look at the common formulas you need for the ACT. Then we ll review the rules for the tested shapes. There are also some practice problems at the end of this
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Fair Game Review. Chapter 4. Name Date. Find the area of the square or rectangle Find the area of the patio.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Find the area of the square or rectangle... ft cm 0 ft cm.. in. d in. d. Find the area of the patio. ft 0 ft Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Green Name
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Find the area of the square or rectangle... ft cm 0 ft cm.. in. d in. d. Find the area of the patio. ft 0 ft Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Green Name
The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three- dimensional figures.
 The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three- dimensional figures. 2.01 Estimate and measure length, perimeter, area, angles, weight, and mass of two- and three-dimensional
The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three- dimensional figures. 2.01 Estimate and measure length, perimeter, area, angles, weight, and mass of two- and three-dimensional
a. $ b. $ c. $
 LESSON 51 Rounding Decimal Name To round decimal numbers: Numbers (page 268) 1. Underline the place value you are rounding to. 2. Circle the digit to its right. 3. If the circled number is 5 or more, add
LESSON 51 Rounding Decimal Name To round decimal numbers: Numbers (page 268) 1. Underline the place value you are rounding to. 2. Circle the digit to its right. 3. If the circled number is 5 or more, add
Grade 4. COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS Correlations
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS Standards for Mathematical Practices CC.K 12.MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. In most Student Edition lessons. Some examples are: 50
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS Standards for Mathematical Practices CC.K 12.MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. In most Student Edition lessons. Some examples are: 50
Areas of Composite Figures 8.4. ACTIVITY: Estimating Area. How can you find the area of. a composite figure?
 .4 Areas of Composite Figures a composite figure? How can you find the area of 1 ACTIVITY: Estimating Area Work with a partner. a. Choose a state. On grid paper, draw a larger outline of the state. b.
.4 Areas of Composite Figures a composite figure? How can you find the area of 1 ACTIVITY: Estimating Area Work with a partner. a. Choose a state. On grid paper, draw a larger outline of the state. b.
Area of Composite Figures. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? 7.G.2.6
 LESSON 9.3 Area of Composite Figures Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, of objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons,. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area
LESSON 9.3 Area of Composite Figures Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, of objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons,. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area
Meet #2. Park Forest Math Team. Self-study Packet
 Park Forest Math Team Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : rea and perimeter of polygons 3. Number Theory:
Park Forest Math Team Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : rea and perimeter of polygons 3. Number Theory:
Perimeter, Circumference, Area and Ratio Long-Term Memory Review Grade 6 Review 1
 Review 1 1. Which procedure is used to find the perimeter of any polygon? A) Add all the lengths B) Multiply length times width (l w) C) Add only one length and one width D) Multiply all of the lengths.
Review 1 1. Which procedure is used to find the perimeter of any polygon? A) Add all the lengths B) Multiply length times width (l w) C) Add only one length and one width D) Multiply all of the lengths.
Selected Answers for Core Connections, Course 2
 Selected Answers for Core Connections, Course 2 Lesson 6.1.1 6-6. x x + 1 3 = 2 b: 2x 2 + 4x x + 2 3 = 2x 2 + 3x 1 6-7. Parts a, c, and d match the perimeter. 6-8. a: 23 20 or 1 3 20 d: 19 15 or 1 4 15
Selected Answers for Core Connections, Course 2 Lesson 6.1.1 6-6. x x + 1 3 = 2 b: 2x 2 + 4x x + 2 3 = 2x 2 + 3x 1 6-7. Parts a, c, and d match the perimeter. 6-8. a: 23 20 or 1 3 20 d: 19 15 or 1 4 15
7 Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core 7 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE Table of Contents 1 Percent and Proportional Relationships GRADE 7 MODULE 4... 3 Topic A: Finding the Whole (7.RP.A.1, 7.RP.A.2c, 7.RP.A.3)...
New York State Common Core 7 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE Table of Contents 1 Percent and Proportional Relationships GRADE 7 MODULE 4... 3 Topic A: Finding the Whole (7.RP.A.1, 7.RP.A.2c, 7.RP.A.3)...
Measurement and Data Core Guide Grade 4
 Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit (Standards 4.MD.1 2) Standard 4.MD.1 Know relative sizes of measurement units within each system
Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit (Standards 4.MD.1 2) Standard 4.MD.1 Know relative sizes of measurement units within each system
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
Mathematics Grade 2. grade 2 17
 Mathematics Grade 2 In Grade 2, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) extending understanding of base-ten notation; (2) building fluency with addition and subtraction; (3) using standard
Mathematics Grade 2 In Grade 2, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) extending understanding of base-ten notation; (2) building fluency with addition and subtraction; (3) using standard
Grade 2: Mathematics Curriculum (2010 Common Core) Warren Hills Cluster (K 8)
 Focus Topic:OA Operations and Algebraic Thinking TSW = The Student Will TSW use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from,
Focus Topic:OA Operations and Algebraic Thinking TSW = The Student Will TSW use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from,
Math + 4 (Red) SEMESTER 1. { Pg. 1 } Unit 1: Whole Number Sense. Unit 2: Whole Number Operations. Unit 3: Applications of Operations
 Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Daily Warmup. - x 2 + x x 2 + x Questions from HW?? (7x - 39) (3x + 17) 1. BD bisects ABC. Find the m ABC.
 Daily Warmup Questions from HW?? B 1. BD bisects ABC. Find the m ABC. (3x + 17) (7x - 39) C 2. The figure below is a regular polygon. Find the value of x. - x 2 + x + 43 A D 4x 2 + x - 37 3. The measure
Daily Warmup Questions from HW?? B 1. BD bisects ABC. Find the m ABC. (3x + 17) (7x - 39) C 2. The figure below is a regular polygon. Find the value of x. - x 2 + x + 43 A D 4x 2 + x - 37 3. The measure
Similar Figures 2.5. ACTIVITY: Reducing Photographs. How can you use proportions to help make decisions in art, design, and magazine layouts?
 .5 Similar Figures How can you use proportions to help make decisions in art, design, and magazine layouts? In a computer art program, when you click and drag on a side of a photograph, you distort it.
.5 Similar Figures How can you use proportions to help make decisions in art, design, and magazine layouts? In a computer art program, when you click and drag on a side of a photograph, you distort it.
5.3. Area of Polygons and Circles Play Area. My Notes ACTIVITY
 Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Grade 6. Prentice Hall. Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units Alaska Standards and Grade Level Expectations. Grade 6
 Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD. We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential
 Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Sixth Grade Spiraling Review Week 1 of Third Six Weeks
 Week 1 of Third Six Weeks Materials: Spiraling Review Cards run on cardstock and cut for each group of students. Note: Record all work in your math journal. Day 1 Spiraling review cards see attachment
Week 1 of Third Six Weeks Materials: Spiraling Review Cards run on cardstock and cut for each group of students. Note: Record all work in your math journal. Day 1 Spiraling review cards see attachment
Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS Math Guide 6-72 Overview NTCM Standards (Grades 3-5) 4-5 Lessons and Terms Vocabulary Flash Cards 45-72
 Contents shapes TABLE OF CONTENTS Math Guide 6-72 Overview 3 NTCM Standards (Grades 3-5) 4-5 Lessons and Terms Lesson 1: Introductory Activity 6-8 Lesson 2: Lines and Angles 9-12 Line and Angle Terms 11-12
Contents shapes TABLE OF CONTENTS Math Guide 6-72 Overview 3 NTCM Standards (Grades 3-5) 4-5 Lessons and Terms Lesson 1: Introductory Activity 6-8 Lesson 2: Lines and Angles 9-12 Line and Angle Terms 11-12
1 Version 2.0. Related Below-Grade and Above-Grade Standards for Purposes of Planning for Vertical Scaling:
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target E [a]: Draw, construct,
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target E [a]: Draw, construct,
7 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 4: Percent and Proportional Relationships (3 weeks) Topic A: Proportional Reasoning with Percents
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 7 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 4: Percent and Proportional Relationships (3 weeks) Topic A: Proportional Reasoning with Percents In Unit 4, students
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 7 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 4: Percent and Proportional Relationships (3 weeks) Topic A: Proportional Reasoning with Percents In Unit 4, students
2 A rectangle 3 cm long and. Find the perimeter and area of each figure. Remember to include the correct units in your answers.
 5- Homework Draw each rectangle on the dot paper. Find the perimeter and area. A rectangle 5 cm long and cm wide A rectangle cm long and cm wide Perimeter = Area = Perimeter = Area = Find the perimeter
5- Homework Draw each rectangle on the dot paper. Find the perimeter and area. A rectangle 5 cm long and cm wide A rectangle cm long and cm wide Perimeter = Area = Perimeter = Area = Find the perimeter
Grade 7, Unit 1 Practice Problems - Open Up Resources
 Grade 7, Unit 1 Practice Problems - Open Up Resources Scale Drawings Lesson 1 Here is a gure that looks like the letter A, along with several other gures. Which gures are scaled copies of the original
Grade 7, Unit 1 Practice Problems - Open Up Resources Scale Drawings Lesson 1 Here is a gure that looks like the letter A, along with several other gures. Which gures are scaled copies of the original
Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7
 Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Simple Solutions Mathematics Level 3. Level 3. Help Pages & Who Knows Drill
 Level 3 & Who Knows Drill 283 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and 1 is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication
Level 3 & Who Knows Drill 283 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and 1 is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication
7 Days: August 17 August 27. Unit 1: Two-Dimensional Figures
 1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Geometry (G) OA.3.5 G.1.1 G.1.2 G.1.3 Generate and analyze patterns. Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent
1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Geometry (G) OA.3.5 G.1.1 G.1.2 G.1.3 Generate and analyze patterns. Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 6th Grade Unit 8
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Minute Simplify: 12( ) = 3. Circle all of the following equal to : % Cross out the three-dimensional shape.
 Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
Objective: Draw polygons with specified attributes to solve problems. (3 minutes) (5 minutes) (60 minutes)
 Lesson 6 3 7 Lesson 6 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (8 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 6 3 7 Lesson 6 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (8 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Area & Perimeter Mega Pack
 Area & Perimeter Mega Pack Area & Perimeter Mega-Pack! This area and perimeter jumbo-bundle has everything your students need to practice, sharpen and hone their skills. Included in this bunch are: - Area
Area & Perimeter Mega Pack Area & Perimeter Mega-Pack! This area and perimeter jumbo-bundle has everything your students need to practice, sharpen and hone their skills. Included in this bunch are: - Area
1. An NFL playing field (not counting the end zones) is 300 feet long and 160 feet wide. What is the perimeter? What is the area?
 Geometry: Perimeter and Area Practice 24 Many sports require a rectangular field of play which is a specific length and width. Use the information given in the problems below to compute the perimeter and
Geometry: Perimeter and Area Practice 24 Many sports require a rectangular field of play which is a specific length and width. Use the information given in the problems below to compute the perimeter and
Common Core State Standards 1 st Edition. Math Pacing Guide
 Common Core State Standards 1 st Edition Math Pacing Guide Fourth Grade 2 nd Nine Week Period 1 st Edition Developed by: Christy Mitchell, Amy Moreman, Natalie Reno ``````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````
Common Core State Standards 1 st Edition Math Pacing Guide Fourth Grade 2 nd Nine Week Period 1 st Edition Developed by: Christy Mitchell, Amy Moreman, Natalie Reno ``````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````
Lesson 1 Pre-Visit Ballpark Figures Part 1
 Lesson 1 Pre-Visit Ballpark Figures Part 1 Objective: Students will be able to: Estimate, measure, and calculate length, perimeter, and area of various rectangles. Time Requirement: 1 class period, longer
Lesson 1 Pre-Visit Ballpark Figures Part 1 Objective: Students will be able to: Estimate, measure, and calculate length, perimeter, and area of various rectangles. Time Requirement: 1 class period, longer
Standard Indicator The Logic Behind the Formula
 Standard Indicator 5.5.1 The Logic Behind the Formula Purpose Students will understand the formulas for the area of a triangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid by comparing them to the area of a related rectangle
Standard Indicator 5.5.1 The Logic Behind the Formula Purpose Students will understand the formulas for the area of a triangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid by comparing them to the area of a related rectangle
9.2 HANDS ON. Count Collections of Coins? Are You Ready? Lesson Opener Making Connections. Resources. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills.
 9.2 HANDS ON Essential Question How can you count a group of pennies, nickels, and dimes How can you count a group of pennies, nickels, and dimes Lesson Opener Making Connections Invite children to tell
9.2 HANDS ON Essential Question How can you count a group of pennies, nickels, and dimes How can you count a group of pennies, nickels, and dimes Lesson Opener Making Connections Invite children to tell
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed KEY STAGE TIERS. First name. Last name. School
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 5 7 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 5 7 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
Area and Perimeter. Practice 1 Area of a Rectangle. Find the area of each figure. Example. one-inch squares.
 Name: Date: Chapter Practice 1 Area of a Rectangle Find the area of each figure. Example There are 3 rows of one-inch squares. Each row has 4 one-inch squares. 3 3 4 5 12 There are 12 one-inch squares
Name: Date: Chapter Practice 1 Area of a Rectangle Find the area of each figure. Example There are 3 rows of one-inch squares. Each row has 4 one-inch squares. 3 3 4 5 12 There are 12 one-inch squares
MASSACHUSETTS COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT SYSTEM
 MASSACHUSETTS COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT SYSTEM PRACTICE TEST Mathematics Grade Student Name School Name District Name Grade Mathematics SESSION This session contains questions. You may not use a calculator
MASSACHUSETTS COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT SYSTEM PRACTICE TEST Mathematics Grade Student Name School Name District Name Grade Mathematics SESSION This session contains questions. You may not use a calculator
