Cardinality and Bijections
|
|
|
- Grant Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Countable and Cardinality and Bijections Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) August 13, 2012
2 Countable and Countable and
3 Countable and How to count elements in a set? How many elements are in a set? Easy for finite sets, just count the elements What about infinite sets? Does it make sense to ask about the number of elements in an infinite set? Can we say this infinite set is larger than that infinite set? Which set is larger, the set of all integers or the set of all even integers?
4 Countable and Cardinality and Bijections If A and B are finite sets, it is not hard to see that they have the same cardinality if and only if there is a bijection from A to B Example: A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {a, b, c}, f = {(1, a), (2, b), (3, c)} Definition Sets A and B (finite or infinite) have the same cardinality if and only if there is a bijection from A to B
5 Countable and Cardinality and Bijections If A and B are finite sets, it is not hard to see that they have the same cardinality if and only if there is a bijection from A to B Example: A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {a, b, c}, f = {(1, a), (2, b), (3, c)} Definition Sets A and B (finite or infinite) have the same cardinality if and only if there is a bijection from A to B The set of all integers has the same cardinality as the set of even integers: f (x) = 2x is a bijection!!
6 Countable and Comparing cardinalities Let A and B be sets. We say A B if there is an injective function from A to B The function f (x) = x is an injective function from the set of even integers into the set of integers If there is an injective function from A to B, but not from B to A, we say A < B If there is an injective function from A to B and an injective function from B to A, we say A and B have the same cardinality
7 Countable and Example Let A be the closed interval [0, 1] (it includes the endpoints) and B be the open interval (0, 1) (it does not include the endpoints) There is a injective function f : A B such that f (x) = 1 3 x There is a injective function g : B A such that g(x) = x Therefore A and B have the same cardinality
8 Countable and Countable and Uncountable Definition A set A is countable if A N. This is because an injective function from A to N can be viewed as assigning numbers to the elements of A, thus counting them Sets that are not countable are uncountable
9 Countable and Examples of Countable Sets The set of all integers: 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3,... The set of odd numbers The set of positive rational numbers The cardinality of the set of natural numbers is denoted by N 0
10 Countable and The Smallest Infinite Set Theorem If A is an infinite set, then A > N 0
11 Countable and Can we make a list of real numbers? Every real number can be represented as an infinite decimal fraction like: Suppose we have constructed a list of all real numbers
12 Countable and 1. a 10.a 11 a 12 a 13 a 14 a 15 a a 20.a 21 a 22 a 23 a 24 a 25 a a 30.a 31 a 32 a 33 a 34 a 35 a a 40.a 41 a 42 a 43 a 44 a 45 a a 50.a 51 a 52 a 53 a 54 a 55 a We construct the following number 0.b 1 b 2 b 3 b 4 b 5 b 6... such that b i a ii for all i.
13 Countable and 1. a 10.a 11 a 12 a 13 a 14 a 15 a a 20.a 21 a 22 a 23 a 24 a 25 a a 30.a 31 a 32 a 33 a 34 a 35 a a 40.a 41 a 42 a 43 a 44 a 45 a a 50.a 51 a 52 a 53 a 54 a 55 a Thus 0.b 1 b 2 b 3 b 4 b 5 b 6... is not in the list!
Sets. Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) August 6, Outline Sets Equality Subset Empty Set Cardinality Power Set
 Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) August 6, 2012 Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich
Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) August 6, 2012 Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich
Cardinality. Hebrew alphabet). We write S = ℵ 0 and say that S has cardinality aleph null.
 Section 2.5 1 Cardinality Definition: The cardinality of a set A is equal to the cardinality of a set B, denoted A = B, if and only if there is a one-to-one correspondence (i.e., a bijection) from A to
Section 2.5 1 Cardinality Definition: The cardinality of a set A is equal to the cardinality of a set B, denoted A = B, if and only if there is a one-to-one correspondence (i.e., a bijection) from A to
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Fall
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Define and compute the cardinality of a set. Use functions to compare the sizes of sets. Classify sets
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Define and compute the cardinality of a set. Use functions to compare the sizes of sets. Classify sets
Countability. Jason Filippou UMCP. Jason Filippou UMCP) Countability / 12
 Countability Jason Filippou CMSC250 @ UMCP 06-23-2016 Jason Filippou (CMSC250 @ UMCP) Countability 06-23-2016 1 / 12 Outline 1 Infinity 2 Countability of integers and rationals 3 Uncountability of R Jason
Countability Jason Filippou CMSC250 @ UMCP 06-23-2016 Jason Filippou (CMSC250 @ UMCP) Countability 06-23-2016 1 / 12 Outline 1 Infinity 2 Countability of integers and rationals 3 Uncountability of R Jason
Finite and Infinite Sets
 Finite and Infinite Sets MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Basic Definitions Definition The empty set has 0 elements. If n N, a set S is said to have
Finite and Infinite Sets MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Basic Definitions Definition The empty set has 0 elements. If n N, a set S is said to have
Cardinality revisited
 Cardinality revisited A set is finite (has finite cardinality) if its cardinality is some (finite) integer n. Two sets A,B have the same cardinality iff there is a one-to-one correspondence from A to B
Cardinality revisited A set is finite (has finite cardinality) if its cardinality is some (finite) integer n. Two sets A,B have the same cardinality iff there is a one-to-one correspondence from A to B
1. Functions and set sizes 2. Infinite set sizes. ! Let X,Y be finite sets, f:x!y a function. ! Theorem: If f is injective then X Y.
 2 Today s Topics: CSE 20: Discrete Mathematics for Computer Science Prof. Miles Jones 1. Functions and set sizes 2. 3 4 1. Functions and set sizes! Theorem: If f is injective then Y.! Try and prove yourself
2 Today s Topics: CSE 20: Discrete Mathematics for Computer Science Prof. Miles Jones 1. Functions and set sizes 2. 3 4 1. Functions and set sizes! Theorem: If f is injective then Y.! Try and prove yourself
DVA325 Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation (FABER)
 DVA325 Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation (FABER) Lecture 1 - Introduction School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Mälardalen University 11 November 2014 Abu Naser Masud FABER November
DVA325 Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation (FABER) Lecture 1 - Introduction School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Mälardalen University 11 November 2014 Abu Naser Masud FABER November
Class 8 - Sets (Lecture Notes)
 Class 8 - Sets (Lecture Notes) What is a Set? A set is a well-defined collection of distinct objects. Example: A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} What is an element of a Set? The objects in a set are called its elements.
Class 8 - Sets (Lecture Notes) What is a Set? A set is a well-defined collection of distinct objects. Example: A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} What is an element of a Set? The objects in a set are called its elements.
Theory of Probability - Brett Bernstein
 Theory of Probability - Brett Bernstein Lecture 3 Finishing Basic Probability Review Exercises 1. Model flipping two fair coins using a sample space and a probability measure. Compute the probability of
Theory of Probability - Brett Bernstein Lecture 3 Finishing Basic Probability Review Exercises 1. Model flipping two fair coins using a sample space and a probability measure. Compute the probability of
1. The empty set is a proper subset of every set. Not true because the empty set is not a proper subset of itself! is the power set of A.
 MAT 101 Solutions to Sample Questions for Exam 1 True or False Questions Answers: 1F, 2F, 3F, 4T, 5T, 6T, 7T 1. The empty set is a proper subset of every set. Not true because the empty set is not a proper
MAT 101 Solutions to Sample Questions for Exam 1 True or False Questions Answers: 1F, 2F, 3F, 4T, 5T, 6T, 7T 1. The empty set is a proper subset of every set. Not true because the empty set is not a proper
Real Numbers and the Number Line. Unit 1 Lesson 3
 Real Numbers and the Number Line Unit 1 Lesson 3 Students will be able to: graph and compare real numbers using the number line. Key Vocabulary: Real Number Rational Number Irrational number Non-Integers
Real Numbers and the Number Line Unit 1 Lesson 3 Students will be able to: graph and compare real numbers using the number line. Key Vocabulary: Real Number Rational Number Irrational number Non-Integers
Cardinality of Accumulation Points of Infinite Sets
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 11, 2016, no. 11, 539-546 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2016.6224 Cardinality of Accumulation Points of Infinite Sets A. Kalapodi CTI
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 11, 2016, no. 11, 539-546 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2016.6224 Cardinality of Accumulation Points of Infinite Sets A. Kalapodi CTI
29. Army Housing (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f ) Totals Totals (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Basketball Positions 32. Guard Forward Center
 Infinite Sets and Their Cardinalities As mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, most of the early work in set theory was done by Georg Cantor He devoted much of his life to a study of the cardinal
Infinite Sets and Their Cardinalities As mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, most of the early work in set theory was done by Georg Cantor He devoted much of his life to a study of the cardinal
In how many ways can we paint 6 rooms, choosing from 15 available colors? What if we want all rooms painted with different colors?
 What can we count? In how many ways can we paint 6 rooms, choosing from 15 available colors? What if we want all rooms painted with different colors? In how many different ways 10 books can be arranged
What can we count? In how many ways can we paint 6 rooms, choosing from 15 available colors? What if we want all rooms painted with different colors? In how many different ways 10 books can be arranged
Chapter 1. Set Theory
 Chapter 1 Set Theory 1 Section 1.1: Types of Sets and Set Notation Set: A collection or group of distinguishable objects. Ex. set of books, the letters of the alphabet, the set of whole numbers. You can
Chapter 1 Set Theory 1 Section 1.1: Types of Sets and Set Notation Set: A collection or group of distinguishable objects. Ex. set of books, the letters of the alphabet, the set of whole numbers. You can
The Math Behind Futurama: The Prisoner of Benda
 of Benda May 7, 2013 The problem (informally) Professor Farnsworth has created a mind-switching machine that switches two bodies, but the switching can t be reversed using just those two bodies. Using
of Benda May 7, 2013 The problem (informally) Professor Farnsworth has created a mind-switching machine that switches two bodies, but the switching can t be reversed using just those two bodies. Using
Permutation Groups. Every permutation can be written as a product of disjoint cycles. This factorization is unique up to the order of the factors.
 Permutation Groups 5-9-2013 A permutation of a set X is a bijective function σ : X X The set of permutations S X of a set X forms a group under function composition The group of permutations of {1,2,,n}
Permutation Groups 5-9-2013 A permutation of a set X is a bijective function σ : X X The set of permutations S X of a set X forms a group under function composition The group of permutations of {1,2,,n}
It is important that you show your work. The total value of this test is 220 points.
 June 27, 2001 Your name It is important that you show your work. The total value of this test is 220 points. 1. (10 points) Use the Euclidean algorithm to solve the decanting problem for decanters of sizes
June 27, 2001 Your name It is important that you show your work. The total value of this test is 220 points. 1. (10 points) Use the Euclidean algorithm to solve the decanting problem for decanters of sizes
Squares and Square roots
 Squares and Square roots Introduction of Squares and Square Roots: LECTURE - 1 If a number is multiplied by itsely, then the product is said to be the square of that number. i.e., If m and n are two natural
Squares and Square roots Introduction of Squares and Square Roots: LECTURE - 1 If a number is multiplied by itsely, then the product is said to be the square of that number. i.e., If m and n are two natural
Sets. Definition A set is an unordered collection of objects called elements or members of the set.
 Sets Definition A set is an unordered collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Sets Definition A set is an unordered collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Examples:
Sets Definition A set is an unordered collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Sets Definition A set is an unordered collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Examples:
Know how to represent permutations in the two rowed notation, and how to multiply permutations using this notation.
 The third exam will be on Monday, November 21, 2011. It will cover Sections 5.1-5.5. Of course, the material is cumulative, and the listed sections depend on earlier sections, which it is assumed that
The third exam will be on Monday, November 21, 2011. It will cover Sections 5.1-5.5. Of course, the material is cumulative, and the listed sections depend on earlier sections, which it is assumed that
An interesting class of problems of a computational nature ask for the standard residue of a power of a number, e.g.,
 Binary exponentiation An interesting class of problems of a computational nature ask for the standard residue of a power of a number, e.g., What are the last two digits of the number 2 284? In the absence
Binary exponentiation An interesting class of problems of a computational nature ask for the standard residue of a power of a number, e.g., What are the last two digits of the number 2 284? In the absence
MATHEMATICS 152, FALL 2004 METHODS OF DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Outline #10 (Sets and Probability)
 MATHEMATICS 152, FALL 2004 METHODS OF DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Outline #10 (Sets and Probability) Last modified: November 10, 2004 This follows very closely Apostol, Chapter 13, the course pack. Attachments
MATHEMATICS 152, FALL 2004 METHODS OF DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Outline #10 (Sets and Probability) Last modified: November 10, 2004 This follows very closely Apostol, Chapter 13, the course pack. Attachments
Hausdorff dimension in groups acting on trees
 of spinal groups in groups acting on trees University of the Basque Country, Bilbao Group St Andrews, Bath, August 4th 2009 in groups acting on trees of spinal groups Contents 1 2 3 of spinal groups in
of spinal groups in groups acting on trees University of the Basque Country, Bilbao Group St Andrews, Bath, August 4th 2009 in groups acting on trees of spinal groups Contents 1 2 3 of spinal groups in
Outline. Sets of Gluing Data. Constructing Manifolds. Lecture 3 - February 3, PM
 Constructing Manifolds Lecture 3 - February 3, 2009-1-2 PM Outline Sets of gluing data The cocycle condition Parametric pseudo-manifolds (PPM s) Conclusions 2 Let n and k be integers such that n 1 and
Constructing Manifolds Lecture 3 - February 3, 2009-1-2 PM Outline Sets of gluing data The cocycle condition Parametric pseudo-manifolds (PPM s) Conclusions 2 Let n and k be integers such that n 1 and
Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 21 st /22 nd, Sets
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Sets Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 21 st /22 nd, 2017 Sets Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing A set is a collection of unique objects i.e.
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Sets Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 21 st /22 nd, 2017 Sets Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing A set is a collection of unique objects i.e.
Sample Spaces, Events, Probability
 Sample Spaces, Events, Probability CS 3130/ECE 3530: Probability and Statistics for Engineers August 28, 2014 Sets A set is a collection of unique objects. Sets A set is a collection of unique objects.
Sample Spaces, Events, Probability CS 3130/ECE 3530: Probability and Statistics for Engineers August 28, 2014 Sets A set is a collection of unique objects. Sets A set is a collection of unique objects.
MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 12: Sign of a permutation (continued). Abstract groups.
 MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 12: Sign of a permutation (continued). Abstract groups. Permutations Let X be a finite set. A permutation of X is a bijection from X to itself. The set of all permutations
MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 12: Sign of a permutation (continued). Abstract groups. Permutations Let X be a finite set. A permutation of X is a bijection from X to itself. The set of all permutations
Beyond Infinity? Joel Feinstein. School of Mathematical Sciences University of Nottingham
 Beyond Infinity? Joel Feinstein School of Mathematical Sciences University of Nottingham 2006-2007 The serious mathematics behind this talk is due to the great mathematicians David Hilbert (1862 1943)
Beyond Infinity? Joel Feinstein School of Mathematical Sciences University of Nottingham 2006-2007 The serious mathematics behind this talk is due to the great mathematicians David Hilbert (1862 1943)
Final exam. Question Points Score. Total: 150
 MATH 11200/20 Final exam DECEMBER 9, 2016 ALAN CHANG Please present your solutions clearly and in an organized way Answer the questions in the space provided on the question sheets If you run out of room
MATH 11200/20 Final exam DECEMBER 9, 2016 ALAN CHANG Please present your solutions clearly and in an organized way Answer the questions in the space provided on the question sheets If you run out of room
Continuous time and Discrete time Signals and Systems
 Continuous time and Discrete time Signals and Systems 1. Systems in Engineering A system is usually understood to be an engineering device in the field, and a mathematical representation of this system
Continuous time and Discrete time Signals and Systems 1. Systems in Engineering A system is usually understood to be an engineering device in the field, and a mathematical representation of this system
The study of probability is concerned with the likelihood of events occurring. Many situations can be analyzed using a simplified model of probability
 The study of probability is concerned with the likelihood of events occurring Like combinatorics, the origins of probability theory can be traced back to the study of gambling games Still a popular branch
The study of probability is concerned with the likelihood of events occurring Like combinatorics, the origins of probability theory can be traced back to the study of gambling games Still a popular branch
8.2 Union, Intersection, and Complement of Events; Odds
 8.2 Union, Intersection, and Complement of Events; Odds Since we defined an event as a subset of a sample space it is natural to consider set operations like union, intersection or complement in the context
8.2 Union, Intersection, and Complement of Events; Odds Since we defined an event as a subset of a sample space it is natural to consider set operations like union, intersection or complement in the context
To be able to determine the quadratic character of an arbitrary number mod p (p an odd prime), we. The first (and most delicate) case concerns 2
 Quadratic Reciprocity To be able to determine the quadratic character of an arbitrary number mod p (p an odd prime), we need to be able to evaluate q for any prime q. The first (and most delicate) case
Quadratic Reciprocity To be able to determine the quadratic character of an arbitrary number mod p (p an odd prime), we need to be able to evaluate q for any prime q. The first (and most delicate) case
14.2 Limits and Continuity
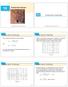 14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
X = {1, 2,...,n} n 1f 2f 3f... nf
 Section 11 Permutations Definition 11.1 Let X be a non-empty set. A bijective function f : X X will be called a permutation of X. Consider the case when X is the finite set with n elements: X {1, 2,...,n}.
Section 11 Permutations Definition 11.1 Let X be a non-empty set. A bijective function f : X X will be called a permutation of X. Consider the case when X is the finite set with n elements: X {1, 2,...,n}.
Order and Compare Rational and Irrational numbers and Locate on the number line
 806.2.1 Order and Compare Rational and Irrational numbers and Locate on the number line Rational Number ~ any number that can be made by dividing one integer by another. The word comes from the word "ratio".
806.2.1 Order and Compare Rational and Irrational numbers and Locate on the number line Rational Number ~ any number that can be made by dividing one integer by another. The word comes from the word "ratio".
Mathematics Competition Practice Session 6. Hagerstown Community College: STEM Club November 20, :00 pm - 1:00 pm STC-170
 2015-2016 Mathematics Competition Practice Session 6 Hagerstown Community College: STEM Club November 20, 2015 12:00 pm - 1:00 pm STC-170 1 Warm-Up (2006 AMC 10B No. 17): Bob and Alice each have a bag
2015-2016 Mathematics Competition Practice Session 6 Hagerstown Community College: STEM Club November 20, 2015 12:00 pm - 1:00 pm STC-170 1 Warm-Up (2006 AMC 10B No. 17): Bob and Alice each have a bag
Pre-Test Unit 7: Real Numbers KEY
 Pre-Test Unit 7: Real Numbers KEY No calculator necessary. Please do not use a calculator. Convert the following fraction to a decimal or decimal to a fraction. (5 pts; 3 pts for correct set-up/work, 2
Pre-Test Unit 7: Real Numbers KEY No calculator necessary. Please do not use a calculator. Convert the following fraction to a decimal or decimal to a fraction. (5 pts; 3 pts for correct set-up/work, 2
Algebra. Recap: Elements of Set Theory.
 January 14, 2018 Arrangements and Derangements. Algebra. Recap: Elements of Set Theory. Arrangements of a subset of distinct objects chosen from a set of distinct objects are permutations [order matters]
January 14, 2018 Arrangements and Derangements. Algebra. Recap: Elements of Set Theory. Arrangements of a subset of distinct objects chosen from a set of distinct objects are permutations [order matters]
Lecture 2: Sum rule, partition method, difference method, bijection method, product rules
 Lecture 2: Sum rule, partition method, difference method, bijection method, product rules References: Relevant parts of chapter 15 of the Math for CS book. Discrete Structures II (Summer 2018) Rutgers
Lecture 2: Sum rule, partition method, difference method, bijection method, product rules References: Relevant parts of chapter 15 of the Math for CS book. Discrete Structures II (Summer 2018) Rutgers
RMT 2015 Power Round Solutions February 14, 2015
 Introduction Fair division is the process of dividing a set of goods among several people in a way that is fair. However, as alluded to in the comic above, what exactly we mean by fairness is deceptively
Introduction Fair division is the process of dividing a set of goods among several people in a way that is fair. However, as alluded to in the comic above, what exactly we mean by fairness is deceptively
Math 127: Equivalence Relations
 Math 127: Equivalence Relations Mary Radcliffe 1 Equivalence Relations Relations can take many forms in mathematics. In these notes, we focus especially on equivalence relations, but there are many other
Math 127: Equivalence Relations Mary Radcliffe 1 Equivalence Relations Relations can take many forms in mathematics. In these notes, we focus especially on equivalence relations, but there are many other
 Ramsey Theory The Ramsey number R(r,s) is the smallest n for which any 2-coloring of K n contains a monochromatic red K r or a monochromatic blue K s where r,s 2. Examples R(2,2) = 2 R(3,3) = 6 R(4,4)
Ramsey Theory The Ramsey number R(r,s) is the smallest n for which any 2-coloring of K n contains a monochromatic red K r or a monochromatic blue K s where r,s 2. Examples R(2,2) = 2 R(3,3) = 6 R(4,4)
An elementary study of Goldbach Conjecture
 An elementary study of Goldbach Conjecture Denise Chemla 26/5/2012 Goldbach Conjecture (7 th, june 1742) states that every even natural integer greater than 4 is the sum of two odd prime numbers. If we
An elementary study of Goldbach Conjecture Denise Chemla 26/5/2012 Goldbach Conjecture (7 th, june 1742) states that every even natural integer greater than 4 is the sum of two odd prime numbers. If we
CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES
 CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 1. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES A) Definition: A function of two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair of real numbers (x,y) in a set D a unique real number
CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 1. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES A) Definition: A function of two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair of real numbers (x,y) in a set D a unique real number
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/82/84793934.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 7 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 7 Notes Goals for this week: Unit FN Functions
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 7 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 7 Notes Goals for this week: Unit FN Functions
Goldbach Conjecture (7 th june 1742)
 Goldbach Conjecture (7 th june 1742) We note P the odd prime numbers set. P = {p 1 = 3, p 2 = 5, p 3 = 7, p 4 = 11,...} n 2N\{0, 2, 4}, p P, p n/2, q P, q n/2, n = p + q We call n s Goldbach decomposition
Goldbach Conjecture (7 th june 1742) We note P the odd prime numbers set. P = {p 1 = 3, p 2 = 5, p 3 = 7, p 4 = 11,...} n 2N\{0, 2, 4}, p P, p n/2, q P, q n/2, n = p + q We call n s Goldbach decomposition
Chapter 1. Probability
 Chapter 1. Probability 1.1 Basic Concepts Scientific method a. For a given problem, we define measures that explains the problem well. b. Data is collected with observation and the measures are calculated.
Chapter 1. Probability 1.1 Basic Concepts Scientific method a. For a given problem, we define measures that explains the problem well. b. Data is collected with observation and the measures are calculated.
CHAPTER 3 DECIMALS. EXERCISE 8 Page Convert 0.65 to a proper fraction may be written as: 100. i.e = =
 CHAPTER 3 DECIMALS EXERCISE 8 Page 21 1. Convert 0.65 to a proper fraction. 0.65 may be written as: 0.65 100 100 i.e. 0.65 65 100 Dividing both numerator and denominator by 5 gives: 65 13 100 20 Hence,
CHAPTER 3 DECIMALS EXERCISE 8 Page 21 1. Convert 0.65 to a proper fraction. 0.65 may be written as: 0.65 100 100 i.e. 0.65 65 100 Dividing both numerator and denominator by 5 gives: 65 13 100 20 Hence,
Number Sense Unit 1 Math 10F Mrs. Kornelsen R.D. Parker Collegiate
 Unit 1 Math 10F Mrs. Kornelsen R.D. Parker Collegiate Lesson One: Rational Numbers New Definitions: Rational Number Is every number a rational number? What about the following? Why or why not? a) b) c)
Unit 1 Math 10F Mrs. Kornelsen R.D. Parker Collegiate Lesson One: Rational Numbers New Definitions: Rational Number Is every number a rational number? What about the following? Why or why not? a) b) c)
18.S34 (FALL, 2007) PROBLEMS ON PROBABILITY
 18.S34 (FALL, 2007) PROBLEMS ON PROBABILITY 1. Three closed boxes lie on a table. One box (you don t know which) contains a $1000 bill. The others are empty. After paying an entry fee, you play the following
18.S34 (FALL, 2007) PROBLEMS ON PROBABILITY 1. Three closed boxes lie on a table. One box (you don t know which) contains a $1000 bill. The others are empty. After paying an entry fee, you play the following
A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES
 Last update: Nov. 6, 2015. A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
Last update: Nov. 6, 2015. A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
ON COMMUTATION PROPERTIES OF THE COMPOSITION RELATION OF CONVERGENT AND DIVERGENT PERMUTATIONS (PART I)
 t m Mathematical Publications DOI: 10.2478/tmmp-2014-0002 Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 58 (2014), 13 22 ON COMMUTATION PROPERTIES OF THE COMPOSITION RELATION OF CONVERGENT AND DIVERGENT PERMUTATIONS (PART I)
t m Mathematical Publications DOI: 10.2478/tmmp-2014-0002 Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 58 (2014), 13 22 ON COMMUTATION PROPERTIES OF THE COMPOSITION RELATION OF CONVERGENT AND DIVERGENT PERMUTATIONS (PART I)
Introduction to Computational Manifolds and Applications
 IMPA - Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil Introduction to Computational Manifolds and Applications Part 1 - Foundations Prof. Jean Gallier jean@cis.upenn.edu Department
IMPA - Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil Introduction to Computational Manifolds and Applications Part 1 - Foundations Prof. Jean Gallier jean@cis.upenn.edu Department
Counting integral solutions
 Thought exercise 2.2 25 Counting integral solutions Question: How many non-negative integer solutions are there of x 1 + x 2 + x 3 + x 4 =10? Give some examples of solutions. Characterize what solutions
Thought exercise 2.2 25 Counting integral solutions Question: How many non-negative integer solutions are there of x 1 + x 2 + x 3 + x 4 =10? Give some examples of solutions. Characterize what solutions
Finite homomorphism-homogeneous permutations via edge colourings of chains
 Finite homomorphism-homogeneous permutations via edge colourings of chains Igor Dolinka dockie@dmi.uns.ac.rs Department of Mathematics and Informatics, University of Novi Sad First of all there is Blue.
Finite homomorphism-homogeneous permutations via edge colourings of chains Igor Dolinka dockie@dmi.uns.ac.rs Department of Mathematics and Informatics, University of Novi Sad First of all there is Blue.
5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 12/28/2010
 48 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 12/28/2010 Properites of Exponents 1. *Simplify each of the following: a. b. 2. c. d. 3. e. 4. f. g. 5. h. i. j. Negative exponents are NOT considered
48 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 12/28/2010 Properites of Exponents 1. *Simplify each of the following: a. b. 2. c. d. 3. e. 4. f. g. 5. h. i. j. Negative exponents are NOT considered
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET 5. Section 9.1
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET 5 Section 9.1 Exercise 2. Recall that for (a, m) = 1 we have ord m a divides φ(m). a) We have φ(11) = 10 thus ord 11 3 {1, 2, 5, 10}. We check 3 1 3 (mod 11), 3 2 9 (mod 11), 3
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET 5 Section 9.1 Exercise 2. Recall that for (a, m) = 1 we have ord m a divides φ(m). a) We have φ(11) = 10 thus ord 11 3 {1, 2, 5, 10}. We check 3 1 3 (mod 11), 3 2 9 (mod 11), 3
Combinatorics. Chapter Permutations. Counting Problems
 Chapter 3 Combinatorics 3.1 Permutations Many problems in probability theory require that we count the number of ways that a particular event can occur. For this, we study the topics of permutations and
Chapter 3 Combinatorics 3.1 Permutations Many problems in probability theory require that we count the number of ways that a particular event can occur. For this, we study the topics of permutations and
November 6, Chapter 8: Probability: The Mathematics of Chance
 Chapter 8: Probability: The Mathematics of Chance November 6, 2013 Last Time Crystallographic notation Groups Crystallographic notation The first symbol is always a p, which indicates that the pattern
Chapter 8: Probability: The Mathematics of Chance November 6, 2013 Last Time Crystallographic notation Groups Crystallographic notation The first symbol is always a p, which indicates that the pattern
An Aperiodic Tiling from a Dynamical System: An Exposition of An Example of Culik and Kari. S. Eigen J. Navarro V. Prasad
 An Aperiodic Tiling from a Dynamical System: An Exposition of An Example of Culik and Kari S. Eigen J. Navarro V. Prasad These tiles can tile the plane But only Aperiodically Example A (Culik-Kari) Dynamical
An Aperiodic Tiling from a Dynamical System: An Exposition of An Example of Culik and Kari S. Eigen J. Navarro V. Prasad These tiles can tile the plane But only Aperiodically Example A (Culik-Kari) Dynamical
Team Name: 1. Remember that a palindrome is a number (or word) that reads the same backwards and forwards. For example, 353 and 2112 are palindromes.
 1. Remember that a palindrome is a number (or word) that reads the same backwards and forwards. or example, 353 and 2112 are palindromes. Observe that the base 2 representation of 2015 is a palindrome.
1. Remember that a palindrome is a number (or word) that reads the same backwards and forwards. or example, 353 and 2112 are palindromes. Observe that the base 2 representation of 2015 is a palindrome.
On first and second countable spaces and the axiom of choice
 Topology and its Applications 143 (2004) 93 103 www.elsevier.com/locate/topol On first and second countable spaces and the axiom of choice Gonçalo Gutierres 1 Departamento de Matemática da Universidade
Topology and its Applications 143 (2004) 93 103 www.elsevier.com/locate/topol On first and second countable spaces and the axiom of choice Gonçalo Gutierres 1 Departamento de Matemática da Universidade
Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals
 Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego October 3, 2016 1 Continuous vs. Discrete signals
Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego October 3, 2016 1 Continuous vs. Discrete signals
NRP Math Challenge Club
 Week 7 : Manic Math Medley 1. You have exactly $4.40 (440 ) in quarters (25 coins), dimes (10 coins), and nickels (5 coins). You have the same number of each type of coin. How many dimes do you have? 2.
Week 7 : Manic Math Medley 1. You have exactly $4.40 (440 ) in quarters (25 coins), dimes (10 coins), and nickels (5 coins). You have the same number of each type of coin. How many dimes do you have? 2.
and problem sheet 7
 1-18 and 15-151 problem sheet 7 Solutions to the following five exercises and optional bonus problem are to be submitted through gradescope by 11:30PM on Friday nd November 018. Problem 1 Let A N + and
1-18 and 15-151 problem sheet 7 Solutions to the following five exercises and optional bonus problem are to be submitted through gradescope by 11:30PM on Friday nd November 018. Problem 1 Let A N + and
SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEM SET 4
 SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEM SET 4 A. A certain integer a gives a remainder of 1 when divided by 2. What can you say about the remainder that a gives when divided by 8? SOLUTION. Let r be the remainder that a
SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEM SET 4 A. A certain integer a gives a remainder of 1 when divided by 2. What can you say about the remainder that a gives when divided by 8? SOLUTION. Let r be the remainder that a
Section Summary. Permutations Combinations Combinatorial Proofs
 Section 6.3 Section Summary Permutations Combinations Combinatorial Proofs Permutations Definition: A permutation of a set of distinct objects is an ordered arrangement of these objects. An ordered arrangement
Section 6.3 Section Summary Permutations Combinations Combinatorial Proofs Permutations Definition: A permutation of a set of distinct objects is an ordered arrangement of these objects. An ordered arrangement
LUCAS-SIERPIŃSKI AND LUCAS-RIESEL NUMBERS
 LUCAS-SIERPIŃSKI AND LUCAS-RIESEL NUMBERS DANIEL BACZKOWSKI, OLAOLU FASORANTI, AND CARRIE E. FINCH Abstract. In this paper, we show that there are infinitely many Sierpiński numbers in the sequence of
LUCAS-SIERPIŃSKI AND LUCAS-RIESEL NUMBERS DANIEL BACZKOWSKI, OLAOLU FASORANTI, AND CARRIE E. FINCH Abstract. In this paper, we show that there are infinitely many Sierpiński numbers in the sequence of
GAP CLOSING. Powers and Roots. Intermediate / Senior Facilitator Guide
 GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Facilitator Guide Powers and Roots Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions...5 Solutions...5
GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Facilitator Guide Powers and Roots Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions...5 Solutions...5
Slide 1 Math 1520, Lecture 13
 Slide 1 Math 1520, Lecture 13 In chapter 7, we discuss background leading up to probability. Probability is one of the most commonly used pieces of mathematics in the world. Understanding the basic concepts
Slide 1 Math 1520, Lecture 13 In chapter 7, we discuss background leading up to probability. Probability is one of the most commonly used pieces of mathematics in the world. Understanding the basic concepts
Section 2.3 Task List
 Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Just like functions of a single variable, functions of several variables can have local and global extrema,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Just like functions of a single variable, functions of several variables can have local and global extrema,
Solutions for the Practice Questions
 Solutions for the Practice Questions Question 1. Find all solutions to the congruence 13x 12 (mod 35). Also, answer the following questions about the solutions to the above congruence. Are there solutions
Solutions for the Practice Questions Question 1. Find all solutions to the congruence 13x 12 (mod 35). Also, answer the following questions about the solutions to the above congruence. Are there solutions
An aperiodic tiling using a dynamical system and Beatty sequences
 Recent Progress in Dynamics MSRI Publications Volume 54, 7 An aperiodic tiling using a dynamical system and Beatty sequences STANLEY EIGEN, JORGE NAVARRO, AND VIDHU S. PRASAD ABSTRACT. Wang tiles are square
Recent Progress in Dynamics MSRI Publications Volume 54, 7 An aperiodic tiling using a dynamical system and Beatty sequences STANLEY EIGEN, JORGE NAVARRO, AND VIDHU S. PRASAD ABSTRACT. Wang tiles are square
A Combinatorial Proof of the Log-Concavity of the Numbers of Permutations with k Runs
 Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 90, 293303 (2000) doi:10.1006jcta.1999.3040, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on A Combinatorial Proof of the Log-Concavity of the Numbers of Permutations
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 90, 293303 (2000) doi:10.1006jcta.1999.3040, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on A Combinatorial Proof of the Log-Concavity of the Numbers of Permutations
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 13 May 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 13 May 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 13 May 2016](/thumbs/90/103725335.jpg) arxiv:1605.04289v1 [math.co] 13 May 2016 Growth Rates of Permutation Classes: Categorization up to the Uncountability Threshold 1. Introduction Jay Pantone Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Hanover,
arxiv:1605.04289v1 [math.co] 13 May 2016 Growth Rates of Permutation Classes: Categorization up to the Uncountability Threshold 1. Introduction Jay Pantone Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Hanover,
GAP CLOSING. Powers and Roots. Intermediate / Senior Student Book GAP CLOSING. Powers and Roots. Intermediate / Senior Student Book
 GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Student Book Intermediate / Senior Student Book Powers and Roots Diagnostic...3 Perfect Squares and Square Roots...6 Powers...
GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Student Book Intermediate / Senior Student Book Powers and Roots Diagnostic...3 Perfect Squares and Square Roots...6 Powers...
Solution: This is sampling without repetition and order matters. Therefore
 June 27, 2001 Your name It is important that you show your work. The total value of this test is 220 points. 1. (10 points) Use the Euclidean algorithm to solve the decanting problem for decanters of sizes
June 27, 2001 Your name It is important that you show your work. The total value of this test is 220 points. 1. (10 points) Use the Euclidean algorithm to solve the decanting problem for decanters of sizes
Directions: Show all of your work. Use units and labels and remember to give complete answers.
 AMS II QTR 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW TRIANGLES/PROBABILITY/UNIT CIRCLE/POLYNOMIALS NAME HOUR This packet will be collected on the day of your final exam. Seniors will turn it in on Friday June 1 st and Juniors
AMS II QTR 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW TRIANGLES/PROBABILITY/UNIT CIRCLE/POLYNOMIALS NAME HOUR This packet will be collected on the day of your final exam. Seniors will turn it in on Friday June 1 st and Juniors
Instruction: Show the class the card. Do not read the number out loud. Allow 3 seconds after reading the card.
 Instruction: Show the class the card. Do not read the number out loud. Allow 3 seconds after reading the card. Question (1) Say: What number is one more than Instruction: Show the class the card. Do not
Instruction: Show the class the card. Do not read the number out loud. Allow 3 seconds after reading the card. Question (1) Say: What number is one more than Instruction: Show the class the card. Do not
Course Syllabus - Online Prealgebra
 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 1.1 Whole Numbers, Place Value Practice Problems for section 1.1 HW 1A 1.2 Adding Whole Numbers Practice Problems for section 1.2 HW 1B 1.3 Subtracting Whole Numbers
Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 1.1 Whole Numbers, Place Value Practice Problems for section 1.1 HW 1A 1.2 Adding Whole Numbers Practice Problems for section 1.2 HW 1B 1.3 Subtracting Whole Numbers
An ordered collection of counters in rows or columns, showing multiplication facts.
 Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 15.053 Optimization Methods in Management Science (Spring 2007) Problem Set 7 Due April 12 th, 2007 at :30 pm. You will need 157 points out of 185 to receive a grade
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 15.053 Optimization Methods in Management Science (Spring 2007) Problem Set 7 Due April 12 th, 2007 at :30 pm. You will need 157 points out of 185 to receive a grade
Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion Notes
 Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion Notes The Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion (often abbreviated PIE is the following general formula used for finding the cardinality of a union of finite sets. Theorem 0.1.
Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion Notes The Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion (often abbreviated PIE is the following general formula used for finding the cardinality of a union of finite sets. Theorem 0.1.
Weighted Polya Theorem. Solitaire
 Weighted Polya Theorem. Solitaire Sasha Patotski Cornell University ap744@cornell.edu December 15, 2015 Sasha Patotski (Cornell University) Weighted Polya Theorem. Solitaire December 15, 2015 1 / 15 Cosets
Weighted Polya Theorem. Solitaire Sasha Patotski Cornell University ap744@cornell.edu December 15, 2015 Sasha Patotski (Cornell University) Weighted Polya Theorem. Solitaire December 15, 2015 1 / 15 Cosets
What I can do for this unit:
 Unit 1: Real Numbers Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 1-1 I can sort a set of numbers into irrationals and rationals,
Unit 1: Real Numbers Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 1-1 I can sort a set of numbers into irrationals and rationals,
Class 8: Square Roots & Cube Roots (Lecture Notes)
 Class 8: Square Roots & Cube Roots (Lecture Notes) SQUARE OF A NUMBER: The Square of a number is that number raised to the power. Examples: Square of 9 = 9 = 9 x 9 = 8 Square of 0. = (0.) = (0.) x (0.)
Class 8: Square Roots & Cube Roots (Lecture Notes) SQUARE OF A NUMBER: The Square of a number is that number raised to the power. Examples: Square of 9 = 9 = 9 x 9 = 8 Square of 0. = (0.) = (0.) x (0.)
6.2 Modular Arithmetic
 6.2 Modular Arithmetic Every reader is familiar with arithmetic from the time they are three or four years old. It is the study of numbers and various ways in which we can combine them, such as through
6.2 Modular Arithmetic Every reader is familiar with arithmetic from the time they are three or four years old. It is the study of numbers and various ways in which we can combine them, such as through
MC215: MATHEMATICAL REASONING AND DISCRETE STRUCTURES
 MC215: MATHEMATICAL REASONING AND DISCRETE STRUCTURES Thursday, 4/17/14 The Addition Principle The Inclusion-Exclusion Principle The Pigeonhole Principle Reading: [J] 6.1, 6.8 [H] 3.5, 12.3 Exercises:
MC215: MATHEMATICAL REASONING AND DISCRETE STRUCTURES Thursday, 4/17/14 The Addition Principle The Inclusion-Exclusion Principle The Pigeonhole Principle Reading: [J] 6.1, 6.8 [H] 3.5, 12.3 Exercises:
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 2006 Senior Preliminary Round Problems & Solutions
 BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 006 Senior Preliminary Round Problems & Solutions 1. Exactly 57.4574% of the people replied yes when asked if they used BLEU-OUT face cream. The fewest
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 006 Senior Preliminary Round Problems & Solutions 1. Exactly 57.4574% of the people replied yes when asked if they used BLEU-OUT face cream. The fewest
Chapter 1. Probability
 Chapter 1. Probability 1.1 Basic Concepts Scientific method a. For a given problem, we define measures that explains the problem well. b. Data is collected with observation and the measures are calculated.
Chapter 1. Probability 1.1 Basic Concepts Scientific method a. For a given problem, we define measures that explains the problem well. b. Data is collected with observation and the measures are calculated.
The topic for the third and final major portion of the course is Probability. We will aim to make sense of statements such as the following:
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2006 Vazirani Lecture 17 Introduction to Probability The topic for the third and final major portion of the course is Probability. We will aim to make sense of
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2006 Vazirani Lecture 17 Introduction to Probability The topic for the third and final major portion of the course is Probability. We will aim to make sense of
How to Gamble Against All Odds
 How to Gamble Against All Odds Gilad Bavly 1 Ron Peretz 2 1 Bar-Ilan University 2 London School of Economics Heidelberg, June 2015 How to Gamble Against All Odds 1 Preface starting with an algorithmic
How to Gamble Against All Odds Gilad Bavly 1 Ron Peretz 2 1 Bar-Ilan University 2 London School of Economics Heidelberg, June 2015 How to Gamble Against All Odds 1 Preface starting with an algorithmic
Enhanced Turing Machines
 Enhanced Turing Machines Lecture 28 Sections 10.1-10.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Enhanced Turing Machines Wed, Nov 2, 2016 1 / 21
Enhanced Turing Machines Lecture 28 Sections 10.1-10.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Enhanced Turing Machines Wed, Nov 2, 2016 1 / 21
CMPT 318: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals
 CMPT 318: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 16, 2006 1 Continuous vs. Discrete
CMPT 318: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 16, 2006 1 Continuous vs. Discrete
Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet
 Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet Target 1: Writing Repeating Decimals in Rational Form Remember the goal is to get rid of the repeating decimal so we can write the number in rational
Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet Target 1: Writing Repeating Decimals in Rational Form Remember the goal is to get rid of the repeating decimal so we can write the number in rational
Continuous vs. Discrete signals. Sampling. Analog to Digital Conversion. CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals
 Continuous vs. Discrete signals CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 22,
Continuous vs. Discrete signals CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 22,
